Smoking cessation
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Smoking Cessation guidelines
- Tobacco Use and Dependence Guideline Panel. Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence: 2008 Update. Rockville (MD): US Department of Health and Human Services; 2008 May. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK63952/.
- Barua, R, Rigotti, N, Benowitz, N. et al. 2018 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on TobaccoCessation Treatment: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Task Force on Clinical ExpertConsensus Documents. JACC. 2018 Dec, 72 (25) 3332-336
- Leone FT, Zhang Y, Evers-Casey S, et al. Initiating Pharmacologic Treatment in Tobacco-Dependent Adults.An Official American Thoracic Society Clinic Practice Guideline. Ma J Respir Crit Care Med.2020;202(2):e5-e31. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202005-1982ST3
Epidemiology of cigarette smoking
- Cigarette smoking remains the leading cause of preventable disease, disability, and death in the US
- accounts for more than 480,000 deaths every year (1 in 5)
Epidemiology of cigarette smoking:
- Gender: ____ > _________
- Age: Highest among ___-____ and __-__ year-olds
- Ethnicity: other, non-_________
- Adults with a _______
- Those with ________ and _________
- Gender: Men > women
- Age: Highest among 25-44 and 45–64 year-olds
- Ethnicity: other, non-Hispanic American Indian/Alaska Native
- Adults w/ a disability
- anxiety and depression
Menthol Cigarettes
• Menthol produces a cooling sensation in the throat
• Easier to inhale, associated with increased use and decreased cessation effects
• More common use in Women, Ages 25-44, Black population
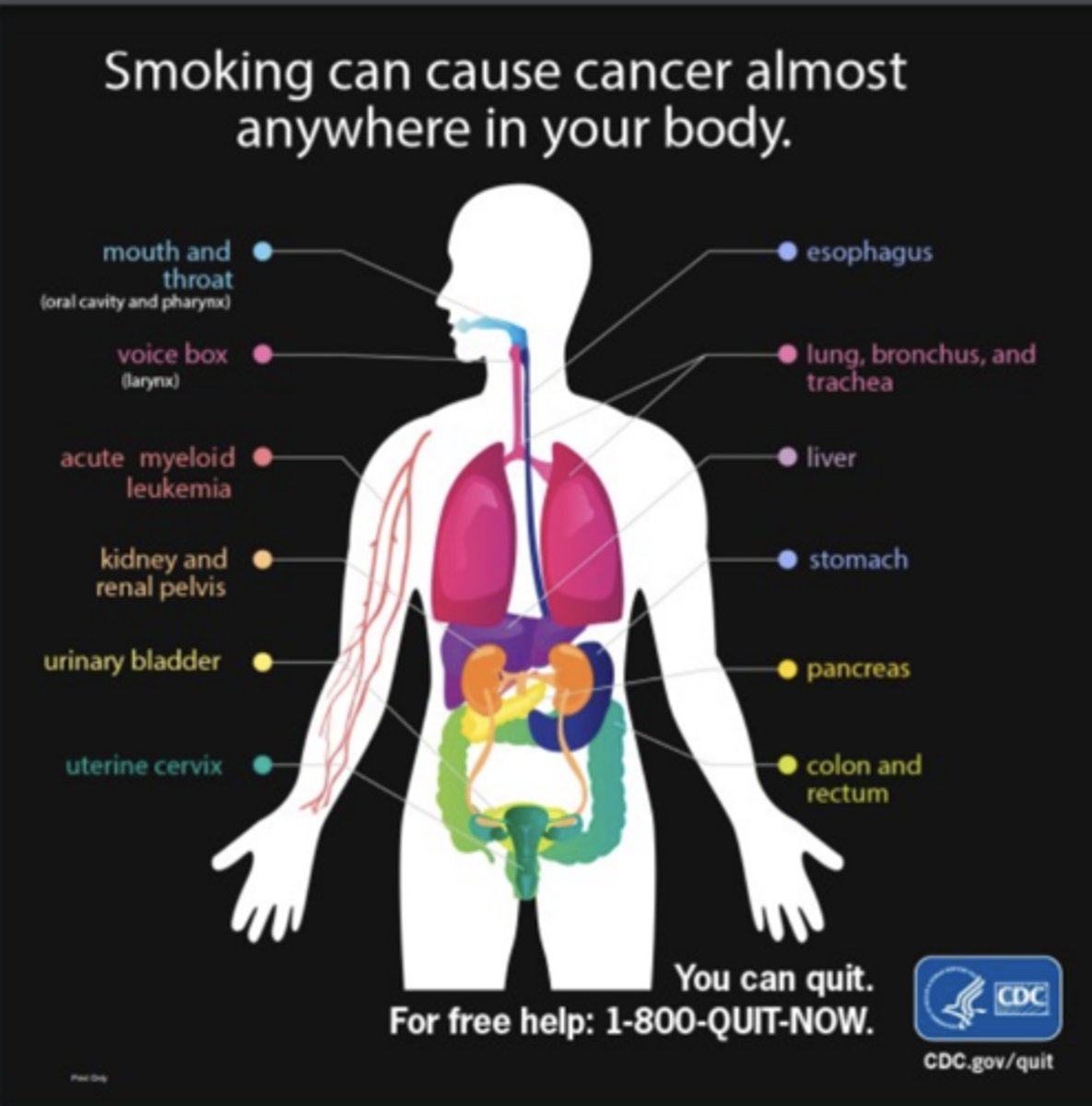
T/F: Smoking can cause cancer just in your lungs/throat
FALSE
can cause cancer almost anywhere in your body
How many cigarettes are in a pack?
A. 10
B. 15
C. 20
D. 25
C. 20
Alprazolam interaction with tobacco smoke
decreases plasma conc. of alprazolam
Caffeine interaction with tobacco smoke**
increases caffeine metabolism and clearance
Clopidogrel interaction with tobacco smoke
increases metabolism to its active form. Effects are enhanced (>10 cigarettes/day)
Insulin interaction with tobacco smoke**
possible decrease in absorption secondary to increased peripheral vasoconstriction. blood flow at insulin injection sites may be decreased, smokers may need more insulin
Olanzapine interaction with tobacco smoke
increases metabolism and clearance of olanzapine, decreases sreum concentrations
Corticosteroids' interaction with tobacco smoke
smokers with asthma have less of a response to inhaled CS
Beta blockers interaction with tobacco smoke**
bbs less effective antihypertensive and HR control
Hormonal contraceptives interaction with tobacco smoke
- increased risk of CV events (stroke, MI, thromboembolism)
- higher VTE risk of with Ortho Evra patch
- Risk increases with age (>35) and heavy smoking
Triptans' interaction with tobacco smoke
may cause coronary vasospasm, caution indicated for possible unrecognized CAD
On average, smoker die ______________ earlier than nonsmokers. The earlier the patient quits, the more _____________ there are
- 10 years
- benefits
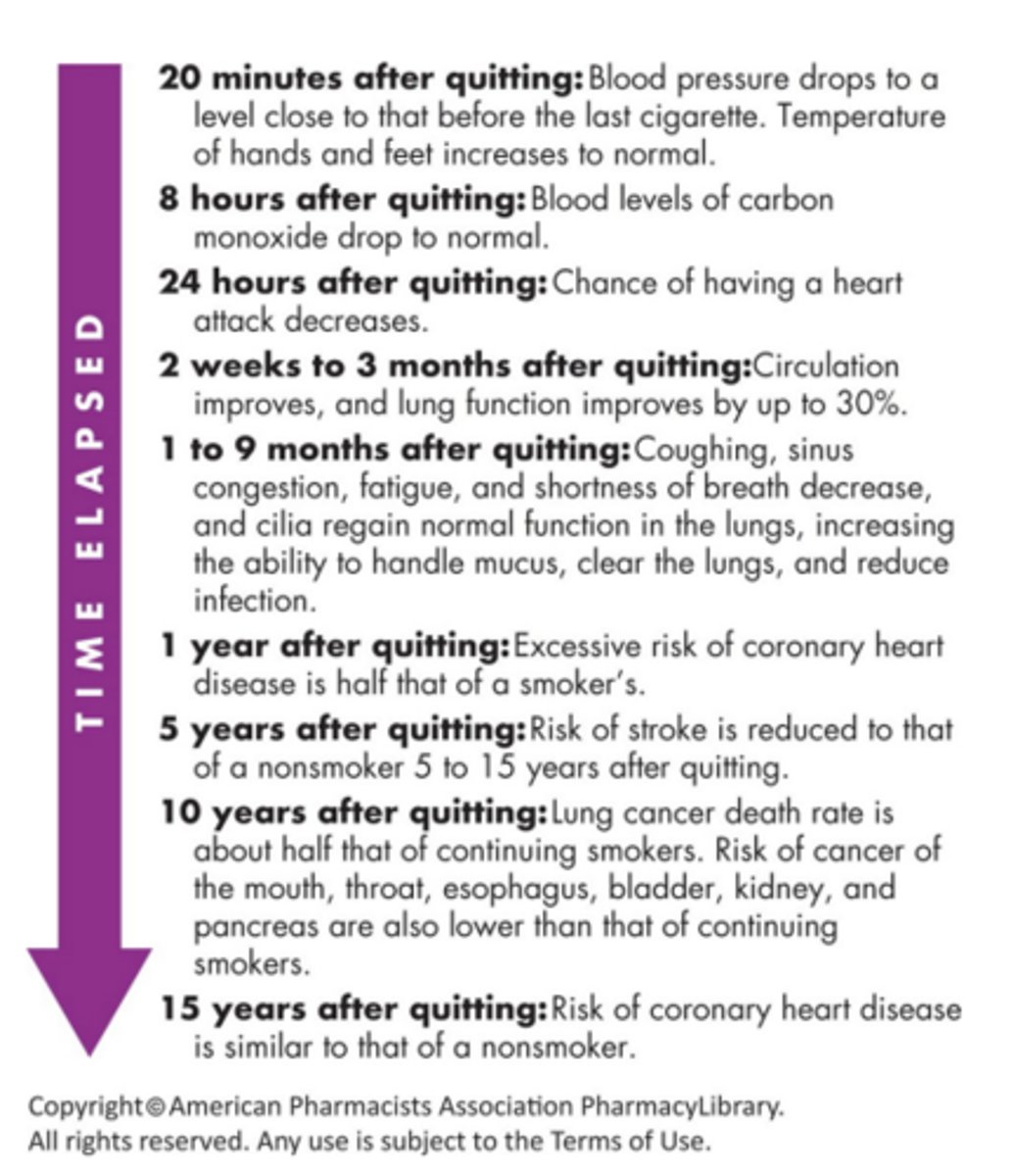
20 minutes after quitting
BP drops to a level close to that before the last cigarette. Temp of hands and feet increase to normal
8 hours after quitting
blood levels of CO drop to normal
24 hours after quitting
The chance of having a heart attack decreases
2 weeks - 3 months after quitting
circulation improves, and lung function improves by up to 30%
1 to 9 months after quitting
- coughing, sinus congestion, fatigue, and SOB decrease
- cilia regain normal function in the lungs, increasing the ability to handle mucus, clear the lungs, and reduce infection
1 year after quitting
excessive risk of coronary heart disease is half that of a smokers
5 years after quitting
risk of stroke is reduced to that of a nonsmoker 5-15 years after quitting
10 years after quitting
lung cancer death rate is about half that of continuing smokers. risk of cancer of mouth, throat, esophagus, bladder, kidney, & pancreas are also lower than that of continuing smokers
15 years after quitting
risk of coronary heart disease is similar to that of a nonsmoker
• Most smokers use the ___________ approach with 95% of these ending unsuccessfully
• Usually requires __________________ before long-term smoking cessation is achieved
• Usually requires both _____________ with ____________________ to help patients quit and prevent relapse
• Primary goal: complete cessation of use of __________________
- cold turkey
- multiple attempts
- pharmacotherapy with counseling
- all-nicotine products
What are the Different types of tobacco products?
