Chapter 17: The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation of Breathing
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
gas exchange
the process of obtaining oxygen from the environment and releasing carbon dioxide
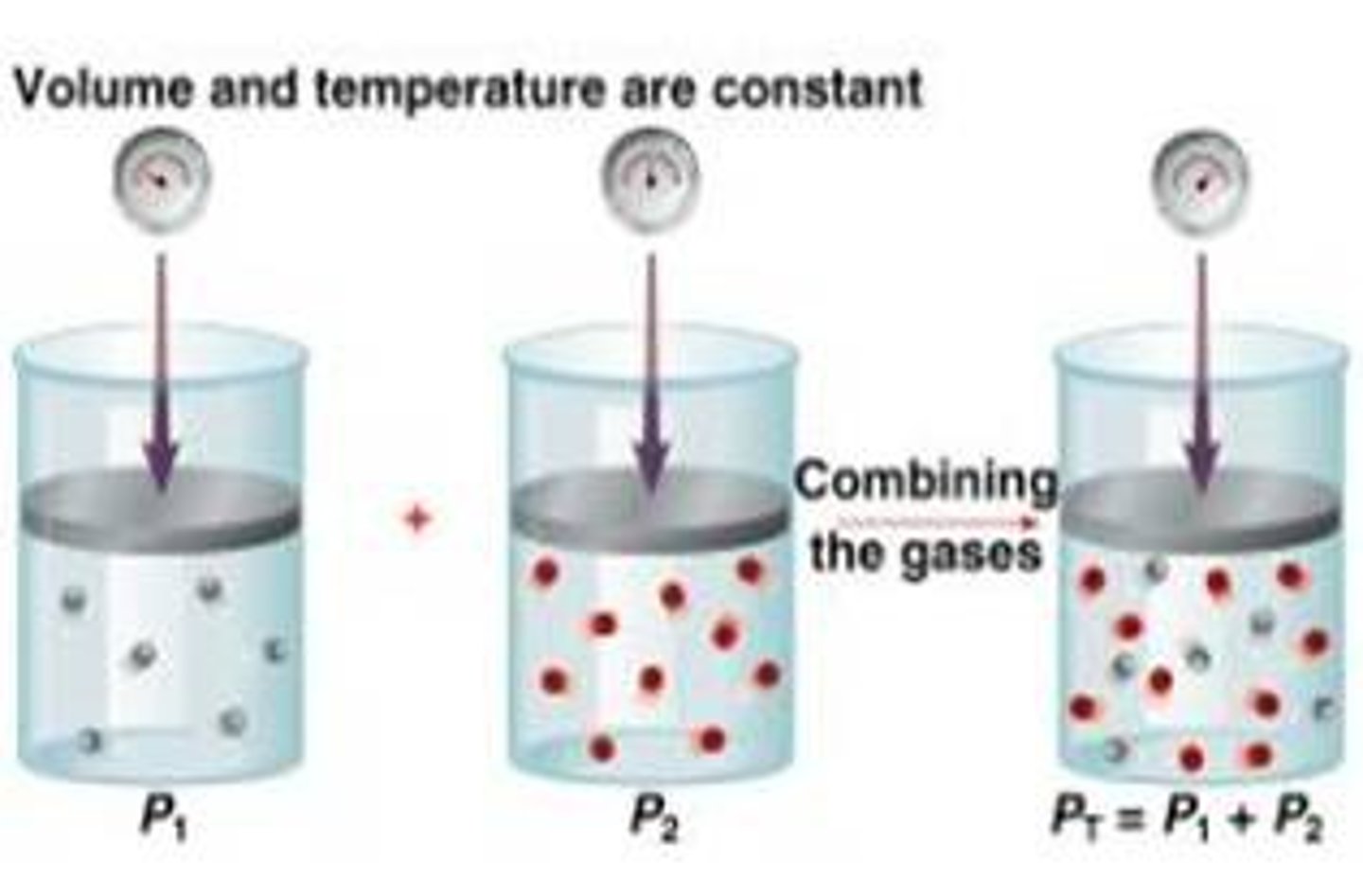
Dalton's Law
at constant volume and temperature, the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases

partial pressure
the contribution each gas in a mixture makes to the total pressure
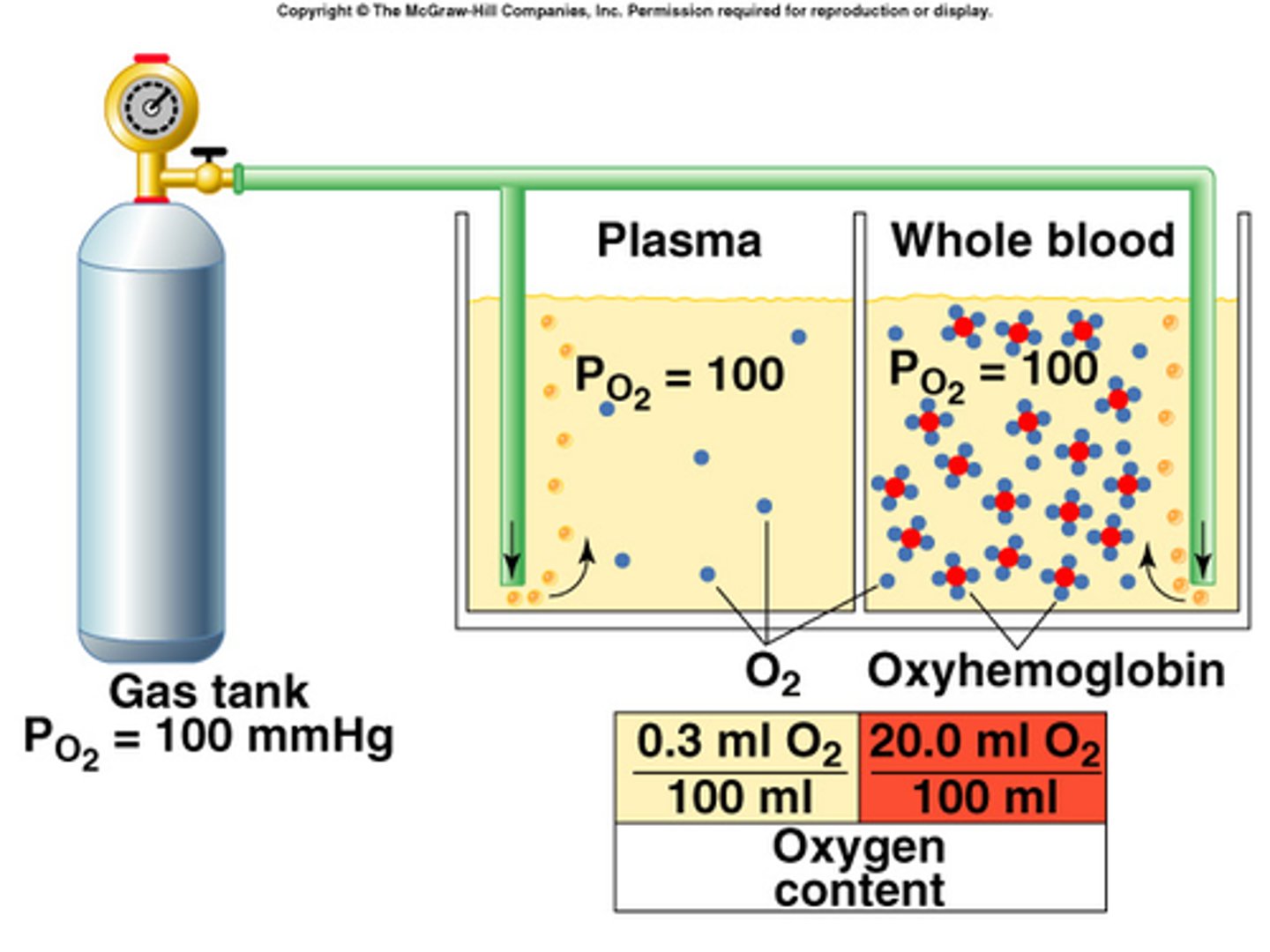
PO2
partial pressure of oxygen
PCO2
partial pressure of carbon dioxide
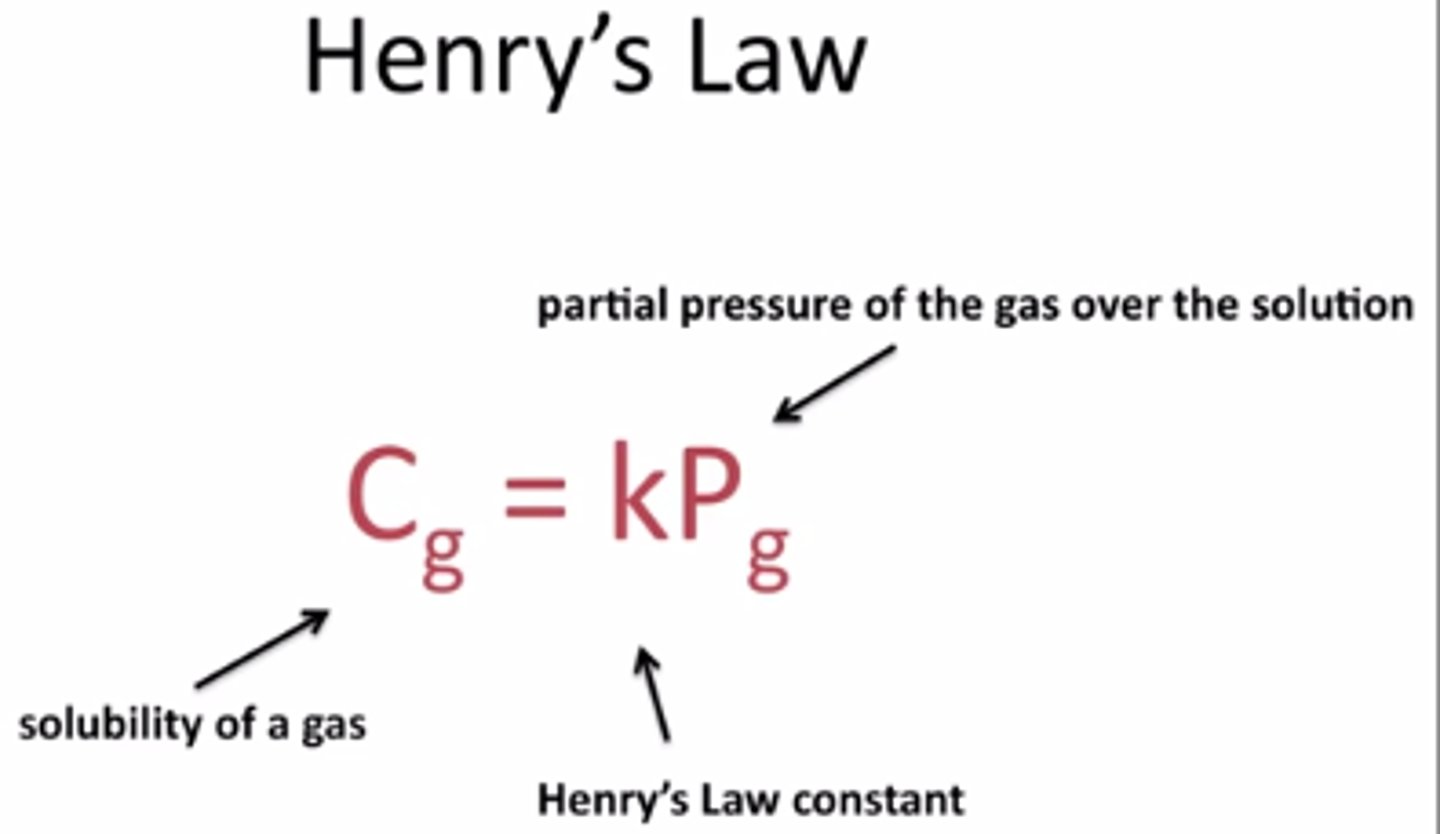
Henry's Law
At a given temperature the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid
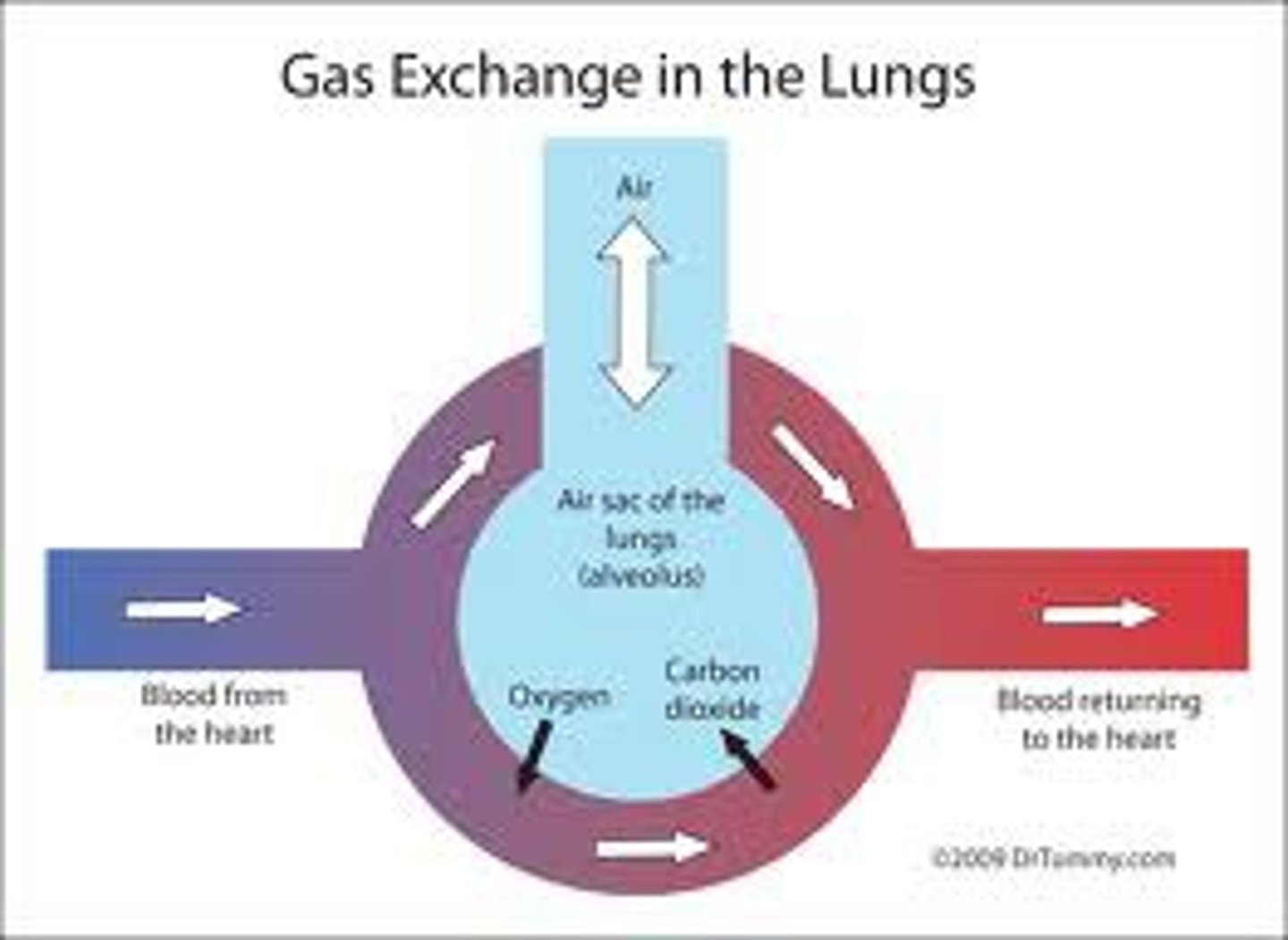
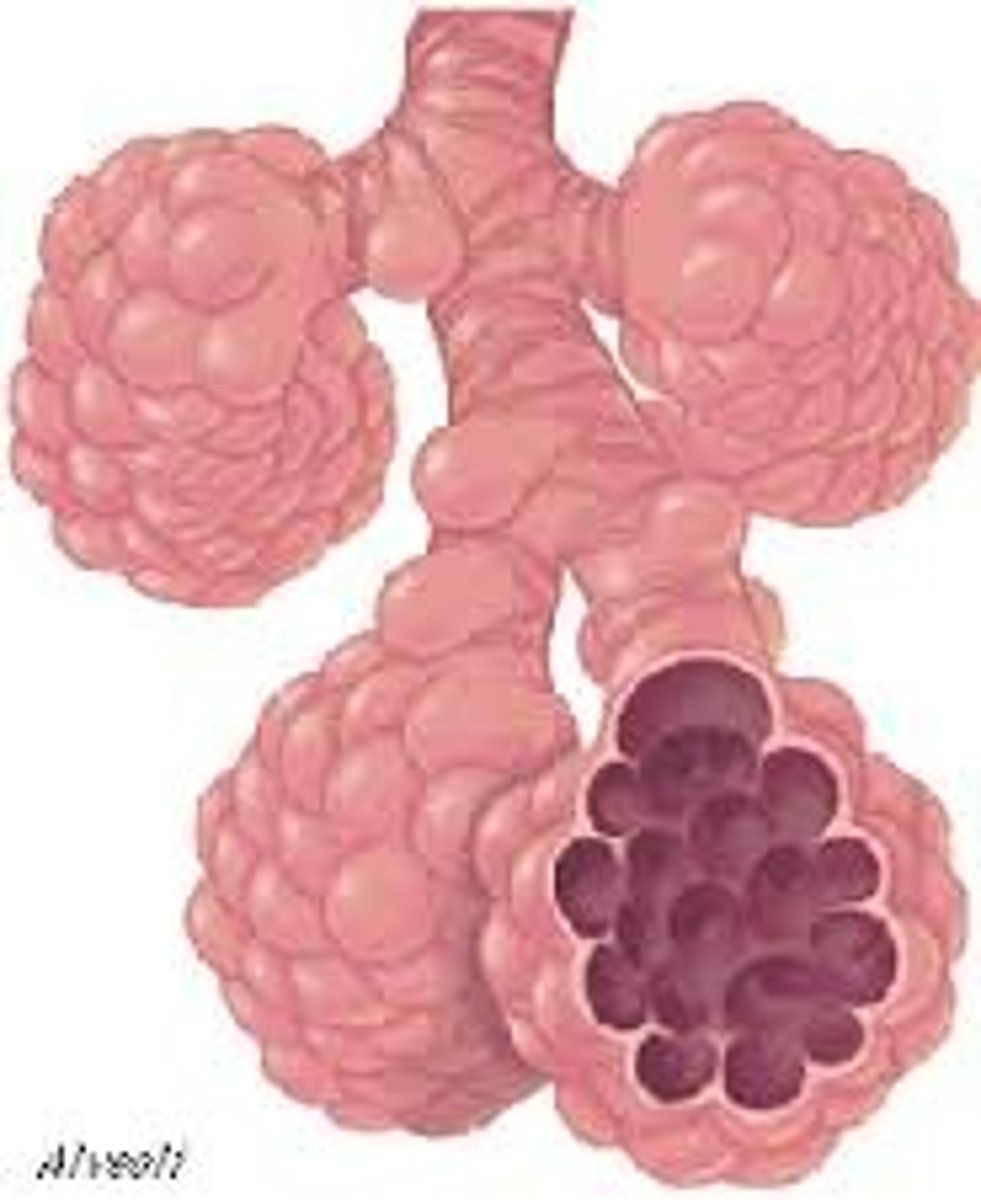
alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
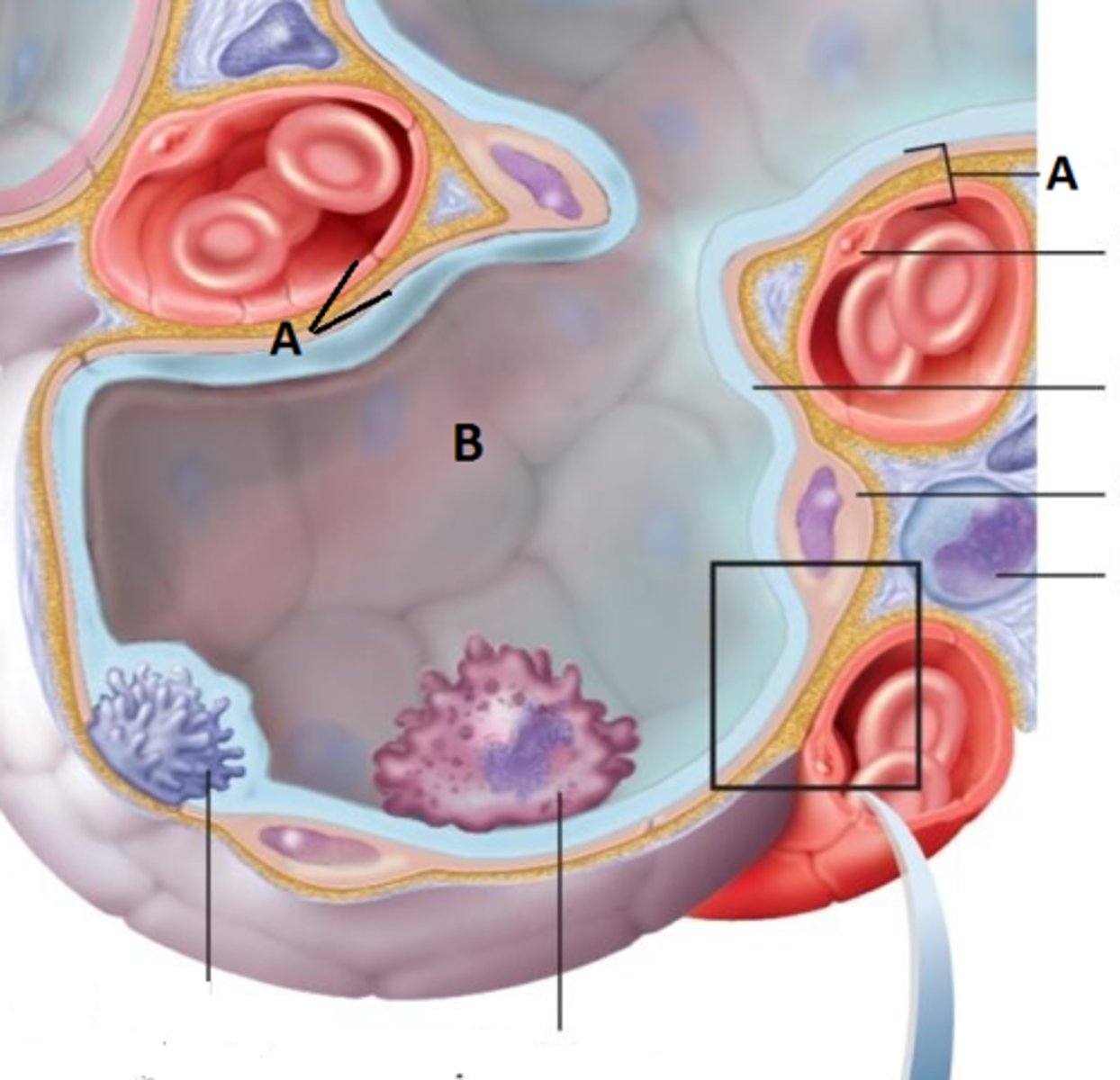
respiratory membrane
where gas exchange occurs between the air on the alveolar side and the blood on the capillary side; the alveolar and capillary walls form the respiratory membrane
