too much damn studying ch7 bones and all that
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
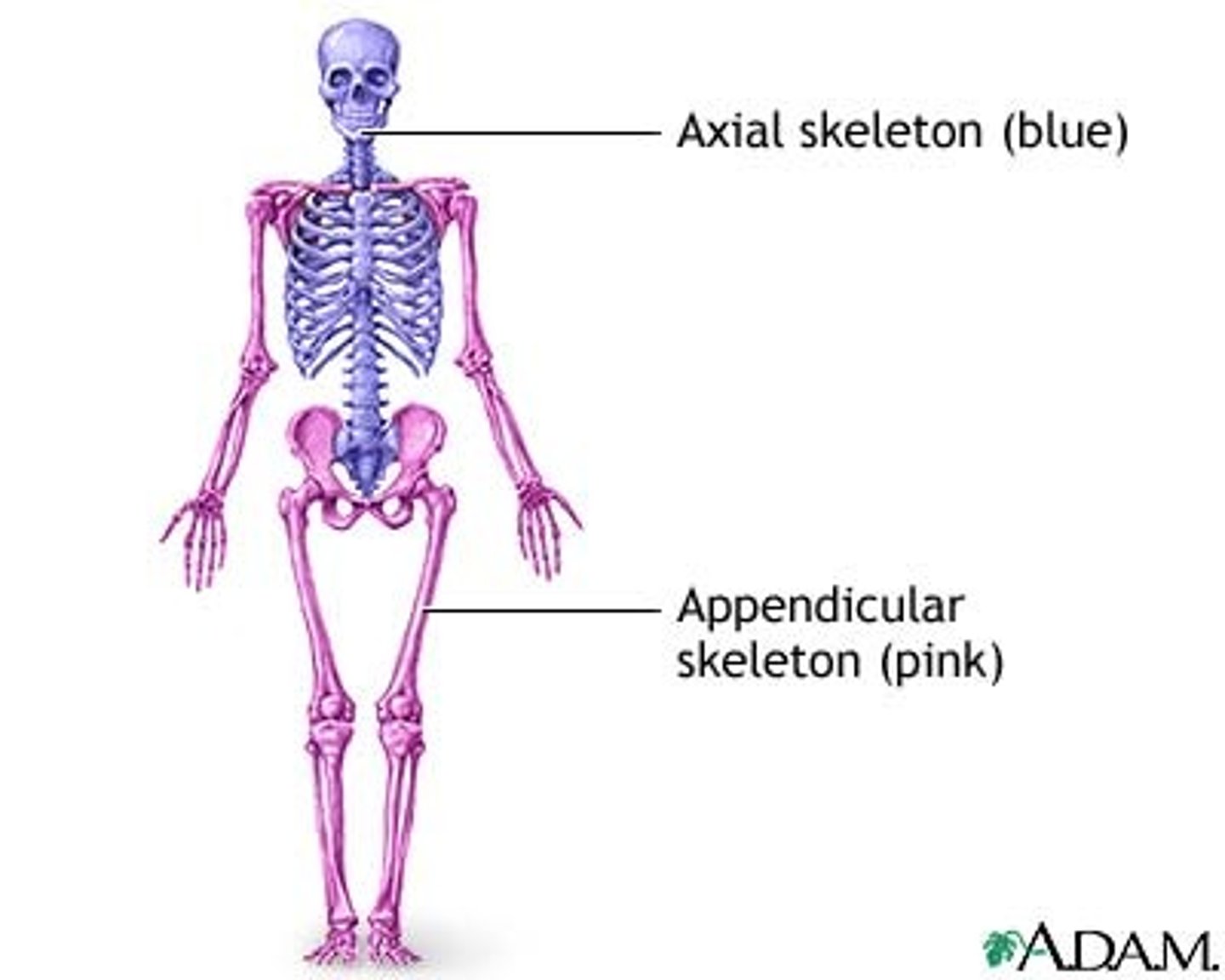
Axial Skeleton
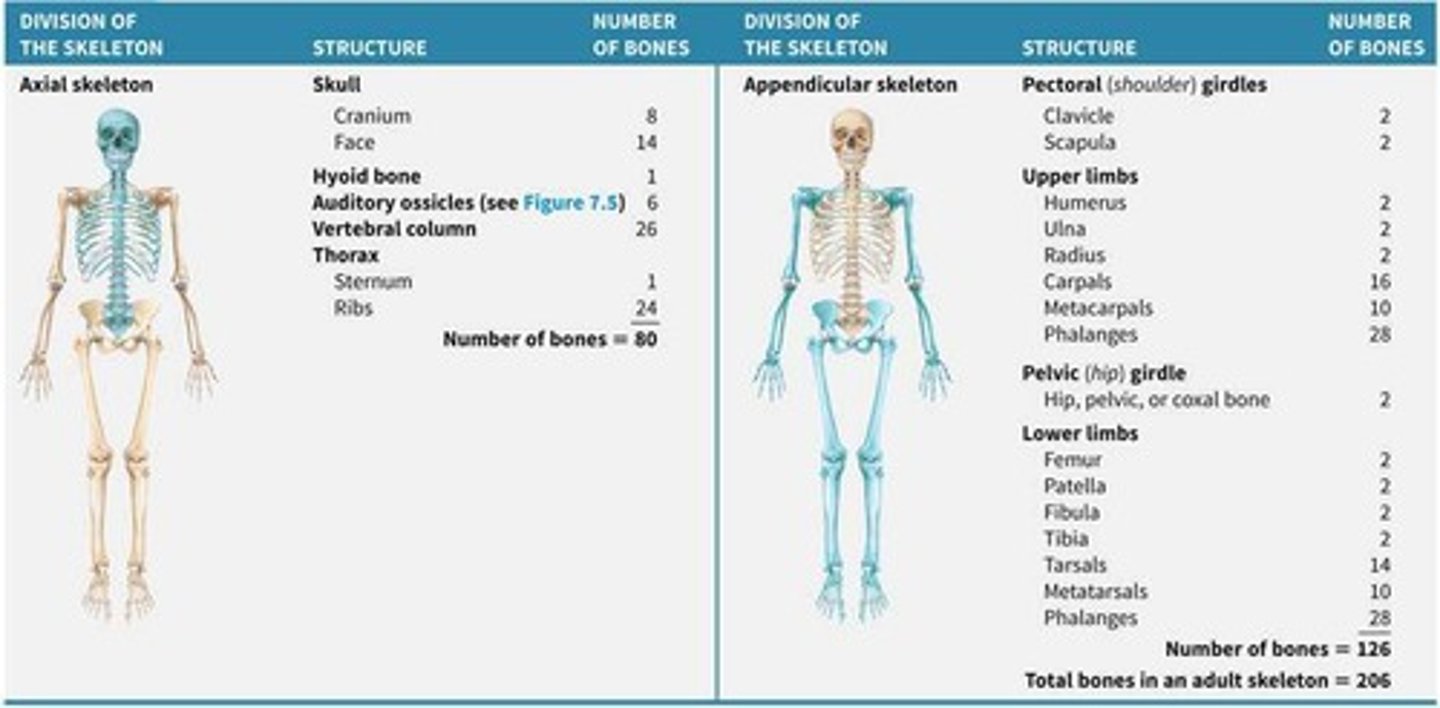
Central part of the skeleton, includes skull and vertebrae. 80 bones
skull
vertebral column
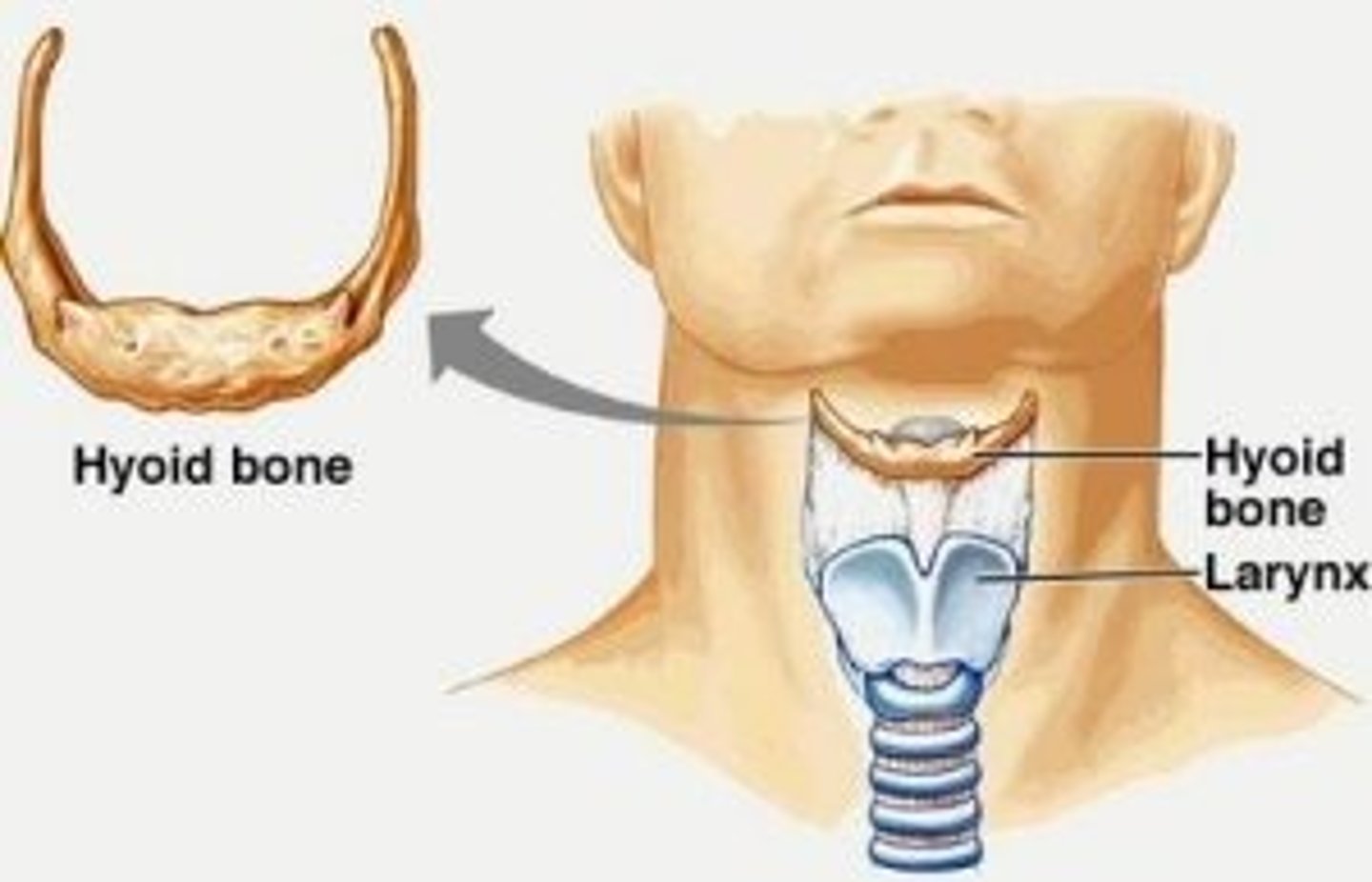
Hyoid
a U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue.
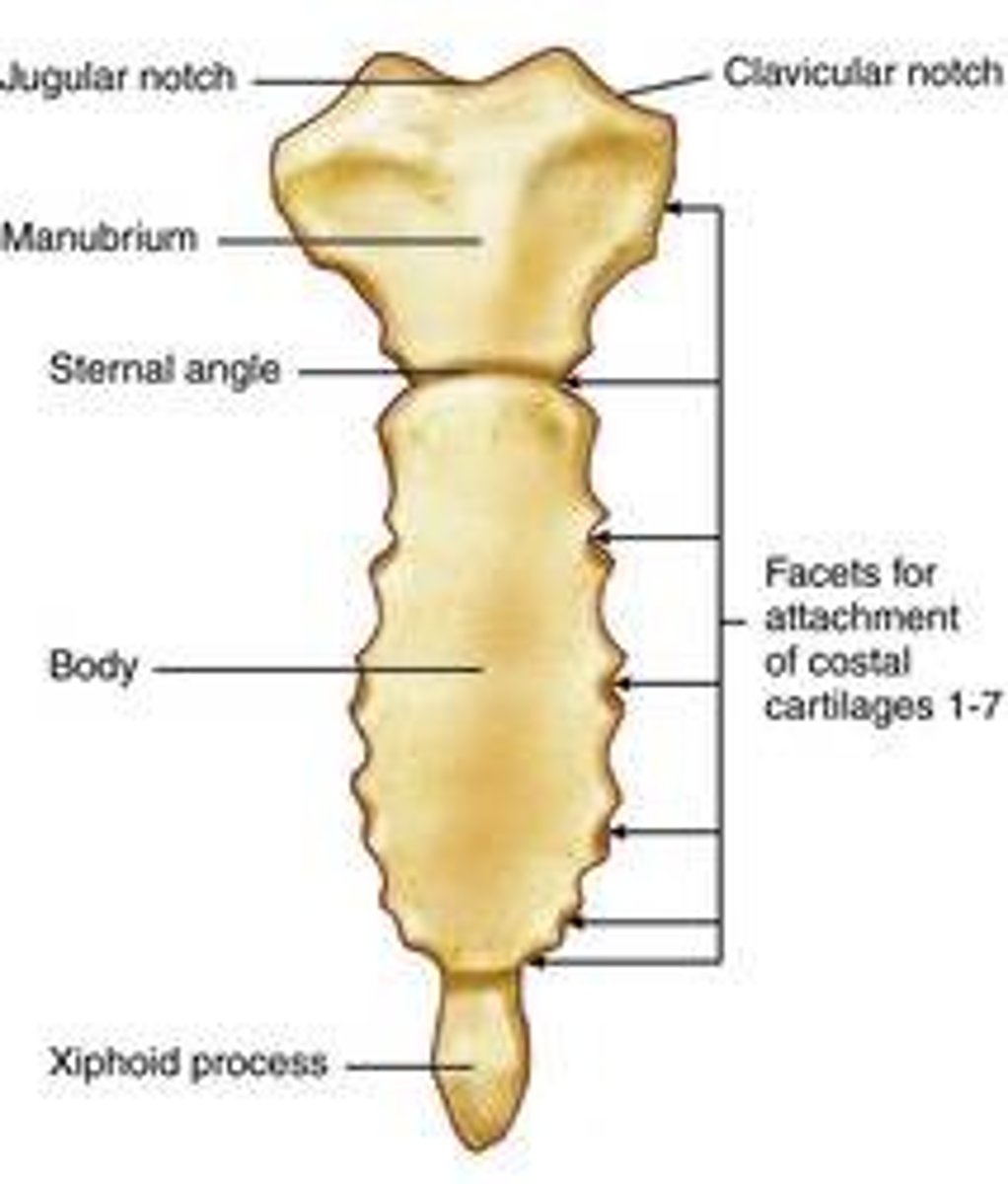
sternum
from superior to inferior composed of manubrium, sternum, and xiphoid process
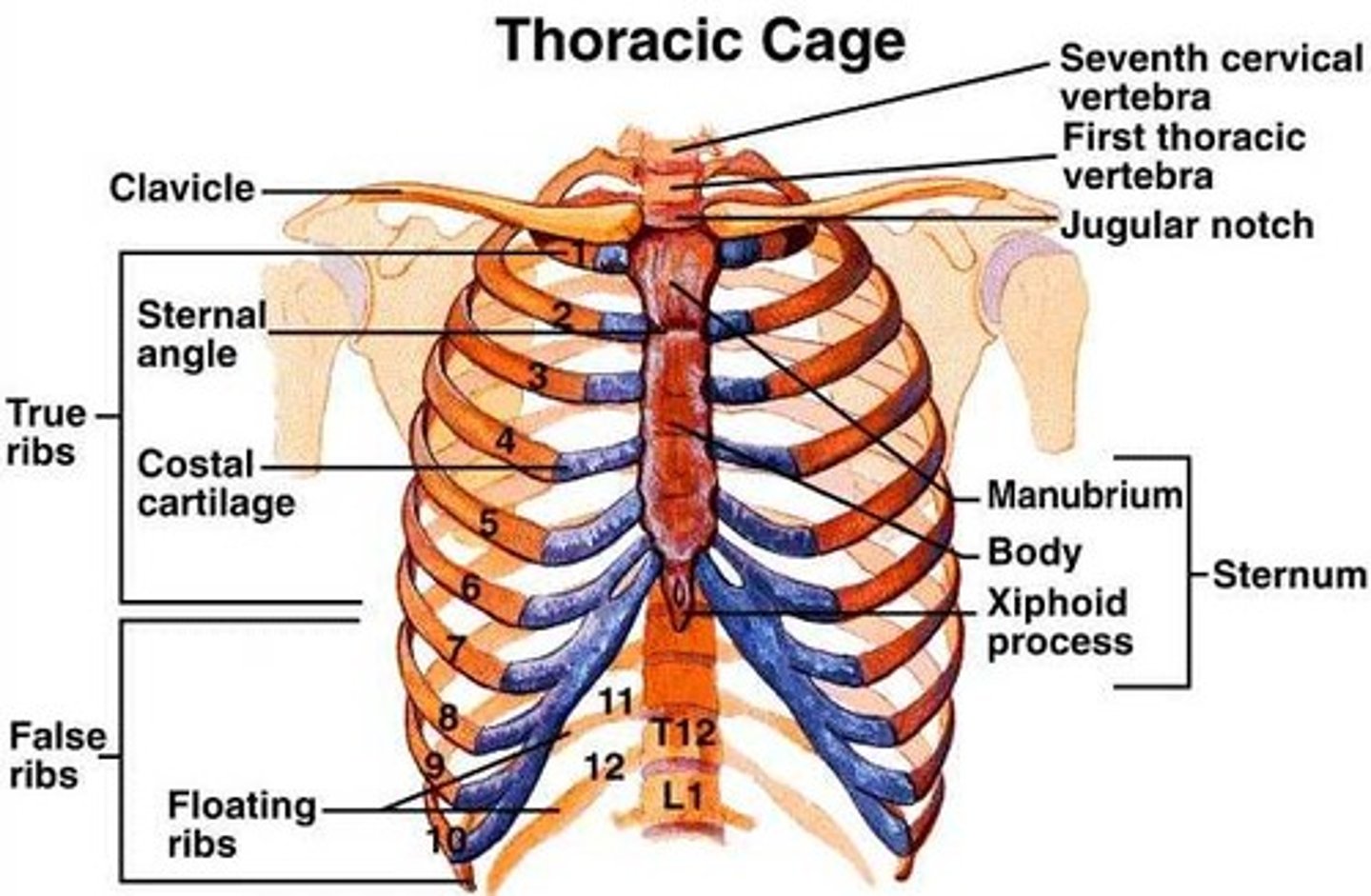
ribs
12 total pairs, 1-7 true ribs, 8-10 false ribs that attach indirectly via cartilage, 11-12 floating ribs
Appendicular Skeleton
Includes limbs, pectoral and pelvic girdle, supporting axial skeleton. 126 bones
Long Bones
Compact bone in diaphysis and spongy in epiphysis
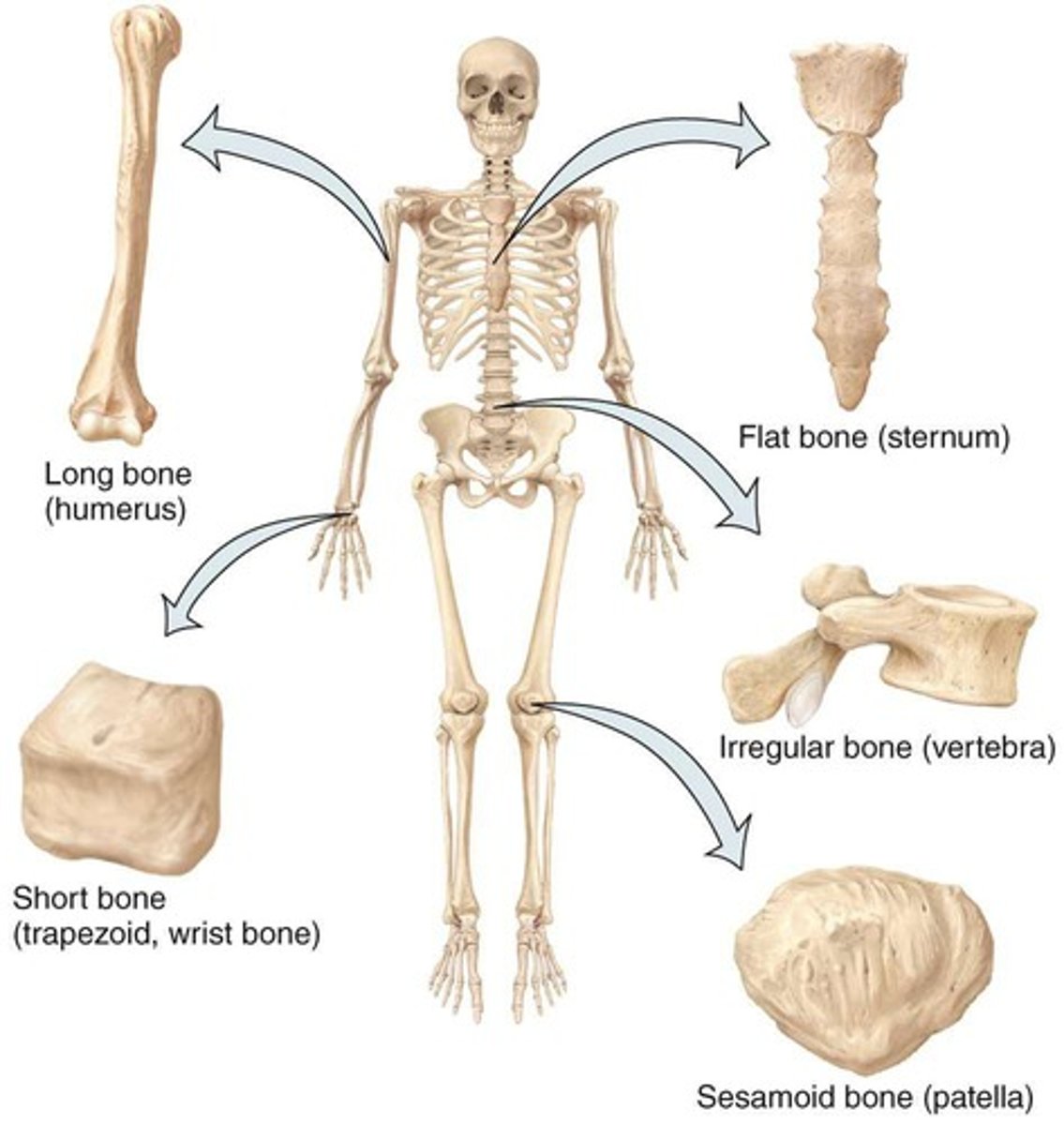
Short Bones
Somewhat cube-shaped, nearly equal in length and width spongy bone (except surface)
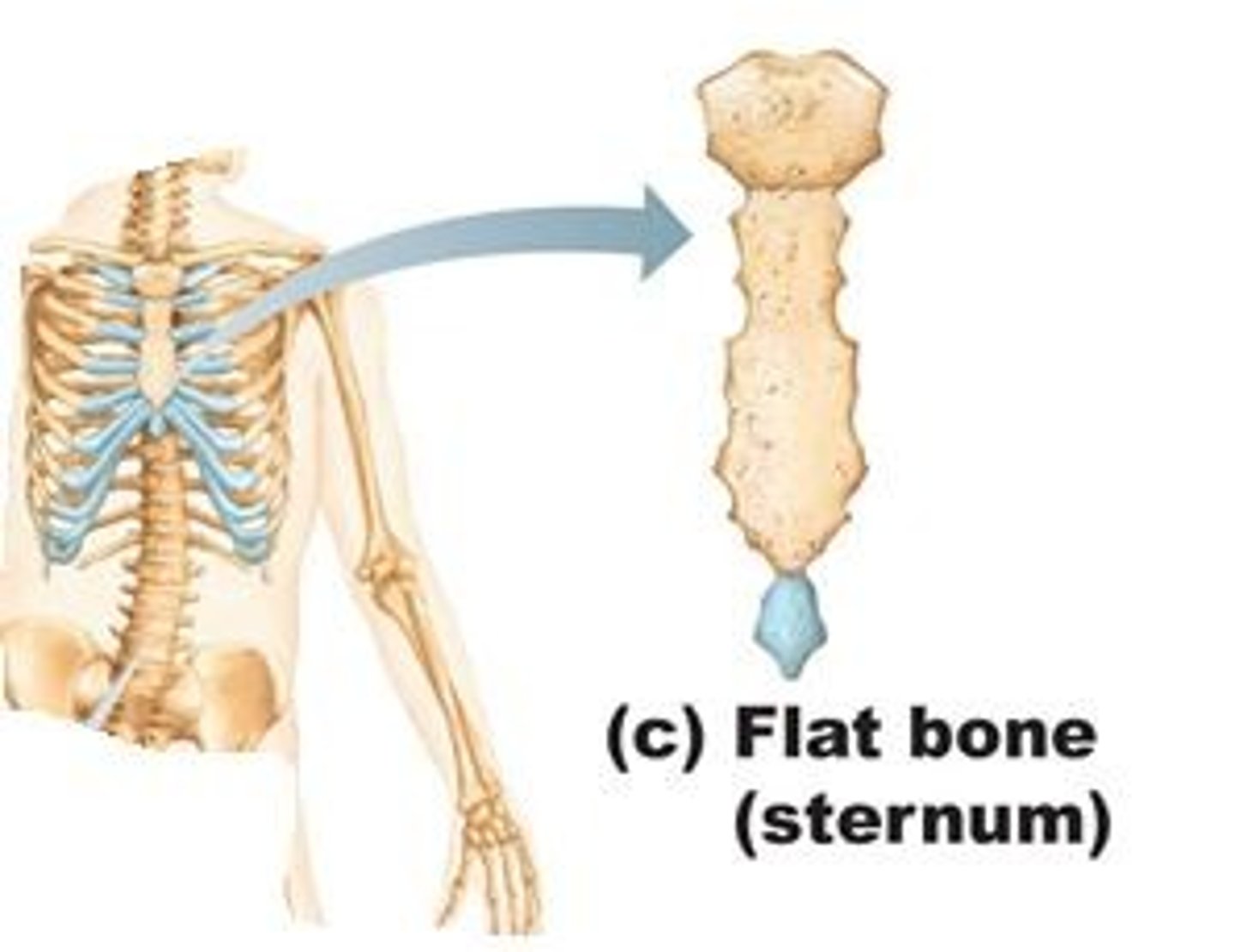
Flat Bones
Generally thin and composed of 2 nearly parallel plates of compact bone
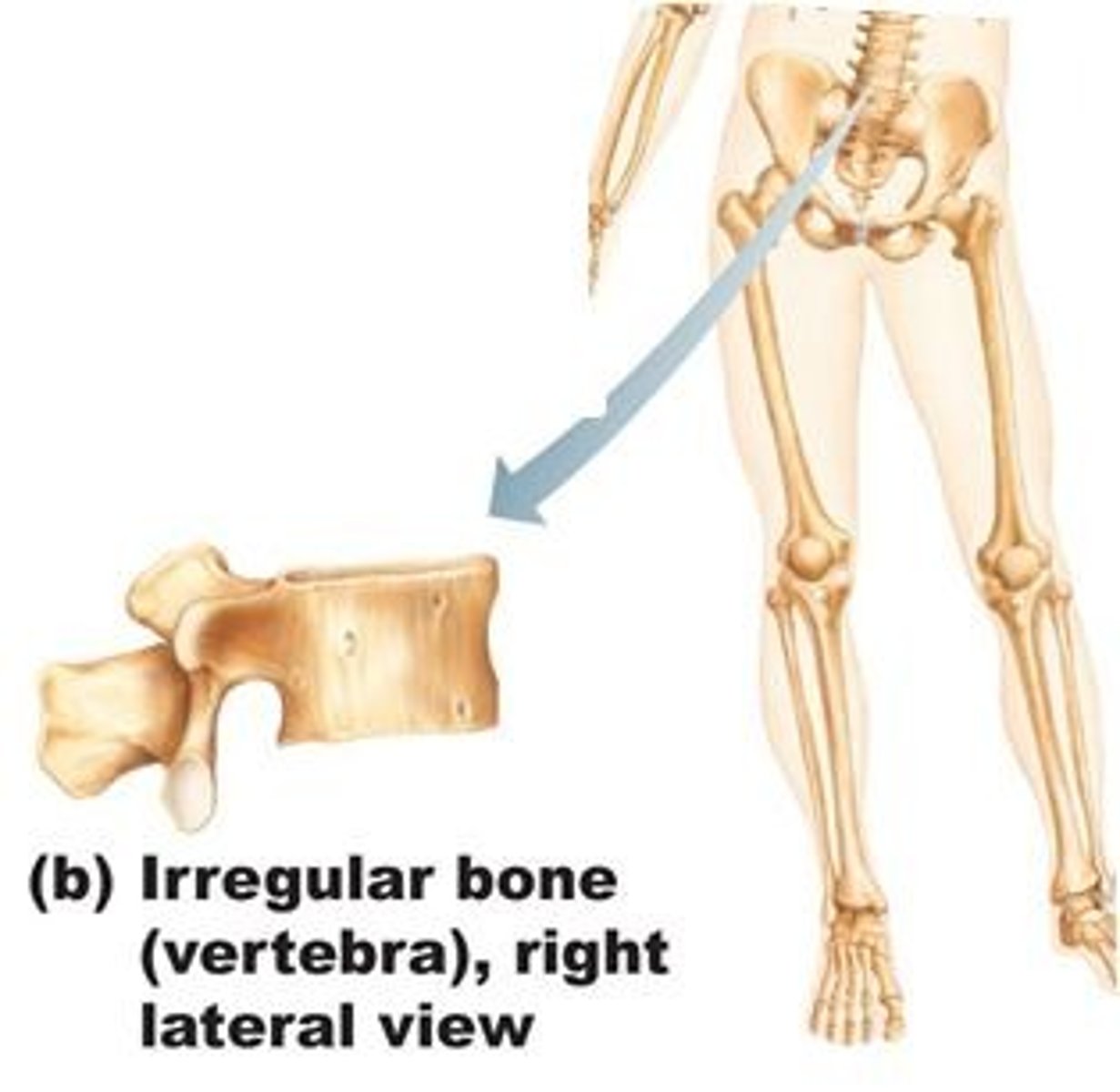
Irregular Bones
Complex-shaped bones, e.g., vertebrae.
