BIOL 112 Lab Exam 3: Lab 7 Protostomes
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Be able to identify * terms. Refer to Lab 6 Flashcards for general background on key characteristics of Kingdom Animalia, 3 types of body symmetry, and tissue layers (& which phylum lack).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What is a coelom?
A fluid-filled body cavity lined with mesoderm
What is the function of a coelom?
-Fluid within body cavity cushions suspended organs
Prevents internal injury
-Allows internal organs to grow and move independently of outer body
Three types of body cavities
-Acoelomate
-Pseudocoelomate
-Coelomate
Acoelomate*
No body cavity

Pseudocoelomate*
-Body cavity between mesoderm & endoderm
-Organs attached at mouth & anus
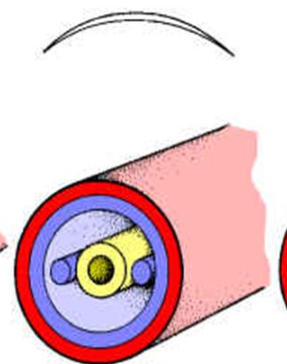
Coelomate*
Body cavity completely lined with mesoderm
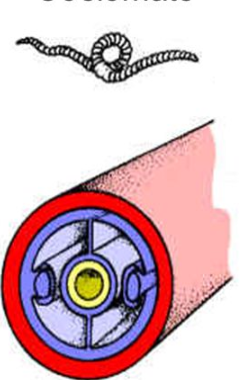
In Protostomes, the blastopore becomes
the mouth
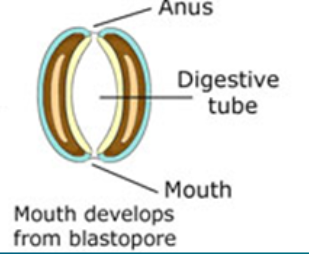
In Deuterostomes, the blastopore becomes
the anus
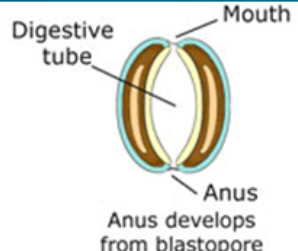
In Protostomes, the coelom formation is
schizocoelous (splitting of mesodermal bands)
In Deuterostomes, the coelom formation is
enterocoelous (outpocketing of the gut)
In Protostomes, the embryo development is
determinate
In Deuterostomes, the embryo development is
indeterminate
Both Protostomes and Deuterostomes have how many germ layers?
Three (triploblastic)
Examples of organisms in Phylum Nematoda
-Round worms
-Vinegar eels
-Ascaris
Phyla Nematoda & Arthopoda belong to
Ecdosozoan Protostomes
How many ecdysozoan species are there?
More than all other animals combined
Level of organization of Nematodoa
Organ system level
Are Nematodoa diploblastic or triploblastic?
Triploblastic
Nematodoa exhibit this type of symmetry
Bilateral symmetry
Which body cavity (if any) do Nematodoa produce?
Pseudocoelom
Characteristics of Phylum Nematadoa
-Complete digestive tract
-Only longitudinal muscles (whip-like motion)
-Dioecious (separate sexes)
-Cuticle that molts
Characteristics of Phylum Arthropoda
-Jointed appendages
-Segmented body (head, throat, abdomen in many)
-Exoskeleton made of chitin
-Open circulatory system
-Specialized respiratory systems (gills, book lungs, spiracles)
Subphyla of Arthropoda
-Myriapoda
Centipedes (1 pair of legs per segment)
Milipedes (2 pairs of legs per segment
-Chelicerate
Horseshoe crabs
Spiders
Scorpions
-Pancrustacea
Hexapoda (insects like grasshoppers)
Crustacea (crayfish)
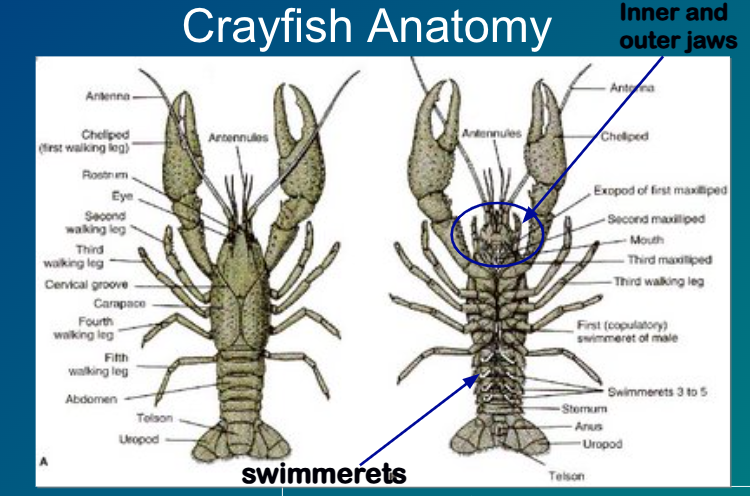
Anatomy of a Crayfish*
-Antennae
-Antennules
-Compound eyes
-Chelipeds
-Rostrum
-Swimmerets
-Head
-Thorax
-Abdomen
-Tail
-Walking legs
-Carapace
Anatomy of a Grasshopper*
-Compound eyes
-Antennae
-Head
-Thorax
-Abdomen
-Tympanic membrane
-Spiracles
-Wings
-Walking legs
Lophotrochozoans
Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic protostome organisms that may have a lophophore feeding structure, a trocophore larval stage, and/or spiral cell division in the embryo
What phyla belong to Lophotrochozoan Protostomes?