- cigarettes
- cigars
- smokeless tobacco (chewing tobacco, snuff)
- dissolvables ex. lozenges
- hookah
- E-cigs- initially advertised as a smoking cessation agent, but not FDA approved for that
The 5 A's of Smoking Cessation
- Ask
- Advise
- Assess
- Assist
- Arrange
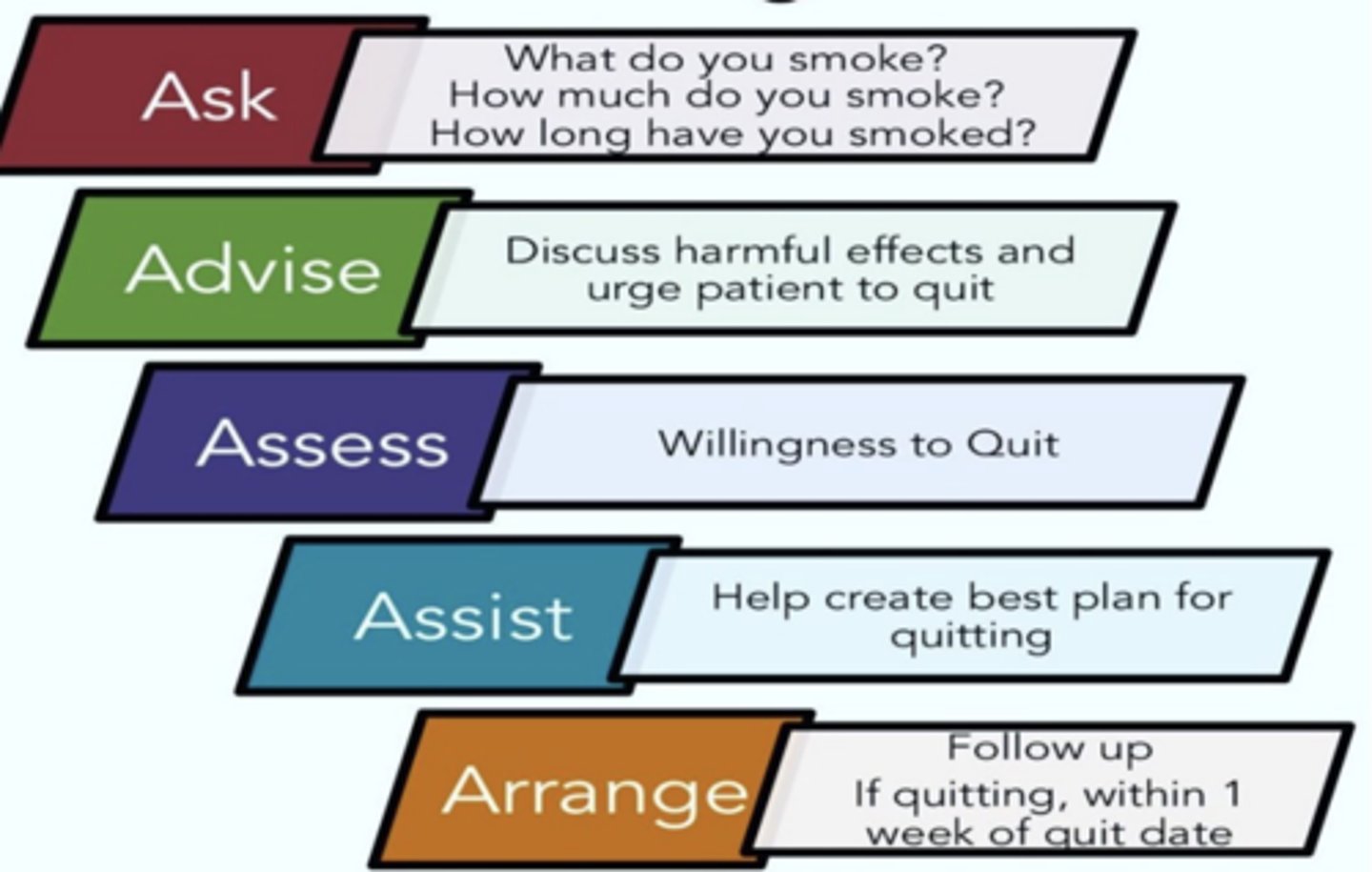
Ask
all pts should be routinely asked if they use tobacco and have their tobacco-use status documented on a regular basis. May also ask about e-cig use specifically
- What do you smoke? How much do you smoke? How long have you smoked? Are you exposed to smoke?

Advise
discuss harmful effects and urge pt to quit
- advice should be clear, strong, personalized
- express concern & willingness to help
- link benefits of smoking cessation to health, medication regimen, personal reasons and effect of smoking on family and friends

Assess
assess pts willingness/readiness to quit
can be characterized as:
- not ready to quit in next month
- ready to quit in next month
- recent quitter within last 6 months
- quit >6 months ago
helps tailer counseling to pts readiness to quit
- Motivational intervention techniques appear to be
effective in increasing a patient's likelihood of making a future quit attempt (evidence = B)

Assist
Help create best plan for quitting, maximize pts chances by creating an individualized plan
- create an individualized plan
- set quit date within next month is possible
- identify type/amount of tobacco used, past quit attempts, triggers, support groups, motivation
- social support
- concerns about withdrawal, weight gain
- facilitate the quitting process, discuss methods, coping strategies, withdrawal symptoms, med counseling, offer to assist through quit attempt

Arrange
Follow up with pt within 1 week of quit date
- assess effectiveness of therapy, side effects
- second follow up recommended within first month after quitting

Triggers
- pattern
- social
- withdrawal
- emotional
Examples of pattern triggers—an activity connected with smoking (6)
- Driving
- Talking on the phone
- Breaks at work
- Watching TV
- Drinking coffee
- After sex
Examples of social triggers- include occasions where other people smoke (3)
• Bars
• Concerts, parties
• Seeing or being with someone else who smokes
Examples of withdrawal triggers- cravings for nicotine
• Craving, smelling or handling cigarettes, matches or lighters
• Needing to do something with hands or mouth
Examples of emotional triggers- used to enhance a good or escape a bad mood
• Stress
• Anxious
• Happy
• Sad
• Lonely
• Bored
How should you deal with pattern triggers?
- find a replacement
- try activities to keep hands busy
- get moving
- change routine

How should you deal with social triggers?
- avoid places where people smoke
- ask friends not to smoke around you
- ask friends/family for support

How should you deal with emotional triggers?
- talk about your emotions
- take some slow, deep breaths
- exercise
- listen to calming music

How should you deal with withdrawal triggers?