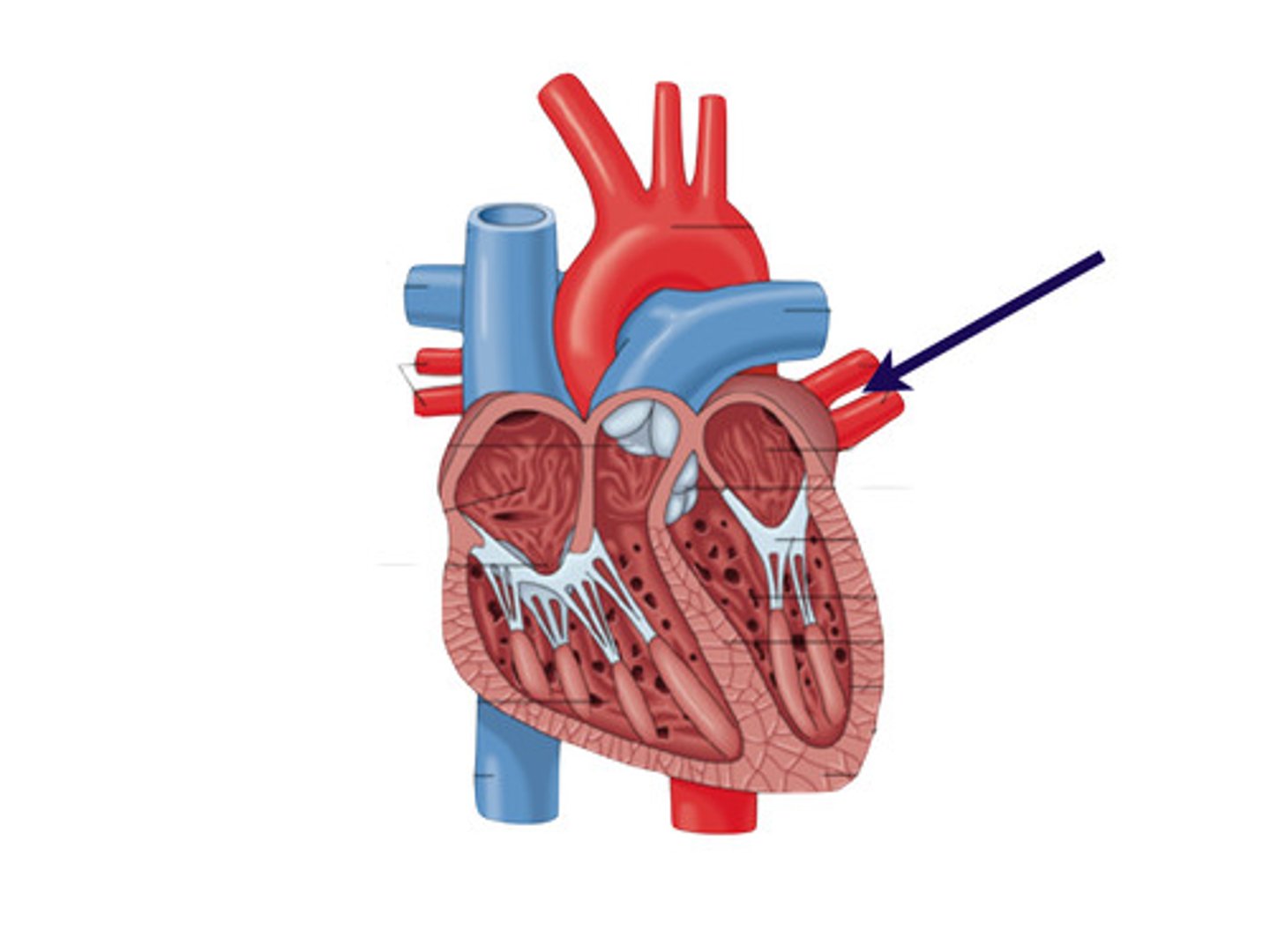
pulmonary arteries
the vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs
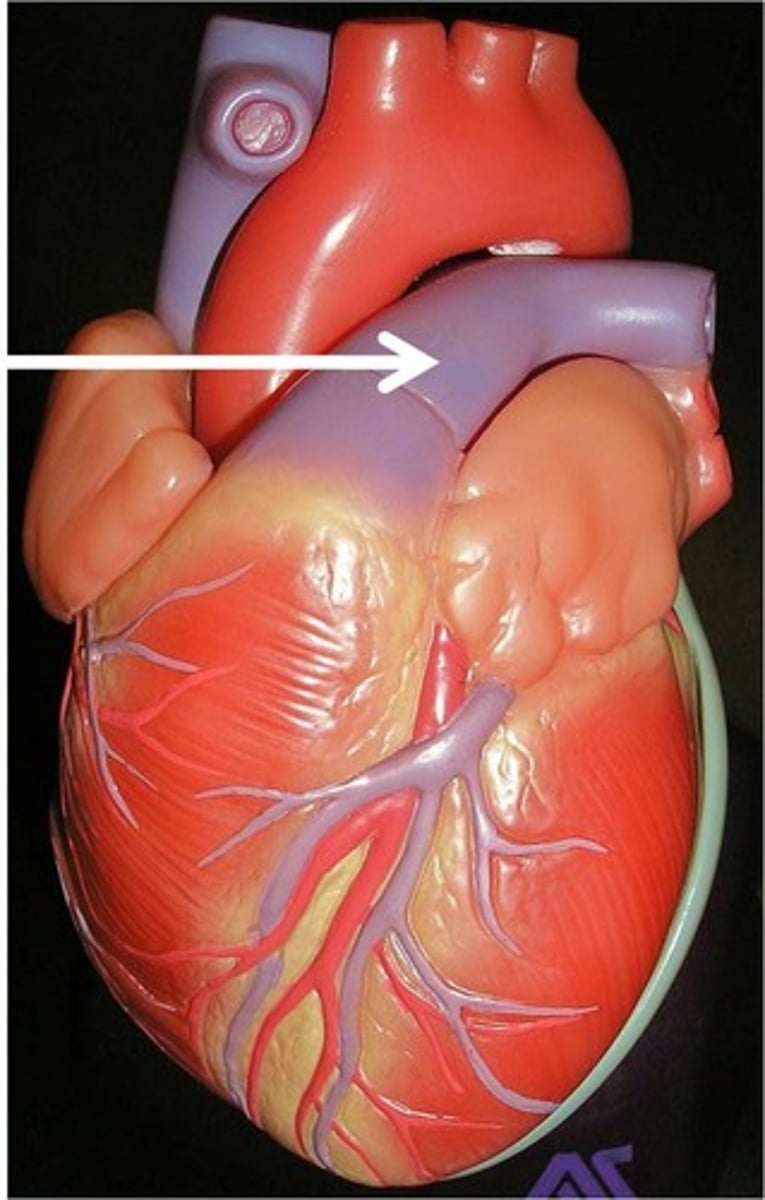
pulmonary veins
carry the oxygenated blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart
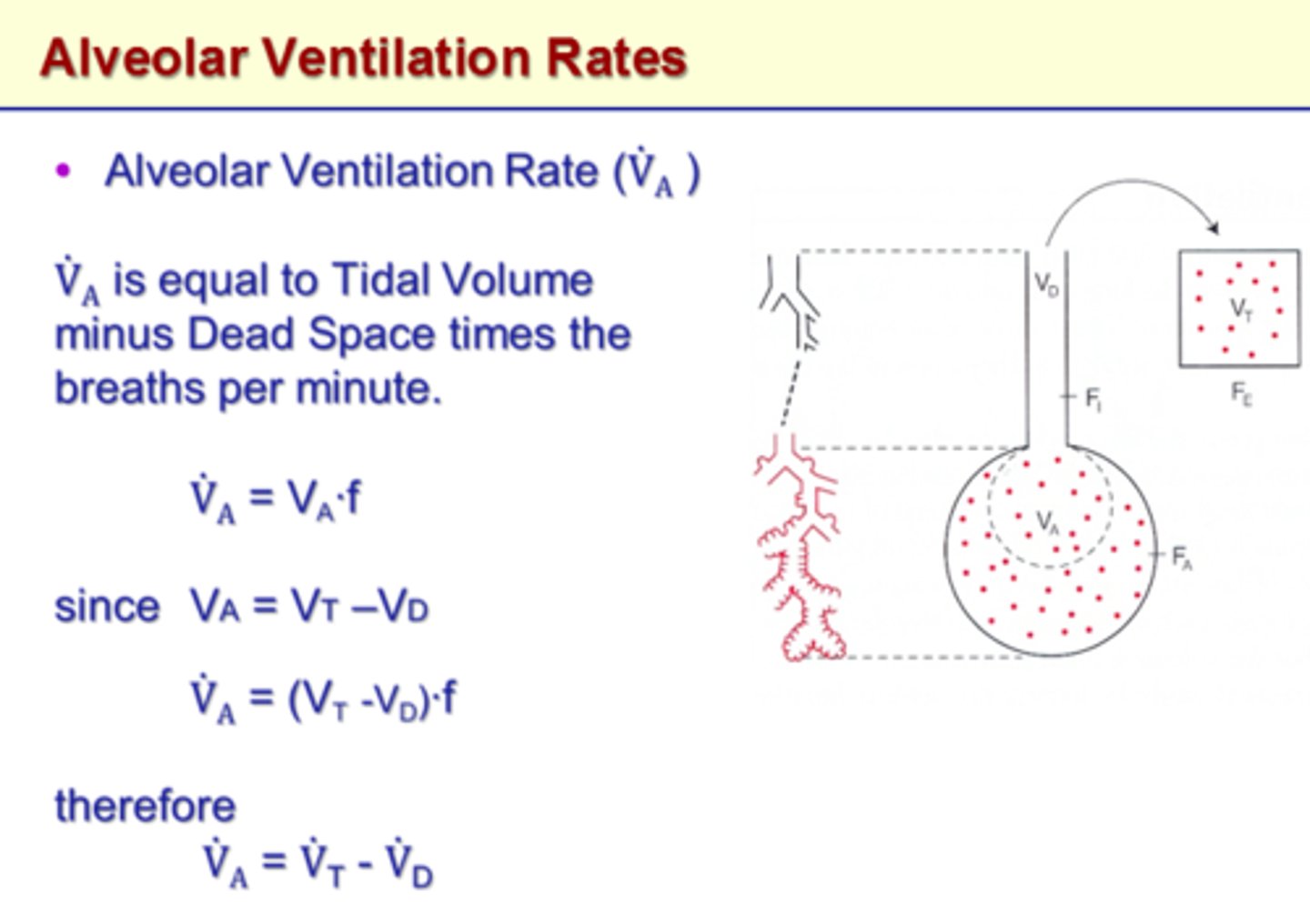
alveolar ventilation
the amount of air that reaches the alveoli
hyperpnea
excessive breathing
dyspnea
difficult or labored breathing

apnea
temporary cessation of breathing
tachypnea
rapid breathing
hyperventilation
the condition of taking abnormally fast, deep breaths

hypoventilation
ventilation of the lungs that does not fulfill the body's gas exchange needs
hypoxia
deficiency in the amount of oxygen reaching the tissues
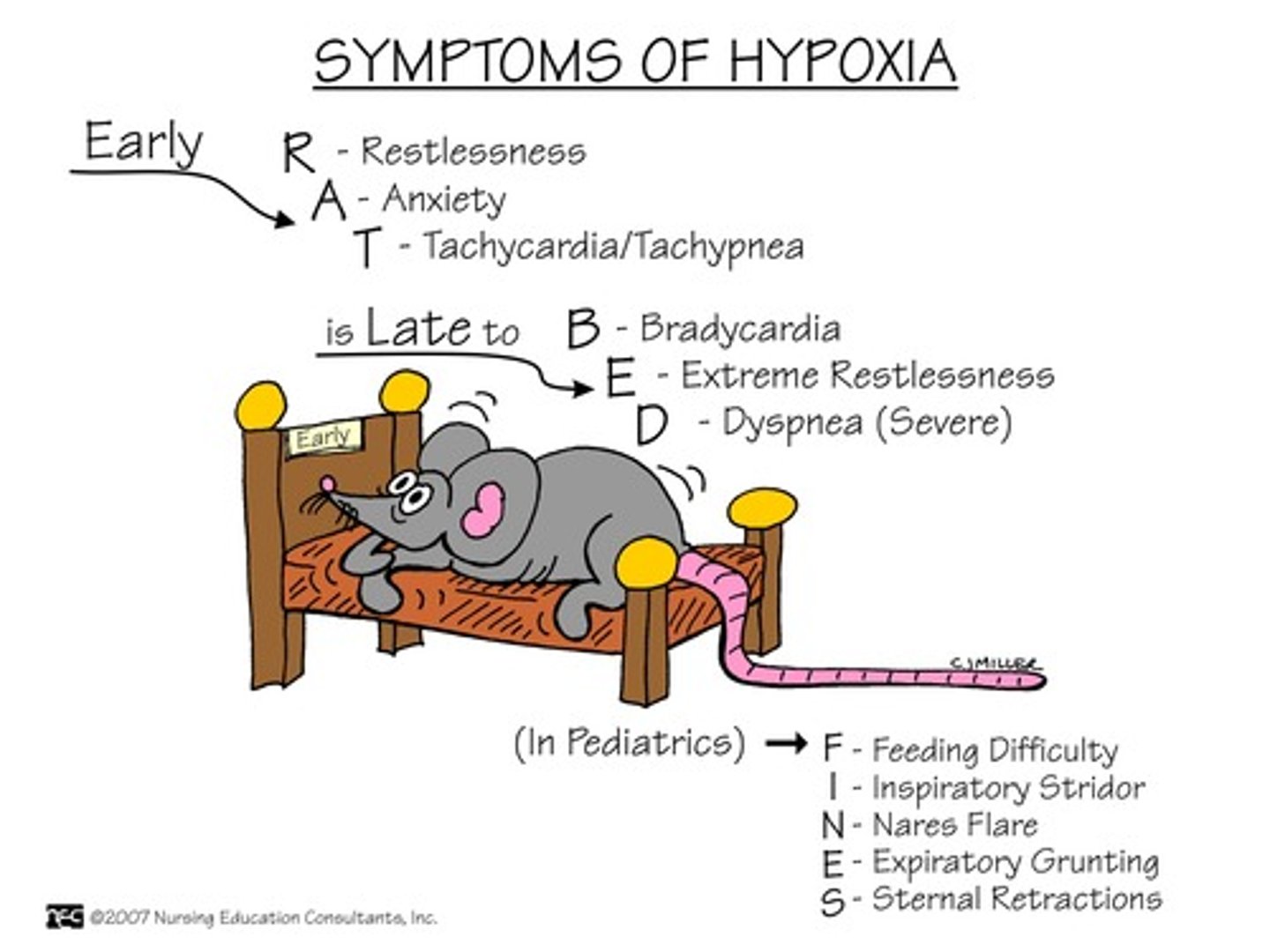
hypoexmia
deficient amount of oxygen in the blood

hypercapnia
excessive carbon dioxide in the blood
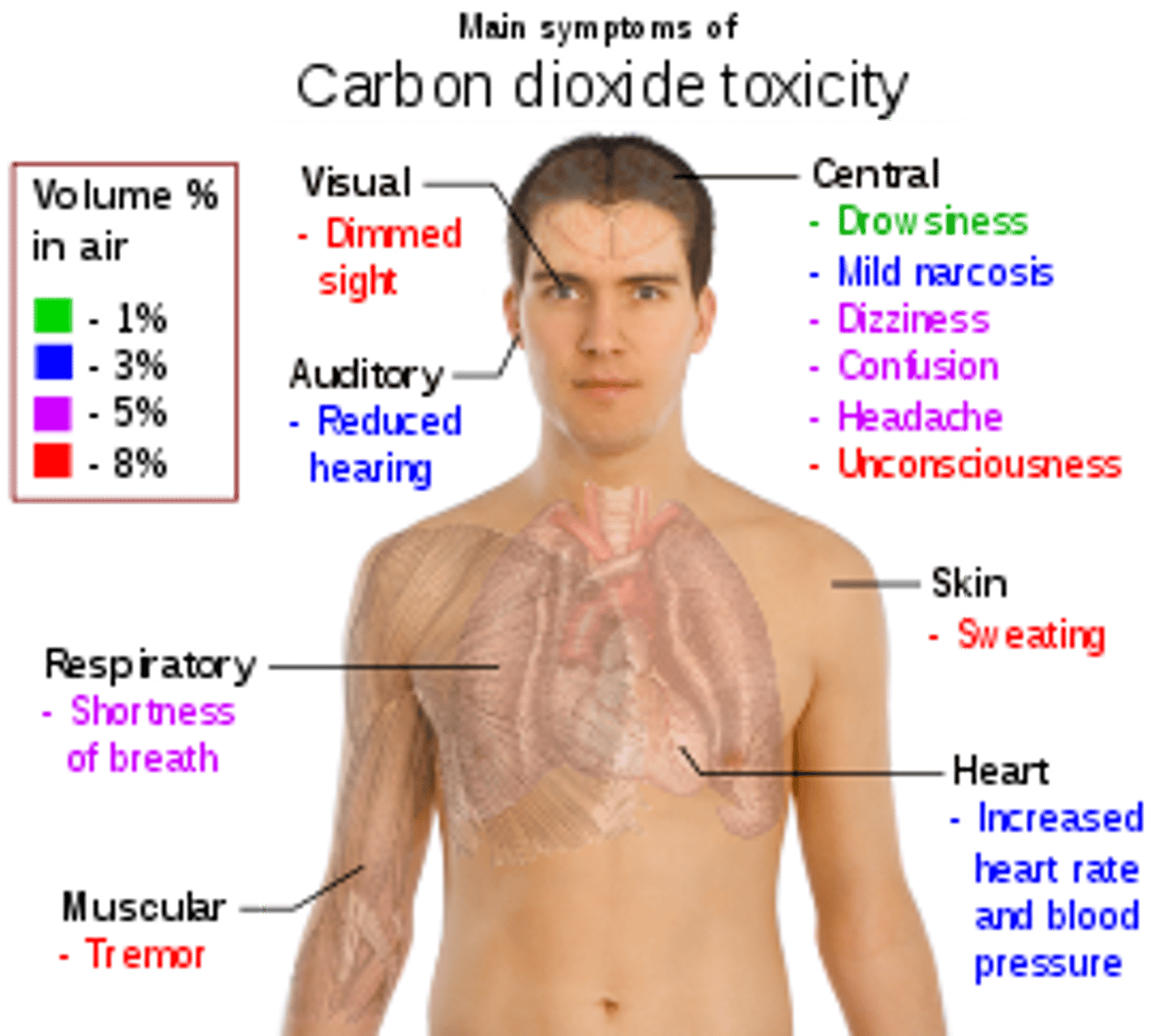
hypocapnia
condition of deficient carbon dioxide (in the blood)

deoxyhemoglobin
hemoglobin without oxygen
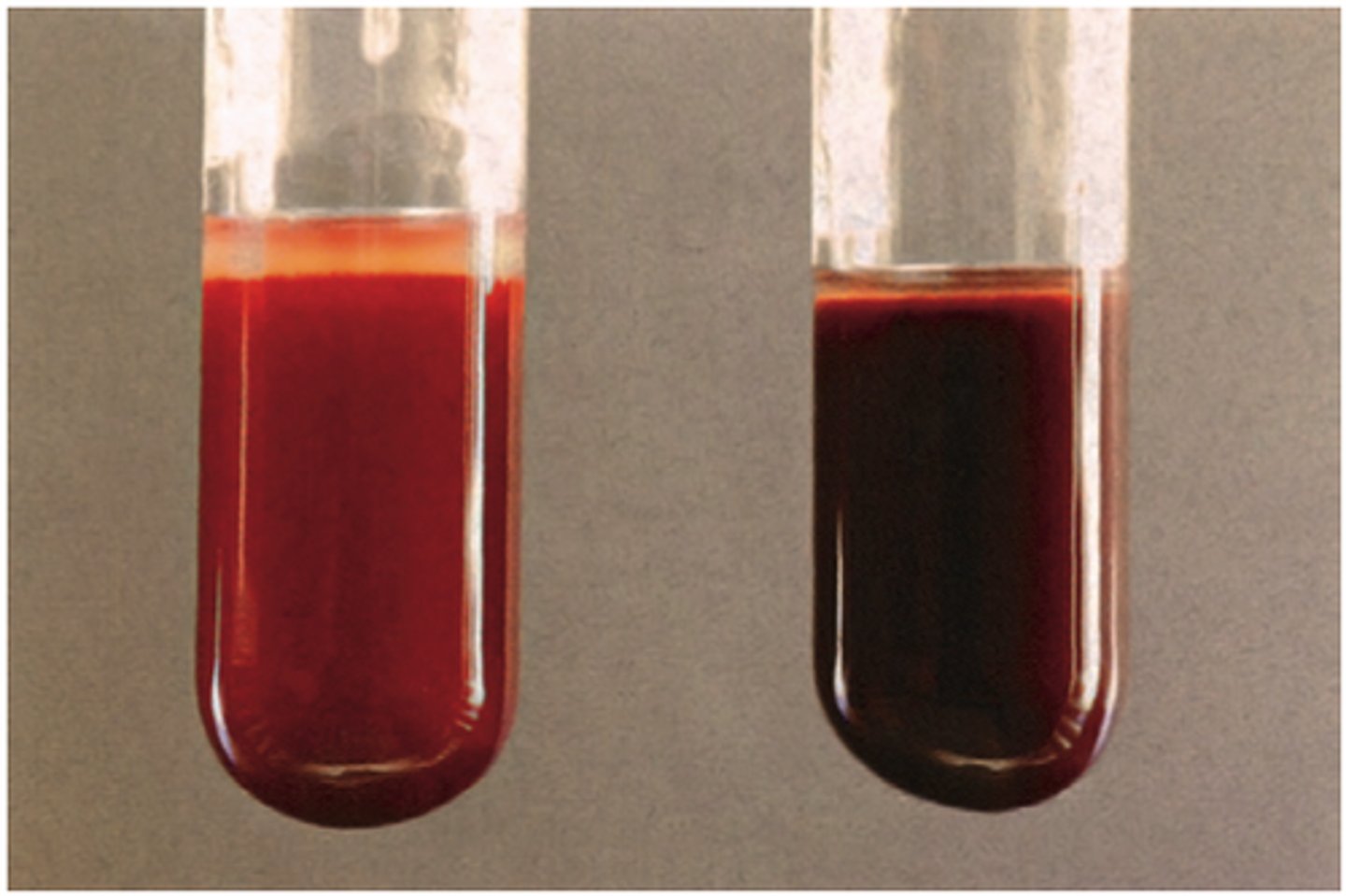
