Physics : P6
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the purpose of waves?
Waves transfer energy from one place to another without transferring any matter
What happens when waves travel through a medium?
The particles of the medium oscillate and transfer energy between each other, but overall, the particles stay the same and only energy is transferred.
What is the amplitude of a wave?
The maximum displacement of a point on the wave from its undisturbed position
What is the wavelength?
The distance between the same point on two adjacent waves e.g. between the trough of one wave and the trough of the wave next to it
What is the frequency?
The number of complete waves passing a certain point per second, measure in herts (Hz).
1 Hz is 1 wave per second
What is the formula for the period of wave?
T = 1/f
Period (s) = 1/frequency (Hz)
What are transverse waves?
The oscillations (vibrations) are perpendicular (at 90 degrees) to the direction of the energy transfer.
What are some common transverse waves?
All electromagnetic waves (light etc.)
Ripples and waves in water
A wave on a string
What are longitudinal waves?
The oscillations are parallel to the direction of the energy transfer.
What is an example of a longitudinal wave?
Sound waves in the air
What is the formula for wave speed?
Wave speed (m/s) = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m)
Define wave speed
The rate at which energy is being transferred, or the speed the Wave is moving at.
[PRACTICAL]
How can an oscilloscope be used to measure the speed of sound?
By attaching a signal generator to a speaker, you can generate sounds with a specific frequency.
You can use two microphones and an oscilloscope to find the wavelength of the sounds generated
Set up the oscilloscope so the detected waves at each microphone are shown as separate waves
Start with both microphones next to the speaker, then slowly move one away until the two waves are aligned on the display, but have moved exactly one wavelength apart
Measure the distance between the microphones to find one wavelength
You can use the formula v=f(wavelength) to find the speed (v) of the sound waves passing through the air - the frequency is the speed the generator is set at
The speed of sound in the air is around 330 m/s
[PRACTICAL]
How can the speed of water ripples be measured using a ripple tank?
Using a signal generator attached to the dipper of a ripple tank you can create water waves at a set frequency
Dim the lights in the lab and turn on the lamp, you should see the wave crests as shadows on the screen below the tank
The distance between each shadow line is equal to one wavelength
Measure the distance between shadow lines that are 10 wavelengths apart, then divide this distance by 10 to find the average wavelength
Use the formula for wavelength speed to find the speed of the waves
[PRACTICAL]
How can the wave equation be used for waves on strings?
Set up the equipment (a vibration transducer connected to a signal generator, connected to a string. The string links to a pulley system with masses) and turn on the signal generator.
The string will start to vibrate
Adjust the frequency of the signal generator until there’s a clear wave on the string.
The frequency you need will depend on the length of the string between the pulley and transducer, and the massews
What 3 things can happen when a wave meets a boundary?
The wave is absorbed = the wave transfers energy to the materials energy stores, often, the energy is transmitted to a thermal energy source, leading to heating
The wave is transmitted = the wave carries on travelling through the new material, leading to refraction.
The wave is reflected = the incoming ray is neither absorbed nor transmitted but instead is ‘sent back’ away from the second material.
What type of waves are electromagnetic waves?
Transverse waves
What are the properties of EM waves?
they all travel at the same speed through air or a vacuum
They arent vibrations of particles, they are vibrations of electric and magnetic fields
They travel at different speeds in different materials
They vary in wavelength from 10(to the power of -15) to more than 10(to the power of 4) metres
What is the EM spectrum?
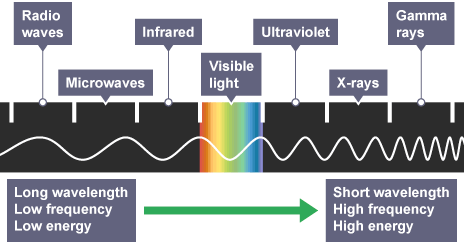
Explain how refraction occurs
When a wave crosses a boundary between two materials it changes speed
If the wave is travelling along the normal it will change speed but NOT be refracted
If the wave hits the boundary at an angle, it changes direction, so is refracted
The wave bends towards the normal if it slows down and away if it speeds up
The higher the density, the slower a wave travels, so the less it is refracted
What are rays?
Rays are straight lines that are perpendicular to wave fronts. They show the dIrection a wave is travel;ling in.
How are ray diagrams drawn?
