paper 1 questions redo
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
H+ A-/ HA
Sulfurous acid = H2SO3
Dissassociates into H+ and HSO3- and then H+ and SO32-
Divide 0.0611/2 and plug into H+ = - log (10)(ph)
Calculate Ka
Calculate pH before acid added suing Ka and initial concentration of A- and HA
Calculate initial moles of HA, A- and Acid Added
FInal moles of acid added = 0
Calculate change in moles using change in moles of acid added (assume 1:1:1 ratio)
Using final moles calculate concentration of HA and A-
Plug into H+ = K x HA/A - and then work out final pH (pH = - Log (10) (h+)
Final pH - Initial pH = Change in PH
answer = 0.08
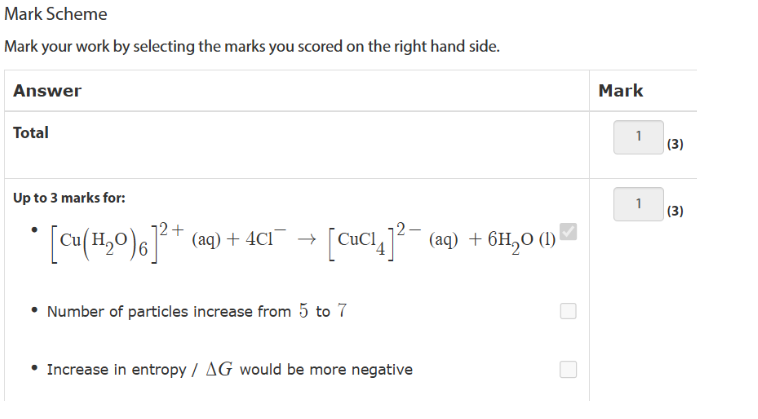
Recognise that Burgundy mixture is made of ½ Na2CO2 and ½ Copper Sulfate
Moles of Hcl = Moles of Burgundy Misture
½ moles of HCL = ½ moles of Na2CO3 (base)
Calculare moles of HCl
Calculate moles of Na2CO3 (½ Hcl)
Scale up to 250
Calculate mass of Na2Co3
Calculate mass of CuSO4 ( mass of burgundy - mass of Na2CO3)
Mass of Cu2+ ions by (mass of CUsO4 x Mr of Cu/ Mr od CuSO4)
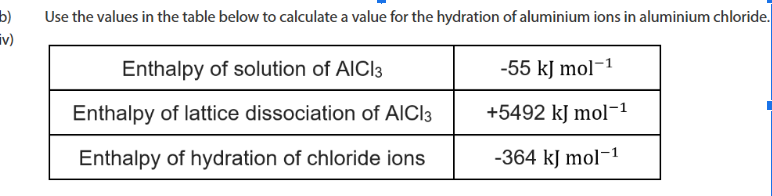
if we use nomral method the mr of hydrated salt is less than moles of salt. We have tp divide scaled up moles by 2 because we found the moles of Al3+ but the formula unit is Al2 (SO4)3 so we need to divide by 2
moles of NaOH (A-)
Moles of HA (butanoic acid)
Moles of HA after A- added = Moles of NaOH - Moles of A-
Sub values into H+ = Ka x HA/A-
ph = -log(10)(h+)
mass of one mole of ions = mass x avogardo constant