- create distractions
- consider NRT

Psychosocial treatment
• Proactive telephone counseling, group counseling, and individual counseling formats are effective and should be used in intervention
• Smoking cessation interventions that are delivered in
multiple formats increase abstinence rates and should be encouraged
• Tailored materials, both print and Web-based, appear
to be effective in helping people quit (evidence=B)
T/F: Medication is more effective for smoking cessation than cousneling
FALSE
the combination of counseling and medication is more effective for smoking cessation than either medication or counseling alone. (there is a strong relation between the number of sessions of counseling when combined with meds, strength of evidence=A)
Types of NRT
- transdermal patches
- gum
- lozenge
- nasal spray (RX)*
- inhaler (RX)*
Non-nicotine therapy
- buproprion (Wellbutrin)( Rx)*
- varenicline (Chantix)(Rx*)
- GLP1s currently being evaluated
First-line medications for smoking cessation (3)
- buproprion SR (wellbutrin or zyban)
- Varenicline Rx only (chantix)
- NRT (OTC: patch, gum, lozenge. RX: inhaler, nasal spray)

MOA of NRT
• Replaces nicotine from tobacco to avoid physical withdrawal symptoms
• At low doses: produces a stimulant effect in the CNS
• in high doses: produces a reward effect in the CNS
Warnings/precautions for NRT (6)
- Pregnancy/lactation: crosses placental
- Heart conditions (history of heart attack, angina, arrhythmia, vasospastic disease)
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Hypertension
- PUD
- Diabetes
Contraindications NRT (2)
- Hypersensitivity to nicotine or any component in the respective delivery system
- Still using tobacco/potential for overdose
What to monitor while using NRT (3)
- chest pain, palpitations or other signs of heart problems
- High blood pressure
- Signs of PUD: Black tarry stools, severe dizziness, fainting or severe stomach/abdominal pain
Which of the following NRT provides a continuous, low level of nicotine?
A. Gum
B. Lozenge
C. Patch
D. Inhaler
C. Patch
T/F: All forms of tobacco need to be stopped by the set quit date when using NRT
TRUE
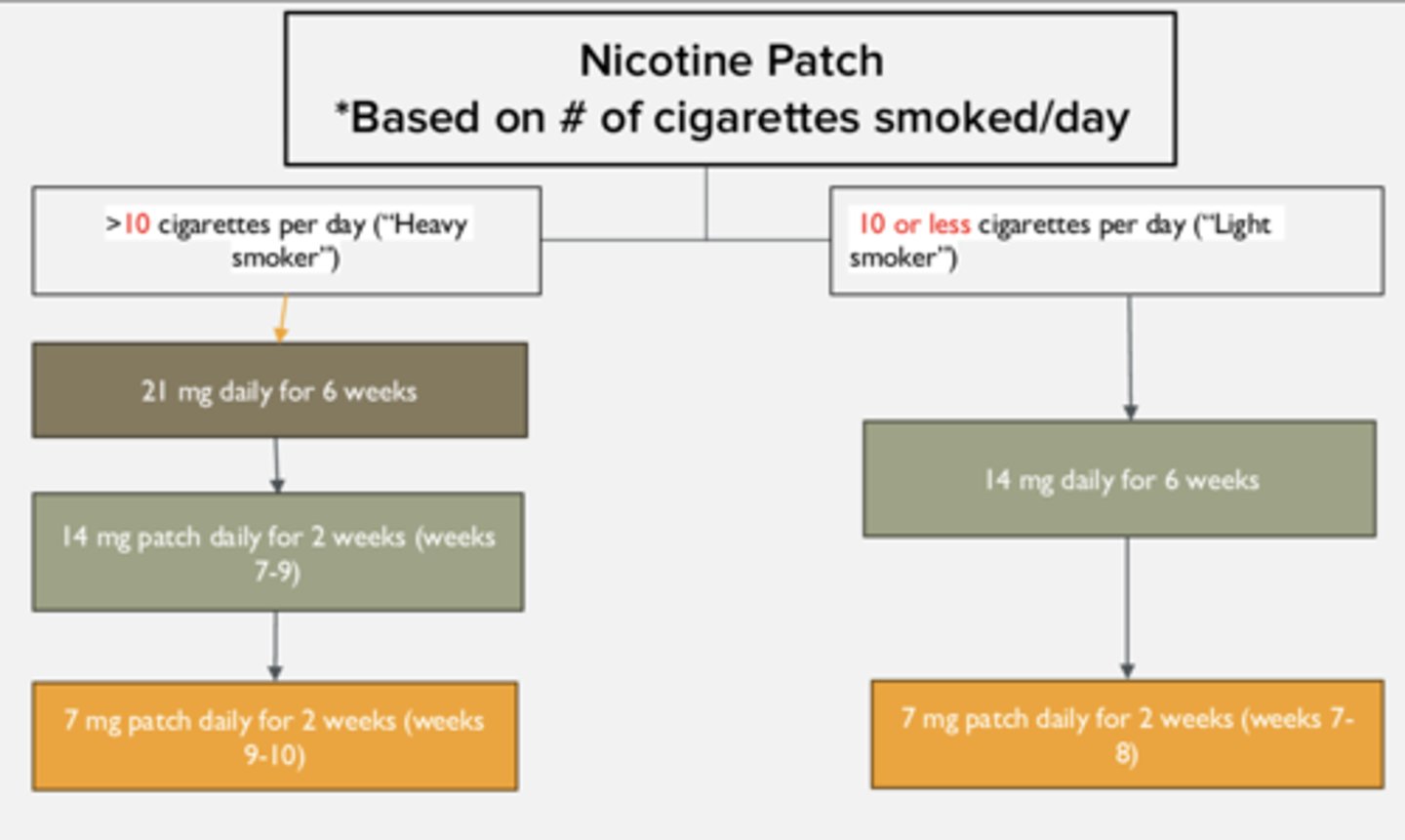
NRT Patch: Instructions for when pt smokes over 10 (>10) cigarettes per day
1. Start with 21 mg patch for 6 weeks
2. Decrease to 14 mg patch for 2 weeks (weeks 7-9)
3. Decrease to 7 mg patch for 2 weeks (weeks 9-10)
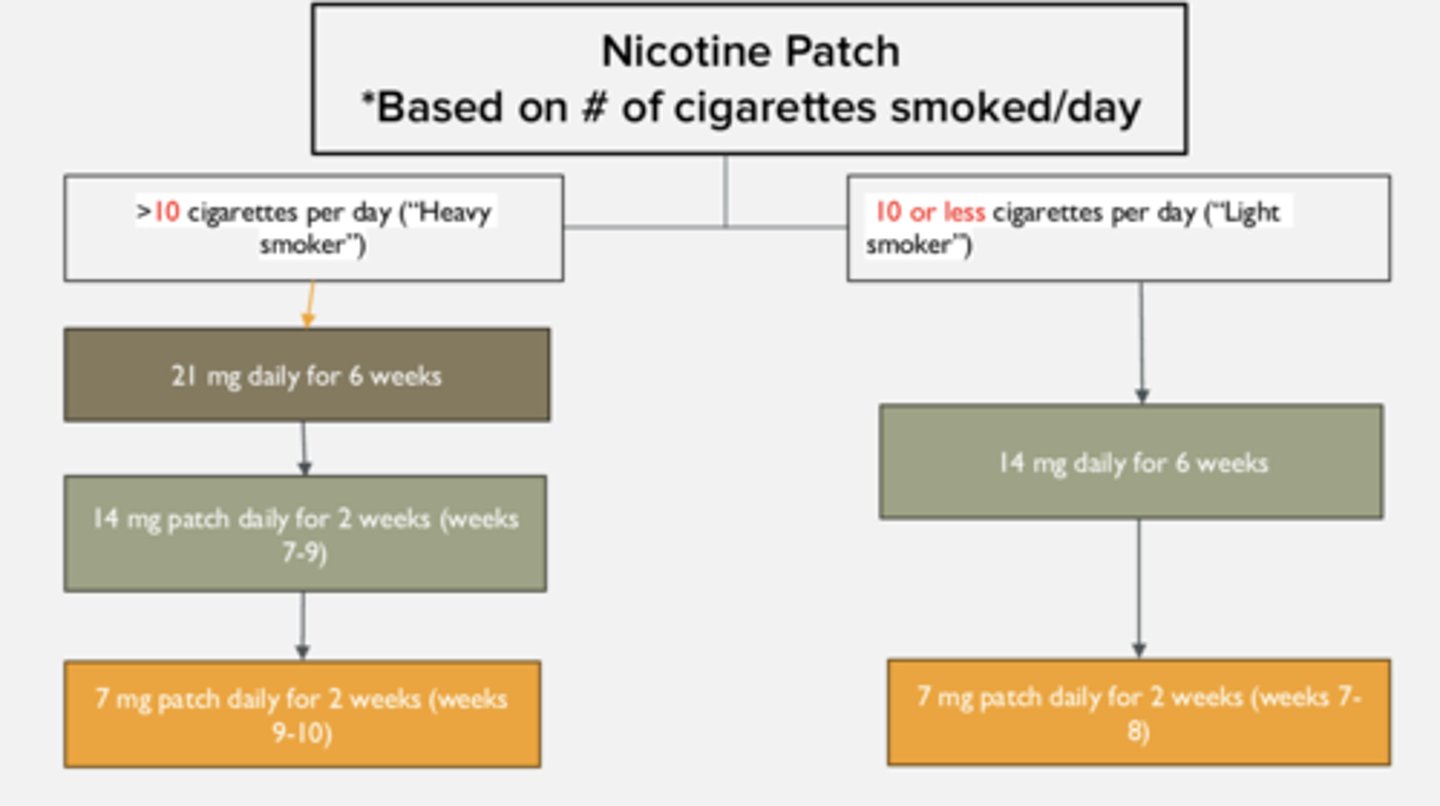
NRT Patch: Instructions for when pt smokes less than 10 (<10) cigarettes per day
1. Start with 14 mg patch for 6 weeks
2. Decrease to 7 mg patch for 2 weeks (weeks 7-8)
Apply NRT patch to....
