B4: PPC/OMM Exam 2
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
true
T/F: when inspecting a pt's lungs, they should be SEATED
1. pt in seated position while relaxed
2. preferable to directly visualize chest wall and skin
3. check posture and level of shoulders
4. observe chest wall diameter/symmetry and respirations
5. look for accessory muscle use, masses, or other abnormalities
6. visualize lips and extremities for cyanosis or clubbing
7. observe spine for curvature or abnormalities
Describe the proper inspection of the lungs.
a.
(dull/hyperresonant) percussions of the chest wall:
-indicate fluid or solid tissue
a. dull
b. hyperresonant
b.
(dull/hyperresonant) percussions of the chest wall:
-indicate increased air --> emphysema, severe asthma, pneumothorax
a. dull
b. hyperresonant
auscultation
What is the most important part of a lung exam?
true
T/F: spoken words and louder with consolidates for bronchophony (e.g., when patient says 99)
true
T/F: whispered sounds are louder and clearer with consolidates
b.
What is the correct order for a lung physical exam?
a. palpation > inspection > percussion > auscultation
b. inspection > palpation > percussion > auscultation
c. inspection > percussion > palpation > auscultation
b. inspection > auscultation > percussion > palpation
d. auscultation > inspection > percussion > palpation
12-20 breaths per minute
What is a normal respiratory rate in adults?
a.
What breathing abnormality:
-labored or difficulty breathing
-pulmonary or cardiac compromise
on exam!!!!
a. dyspnea
b. bradypnea
c. tachypnea
d. hyperventilation
e. orthopnea
f. paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
b.
What breathing abnormality:
-RR <12 breaths per minute
-neurologic compromise, electrolyte abnormalities
on exam!!!!
a. dyspnea
b. bradypnea
c. tachypnea
d. hyperventilation
e. orthopnea
f. paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
c.
What breathing abnormality:
-RR > 20 breaths/min
-stress, anxiety, fever
on exam!!!!
a. kussmaul breathing
b. cheyne-strokes respiration
c. tachypnea
d. hyperventilation
e. orthopnea
f. paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
d.
What breathing abnormality:
-rapid, shallow breathing
-associated w/ rib fracture (splinting from pain), anxiety
on exam!!!!
a. kussmaul breathing
b. cheyne-strokes respiration
c. tachypnea
d. hyperventilation
e. orthopnea
f. paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
e.
What breathing abnormality:
-SOB when lying down
-associated w/ CHF
on exam!!!!
a. kussmaul breathing
b. cheyne-strokes respiration
c. tachypnea
d. hyperventilation
e. orthopnea
f. paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
f.
What breathing abnormality:
-sudden onset of SOB after period of sleep
on exam!!!!
a. kussmaul breathing
b. cheyne-strokes respiration
c. tachypnea
d. hyperventilation
e. orthopnea
f. paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
a.
What breathing abnormality:
-deep and rapid
-metabolic acidosis
on exam!!!!
a. kussmaul breathing
b. cheyne-strokes respiration
c. tachypnea
d. hyperventilation
e. orthopnea
f. paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
b.
What breathing abnormality:
-deep periods of breathing w/ intervals of apnea
-seriously ill, brain damage
on exam!!!!
a. kussmaul breathing
b. cheyne-strokes respiration
c. tachypnea
d. hyperventilation
e. orthopnea
f. paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
CN X, cervical and thoracic nerves
What nerves innervate the lungs?
a.
What is the anterior chapman point for the upper lung?
a. 3rd ICS near sternum
b. 4th ICS near sternum
c. T2 and T3 inferior facet
d. T4 inferior facet
b.
What is the anterior chapman point for the lower lung?
a. 3rd ICS near sternum
b. 4th ICS near sternum
c. T2 and T3 inferior facet
d. T4 inferior facet
c.
What is the posterior chapman point for the upper lung?
a. 3rd ICS near sternum
b. 4th ICS near sternum
c. T2 and T3 inferior facet
d. T4 inferior facet
d.
What is the posterior chapman point for the lower lung?
a. 3rd ICS near sternum
b. 4th ICS near sternum
c. T2 and T3 inferior facet
d. T4 inferior facet
a.
(sympathetics/parasympathetics) to the lungs:
-preganglionic neurons T2-T7
-synapse in the superior, middle, inferior cervical ganglia T1-T4
-post-ganglionic fibers to pulmonary plexus
-result = stimulation --> bronchial dilation, more viscous fluid
on exam!!
a. sympathetics
b. parasympathetics
b.
