Chapter 9 Quiz: molecular structure of chromosomes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
If Type IIR cells are mixed with DNA from heat-killed IIIS cells and serum that precipitates IIR cells from the mixture, what else must be added to prevent colonies from growing?
DNase
RNA’s
Protease
DNase
What is DNase?
Short for Deoxyribonuclease. This is an enzyme that breaks down DNA by catalyzing the hydrolysis of phosphodiester linkages in the DNA backbone, thus degrading DNA
In the T2 phage, it was demonstrated that DNA is the genetic material. How was this experiment done?
A. X-ray diffraction
B. Mixing T2 with E. Coli and looking for phenotypic changes
C. Labeling T2 phage with radioactivity and determine which molecule was injected into the host cells
D. Analyzing T2 and determining the rate of spontaneous mutation
Labeling T2 phage with radioactivity and determining which molecule was injected into the host cells (DNA was found to be the genetic material so it attacked DNA!!)
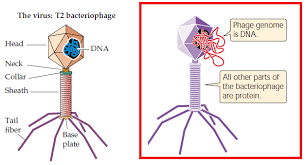
What is T2 phage?
Enterobacteria phage T2 is a virus that infects and kills E. Coli. Its genome consists of linear double-stranded DNA
What is a genome?
A genome is the complete set of DNA in an organism
What is a folded genome?
A. How DNA runs on a gel
B. the functional state of the bacterial genome
C. The DNA after isolation
D. A compact structure of the viral genome for packing into a phage head
The functional state of the bacterial genome
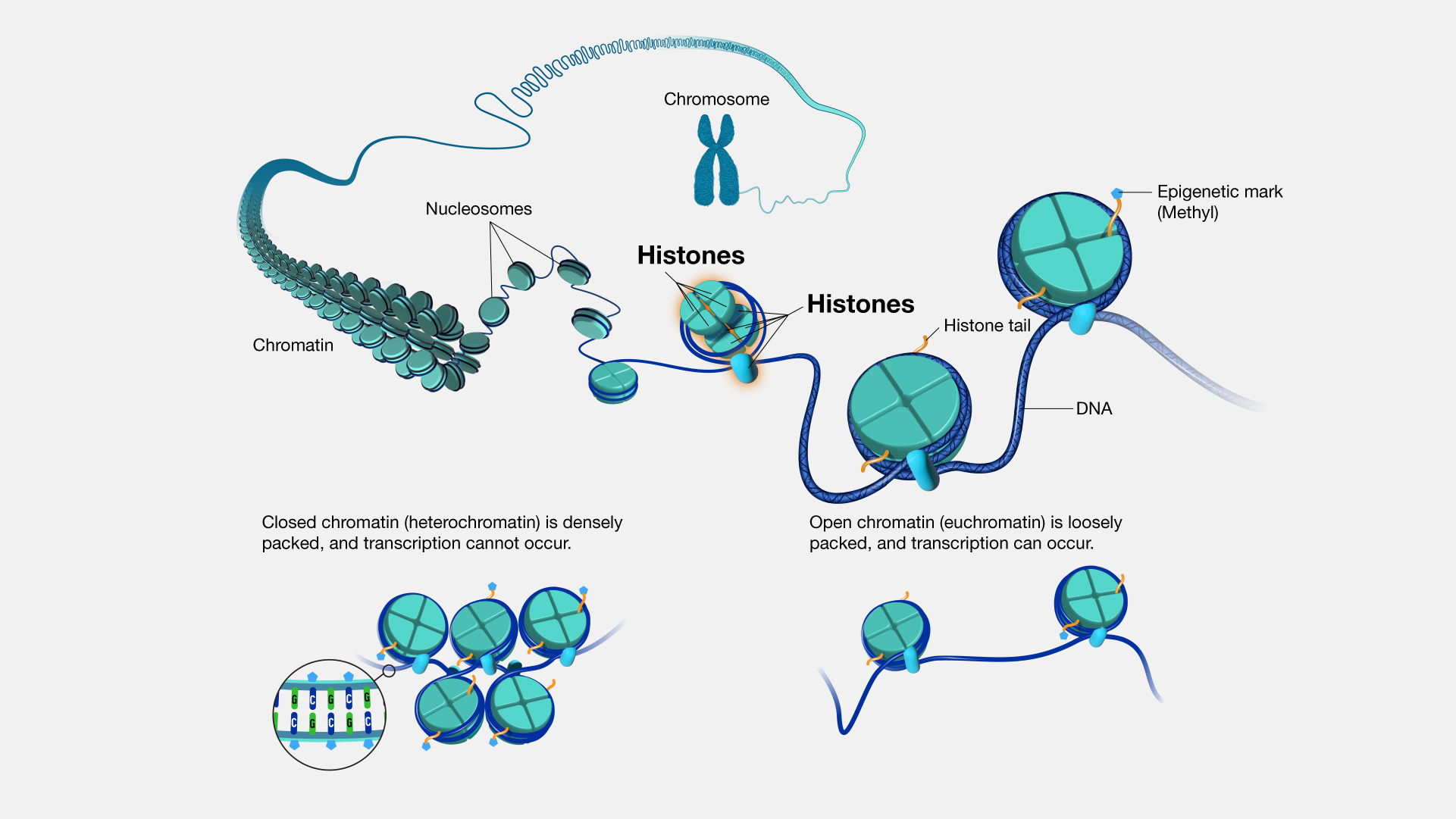
What is the function of the histone proteins in human chromosomes?