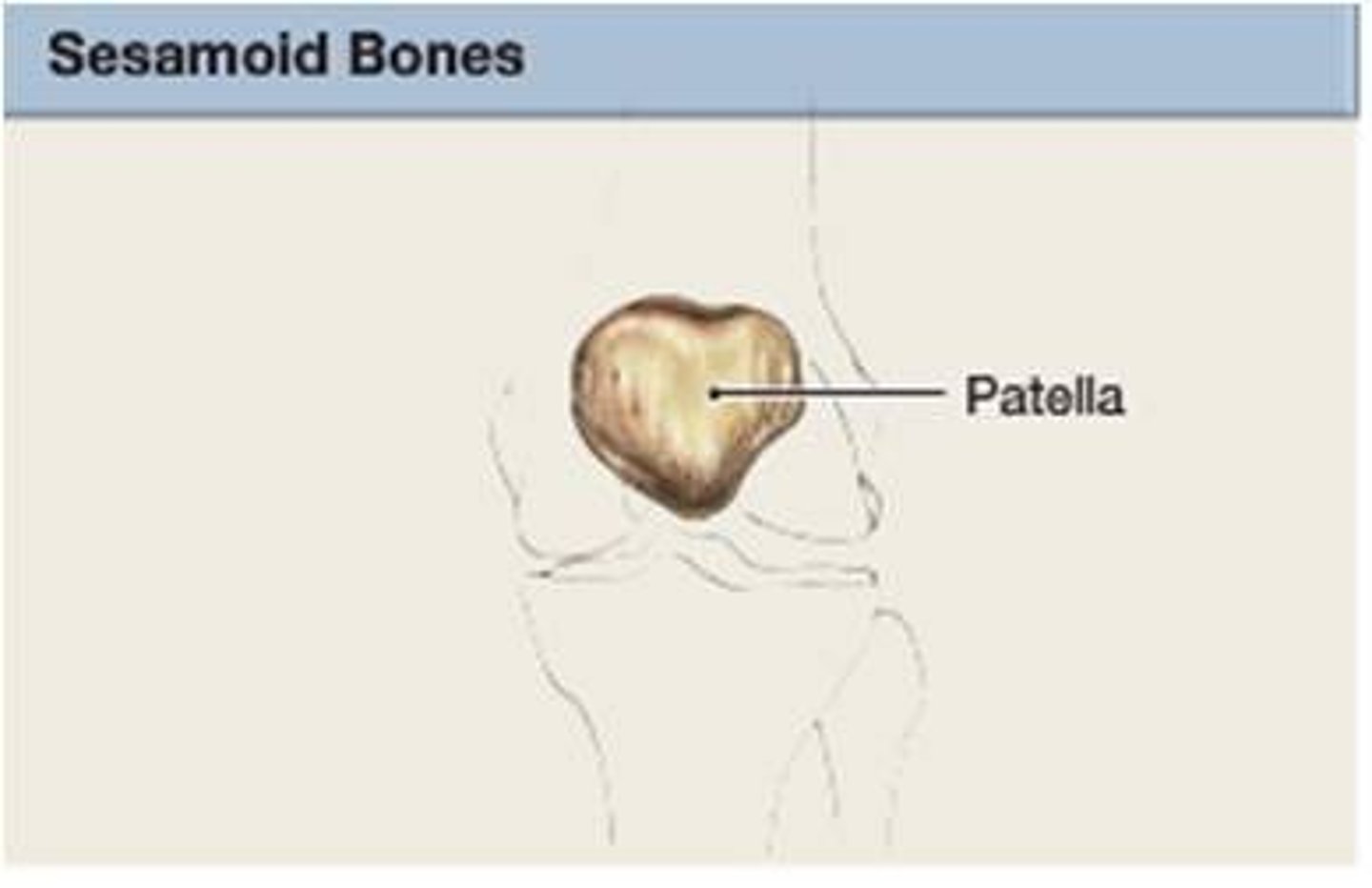
Sesamoid Bones
Develop in certain tendons where there is considerable friction, tension, and physical stress
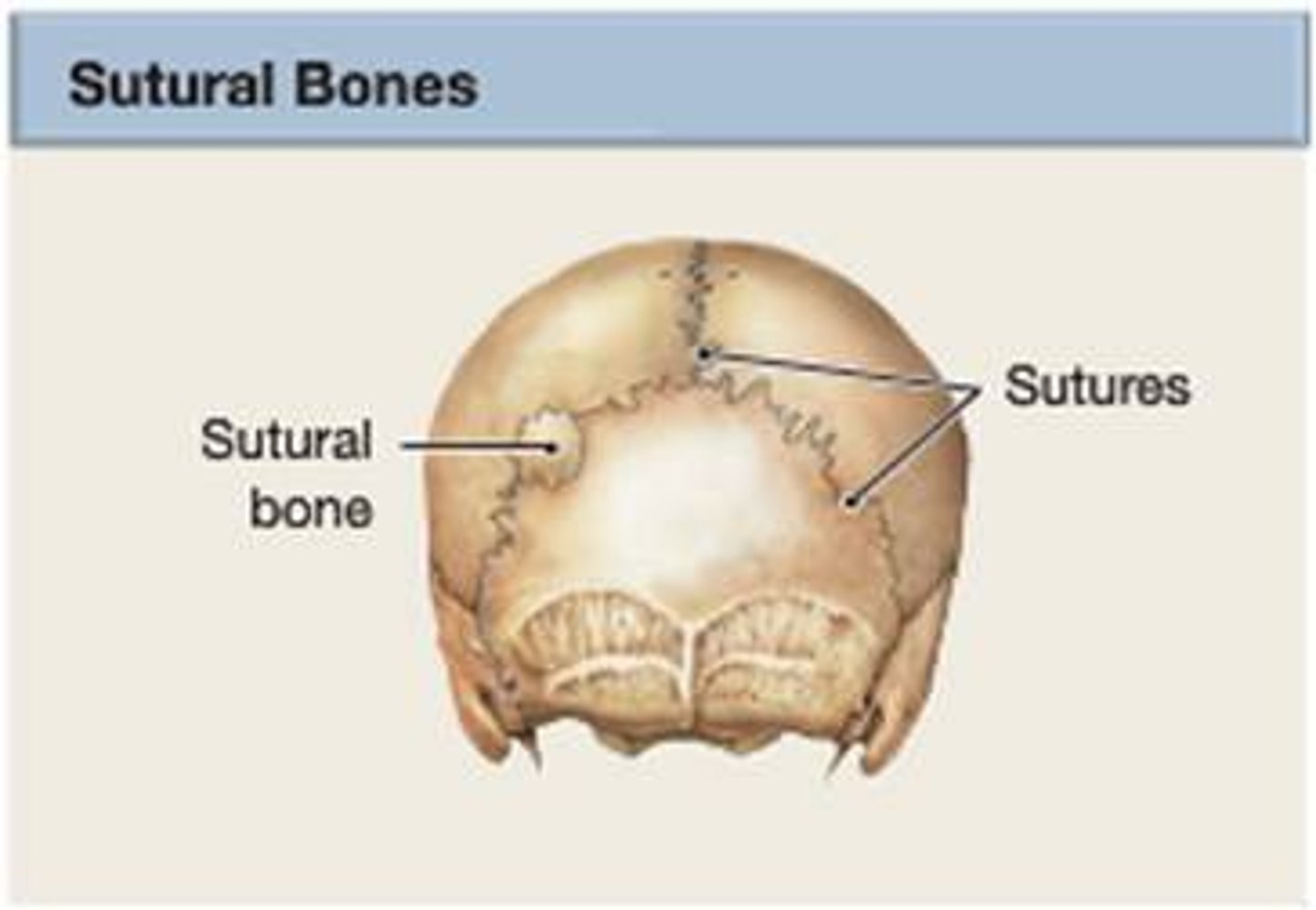
Sutural Bones
- Small bones located within joints (sutures) between certain cranial bones
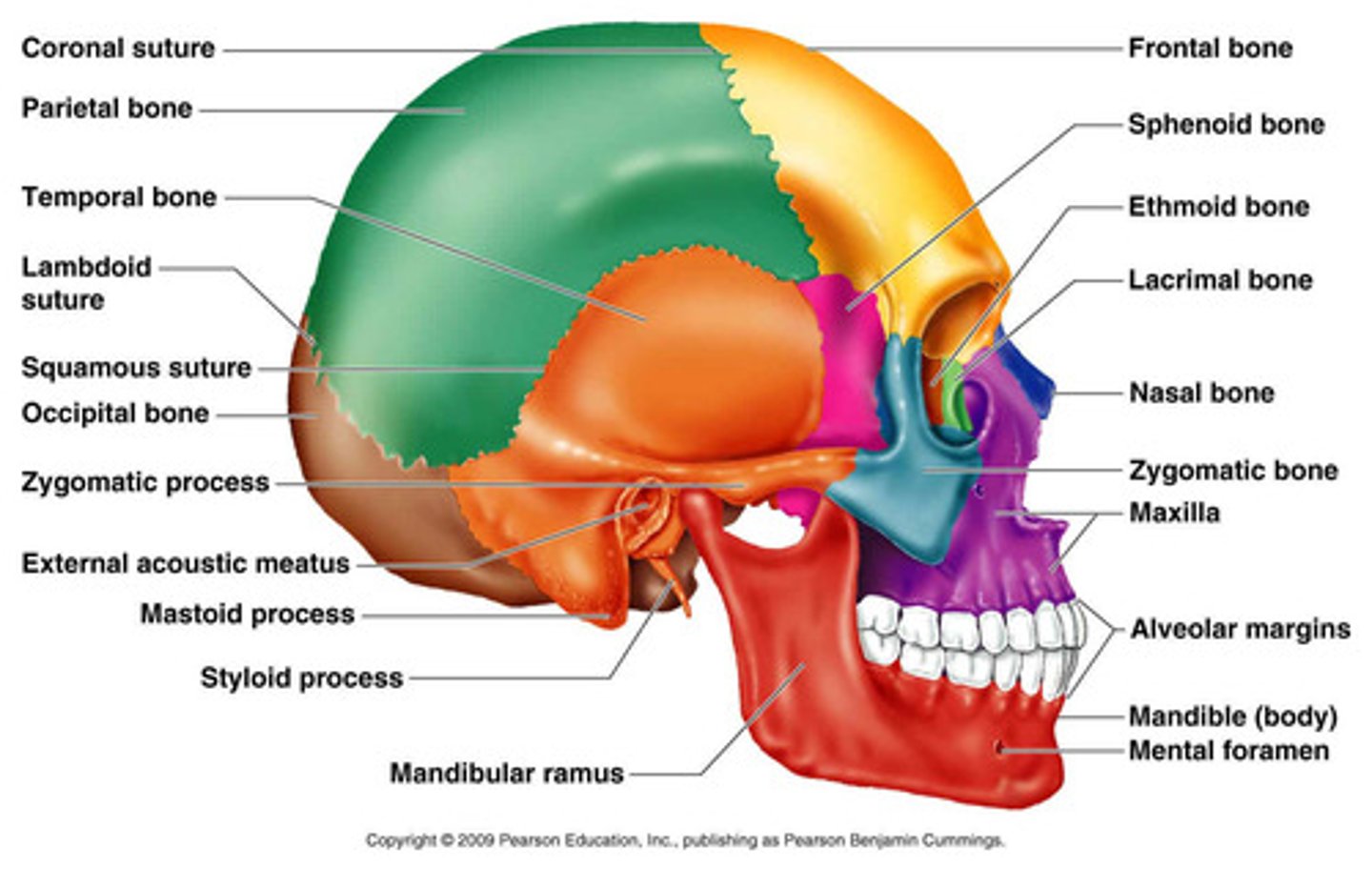
Sutures
Joints where flat bones of the skull meet.
Coronal - Squamous - Lambdoid - Sagittal
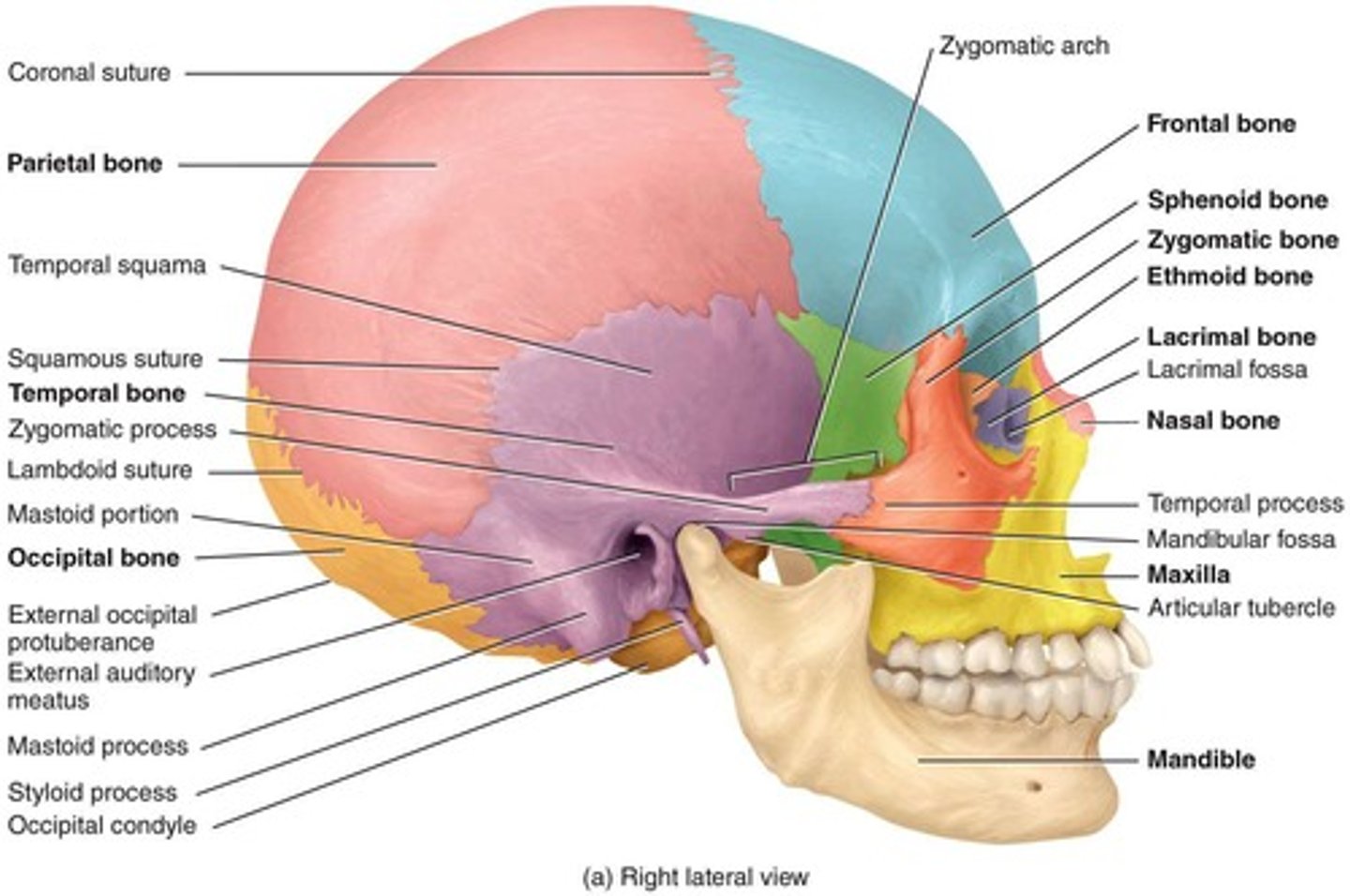
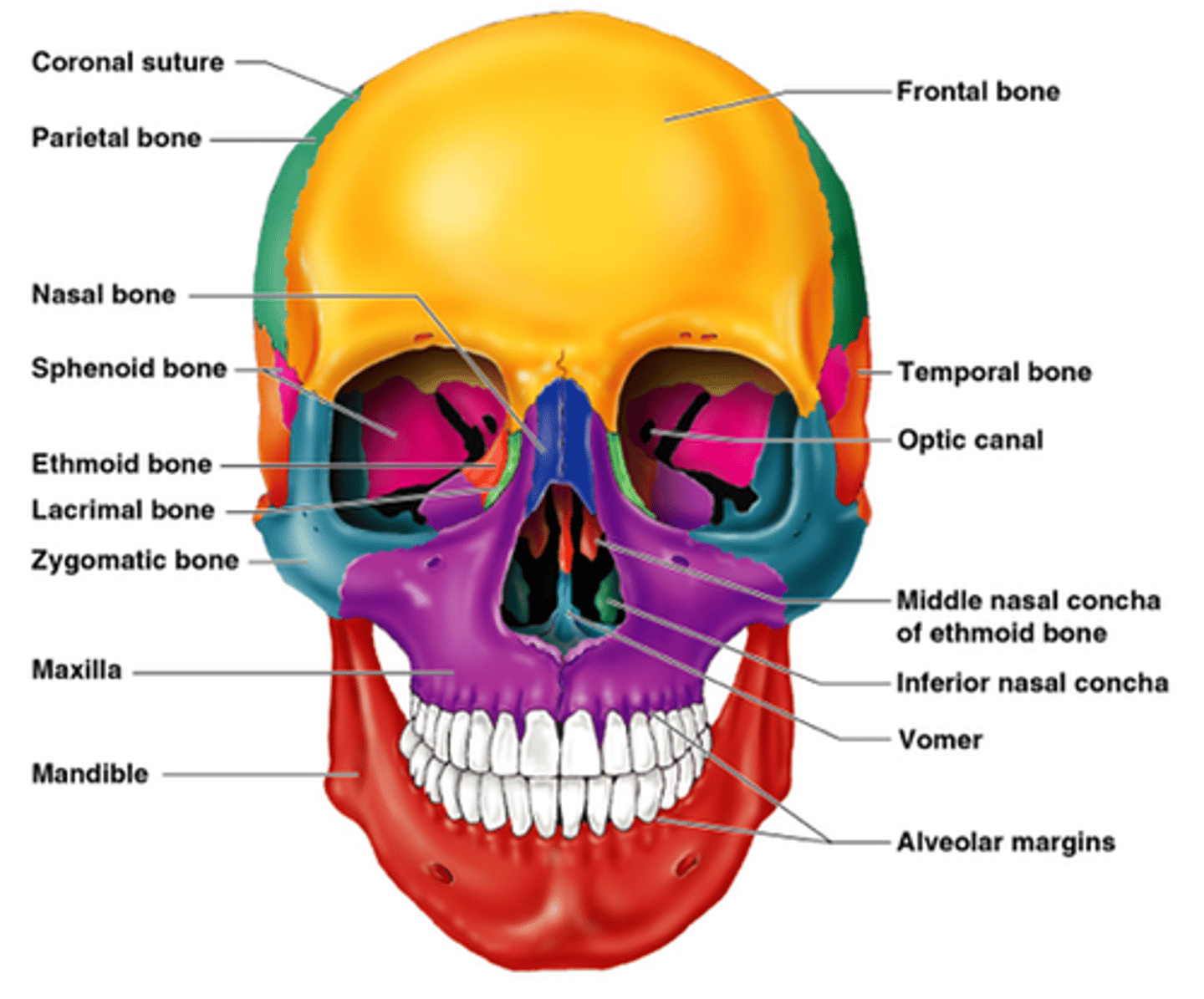
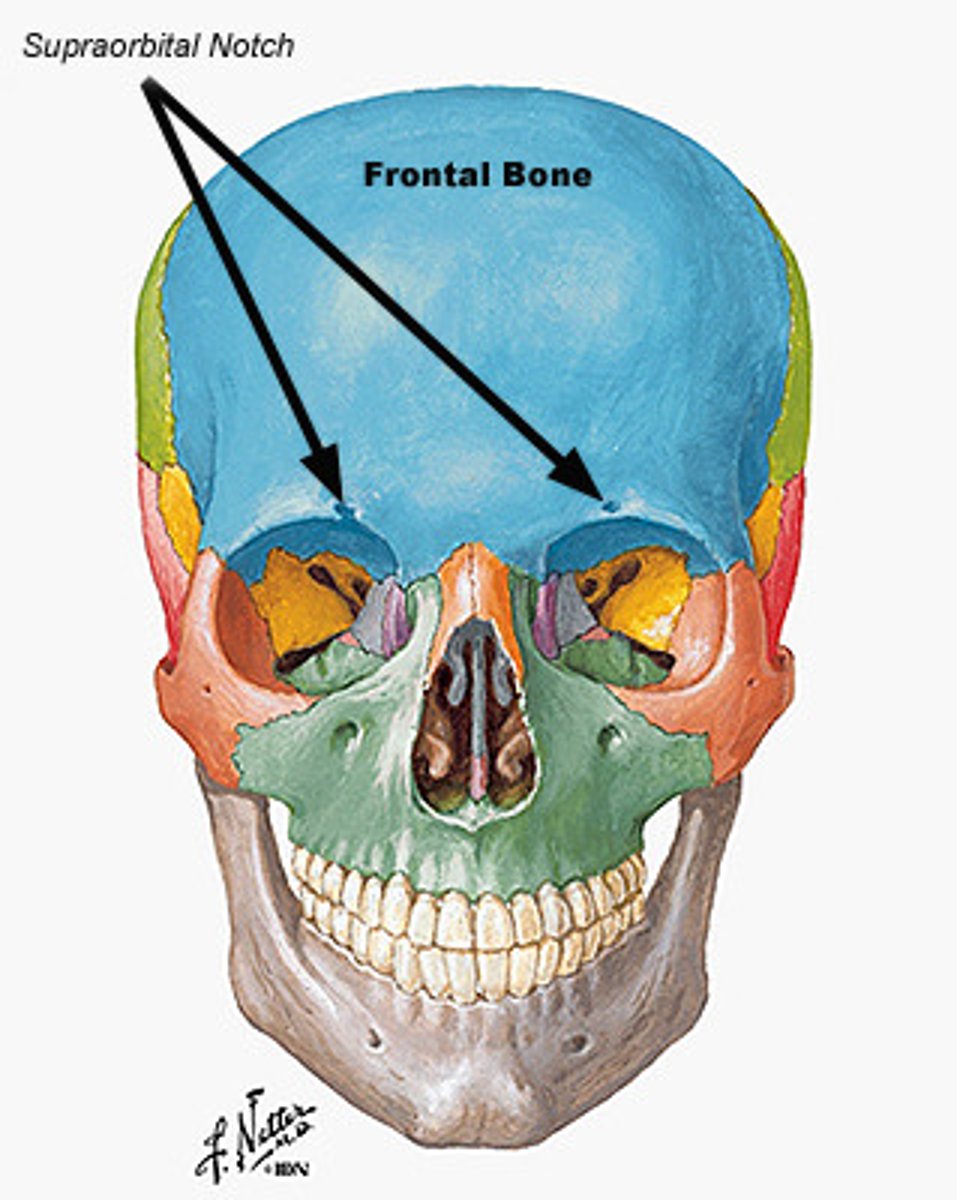
Frontal Bone
Forehead bone, part of the cranial structure.