(sympathetics/parasympathetics) to the lungs:
-preganglionic neurons = CN X in medulla
-synapse in parasympathetic ganglia in walls of airway
-post-ganglionic fibers to bronchial smooth mm., glands, vessels
-result = stimulation --> bronchoconstriction, hypersecretion of serous fluid, vasodilation
on exam!!!
a. sympathetics
b. parasympathetics
pre-participation examination
What is primarily used to:
-Screen for potentially life threatening or disabling conditions before allowing sport participation
-ID pre-existing conditions that may predispose injury risk (e.g., CHD, asthma, HTN, etc.)
-satisfy legal requirement
pre-participation examination
What is secondarily used to:
-promote health and safety of athletes
-introduce to sports medicine healthcare system
-foster physician-pt relationship
-be an opportunity for general health assessment
d.
When is a pre-participation examination NOT recommended?
a. before entry in middle school
b. before entry in high school
c. before entry in new exercise program
d. before entry in graduate school
e. before entry in college
false
T/F: a comprehensive pre-participation exam is completed every year
true
T/F: a comprehensive pre-participation exam is completed every 2 years
a.
What type of pre-participation exam implementation:
-can be time consuming
-complete H + P
-establish continuity
-medical records
-privacy
a. office based
b. station based
c. athletic training room
b.
What type of pre-participation exam implementation:
-large, noisy, lack of continuity + privacy, PCP not involved
-multi-station, specialized personnel may be present
-time and cost effective!!!!!!!!!
-additional testing facilitated
a. office based
b. station based
c. athletic training room
standing and valsalva
What special movement/test will decrease venous return to the heart, thus should decrease the severity of a murmur (except in HCM and mitral valve prolapse)?
squatting
What special movement/test will increase preload to the heart, thus should increase the severity of a murmur (except in HCM)?
1. systolic murmur >3/6
2. diastolic murmur
3. any murmur that increases with standing or decreases with squatting
4. unsure type or cardiac Sx by history
5. pt has other RFs as described by AHA
When should you investigate a murmur further?
1. exertional SOB or syncope
2. FMHx of sudden cardiac death
3. systolic murmur grade 3/6
4. any diastolic murmur
5. murmur worse w/ valsalva
6. murmur improves w/ squatting
What are red flags during a cardiac evaluation (typically found during pre-participation exam) which require further testing (ECG, ECHO, exercise stress test)?
true
T/F: if any red flags are present during pre-participation exam, the pt must be withheld from activity until cleared
coronary artery disease
What is the #1 cause of sudden cardiac death over the age of 35?
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
What is the #1 cause of sudden cardiac death under the age of 35?
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
What disorder:
-2/3 of all sudden cardiac death in young athletes
-inherited disease caused by mutations in genes encoding myofilament proteins of the cardiac sarcomere
-causes LVH, myofiber disarray and fibrosis
-ECG will show increased voltage, Transthoracic Echo (TTE) with left ventricle thickness > 15 mm
-Tx = BB, ICD, surgery, activity restriction
-SHOULD NOT PARTICIPATE IN SPORTS!!
anomalous coronary a.
What disorder:
-inborn disease w/ abnormal coronary course --> intramural compression, severe arterial angle kinking, compression by aorta or pulmonary a.