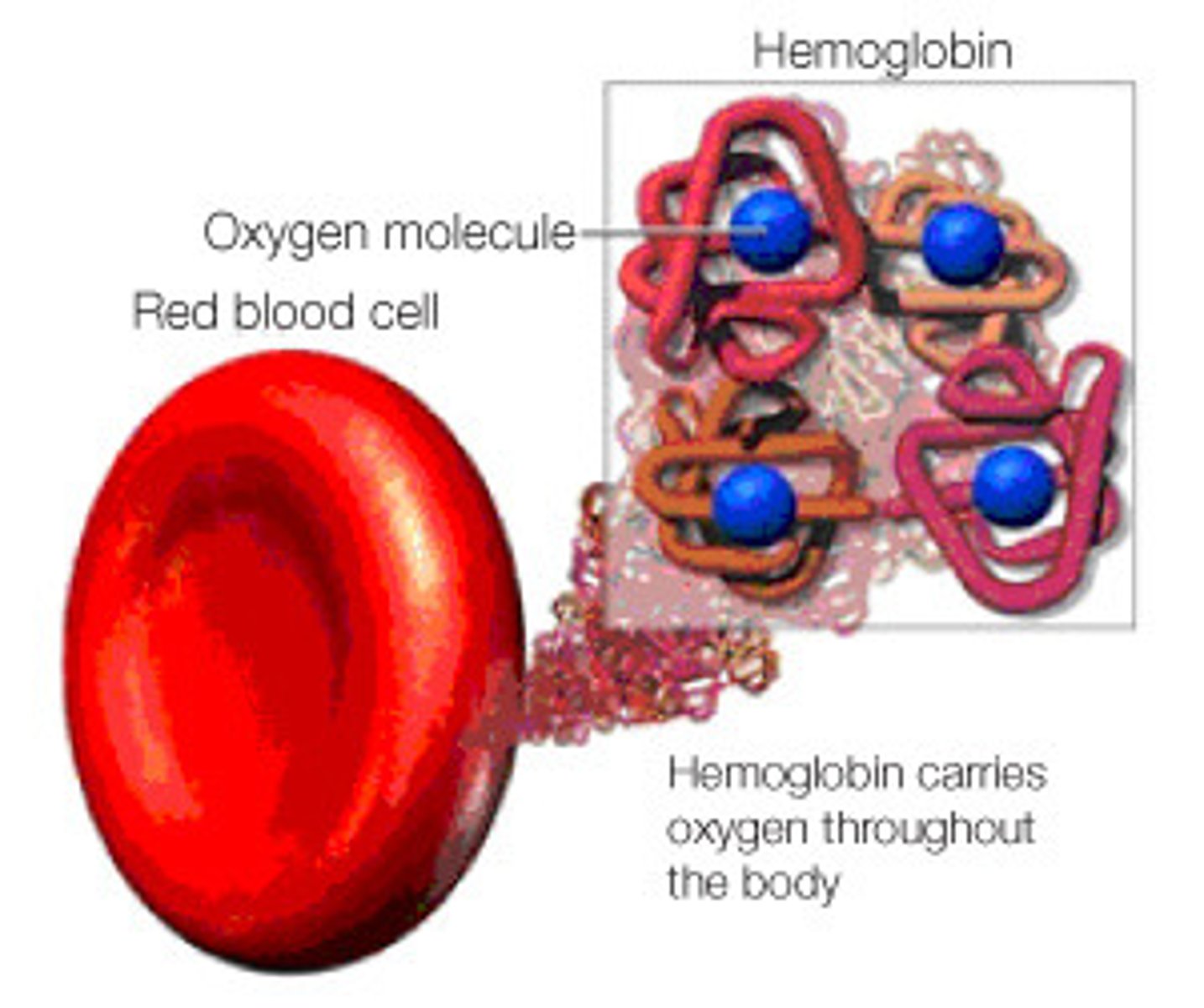
oxyhemoglobin
hemoglobin bound to oxygen
law of mass action
The rate of a chemical reaction is proportional to the product of the concentrations of the reactants
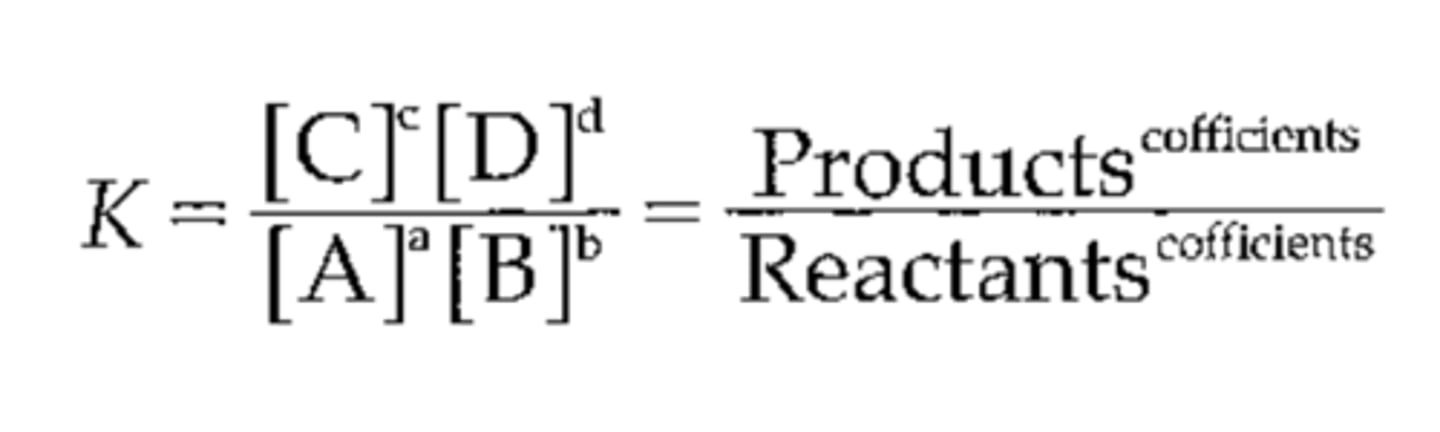
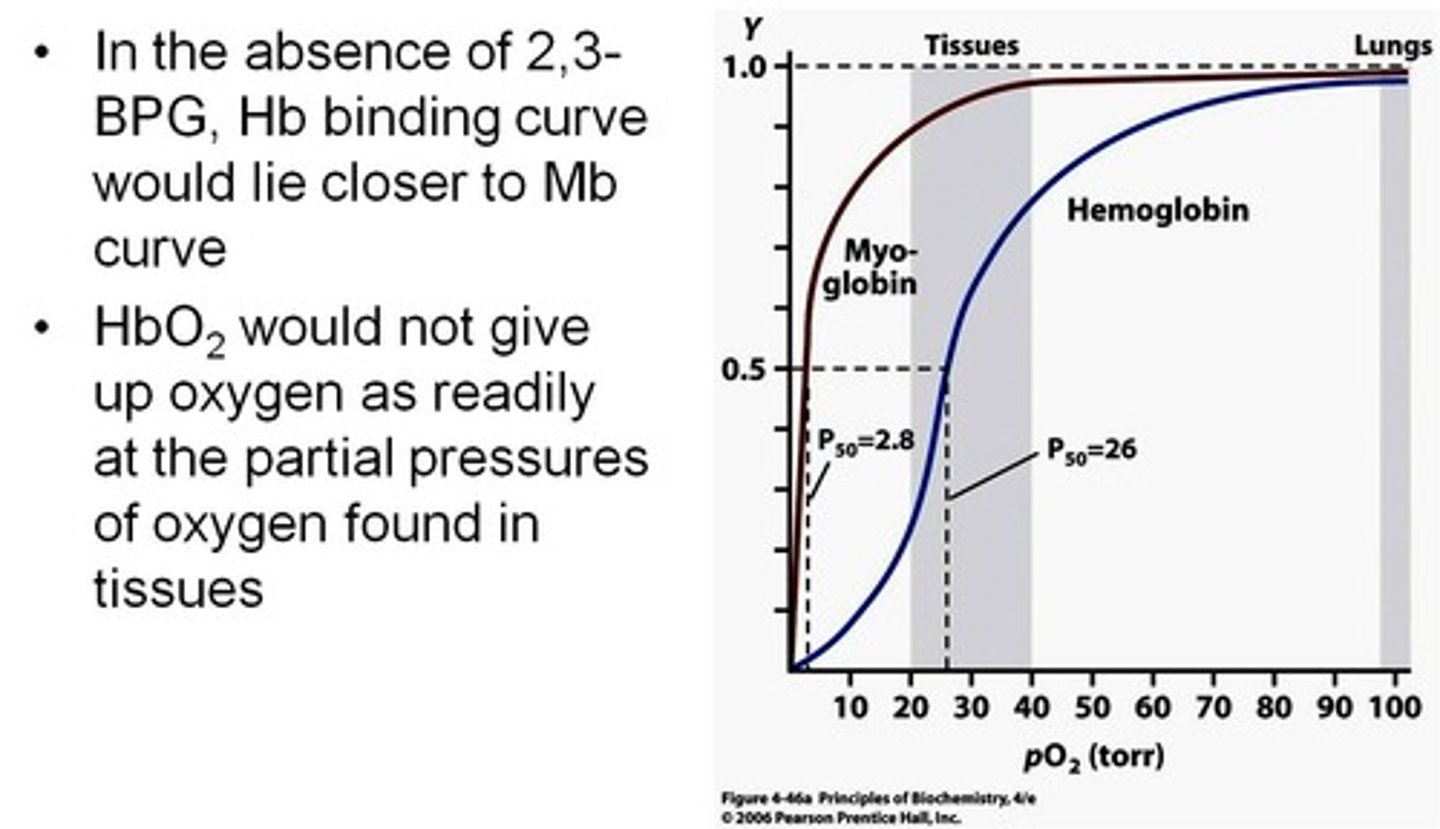
hemoglobin saturation
percentage of heme units containing bound oxygen
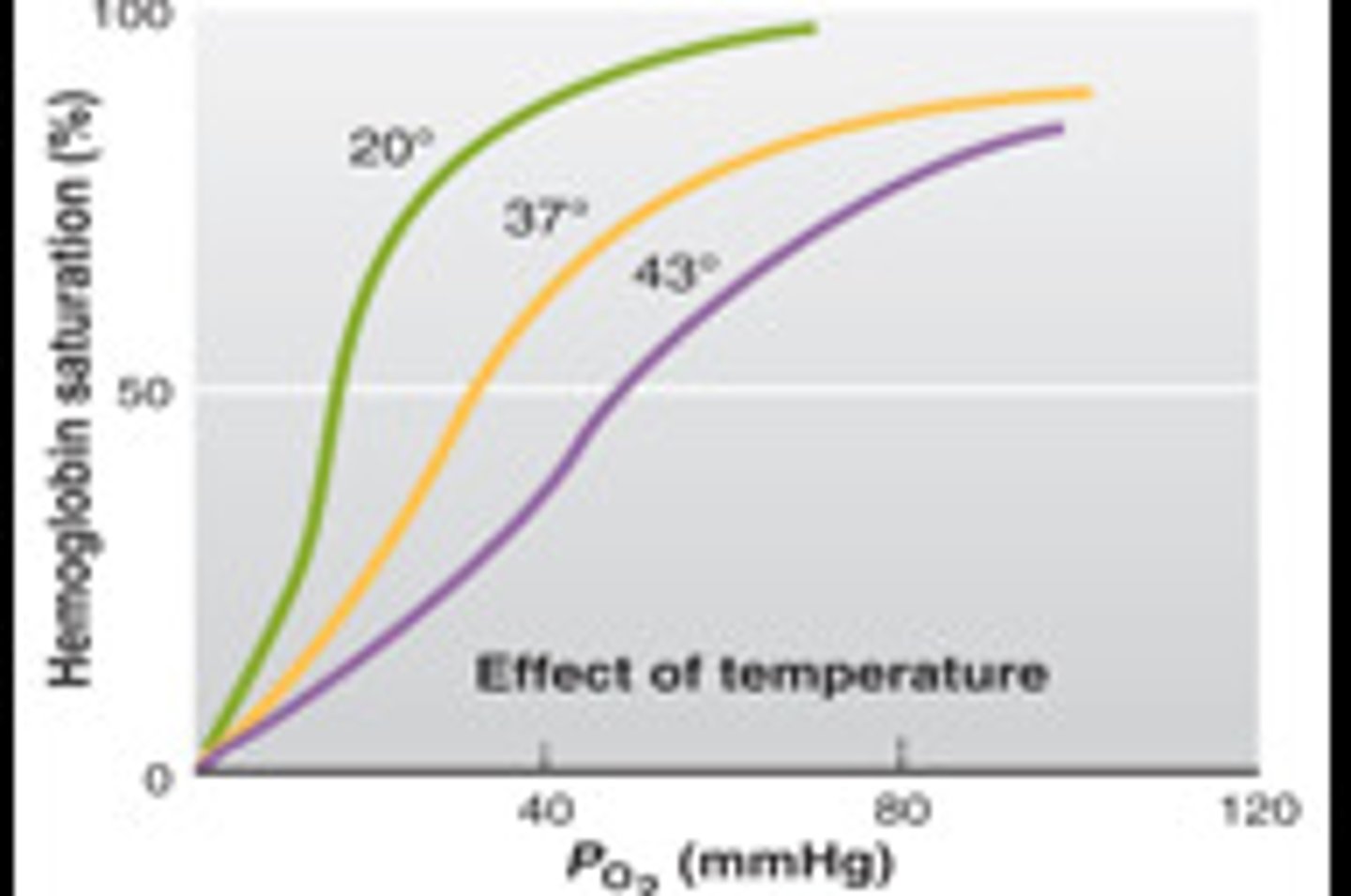
hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve
a curve that plots the proportion of hemoglobin in its saturated (oxygen-laden) form on the vertical axis against the prevailing oxygen tension on the horizontal axis
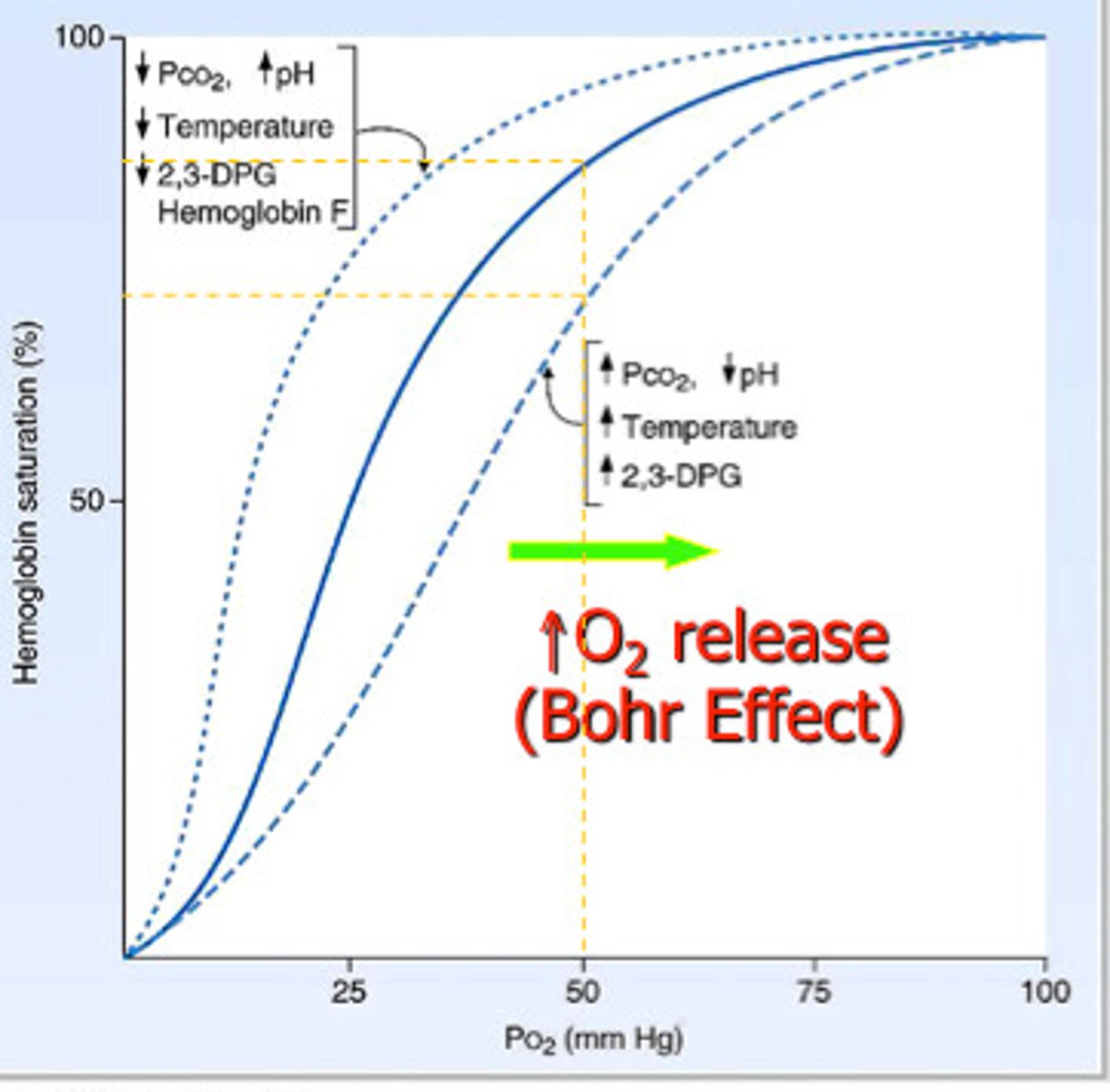
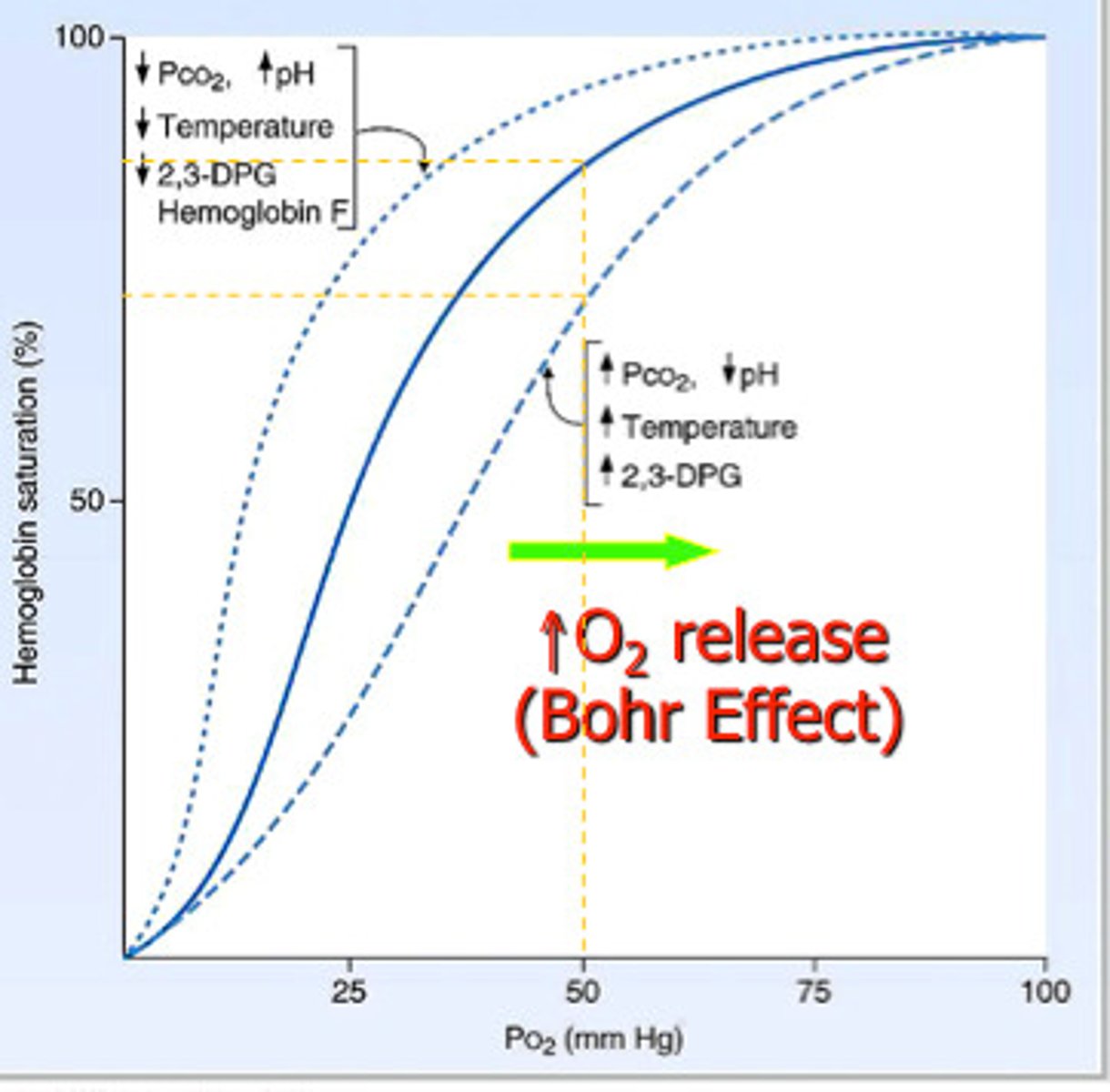
right shift
A shift of the curve to the right indicates decreased affinity of the hemoglobin for oxygen and hence an increased tendency to give up oxygen to the tissues
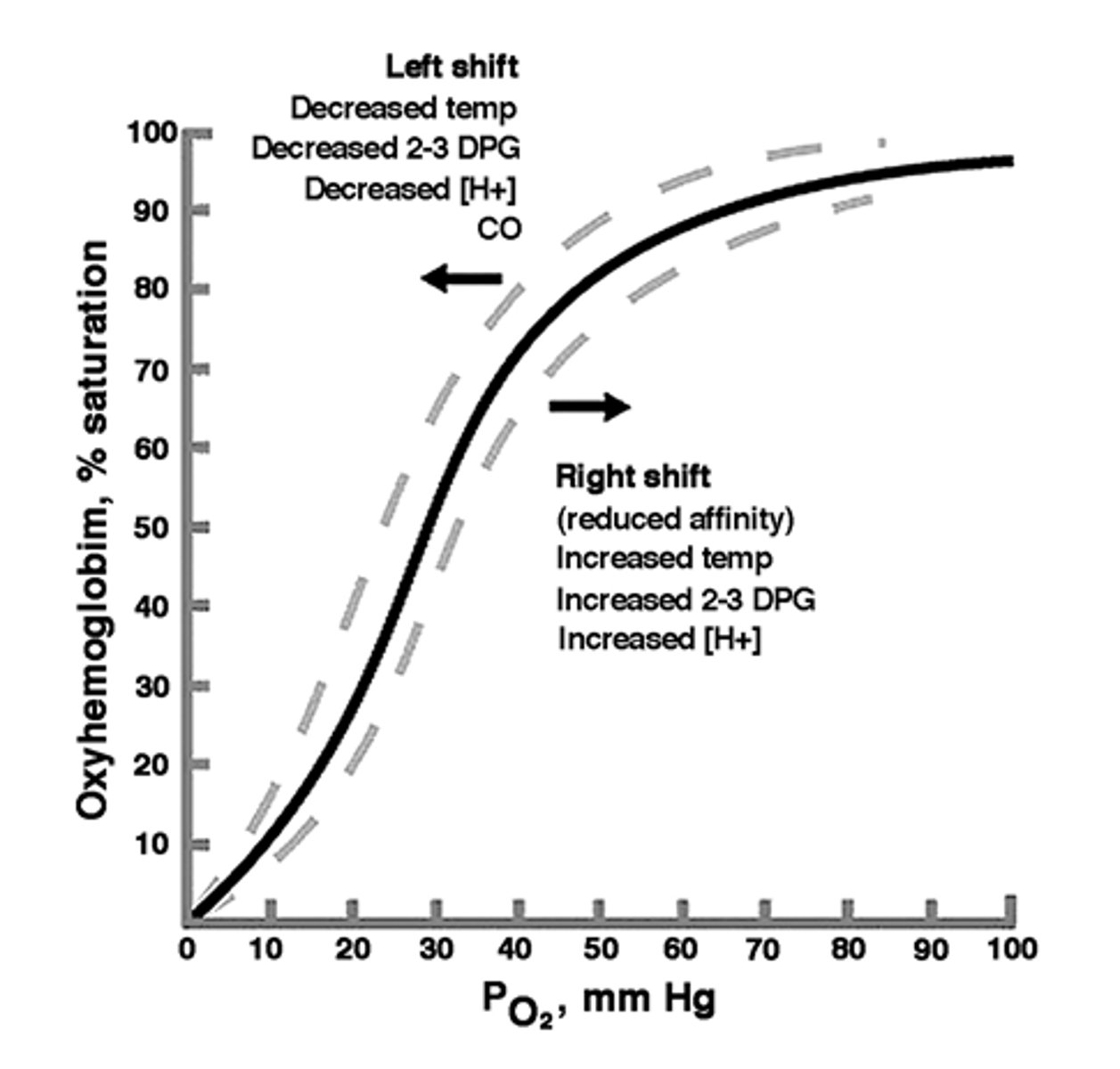
left shift
A shift to the left indicates increased affinity and so an increased tendency for hemoglobin to take up and retain oxygen.