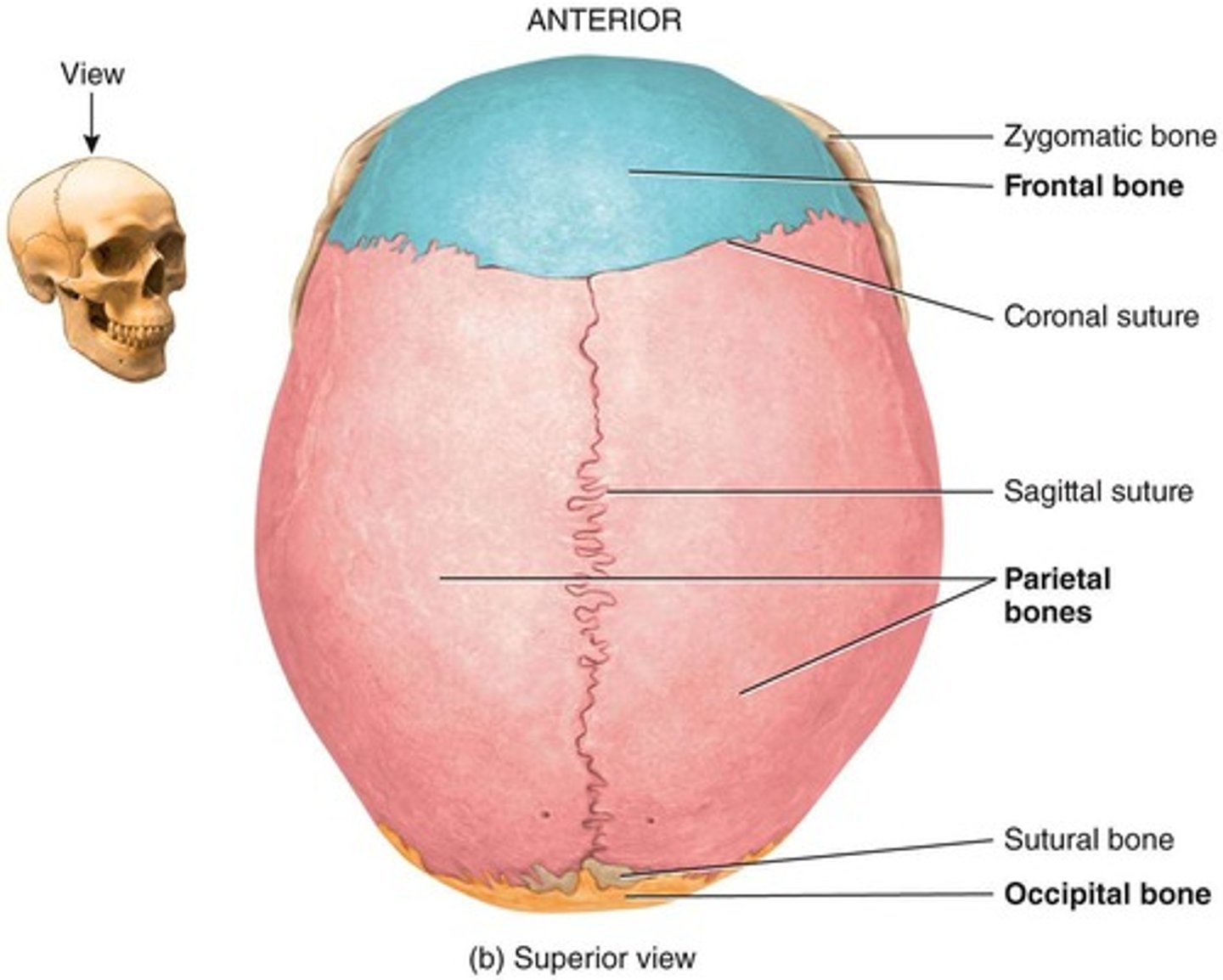
Parietal Bone
Two bones forming the top and sides of the skull.
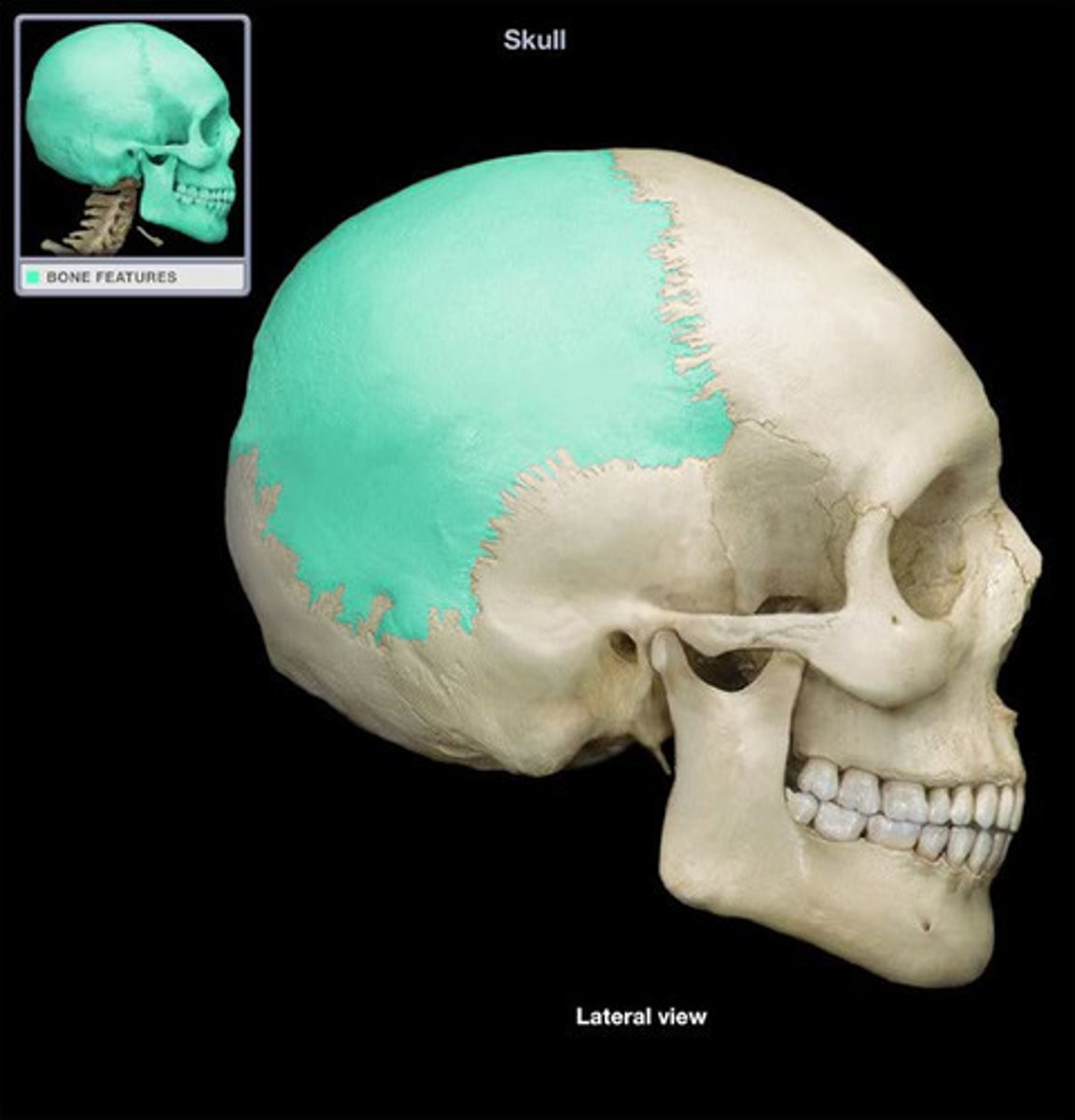
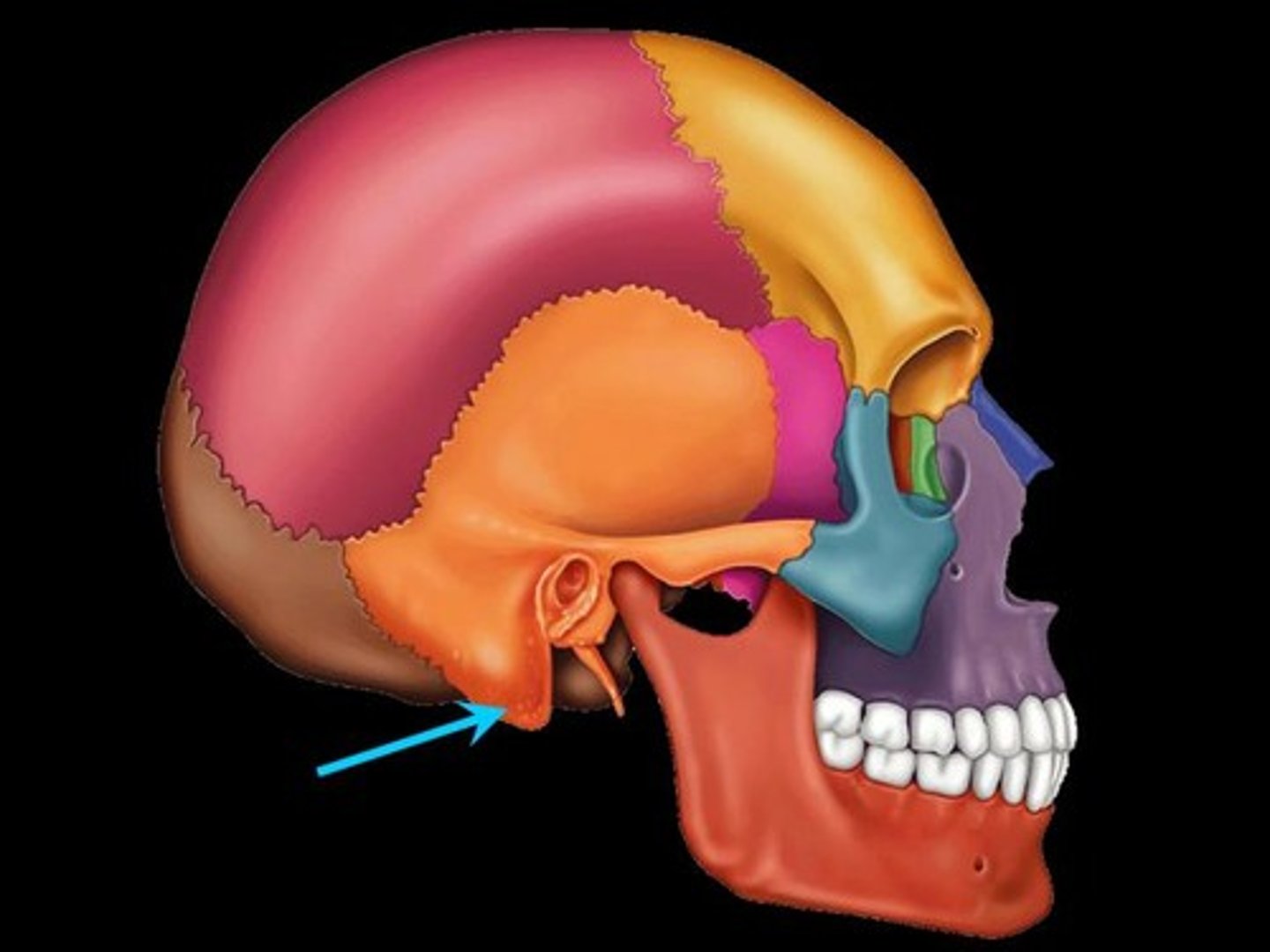
Temporal Bone
Bones located at the sides of the skull.
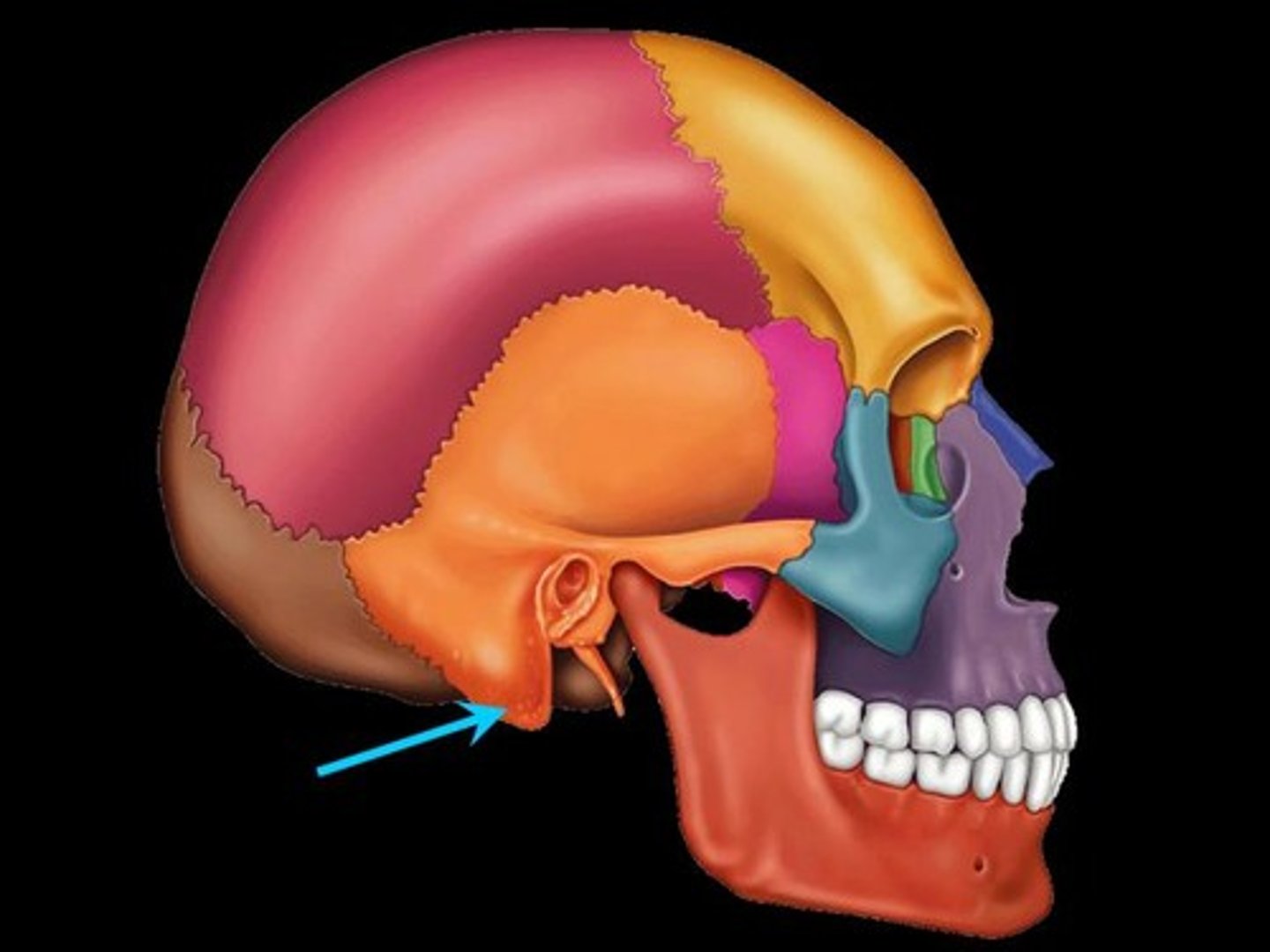
Processes
Projections/outgrowths • Help form joints • Attachment points for connective tissue • Ex: ligaments, tendons
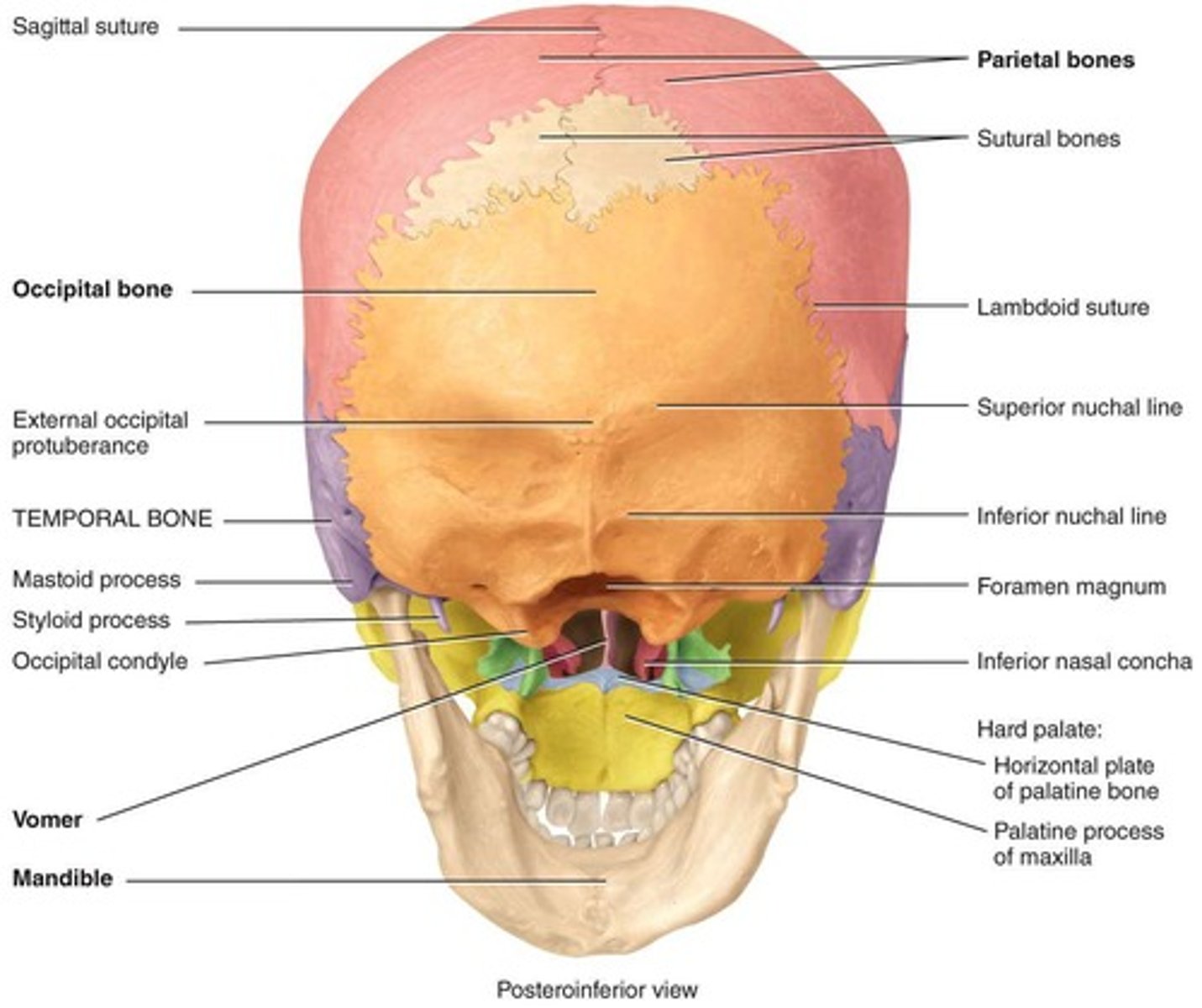
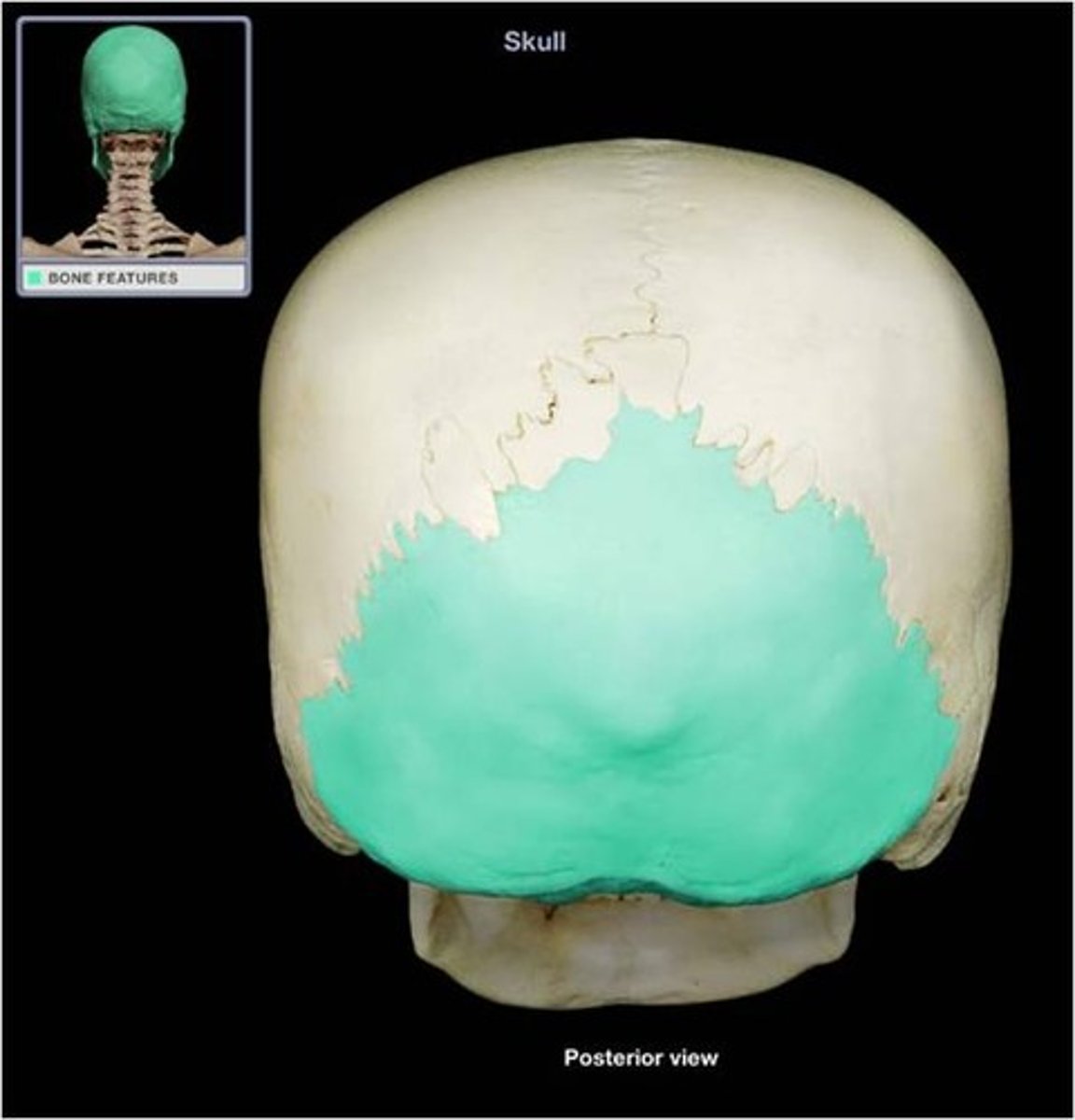
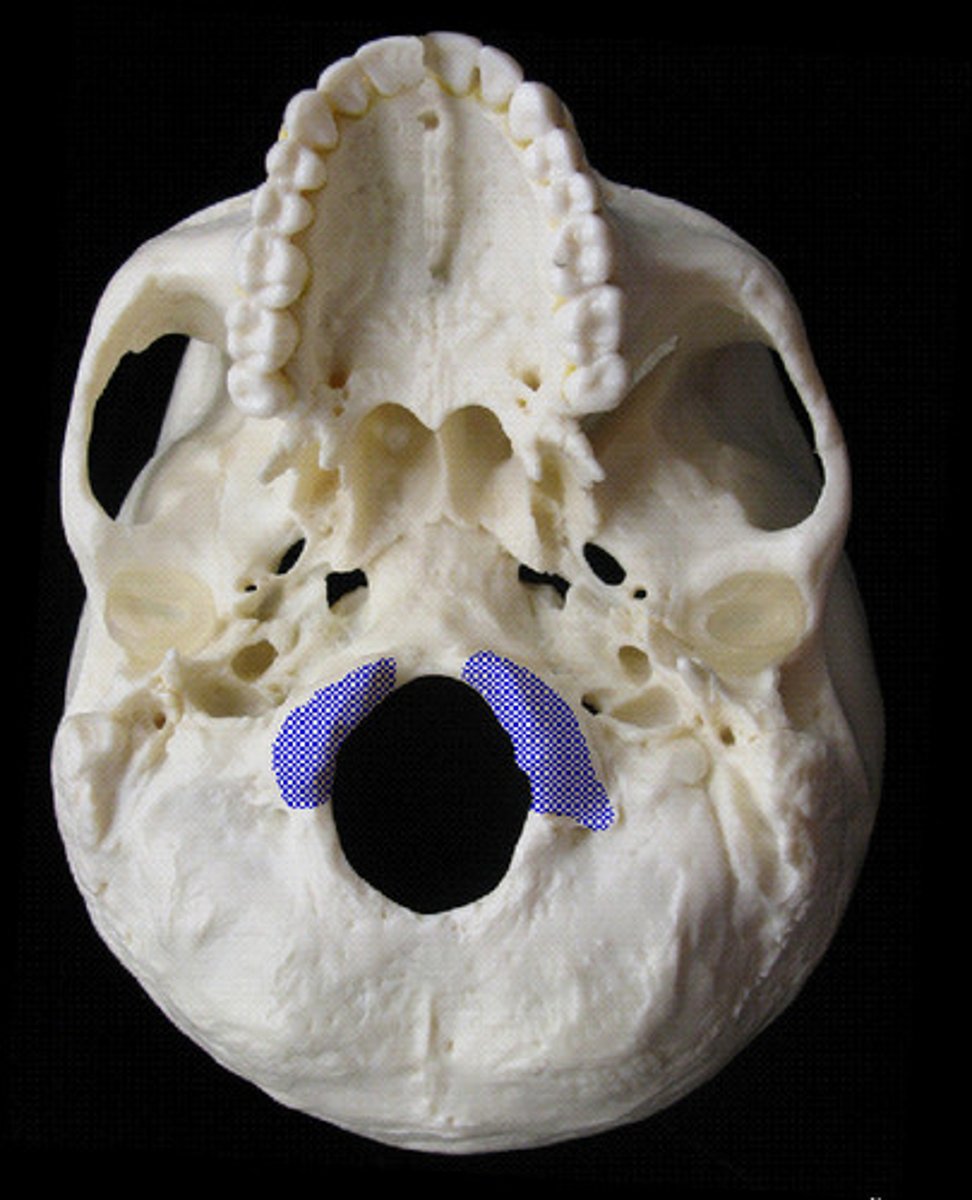
Occipital Bone
Bone forming the back of the skull.
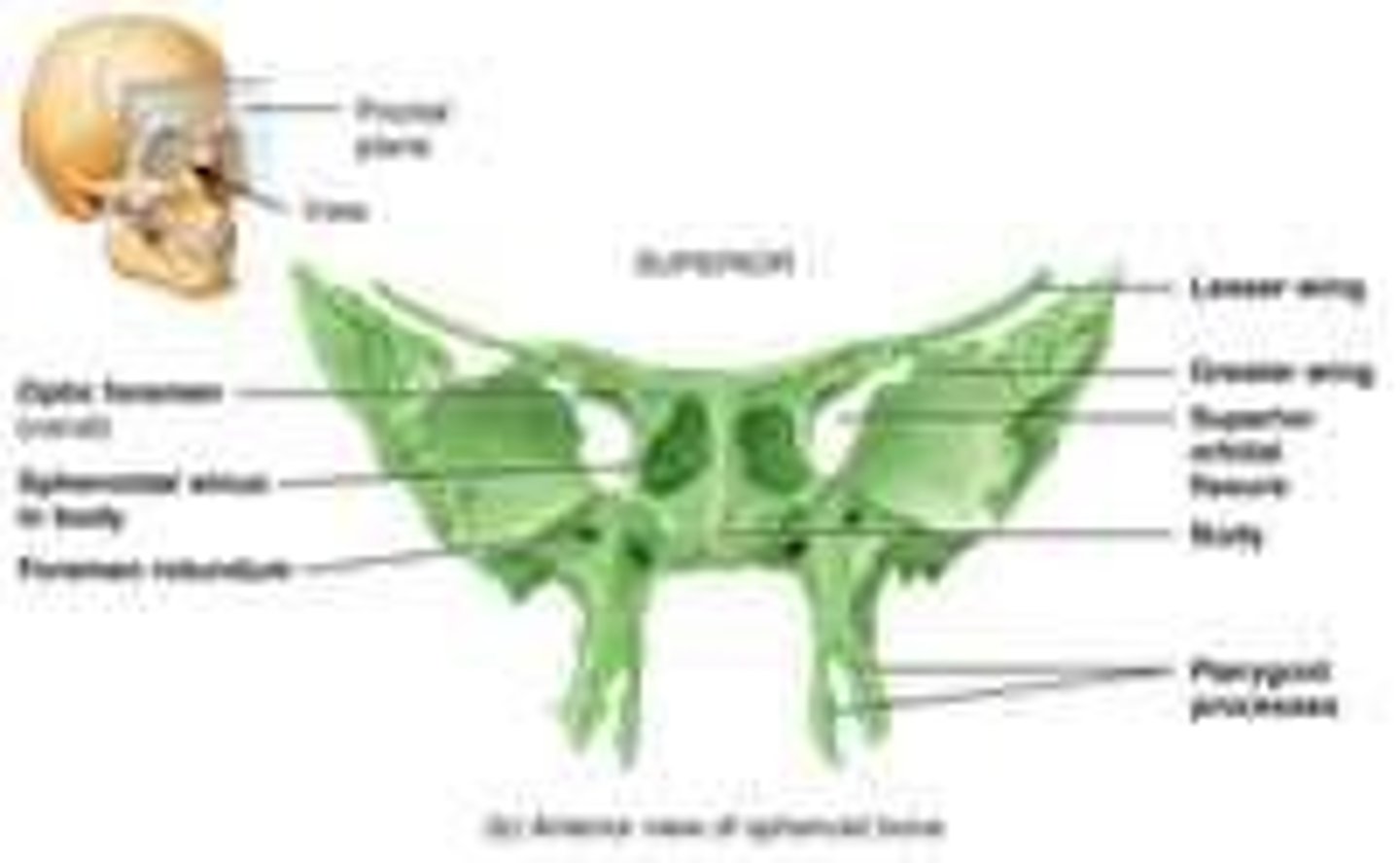
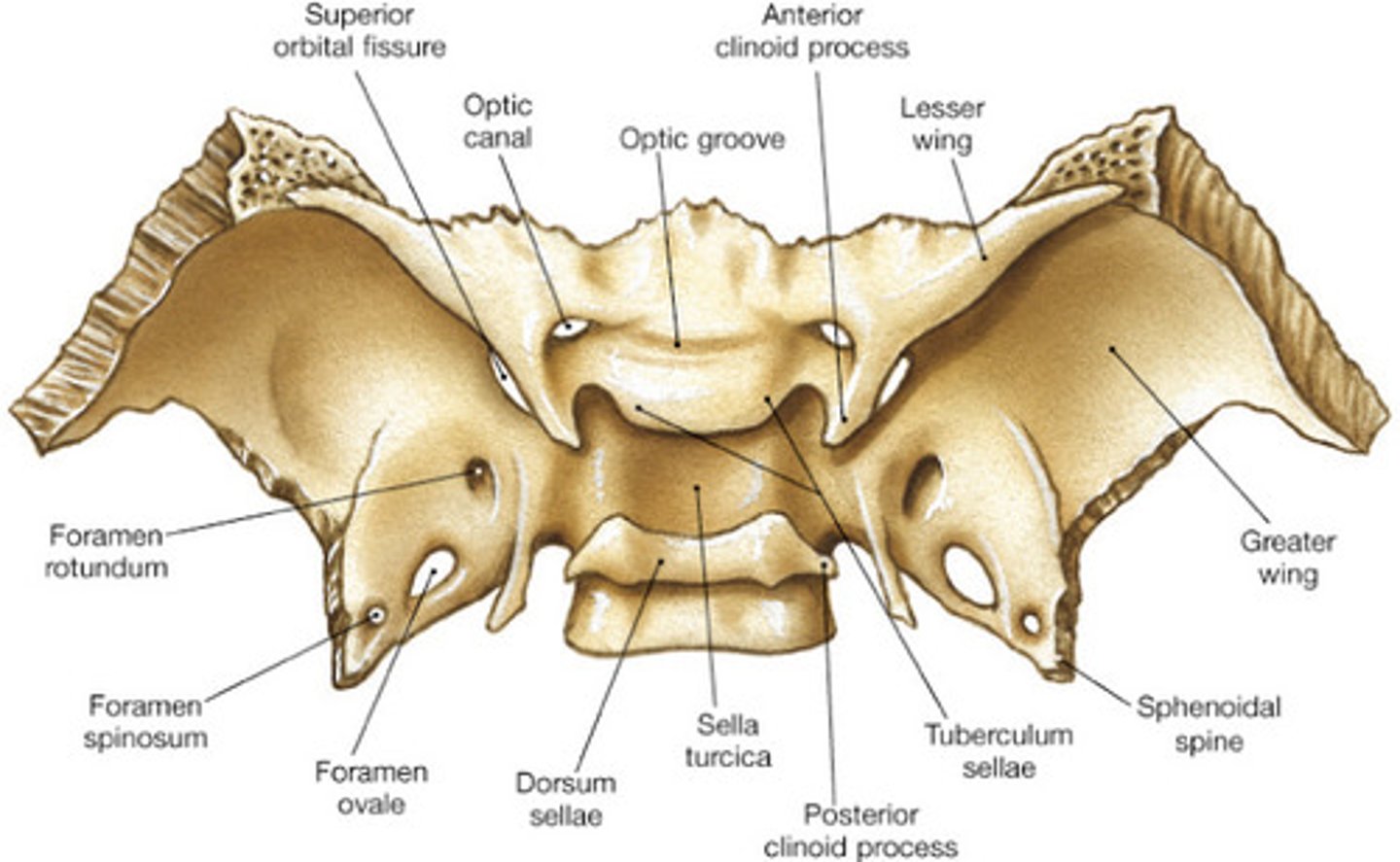
Sphenoid Bone
Butterfly-shaped bone at the base of the skull.
Articulates with all other cranial bones, holding them together • Forms part of floor, sidewalls, and rear wall of orbit
Ethmoid Bone
• Major superior supporting structure of nasal cavity