-Diagnosis via MRI, CTA
-Tx = activity modification, surgical release, surgical graft
long QT
What disorder:
-disorder of ventricular myocardium repolarization
-80% inherited ion channel mutations
-20% non-inherited
-can progress to torsade de points
-QTc >440 ms
early repolarization
What disorder:
-J point elevation >0.1 mV in 2 adjacent leads w/ slurred or notched morphology
-increased in athletes
-relationship with intraventricular septal thickness
-typically benign unless associated with syncope or SCA
brugada syndrome
What disorder:
-mutation in cardiac sodium channel gene
-50% are spontaneous mutations
-EKG findings may be transient
-treatment includes ICD
-unable to participate in sports
-after ST elevation they will have inverted T wave
-deep S wave
brugada syndrome
ID
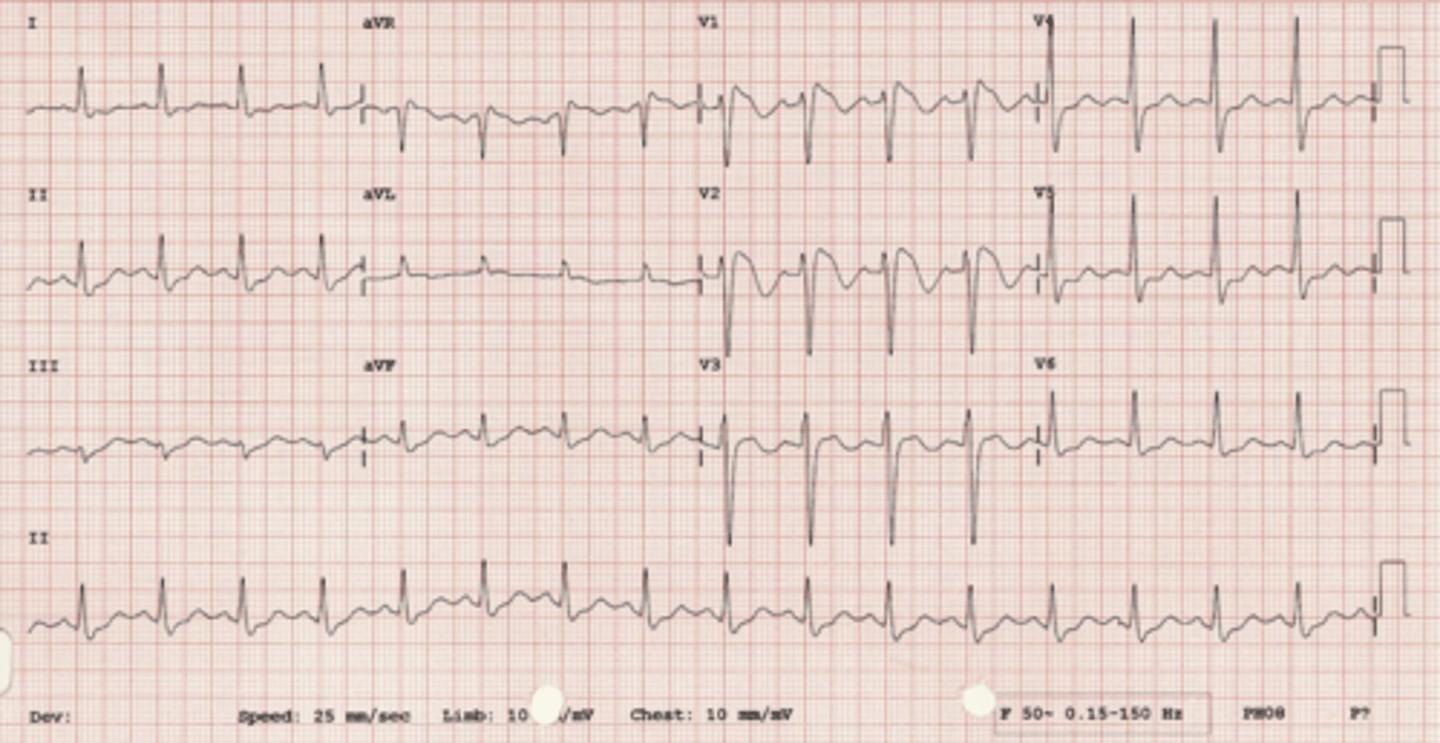
early repolarization
ID
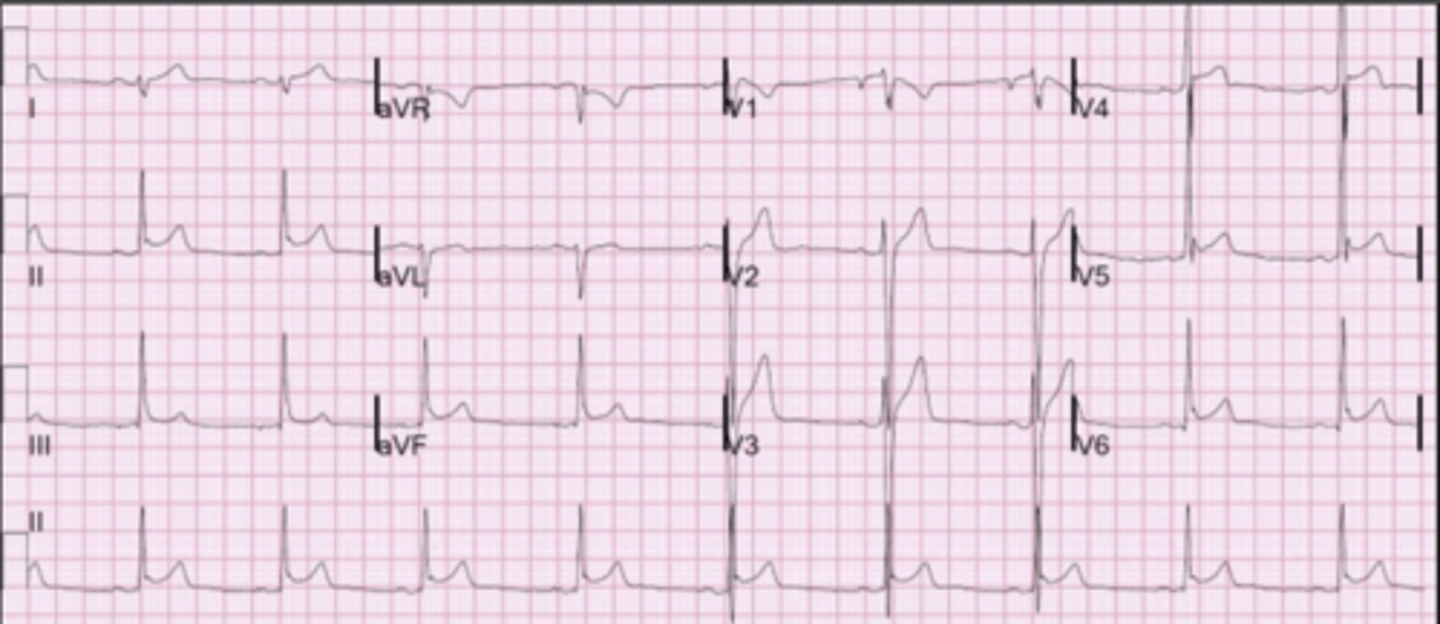
polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
What disorder:
-wide complex tachycardia, rate >100 with varying QRS morphology
-catecholaminergic PVT: congenital etiology causing calcium overload in the setting of increased stress
-resting EKG normal
-genetic testing and exercise testing
-Tx: BB, amiodarone, ICD
a.
What is the activity recommendation for pts with prolonged QT?
a. moderate-intensity and many low-intensity recreational or leisure time activities
b. once treated, may participate in competitive sport
c. avoid sports
d. category 1C activities
b.
What is the activity recommendation for pts with wolff parkinson white?
a. moderate-intensity and many low-intensity recreational or leisure time activities
b. once treated, may participate in competitive sport
c. avoid sports