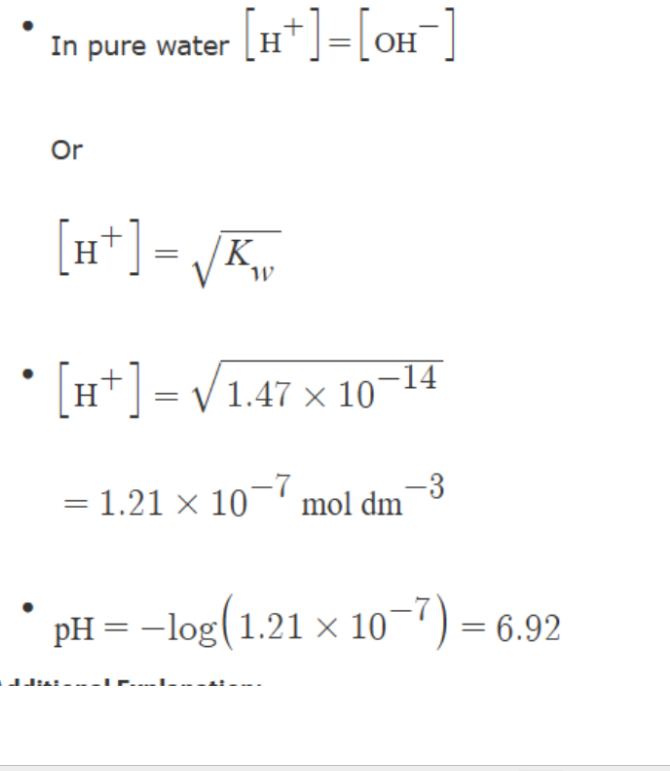

balance atoms (S) first
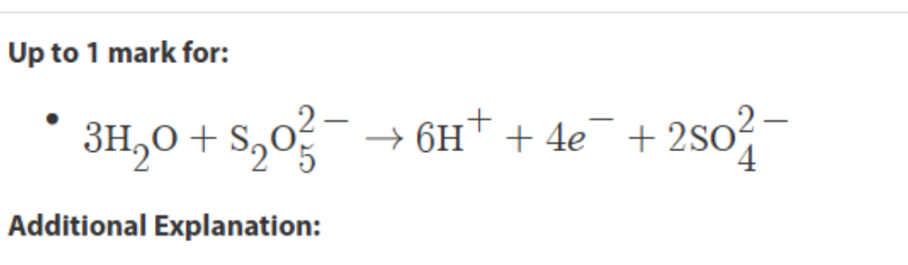

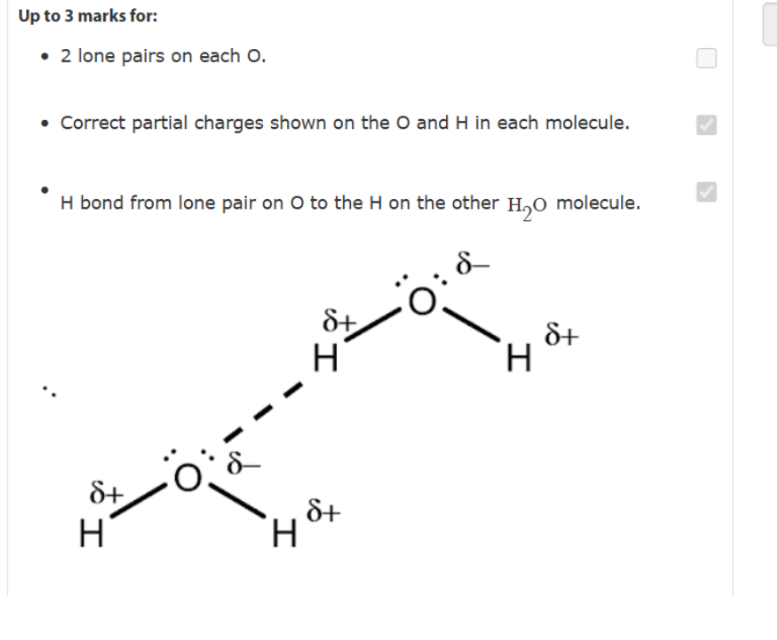
add 2 lone pairs on oxygen

when doing gibbs calculaitons remember
gibbs energy eqaution = H - T (S/1000)








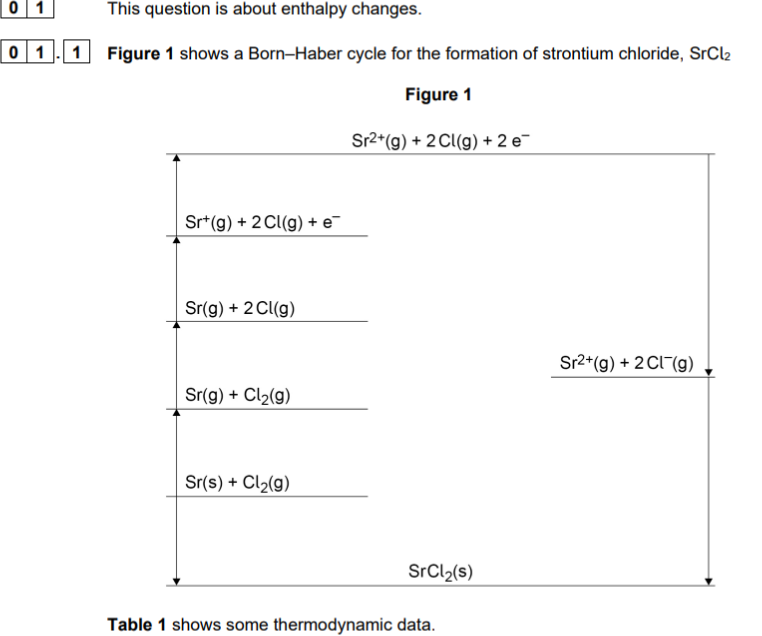
which values need to be X2
aomisaiton of chlorine (2 moleucles of chlrine be atomised)
Electron affinity of chlorine (2 moles of electron added to chlorine)