-Platyhelminthes
-Brachiopoda
-Mollusca
-Annelida
Examples of Platyhelminthes
-Planaria
-Tapeworm
-Flatworms
Eye spots/Ocelli*
-Two dark spots on head
-Light-sensitive structures that help the flatworm detect light and dark (NOT true eyes
-Found in Planaria
Auricles*
-Triangular projections on either side of the head
-Chemoreceptors used to detect food or chemicals in the environment
-Found in Planarians
Pharynx*
-On mid-ventral side (but can be extended out of the body)
-Muscular tube used to ingest food and expel waste (same opening)
-Found in Planarians and some parasitic flatworms
Incomplete gut*
-Digestive system with only one opening
Food goes in and waste goes out of same hole
-Found in all Flatworms (except tapeworms who lack a gut entirely)
Characteristics of Flatworms
-Acoelomate
-Triploblastic
-Bilateral symmetry
-Cephalization
-Hermaphroditic
-Simple nervous sytem
-Protonephridia (flame cells)
Cephalization
Beginning of a defined head
Simple nervous system
Has longitudinal nerve chords and small brain-like ganglion
Protonephridia (flame cells)
Excretory/osmoregulatory system
Characteristics of Phylum Mollusca
-Bilateral symmetry
-Triploblastic
-Coelomate
-Soft-bodied (many with calcium carbonate shell)
Most have:
Foot, visceral mass, mantle, radula
-Trochophore larvae
Which specific Mollusc class has a closed circulatory system?
Class Cephalopoda
What organisms belong to Class Cephalopoda?
-Squid
-Snails
-Clams
-Brachiopods
-Chiton
-Octopus
-Shells & bivalves
-Octopus
Characteristics making Cephalopods the most advanced invertebrates?
-Closed circulatory system
With 3 hearts
-Highly developed brain & complex nervous system
-Excellent vision
-Camouflage abilities with chromatophores
-Jet propulsion
-Internalized shell
Chromatophores
Color changing cells
Jet propulsion
-Ability to use a siphon to allow Cephalopods to move through water quickly
-Typically used for hunting or fleeing
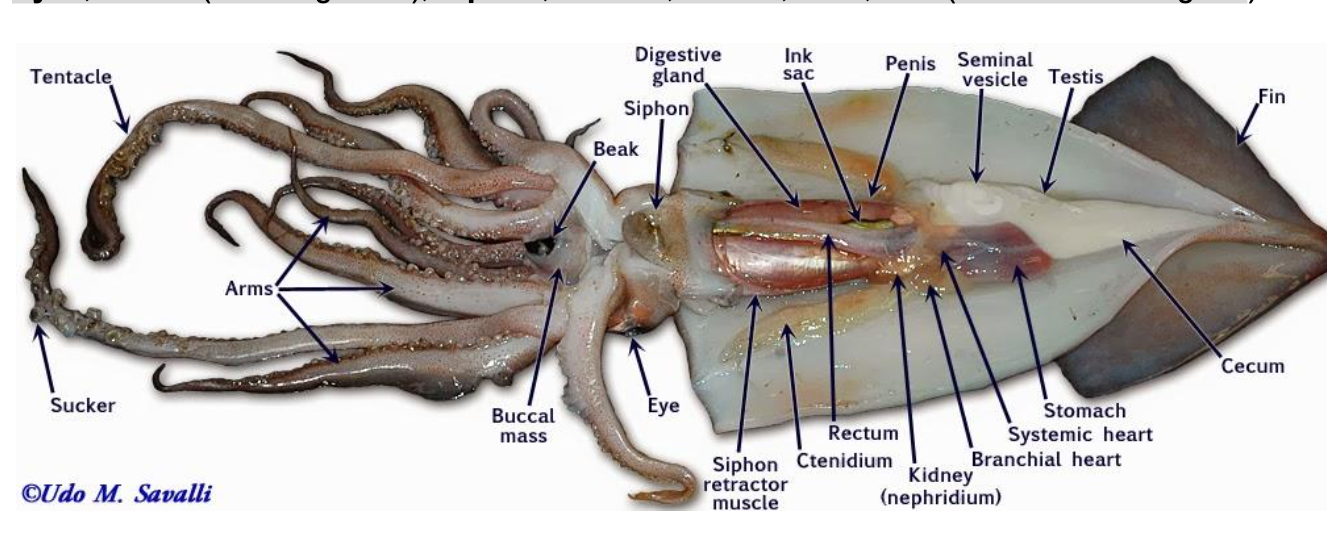
Anatomy of a Squid*
-Suckers
-Tentacle
-Arm
-Head
-Eyes
-Mouth (including beak)
-Siphon
-Ink sac
-Mantle
-Gills
-Pen (may not be shown in diagram)
Organisms belonging to Phylum Annelida
-Leeches
-Earthworm (disected)
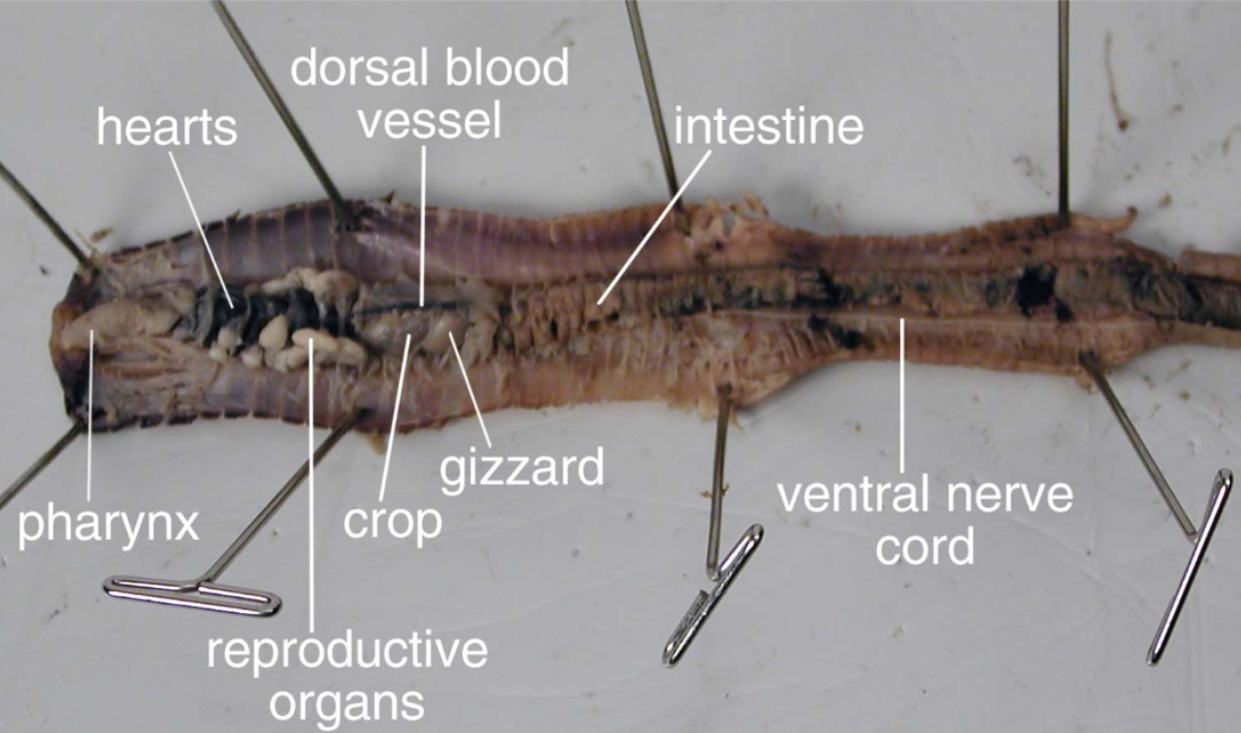
Anatomy of an Earthworm*
-Mouth
-Anus
-Pharynx
-Crop
-Gizzard
-Intestine
-Septa
-Clitellum