Tissues— connective
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
what are the general characteristics and functions of connective tissue?
connective tissue is the most abundant tissue. its extracellular matrix consists of protein fibers and ground substance, and varies from fluid to semi solid to solid. most have good supply, are well-nourished, but vascularity varies among tissue types. Its function is to bind structures together, provide support and protection, serve as frameworks, fill spaces, store fat, produce blood cells, protect against infections, and help repair tissue damage
what are the functions of a normal extracellular matrix?
participates in scaffolding that organizes and anchors cells into tissues, relays chemical signals that control cell division and differentiation, tissue repair, and cell migration
name the 3 major cell types
fibroblasts, macrophages/histiocytes, and mast cells
characteristics and function of fibroblasts
fixed cells because they reside in the specific connective tissue type for an extended period, most common sized cell, large star-shaped. fibroblasts secrete fibers into ECM
characteristics and function of macrophages/histiocytes
wandering/scavanger cells that move through and appear in tissues temporarily, usually in response to an injury or infection. they originate as white blood cells and perform phagocytosis. when they are not wandering they are usually attached to fibers.
characteristics and function of mast cells
fixed, large cells that usually reside near blood vessels. Mast cells release heparin to prevent blood clotting and release histamine that increases blood flow as a result of an inflammatory response.
___ produce 3 types of fibers in connective tissue. name these 3
fibroblasts; collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers
characteristics and function of collagen fibers + location
grouped in long, parallel bundles, collagen is produced from procollagen, and is the body’s pain structural protein. It is grouped in long, parallel bundles. Collagen is flexible, only slightly elastic, provide great tensile strength. They are found in ligaments (bones to bones) and tendons (muscles to bones). There are 2 types: dense and loose connective tissue.
loose connective tissue vs dense connective tissue
loose connective tissue has fewer collagen fibers and has gaps/spaced. dense connective tissue, also called white fibers, contain an a lot of collagen fibers and are tightly packed
characteristics and function of elastic fibers + location
elastic fibers appear yellow and are composed of elastin protein branching. Elastic fibers are elastic, but not very strong. They are found in vocal cords and respiratory air passages
characteristics and function of reticular fibers
reticular fibers are thin, branching fibers of collagen. They form delicate, supporting networks. reticular fibers are found in the spleen and liver.
collagen makes up over __ percent of the protein in bone and cartilage, and to percent of dry weight of skin, tendons, and ligaments. (collagen are in our eyes, blood vessel linings, basement membranes, and connective tissue)
60; 50, 90
name the disease/disorder: collagen chains are asymmetric and too wide, causing stunted growth and deformed joints
chondrodysplasia
name the disease/disorder: short collagen chains that result in joint pain, degeneration of retina and fluid around it
stickler syndrome
name the disease/disorder: deficiency of the protein fibrillin leads to long limbs, spindly fingers, sunken chest, weak aorta, and dislocation of the lens of the eye
marfan syndrome
what does connective tissue proper refer to?
refers to loose or dense connective tissue
what does specialized connective tissue refer to?
cartilage, bone, and blood
name the 3 types of loose connective tissue
areolar, adipose, and reticular
characteristics and function of areolar connective tissue + type of connective tissue (loose/dense)
areolar loose connective tissue forms delicate, thin membranes through the body. It is mainly composed of fibroblasts, which secrete collagen and elastic fibers. areolar connective tissue lies beneath the subcutaneous layers where its many blood vessels nourish nearby epithelial cells. It binds the skin to the underlying organs and fills spaces between muscles.
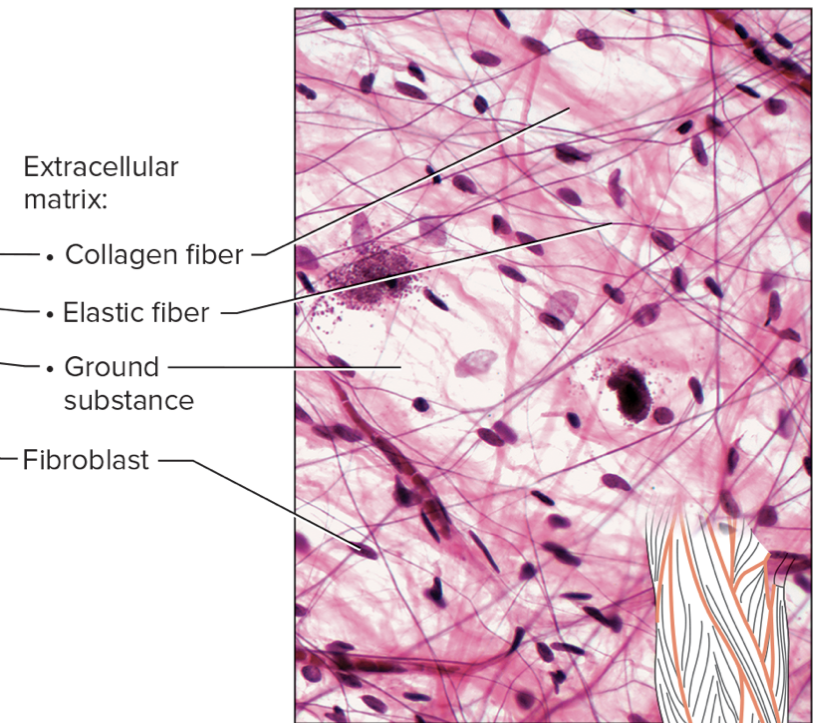
name the tissue + type of connective tissue (loose/dense/specialized)
areolar loose connective tissue
characteristics and function of adipose connective tissue + type of connective tissue (loose/dense)
adipose loose connective tissue develops when adipocytes store fat in the form of droplets in their cytoplasm and begin to crowd. Initially, they resemble fibroblasts, then they accumulate fat causing them to enlarge, pushing the nuclei to the side. adipose tissue insulates and cushions joints, membranes, and organs, and stores energy (in fat molecules). They can be categorized into white and brown adipose tissue. white fat stores nutrients for nearby cells to use and brown fat have mitochondria that can break down nutrients to generate heat (abundant in back, neck, around kidneys).