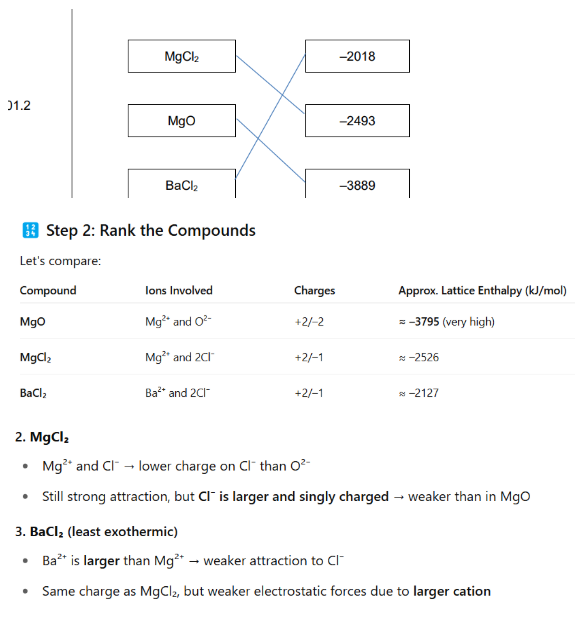
rank charges
rank size of cation
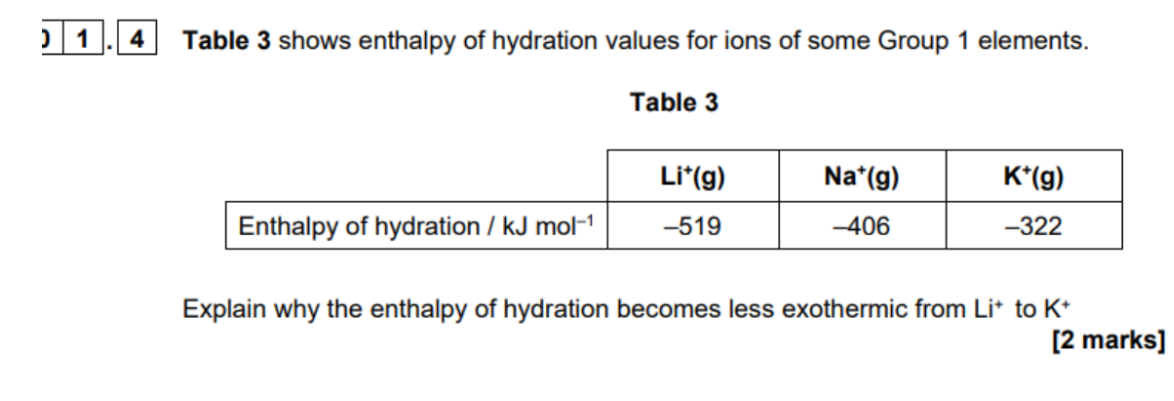

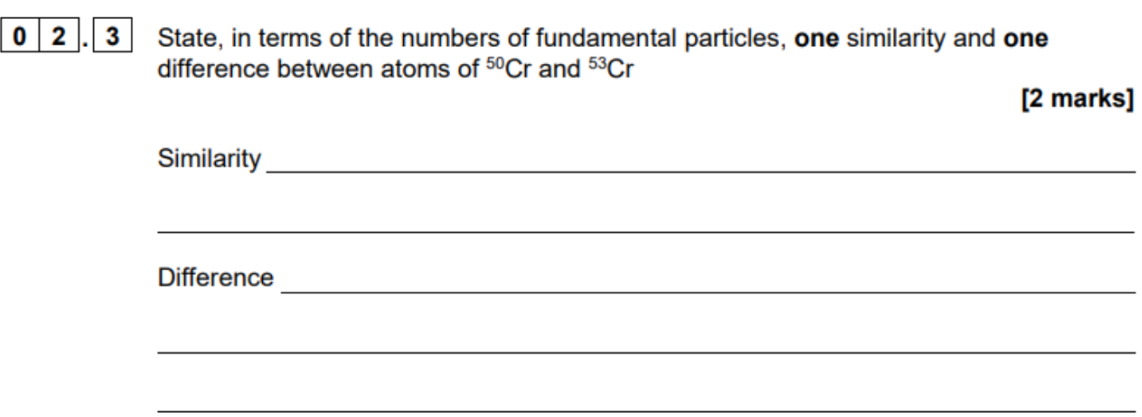
same atomic number
different mass number

