The ULTIMATE MEDIA CARDS - edit using ai
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Curran and Seaton - Power and Media Industries (Media Industries)
Patterns of ownership and control are the most significant factors in how the media operate.
Media industries follow the normal capitalist pattern of increasing concentration of ownership in fewer and fewer hands - by structuring businesses through horizontal and vertical integration. This leads to a narrowing of the range of opinions represented and a pursuit of profit at the expense of quality or creativity.
The internet, in the grasp of big tech, has not provided the rich global platform and accessibility it promised for diverse voices to be heard. It is constrained by nationalism and state censorship. News is still controlled by powerful news organisations, who have political ideologies and agendas that influence the content of their publications.

Livingston and Lunt - Regulation (Media Industries)
The needs of a citizen are in conflict with the needs of the consumer, because protection can limit freedom. They noticed that regulating media to protect citizens from harmful content can limit freedom of expression There is an increasing tendency in recent UK regulation policy to place the interests of consumers above those of citizens. Traditional regulation is being put at risk by: increasingly globalised media industries, the rise of the digital media, and media convergence. Each culture tends to have its own views on elements such as nudity, sex and violence. This means products might have to be edited when published in other countries. Decisions as to what is considered 'harmful' are subjective and open to misinterpretation and abuses of power that threaten freedom of expression and access to information.

Baudrillard - Postmodernism (Media Language)
We are living in a hyperreal age where the lines between the real world and media are blurred, where we make media about media, and where the idea of a single definable truth is lost into a range of truths that you take your pick from.
These simulacra or hyperreal copies precede our lives, such that our television friends may seem more 'alive' to us than the real person playing that character.
Postmodern texts might include irony, parody, pastiche, homage, intertextuality, fragmented narratives.

Clay Shirky - End of Audience Theory (Audience)
The idea that the Internet and digital technologies have had a profound effect on the relations between media and individuals. Clay Shirky argued audience behaviour has progressed from the passive consumption of media texts to a much more interactive experience with the products and each other.
New digital technologies and social media has made connecting and collaborating incredibly easy. We want to like, follow, tweet, repost, cross-post, comment, review and subscribe. When we create our own content on our smartphones (user generated content) and share our thoughts with the world, the difference between producer and consumer (prosumer) becomes increasingly difficult to define. It is the end of audience.

Steve Neale - Genre Theory (Media Language)
Genre as Repetition and Difference: "Genre is familiar to audiences through the repetition of conventions like a physically strong, dynamic, violent, male hero in Action Adventure Video Games like Assassin's Creed but is challenged by the introduction of female lead characters in later releases. Audiences need to be able to instantly identify genre to engage with the text to fulfill the desired uses and gratifications however genres evolve over time to create new conventions eg horror films since Kiss of the Vampire