name the tissue + type of connective tissue (loose/dense/specialized)
adipose loose connective tissue
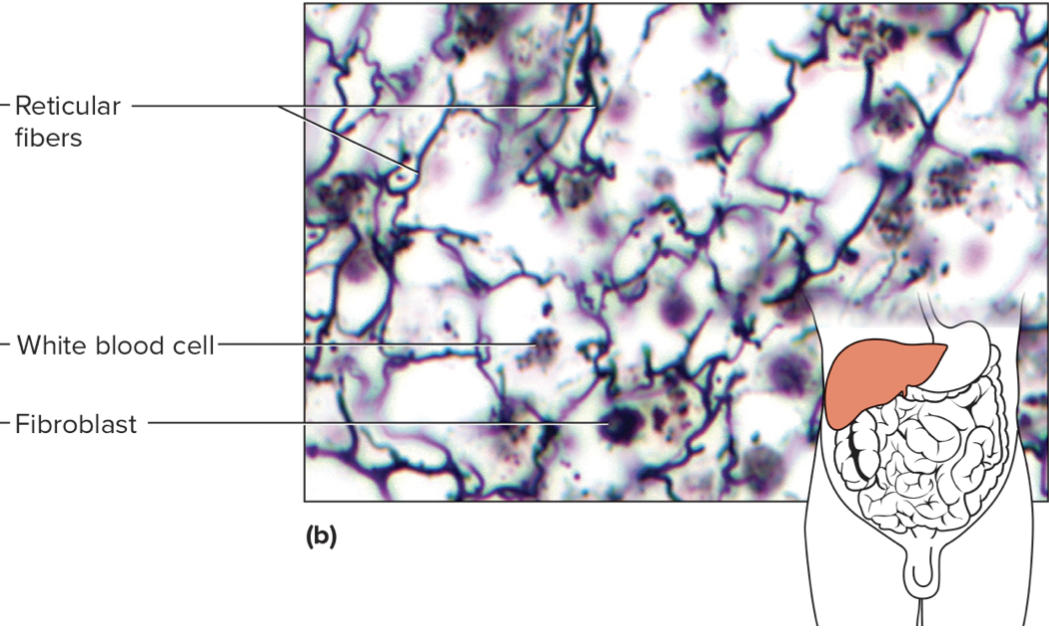
name the tissue + type of connective tissue (loose/dense/specialized)
reticular loose connective tissue
characteristics and function of reticular connective tissue + type of connective tissue (loose/dense)
reticular loose connective tissue is composed of thin, reticular fibers in a three-dimensional network. It helps provide the framework of certain internal organs (e.g. spleen, liver)
name the 3 types of dense connective tissue
dense regular, dense irregular, and elastic tissue
characteristics and function of dense regular connective tissue
dense regular connective tissue mainly consists of closely packed, thick, collagen fibers, a fine network of elastic fibers, and a few cells (mostly fibroblasts). Dense regular connective tissue binds body structures as part of tendons and ligaments. Its blood supply is poor, resulting in slow tissue repair

what type of connective tissue is this?
dense regular connective tissue
characteristics and function of dense irregular connective tissue
dense irregular connective tissue is thicket, interwoven, and has more randomly distributed fibers which allows the tissue to sustain tension exerted from many directions. Dense irregular connective tissue covers bones (periosteum), covers cartilage (perichondrium), and are found on capsules of some organs and the dermis (inner skin layer). Dense irregular connective tissue also surrounds individuals skeletal muscles (fascia) and separates each muscle into bundles of skeletal muscle cells, each surrounded by areolar connective tissue.