clean, dry, hairless area of the skin on the upper body or upper outer part of the arm
- wash hands after applying/removing
- do not cut patches in half
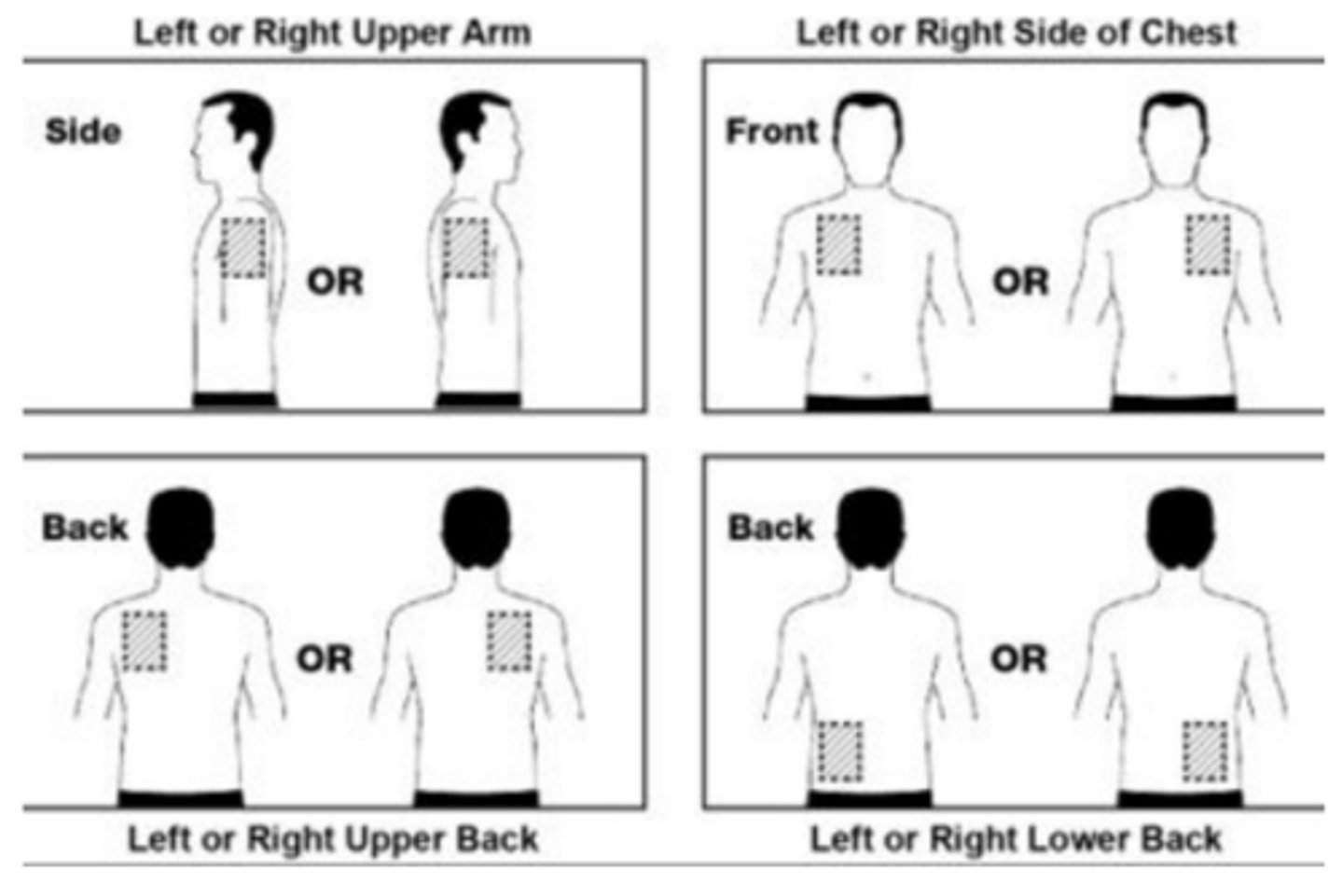
Apply NRT patch to a _________________ each day, avoid ______________ and __________ for 1 week
- different site
- tattoos
- same area
Apply firm pressure to NRT patch for at least...
10 sec
Do not leave patch on skin for more than....
24 hours
T/F: water will reduce effectiveness of the NRT patch
FALSE
will not reduce effectiveness if applied correctly
How do you discard an NRT patch?
by folding it onto itself, completely covering the area
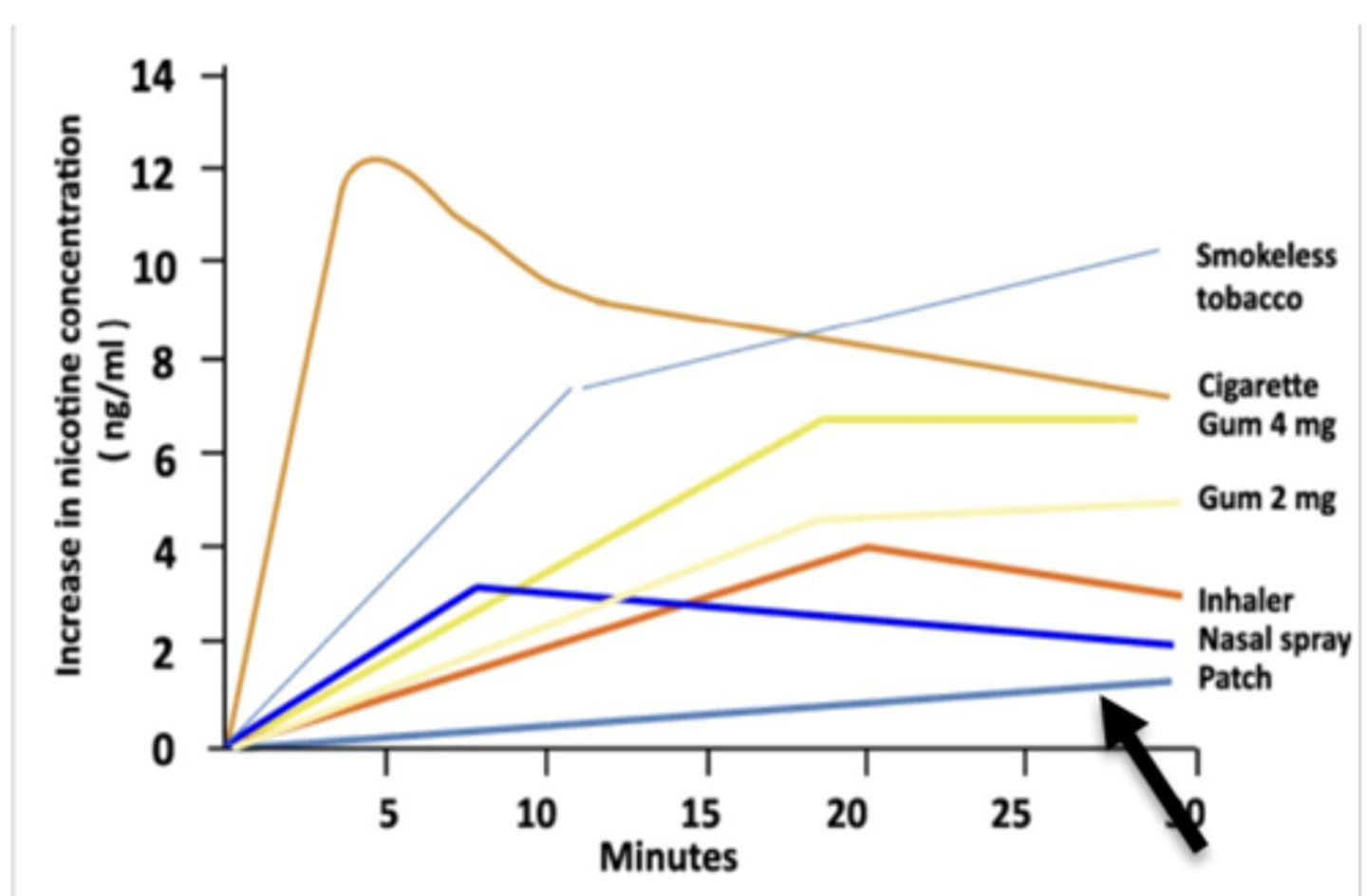
Patch Pharmacokinetics:
- delivers continuous, _____ levels of nicotine over ________________
- peak levels occur between _______________ hours after application
- after removal of the patch, what is the half-life of nicotine?