d. category 1C activities
history
What is the most cost effective screen for cardiovascular disease?
1. condition should be important
2. test should be acceptable
3. treatable
4. cost-effective
What are the 4 components of a good screening test?
b.
(static/dynamic) sports:
-endurance training
-increase VO2 demands
-may cause eccentric hypertrophy
a. static
b. dynamic
a.
(static/dynamic) sports:
-resistance training
-increased pressure due to BP
-may cause concentric hypertrophy
a. static
b. dynamic
true
T/F: the use of ECG for pre-participation exam is debated, it is more sensitive to PPE alone b/c you can look at electrical activity but it has a high false positive rate
on exam!!!
to detect pre-existing conditions that could harm the athlete and to encourage safe participation in athletics, not to disqualify
What is the primary objective of a pre-participation exam?
a.
What type of abnormal pulse:
-indicates low volume
-associated w/ HF, aortic stenosis
a. weak pulse
b. large bounding pulse
c. pulsus alternans
d. bigeminal pulse
e. paradoxical pulse
b.
What type of abnormal pulse:
-indicates inc. stroke volume or dec. peripheral resistance
-associated w/ fever, anemia, hyperthyroidism, aortic regurg, PDA
a. weak pulse
b. large bounding pulse
c. pulsus alternans
d. bigeminal pulse
e. paradoxical pulse
c.
What type of abnormal pulse:
-indicates alternating amplitude of pulse
-associated w/ aortic stenosis
a. weak pulse
b. large bounding pulse
c. pulsus alternans
d. bigeminal pulse
e. paradoxical pulse
d.
What type of abnormal pulse:
-indicates rhythm alteration that mimics pulsus alternans
a. weak pulse
b. large bounding pulse
c. pulsus alternans
d. bigeminal pulse
e. paradoxical pulse
e.