Forms: - Part of anterior portion of cranial floor - Medial wall of orbits - Superior portions of nasal septum - Most of superior sidewalls of nasal cavity
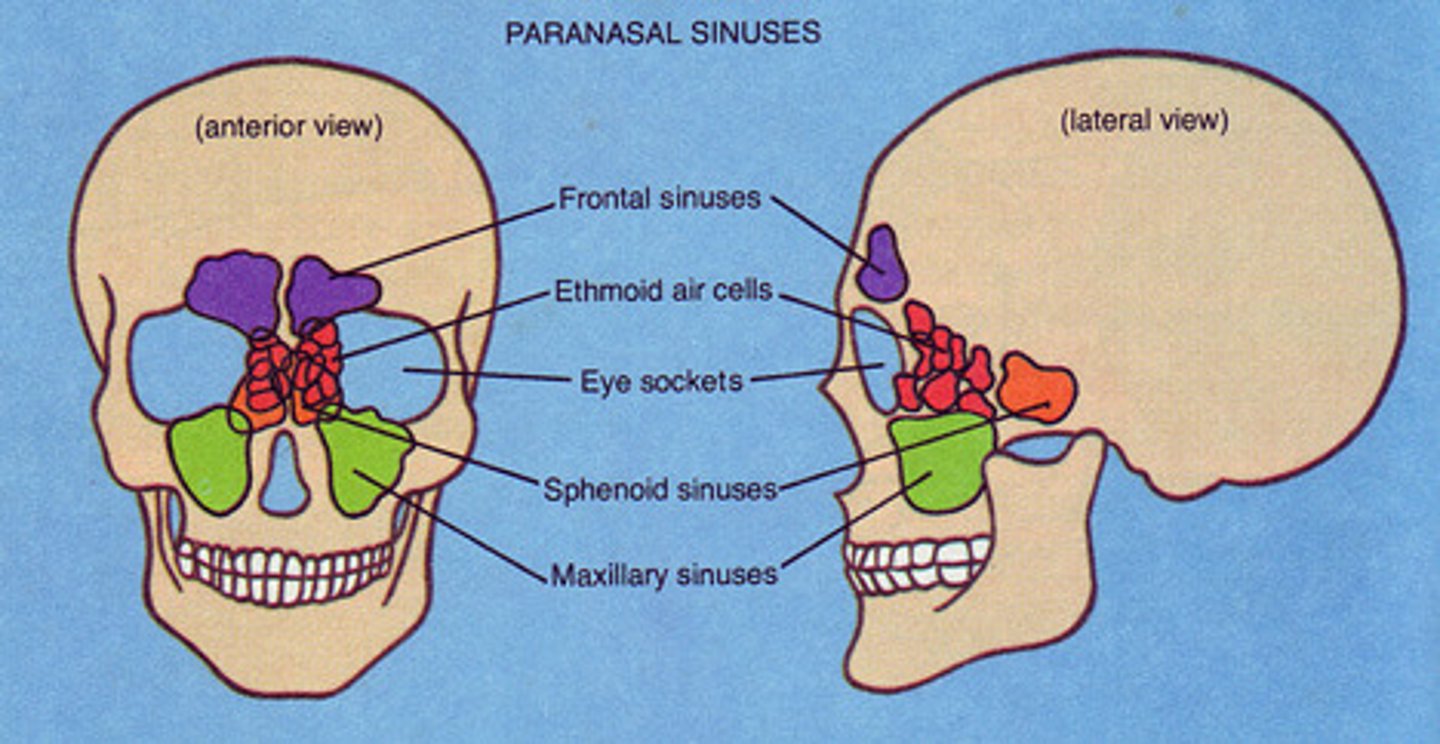
Paranasal Sinuses
Paired cavities in frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary bones • Lined with mucous membranes that are continuous with lining of nasal cavity• Functions - Produces mucus - Resonating chambers for sound
skull functions
• Protect and provide support for brain, nerves, blood vessels, and special sense organs• Attachment for muscles on outer surface • Facial bones form framework of face
frontal bone landmarks
Supraorbital foramen, Frontal sinuses
temporal bone landmarks
- Mandibular fossa - External auditory meatus - Mastoid process - Internal auditory meatus - Styloid process - Carotid foramen - Jugular foramen
occipital landmarks
