Lecture 6: Instrumental Variables
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
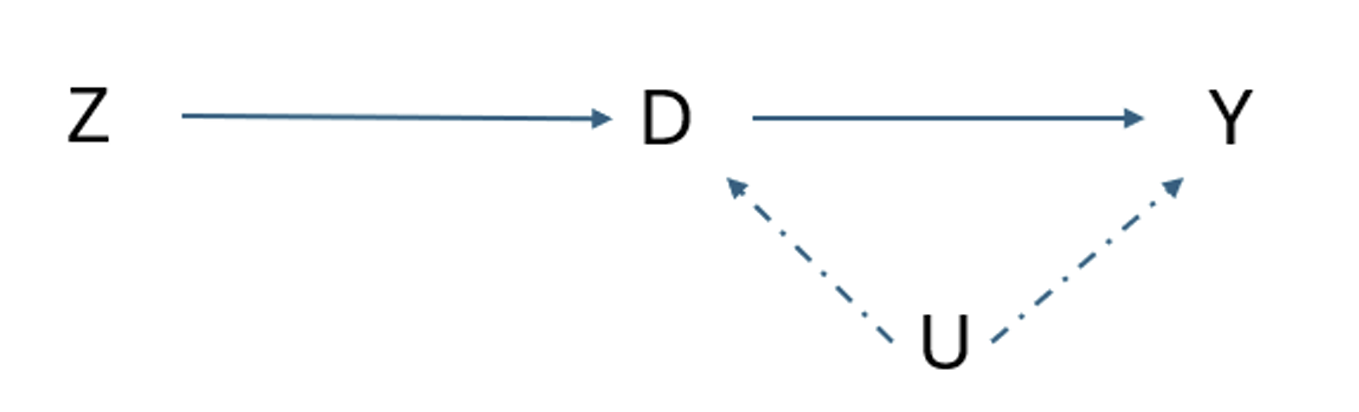
What is the backdoor?
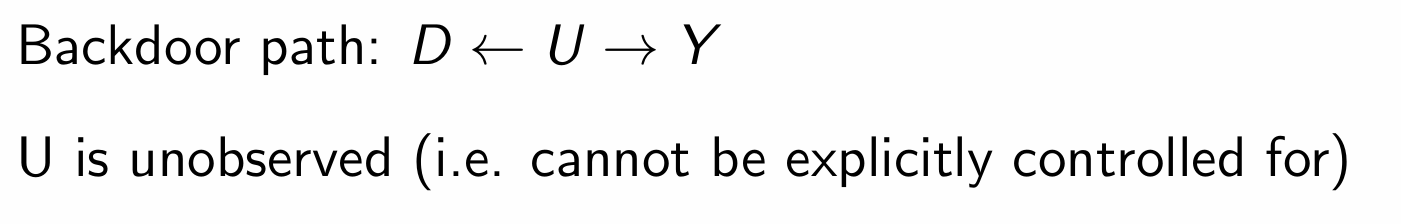
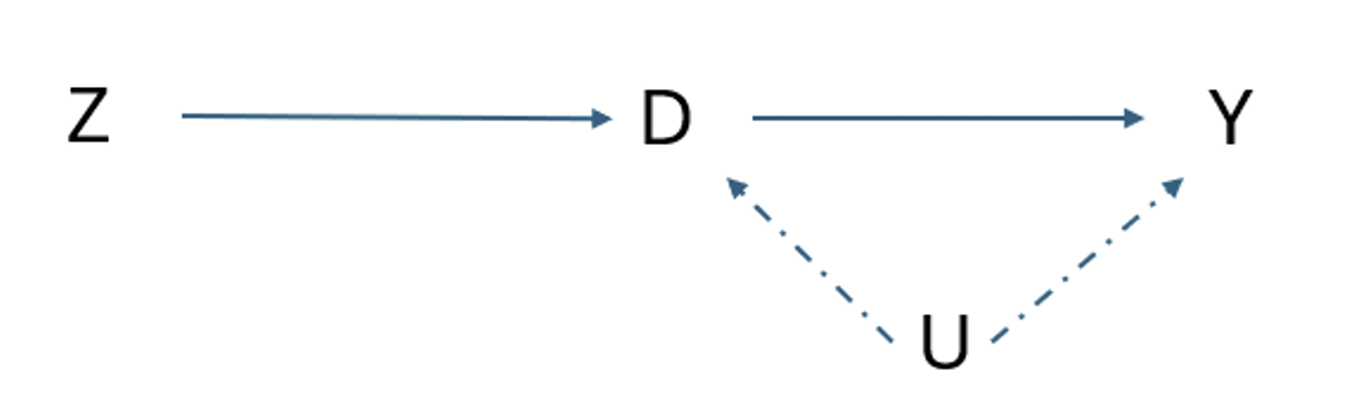
What is the other pathway?

What happens if a shock Z induces a change in D?
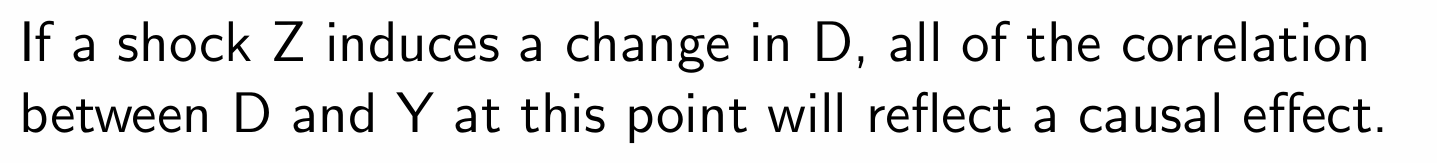
What happens if the shock Z only impacts a subset of D?

What two conditions can be observed from the impact of Z?

What are some common uses of instrumental variables?

How do constant and heterogenous treatment effects differ for university education?

What are the two groups of estimators for instrumental variables?

What is the main purpose of IV?
Mimic randomised experiments when actual randomisation isn’t possible
What are the steps to mimic a randomised experiment using IV?

