Globular Proteins Fibrous Proteins Post-translational modifications of proteins (Lec 5)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Antibodies: Immunoglobulin G
Structure is amino terminals, the carboxy terminal, and dissulfide brides
antibodies are important because they are a part of our immune system
the dissulfide bonds holds the heavy and light chains together
hinge regions allow for the protein to be flexible to move the arm chains around and angle the protein to allow for binding with antigen
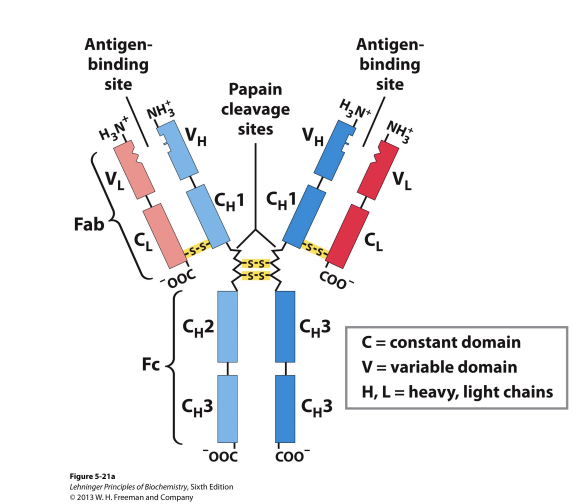
Antibodies are composed of two heavy chains & two light chains
both are binded to the antigen (the molecule the the body recognizes)
In the antigen binding side there is an epitope
the function of the anitbody’s variable regions is to recognize epitodes in an antigen
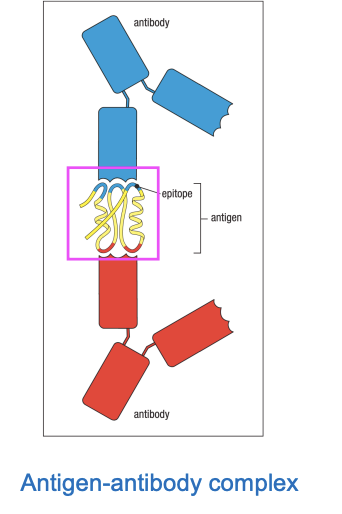
Antibodies are used in a lot of biochemical analysis
Hinge region: allows rotation around the polupeptide so that the molecule can bind to the antigen
it purpose is basically flexbibility
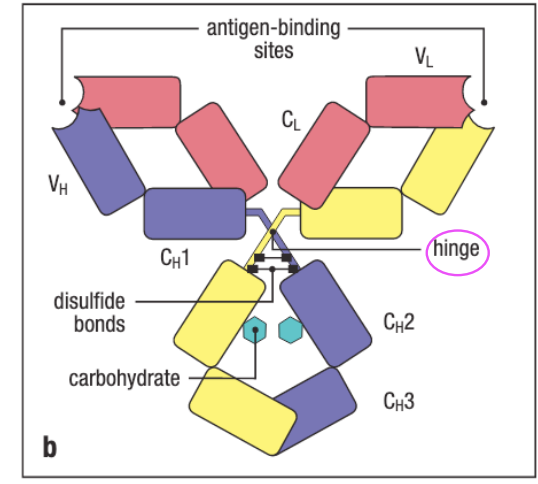
Noncovalent interacitons btwn an antibody and its antigen
All are govern by the non covalent interactions (electrostatic forces, H bonds, ven der waals forces, hydrophobic forces, calton-pi interaciton)
the noncovalent interactions govern the interactions betwen an antibody and its antigen
The peptide bond formation is only covalent
Funciton of antibodies
Neutralization: prevents their ability to infect cells ( blocking )
Opsonization: the antibody Fc regions binds to Fc receptors to help cells ingest & kill pathogens
Complement activation: antibodies trigger complement by activating C1
The main goal of the antibody in humans is to act as a messenger molecule to the immune system to actifivate the imune system
al the activation of the imune system can over activate and the antibody can attect our own tisses —> which can result in immune issues
Fibrous Proteins: from structure to function
B conformation —> Soft, fexible filaments
Ahelix cross linked by dissulfide bonds —> tough insoluble protective structures with varying hardness & flexbility