Foramen magnum - Occipital condyles
sphenoid landmarks
Sella turcica - Greater wings - Lesser wings - Optic foramen - Sphenoidal sinuses
ethmoid landmarks
Cribriform plate - Olfactory foramina - Crista galli - Perpendicular plate - Middle nasal concha - Ethmoid sinuses
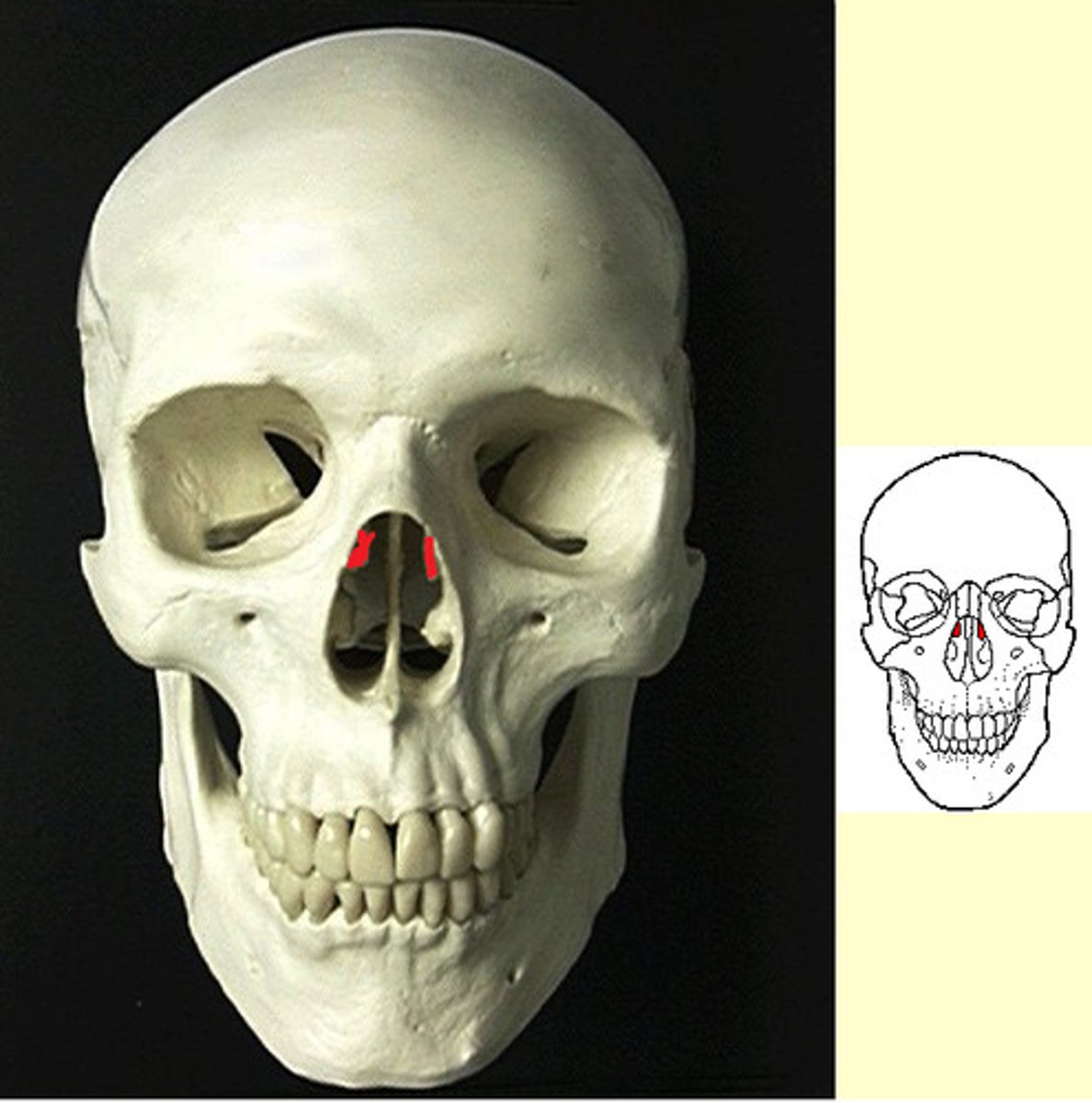
Nasal bone
bridge of nose

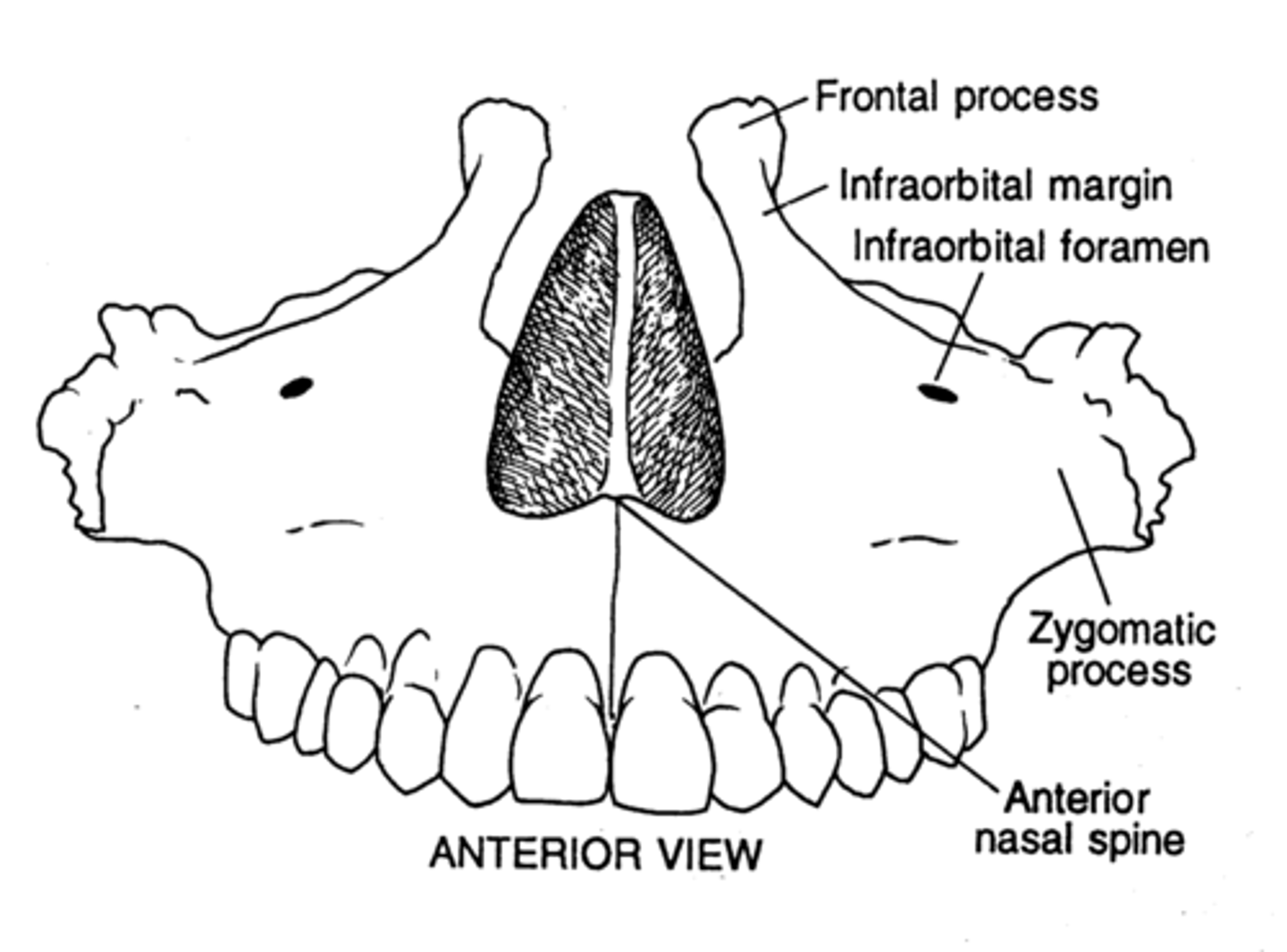
maxilla
Forms part of the floors of the orbits, part of the lateral walls and floor of the nasal cavity, and most of the hard palate
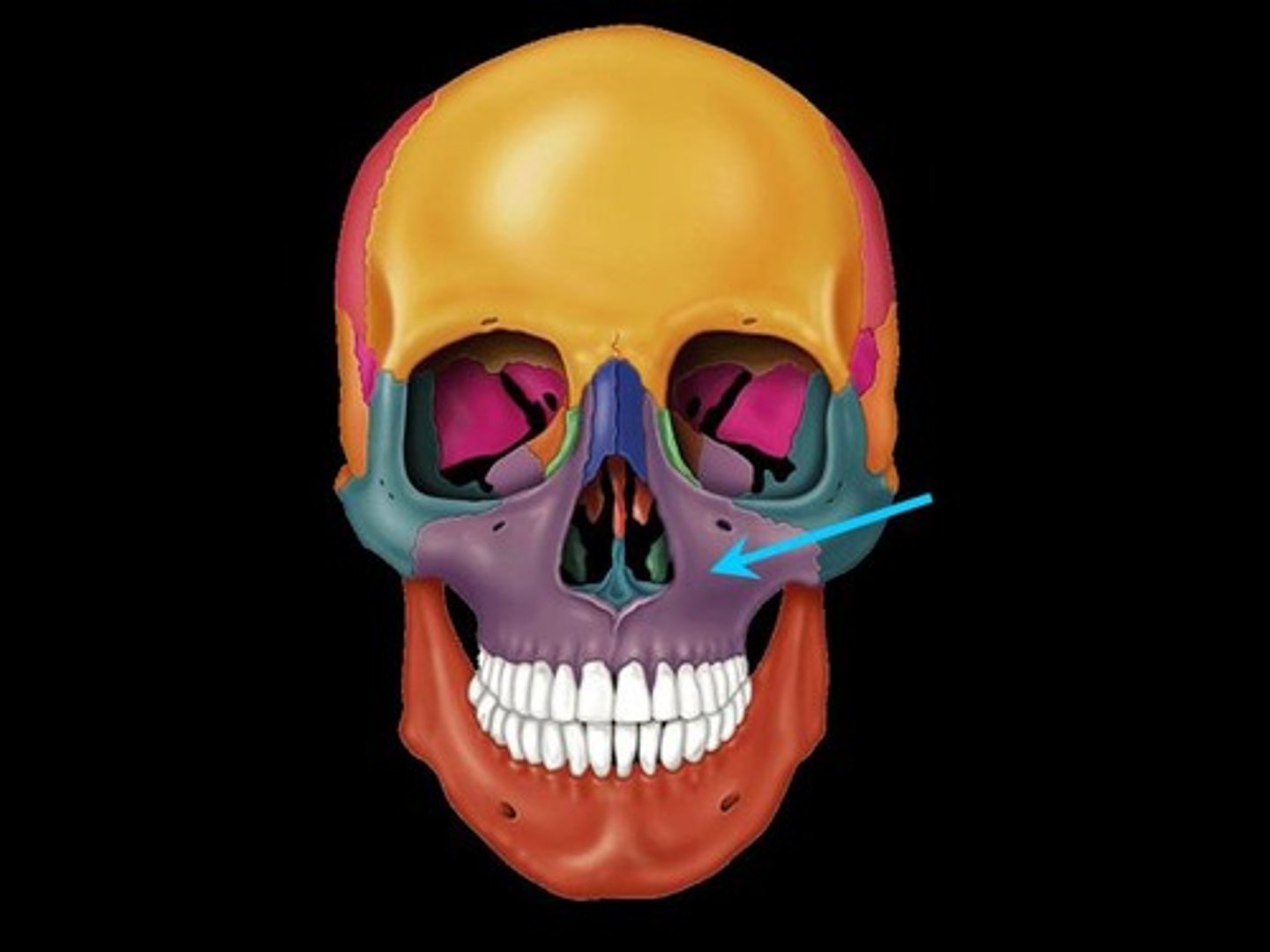
zygoma
Articulates with frontal, maxillae, sphenoid, and temporal bones
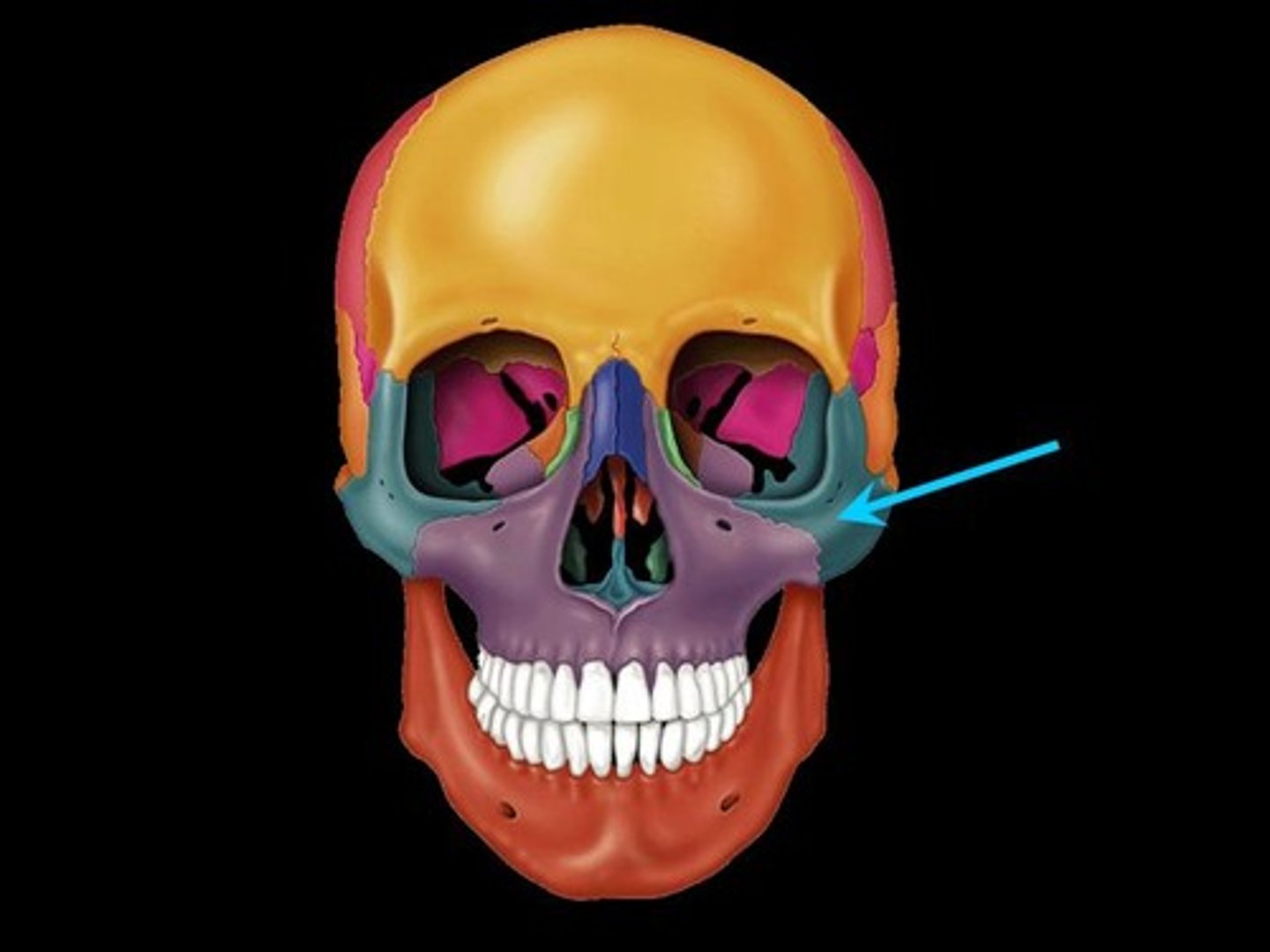
lacrimal bone
lacrimal=tears
Smallest bones of the face
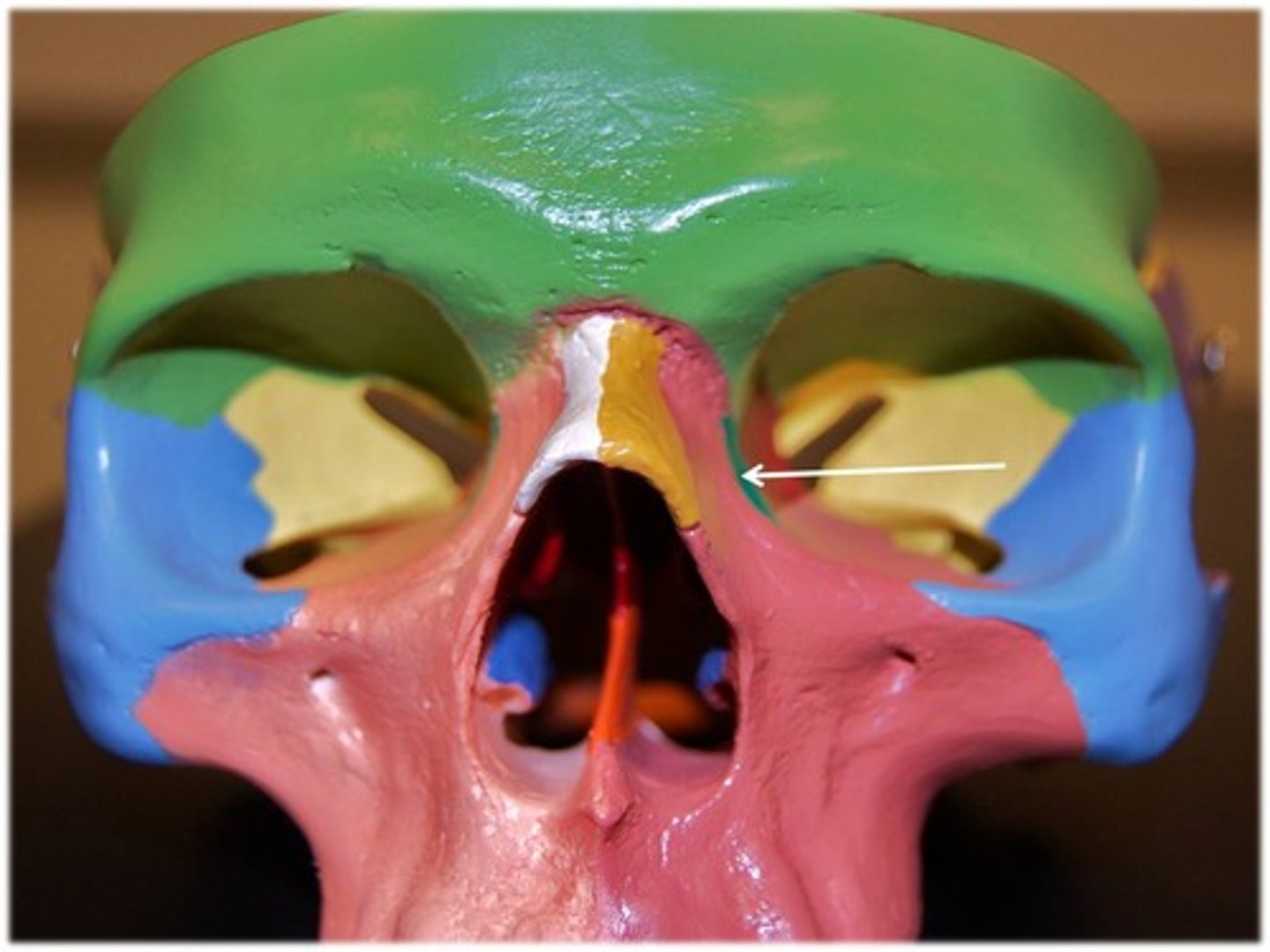
palatine bone
L-shaped bones forming the posterior portion of the hard palate, part of the floor and lateral wall of the nasal cavity, and small portion of the floors of the orbits