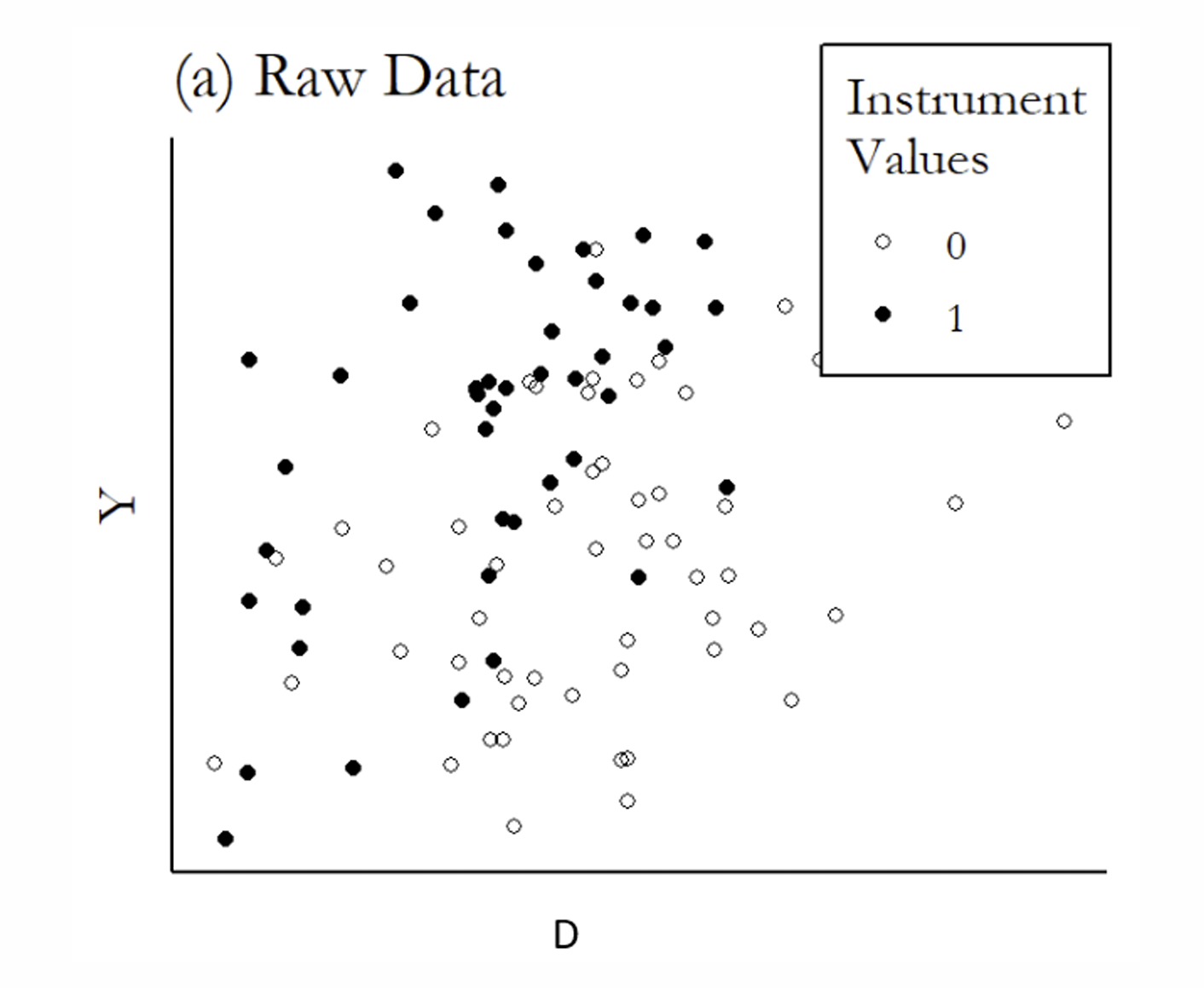
What is the next step?
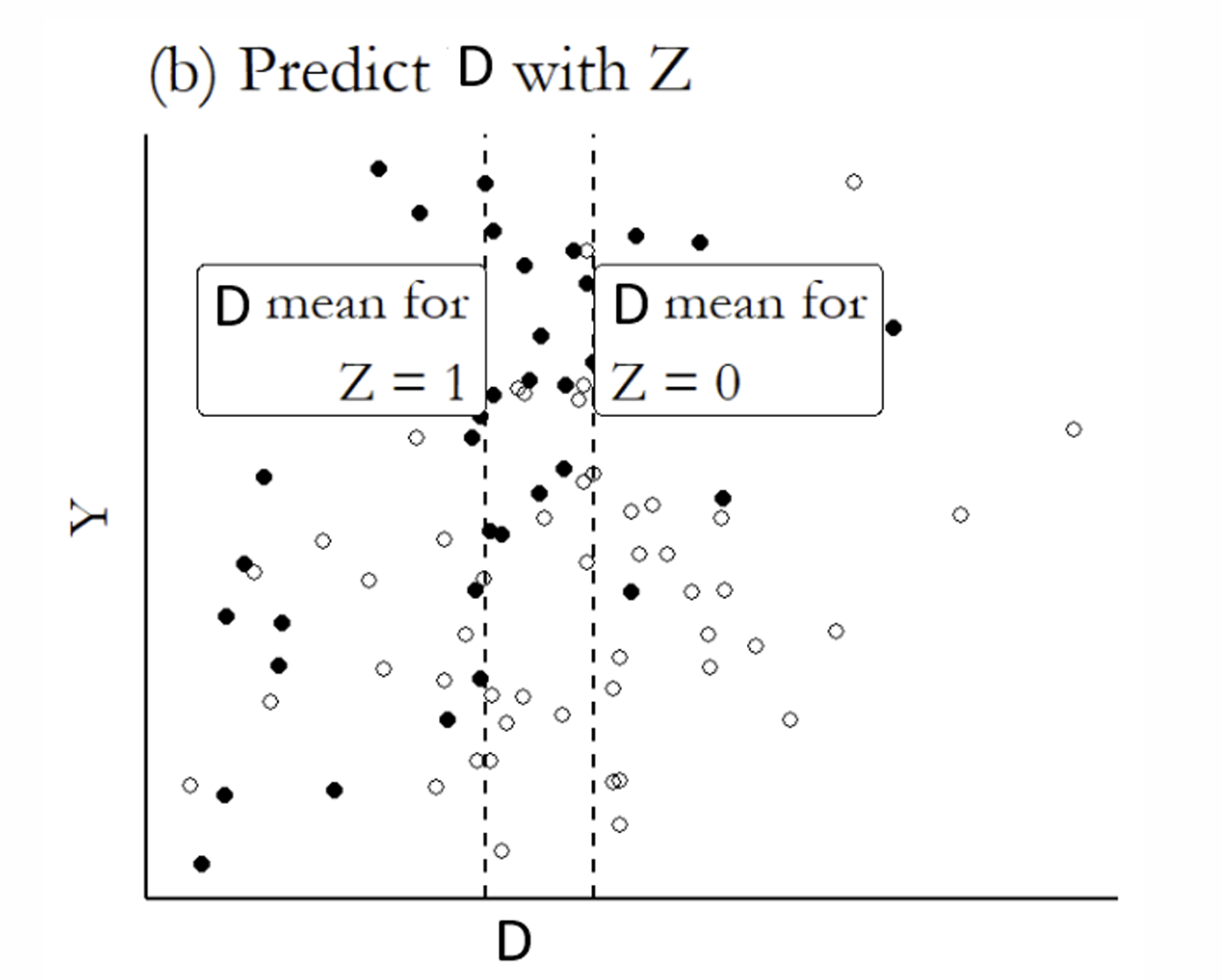
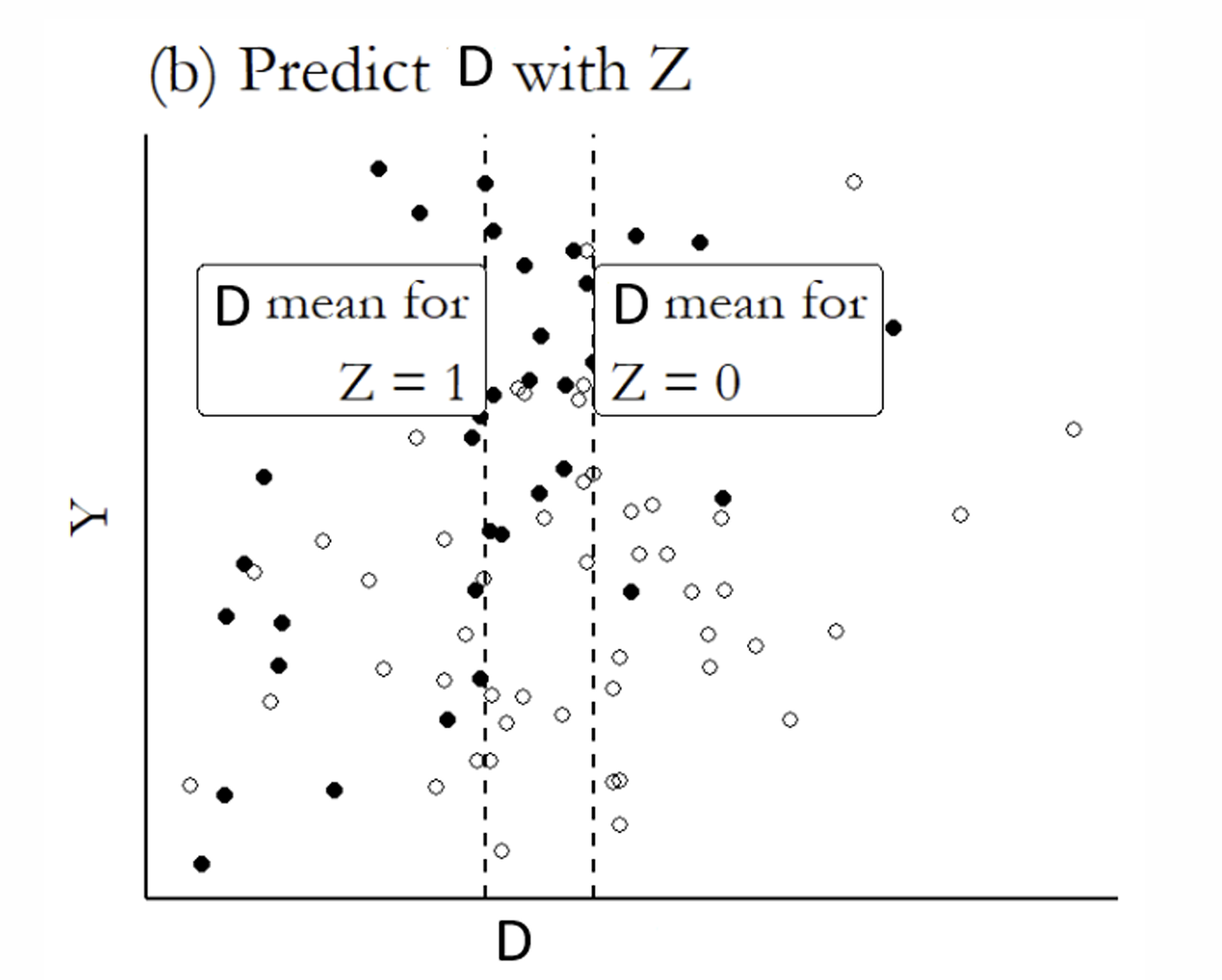
What is the next step?
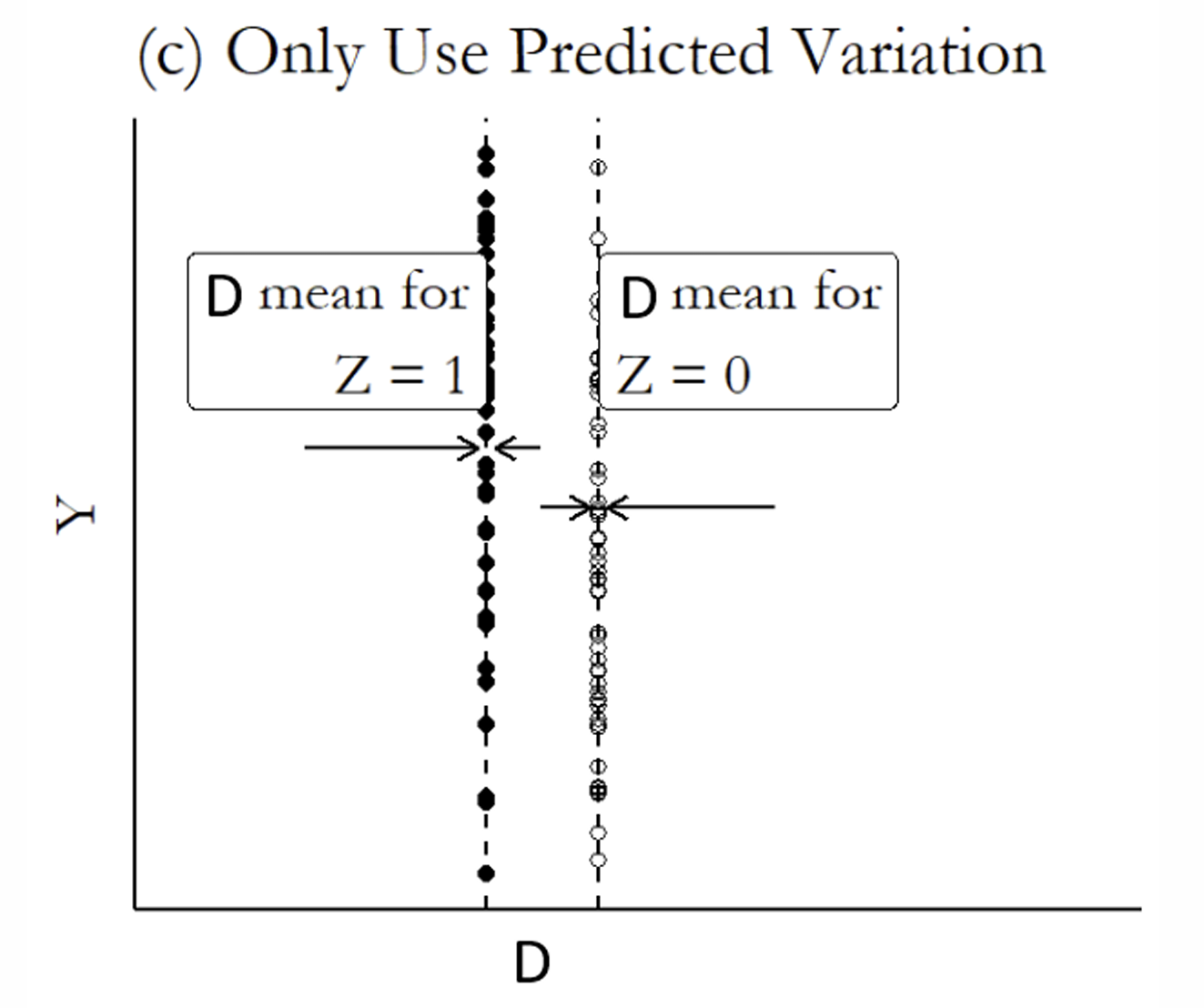
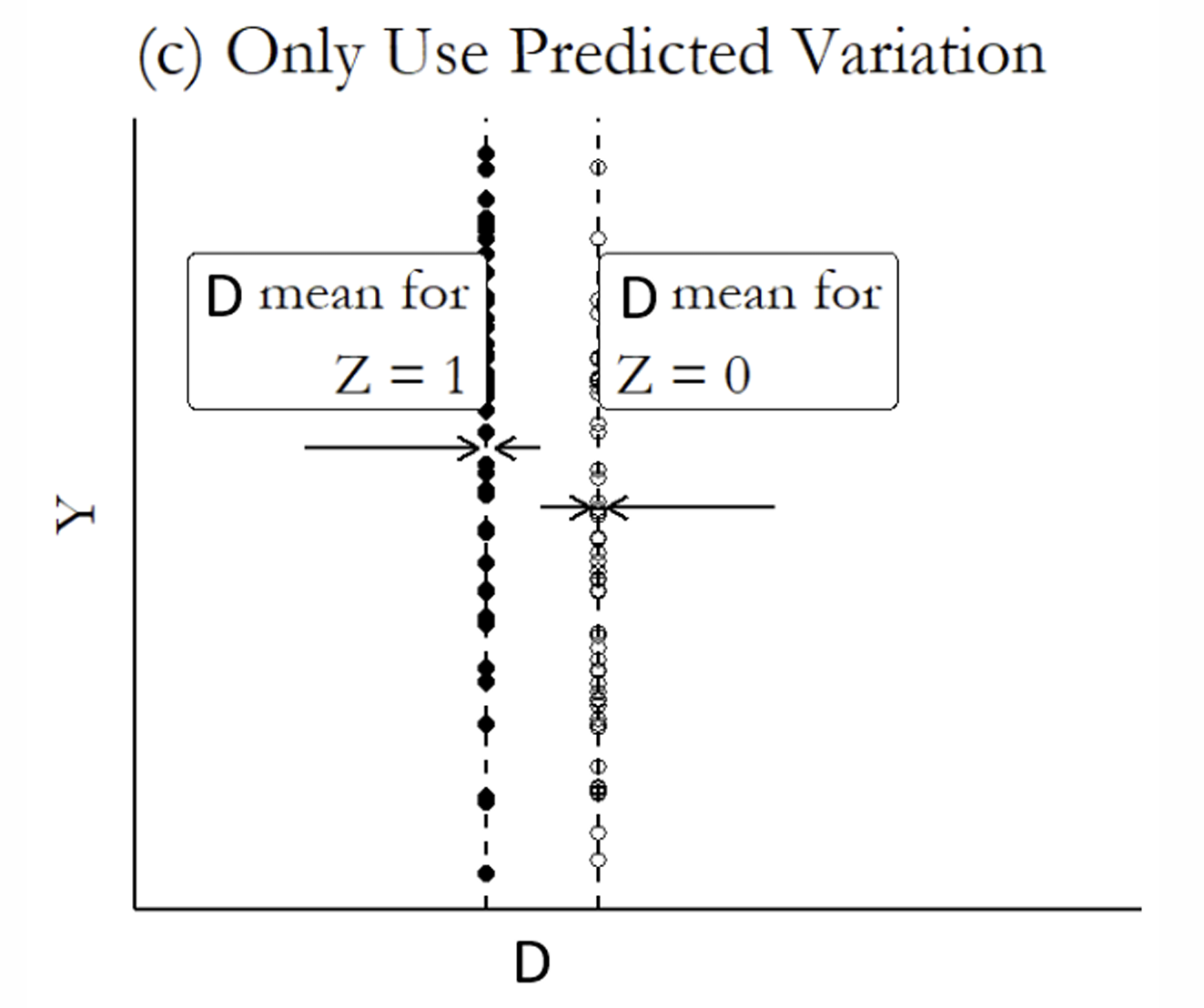
What is the next step?