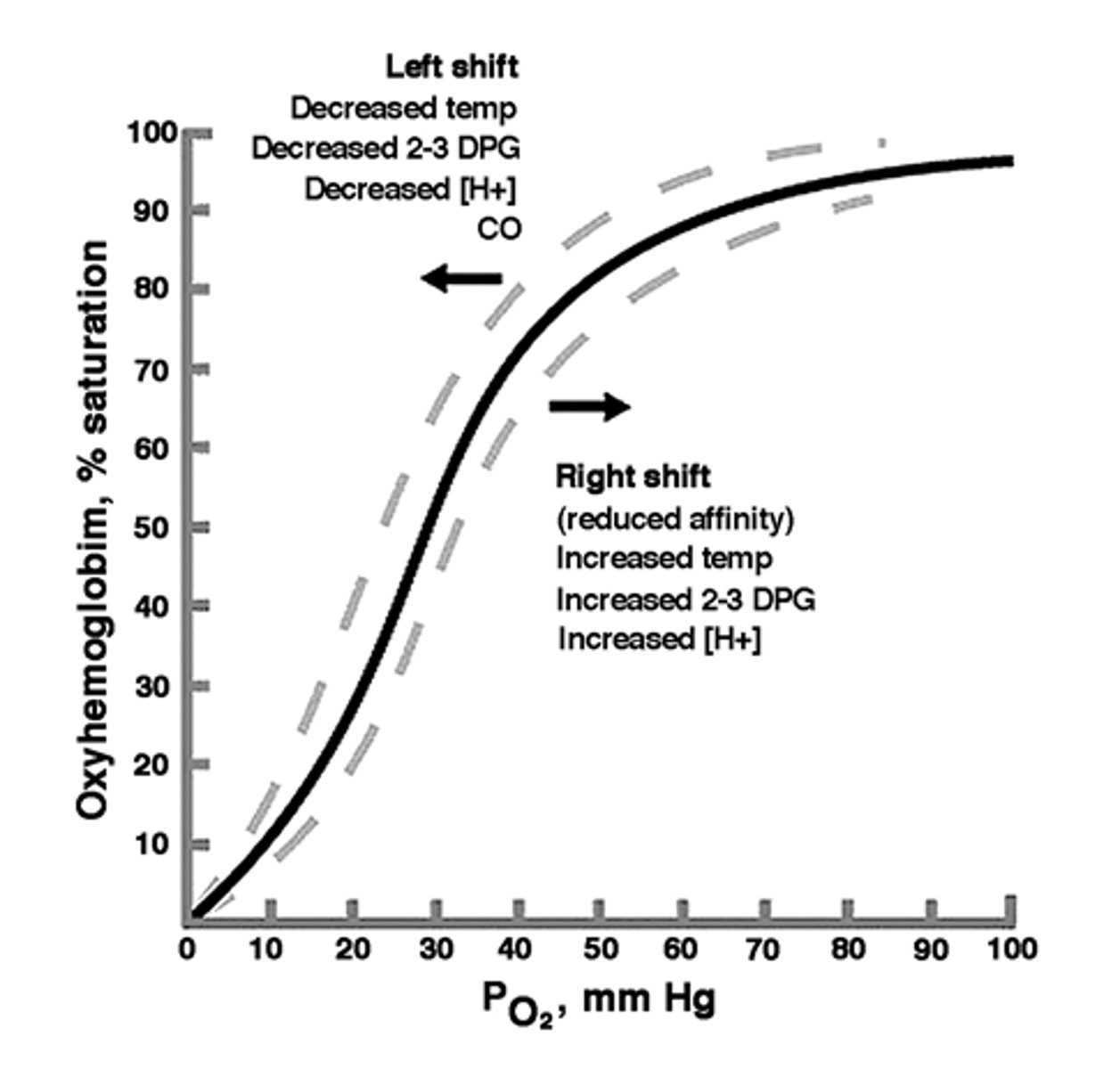
Bohr effect
describes hemoglobin's lower affinity for oxygen secondary to increases in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide and/or decreased blood pH. This lower affinity, in turn, enhances the unloading of oxygen into tissues to meet the oxygen demand of the tissue
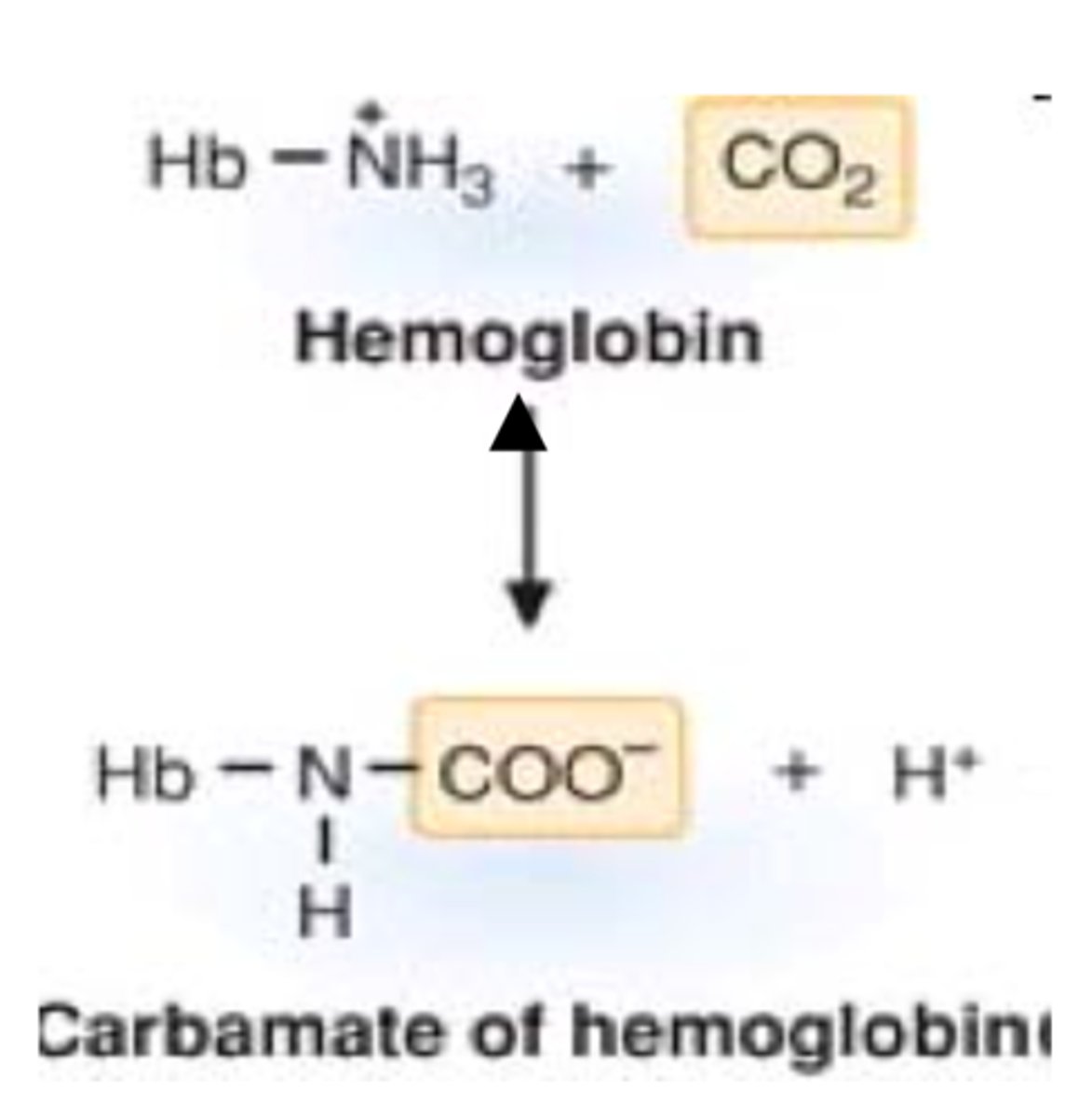
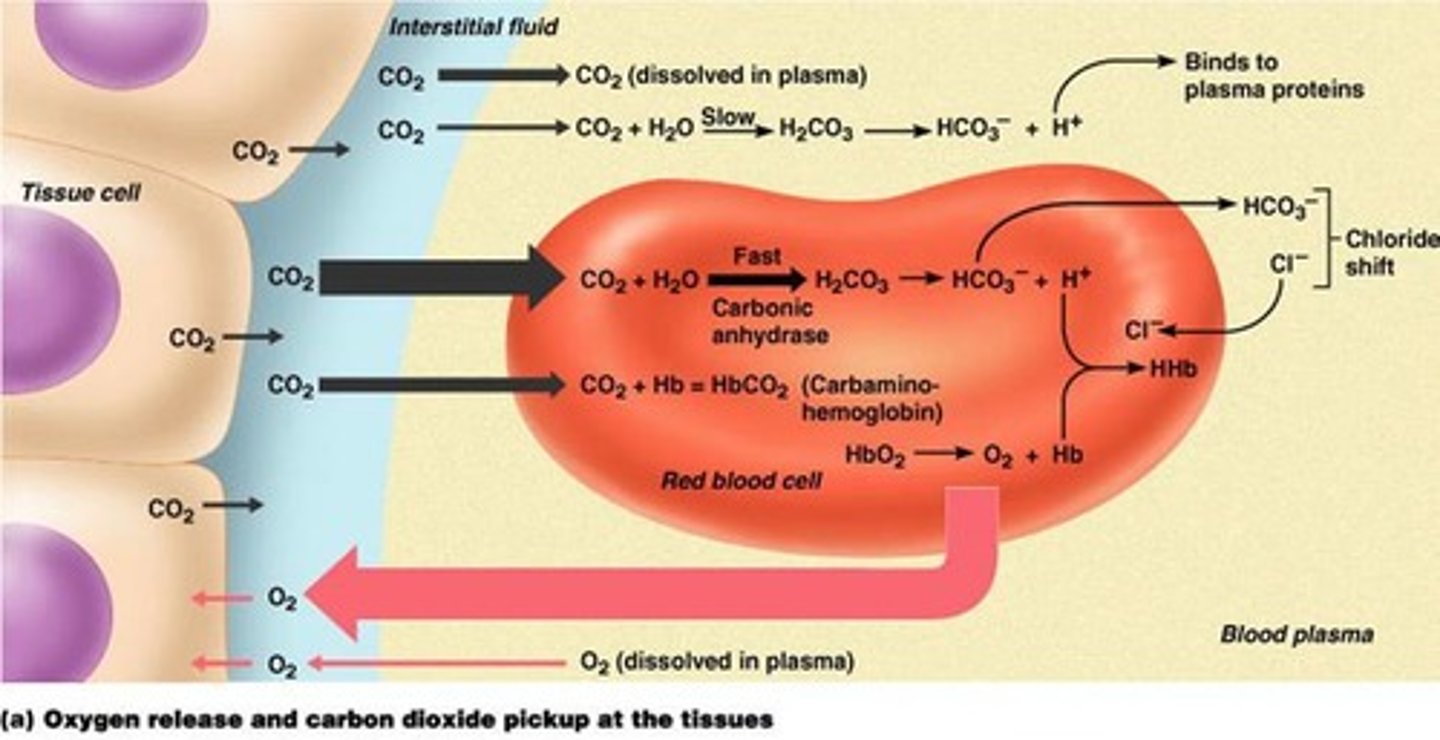
carbaminohemoglobin
the compound formed by the union of carbon dioxide with hemoglobin
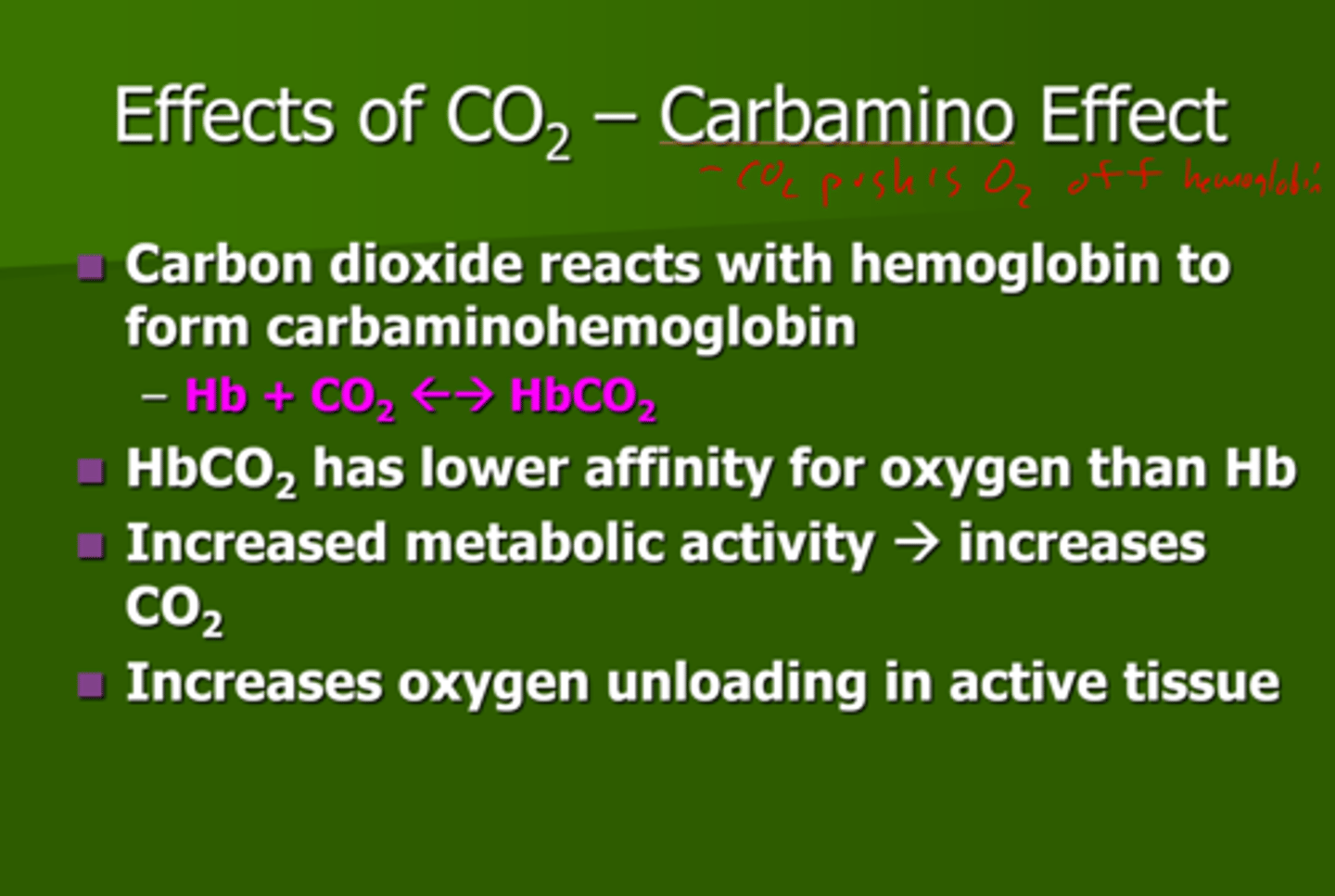
carbamino effect
Describes a change in the confirmation of hemoglobin that is induced by an increase in CO2
BPG (biphosphoglycerate)
also known as 2,3-Disphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG), promotes hemoglobin transition from a high-oxygen-affinity state to a low-oxygen-affinity state
carbon monoxide
a colorless, odorless toxic flammable gas formed by incomplete combustion of carbon.

carbonic anhydrase
enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between carbon dioxide and water to form carbonic acid
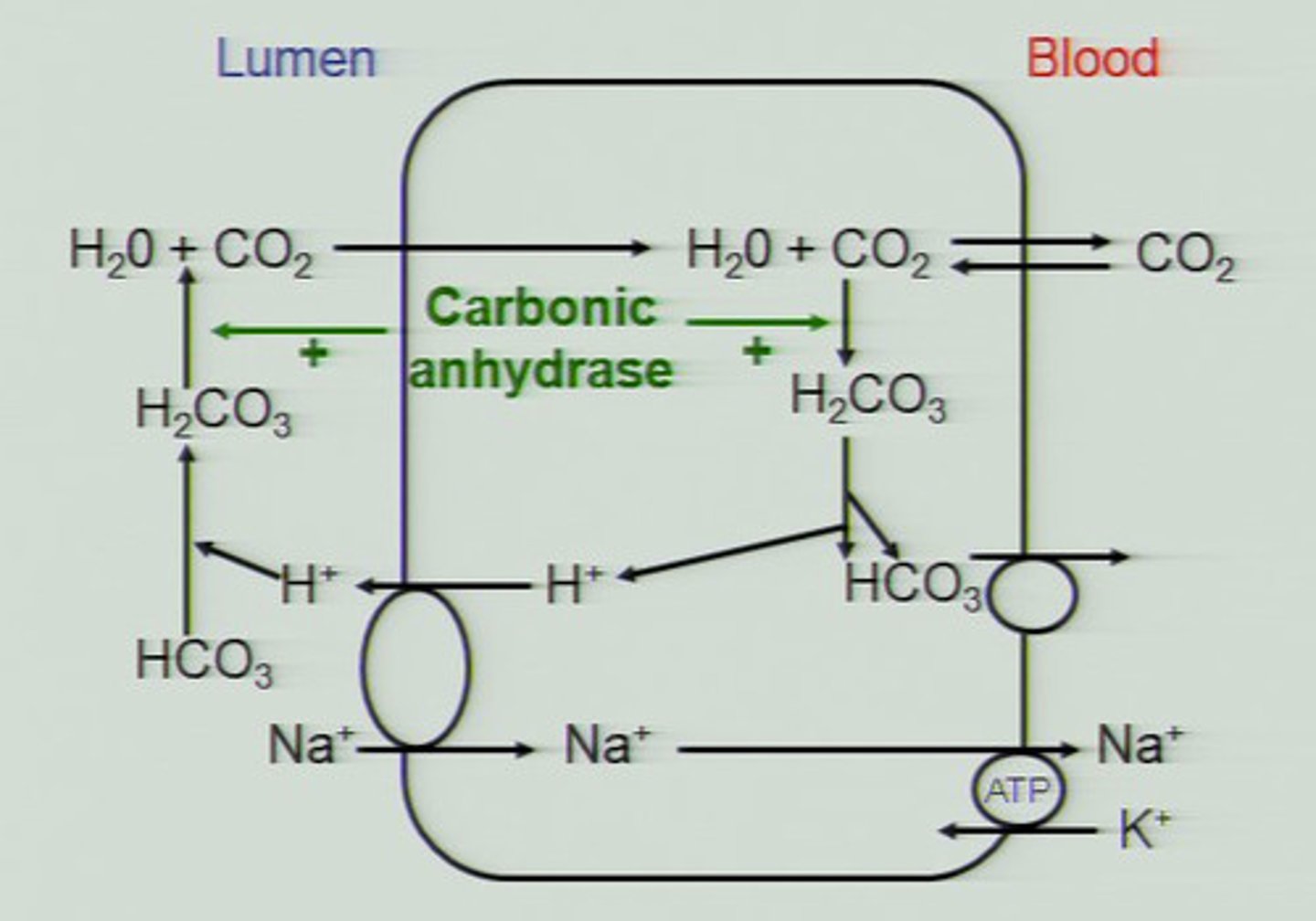
bicarbonate ions
enzyme that changes carbon dioxide into water so it is not poisonous to the body
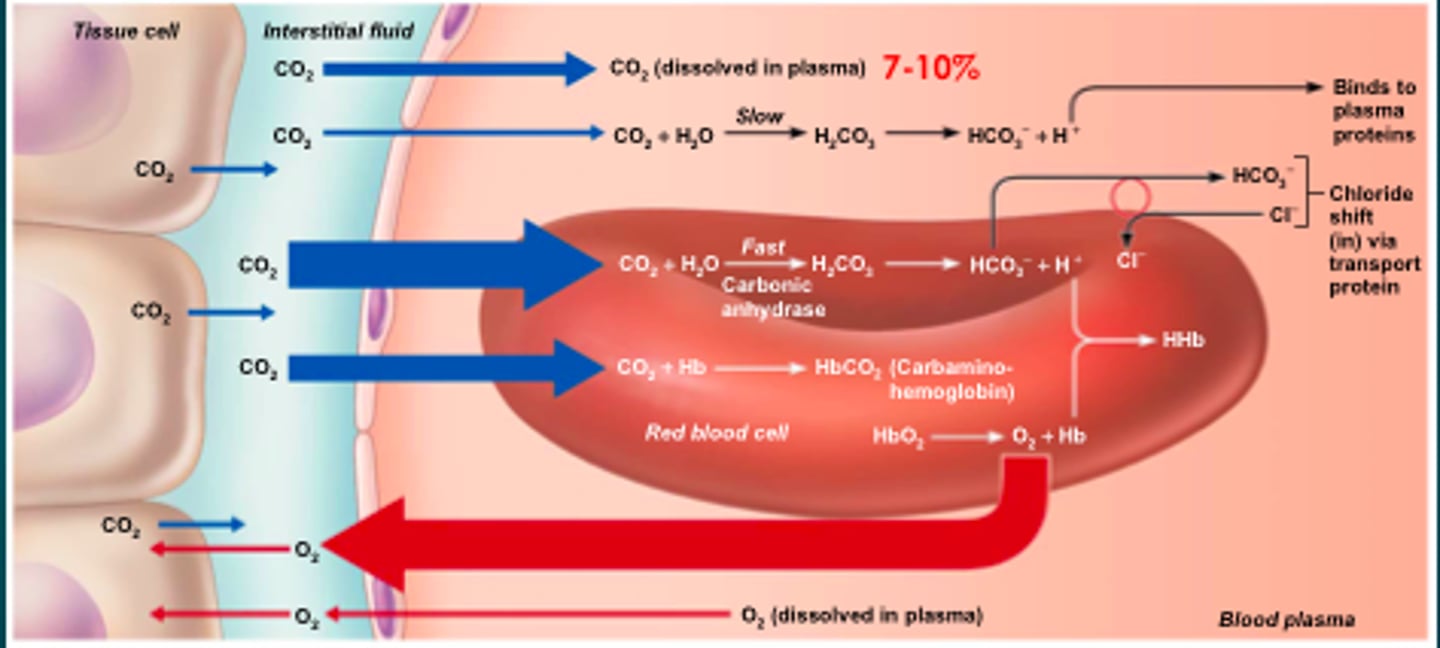
chloride shift
the movement of chloride ions into the red blood cells as hydrogen ions move out
to maintain the electrochemical equilibrium.