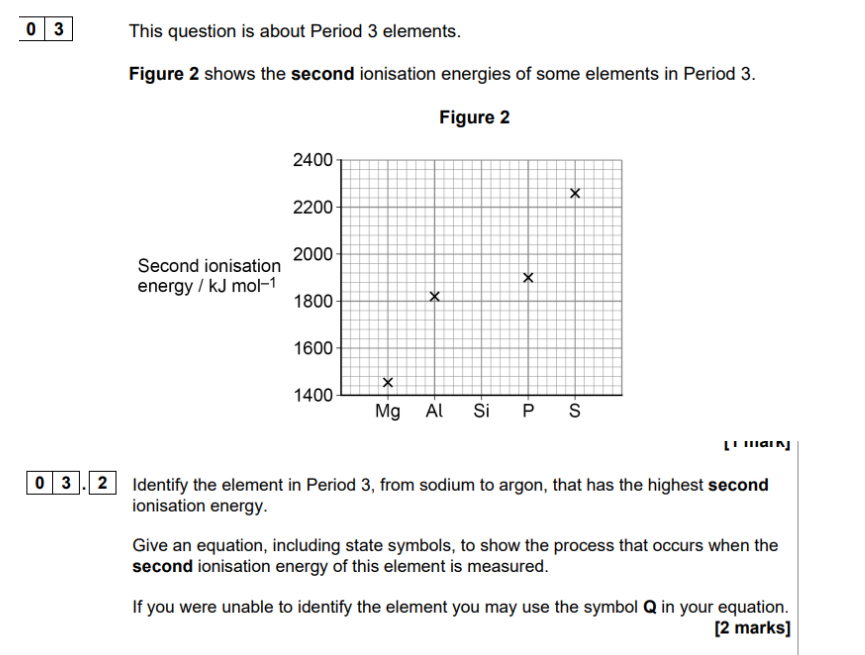
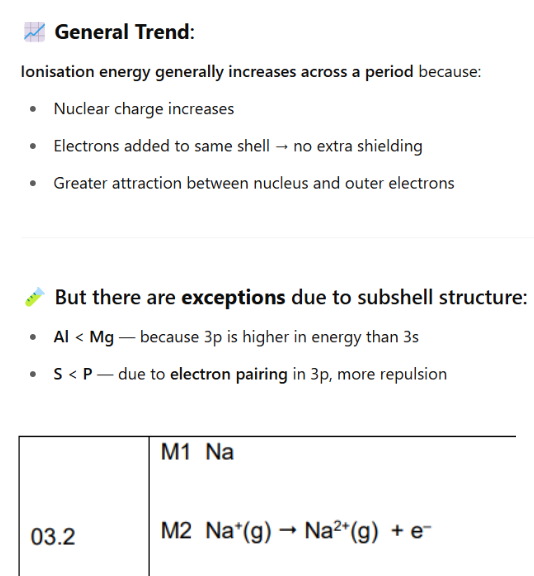
ionisation energy = removing electrons (so more postive)
remeber 2nd ionistion energy so write first ionisation energy and then 2nd
NA— NA+ +e-
Na—- Na2+ + e-

not the information in the quesiotn that we have been given
USe euqaiton C1V1=C2V2
Calculate H+ = Sqaure root KA x HA
Calcualte Ph
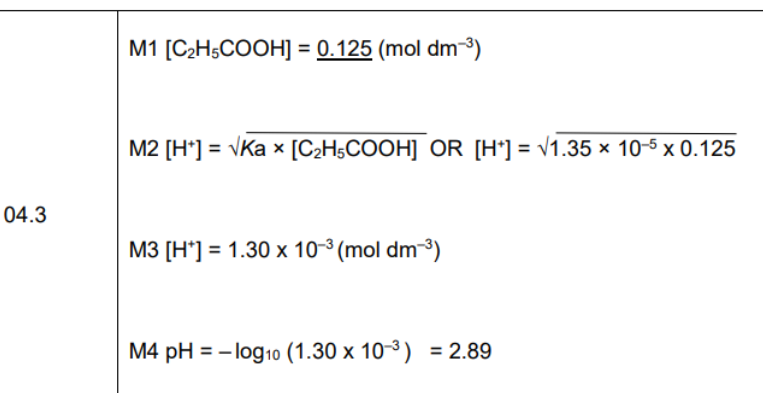
calculate Ph
Rearrnage Ka equation
remeber we are only squar rooting the numberator not the whole equation
TO reaarnge for H+ swap A- and H+
Calulate conc (plug values into equation
Calculate Moles (remember to half the volume)
Calculate mr
Calculate mass