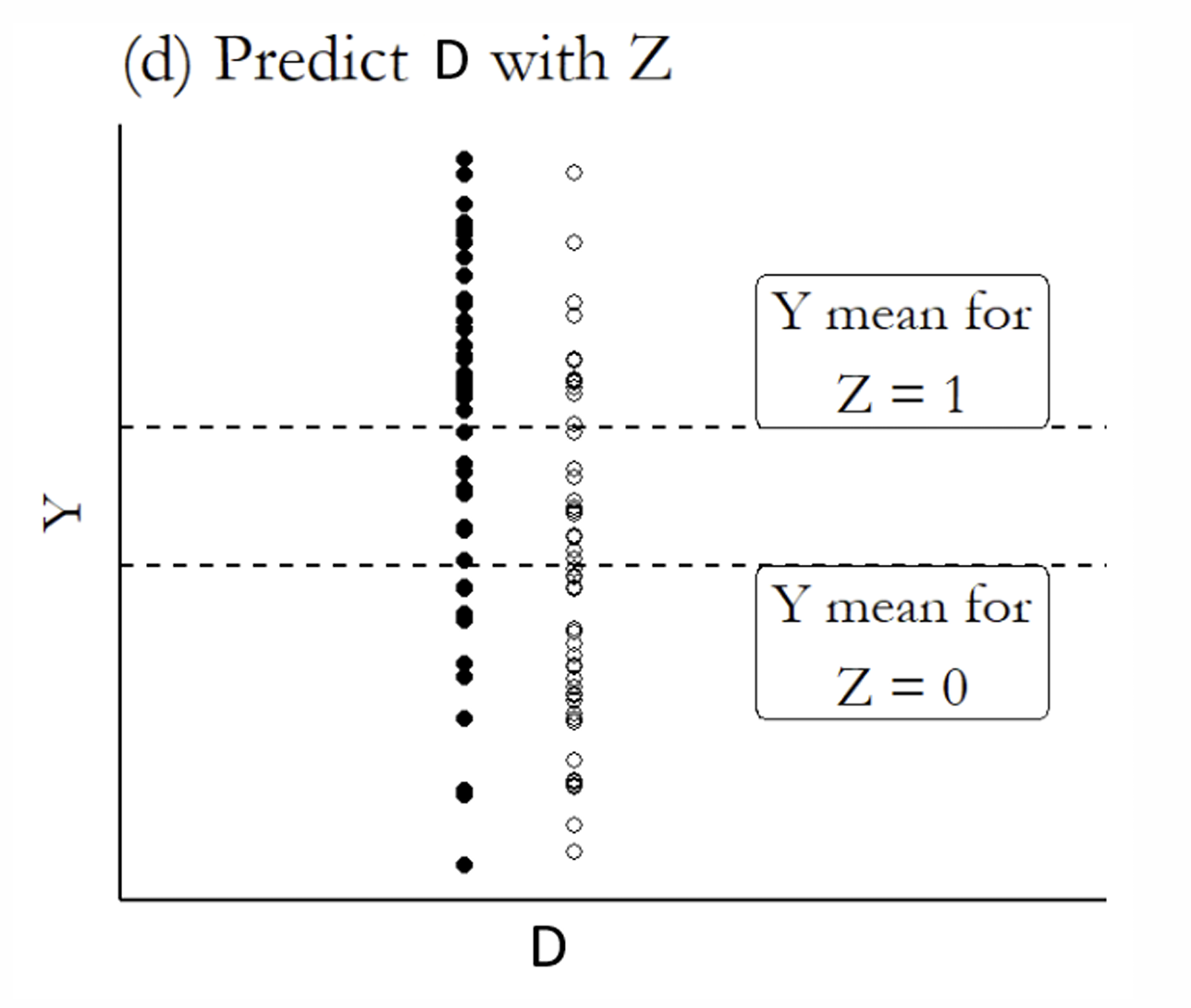
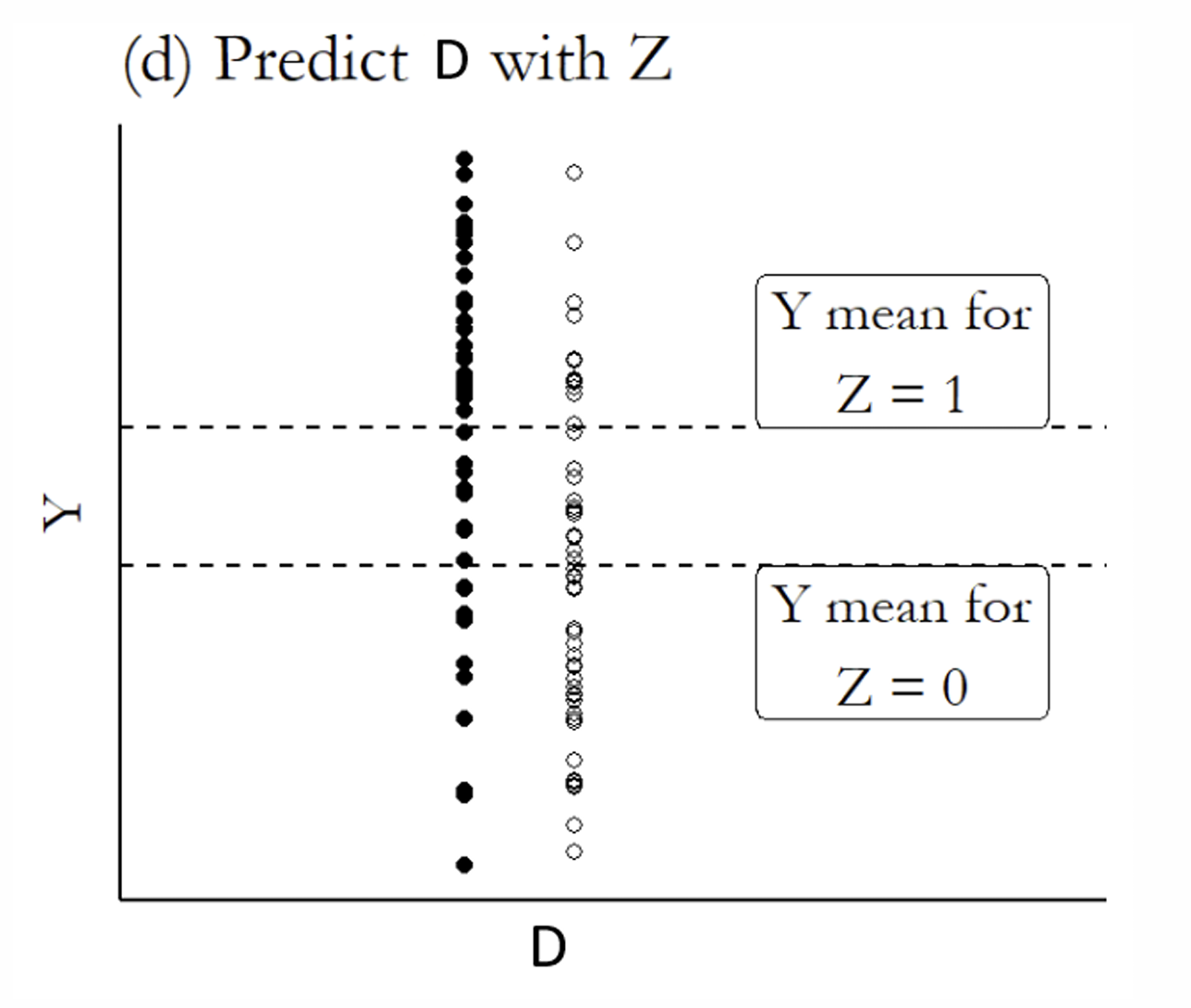
What is the next step?
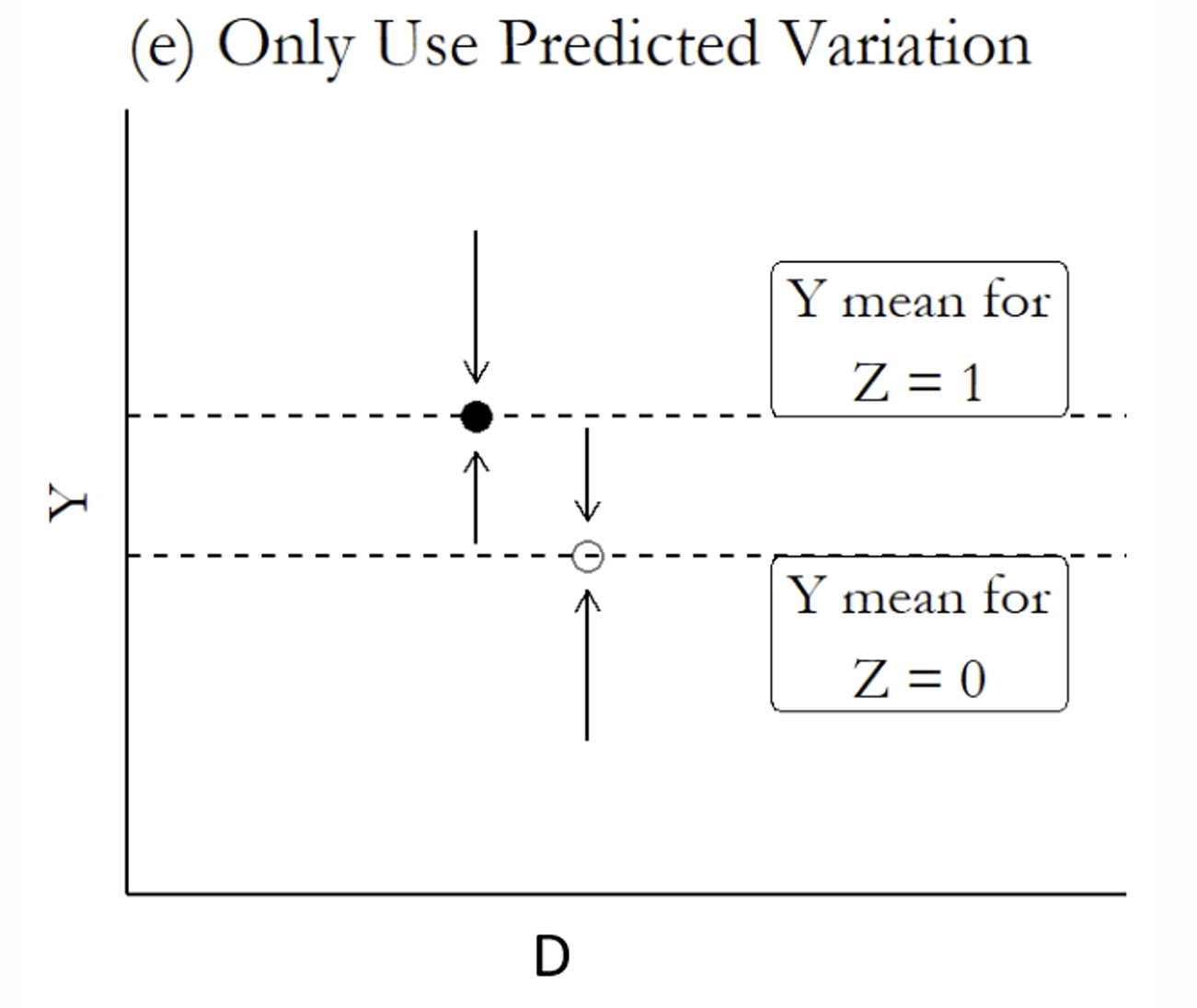
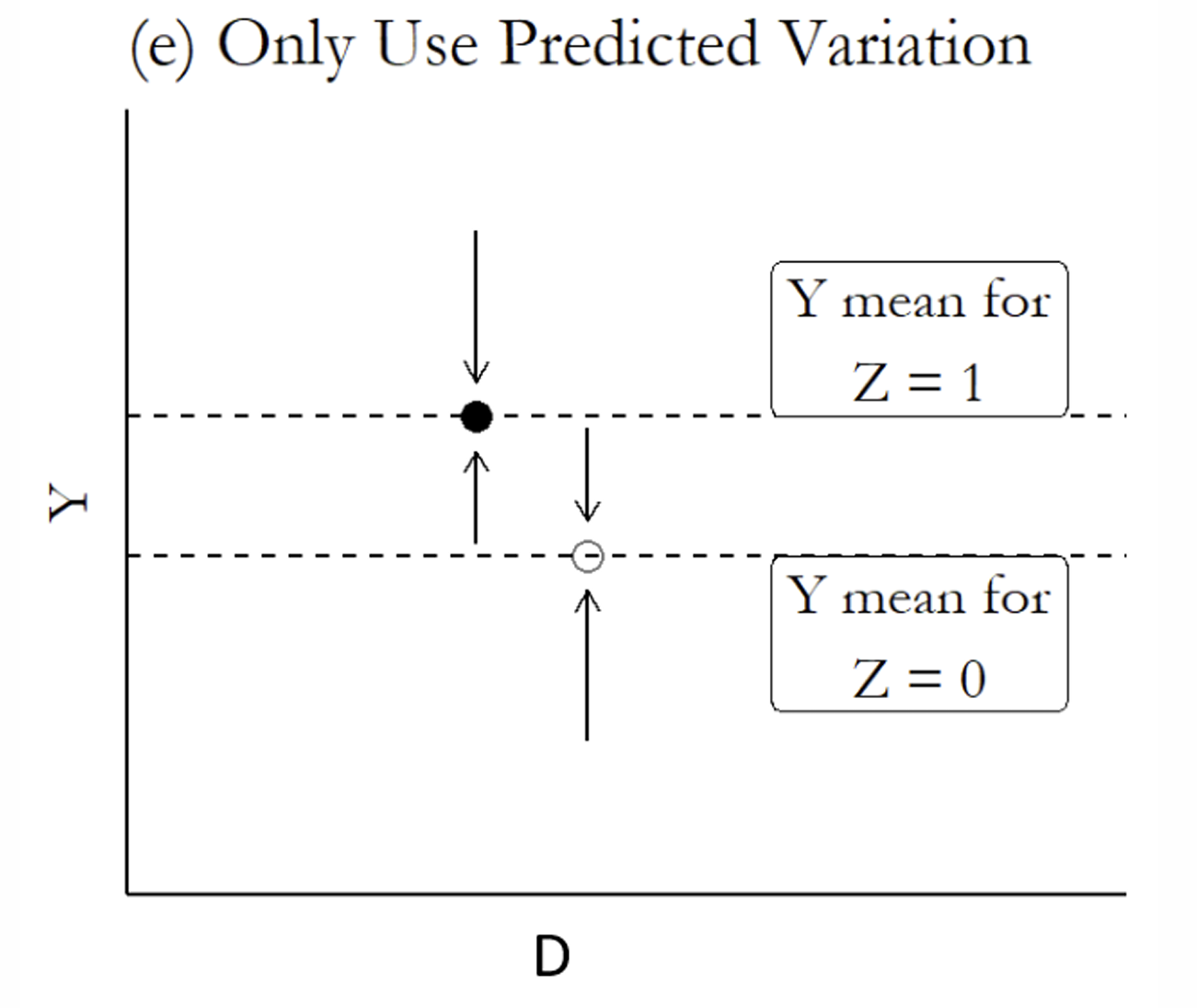
What is the next step?
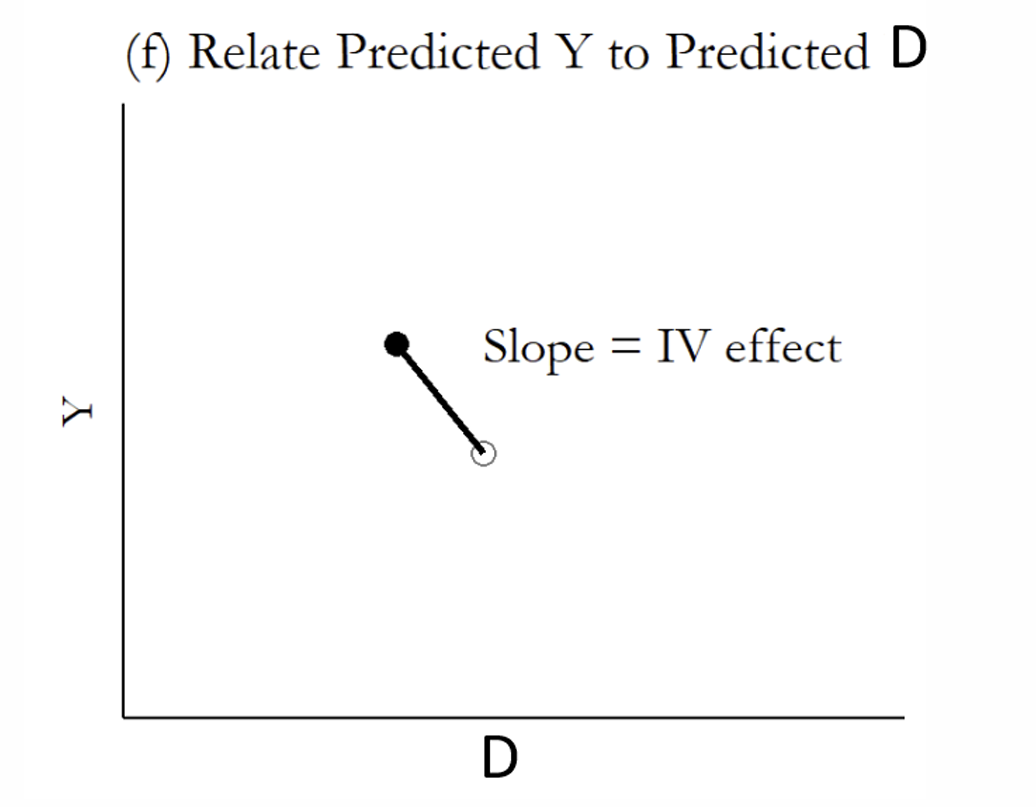
How do IVs differ to just controlling for variables?