A. Form the chromatin
B. Compact the DNA into the nucleosomes
C. Compact the DNA into the folded genome
D. Supercool the DNA
Compact the DNA into the nucleosomes
Plays a key role in regulating gene expression by controlling DNA accessibility
Which of the following descriptions of the DNA double helix is accurate?
A. The F plasmid is transferred as a single stranded molecule
B. each chromosome is composed of four nucleotides
C. One double stranded helix per linear chromosome
D. More than one double stranded helix per linear chromosome
One double stranded helix per line are chromosome
What is the function of histone H1?
Stabilize the 10 nm fiber
Form the 30 nm fiber
What is satellite DNA?
A. Specific DNA sequences that are repeated many times
B. Intervening genes
C. Telomeres
D. Centromeres
Specific DNA sequences that are repeated many times
By labeling T2 phage with radioactive isotopes, Hershey and Chase were able to tell that DNA was the genetic material when ______ was found in the cells of test organisms
A. Labeled sulfur
B. Nothing
C. Labled phosphorus
D. Bacteriophage T2
Labeled phosphorous (DNA was tagged with a radioactive isotope)
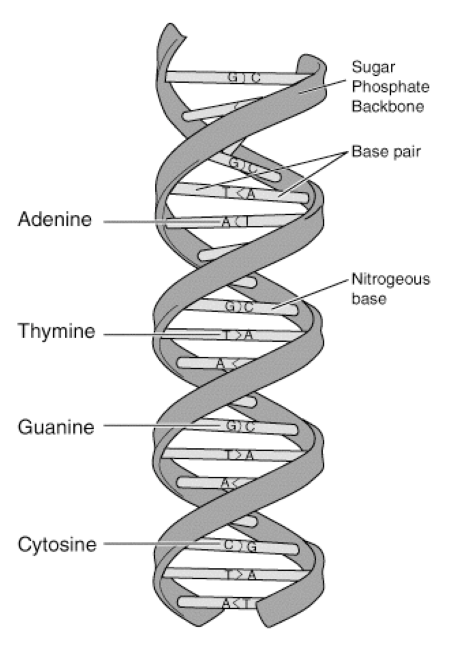
Which of the following is true about double stranded DNA?
A. 50% of the composition of DNA is C
B. 50% of the bases are purines
C. A+T=G+C
D. It is 25% of each A, T, G, and C
50% of the bases are purines
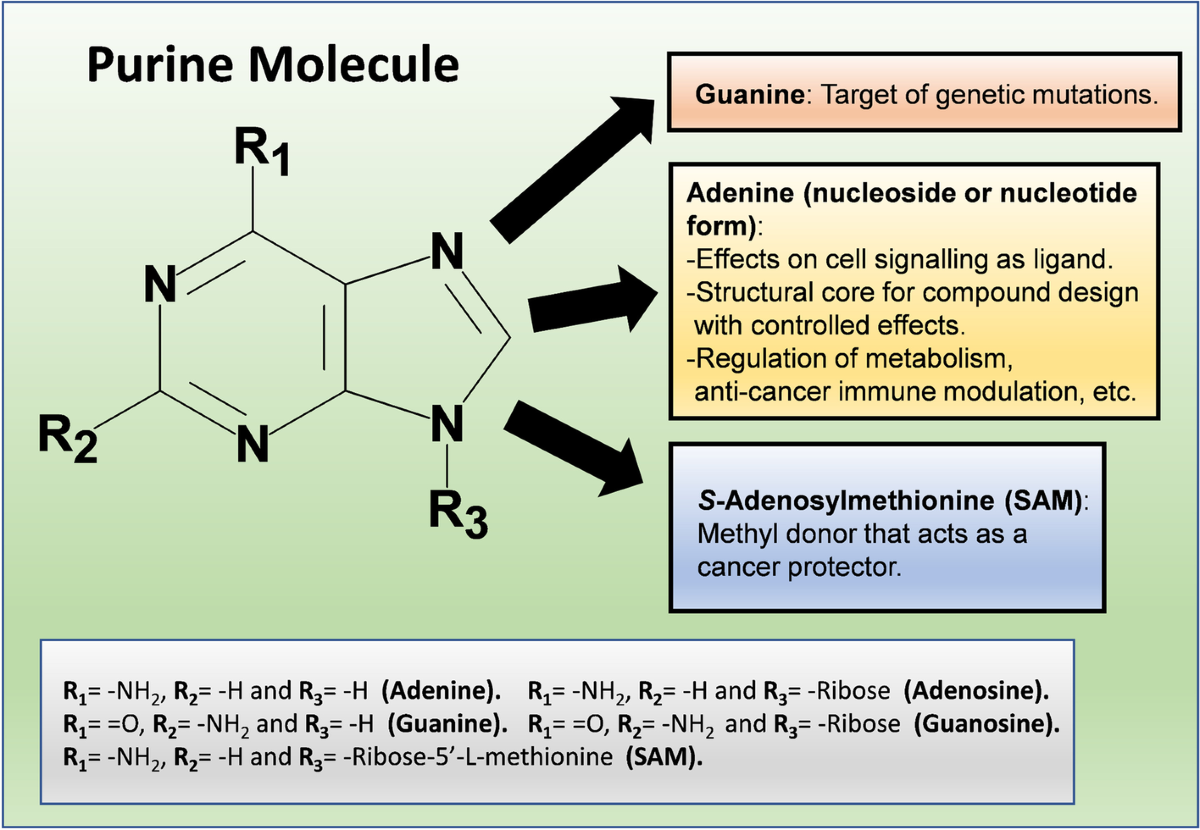
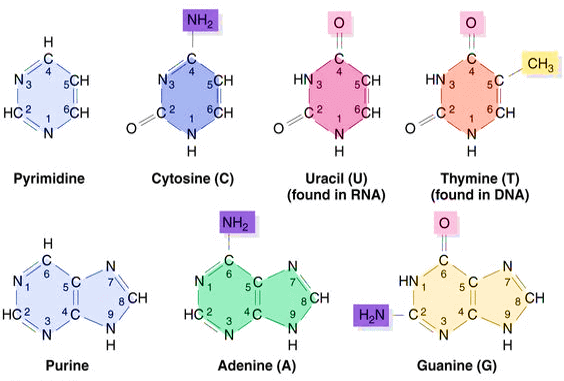
What are purines?
Purines are found in DNA that consist of adenine and guanine. These are the two types of purine bases that make up the building blocks of DNA along side pyrimidine bases, cytosine and thymine
What is the function of negative supercoiling bacteria?
To condense the bacterial genome so it will fit into the cell
How is it demonstrated that DNA is the “transforming principle”?