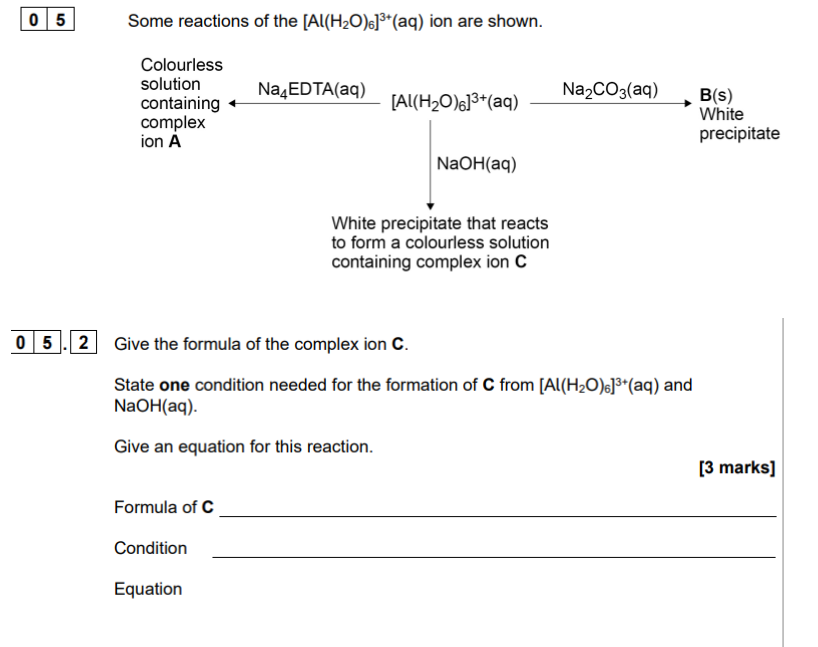
in excess replace all H2O ligands
Change Charge to -3
Remember to start from Al(H20)6 3+
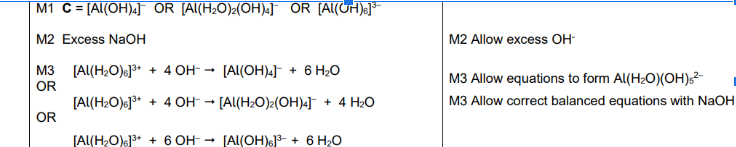

reacts as an acid in wate r
Aq + H20 = aq (1 less h2o) (OH) i less charge + H3O+
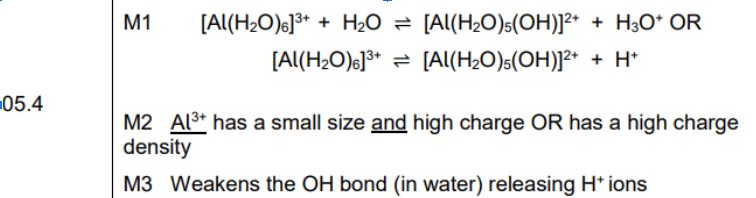
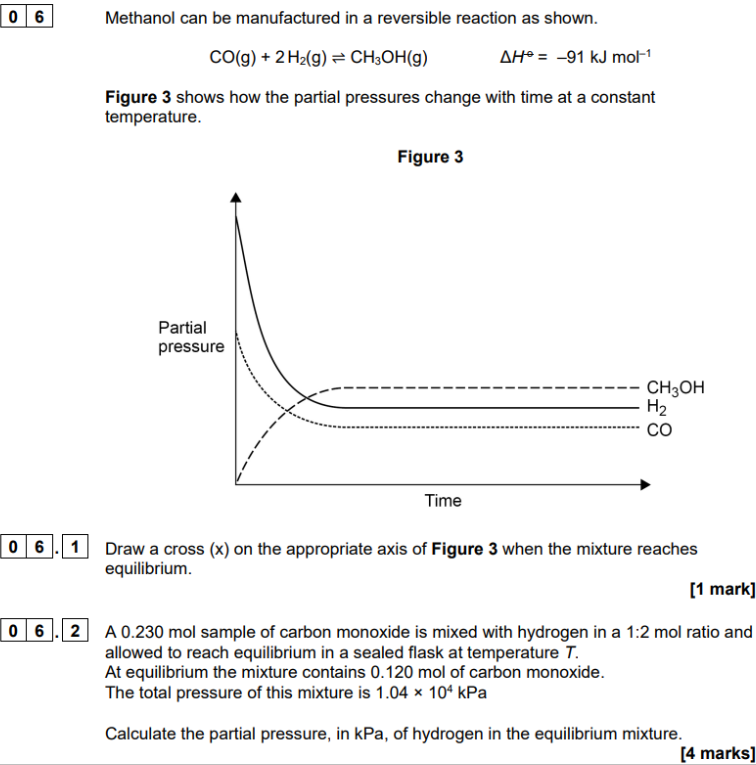
1:2 initial mole ratio with H so H is not 0 but 2 x CO


label acid and base in reaction
Produces HCl = misty fumes and NaHSO4
Remember Cl and any H most likely
H2SO4 is a stronger acid so NaCL is a base
A base (accoridng to bronsted lowry) accepts a proton