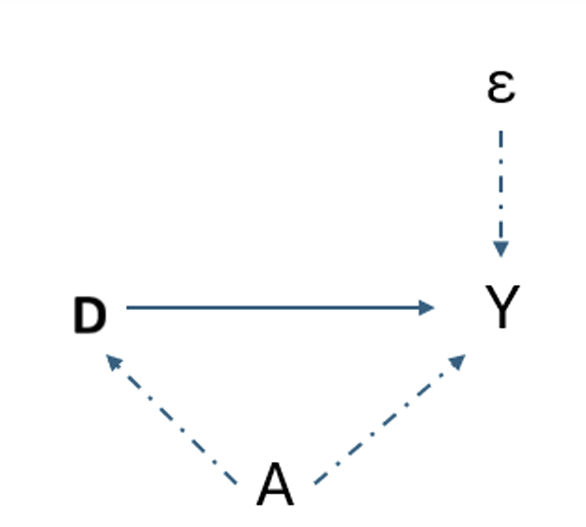
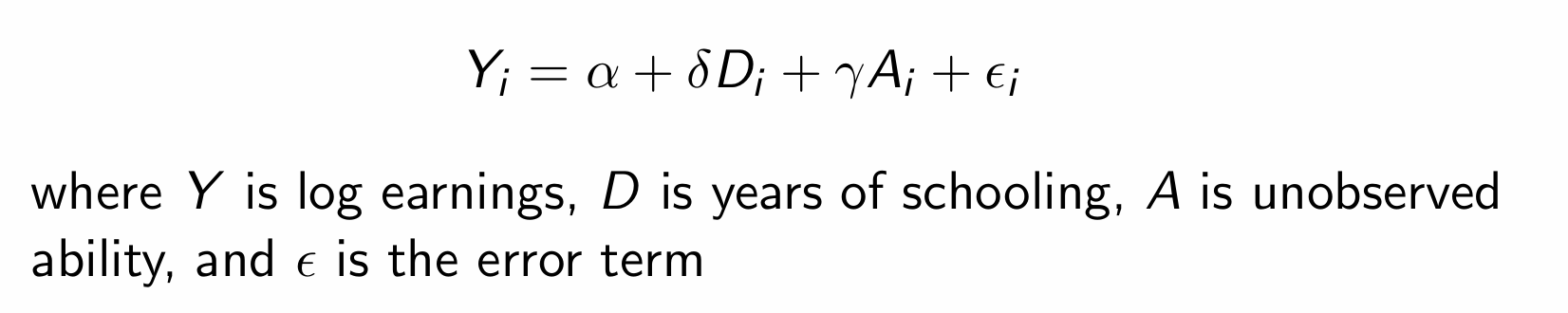
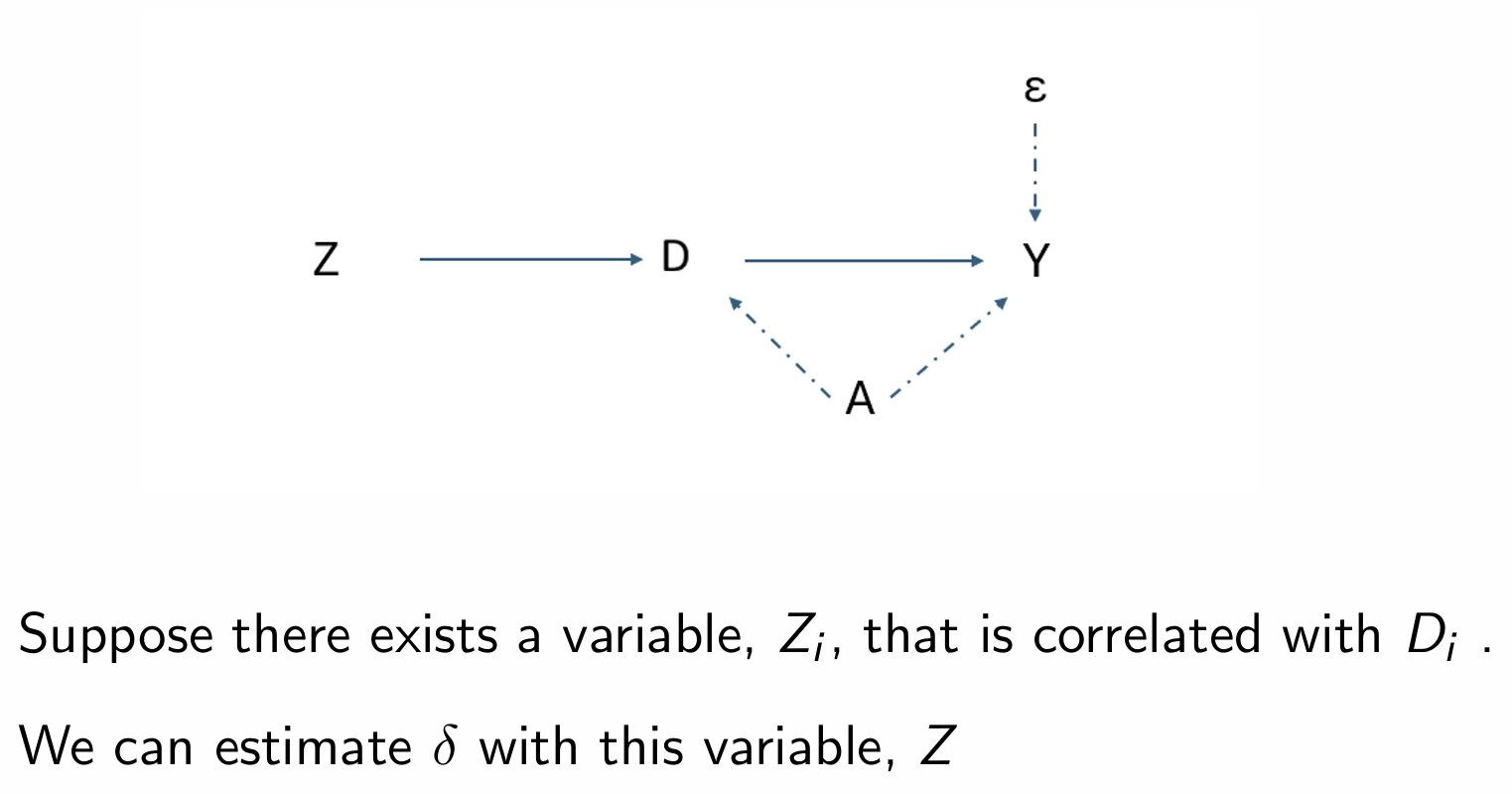
How can we estimate δ (i.e. the Cov(Y,Z))?
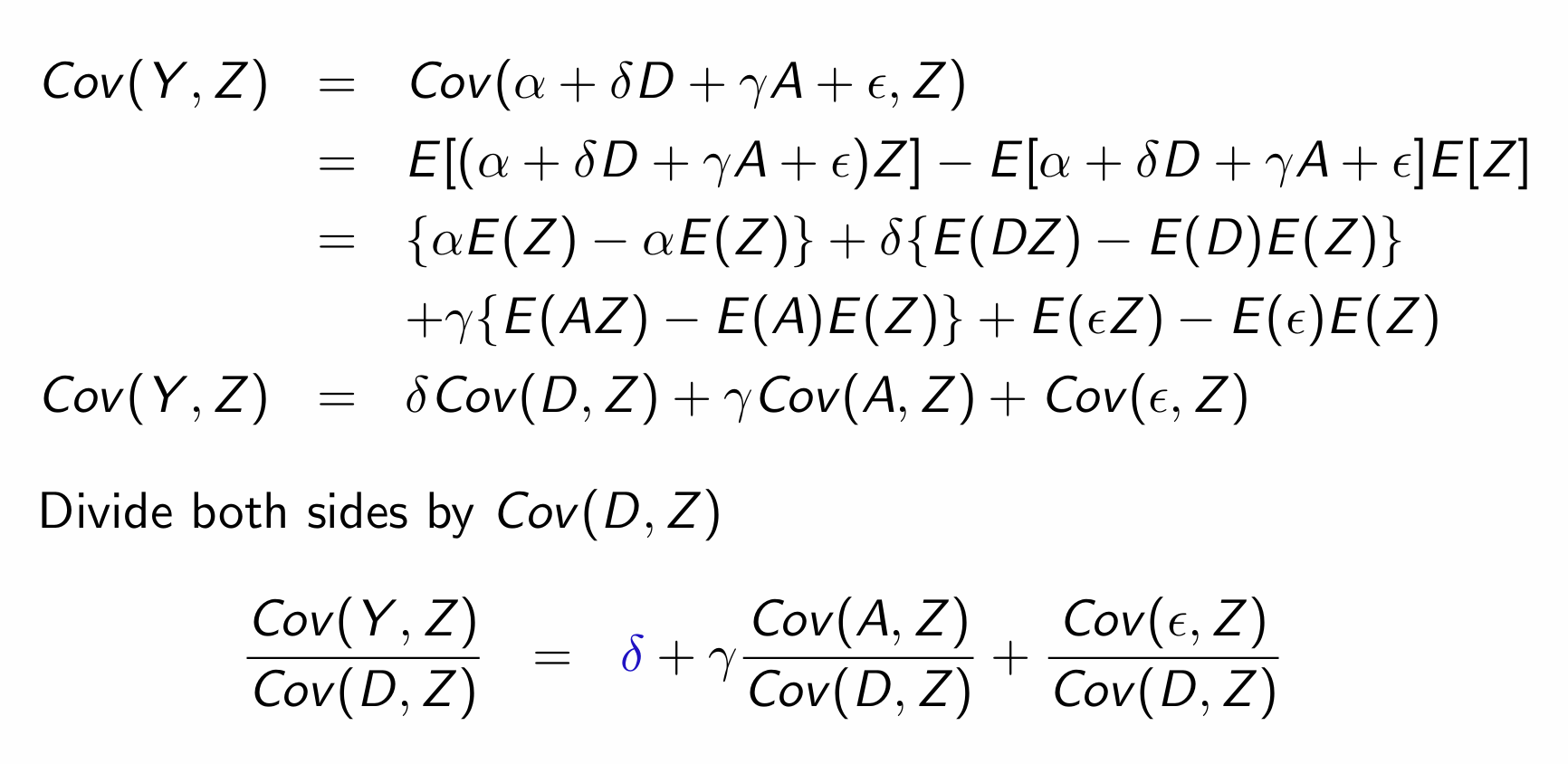
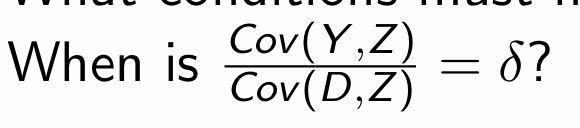
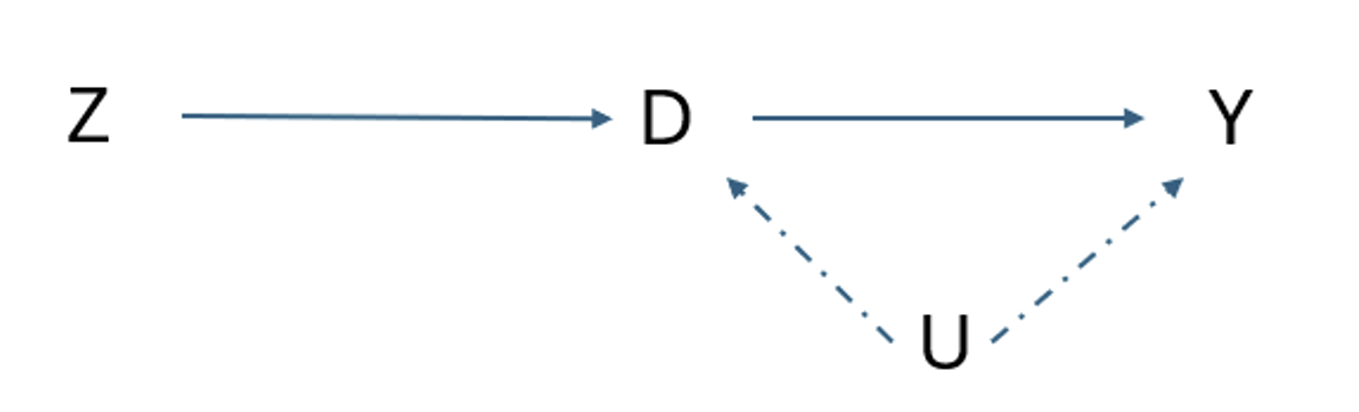
i.e. What are the two conditions required for it to equal the treatment effect?
i.e 1. Relevance - Instrument Z affects treatment D and 2. Exclusion Restriction - Z affects outcome Y only through D