Draw a boundary between two materials and the normal. The normal is a line that is perpendicular to the point where the incoming ray hits the boundary
Draw an incident ray that meets the normal at the boundary
The angle between the incident ray and the normal is the angle of incidence
Now draw the refracted ray on the other side of the boundary
The angle of refraction is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal
How are wave front diagrams drawn?
A wave front is a line showing all of the points on a wave that are in the same position as each other after a given number of wavelengths
When a wave crosses a boundary at an angle, only part of a wave front crosses the boundary at first
If its travelling into a denser material, that part travels slower than the rest of the wave front
So, by the time the whole wave front crosses the boundary, the faster part of the wave front will have travelled further than the slower part of the wavefront
This difference can be shown with the bend in waves
How can radio waves be produced from EM waves?
Use an alternating current in an electrical circuit so the oscillation of the charges produces oscillating electric and magnetic fields i.e. EM waves.
The object that creates these waves is called a transmitter and when the transmitted waves reach a receiver, the waves are absorbed and the electrons oscillate to complete the electrical circuit.
Why are radio waves useful?
Radio waves are EM radition with wavelengths longer than 10cm.
Long wave radio wavelengths can be transmitted over halfway across the world because they can diffract (bend) around the curved surface, hills and into tunnels etc.
Short wave length radio signals can be received over long distances and they are reflected from the ionosphere.
This makes them useful for communication, TV, radio etc.
What are microwaves?
Waves that can pass easily through or penetrate water molecules such as the Earth’s watery atmosphere
What can infrared radiation be used for?
Infrared radition is given out by all objects - the hotter the object, the more IR given out
Infrared cameras can be used to detect IR and monitor temperature. The camera detects the IR radition and turns it to an electrical signal, displayed on screen as a picture.
Absorbing IR allows objects to get hotter, the temperature inside an object increases as it can absorb the IR
How do fibre optic cables work?
Optical fibres are thin glass or plastic fibres that can carry data over long distances as pulses of visible light
They work because of reflection; the light rays are bounced back and forth until they reach the end of the fibre
Visible light is used in optical fibres because it is easy to refract light enough so that it remains in a narrow fibre
What is fluorescence?
A property of certain chemicals, where ultra-violet (UV) radiation is absorbed and then visible light is emitted
How do fluorescent lights work?
They generate UV radition, which is absorbed and re-emitted as visible light by a layer of a compound called phosphor on the inside of the bulb.
How are gamma rays used in healthcare?
X-rays pass easily through flesh but not so easily through denser material such as bones or metal.
This is because gamma rays are used and the amount of radiation that’s absorbed gives the X-ray image.
Gamma is also used for radiotherapy to kill cancer cells.
Gamma can also be used as a medical tracer.
[PRACTICAL]
How can emission be investigated using a Leslie cube?
Place an empty Leslie cube on a heat-proof mat
Boil water in a kettle and fill the Leslie cube with boiling water
Wait for the cube to warm up, then hold a thermometer against each of the four vertical faces, all should be the same temperature
Hold an infrared detector a set distance (e.g. 10cm) away from one of the cubes faces and record the amount of IR radiation it detects
Repeat this measurement for each of the cube’s vertical faces, making sure the detector is at the same distance from the cube each time
You should fine more infrared radiation is detected form the black matte surfaces than the white or shiny ones.
Repeat the experiment.
[PRACTICAL]
How can absorption be investigated using melting wax?
Set up two identical metal plates, one with a matte black side and one with a silver side, place a wax and ball bearing in the middle. Two ball bearings are each stuck to one side of the metal plate with two solid pieces of candle wax. The other sides of these plates are pointed towards the flame.
The sides of the plates facing toward the flame are the different sides.
The ball bearing on the black plate will fall first as it absorbed more IR, transferring more energy to the thermal energy store of the wax, meaning the wax melts first.
How can EM radiation be harmful?
Long frequency waves don’t transfer much energy and mostly pass through soft tissue without being absorbed.
High frequency waves all transfer lots of energy so can cause lots of damage.
UV radiation damages surface cells, and can have serious effects.
X-rays and gamma rays are types of ionising radiation which can cause gene mutation, cell destruction, or cancer.
What are Sieverts?
Sieverts are a measure of the risk of harm from the body being exposed to radiation.
1000 milisieverts = 1 sievert