Br2 + SO2 + H2O


when Cl is added to NaBr yellow orange solution forms because Br2 is produced which is oraange bronw in water
Write reaction eqaution = displacement reaciton
Cl2 + NaBr ==== NaCl + Br2
Idenitfy OA and RA
Cl2 —— CL-
Br - ——— Br2
balance atoms
Balance H and O (not relevant)
Balance charge
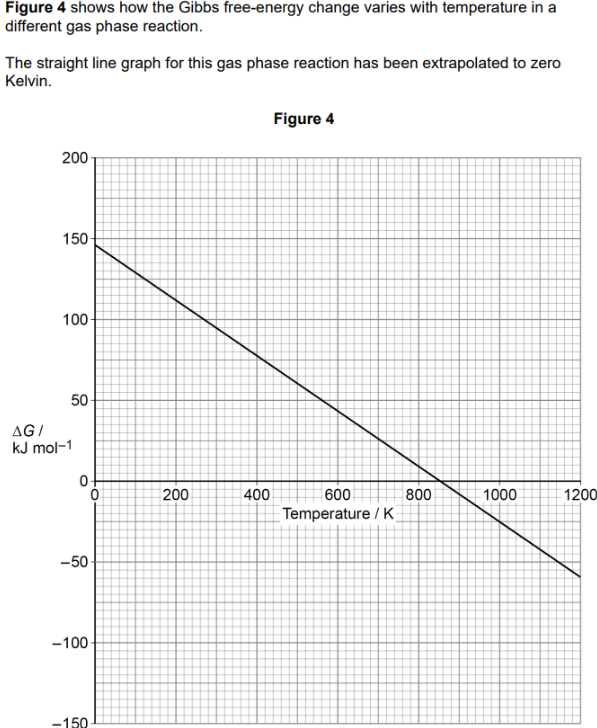
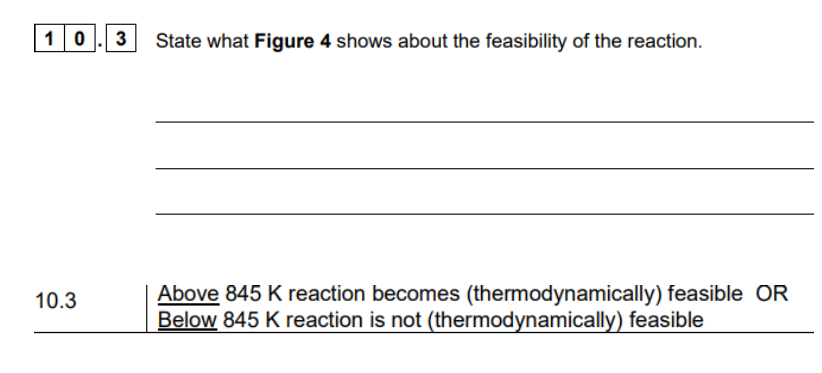