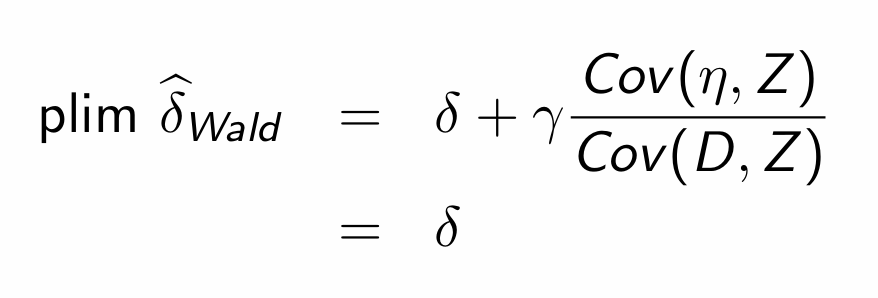
What other assumptions also apply to IVs?
The regular OLS assumptions
What regressions are involved in 2SLS?
Causal model, First-stage regression, second-stage regression, reduced form model
What is the equation for the causal model?
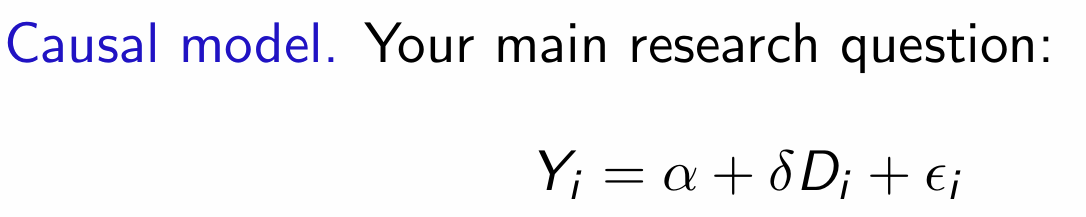
What is the equation for the first-stage regression model?
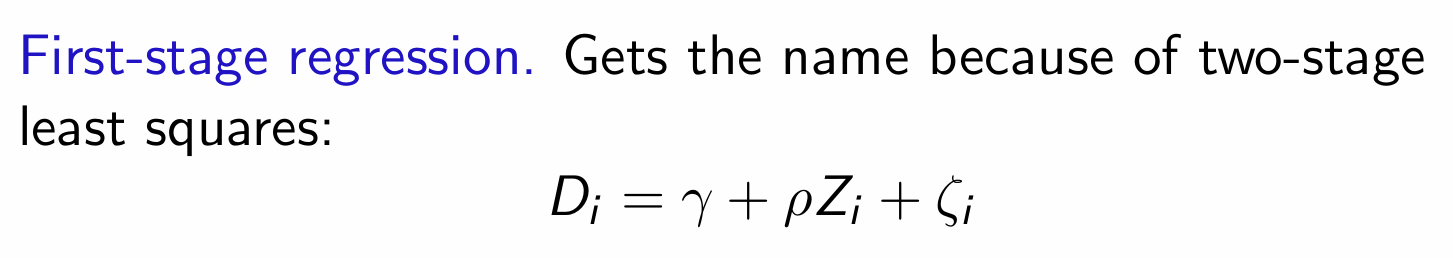
What is the equation for the second-stage regression model?