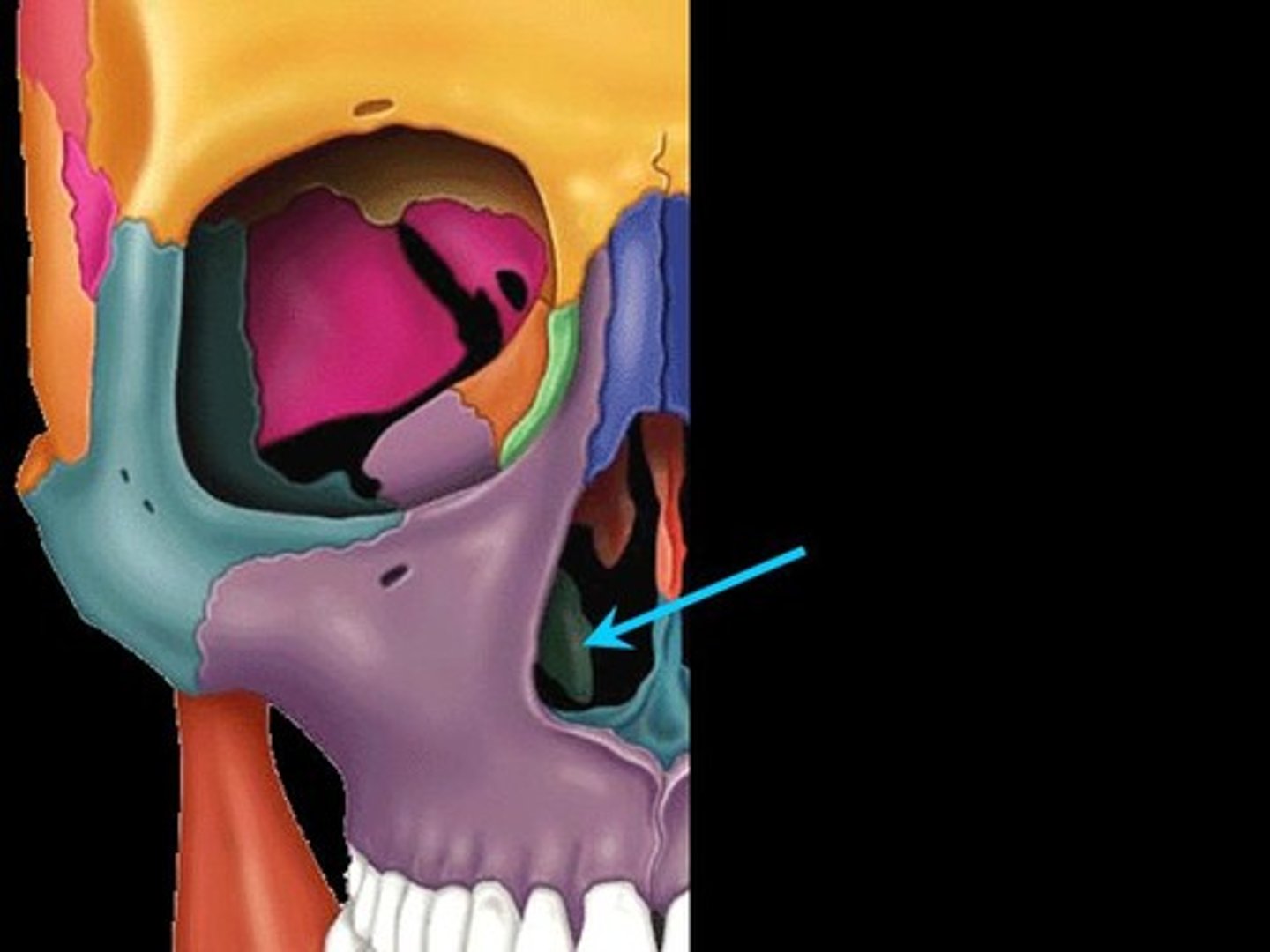
inferior nasal conchae
form lower part of lateral walls of nasal cavity (turbinates)
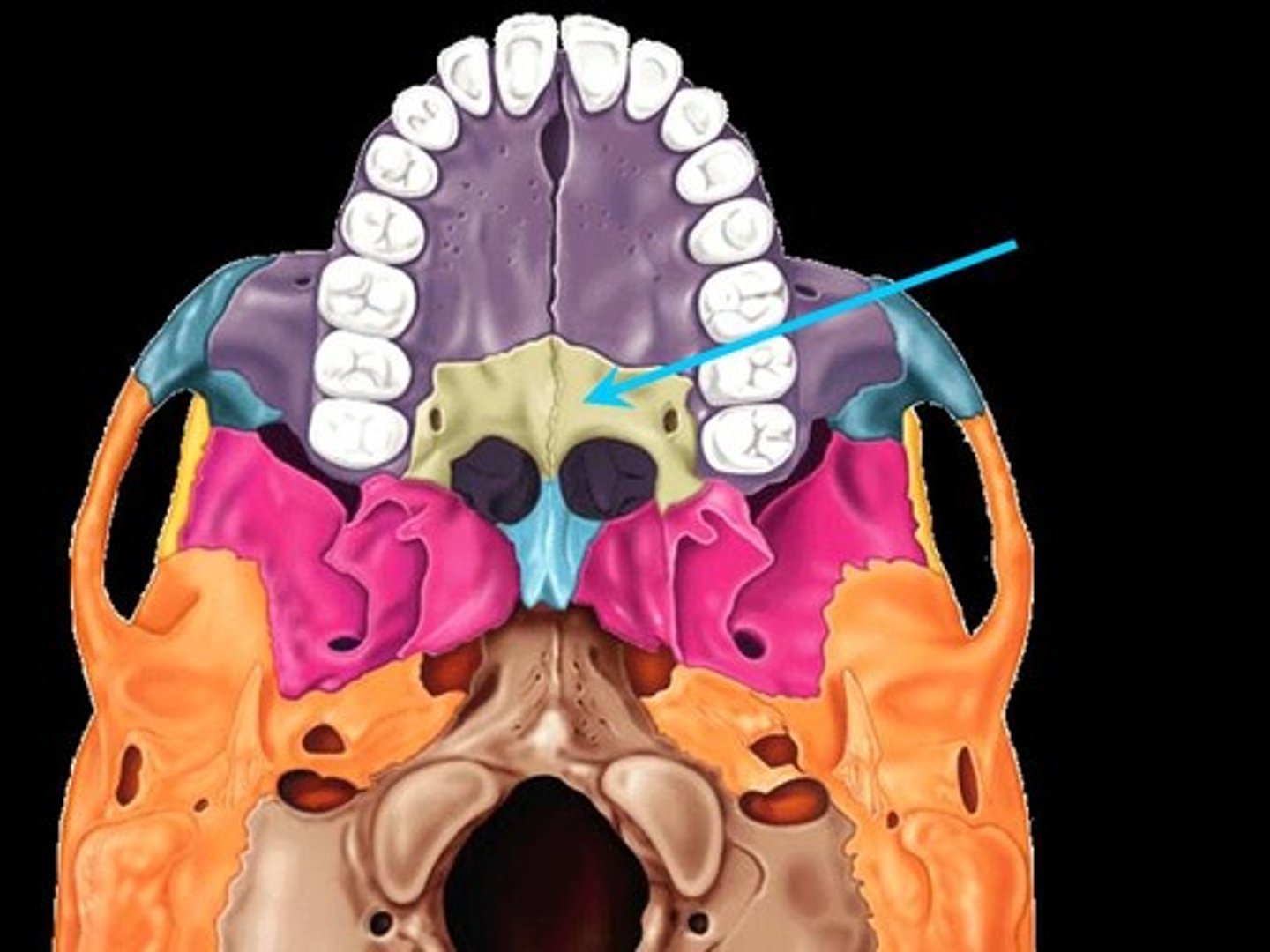
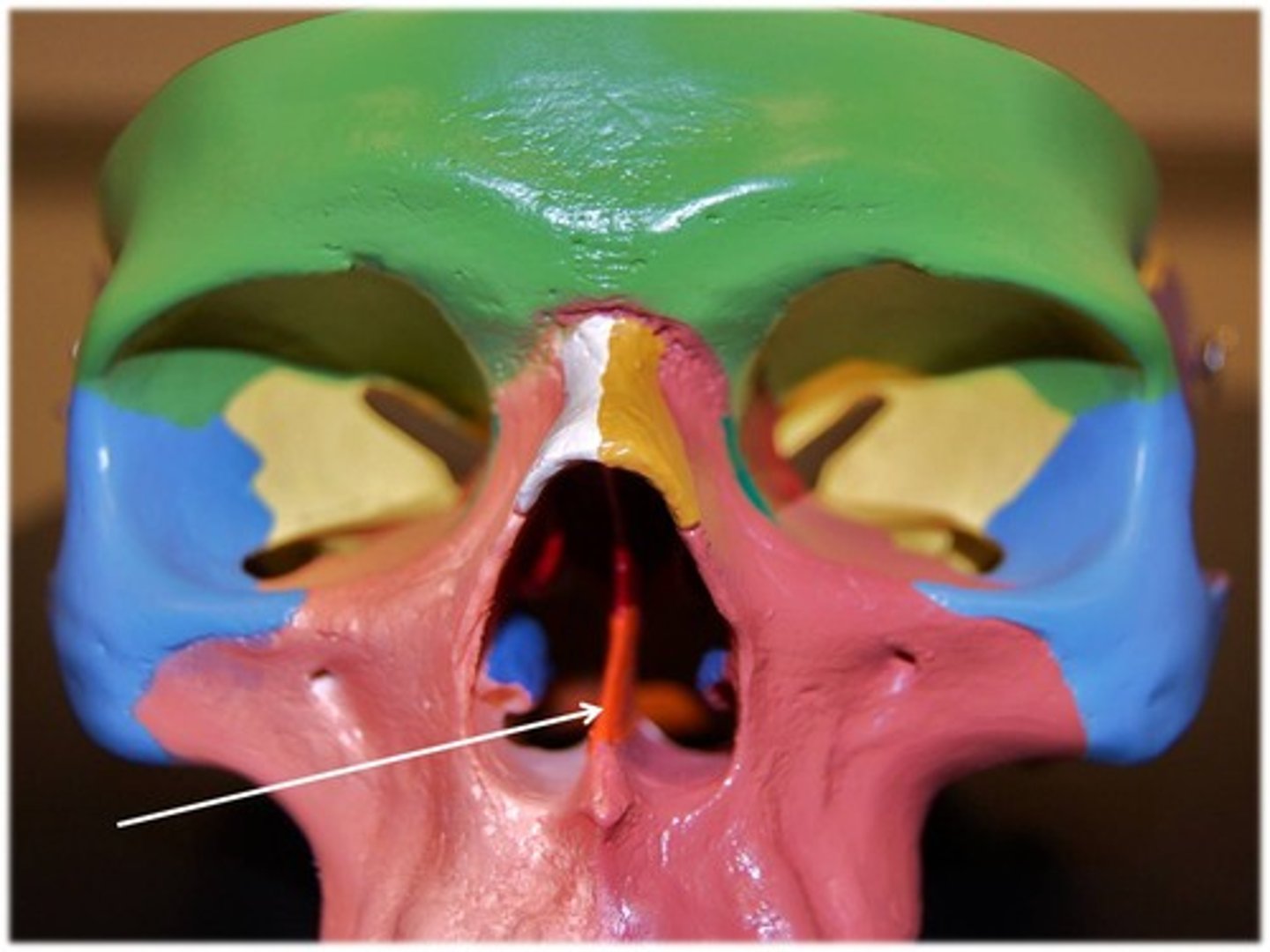
vomer
Articulates with the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid, maxillae and palatine bones along the midline
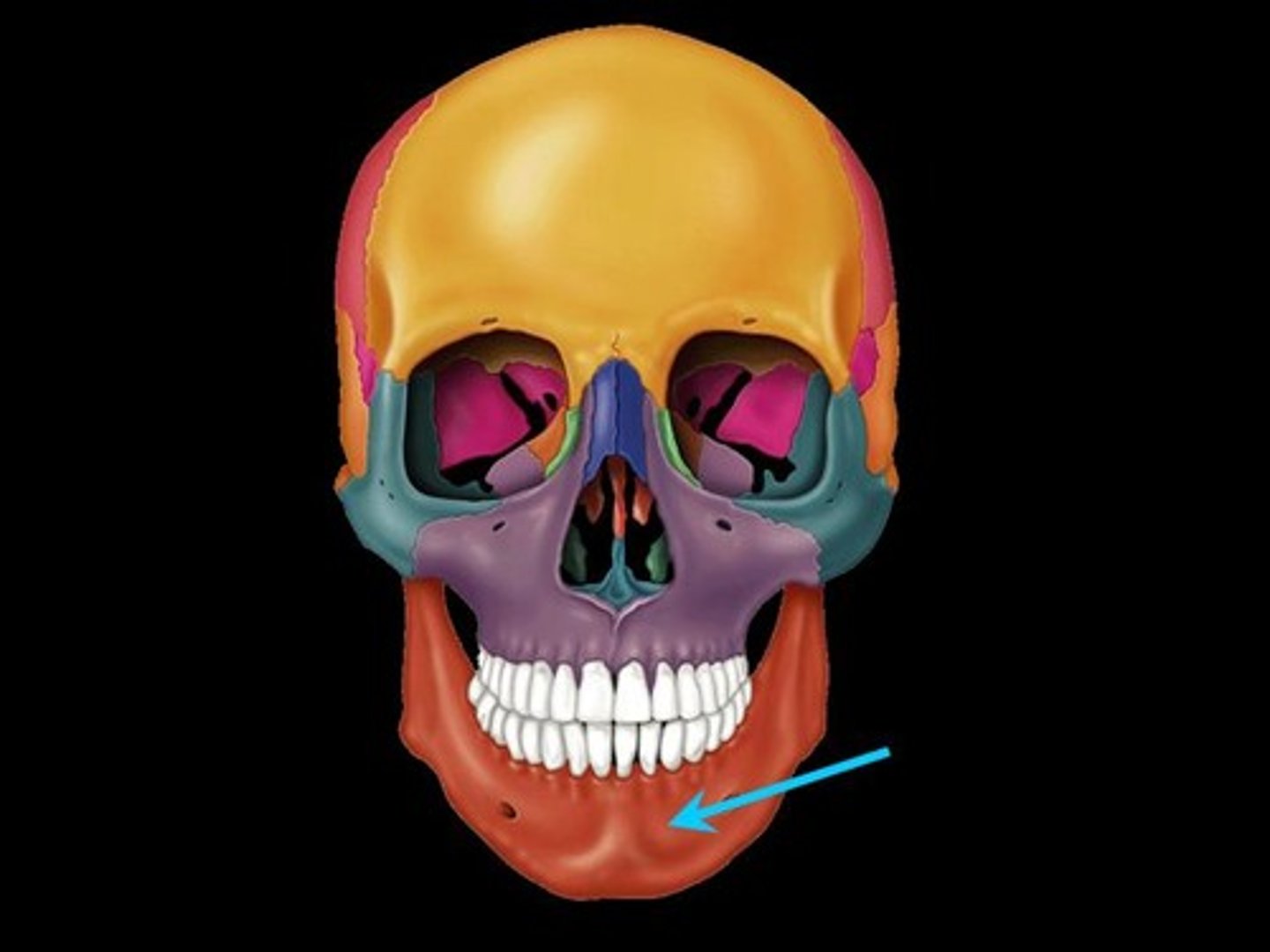
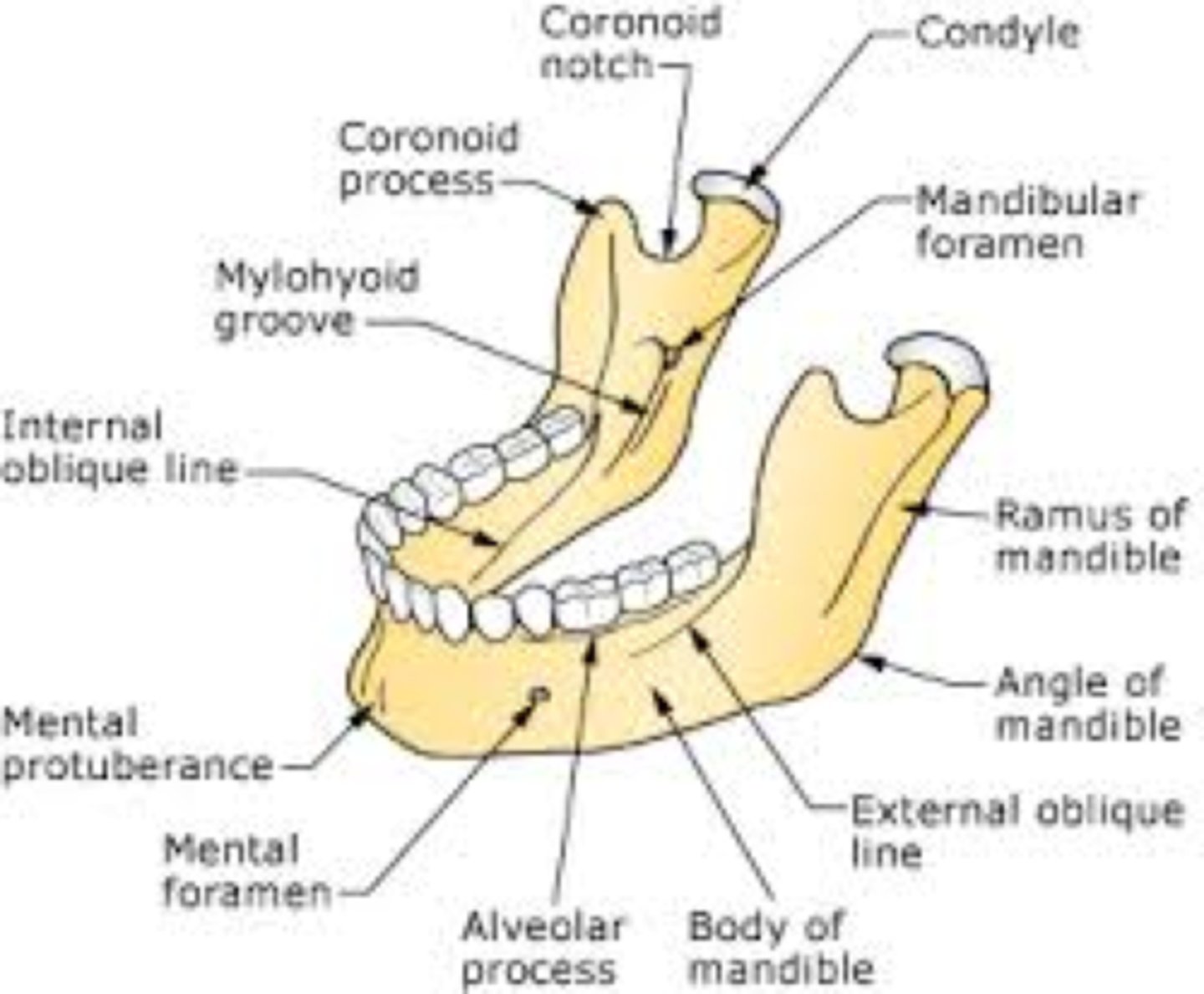
Mandible
lower jaw
Maxillae landmarks
Infraorbital foramen - Maxillary sinus
mandible landmarks
Condylar process - Coronoid process - Mental foramen - Mandibular foramen
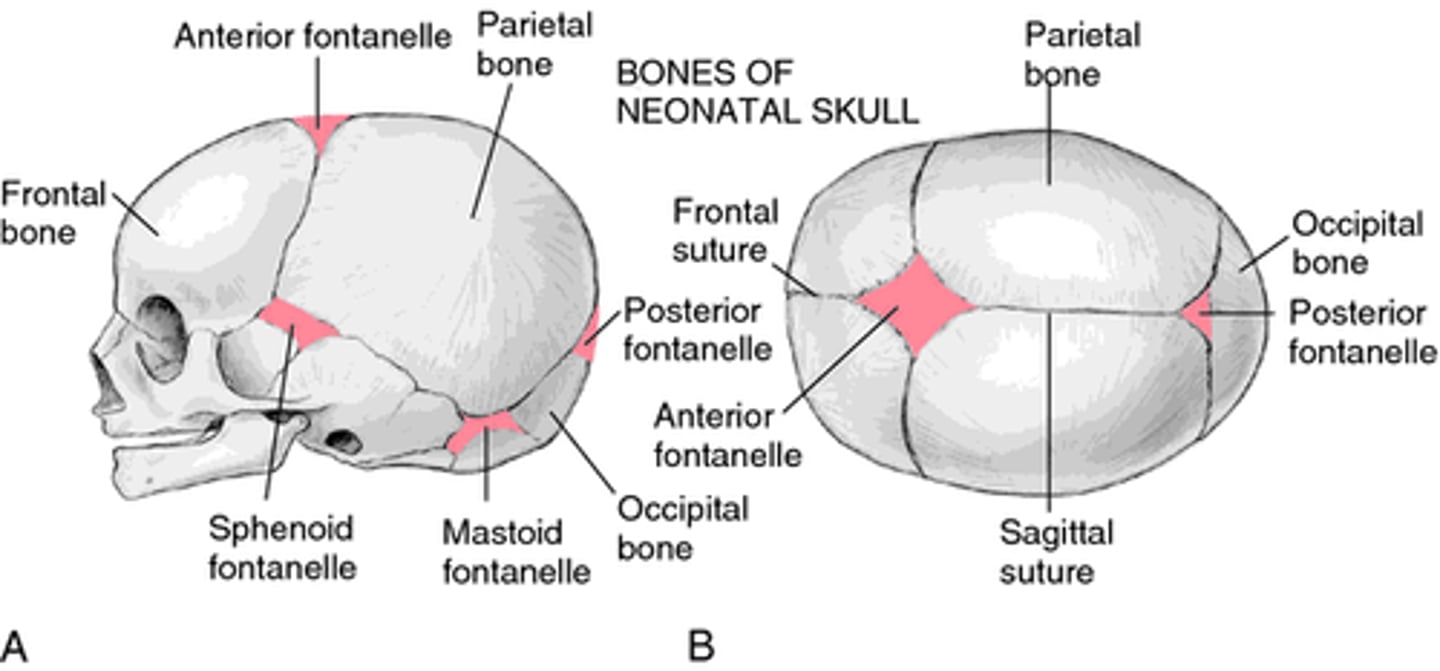
fontanelles
Enables fetal skull to modify size and shape for birth - Permits rapid growth of brain in infancy
uses intramembranous ossification
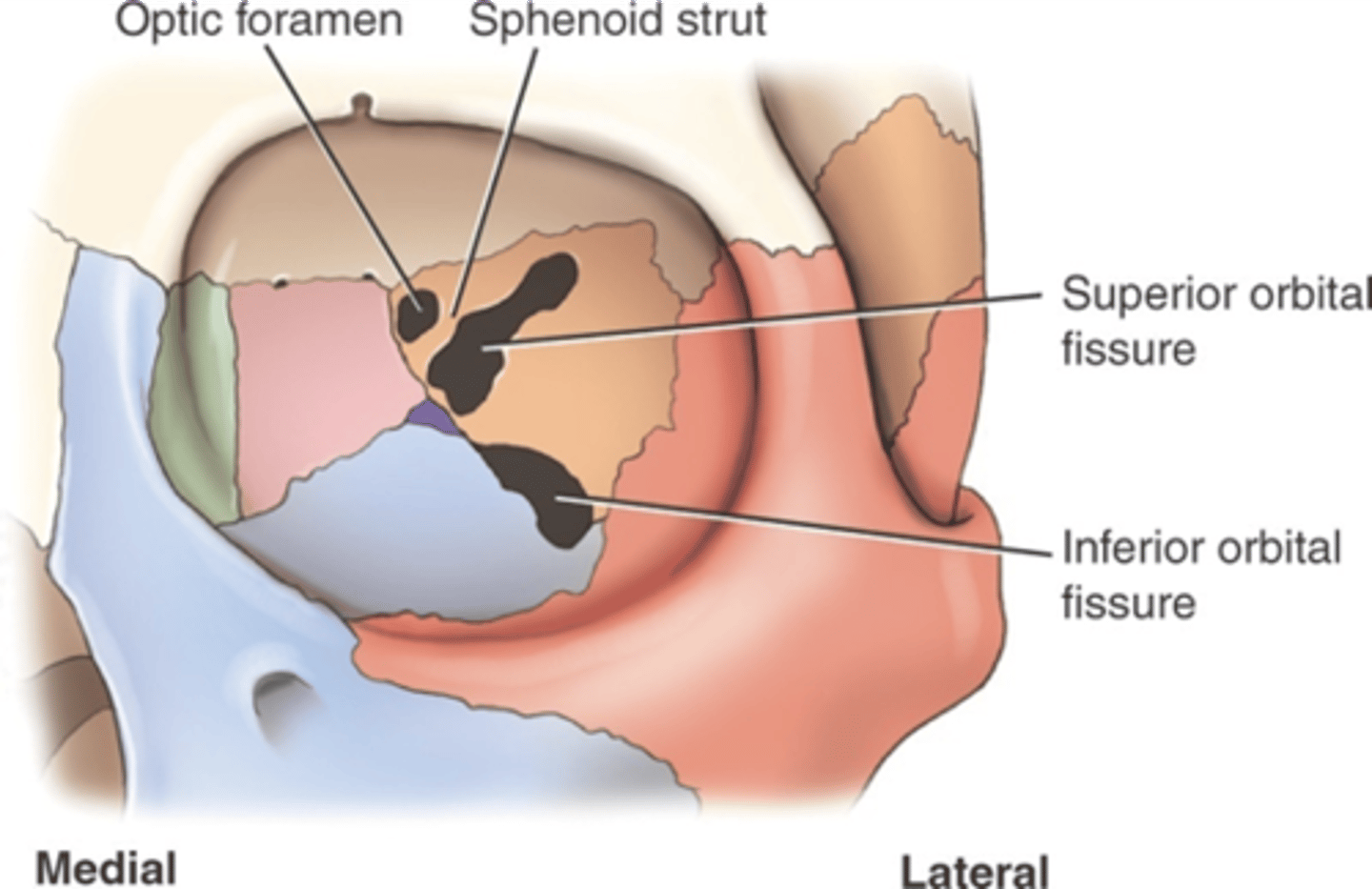
orbit openings