A. Treat extracts of type IIIS with different enzymes to look for loss of transforming factor
B. isolate and study chromosome structure
C. X-ray diffraction of DNA structure
D. Inject the mouse with two types of streptococcus cells and look for death
Treat extracts of type IIIS with different enzymes to look for loss of transforming factor
What is type IIIS?
Type IIS refers to “Type III Secretion System (T3SS)”. This allows certain gram-negative bacteria to inject proteins directly into host cells
Can manipulate the host’s cellular functions to promote infection
Bacteria uses a needle-like structure to “inject” harmful proteins into the host cell cytoplasm
What is gram negative bacteria?
This is bacteria that are enclosed in a protective capsule. This capsule helps prevent white blood cells (which fight infections) from ingesting the bacteria. Under the capsule, gram negative bacteria have an outer membrane that protects them against certain antibiotics, like penicillin
Who deduced that the structure of DNA is a double helix?
Watson, Crick, Wilkins, and Franklin
DNA in a double helix is antiparallel. What does antiparallel mean?
One strand runs in a 5’ to 3’ direction, and the other strand runs in a 3’ to 5’ direction
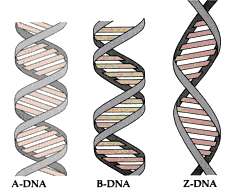
There are several alternative forms of double helical DNA. The B DNA form is:
A. The standard right-handed double helical structure
B. A left-handed structure
C. A DNA-RNA hybrid structure
D. Seen in partially dehydrated conditions
the standard right-handed helical structure
Purines have _______ and pyrimidines have _______
Double ring bases, single ring bases
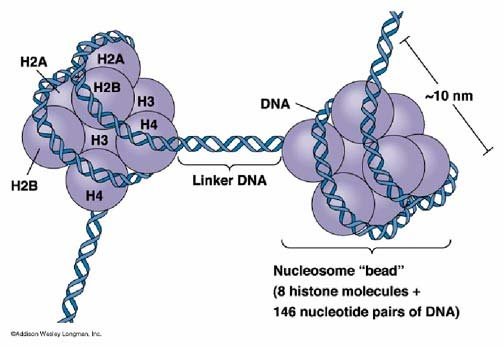
Each nucleosome:
A. Has 146 nucleotide pairs of DNA wrapped around the octamer of histones
B. Consist of the 30 nm fiber
C. Holds one negative supercool
D. Must use histone H1 for stabilization
Has 146 nucleotide pairs of DNA wrapped around the octomer of histones