What is the equation for the reduced form regression model?
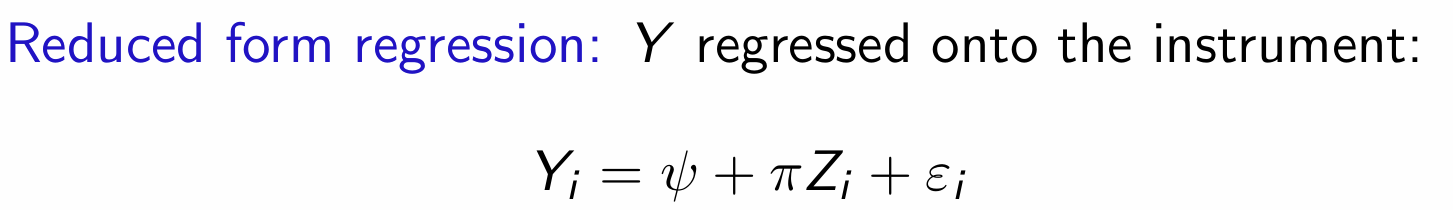

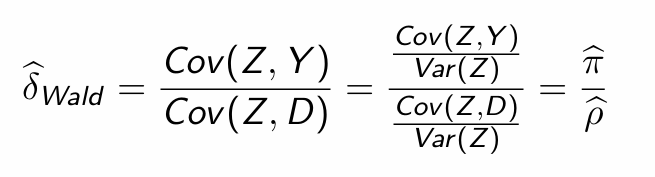
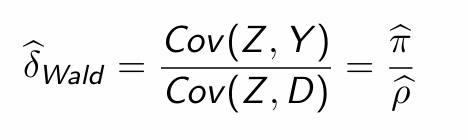
What does this tell us?

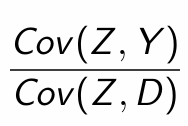
What does this tell us?
What happens if Z does not explain any part of D?

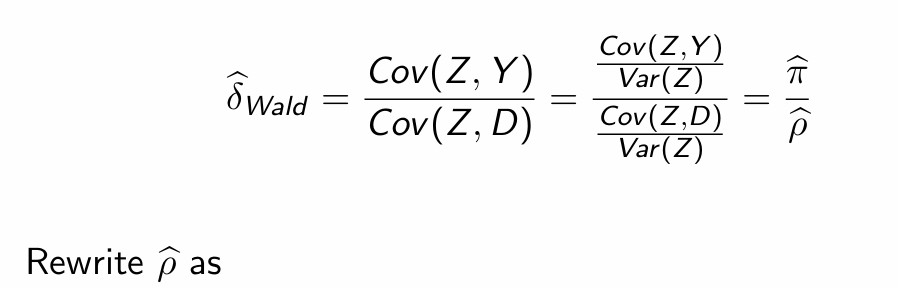
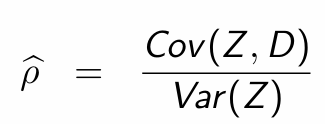
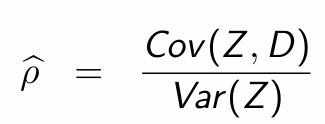
Rearrange to obtain Var(Z)
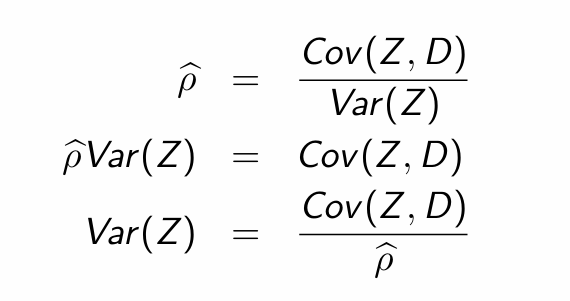
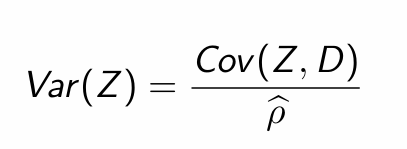
Substitute into Wald estimator and simplify
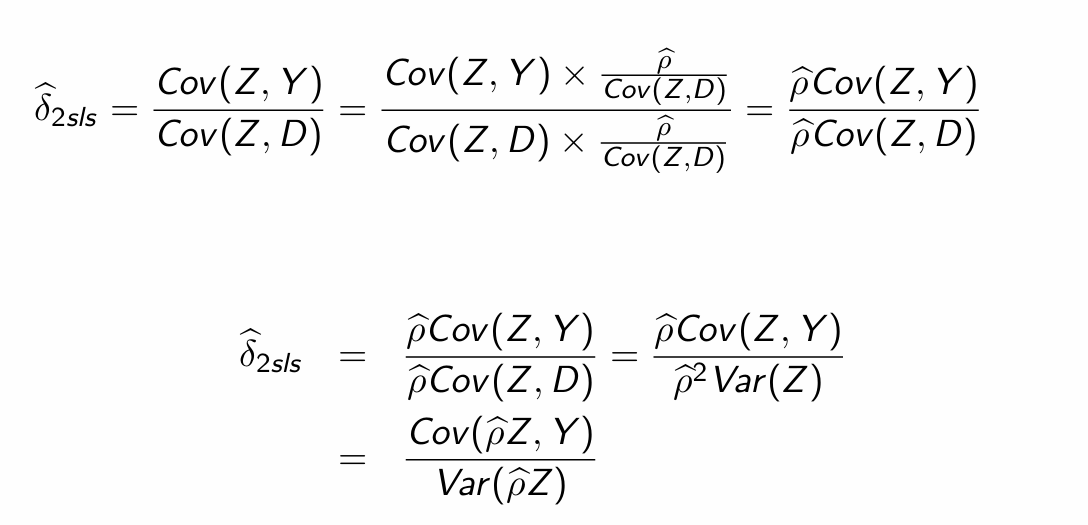
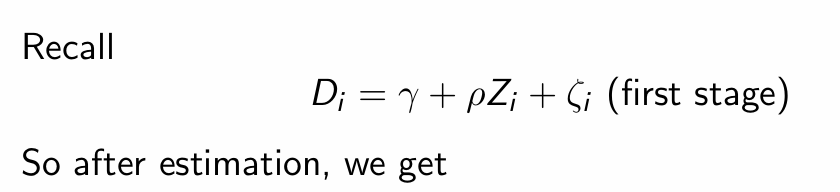
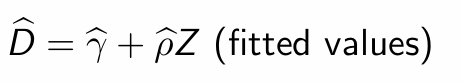
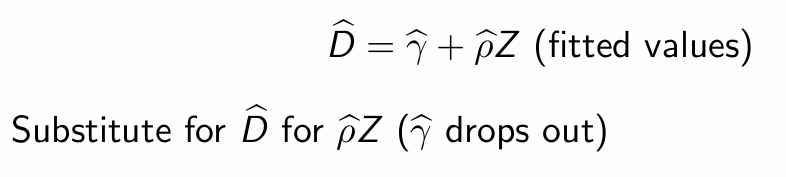
i.e. substitute into 2SLS estimator
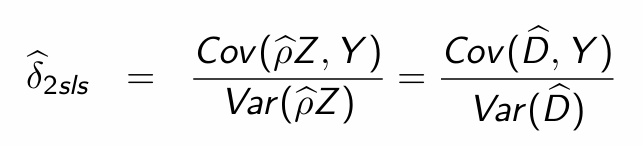
What is equivalent to the 2SLS estimator?

If you are using the fitted values of the endogenous regressor from the first stage, what variation should you use?

How do we define an instrument?

How was the gender ratio used as an instrument in Angrist and Evans?

How do we determine whether an instrument is good or not?


How did exogenous shocks impact the supply of the drug?