- delivers continuous, low levels of nicotine over 24 hours
- peak levels occur between 4 and 12 hours after application
- 3-4 hours
Side effects of NRT patch
• Local skin reactions (burning, erythema, pruritis)—usually due to adhesive
• Sleep disturbances from nocturnal nicotine absorption—remove patch at night and apply in AM
Warnings/precautions of NRT patch
• Consider alternative NRT if have severe psoriasis, eczema or atopic dermatitis
• Rotate application sites, allowing 1 week between sites
• Caution in those with CV disease (post MI, arrhythmias, unstable angina)
How do you determine what strength to start with when using the gum or lozenge?
A. How many cigarettes smoked/day
B. How long the patient has been smoking
C. Time to first cigarette
C. Time to first cigarette
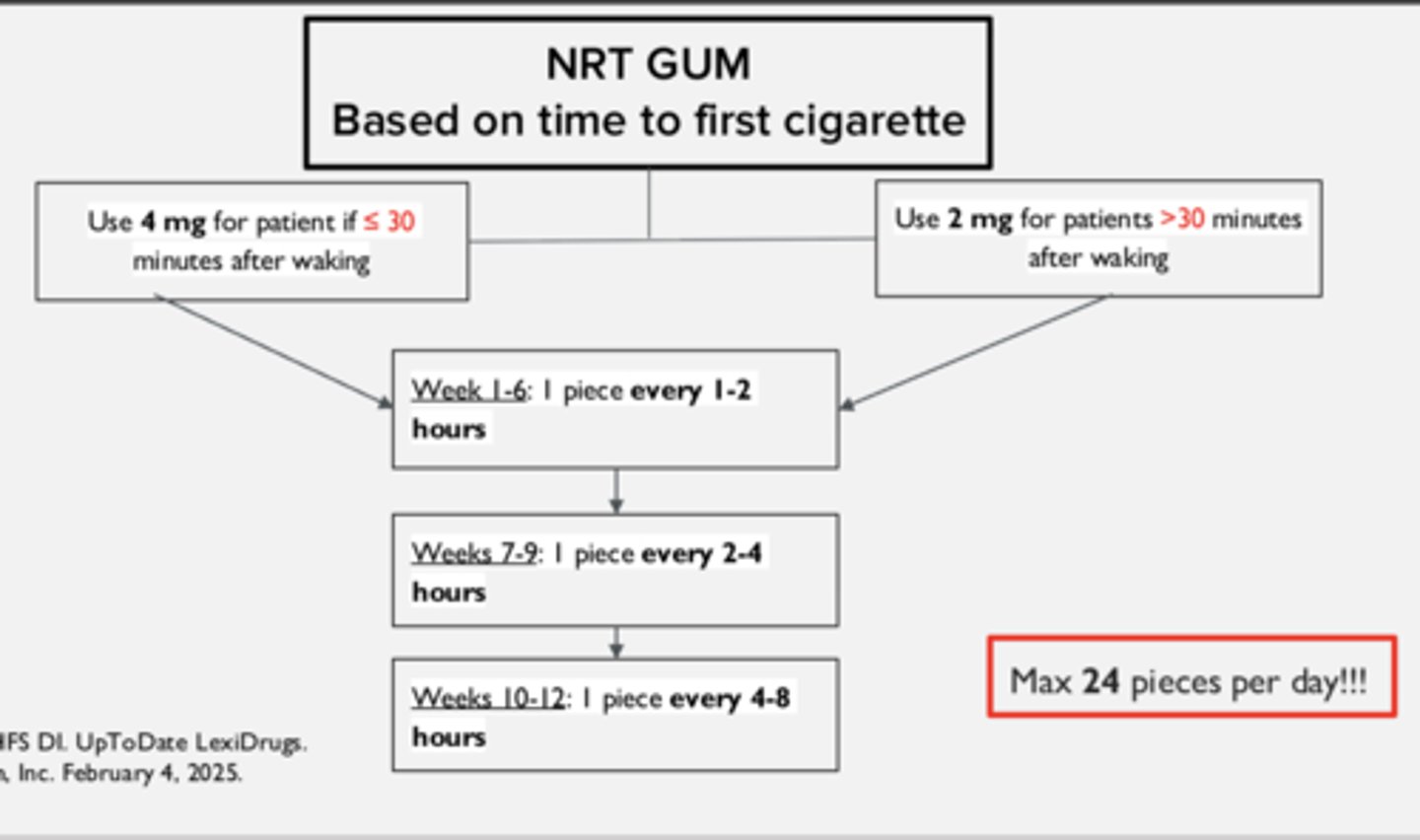
Instructions on how to use NRT gum if the time to first cigarette is < 30 minutes after waking
Start with 4 mg
- weeks 1-6: chew 1 piece every 1-2 hours
- weeks 7-9: chew 1 piece every 2-4 hours
- weeks 10-12: chew 1 piece every 4-8 hours
Instructions on how to use NRT gum if the time to first cigarette is > 30 minutes after waking
Start with 2 mg
- weeks 1-6: chew 1 piece every 1-2 hours
- weeks 7-9: chew 1 piece every 2-4 hours
- weeks 10-12: chew 1 piece every 4-8 hours
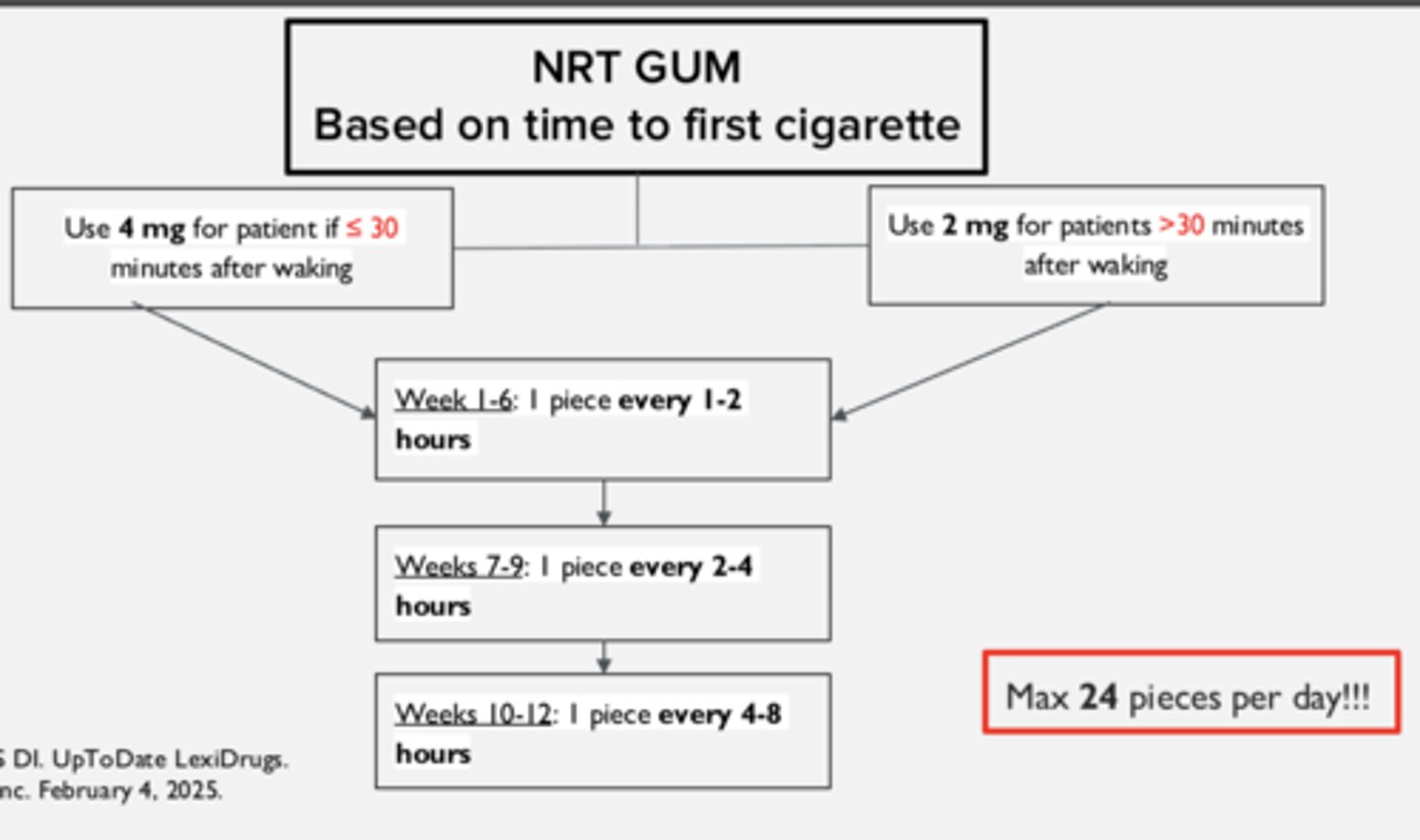
For the NRT gum, begin with a minimum of ___________ pieces daily
Max of ________ pieces daily
- 9 pieces
- 24 pieces
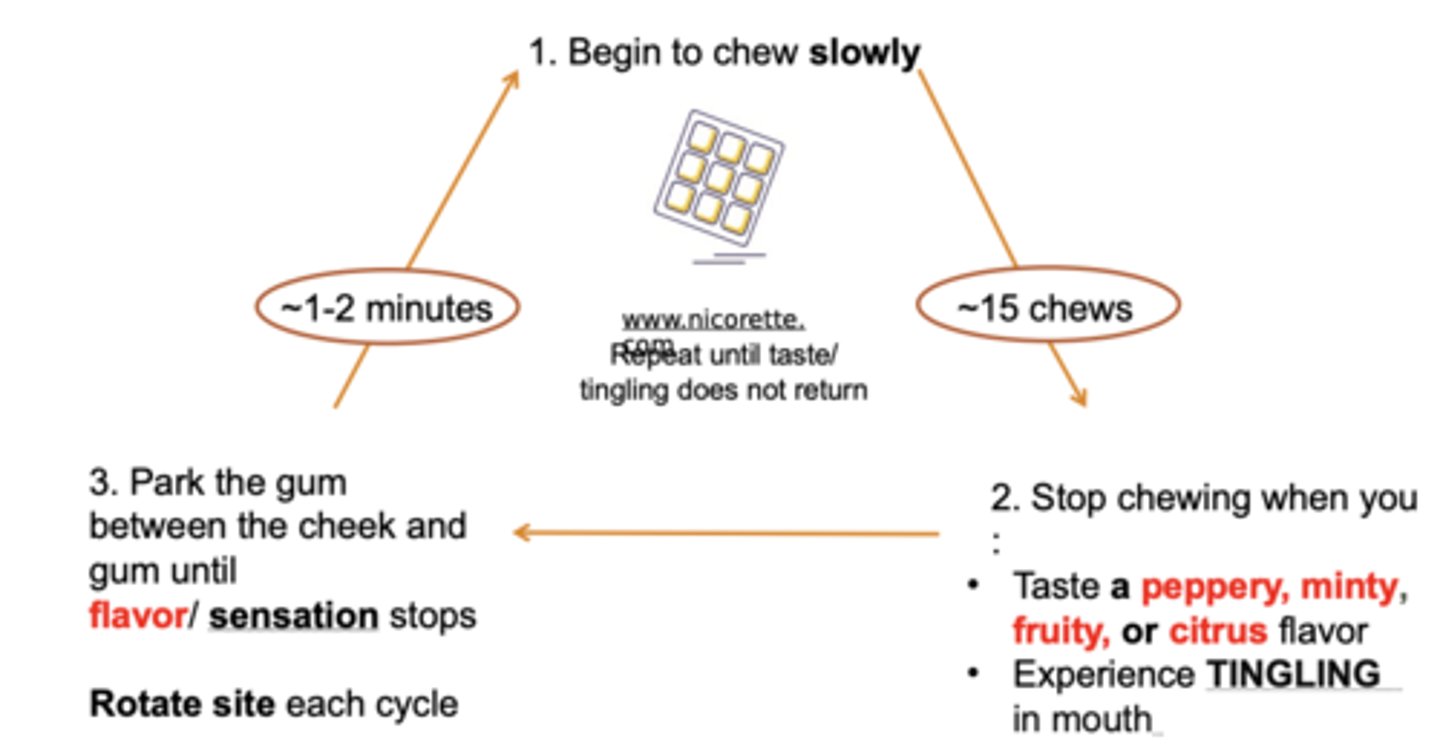
Steps on how to use the gum
1. Begin to chew slowly
2. Stop chewing gum when you taste a peppery, minty, fruity, or citrus flavor or experience TINGLING in mouth
3. Park the gum between the cheek and gum until flavor/sensation stops
