HmEc- Lipids
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Elemental composition of lipids
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Chemical structure of lipids
triglycerides CH3(CH2)nCOOH
Triglyceride composition
one glycerol molecule with three fatty acid molecules

What is this?
Triglyceride moelcule
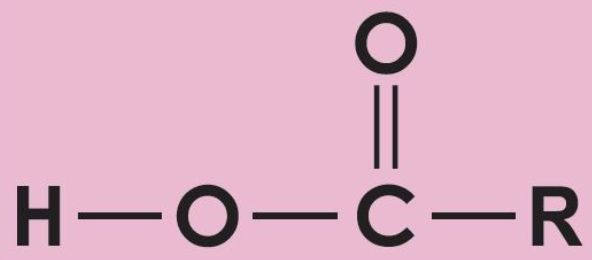
What is this?
Fatty acid moleule
How is a triglyceride made?
When a glycerol molecule joins three fatty acids, resulting in the loss of three water molecules
Classification of lipids
Saturated fatty acids, mono-unsaturated fatty acids, poly-unsaturated fatty acids
Carbon quota saturated fatty acids
each carbons has full quota of hydrogen atoms
Carbon bonding in saturated fatty acids
no double bonds between carbon atoms
Saturated fatty acids state at room temperature
solid
Carbon quota mono-unsaturated fatty acids
not all carbons saturated with hydrogen
Mono-unsaturated fatty acids state at room temperature
soft
Carbon bonding of mono-unsaturated fatty acids
one double bonds between carbon atoms
Carbon quota poly-unsaturated fatty acids
not all carbons saturated with hydrogen
Carbon bonding of poly-unsaturated fatty acids
more than one double bond between carbons
Poly-unsaturated fatty acids state at room temperature
soft/liquid
Sources of saturated fatty acids
animal
Sources of mono-unsaturated fatty acids
plant/fish
Sources of poly-unsaturated fatty acids
plant/fish
melting point of saturated fatty acids
high
melting point of monosaturated fatty acids
low
melting point of polyunsaturated fatty acids
lowest of all acids
example of saturated fatty acid
butyric acid in butter
example of mono-unsaturated fatty acid
oleic acid in olive oil
example of poly-unsaturated acid
linoleic acid in nuts
Distributions of types of fats in butter
52% saturated, 21% mono-unsaturated, 3% polyunsaturated
Distribution of types of fats in olive oil
14% saturated, 73% mono-unsaturated, 8% polyunsaturated
Distributions of types of fats in block margarine
26% saturated, 34% mono-unsaturated, 12% polyunsaturated
Sources of essential fatty acids
nuts, seeds, olive oil, oily fish
Biological functions of essential fatty acids
aids cell membrane formation, reduced CHD by raising high density lipoprotein
What does high density lipoprotein do?
removed cholesterol from the blood and lowers low density lipoprotein
Examples of essential fatty acids
Linoleic, linolenic and arachidonic acids
Sources of omega-3 acids
oily fish
Functions of omega-3 acid
lower blood fat levels and aids foetal brain development
Two types of omega-3 acids
Eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic
Chemical structure of omega-3 acids
double bond between third and fourth carbons
Cis-fatty acids
mono and polyunsaturated fats when hydrogen atoms on either side of double bond are both above or below hydrocarbon chain
Trans-fatty acids
mono and polyunsaturated fats when the hydrogens either side of the double bond are on opposite sides of hydrocarbon chain
Source of cis-fatty acids
sunflower oil
Source of trans-fatty acids
margarine
Properties of lipids
Solubility, Absorption, Heating, Emulsions, Emulsifiers, Hydrogen, Rancidity, Plasticity
Solubility of lipids
insoluble in water but soluble in solvents such as ether and benzene
Plasticity of lipids
solid, liquid or spreadable, determined by degree of unsaturation: fewer unsaturated fatty acids=more solid
Hydrogenation of lipids
hydrogen pumped through liquid unsaturated fat, converts to solid saturated fat, double bonds split and absorb hydrogen
What is hydrogenation used to make
margarine
Lipids absorption of flavours
readily absorb flavours, keep covered
Melting point of fat
30-40 degrees
Smoke point of oil
250 degrees
smoke point of fat
200 degrees
What happens if lipids are overheated
glycerol seperates from fatty acids and turns to acrolein, makes blue haze or smoke and smells
What is a flash point
when extreme overheating causes vapour to spontaneously ignite
Flash point for oils
325 degrees
Flash point for fats
310 degrees
What is an emulsion
colloidal solution with two immiscible solutions forced to mix together
types of emulsions
temporary or permanent
Emulsifier definition
molecule with hydrophillic head and hydrophobic tail
How does an emulsifier form a permanent emulsion
head attaches to water and tail attaches to oil, eg lecithin in mayonnaise
Stabiliser defintion
long chained molecules used to maintain emulsion and separate oil droplets to prevent coalescing, eg gums in yoghurt
Rancidity definition
the spoilage of foods
Two types of rancidity
oxidative and hydrolytic
How does oxidative rancidity occur?
oxygen combines with carbon atom in double bond, bad smell, aided by light
How does hydrolytic rancidity occur?
enzymes and bacteria hydrolyse lipids and change them to fatty acid and glycerol, bad smell and taste, can happen in freezer
How to prevent rancidity
store in cool, dark place, wrap well, add antioxidants in production
Function of antioxidants
prevent oxidative rancidity by attaching to oxygen so its unable to bond
antioxidative vitamins
A,C,E
What does antioxidant BHT stand for
Butylated Hydroxytoluene
What does antioxidant BHA stand for?
Butylated Hydroxyanisole
Biological function of lipids
heat and energy
excess stored as adipose
protect vital organs
provide fat-soluble vitamins
provide essential fatty acids
delay hunger
help lower cholesterol
RDA of lipids
max 70g/day, max 30g saturated fat for men and 20g saturated fat for women
Energy value of lipids
1g=9kcal/37kj
Associated dietary disorders of lipids
obesity, CHD, high cholesterol, strokes
Digestion of lipids in mouth
food chewed into smaller pieces
Digestion of lipids in stomach
heat melts fat
Digestion of lipids in liver
bile in duodenum emulsifies large fat molecules into smaller ones
Digestion of fat in the pancreas
pancreatic juice in duodenum contains lipase to break lipids into fatty acid and glycerol
Digestion in small intestine
ileum secretes lipase
Absorption of lipids
pass through wall of villi into lacteals in lymphatic system, onto thoracic duct into bloodstream through subclavian vein
Where is the subclavian vein?
left side of neck
Digestion of lipids
subclavian vein transfers fatty acid and glycerol to liver, then oxidised for functions, excess stored as adipose tissue under skin
How to reduce fat intake
reduce saturated fats
choose low-fat dairy
choose lean red meat and skinless chicken
increase oily fish
grill and steam, no fry
choose fruit snacks