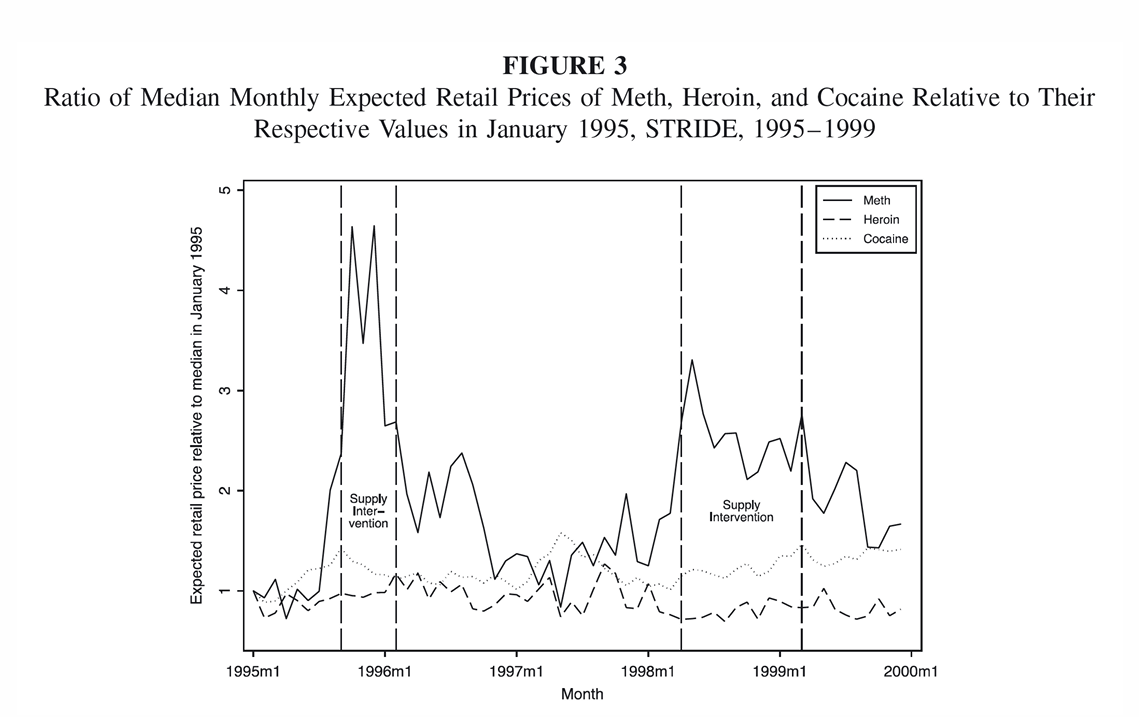
What can we infer about the instrument quality?

What is the first stage for the drug example? And how can we measure D?

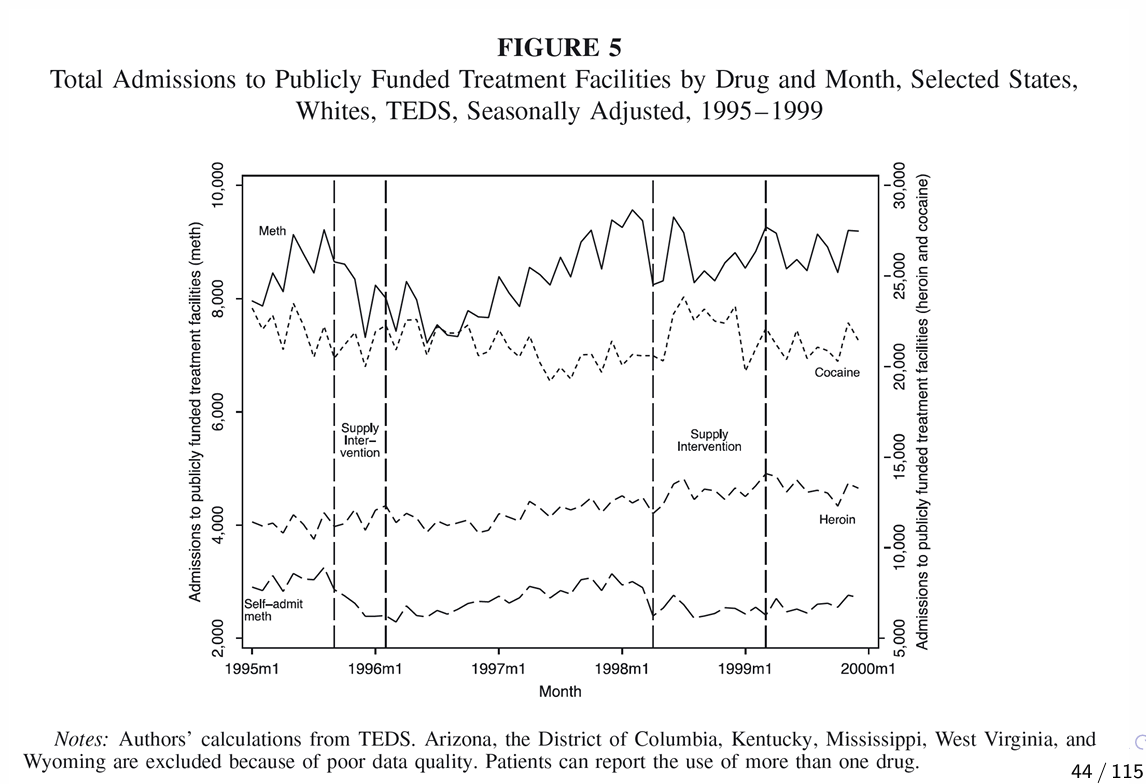
What can we infer from the first stage output?

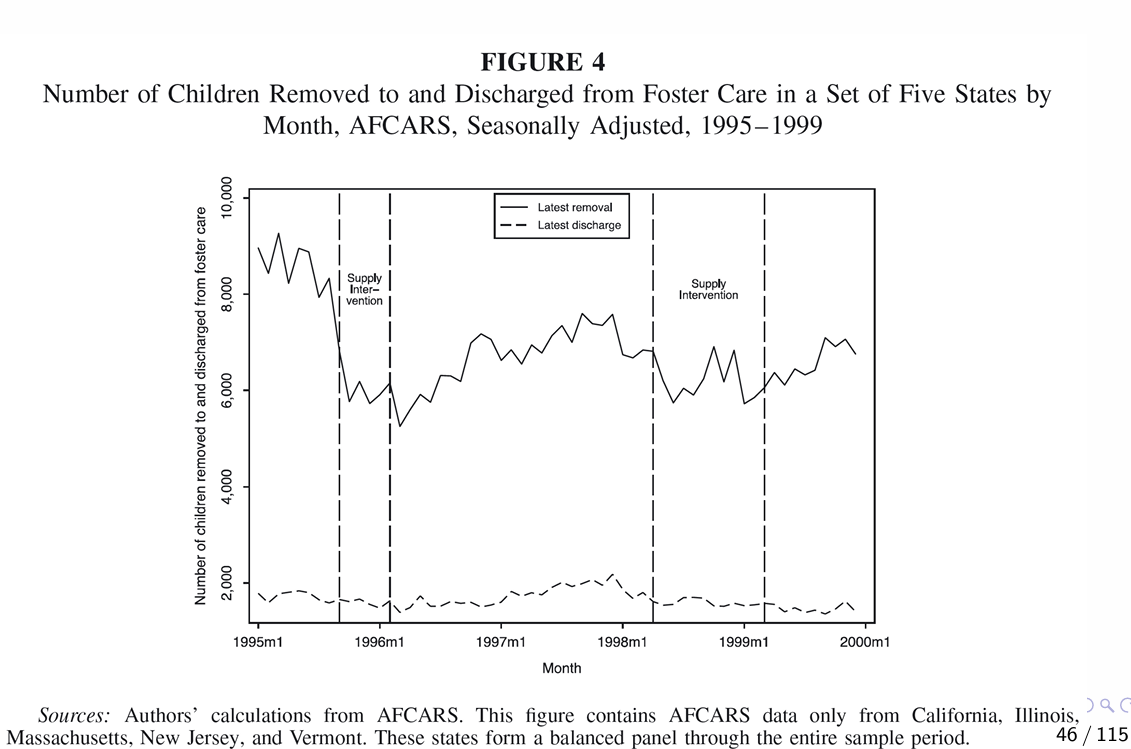
What can we infer from the output of the reduced form?

Why would price hikes in meth cause a child not to be placed in foster care?
Higher prices may see a reduction in consumption of meth → reduction in harm
What is the best method of showcasing 2SLS results? What should be included in it?

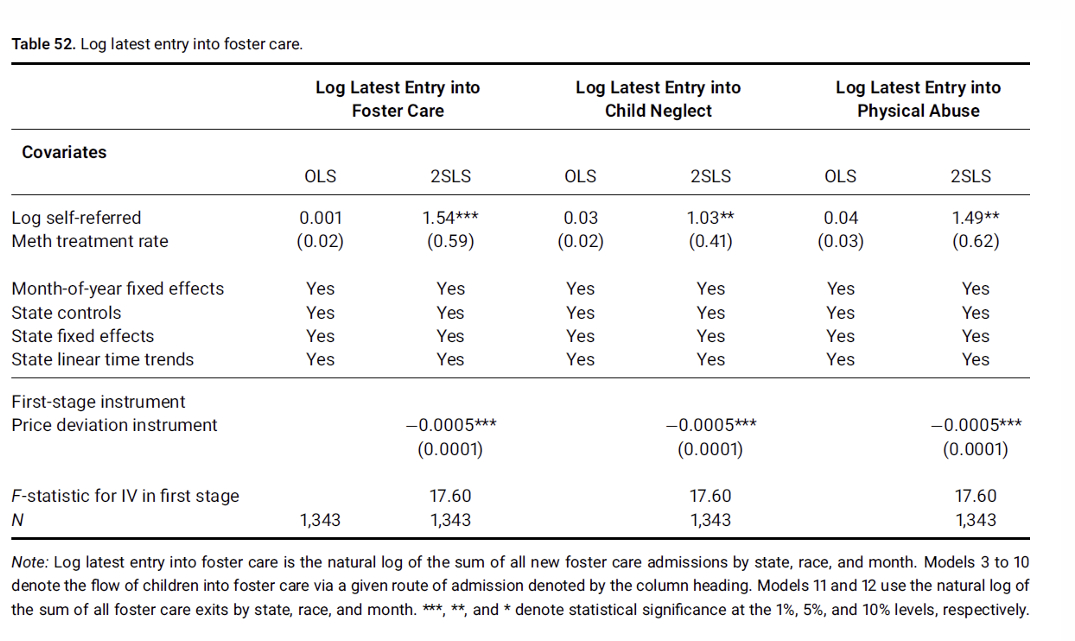
What can we infer from the table about OLS, first stage and second stage regressions?

What are the benefits of IV?

What are the main weaknesses of IV?