What type of abnormal pulse:
-indicates palpable dec. in pulse amplitude w/ quiet inspiration
-associated w/ >10 mmHg drop in systolic BP, pericardial tamponade, and exacerbation of asthma and COPD
a. weak pulse
b. large bounding pulse
c. pulsus alternans
d. bigeminal pulse
e. paradoxical pulse
true
T/F: elevated JVP is >95% specific for inc. LVP and dec. EF
carotid artery pathology or radiation from aortic valve
If a bruit is heard in the carotid artery, it is from _______
a.
you should listen to the carotid arteries with the (bell/diaphragm) of the stethoscope while the pt is holding their breath
a. bell
b. diaphragm
1. angle of jaw
2. mid-cervical area
3. base of neck
What are the 3 areas you should auscultate the carotid artery?
a.
Which heart sound:
-mitral and tricuspid valve closures
a. S1
b. S2
c. S3
d. S4
b.
Which heart sound:
-aortic and pulmonic valve closures
a. S1
b. S2
c. S3
d. S4
c.
Which heart sound:
-in early diastole during rapid ventricular filling phase- associated with increased filling pressure (MR and HF) or dilated ventricles
a. S1
b. S2
c. S3
d. S4
d.
Which heart sound:
-late diastole, best heard at the apex, associated with ventricular hypertrophy (left atrium pushing against stiff LV wall)
a. S1
b. S2
c. S3
d. S4
a.
________ splitting:
-Inspiration result in drop of intrathoracic pressure leading to increased venous return, resulting in delayed closure of the pulmonic valve
a. normal
b. wide
c. fixed
d. paradoxical
b.
________ splitting:
-Conditions of delayed RV emptying, such as pulmonic stenosis and RBBB
a. normal
b. wide
c. fixed
d. paradoxical
c.
________ splitting:
-Not dependent upon breath. Seen in conditions that result in left to right shunt and increase right sided volumes, pulmonic closure is greatly delayed
a. normal
b. wide
c. fixed
d. paradoxical
d.
________ splitting:
-Due to delayed aortic valve closure (after pulmonic valve) due to AS or LBBB. Splitting is "paradoxically" eliminated during inspiration
a. normal
b. wide
c. fixed
d. paradoxical
a.
(systolic/diastolic) murmurs are between S1 and S2
a. systolic
b. diastolic
b.
(systolic/diastolic) murmurs are between S2 and S1
a. systolic
b. diastolic
a.
What grade heart murmur:
-barely audible
a. grade 1
b. grade 2
c. grade 3
d. grade 4
e. grade 5
f. grade 6
b.
What grade heart murmur:
-little louder
a. grade 1
b. grade 2
c. grade 3
d. grade 4
e. grade 5
f. grade 6
c.
What grade heart murmur:
-clearly audible -- no thrill
a. grade 1
b. grade 2
c. grade 3
d. grade 4
e. grade 5
f. grade 6
d.
What grade heart murmur:
-thrill palpable
a. grade 1
b. grade 2
c. grade 3
d. grade 4
e. grade 5
f. grade 6
e.
What grade heart murmur:
-audible w/ stethoscope partly off chest + thrill
a. grade 1
b. grade 2
c. grade 3
d. grade 4
e. grade 5
f. grade 6
f.
What grade heart murmur:
-audible w/o stethoscope
a. grade 1
b. grade 2
c. grade 3
d. grade 4
e. grade 5
f. grade 6
a.
which manuever increases the following murmurs:
-aortic stenosis
-aortic regurg
-pericardial rubs
a. sitting up, leaning forward, holding exhalation
b. L lateral decubitus
c. valsalva
d. squatting
b.
which manuever increases the following murmurs:
-S3
-S4
-mitral stenosis
a. sitting up, leaning forward, holding exhalation
b. L lateral decubitus
c. valsalva
d. squatting
c.
which manuever increases the following murmurs:
-inc. mitral valve prolapse
-inc. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-dec. aortic stenosis
a. sitting up, leaning forward, holding exhalation
b. L lateral decubitus
c. valsalva
d. squatting
d.
which manuever increases the following murmurs:
-dec. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-inc. aortic stenosis
a. sitting up, leaning forward, holding exhalation
b. L lateral decubitus
c. valsalva
d. squatting
a.
What murmur:
-R 2nd ICS
-radiates to carotids, apex, and LSB
-variable in intensity, may be loud w/ thrill
-can be harsh
-crescendo-decrescendo
-increases when pt leads forward and sits
a. aortic stenosis
b. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
c. aortic regurg
d. mitral stenosis
b.