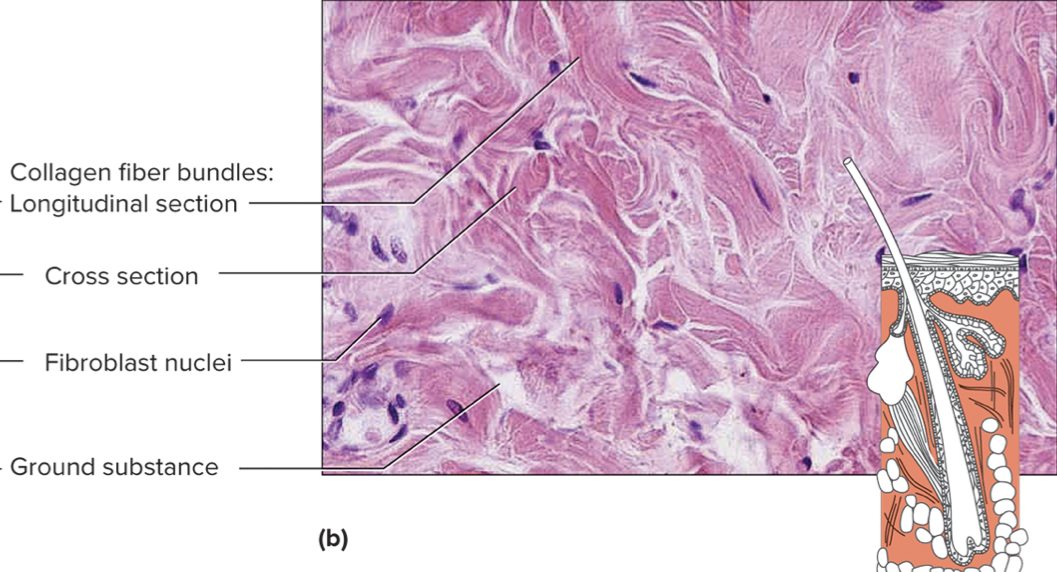
what specific connective tissue is this?
dense irregular connective tissue
characteristics and function of dense elastic connective tissue?
dense elastic connective tissue consists of yellow, elastic fibers in parallel strand or in branching networks. between elastic connective tissue are collagen fiber and fibroblasts. elastic connective tissue is found in attachments between bones and spinal column, and in layers within walls of certain hollow internal organs (larger arteries, some portions of the heart, larger airways)
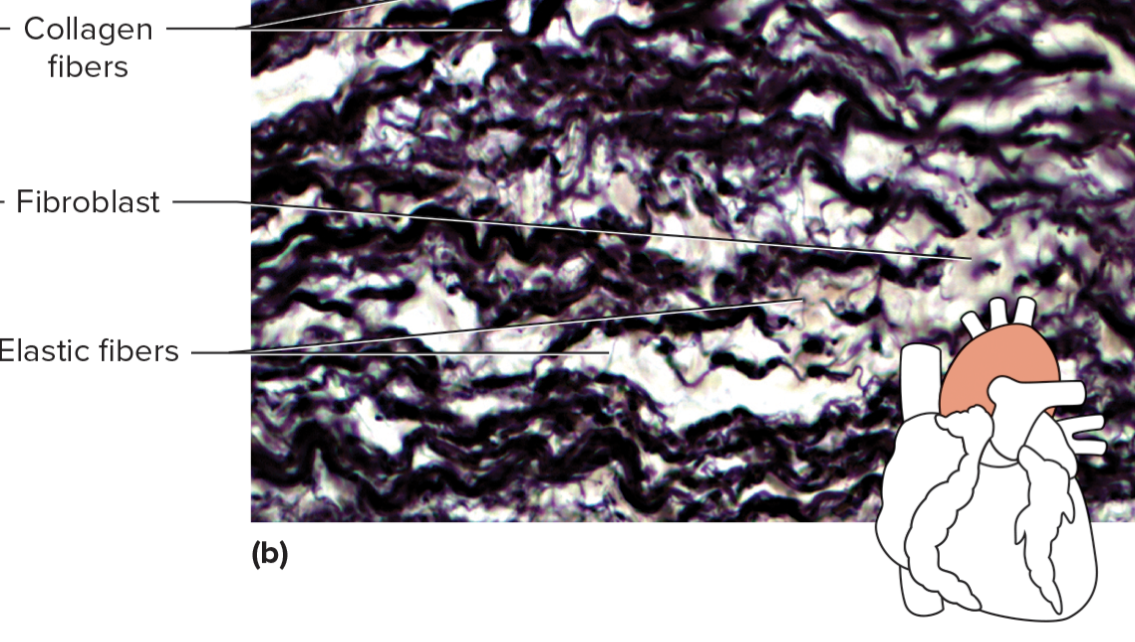
what specific kind of connective tissue is this?
dense elastic connective tissue