Hu T cell Lectures
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:43 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
T cell maturation site
•Thymus is the major organ for T cell maturation
•Thymus provides the environment and stimulating signals for T cell proliferation and maturation
•The majority of thymocytes differentiate to alpha beta T cells; very few differentiate into gamma theta cells
•Thymus provides the environment and stimulating signals for T cell proliferation and maturation
•The majority of thymocytes differentiate to alpha beta T cells; very few differentiate into gamma theta cells
2
New cards
Double negative cells
no CD4 or CD8
3
New cards
Double positive cells
both CD4 &CD8
4
New cards
T cell maturation Process
1)Progenitor T cells
→ Double negative
→Rearrangement of TCRbeta chain
\
2)Pre T-cells
→Double positive
\
3)Immature T cells
→Rearrangement of TCRalpha chain
\
4)Mature T cells
\
→Single positive
→ Double negative
→Rearrangement of TCRbeta chain
\
2)Pre T-cells
→Double positive
\
3)Immature T cells
→Rearrangement of TCRalpha chain
\
4)Mature T cells
\
→Single positive
5
New cards
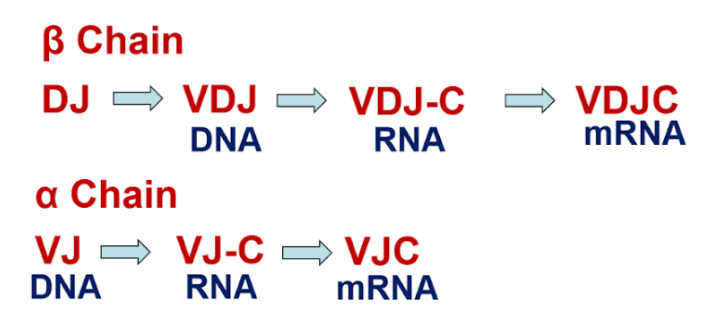
TCR (T cell receptor) rearrangement
1) alpha chain: V,J
2) Beta chain: V,D,J
\
VDJ= variability, diversity and joining
\
•Beta chain occurs first
\
•alpha chain occurs second
2) Beta chain: V,D,J
\
VDJ= variability, diversity and joining
\
•Beta chain occurs first
\
•alpha chain occurs second
6
New cards
Thymus selection
negative and positive selection
7
New cards
Positive selection
MHC restriction (CD4 or CD8)
MHCI: CD8+
MHC II: CD4+
MHCI: CD8+
MHC II: CD4+
8
New cards
Negative selection
when moderate degree of binding leads to positive selection, TCRs that bind **too strongly** are destined to cell death, thereby eradicating immature t cell that have high likelihood of attacking our own cells
9
New cards
Alpha beta T cell and Gamma Theta T cell
•TCR difference
•In vivo distribution, antigen recognition, CD4/8 expression diversity
•Alpha beta T cell for adaptive immune response
• Gamma theta T cell for innate immune response
•In vivo distribution, antigen recognition, CD4/8 expression diversity
•Alpha beta T cell for adaptive immune response
• Gamma theta T cell for innate immune response
10
New cards
CD4+ T Cell & CD8 T cell
•mature alpha beta T cells only express CD4 or CD8
•Other cell phenotypes can also express CD4 or CD8
•CD4+ T cells will differentiate to T helper cells and T regulatory cells after antigen recognition
•CD8+ T cells will differentiate to cytotoxic T cells
•Other cell phenotypes can also express CD4 or CD8
•CD4+ T cells will differentiate to T helper cells and T regulatory cells after antigen recognition
•CD8+ T cells will differentiate to cytotoxic T cells
11
New cards
Naive T cell
•G0 cycle, short life span
•No interaction with antigen
•Express CD45RA and high level L selectin, re circulate in the lymphatic systems
•Function: Recignize antigen
•After antigen presenting cells stimulation, it can differentiate to effector t cells and memory t cells
•No interaction with antigen
•Express CD45RA and high level L selectin, re circulate in the lymphatic systems
•Function: Recignize antigen
•After antigen presenting cells stimulation, it can differentiate to effector t cells and memory t cells
12
New cards
Effector t cells
•G1 cycle, short life span
•Express high level IL2 receptors
•Come from Naive t cell or t memory vells after antigen restimulation
•Differentiate to Th cells, Treg cells, or CTL (CD8+ T)
•Express integrin proteins and adhesion molecules to migrate to infection/inflammation site
•Express high level IL2 receptors
•Come from Naive t cell or t memory vells after antigen restimulation
•Differentiate to Th cells, Treg cells, or CTL (CD8+ T)
•Express integrin proteins and adhesion molecules to migrate to infection/inflammation site
13
New cards
Memory t cells
•G0 cycle, extremely long life span of years
•Re stimulated by the same antigen
•Express high level IL2 receptors
**•Differentiation into effector t cells and memory t cells**
•Express integrin proteins and adhesion molecules to migrate to infection/inflammation site
•Re stimulated by the same antigen
•Express high level IL2 receptors
**•Differentiation into effector t cells and memory t cells**
•Express integrin proteins and adhesion molecules to migrate to infection/inflammation site
14
New cards
T helper cell
•Results from CD4+ cell differentiation
•Th1, Th2, Th17
•Th1 for cell immunity, Th2 for humoral immunity