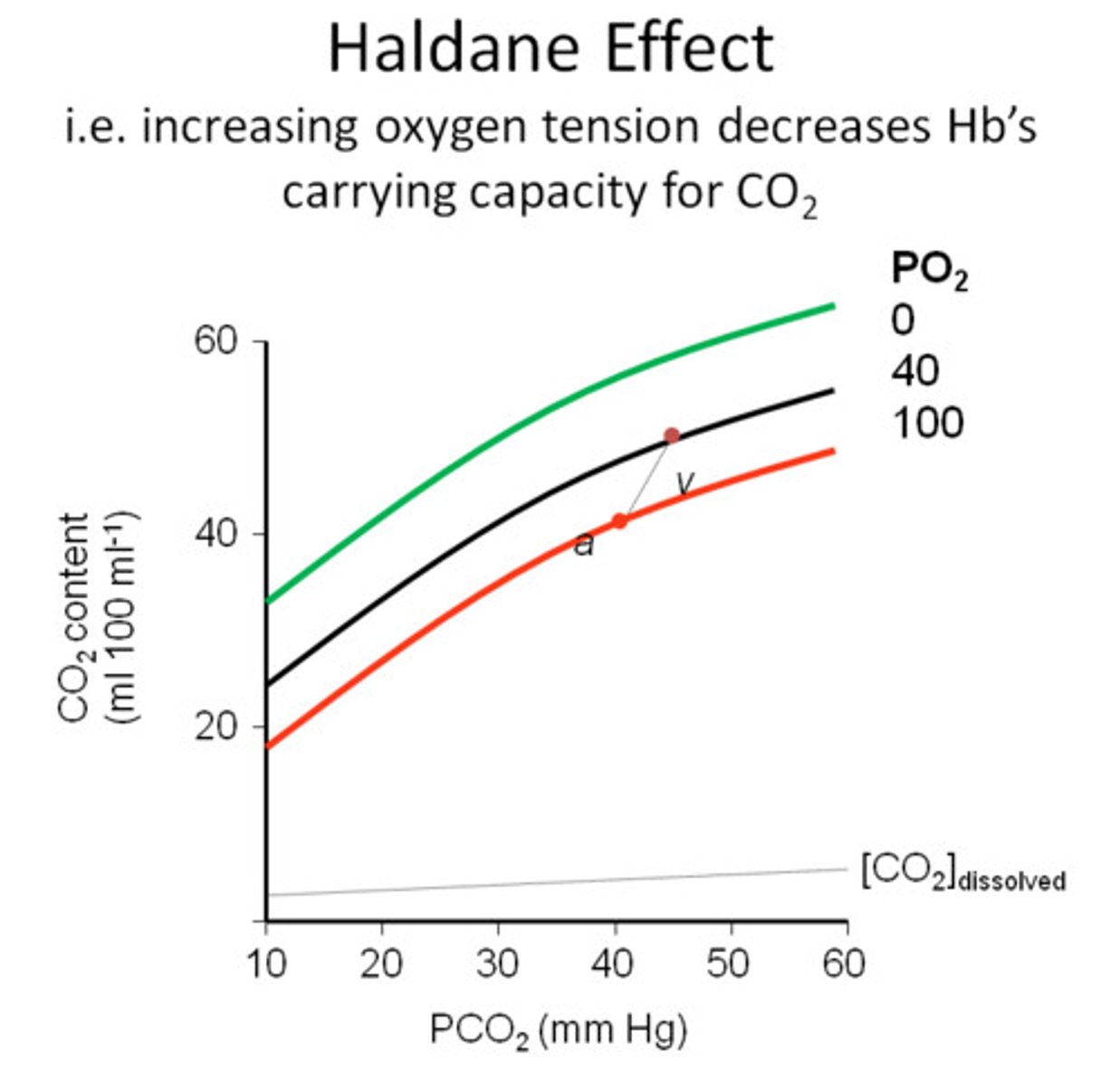
Haldane effect
Oxygenation of blood in the lungs displaces carbon dioxide from hemoglobin which increases the removal of carbon dioxide.
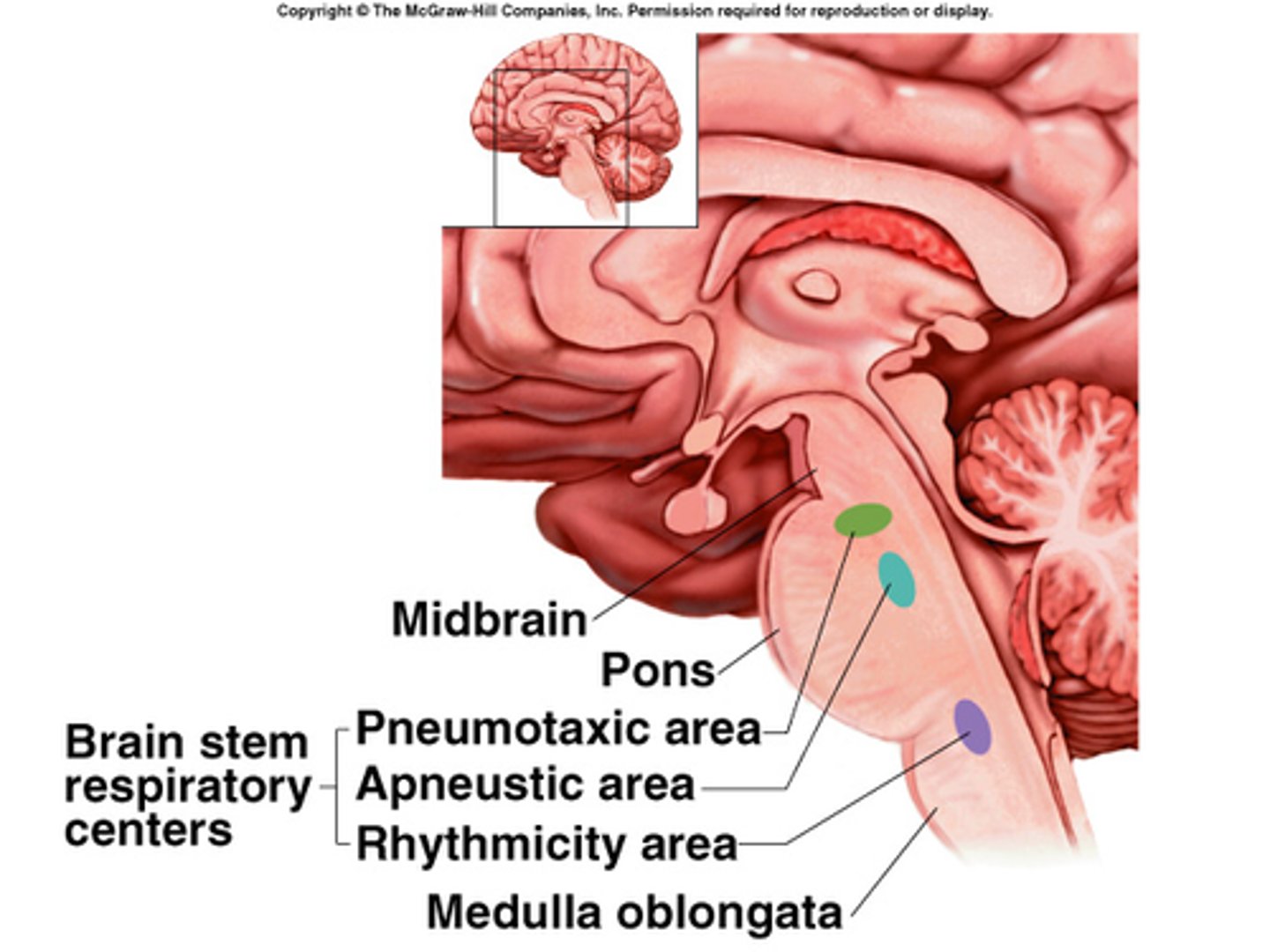
respiratory centers
autonomic centers located in the medulla oblongata and the pons that establish breathing rate and depth
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions
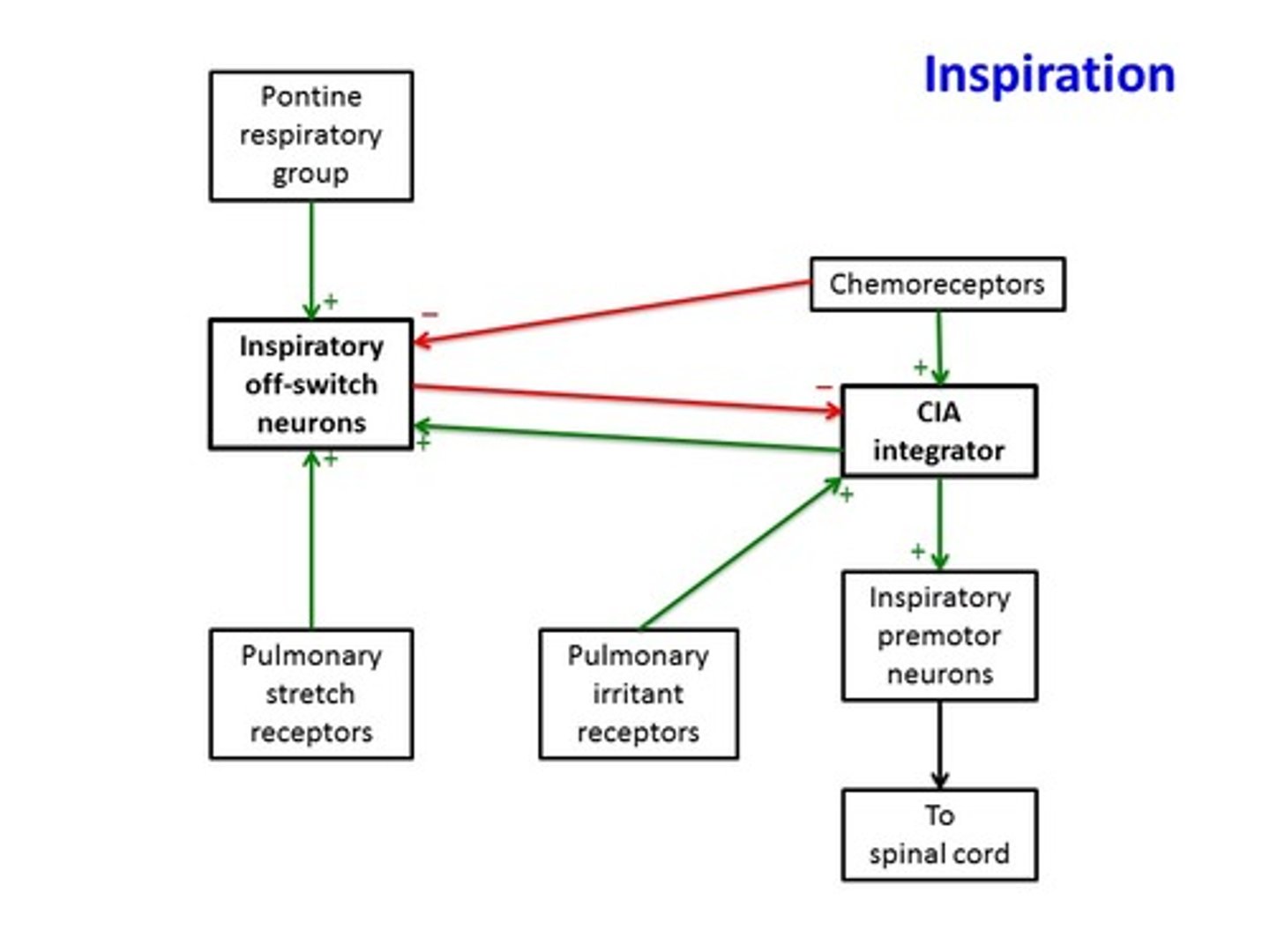
inspiratory neurons
depolarize during inspiration
somatic motor neurons
nerve cells whose cell bodies are in the brainstem and spinal cord that serve skeletal muscles
phrenic nerve
Carries impulses to the diaphragm from the brain.
diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
external intercostal nerve
originating in thoracic segments of the spinal cord
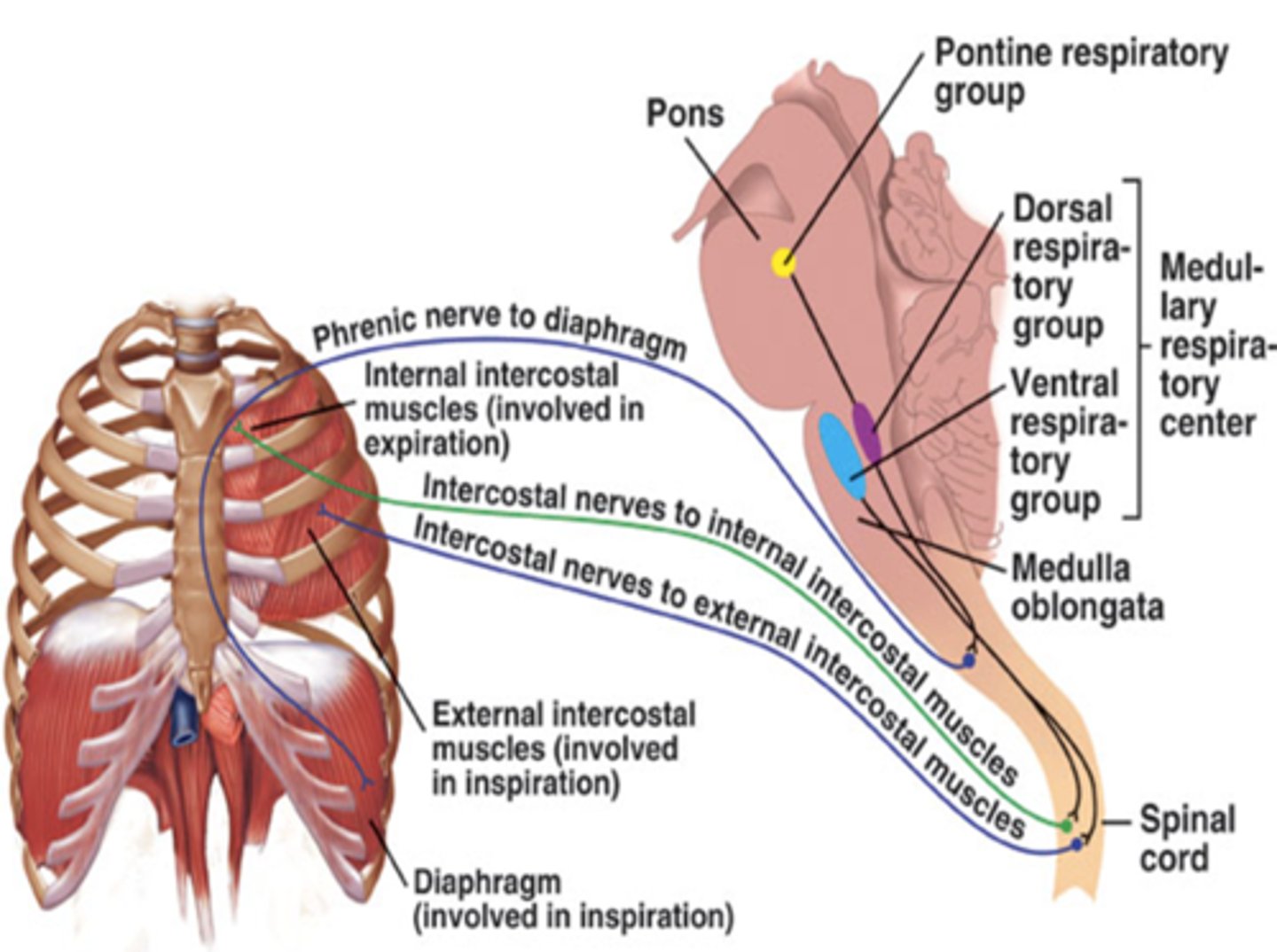
external intercostal muscles
A muscle that raises the rib cage, decreasing pressure inside the chest cavity
expiratory neurons
fire during forced expiration

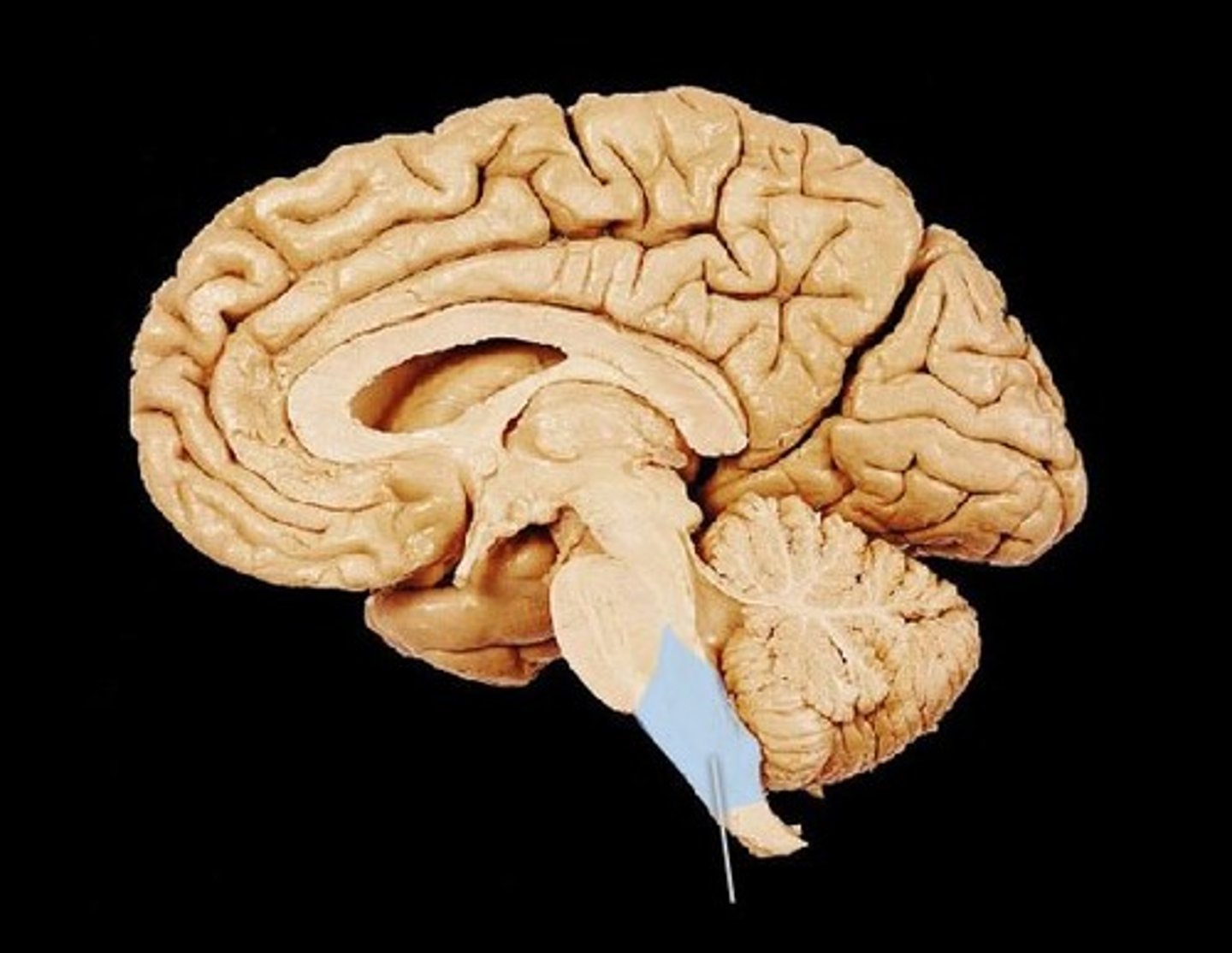
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
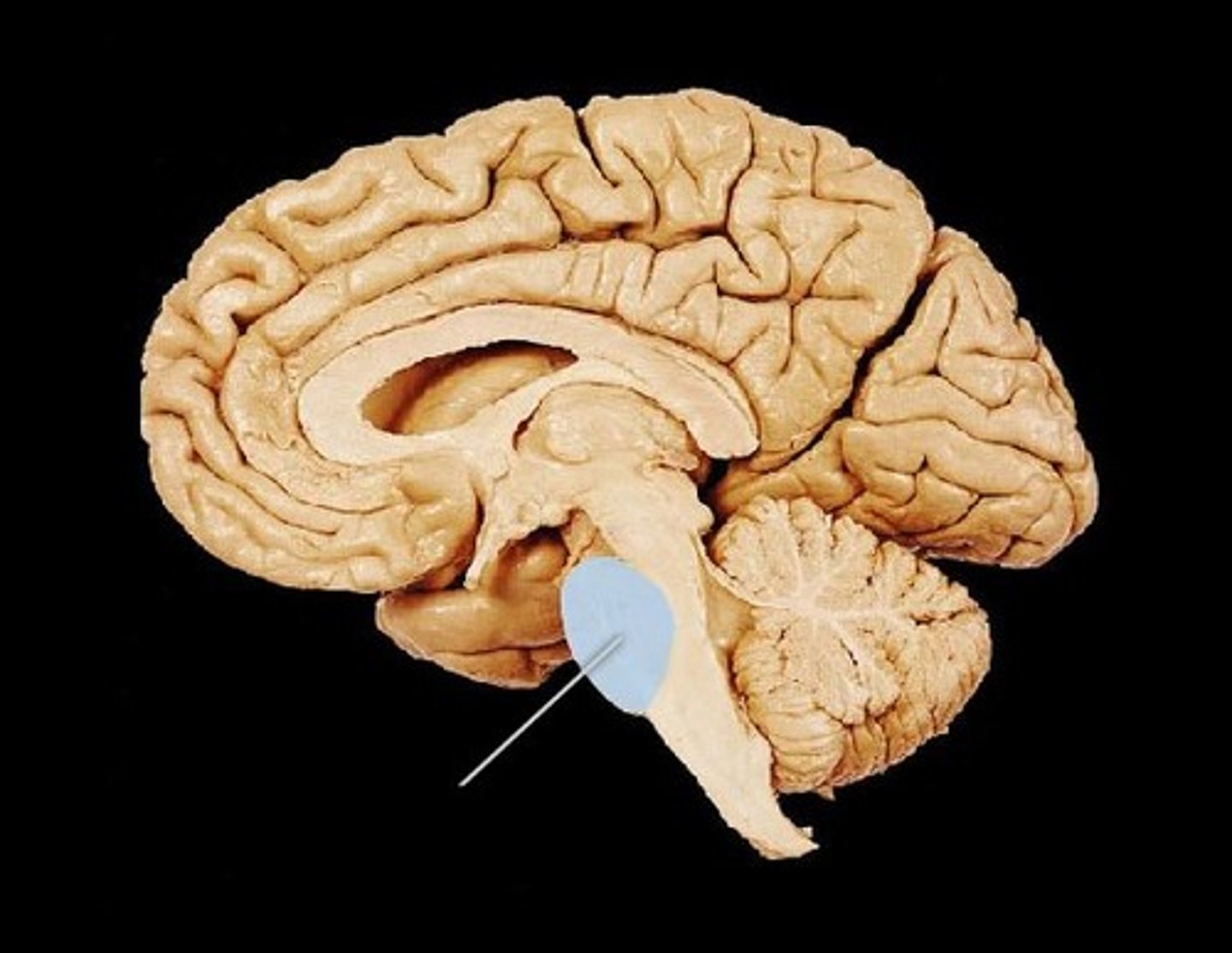