Optic foramen - sphenoid bone - Superior orbital fissure - sphenoid bone - Inferior orbital fissure - maxillary bone - Supraorbital foramen - frontal bone - Lacrimal fossa - lacrimal bone
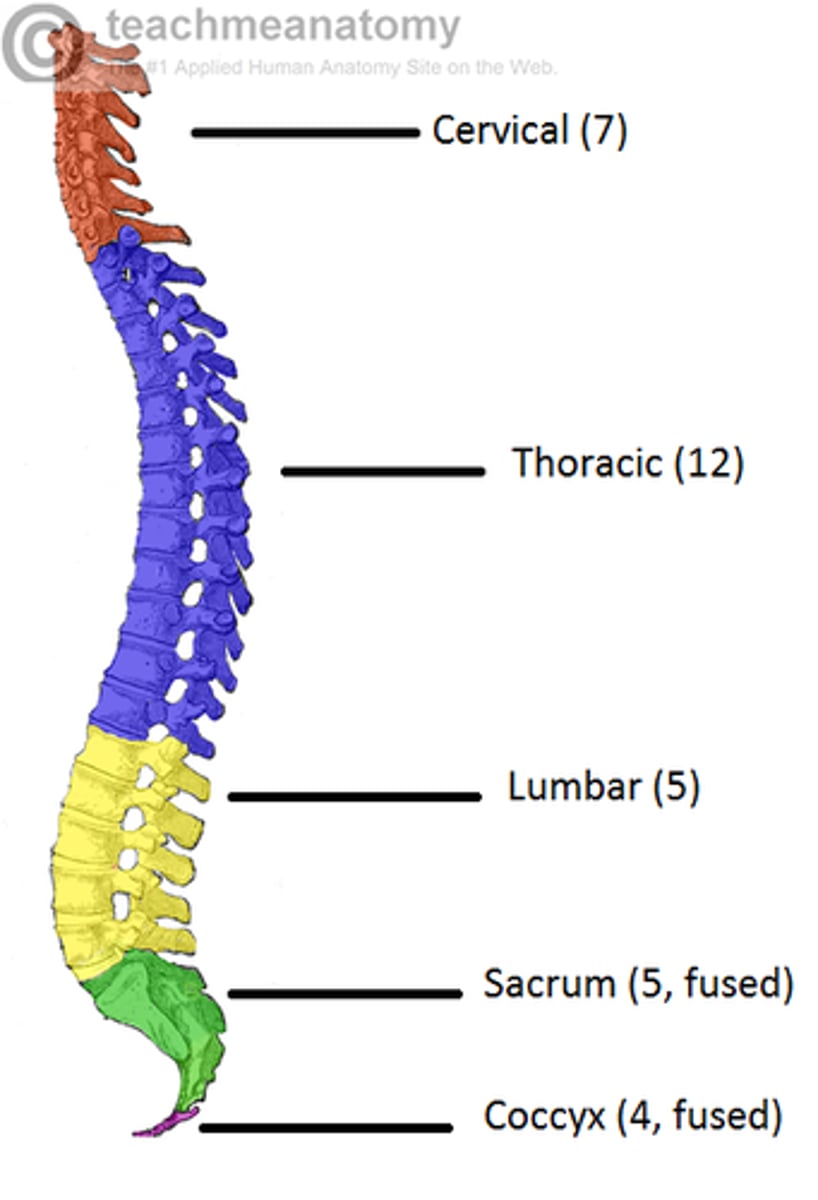
cervical vertebrae number
7 vertebrae
c1-atlas
c2 axis
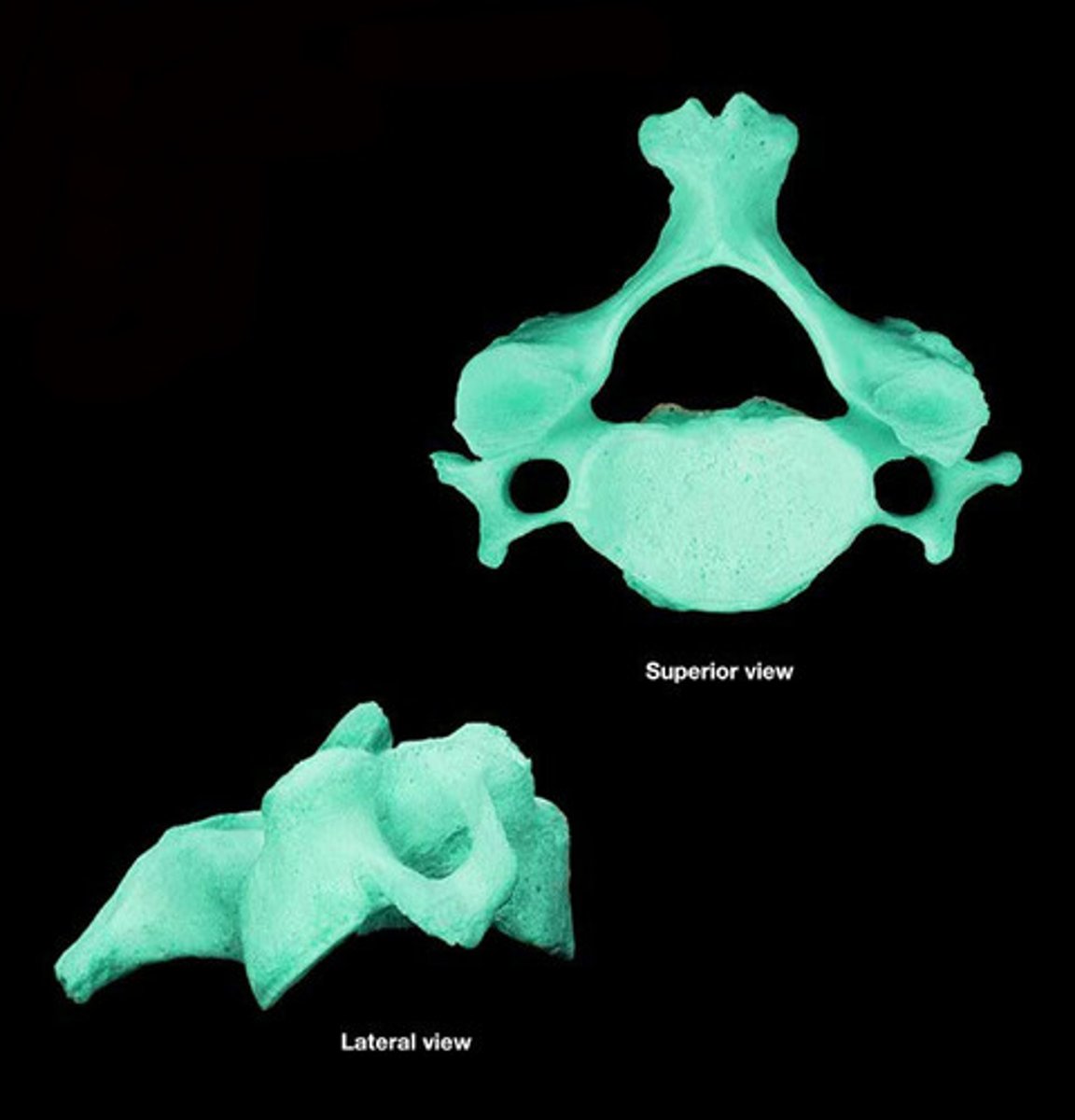
thoracic vertebrae number
12 vertebrae
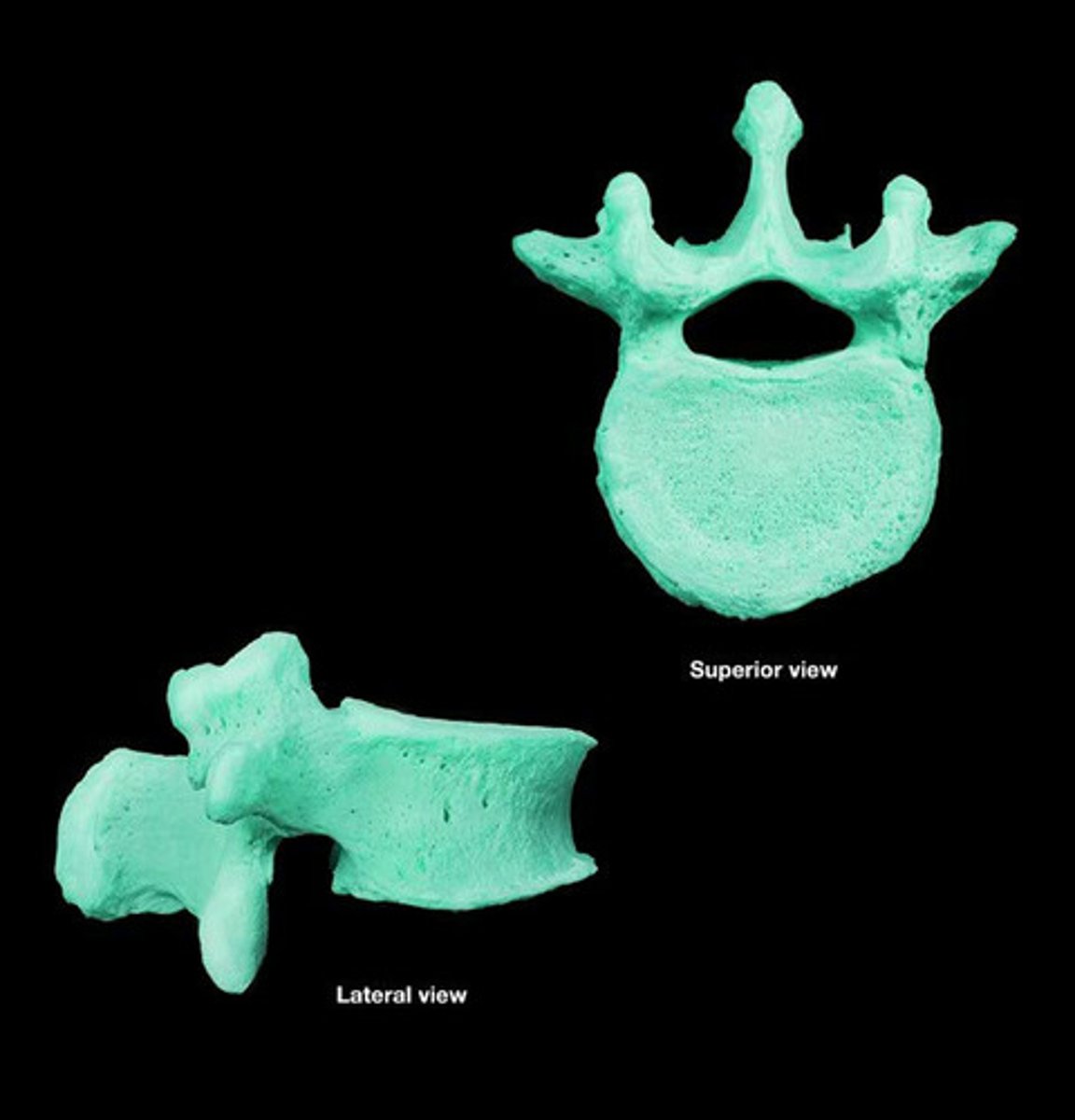
lumbar vertebrae number
5 vertebrae
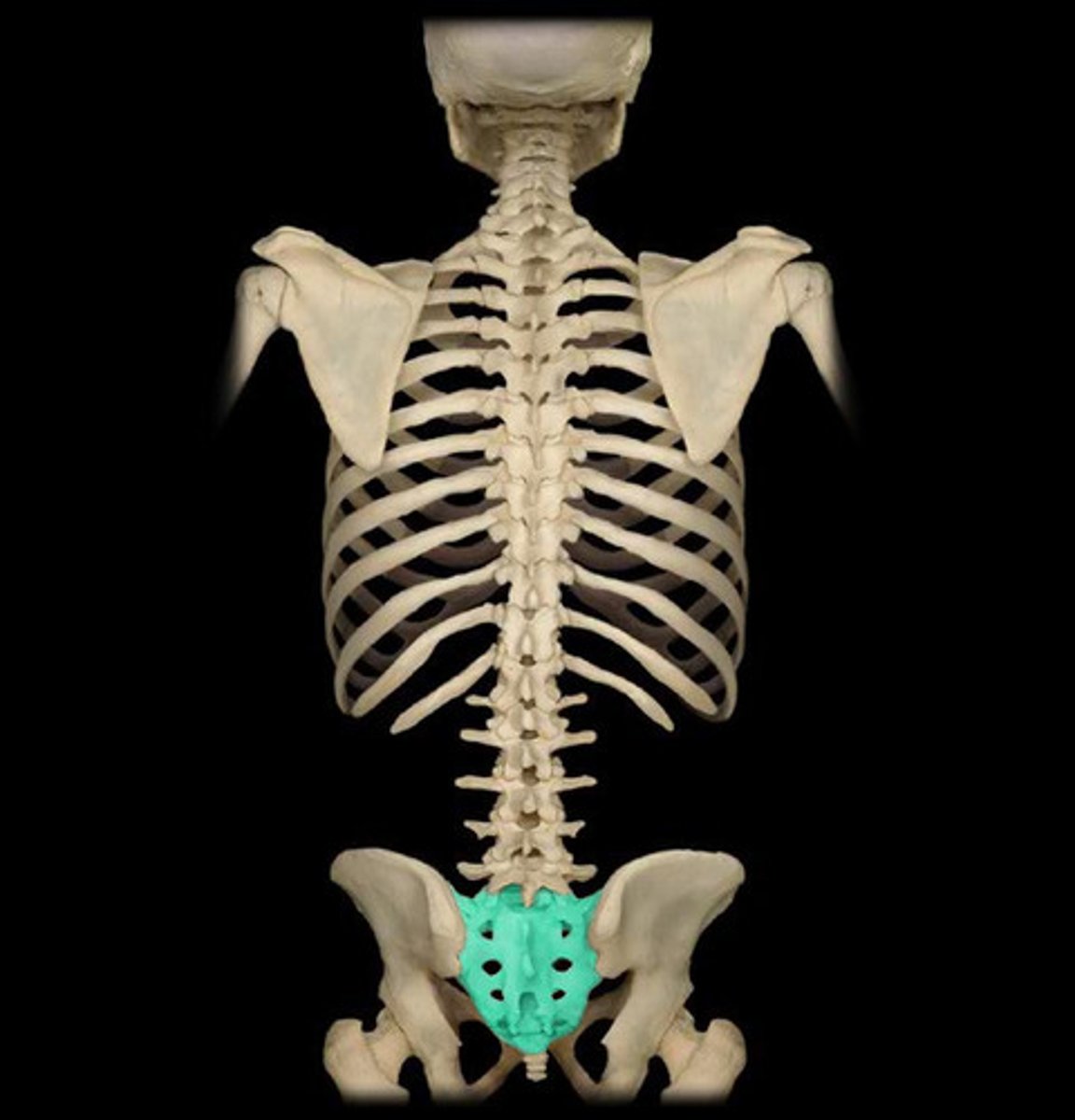
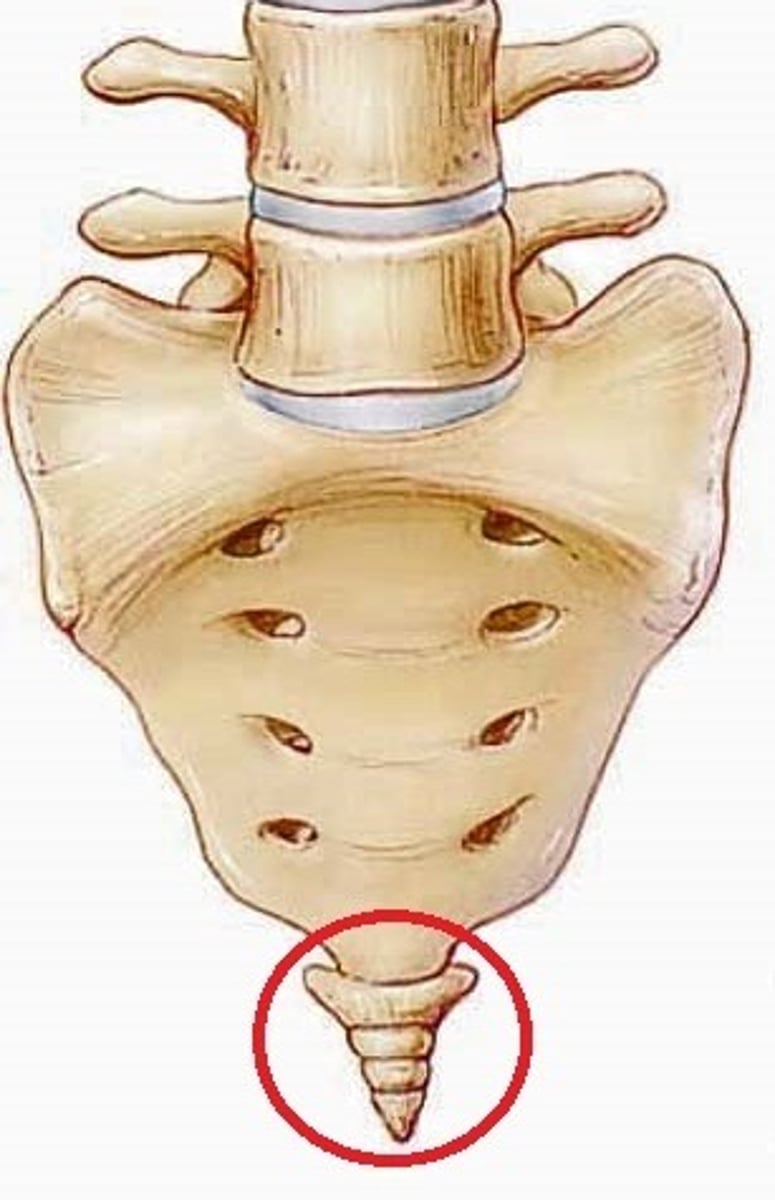
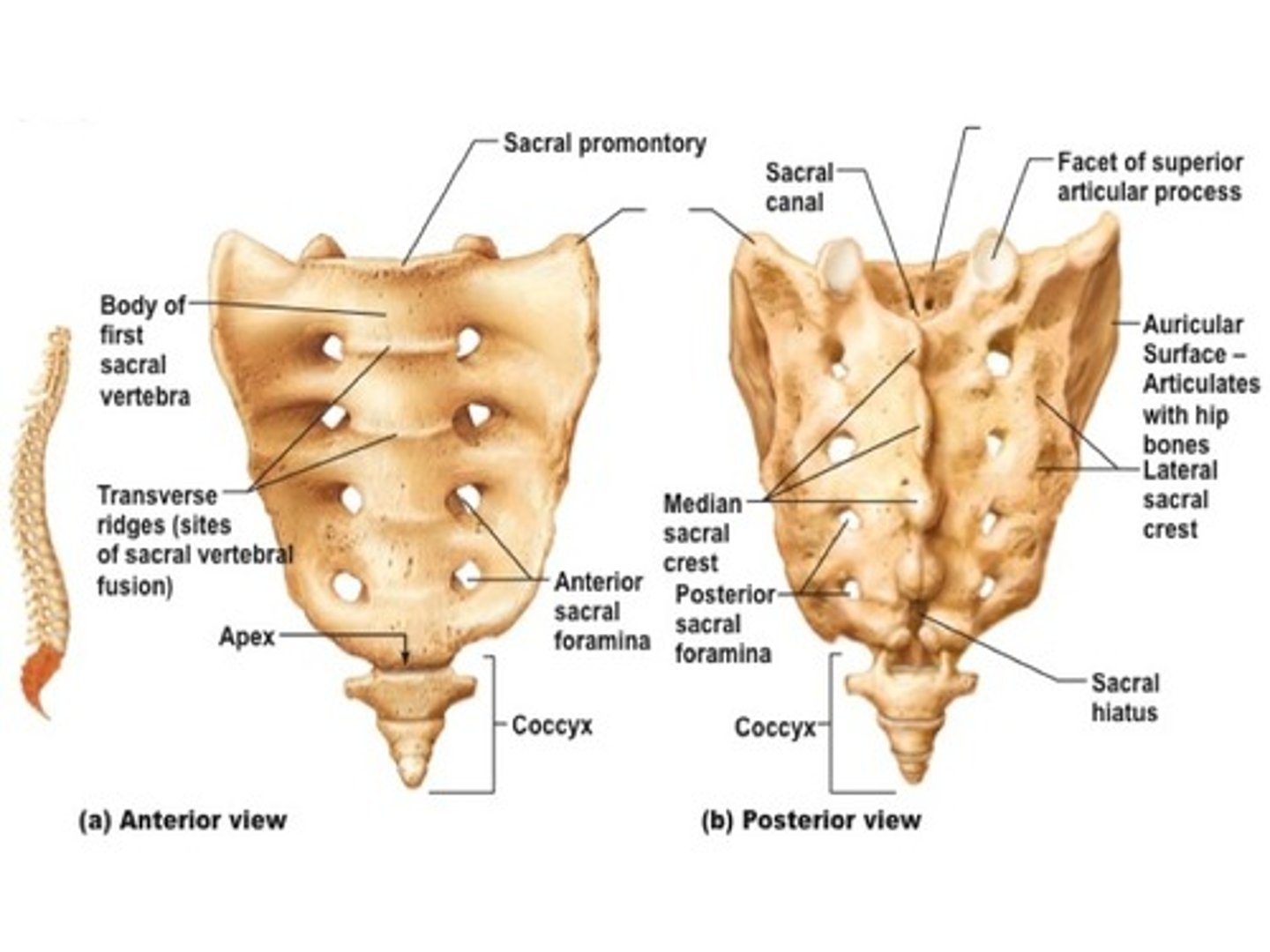
sacral number vertebrae
1 made up of 5 fused vertebrae
coccyx vertebrae number
1 made of 4 fused vertebrae
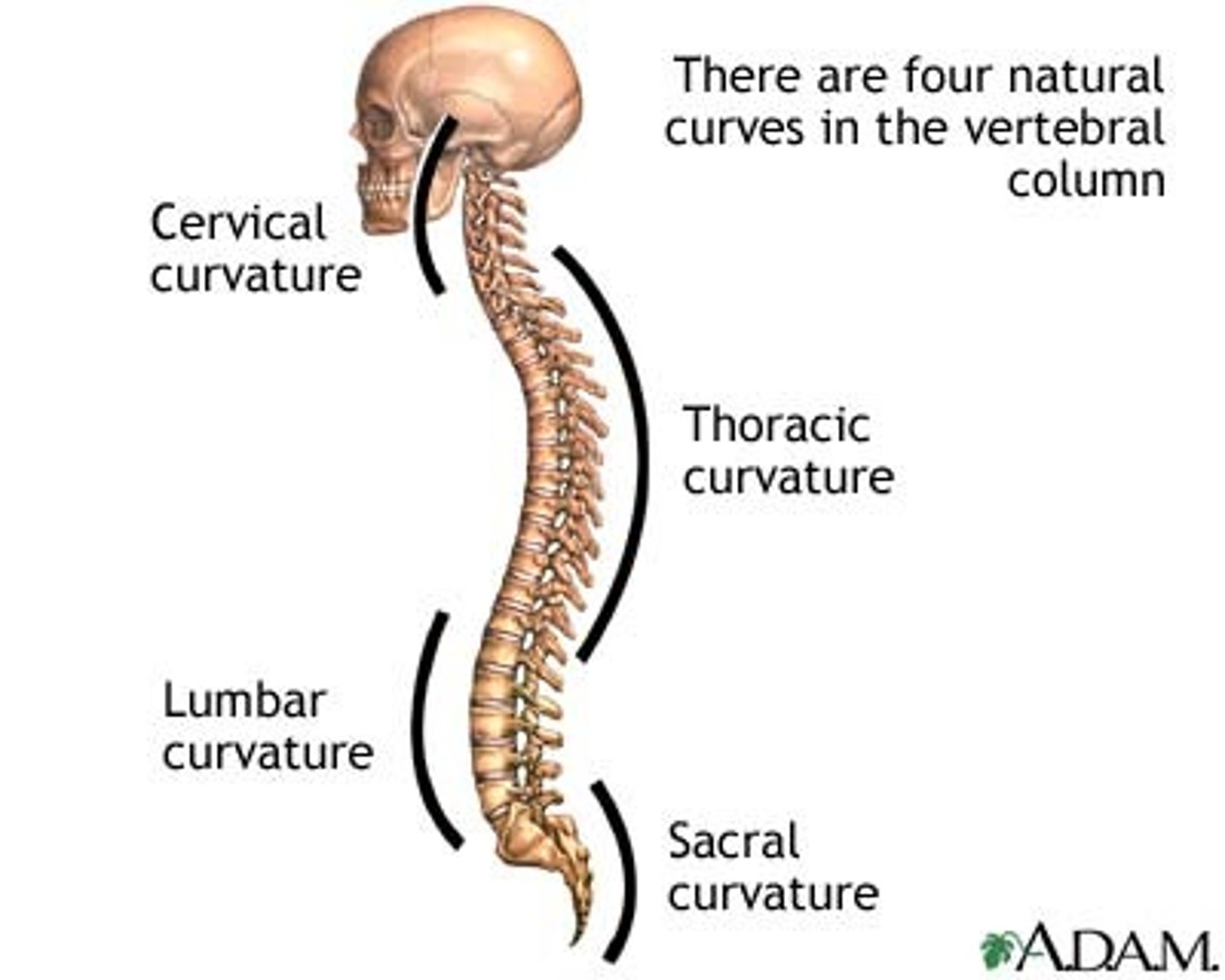
anteriorly convex
bulging out
lumbar and cervical
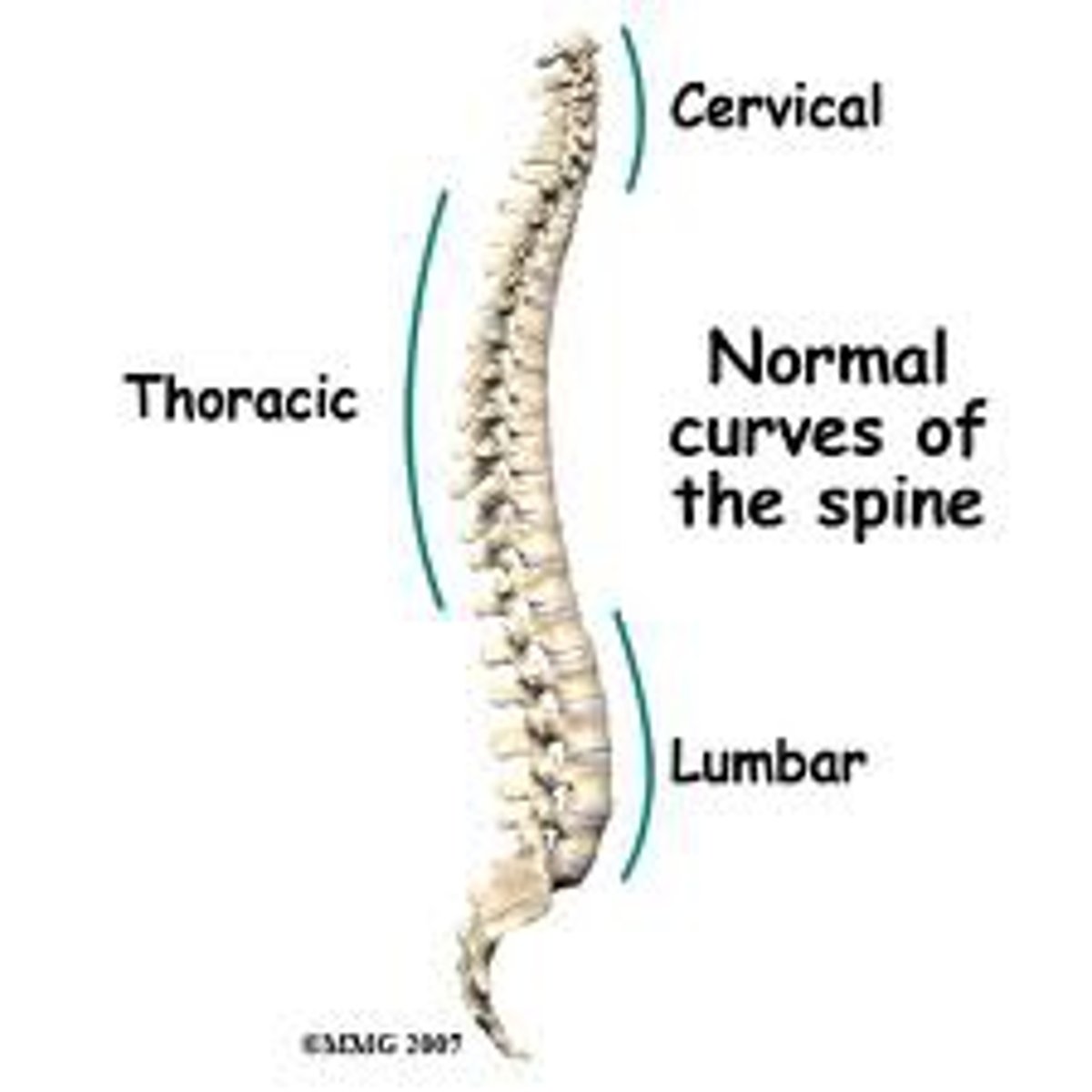
anteriorly concave
cupping in
thoracic and sacral
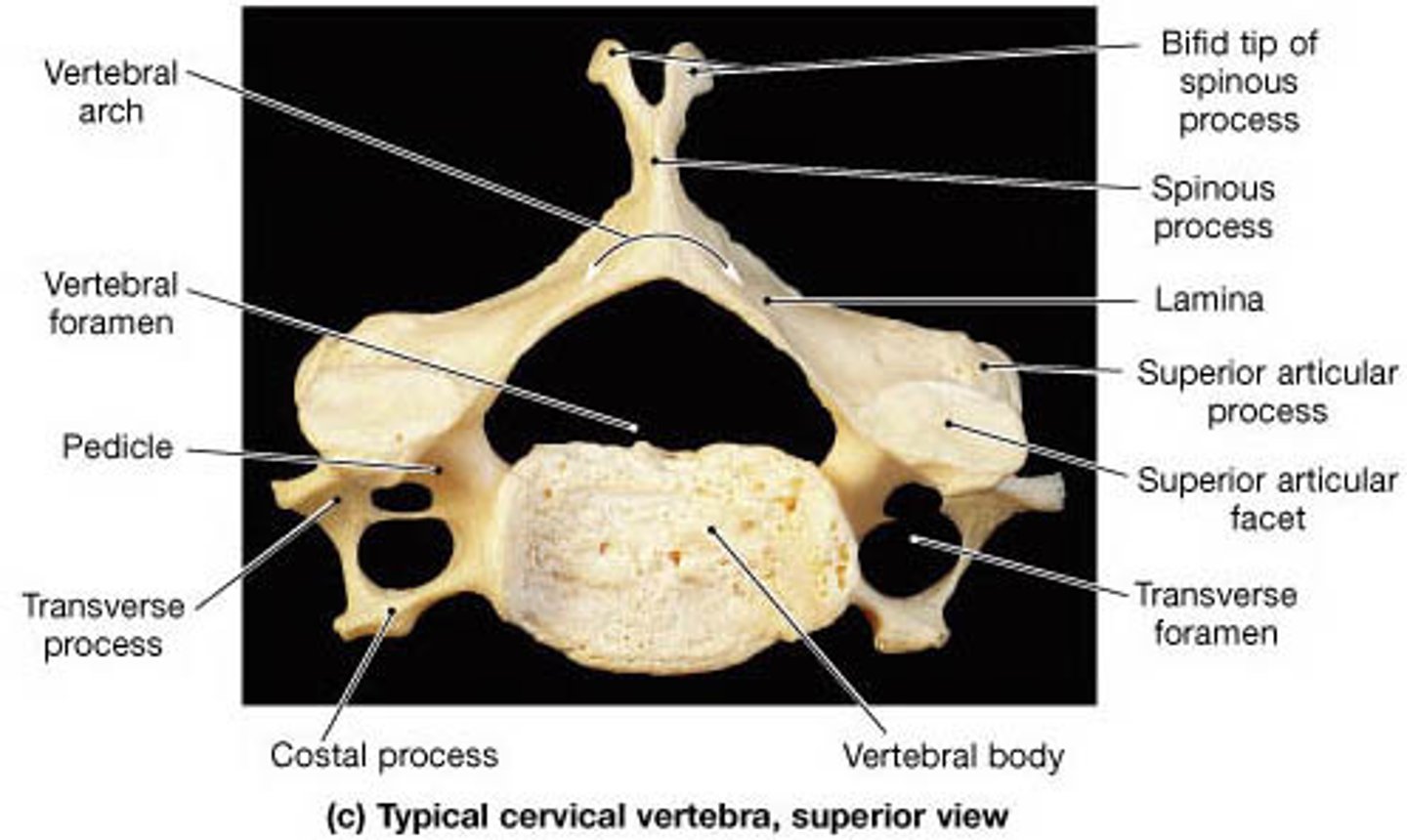
cervical characteristics
