DNA replication + Transciption + Translation
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Topoisoherase (2)
Enzyme that relieves the tension of the helix
enables it to unwind
Helicase
Enzyme that breaks hydrogen bonds that hold the two complementary strands together (unzips them)
Single strand binding proteins
Sticks to each strand of DNA, preventing them from reattaching together
What is Primase and how is it used by DNA?
Enzyme that lays down RNA primers
Used by DNA as a marker to build the complementary strands
True or false: DNA polymerase can only move from 5 prime - 3 prime
False, it only moves from 3 prime - 5 prime (on the DNA strand because of the leading strand)
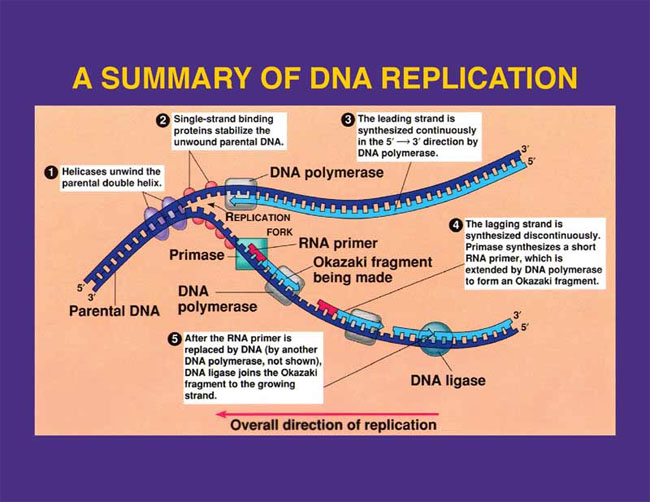
True or false the leading strand is built towards the replication fork (3 prime- 5 prime)
True
True or false a lagging strand is built away from the replication fork continuously
False. Its built away from the replication fork discontinuously
Okazaki fragments
short discontinuous segments of DNA on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
DNA ligase
Joins the gaps with okazaki fragments by creating phosphodiester bonds
True or false: DNA replication takes place during Interphase
False, it takes place during synthesis
Replication bubbles
Bubbles that form on a DNA molecule & cause it to unzip
How do replication bubbles make DNA replication faster
Because there is many happening on 1 strand of DNA
Why can’t DNA leave the nucleus
Its too dangerous, there are things that could damage it
What are 2 advantages of DNA being transcribed into RNA
Protects original copy of DNA
RNA is an efficient information transferer (Sends DNA codes throughout the cell)
3 types of RNA
mRNA (messenger)
tRNA (transfer)
rRNA (ribosomal)
What is the role of mRNA?
Carries DNA information into the ribosome/cytoplasm
What is the role of tRNA?
Delivers Amino Acids to the ribosomes
What is the role of rRNA?
It is the nucleic acid code and it is apart of the ribosome
What is transcription?
Process where DNA is used to create a complementary mRNA strand
3 stages of transcription
initiation
elongation
termination
True or false: Transcription and translation have the same 3 steps
True
True or false: all 3 stages of transcriptions require enzymes
True
What is a codon?
Code/ sequence of 3 nucleotides
EX. AUG
There can be up to ____ codons found in DNA
64
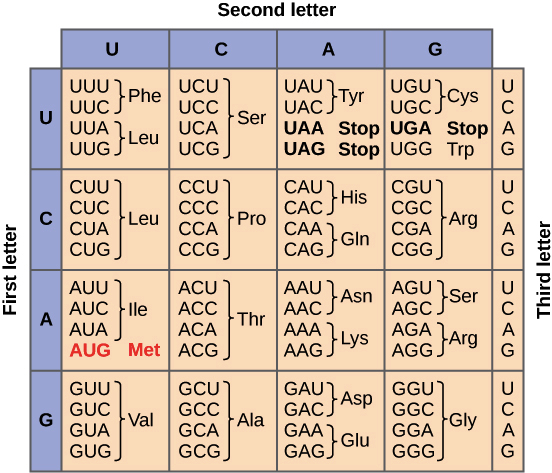
True or false: Each codon codes for a different amino acid
multiple codons may code for the same amino acid
True or false: codons are not continuous, they can overlapp, or have spaces
False, They are continuous and they DONT have any spaces, and overlapp
True or False: Almost all organisms build proteins using the genetic code table
True
Explain the process of initiation in transcription (2)
DNA unwinds
An enzyme called RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter region of the gene and starts building the RNA
Now transcription is initated
True or False: binding RNA polymerase to DNA upstream prevents mistakes
True
The bubble spot in transcription is called the _________
promoter
Explain the process of elongation in transcription (3)
RNA polymerase moves along the DNA, reading the template strand.
It adds RNA nucleotides that are complementary to the DNA.
The mRNA strand gets longer as more bases are added.
Explain the process of termination in transcription (3)
RNA polymerase reaches a termination signal (a stop sequence on the DNA).
It stops building the mRNA.
The mRNA is released, and the DNA rewinds.
4 post transcriptional modifications
5 prime cap
poly a-tail
exons
introns
What is the 5 prime capping method?
7-methylguanosine is added to the 5 prime end of the mRNA
What is the poly-a tail tailing method?
Adding a string of 200 Adenine nucleotides to the 3 prime end of mRNA
Why is the capping and tailing method useful?
It protects the mRNA from being digested by the nuclei and phosphates as it exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm
Exons
coding regions of DNA
Introns
non coding regions of DNA
How are introns advantageous?
It protects mRNA from mutations
Where does translation take place?
In the ribosome
Explain initiation in translation (2)
The ribosome opens up to bind to mRNA
Initiation begins when the mRNA reaches the start codon
True or False: The ribosome reads from 5 prime - 3 prime
True
Explain the process of elongation in translation (6)
tRNA enters the p-site
the anti-codons from tRNA and codons from mRNA match up
a second tRNA enters the A-site
The amino acids from both tRNA molecules bond together
another tRNA enters the p site as the other leaves
This process repeats until the ribosome reaches the stop codon
True or false: The mRNA molecule moves from 5 prime to 3 prime during translation
false, it’s the ribosome that moves NOT the mRNA
the mRNA is stationary
What happens after translation (post translation)
the peptide chain must form a structure
primary
secondary
tertiary
quatenary