Collagen triple helix —> high tensile strneght w/o stretch
Collagen
It is the most abundant protein in humans
it provides structural support to extracellualr space of conenctive tissues
very rigid and resistant to stretching (perfect matrix for skeletal)
It is made up of fibrous proteins
Synthesis of collagen
Translation and posttranslation modification (PTM)causes collagen synthesis
PTM is esential for folding, asseemble & the structural integraty & funciton of the final collagen moelcule
Single pepetide chais become aggregated or assembled
The unique AA compositon of collagen
Collagen is a polymer of Gly-X-Y repeating where Y is frequently hydroxylysine or hydroxyproline and x is any other AA in colagen
glycine is chosen because it is so small so it can fit into the rope like sturcture (because glycine is only H side chain)
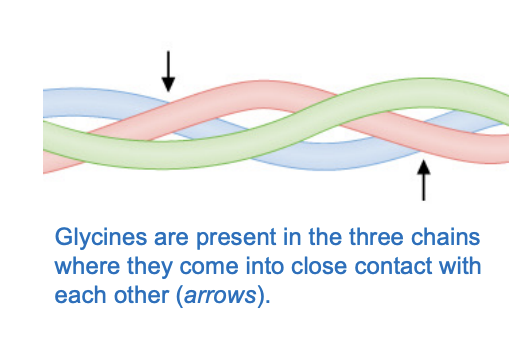
Triple-stranded helix of collagen shows the significance of glycine
Triple-stranded helix of coallgen
It is a rigid structure, and they are intertwined
the whole polpeptide chaine is Gly-X-Y
three polypeotides (collagen a chains) are wound around one another in a rope-like triple helix
Fibrous protiens: from strucutr to fucntion
Collagen —> made. up of fibrous proteins
Collagen composition
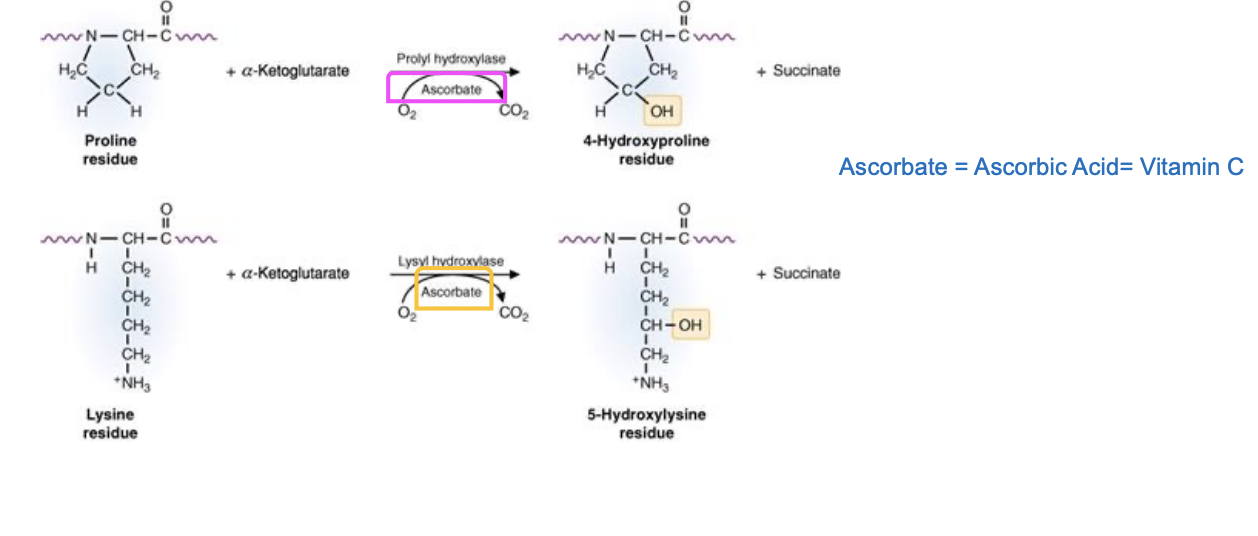
rich in proline and Glycine (Gly-X-Y) (the Y can be hydroxy proline or hydroxy lysine and X is any another AA)
hydroxy proline: invovles h bond formation that stabalizes the triple helix
hydroxy lysine: the attachment sites of disaccharide moieties (galactose-glucose)
OH groups are important for h bonding between the peptide chain
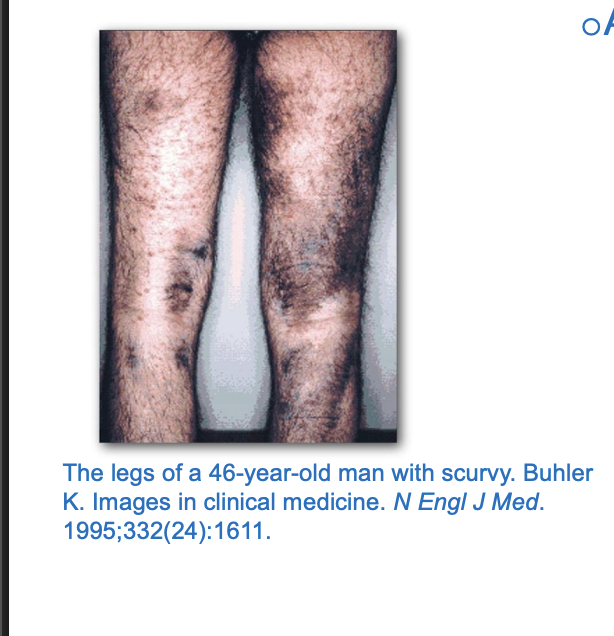
Scurvy
Occurs due to the lack of vitamin C
lack of vitamin c —> hdyroxylation is imapcted —> leads to weak colalgen formation
loss of inter-strand hydrogen bond formaiton
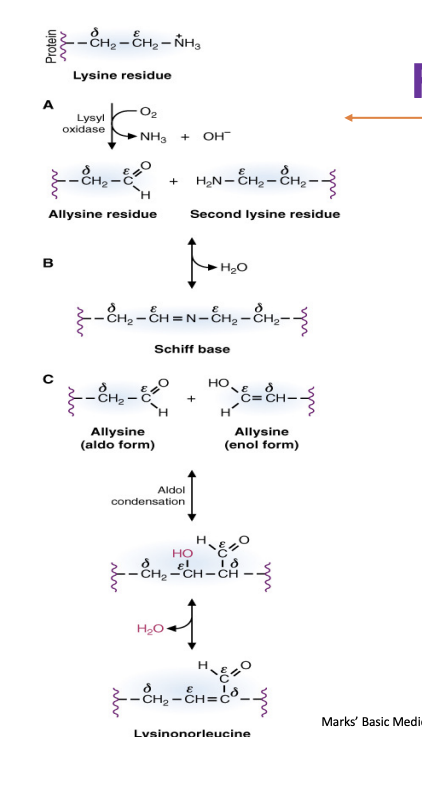
Formation of crosslinks of colalgen
when the side chains of lysine are oxideized to form an aldehyde
two aldehyde groups can attach with one another via aldol condensation and forms the lysinorleucine
the aldehydes are also two moieties —> forms a covalent bond