3 Foramina - Vertebral - Transverse (2)
• Unique Landmarks - Transverse foramen C1-C7 - Bifid spinous processes of C2-C6
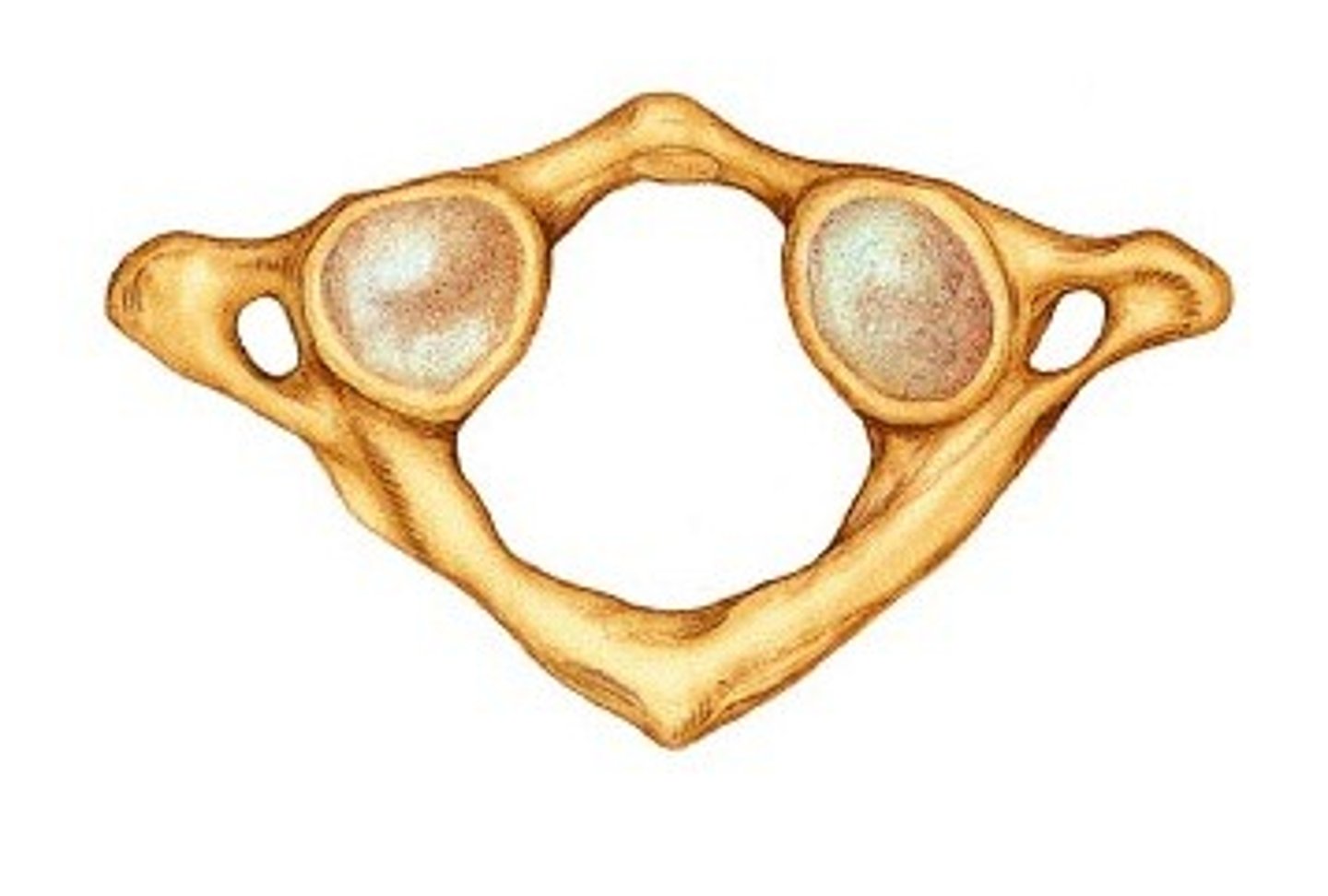
atlas c1
- NO body or spinous process - Permits up and down movement of the head as to signify "yes" - Atlanto-occipital joint
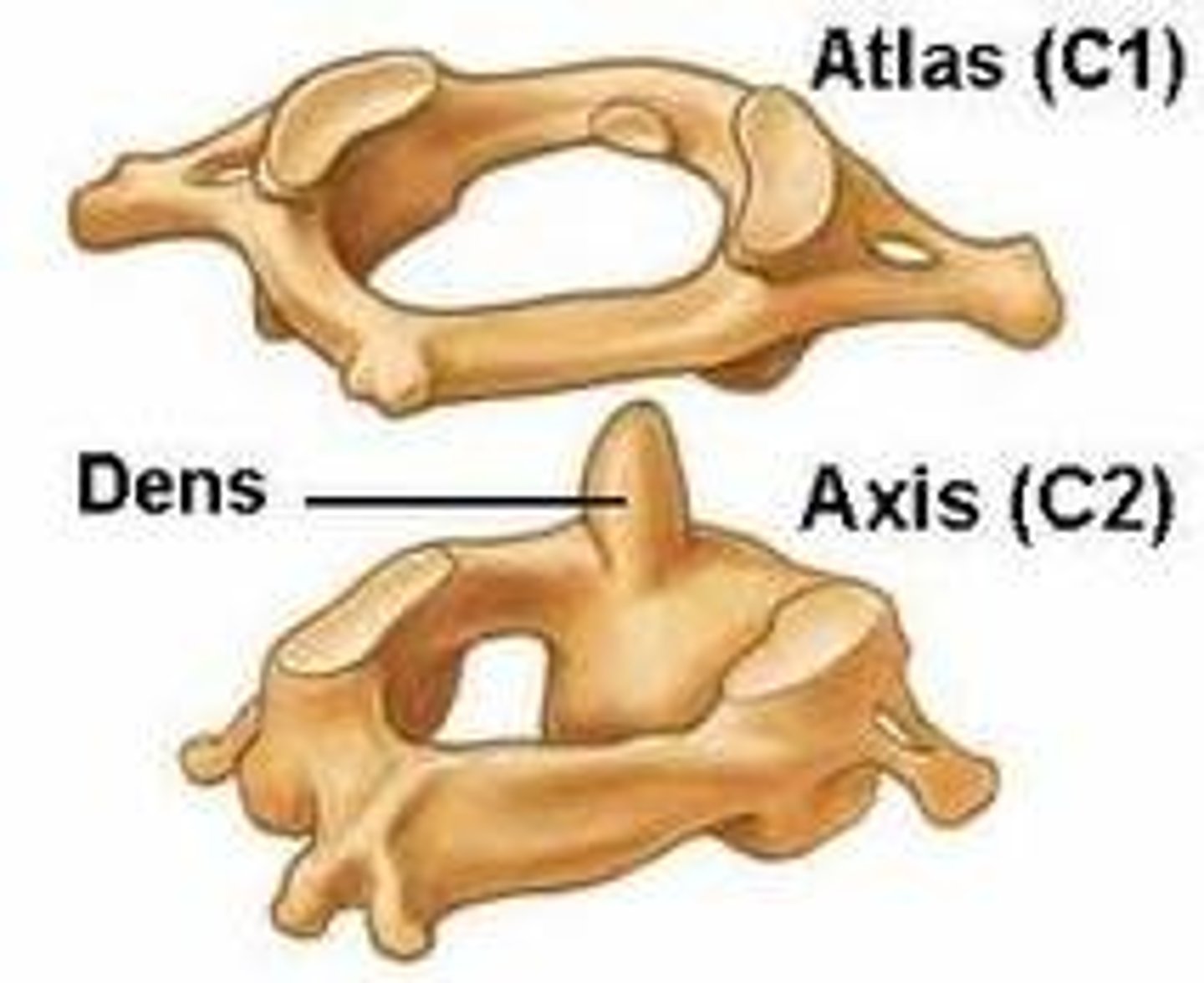
axis c2
Axis C2 - Permits side-to-side rotation of the head to signify "no" - Atlanto-axial joint - Unique Landmark • Dens
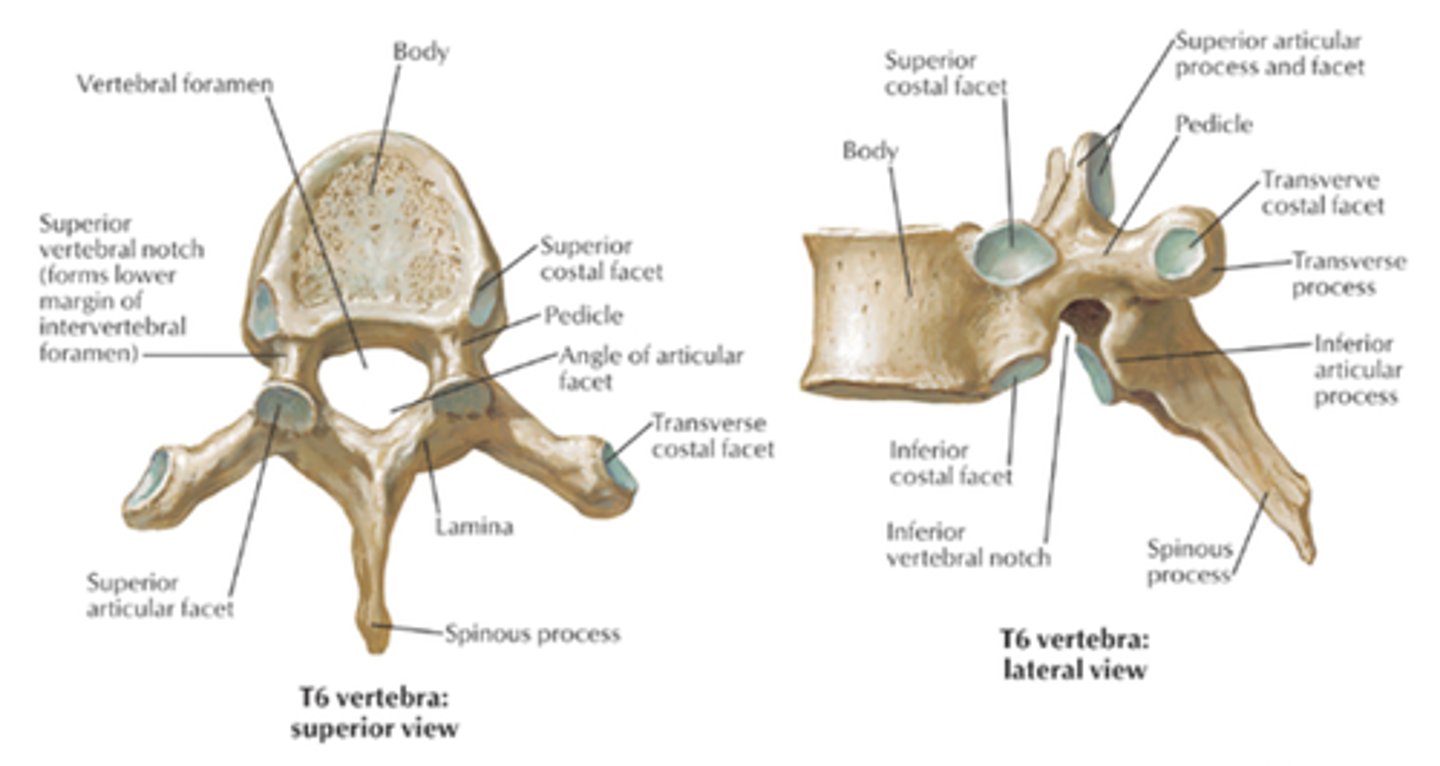
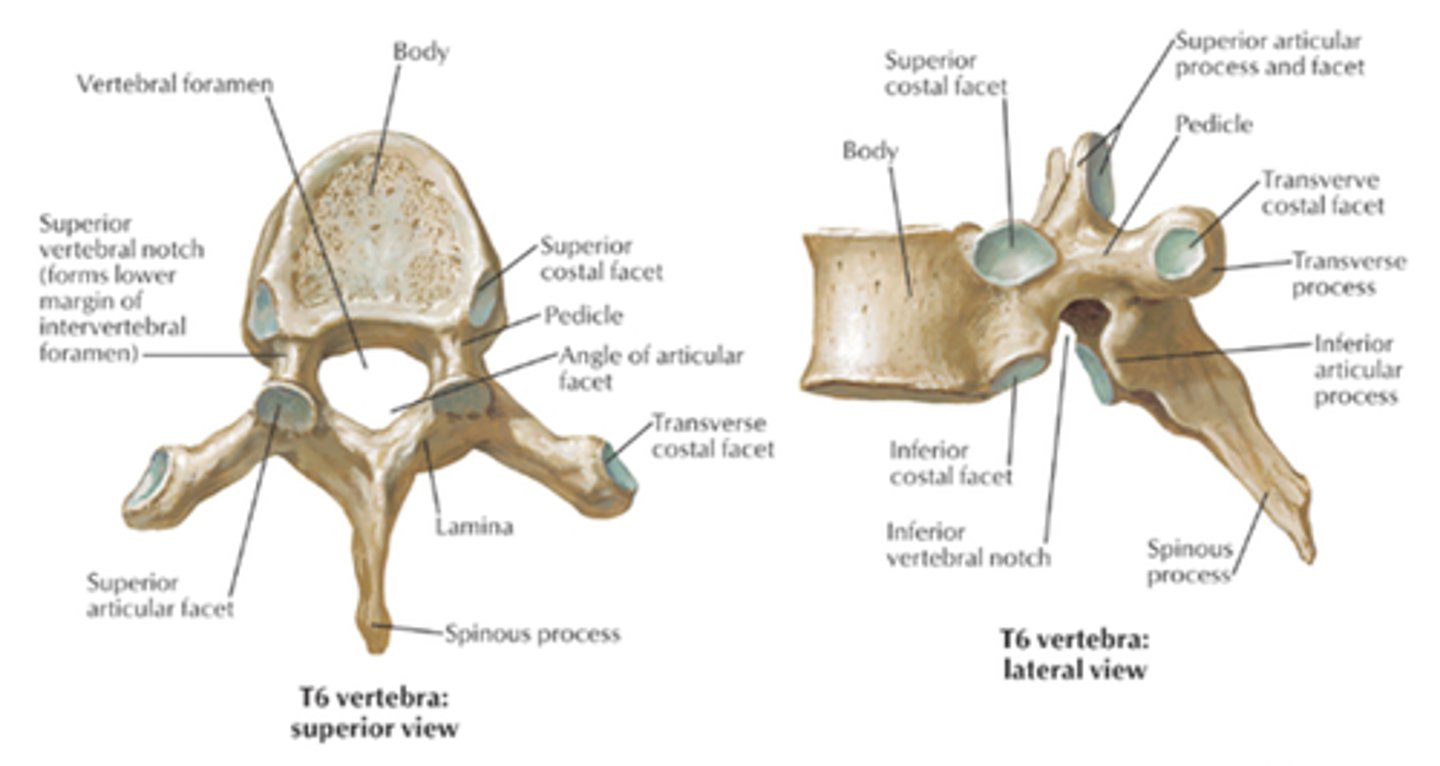
thoracic characteristics
Unique Landmarks - Facets - Demifacets - superior and inferior
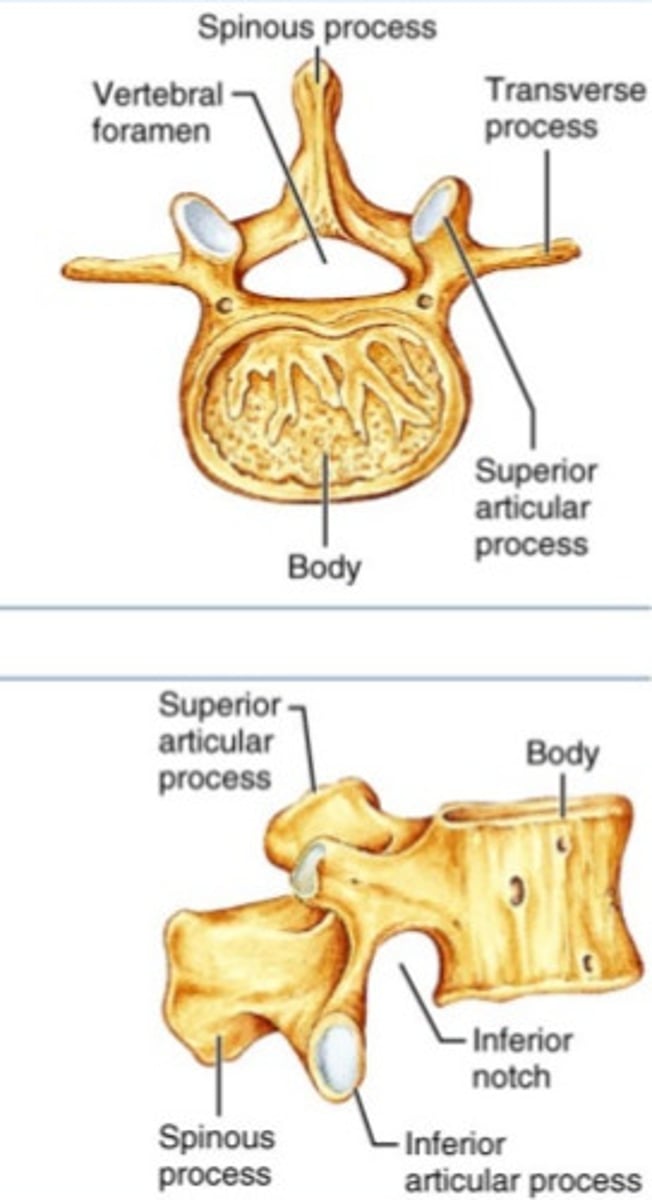
lumbar vertebrae
strongest
sacrum characteristics
Unique Anterior Landmarks - Sacral promontory - Anterior and posterior sacral foramina - Sacral canal
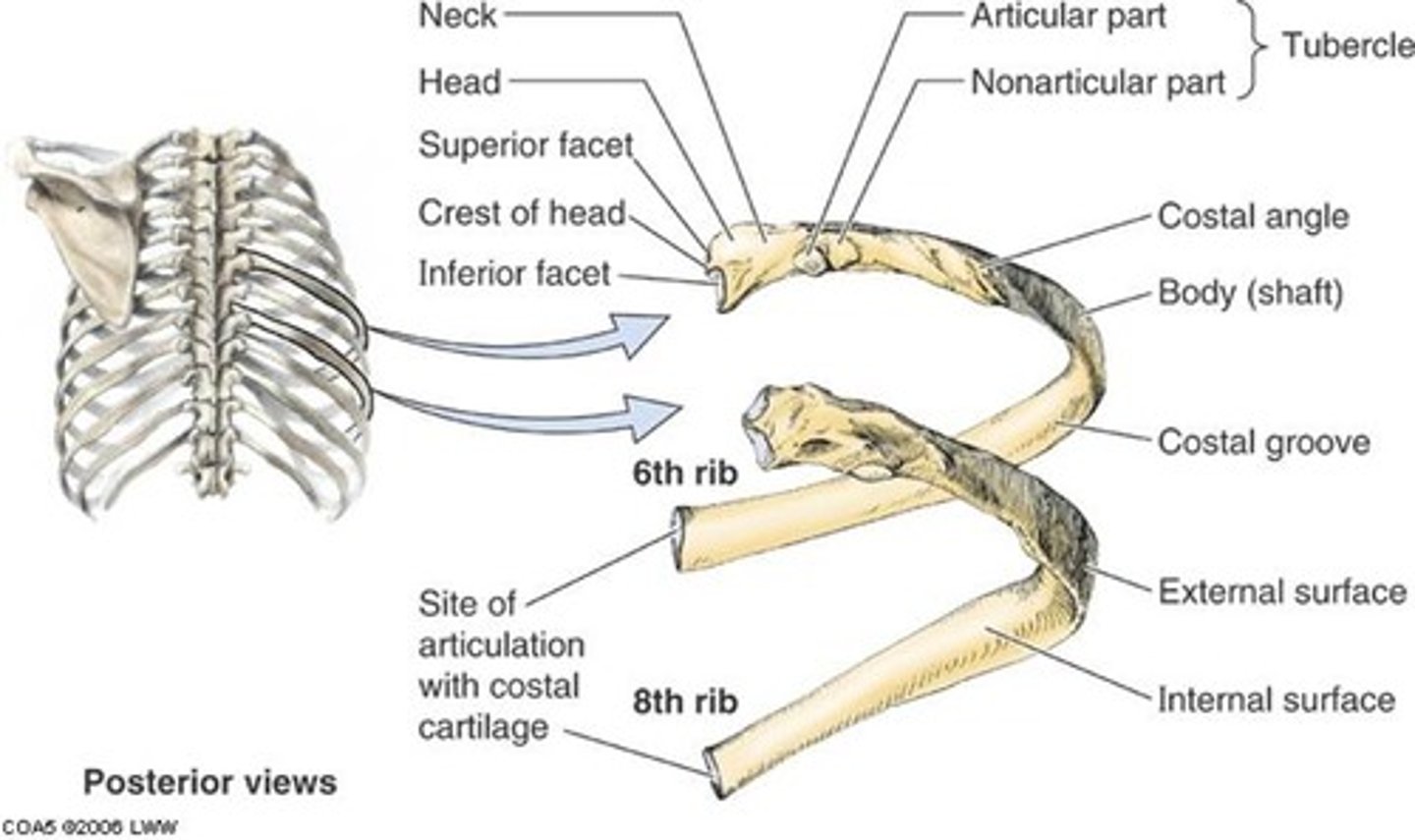
rib landmarks
Head - Neck - Tubercle