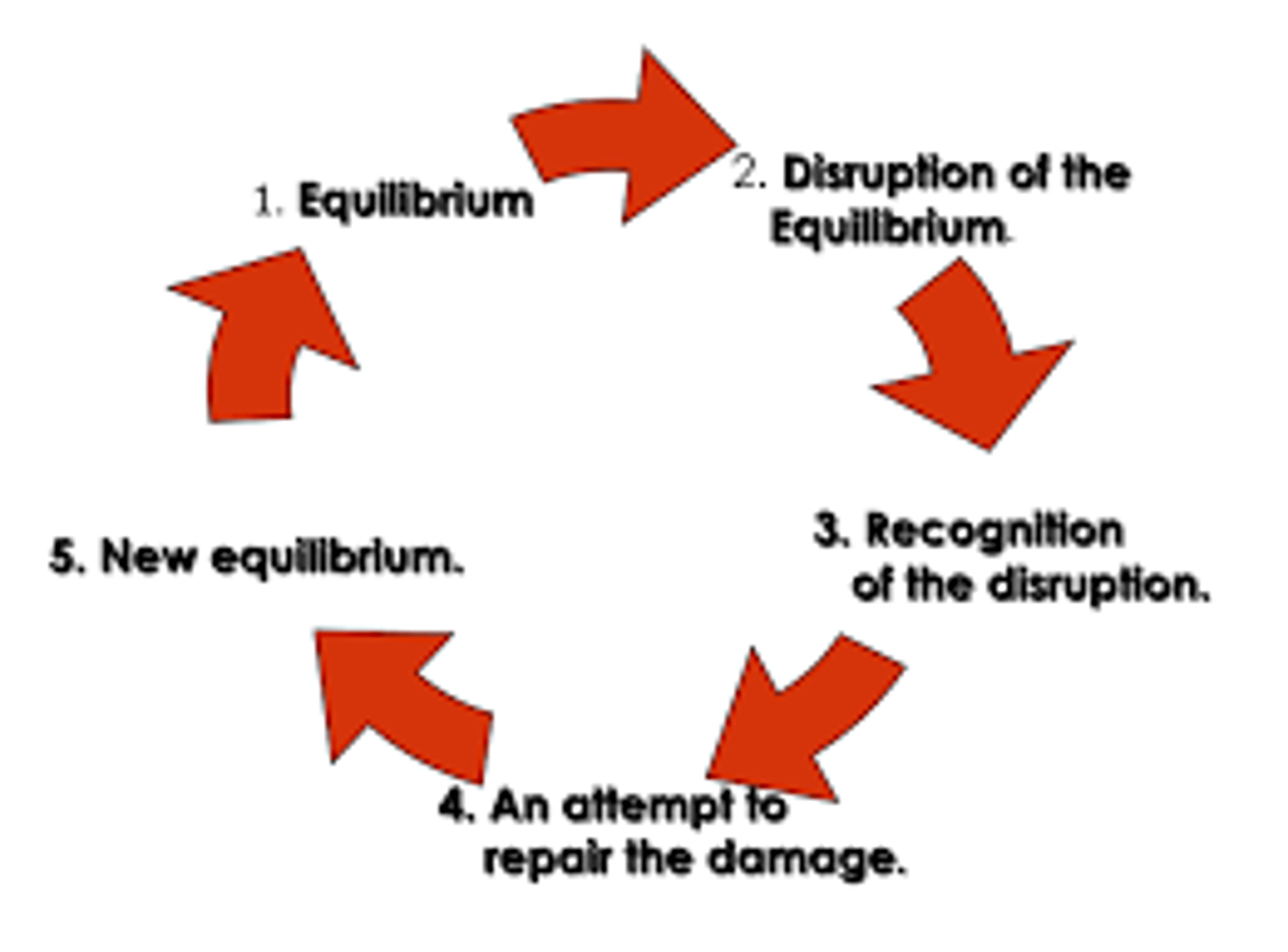
Todorov's Narrative Theory (Media Language)
Stories are structured like a wheel:
An ‘equilibrium’ where everything is ‘normal’
A problem occurs
The problem is recognised by the characters
The characters try to solve the problem
A new ‘equilibrium’ – there is normality again, but it might be a ‘new normal.
Albert Bandura: Social Learning Theory (Audience)
Bandura believes that the media can have a direct influence on the values and behaviour of audience members. The media can also have an indirect influence through social networks. He argues that audiences may imitate behaviours they see represented in the media (BoBo Doll Experiment)
This theory can be applied when considering moral panic created around violent media texts such as video games and the demand for stricter regulation.