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
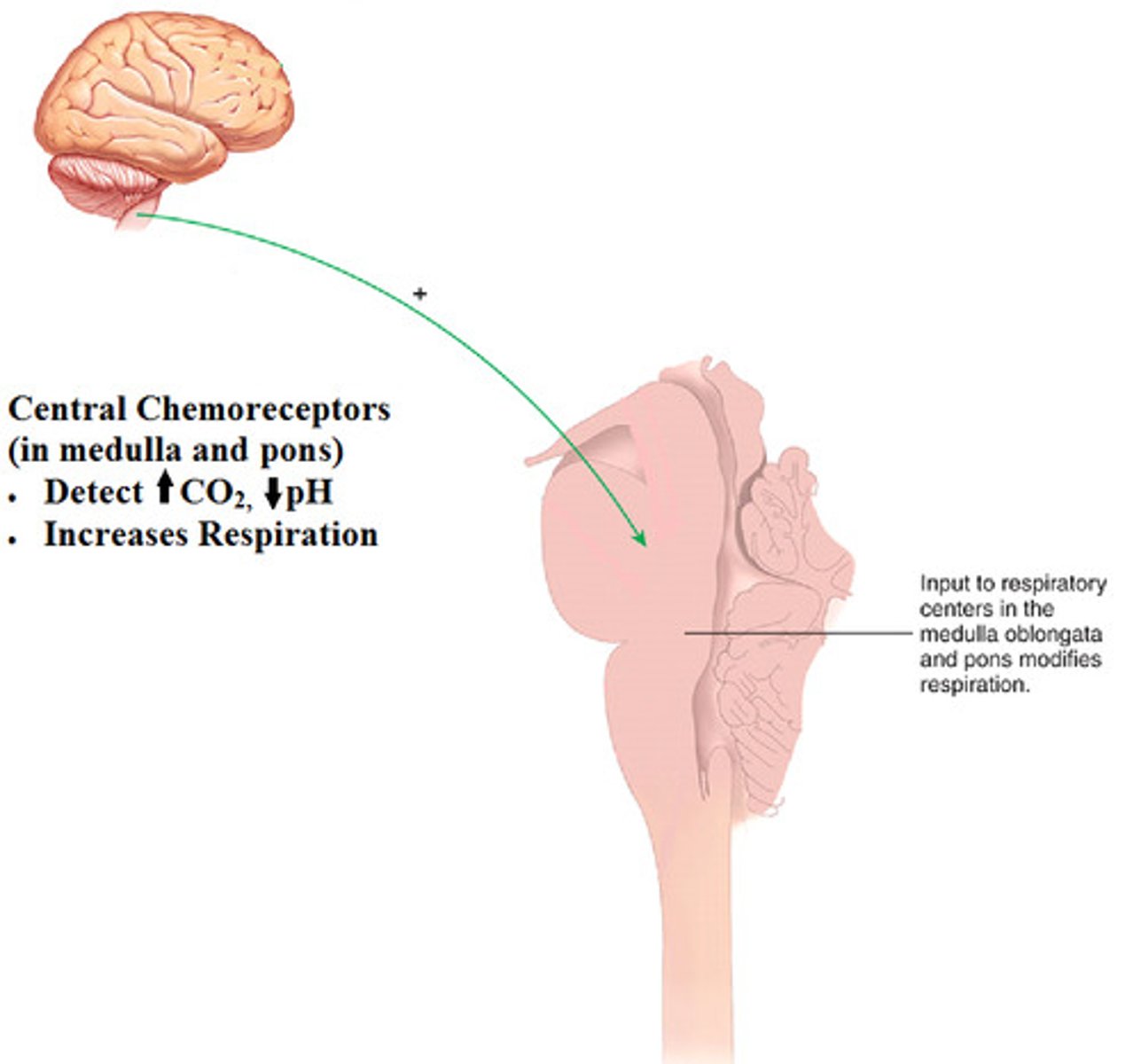
central chemoreceptors
brainstem neurons that respond to changes in pH of cerebrospinal fluid
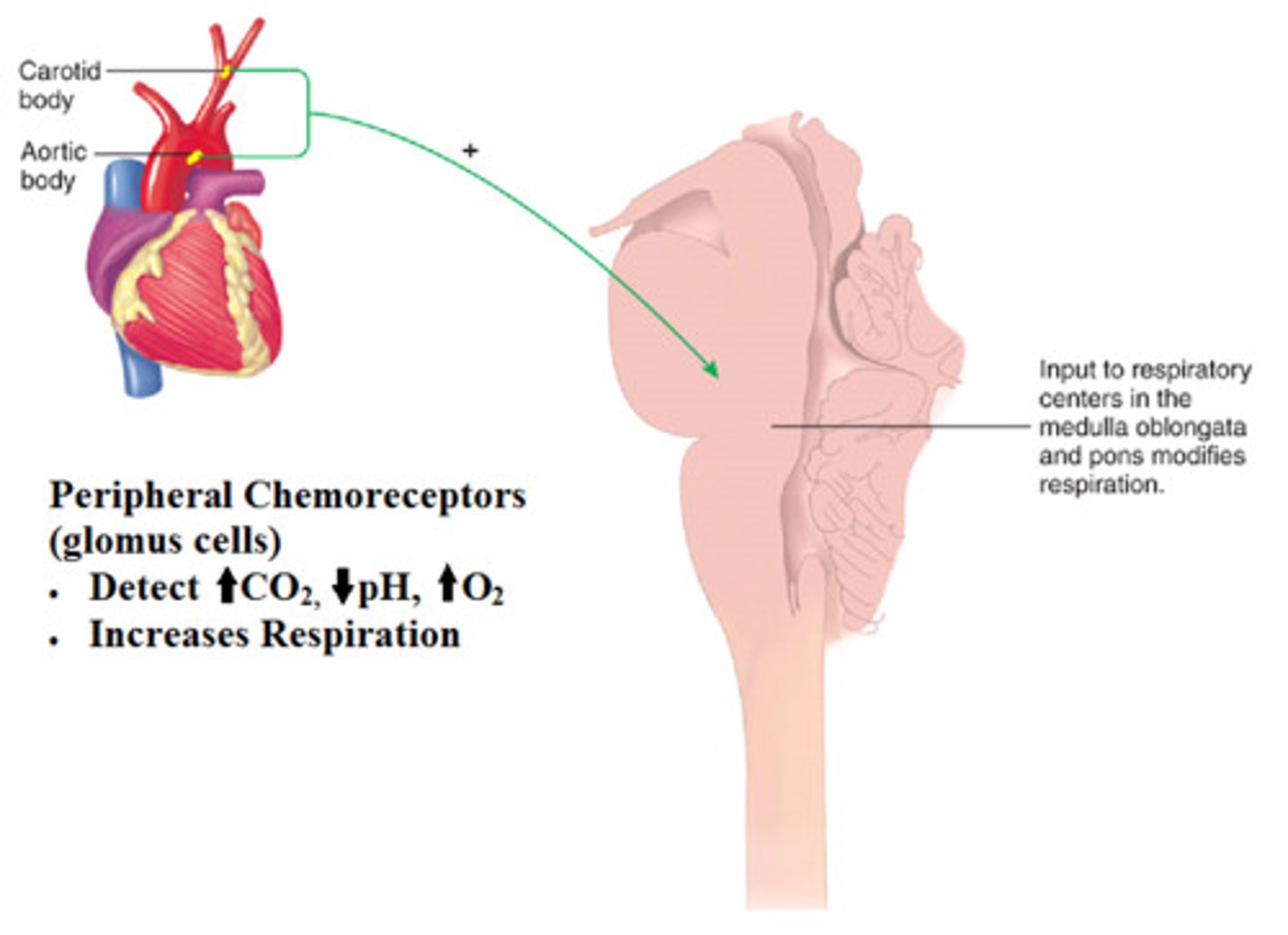
peripheral chemoreceptors
sensory receptor cells located in the aortic arch and carotid arteries that are sensitive to changes in blood oxygen level
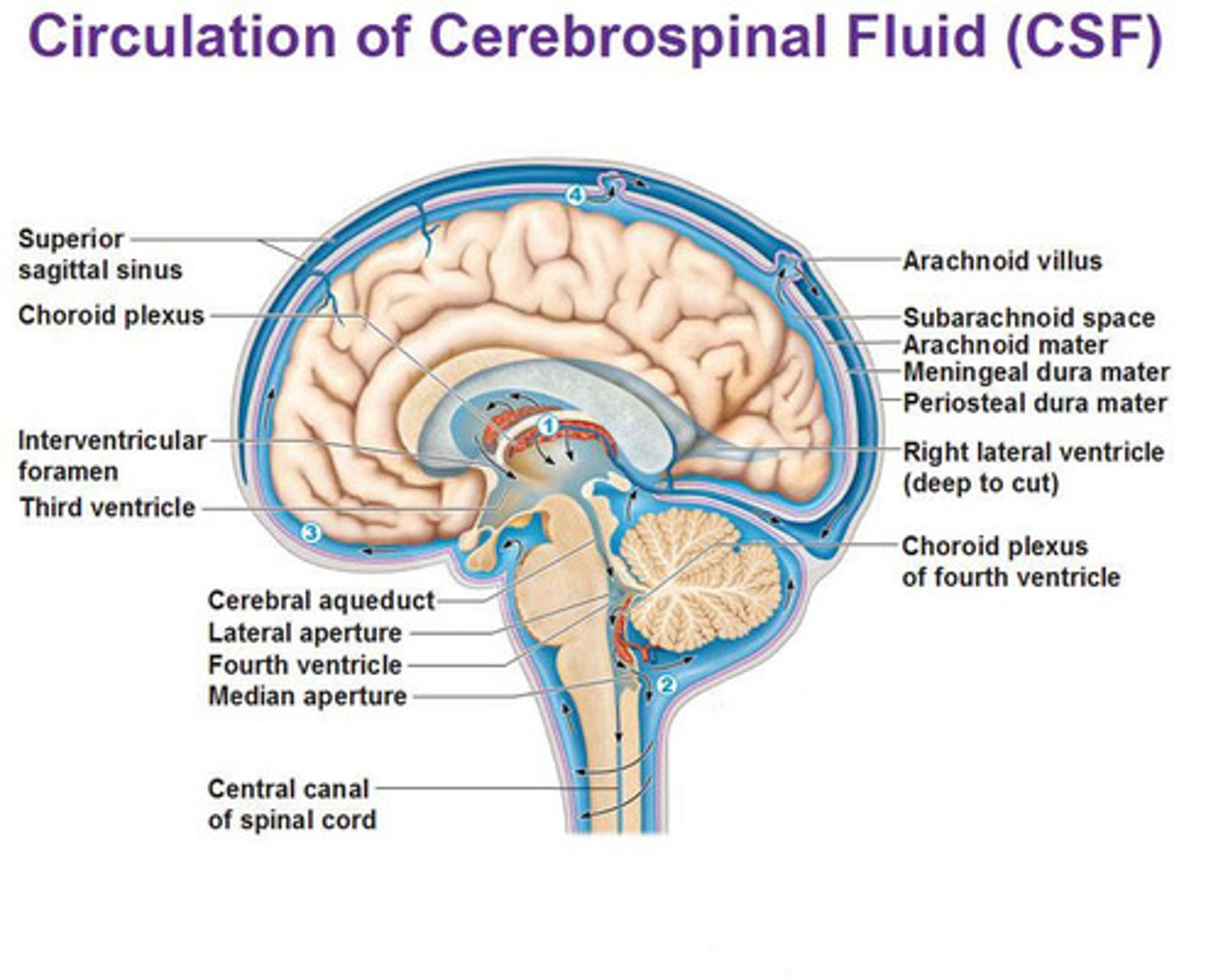
CSF
cerebrospinal fluid
carotid bodies
chemoreceptors located in the internal carotid artery; respond to changes in arterial PO2, PCO2, and pH
ventilation-perfusion coupling
matching of alveolar ventilation with pulmonary blood perfusion
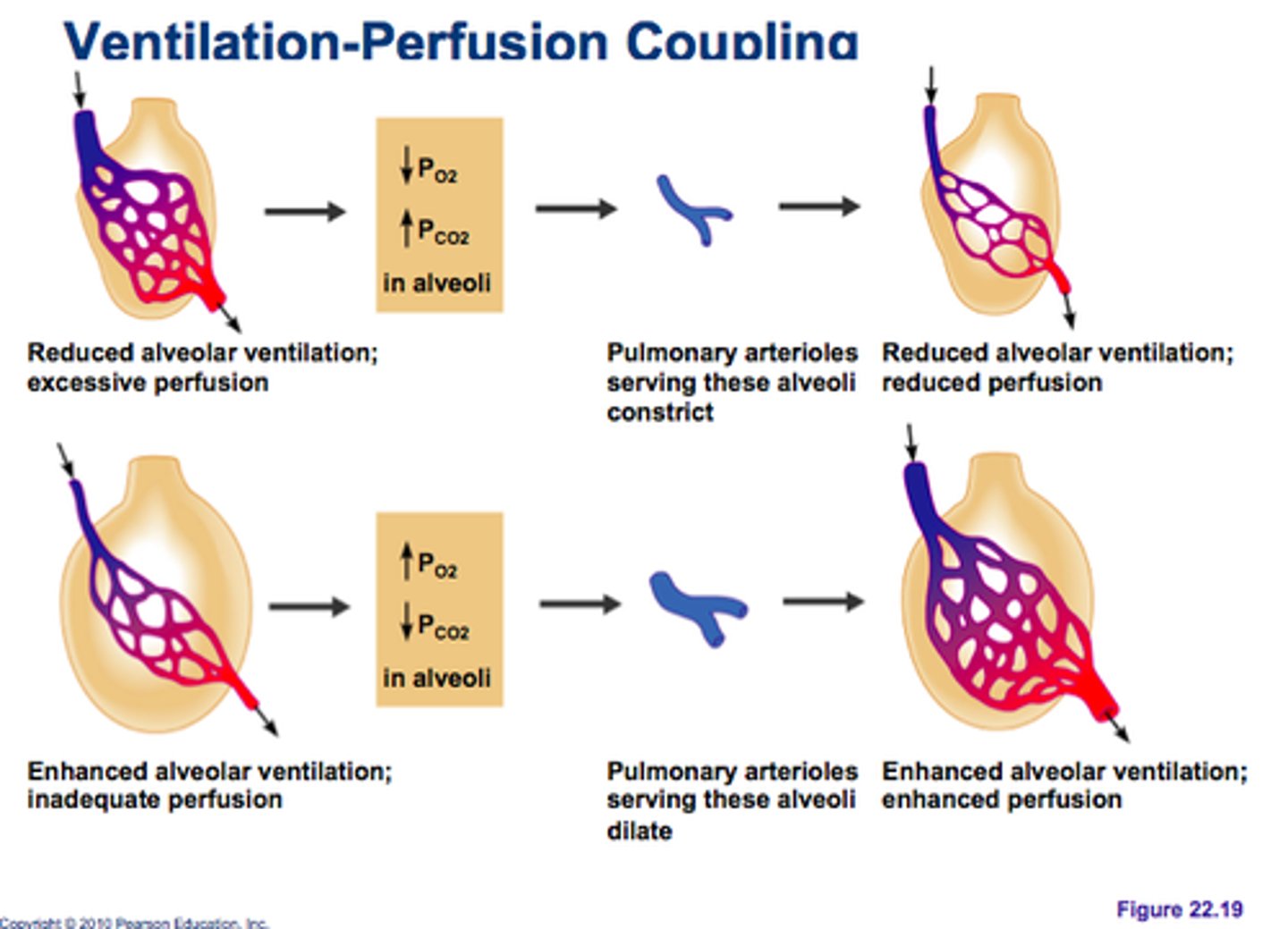
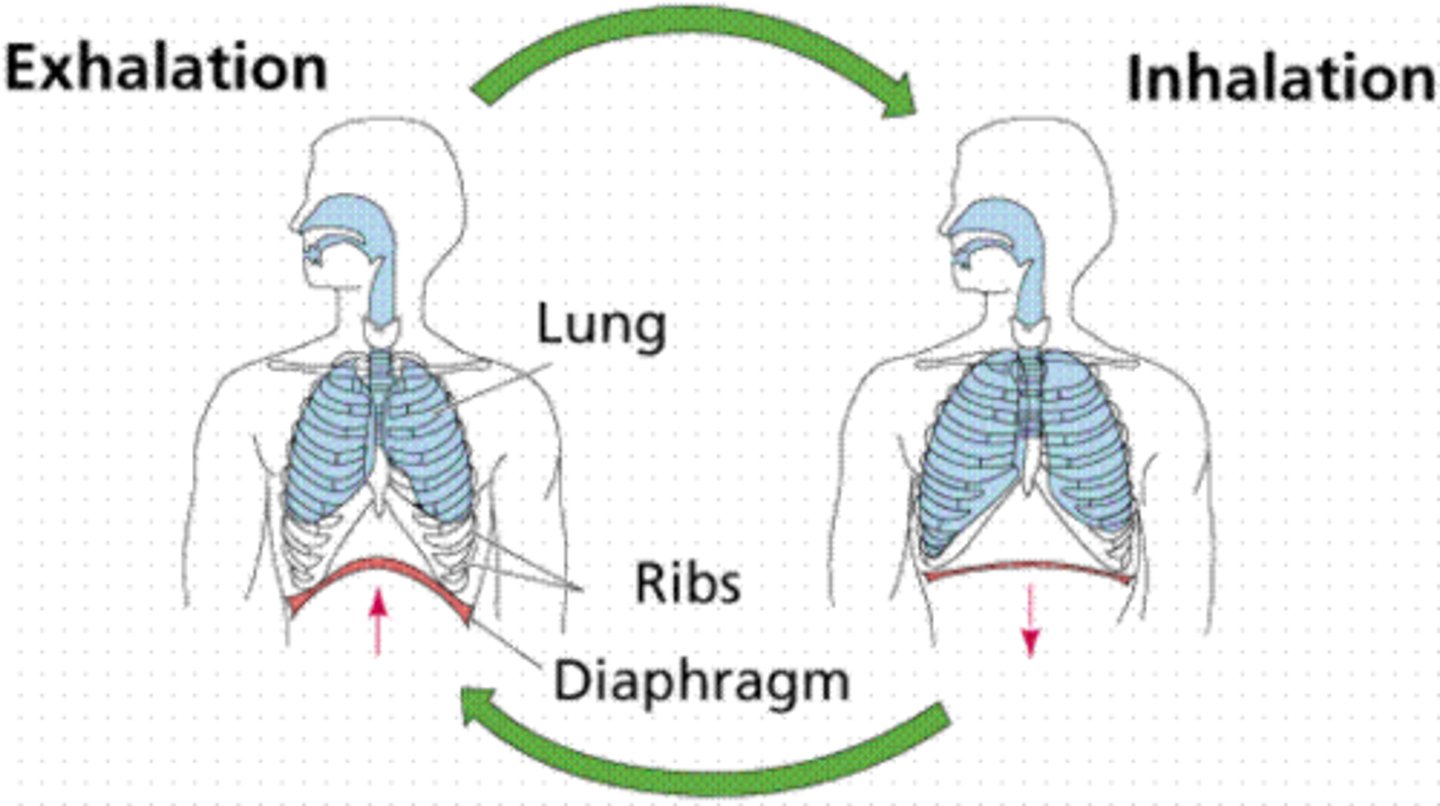
ventilation
movement of air in and out of the lungs
perfusion
The supply of oxygen to and removal of wastes from the cells and tissues of the body as a result of the flow of blood through the capillaries.

Alveolar PO2
partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli (usually around 100 mmHg)
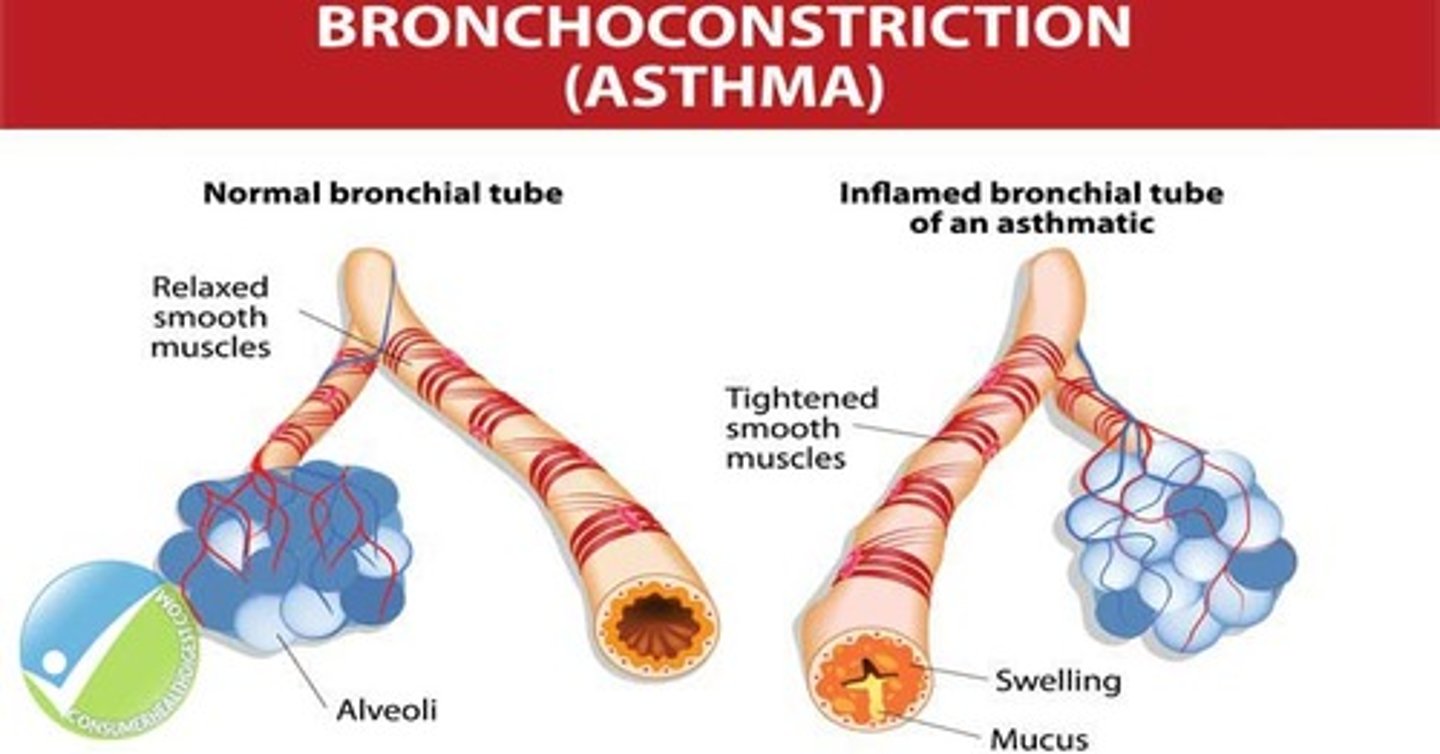
bronchoconstriction
Constriction, or blockage, of the bronchi that lead from the trachea to the lungs.