What murmur:
-3rd and 4th L intercostal space
-radiates to apex and LSB
-varies in intensity
-medium pitch
-harsh
-decreases w/ squat
a. aortic stenosis
b. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
c. aortic regurg
d. mitral stenosis
c.
What murmur:
-2nd to 4th L intercostal space
-radiates to apex and R sternal border
-grade 1-3
-high pitch
-blowing
-descrendo
-increases when pt sits, leans forward, and holds breath in exhalation
a. aortic stenosis
b. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
c. aortic regurg
d. mitral stenosis
d.
What murmur:
-heart at apex
-little radiation
-1-4
-descrendo
-low pitch rumble
-heard best in exhalation and L lateral decubitus
a. aortic stenosis
b. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
c. aortic regurg
d. mitral stenosis
a.
(sympathetics/parasympathetics) to the heart:
-pre-ganglionic neurons = nucleus intermediolateralis in lateral horn spinal cord levels T1-T5
-synapse in superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglia
-post-ganglionic fibers to cardiac plexus
-results = stimulation --> speeds the heart
on exam!!
a. sympathetics
b. parasympathetics
b.
(sympathetics/parasympathetics) to the heart:
-pre-ganglionic neurons = CN X nuclei in medulla
-synapse in wristberg's ganglia
-post-ganglionic fibers to SA and AV nodes
-results = stimulation --> slows the heart
on exam!!
a. sympathetics
b. parasympathetics
e.
What is the anterior chapman point for the heart?
a. 3rd ICS near sternum
b. 4th ICS near sternum
c. T2 and T3 inferior facet
d. T4 inferior facet
e. 2nd ICS near sternum
e.
What is the posterior chapman point for the heart?
a. 3rd ICS near sternum
b. 4th ICS near sternum
c. T2 and T3 inferior facet
d. T4 inferior facet
e. T3 superior facet
a.
What character of CP:
-retrosternal
-pressing
-discomfort
-1-3 min
-aggravated w/ exertion
-relieved w/ rest or nitroglycerin
a. angina
b. pericarditis
c. dissecting aortic aneurysm
d. tracheobronchitis
e. pleuritic pain
f. GERD
b.
What character of CP:
-precordial
-sharp
-severe
-persistent
-aggravated w/ breathing, lying down
-relieved w/ sitting up and leaning forward
a. angina
b. pericarditis
c. dissecting aortic aneurysm
d. tracheobronchitis
e. pleuritic pain
f. GERD
c.
What character of CP:
-anterior, radiates to back
-ripping/tearing
-very severe
-sudden onset
-aggravated w/ HTN
a. angina
b. pericarditis
c. dissecting aortic aneurysm
d. tracheobronchitis
e. pleuritic pain
f. GERD
d.
What character of CP:
-sternum and beside
-burning
-mild-to-moderate
-aggravated w/ cough
-relieved w/ lying on side
a. angina
b. pericarditis
c. dissecting aortic aneurysm
d. tracheobronchitis
e. pleuritic pain
f. GERD
e.
What character of CP:
-chest wall oveerlying area
-sharp, knife-like
-severe
-persistent
-aggravated w/ inspiration, motion of trunk, coughing
-relieved w/ not moving
a. angina
b. pericarditis
c. dissecting aortic aneurysm
d. tracheobronchitis
e. pleuritic pain
f. GERD
f.
What character of CP:
-retrosternal, can radiate to back
-burning, squeezing
-mild-to-severe
-aggravated w/ large meal, bending, lying down
-relieved w/ antacids, belching
a. angina
b. pericarditis
c. dissecting aortic aneurysm
d. tracheobronchitis
e. pleuritic pain
f. GERD
EKG
what is the first step in assessing CAD risk?
a.
(inhaled/exhaled) rib SDs:
-ribs move easily into inhalation, do not move well with exhalation
-Pump handle ribs will rise up, but not move down so well, or will remain up while other side moves downward
-Bucket handle ribs will move laterally then, drag when it is time to move medially with exhalation, or an asymmetry in motion, left to right
a. inhaled
b. exhaled
b.
(inhaled/exhaled) rib SDs:
-ribs do not move well with inhalation, and move easily with exhalation
-Pump handle ribs remain down instead of moving cephalad with breathing in, or one side may remain down, as the other rises with inhalation.
-Bucket handle ribs do not move laterally with inhalation, or one side moves lateral and medial, while the other side just moves medial with exhalation
a. inhaled
b. exhaled