- Rotate site each cycle
- on average, gum lasts 30 min.
- for cravings
Counseling tips for nicotine gum (6)
- to minimize withdrawal symptoms, use scheduled, not PRN
- Alternative: Use when craving a cigarette, titrate dose based on response and tolerance
- no more than 24 pieces/day
- acidic beverages (coffee, soda, juices) may decrease absorption. drink only water 15. min before using gum
- chewing gum too quickly will release more nicotine
- nicotine swallowed will have similar effects to excessive smoking (nausea, throat irritation, light-headedness, hiccups
- contact doctor if treatment required is >12 weeks
Gum discontinuation
• If patient has successfully stopped smoking, may ____ gum or _________________ if pt is chewing >__ pieces per day
• Reduce gum by __ or _______ pieces every ___-_____ days as tolerated
• Can also reduce chewing time to ___-____ minutes for ___-___ days then decrease ________________
• Tip: may substitute _______________ to help with discontinuation
• If patient has successfully stopped smoking, may d/c gum or gradually withdraw if pt is chewing >2 pieces per day
• Reduce gum by 1 or more pieces every 4 to 7 days as tolerated
• Can also reduce chewing time to 10-15 minutes for 4-7 days then decrease daily consumption
• Tip: may substitute sugar-free gum to help with discontinuation
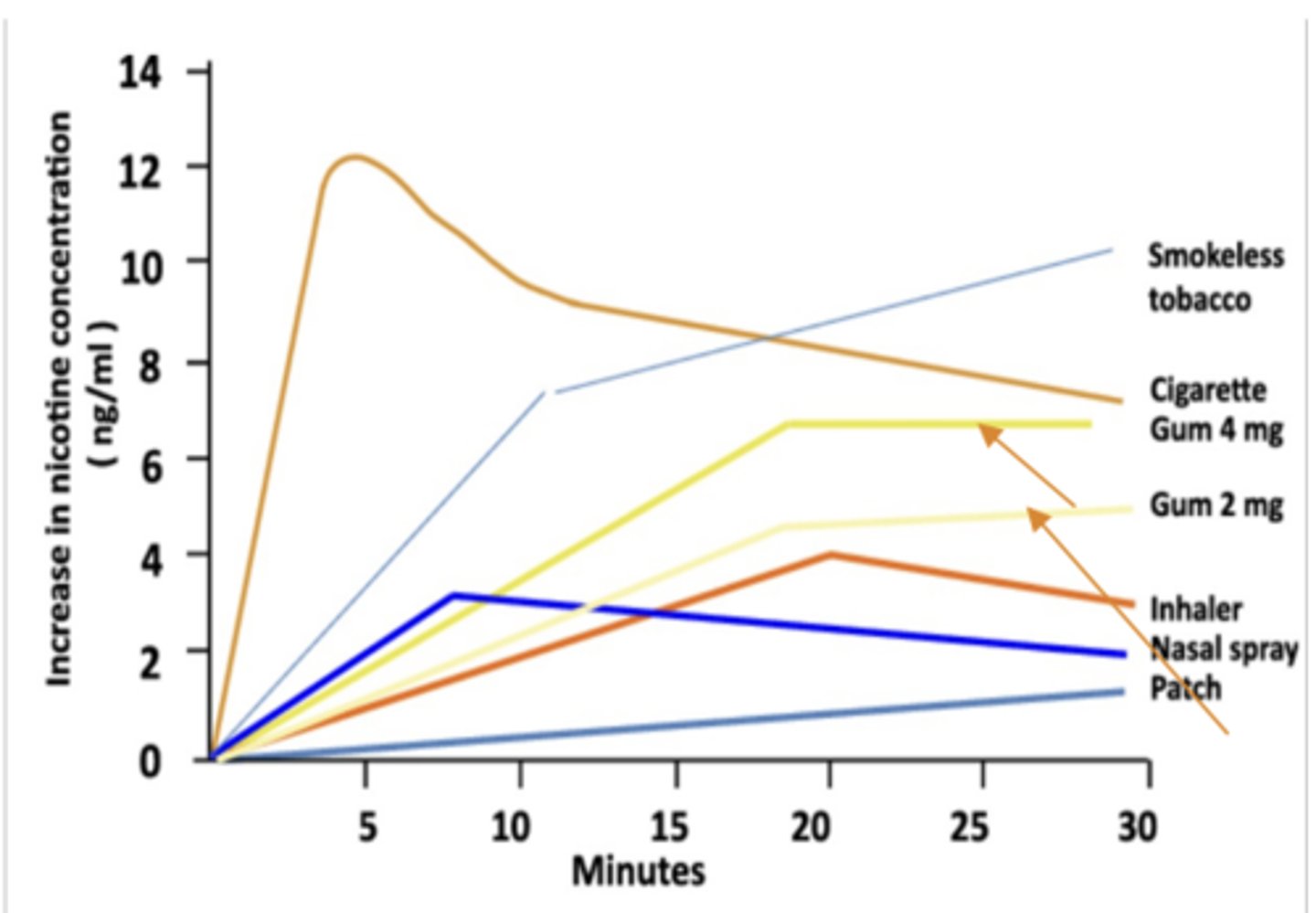
NRT Gum pharmacokinetics
• Absorption is through __________
• Time to peak:
• Patients absorb about ________ of the strength
• Absorption is through buccal tissue in mouth
• Time to peak: between 15 and 30 minutes
• Patients absorb about half of the strength (if 2 mg, will absorb 1 mg)
Which of the following will interfere with the absorption of nicotine gum/lozenge?