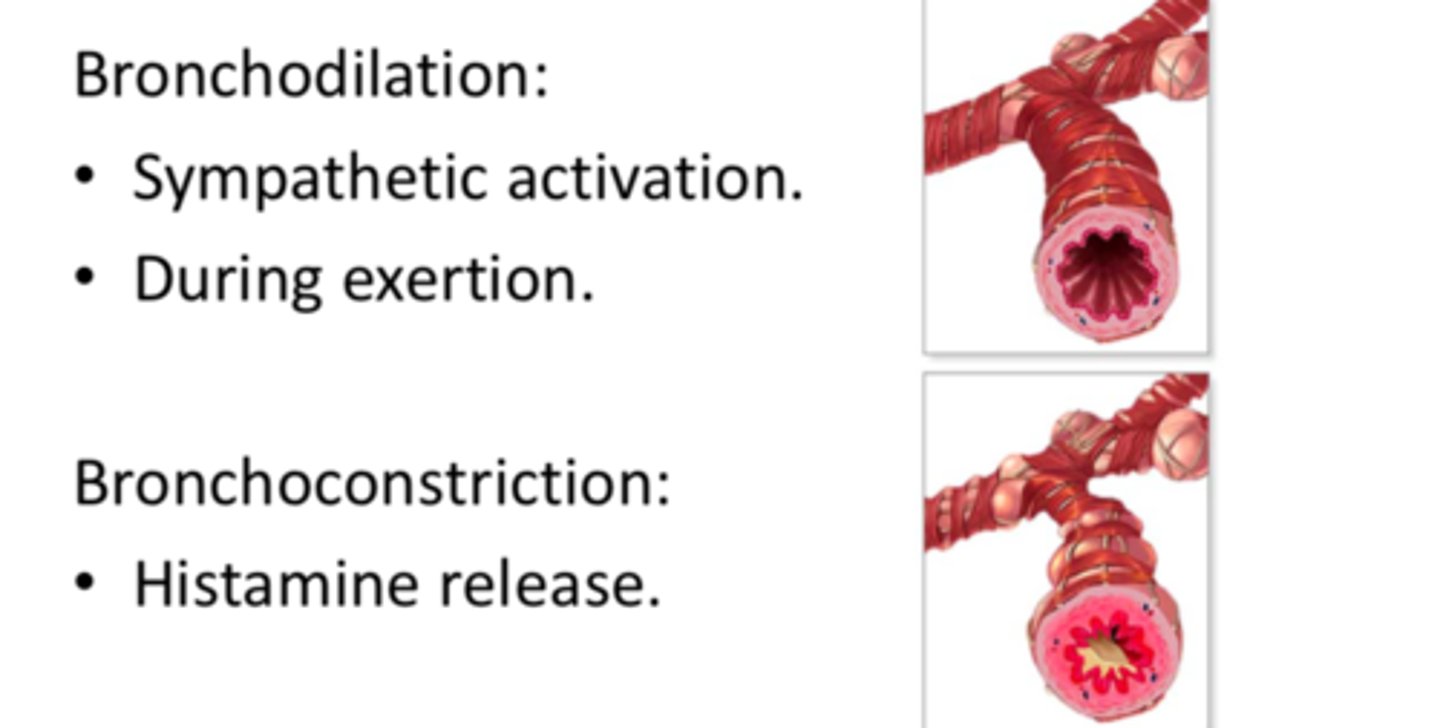
bronchodilation
expansion of the bronchial air passages
Blood pH
7.35-7.45
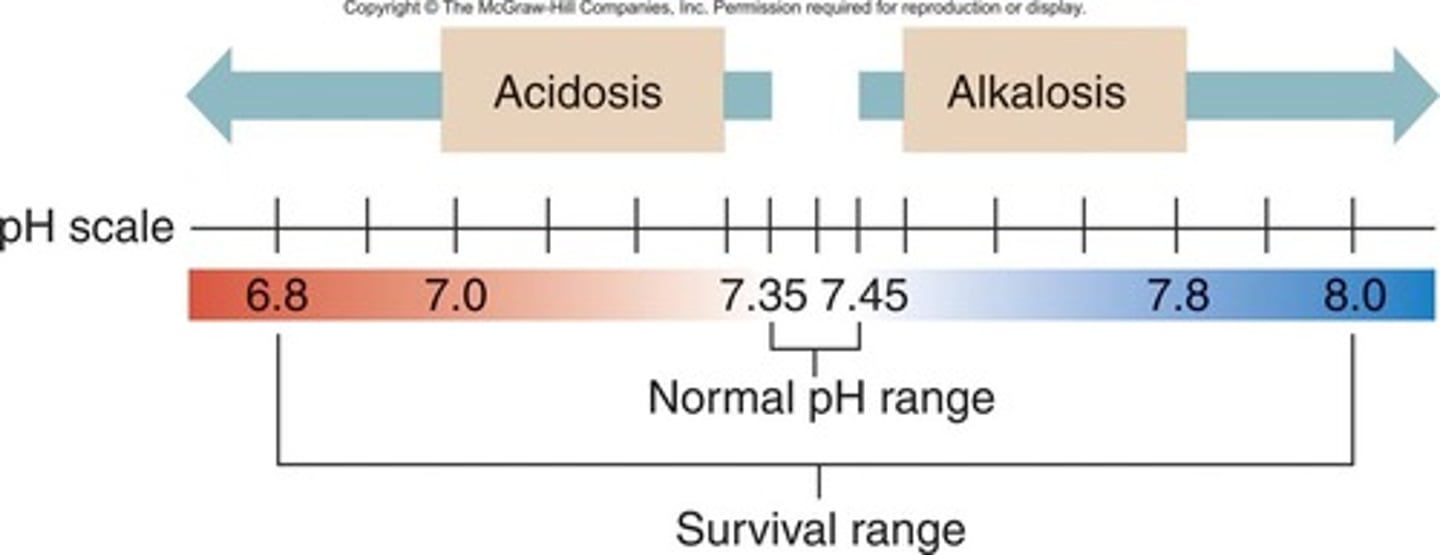
acidosis
excessive acidity of body fluids
alkalosis
The buildup of excess base (lack of acids) in the body fluids.
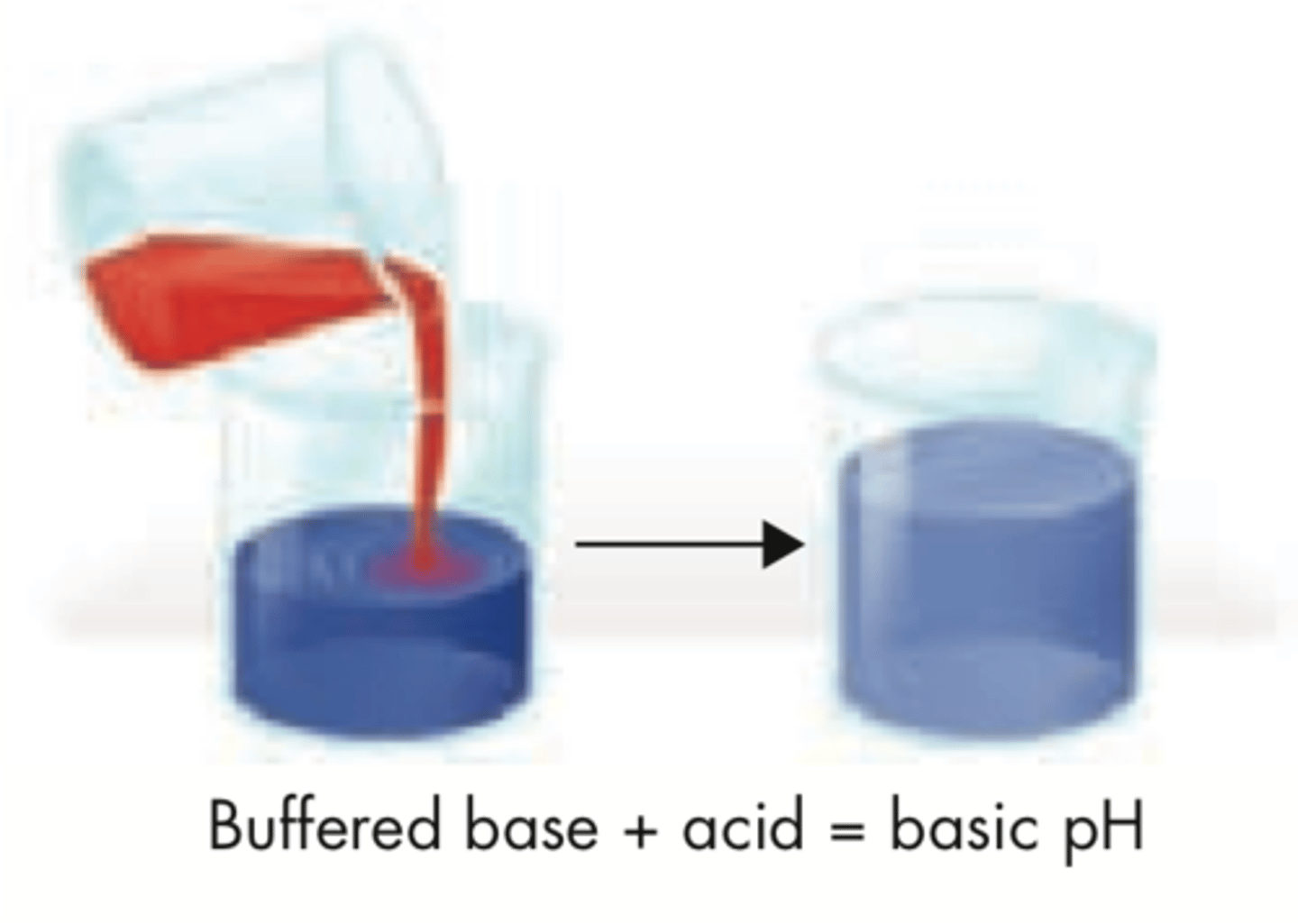
buffers
weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH
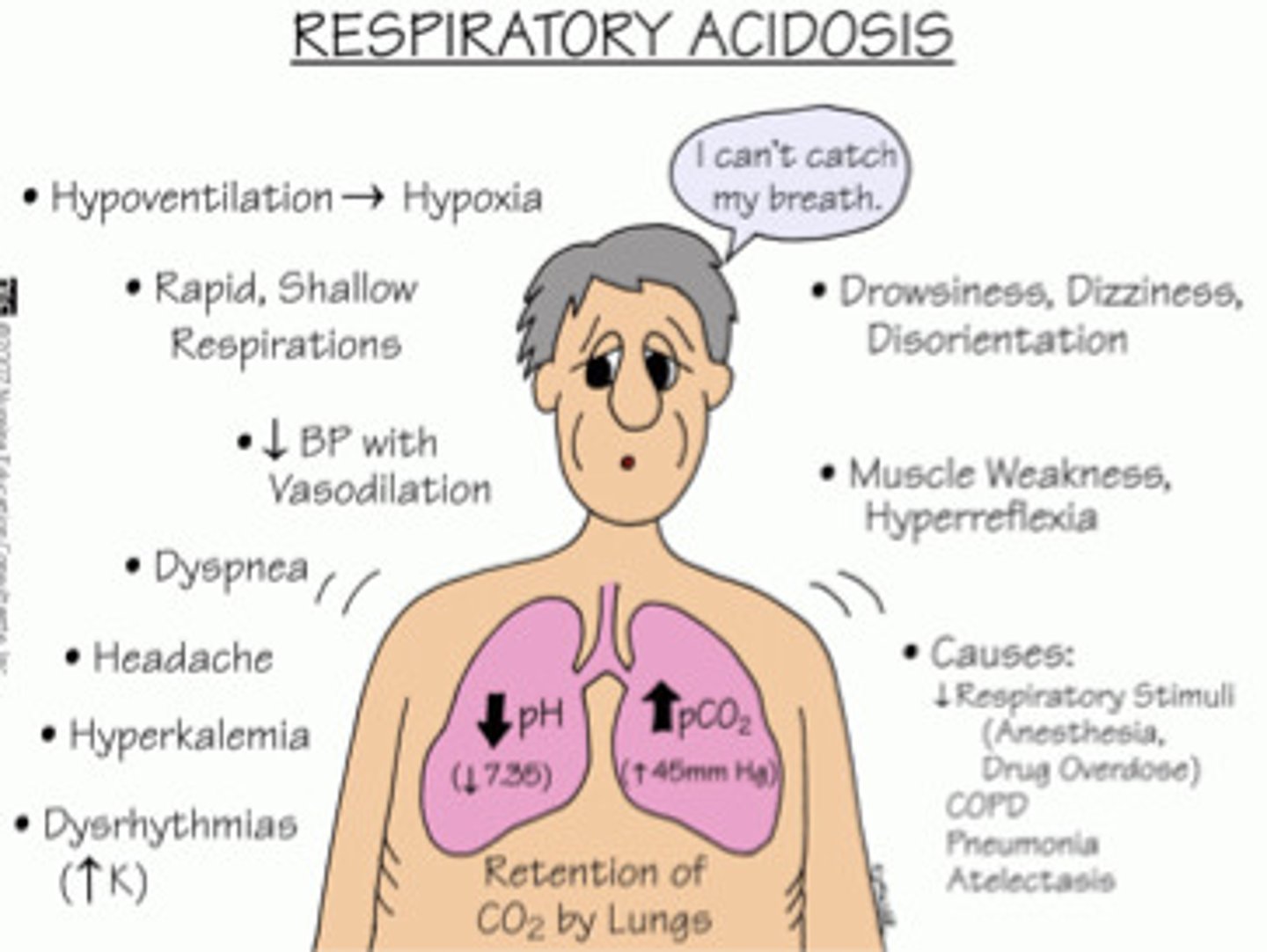
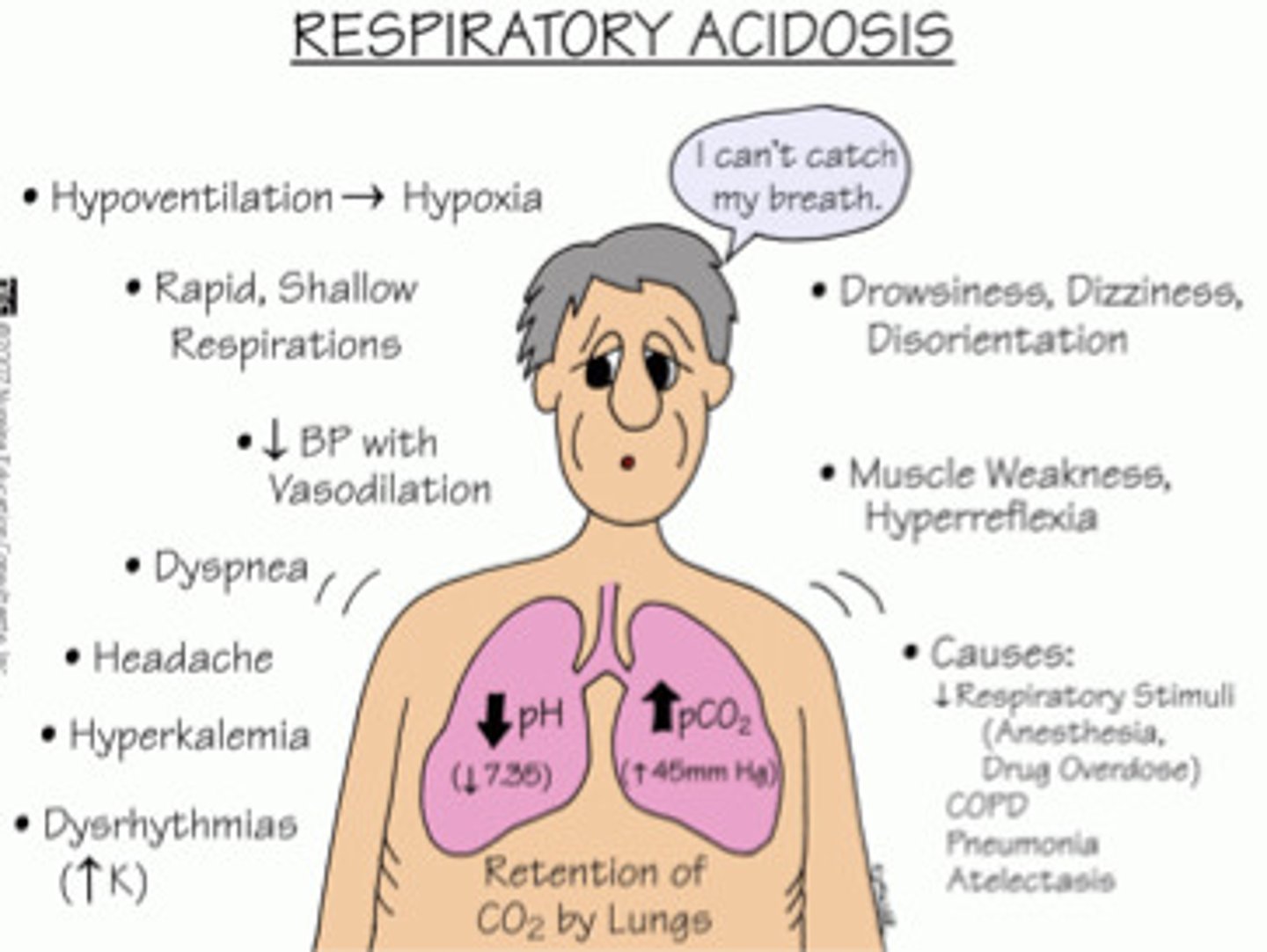
respiratory acidosis
A drop in blood pH due to hypoventilation (too little breathing) and a resulting accumulation of Co2.
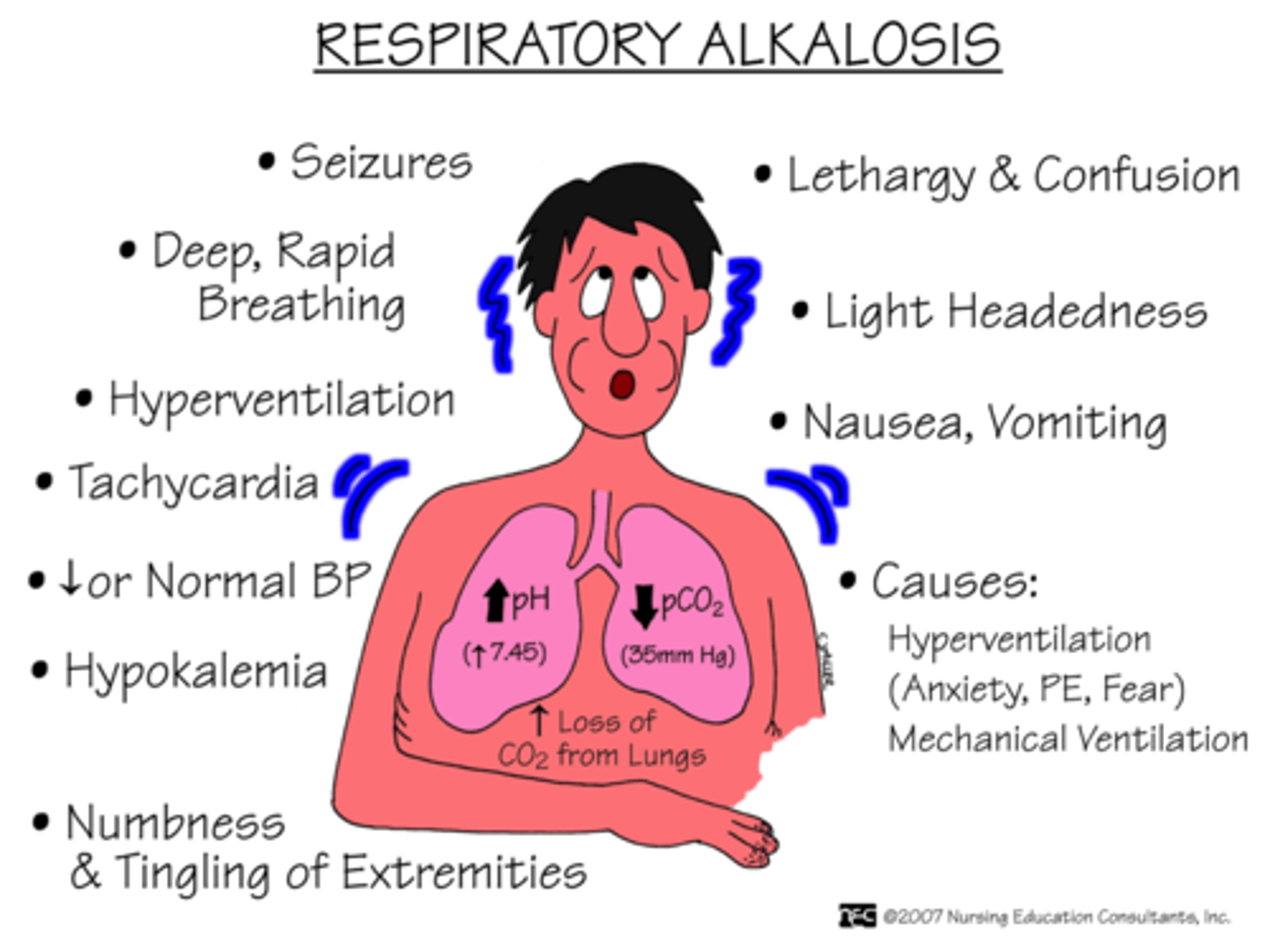
respiratory alkalosis
Arise in blood pH due to hyperventilation (excessive breathing) and a resulting decrease in CO2.