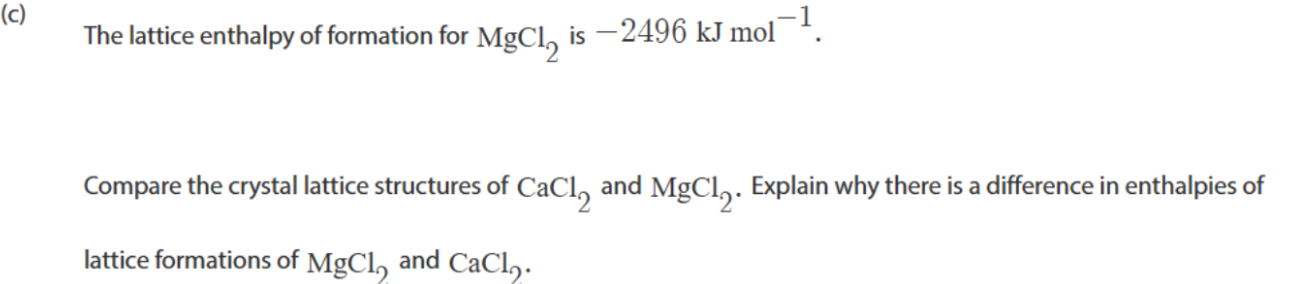


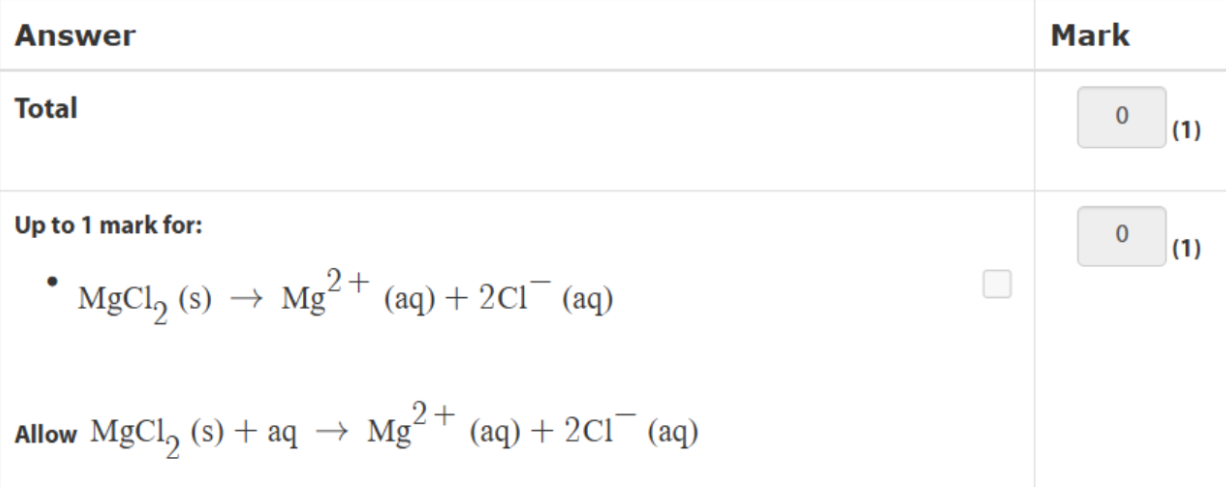
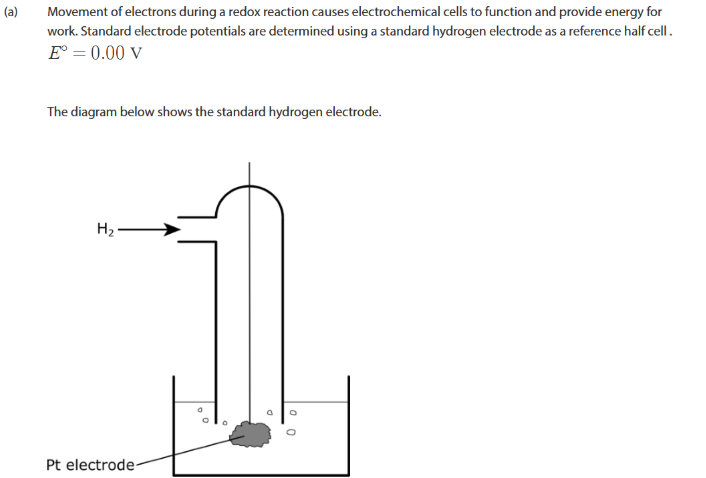
what are the standard conditons
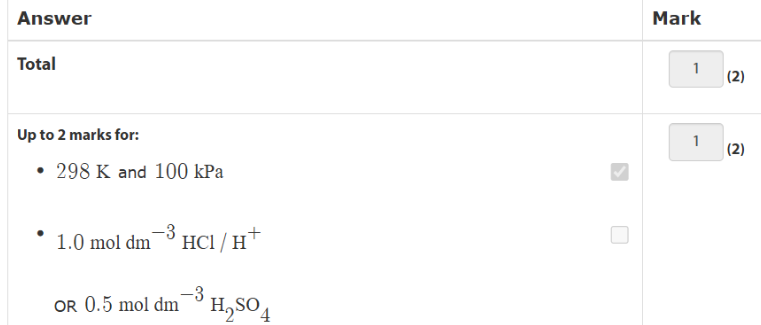