A. Water
B. Coffee
C. Milk
D. Tea
B. Coffee
Side effects of NRT gum (6)
- Unpleasant taste
- Mouth irritation
- Jaw muscle soreness or fatigue
- Hypersalivation
- Hiccups, belching
- Dyspepsia
Warnings/precautions of NRT gum (3)
- Active temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disease
- Gum more likely to adhere to fillings, bridges, dentures, crowns and braces
- Consider alternative NRT
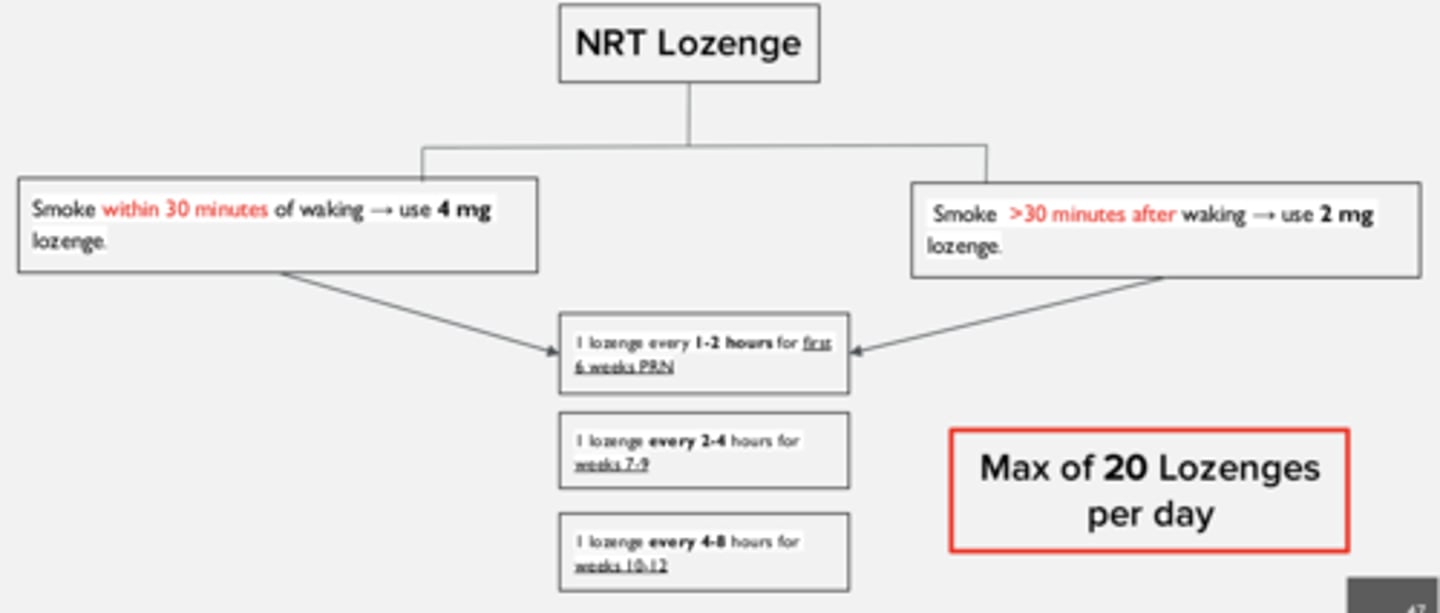
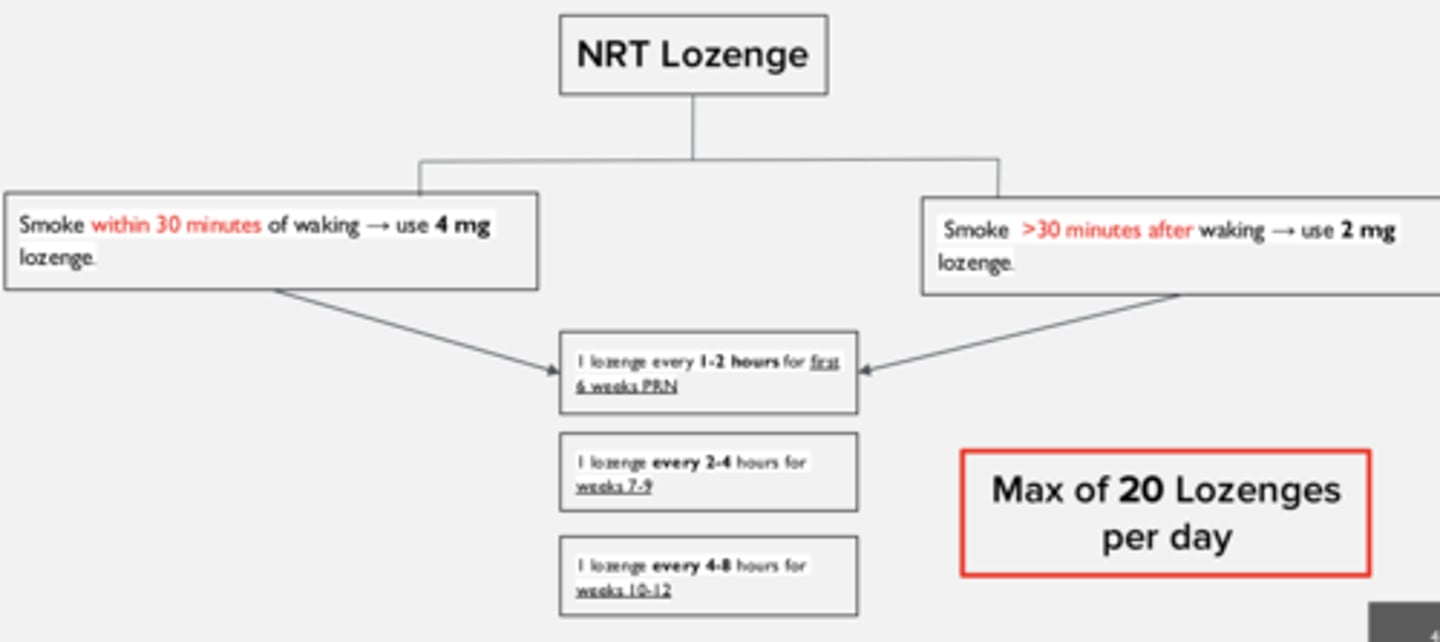
Instructions on how to use NRT lozenge if the time to first cigarette is < 30 minutes after waking
Start with 4 mg
- weeks 1-6: 1 lozenge every 1-2 hours
- weeks 7-9: 1 lozenge every 2-4 hours
- weeks 10-12: 1 lozenge every 4-8 hours
Instructions on how to use NRT lozenge if the time to first cigarette is > 30 minutes after waking
Start with 2 mg
- weeks 1-6: 1 lozenge every 1-2 hours
- weeks 7-9: 1 lozenge every 2-4 hours
- weeks 10-12: 1 lozenge every 4-8 hours
Steps on how to use the lozenges (4)
• Place and dissolve lozenge slowly in the mouth (~20 - 30 min for regular, 10 min for mini)
• As the nicotine is released the patient may experience a warm, tingling sensation
• DO NOT chew or swallow the lozenge
• Occasionally rotate the lozenge around the mouth to decrease mouth irritation
Counseling tips for nicotine lozenges (7)
• Used for cravings
• Use one lozenge at a time
• Do not use more than 5 lozenges in 6 hours or more than 20 lozenges per day.
• Acidic beverages may decrease absorption and should be avoided for 15 min. prior to using lozenges
• Have nicotine lozenges readily available and in the same place you previously kept your cigarettes
• Use at least 9 lozenges/ day for the first 6 weeks
• Contact Doctor if treatment required is > 12 weeks
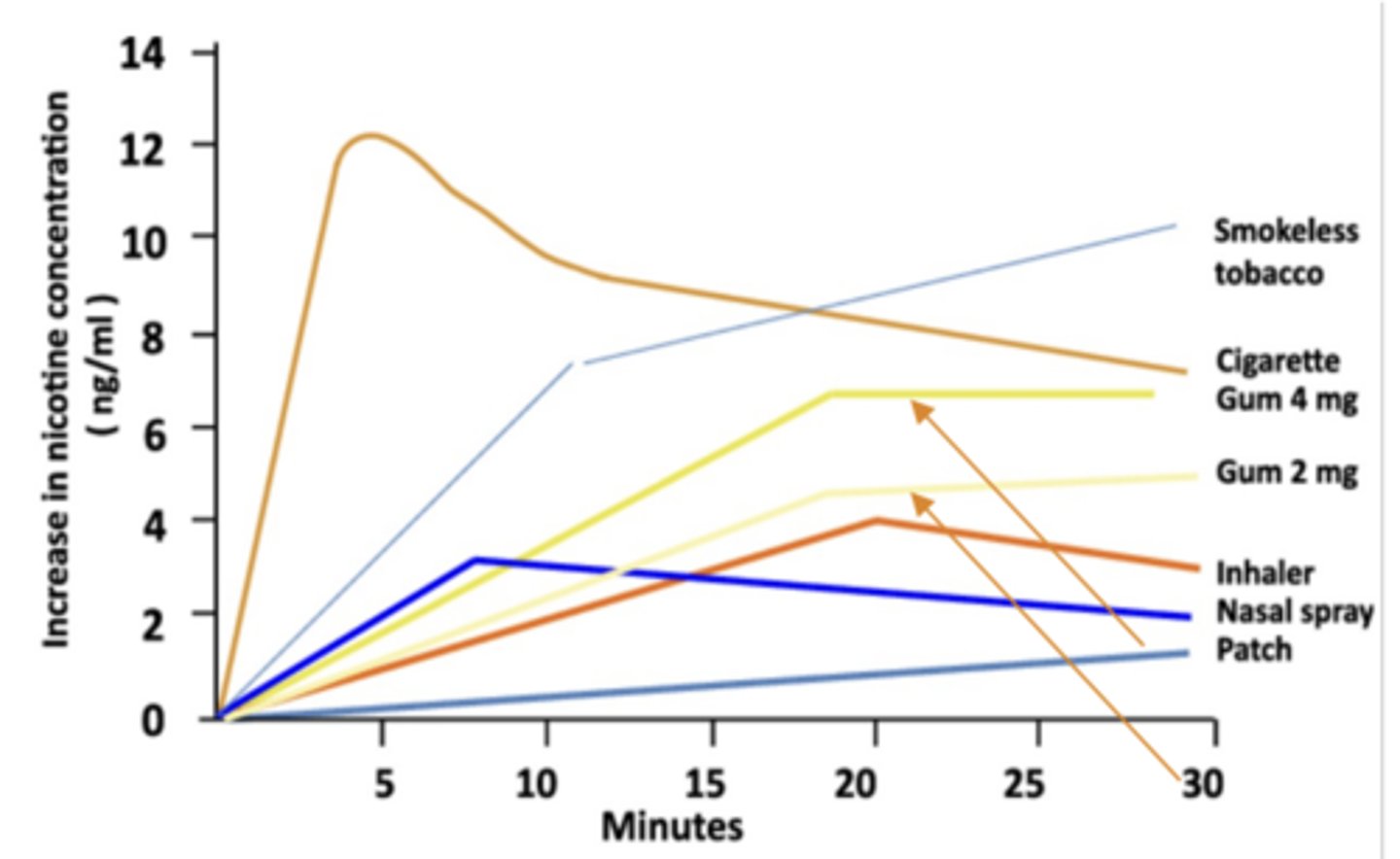
NRT Lozenge Pharmacokinetics
• Peak levels occur between ________________
• Lozenge delivers _______ more nicotine than gum equivalent due to complete __________________
• Peak levels occur between 15 and 30 minutes (similar to gum)
• Lozenge delivers 25% more nicotine than gum equivalent due to complete dissolution of lozenge
Side effects of NRT lozenge (8)
• Mouth irritation
• Nausea
• Hiccups
• Heartburn
• Sore throat
Warnings/precautions of NRT lozenge (3)
• Sodium-restricted diets
• Stomach ulcers
• Diabetes
• Hx of seizures
NRT: Nasal spray
- Dose: ___ spray in each nostril q _-_h
- One dose = _____ sprays = ____ mg
- Max doses/hour? Per day?