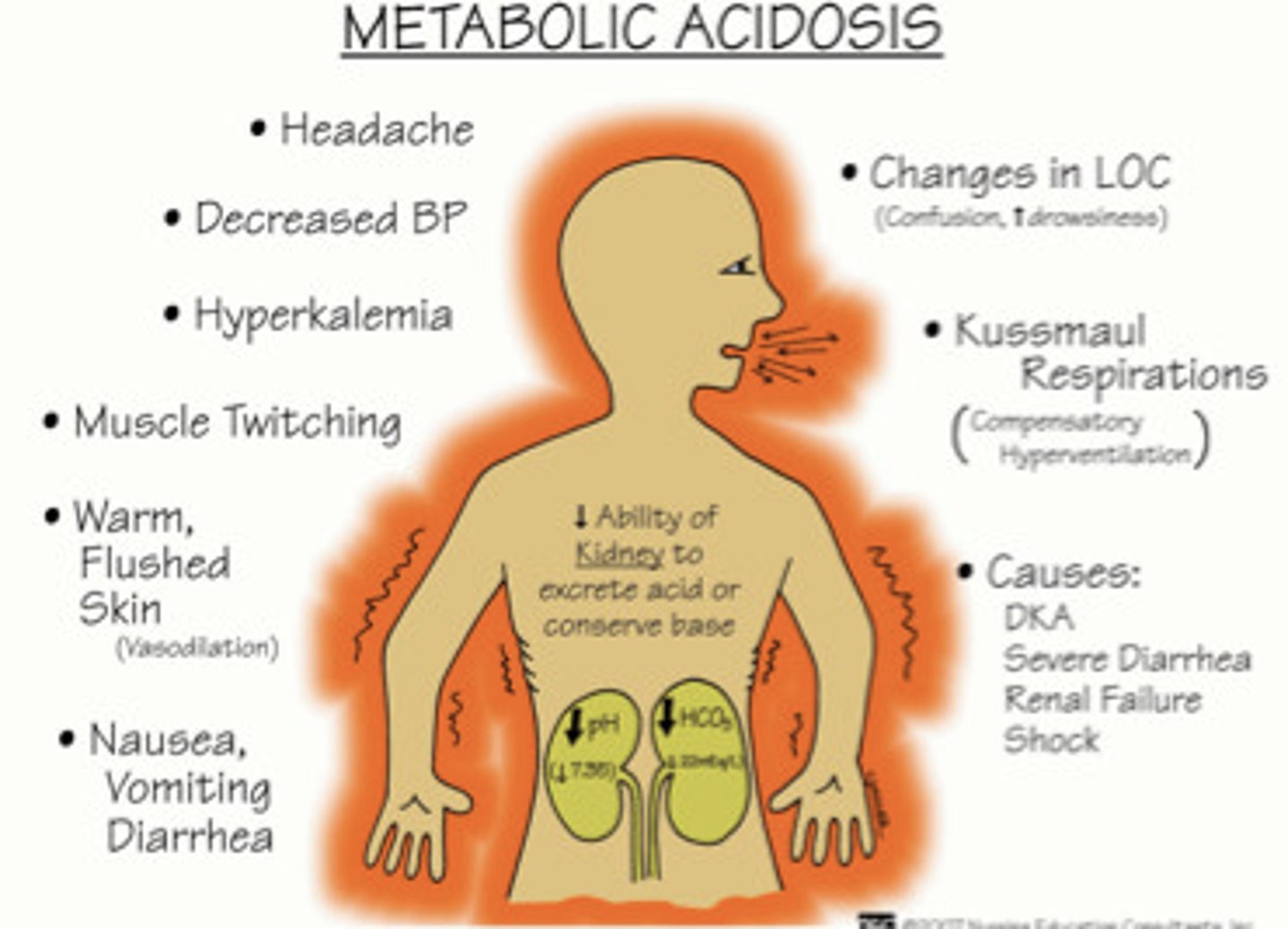
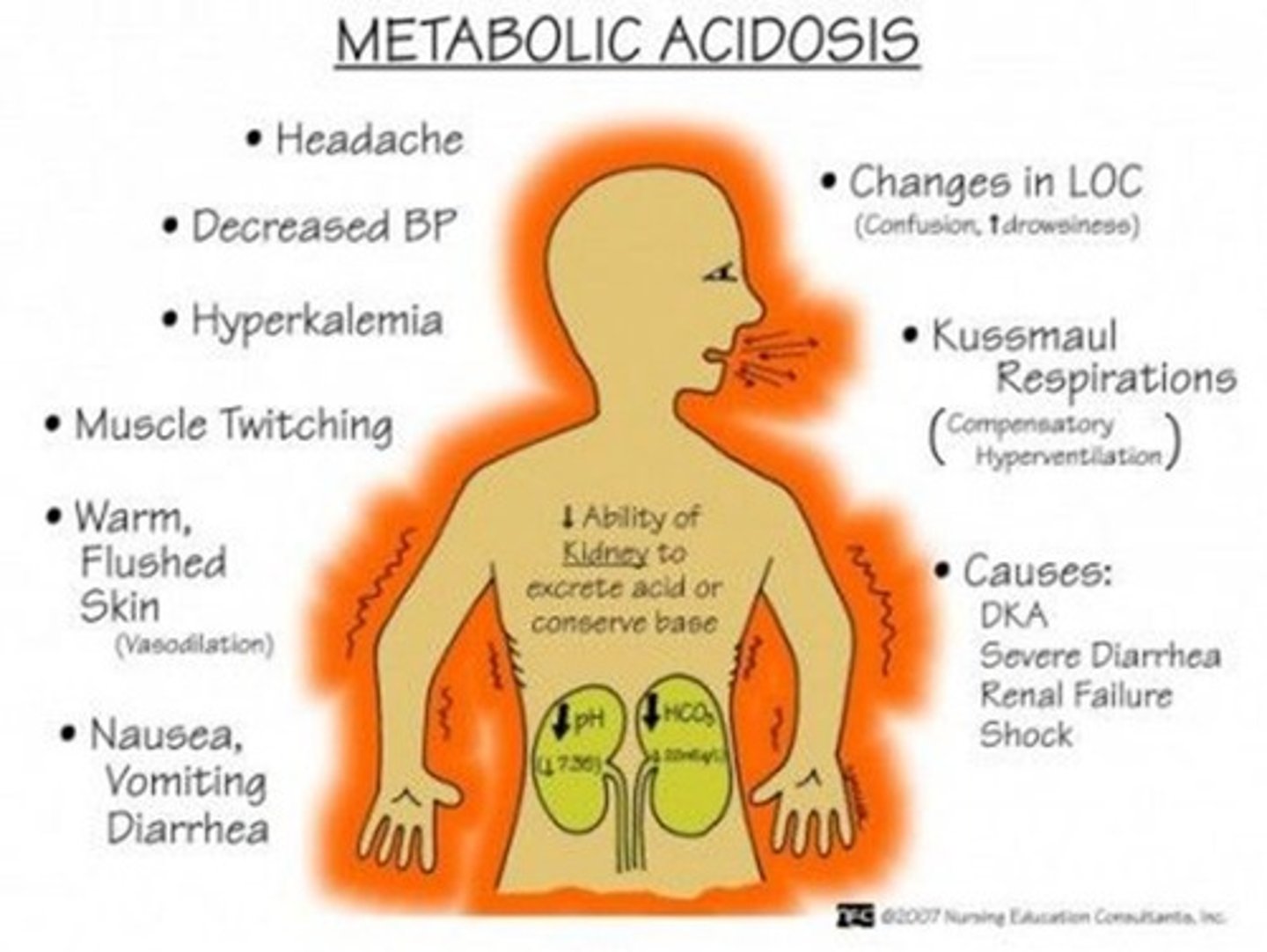
metabolic acidosis
decreased pH in blood and body tissues as a result of an upset in metabolism
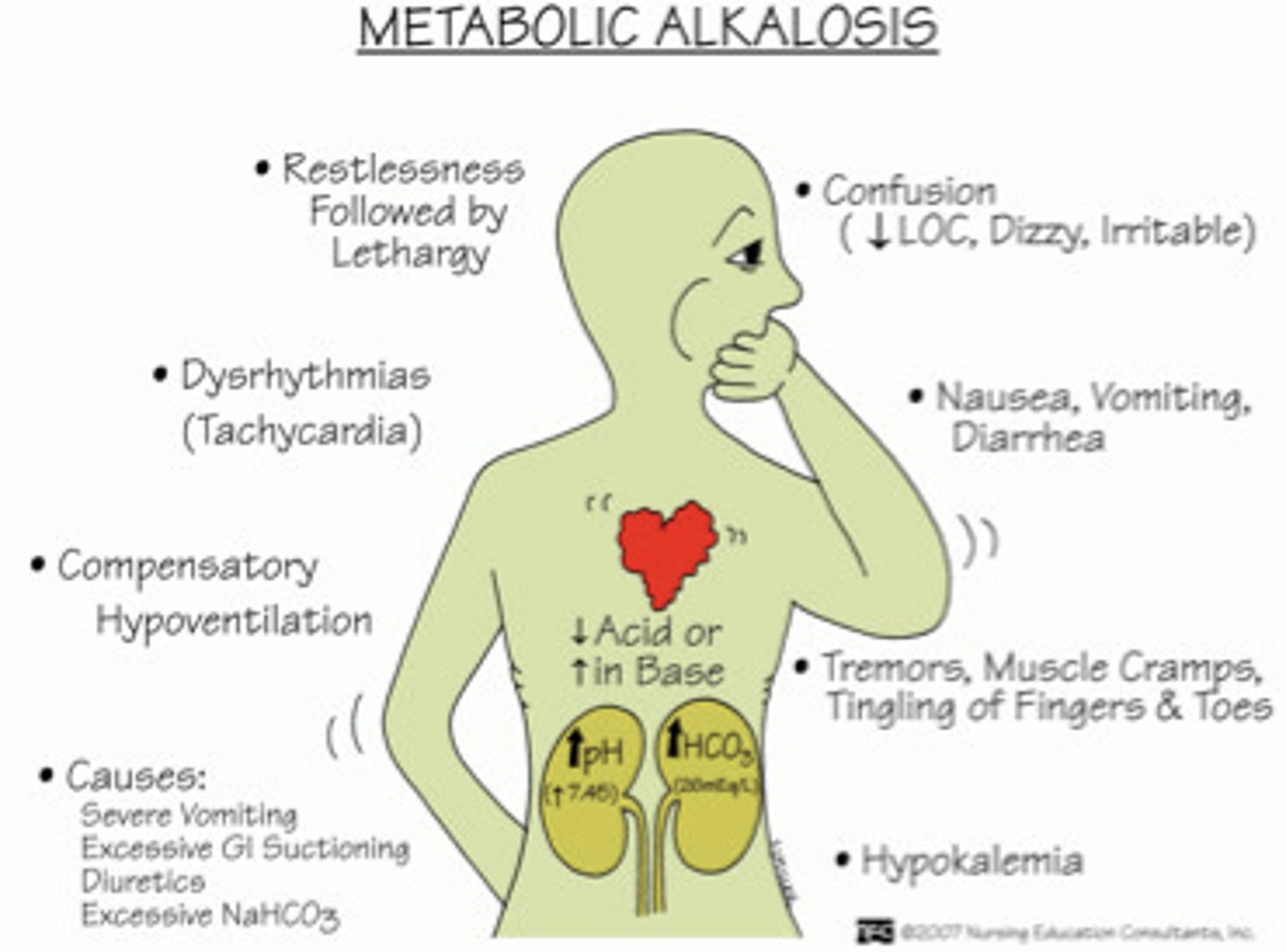
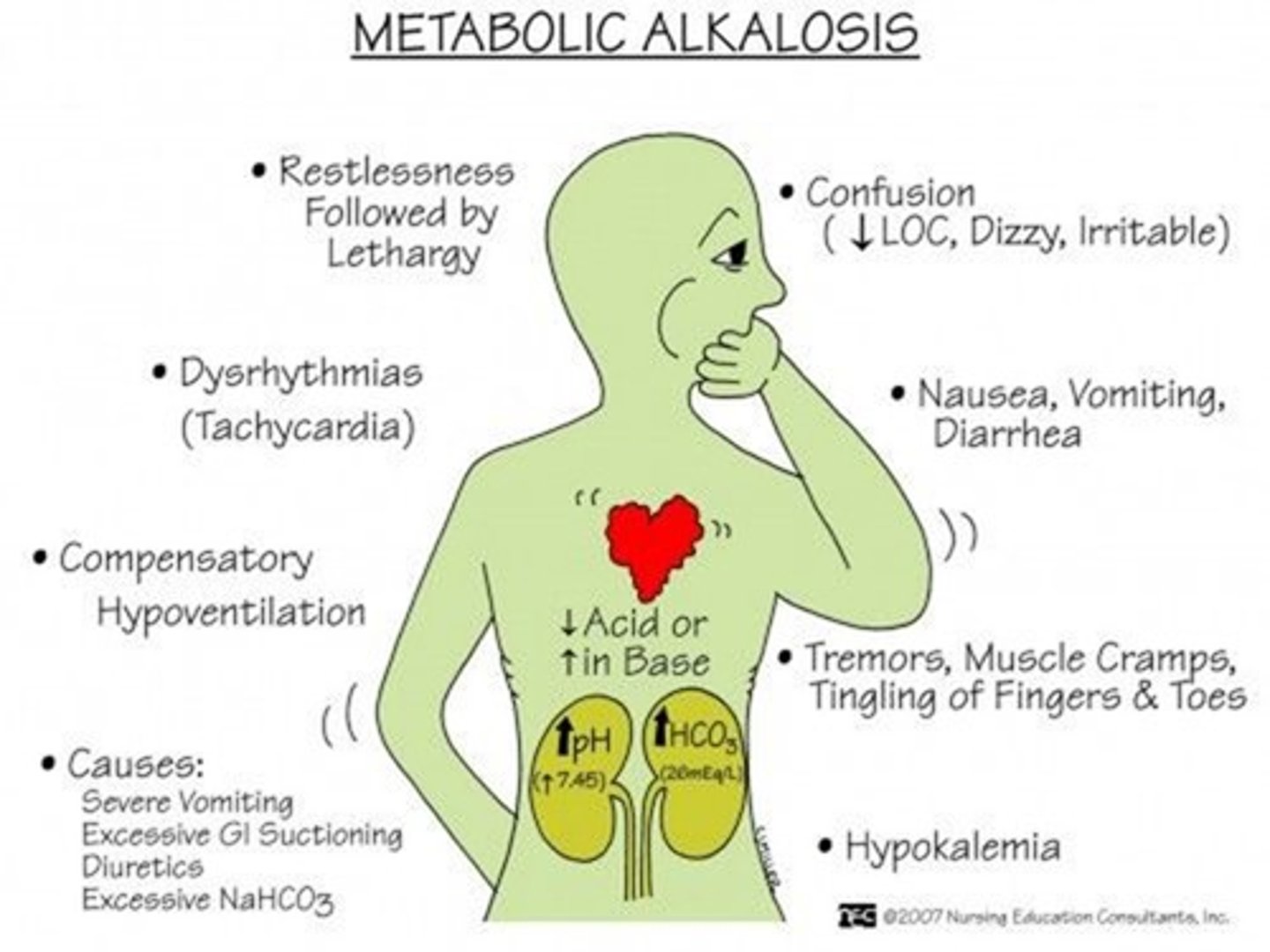
metabolic alkalosis
elevation of HCO3- usually caused by an excessive loss of metabolic acids
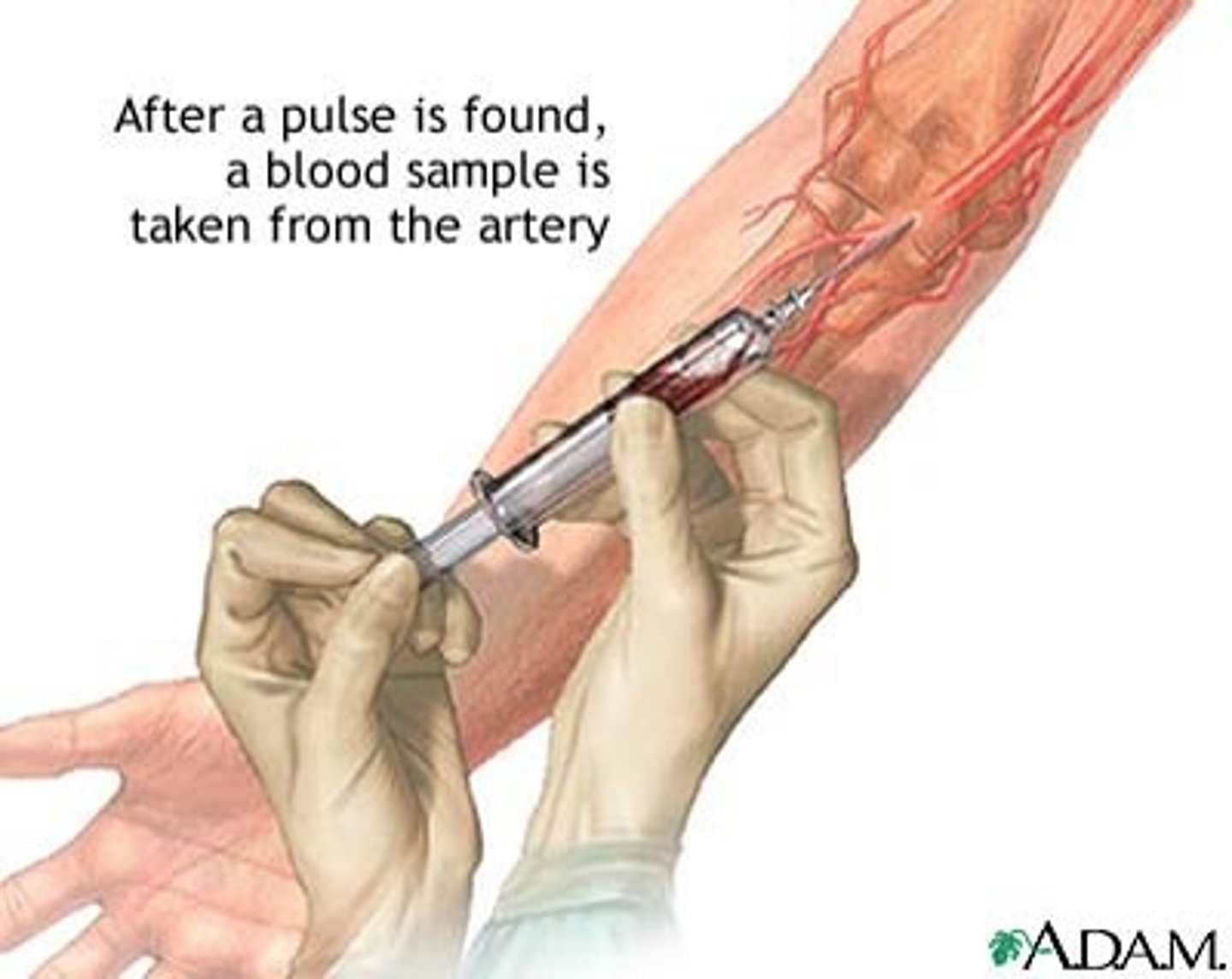
arterial blood gas
a diagnostic test examining arterial blood; used to determine the pressure exerted by oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood
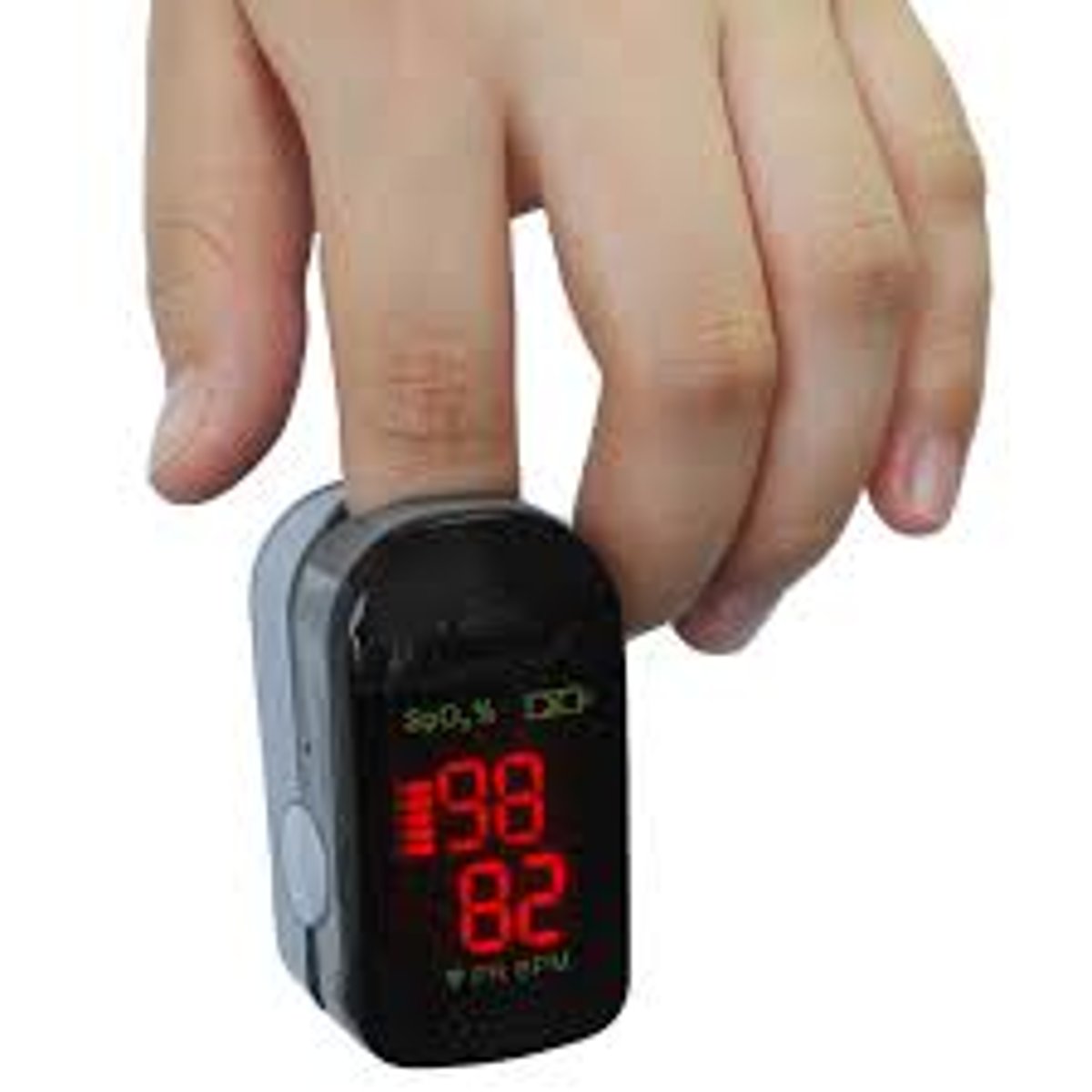
pulse oximeter
an external monitor placed on the patient's finger or earlobe to measure the oxygen saturation level in the blood
capnograph
A device that measures expired CO2 levels