•Th17: express IL17 for immune response
•Th1, Th2, Th17
•Th1 for cell immunity, Th2 for humoral immunity
•Th17: express IL17 for immune response
15
New cards
T regulatory cells
•Highly express CD25 and Foxp3
•Negatively regulate immune activation for self tolerance
•Negatively regulate immune activation for self tolerance
16
New cards
Cytotoxic T cells
•Resulted from CD8+ cell differentiation
•Th1, Th2, Th17 helper cells facilitate CTL’s proliferation and differentiation
•Kill the infected cells or tumor cells through direct contact
•In very few cases, cytotoxic t cells could be CD4+ effector t cells
•Th1, Th2, Th17 helper cells facilitate CTL’s proliferation and differentiation
•Kill the infected cells or tumor cells through direct contact
•In very few cases, cytotoxic t cells could be CD4+ effector t cells
17
New cards
Two signals requirement in T cell activation
\
1. TCR-(Antigen-MHC complex)
2. Adhesion molecules→ enhanced adhesion, immunological synapses
1. TCR-(Antigen-MHC complex)
2. Adhesion molecules→ enhanced adhesion, immunological synapses
18
New cards
CD8+ T cell: killing mechanism
\
•Conjugate Formation
•Membrane attack
•Dissociation
•Target cell death
•Conjugate Formation
•Membrane attack
•Dissociation
•Target cell death
19
New cards
Conjugate Formation
→Cell adhesion
→Recognition of MHC I antigen peptide on target cells
→Recognition of MHC I antigen peptide on target cells
20
New cards
Membrane attack
→Granules in cytotoxic CD8+ T cells; perforin, granzymes
→Exocytosis of granule contents
Perforin action: pore forming
Granzymes act as nucleases (apoptosis)
→Fas ligand to Fas triggers target cell death (mediated by caspase)
→Exocytosis of granule contents
Perforin action: pore forming
Granzymes act as nucleases (apoptosis)
→Fas ligand to Fas triggers target cell death (mediated by caspase)
21
New cards
Dissociation
→Cytotoxic Cd8+ cells interact for about five minutes
→Dissociates and can conjugate with other target cells
→Dissociates and can conjugate with other target cells
22
New cards
TCR T Cells
•T cell receptor
\
•Requires MHC matching
\
•require 1 antigen on target
\
•Requires MHC matching
\
•require 1 antigen on target
23
New cards
CAR T Cells
•Chimeric Antigen receptors
•Single fusion molecule with antigen specificity plus signaling domain
They are made by collecting T cells from the patient and re-engineering them in the laboratory to produce proteins on their surface called chimeric antigen receptors, or CARs. The CARs recognize and bind to specific proteins, or antigens, on the surface of cancer cel
\n
•MHC independent
•Require 100 antigen on target
\n \n
Advantages:
•Live drug
•Tumor recognition independent of antigen presentation
•Multiple selection on antigen
•design flexibility
•Single fusion molecule with antigen specificity plus signaling domain
They are made by collecting T cells from the patient and re-engineering them in the laboratory to produce proteins on their surface called chimeric antigen receptors, or CARs. The CARs recognize and bind to specific proteins, or antigens, on the surface of cancer cel
\n
•MHC independent
•Require 100 antigen on target
\n \n
Advantages:
•Live drug
•Tumor recognition independent of antigen presentation
•Multiple selection on antigen
•design flexibility
24
New cards
CD19/CD20 CAR-T cells for liquid cancer treatment
25
New cards
\
CAR-T cells for liquid cancer side effects
CAR-T cells for liquid cancer side effects
•Cytokine release syndrome- Fever, myalgia, headache, anorexia, nausea, vomiting
•Graft- versus-host disease- Rash, diarrheam, hyperbilirubinemia
•Neurologic symptoms- confusion, Bcell aphasia, unresponsiveness, seizures
•Tumor lysis syndrome- hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, hperuricemia
•Graft- versus-host disease- Rash, diarrheam, hyperbilirubinemia
•Neurologic symptoms- confusion, Bcell aphasia, unresponsiveness, seizures
•Tumor lysis syndrome- hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, hperuricemia
26
New cards
barriers for using CAR-T cells to treat solid tumors
•Immunosupressive pathways
•Physical barriers
•Metabolic restriction
•Immunosuppresive microenvironment
•Physical barriers
•Metabolic restriction
•Immunosuppresive microenvironment
27
New cards
Immunosuppressive cells
•Th17
•Treg
•TAM: tumor associated macrophage
•DCreg: regulatory dendritic cells
•TAN: Tumor associated neutrophil
•Treg
•TAM: tumor associated macrophage
•DCreg: regulatory dendritic cells
•TAN: Tumor associated neutrophil
28
New cards
29
New cards
30
New cards