- Should not be used longer than what?
• Dose: 1 spray in each nostril q 1-2 hours prn
• One dose=2 sprays (1/nostril)=1 mg
• Max: 5 doses (10 sprays) per hour or 40 doses (80 sprays) per day
• Should not be used longer than 3 months
Max NRT nasal sprays/day
max 80 sprays/day
How to use nasal spray
● Do not sniff or inhale through the nose as the spray is being administered
● Tilt head back slightly while administering
● Do not allow solution to contact any area other than nasal membranes
● If spilled, avoid contact with skin.
● Dispose of in waste out of reach of children and pets
Pharmacokinetics of nasal spray
- absorption occurs on nasal membranes
- peak levels occur between 4-15 minutes
- most closely approximates cigarettes compared to all other NRT
- still slower than cigarettes (cig peak occurs within 1-2 min)
- Time to peak is prolonged and extent of absorption is decreased in patients with a cold/rhinitis and by use of nasal decongestants
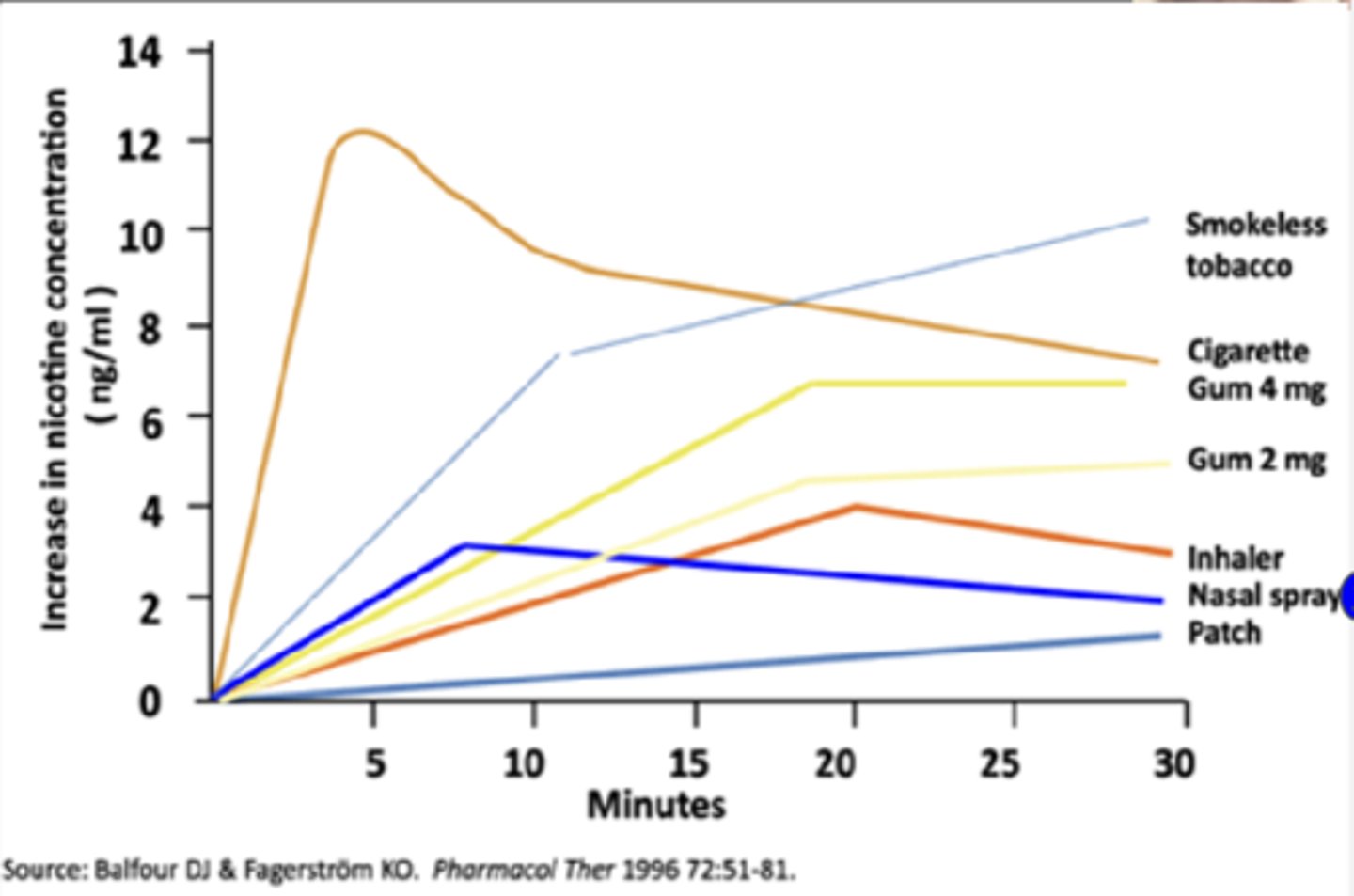
Adverse effects of NRT nasal spray
- nasal, throat, eye irritation
- rhinitis
- sneezing
- coughing
- tearing
Warnings/precautions of NRT nasal spray
- pts w/ airway disease (COPD, asthma)
- consider alternative NRT
NRT inhaler
- no longer available
- dose: use 1 cartridge q1-2h
- cartridge contains 80 puffs
- each cartridge for use in inhaler contains 10 mg nicotine
- max: 16 cartridges per day
- tapering use after 6-12 weeks of use
NRT inhaler: Use beyond ___________ is NOT recommended
6 months
Nicotine withdrawal symptoms
- craving for nicotine
- mood changes (anxiety, irritability)
- restlessness
- increased appetite/weight gain
- fatigue
- nervousness
- drowsiness
- trouble concentrating
- headaches
- muscular pain
- constipation
MOA of buproprion (Wellbutrin)
inhibits reuptake & activity of NE and dopamine
buproprion (Wellbutrin) dose
- Formulation?
- Dose?
- Duration?
• Must be 12 hour extended release (sustained release) formulation SR
• 150 mg qam x3 days → 150 mg BID
• Duration: 7-12 weeks
• Initiate treatment at least one week before quit date**
Potential benefits of buproprion
• Can further assist with depression
• Delays in weight gain
Side effects of buproprion
• Dry mouth
• Insomnia
• Nervousness, anxiety
• Weight loss
• Sweating
• Constipation
• Tachycardia
• NV
• Nasopharyngitis
• Rhinitis
Warnings/contraindications of buproprion, Do not use if....
• Taking MAOI
• Using bupropion in any other form
• Hx of seizure
• Hx of eating disorders or binge drinking
• Hx of bipolar disorder
Varenicline (Chantix) MOA
ᾳ4β2 receptor agonist: binds to nicotinic receptors, allows for release of dopamine (but much less than nicotine)
Varenicline (Chantix) Dose
- Days 1-3:
- Days 4-7:
- Day 8+:
- Days 1-3: 0.5 mg DAILY
- Days 4-7: 0.5 mg BID
- Day 8+: 1 mg BID
Varenicline (Chantix) setting a quit date
- start 1 week before quit date
- typically quit on day 8
- optional: quit between day 8-35
Side effects of varenicline (Chantix)
• Nausea*
• Vomiting
• Headache
• Irritability
• Insomnia
• Abnormal Dreams