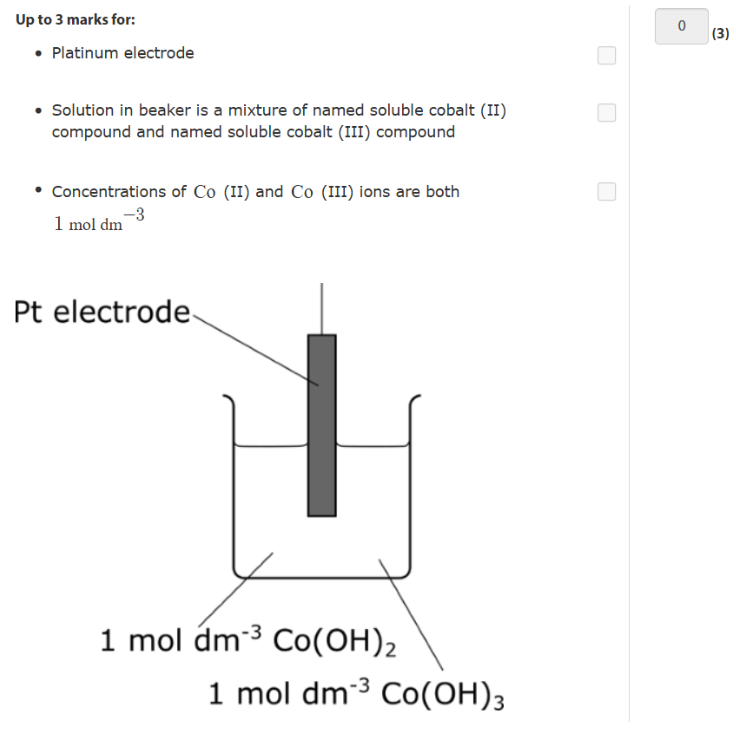
Co (OH) and Co (OH)3

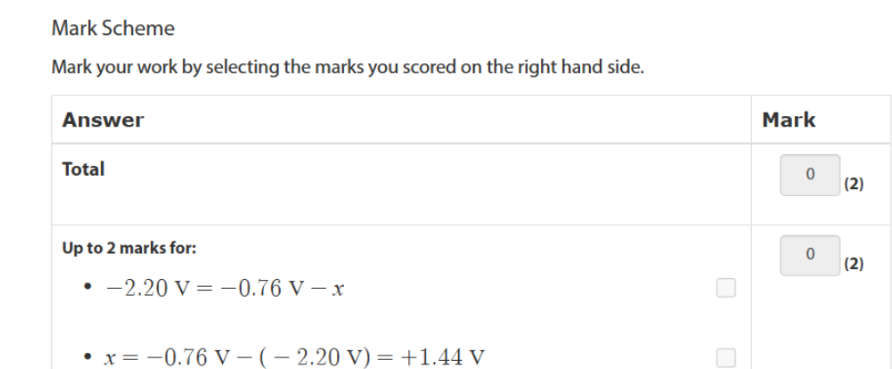
-0.76 = right/ reduced


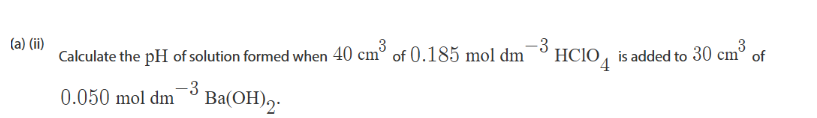
use ph resulting solution tabkek
calculate moles of HA
HClO4 so 1 dissaosscairon of H+ so moles of HA = Moles of H+
Calculate moles of A-
Calculate moles of H+ in A- (hydroxixde)
Calculate resulting moles of H+ = Moles of Acid - moles of H+ in Base
Calculate Conc of H+


calculate moels of acid
Calculate moles of base
Calculate leftover moles of OH
H+ = kw/ OH (leftover moels)

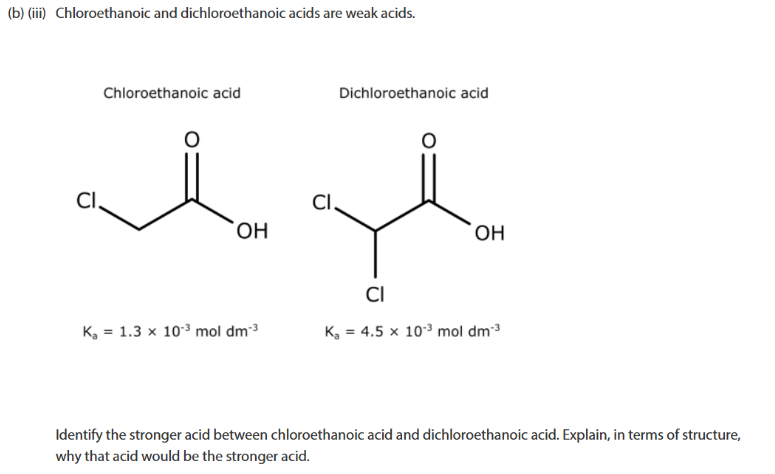
higher ka = stornger acid
polarisis/ weaknens OH bond
Cl is highly electrongative so attracts electrons more strongly


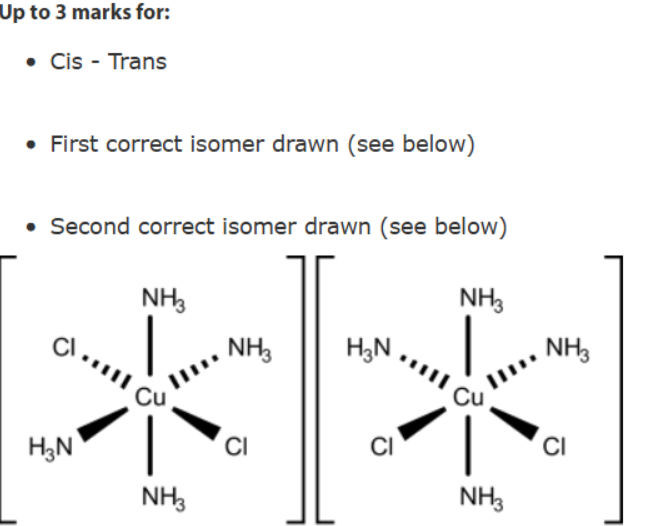
Cis same side (next to or one aqay form eachother)
Trans - oppsoitve side
to draw trans make sure the cl is more than one away from eachthe r