Henry Jenkins: Fandom theory (Audience)
He believes that fans are active participants in the construction and circulation of textual meanings
He believes that fans take media texts, and sometimes interpret them / use them in ways which were not intended by the producers and he calls this 'textual poaching'.
He believes that fans construct their social and cultural identities by borrowing and adapting media texts / images and that this is a vital part of society. Fans create a participatory culture around a media text.
Although not Jenkin's theory, the idea of parasocial relationships can also be consider within Fandom Theory as fans believe that they are interacting with the star and have a two-way relationship with them. eg 'Swifties' - the fans of Taylor Swift or followers of Zoella.
What is semiotics in media language?
Semiotics is the study of how texts are constructed through signs, which consist of denotations and connotations.
What are denotations and connotations in semiotics?
Denotations are the literal meanings of signs, while connotations are the metaphorical meanings or myths associated with them.
How do media texts communicate messages?
Media texts combine signs to create codes that quickly communicate messages to audiences.
What role do codes play in media?
Codes are used repeatedly by media producers to create conventions for audiences to easily recognize genre, narrative, and form.
What does it mean for texts to be pluralistic?
Pluralistic texts can be interpreted in a range of ways, allowing multiple interpretations based on context.
What is polysemy in relation to codes?
Polysemy refers to codes having multiple meanings, requiring audiences to consider the context of the text and their own experiences.
What is the main idea of Levi-Strauss's structuralism in media language?
Meaning is created through the structure of society and its binary opposites.
How do media producers use binary opposition?
Media producers use binary opposition to quickly communicate messages, allowing audiences to categorize things like hero/villain and rich/poor.
What impact does binary opposition have on audience interpretation?
Binary opposition leads audiences to quickly judge and limits alternative interpretations of texts, restricting minority representations in the media.
What is Hall's Reception Theory?
Hall's Reception Theory posits that media producers encode values and ideologies into their media texts, which audiences then decode based on their own experiences and knowledge.
What are the three ways a text can be received according to Hall?
A text can be received in one of three ways: preferred reading, negotiated reading, or oppositional reading.
What factors influence how audiences decode media texts?
Audiences decode texts based on their own life experiences, cultural capital, and the socio-historical, economic, and cultural context of both the text and the audience.
What is representation in media according to Hall?
Representation is the process by which members of a culture use language to create meaning.
How does Hall describe the influence of mass media on identity?
Hall argues that the social and cultural construction of identity is highly influenced by mass media communication, linked to value and power structures within societies.
What impact do hegemonic producers have on media representation?
Hegemonic producers use reductive stereotypes of social groups to communicate preferred readings, potentially damaging the status of non-hegemonic social groups in society.
What does Gauntlett's theory suggest about audience behavior?
Gauntlett argues that audiences no longer passively consume a preferred reading of a text; instead, they actively construct their own identities from various media texts and societal influences.
How do identities function according to Gauntlett?
Identities are fluid and can change, although some elements, such as race, remain fixed. Audiences seek out shared identity elements for social connections.
What role does new media play in identity construction?
New media empowers audiences to become media producers, allowing them to create texts that reflect a diverse range of identities and gain control over their own representations.
What does Van Zoonen argue about the representation of women in media?
Van Zoonen argues that the media portray images of stereotypical women, reinforcing societal views and perpetuating patriarchal dominant values through male-produced texts.
How are women portrayed in media according to Van Zoonen?
Women are reductively represented in binary roles, such as housewife or femme fatale, compartmentalizing their identities and limiting their complexity.
What concept does Van Zoonen relate to the objectification of women's bodies?
Van Zoonen connects the objectification of women's bodies in media to the male gaze, as described by Mulvey, where women's bodies are presented to please men.
What does bell hooks argue about the intersectionality of oppression?
bell hooks argues that the fight against the patriarchy must address the prejudice of race and class, emphasizing that social classifications are interconnected.
How does bell hooks view women in terms of social classification?
bell hooks asserts that women should not be viewed as a homogenous social group, as their experiences are influenced by factors such as race, gender, sexual identity, and class.
What is the consequence of ignoring intersectionality according to bell hooks?
Ignoring intersectionality creates oppression towards women and alters their experiences of living as women in society.
What does Gilroy argue about the representation of non-hegemonic social groups in mainstream media?
Gilroy argues that non-hegemonic social groups are represented as 'Other', with racist ideologies of colonialism persisting in mainstream media narratives.
How do post-colonial structures affect society according to Gilroy?
Post-colonial structures and ideologies are intricately woven into the fabric of society and are consistently reinforced by media representations.
What is cultural appropriation and how does it affect minority cultures?
Cultural appropriation involves the adoption of traditions by the dominant culture, which undermines minority cultures and reinforces reductive stereotypes, such as with practices like wearing hair beads or mehndi.
What is Gerbner's Cultivation Theory?
Gerbner's Cultivation Theory suggests that over time, repeated exposure to media cultivates the belief that the messages conveyed by media apply to the real world, shaping audience perceptions, beliefs, values, and attitudes.
What is the Mean World Syndrome?
Mean World Syndrome refers to the phenomenon where violent depictions of society in media create a distorted perception of reality, leading audiences to believe the world is more dangerous than it actually is.
How do audiences perceive reality according to Gerbner's findings?
Audiences often believe that the reality they see on TV is a more accurate representation of the world than their own lived experiences.
What is the central idea of Butler's theory on gender performativity?
Butler's theory posits that gender is constructed through the performance of gendered acts, suggesting that gender is not an inherent quality but rather a series of behaviors and performances.
How do dominant representations influence gender according to Butler?
Dominant representations shape our understanding of gender by providing learned performances that individuals mimic, reinforcing societal norms around gender.
What role do conventional behaviors play in society's view of gender?
Conventional behaviors become societal norms, influencing expectations of how individuals should express their gender and perpetuating the performance of gender roles.
What factors contribute to high risk in the cultural industries?
Risk is high in the cultural industries due to the difficulty in predicting success, high production costs, low reproduction costs, and the nature of media products as 'public goods' that can be reproduced after consumption.
How do cultural industries minimize risk and maximize profits?
Cultural industries rely on 'big hits' to cover the costs of failures, using repetition through stars, genres, franchises, and repeatable narratives to sell formats to audiences.
What impact has the internet had on cultural production according to Hesmondhalgh?
While the internet has created powerful IT corporations, it has not transformed cultural production in a liberating way; instead, it has sped up work, commercialized leisure time, and increased surveillance by government and companies.