Small sample bias: Plug in covariance for the 2SLS estimator
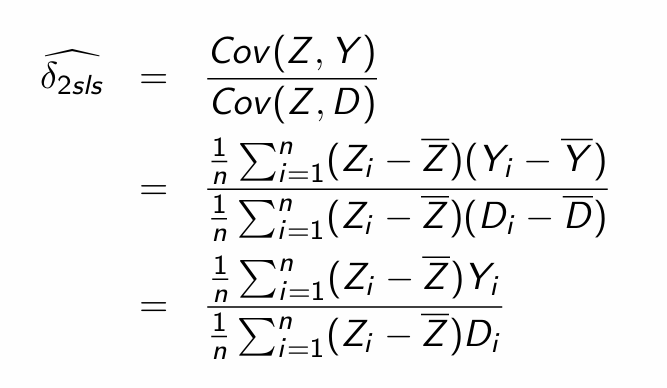
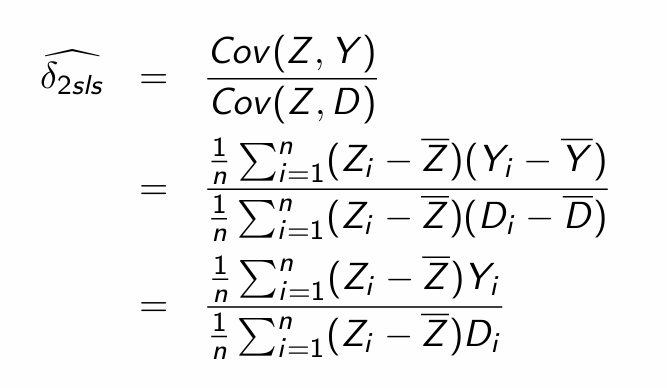
Substitute in the causal model definition of Y
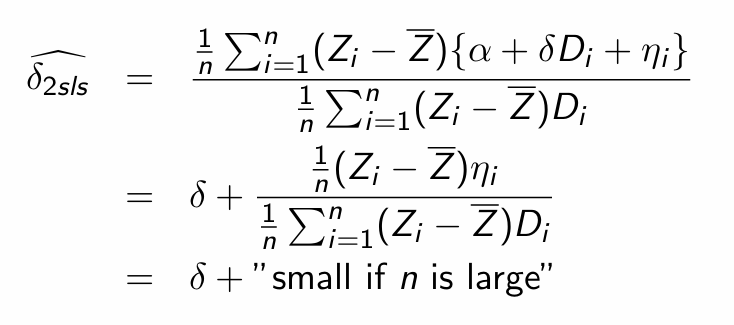
When does the mean of the IV estimator’s sampling distribution approach the population parameter?

What happens to corr(Z, η) in infinite (and finite) samples if Z is a valid instrument?

The smaller the sample is, what happens to corr(Z, η)?

When do we see a smaller bias?

Why is it important to not use IV in small samples?

What is the issue with Z being exogenous?

When would we see weak instruments?

What is the bias of the 2SLS centered on if we have a weak instrument?
Centered on the bias of OLS
What is the most common test of instrument relevance?
First stage F-statistic
How do we observe the first stage F-statistic?

What is the general principle around the F-statistic for 2SLS?

How did stock and Yogo (2005) assess the bias for IV?

What were the cut-offs depending on the number of endogenous variables and instruments?


What instrumental variable did Angrist and Krueger (1991) use?
Quarter of year an individual was born in
Why was this chosen as an instrumental variable (i.e. why would birth quarter cause earnings in the reduced form)?
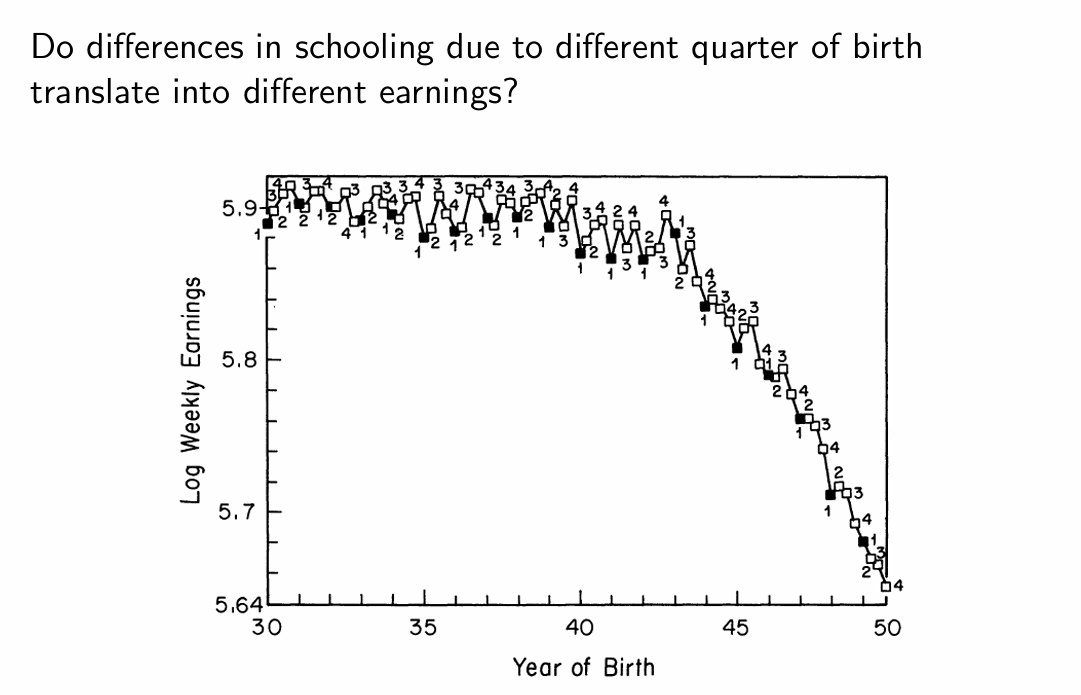
Why is good data visualisation important for IV?
Scrutiny around the design; key for showing the first stage and reduced form
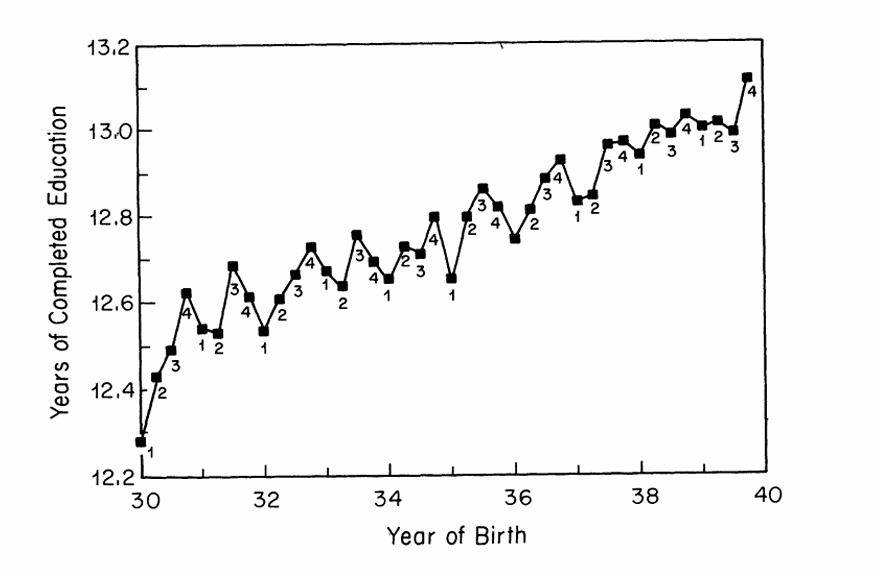
What do we observe from the first stage for Angrist and Krueger (1991)?

X
How did Angrist and Krueger (1991) instrument for schooling in their model?
Used three quarter of birth dummies: a dummies for 1st, 2nd and 3rd qob
What was their initial first stage regression?
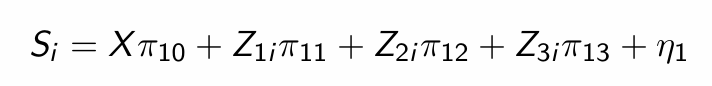
What was their second stage regression (including all controls as X)?
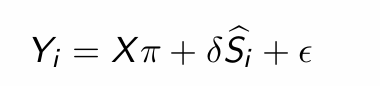
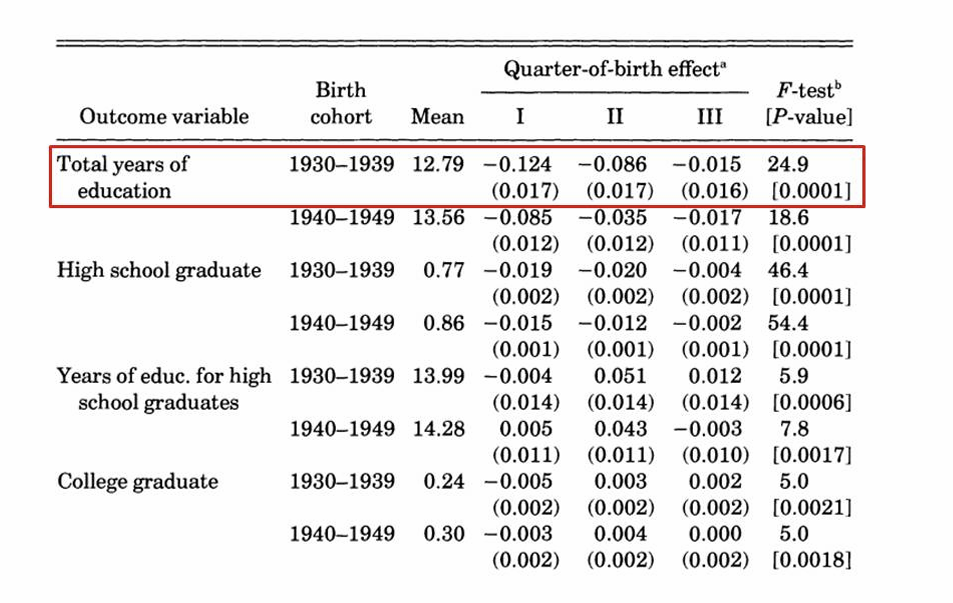
What can we observe from their first stage regression results?
Quarter of birth is a strong predictor of total years of education
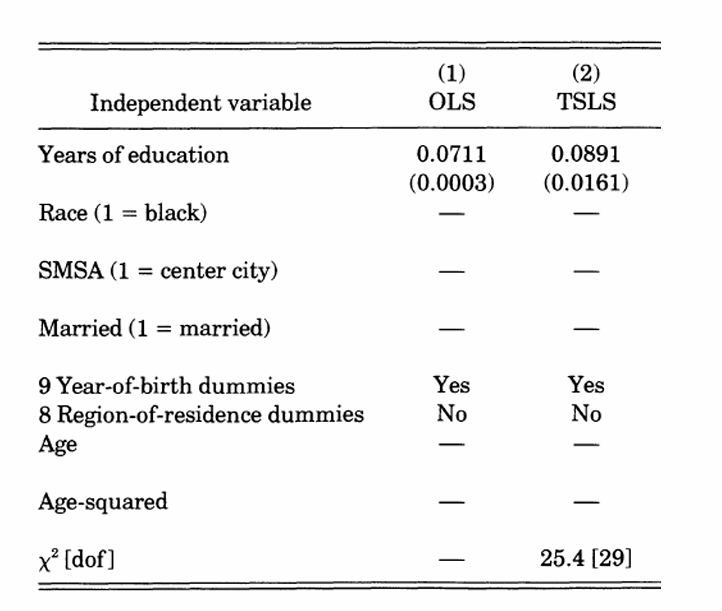
How did the OLS and 2SLS results compare?
X
How did they improve precision in their 2SLS model?
Included more instruments
What is the benefit of including more instruments?
Can increase variation in the predicted schooling variable, lowering standard errors and tightening confidence intervals
How did they incorporate more instruments?
Three QoB dummies interacted with 50 state-of-birth dummies + 3 QoB dummies interacted with 9 year-of-birth dummies (180 instruments)
Why did they include 50 state-of-birth dummies?
Includes 50 state-of-birth dummies so variability in education in 2SLS is solely due to differences in seasons of birth and this is allowed to vary by state and birth year for the first time
Will all the added instruments have sufficient correlation with schooling?

What happens if we add multiple weak instruments?

When would weak instrument bias be less of a problem?
If the model is “just identified”– the same number of instrumental variables as there are endogenous covariates
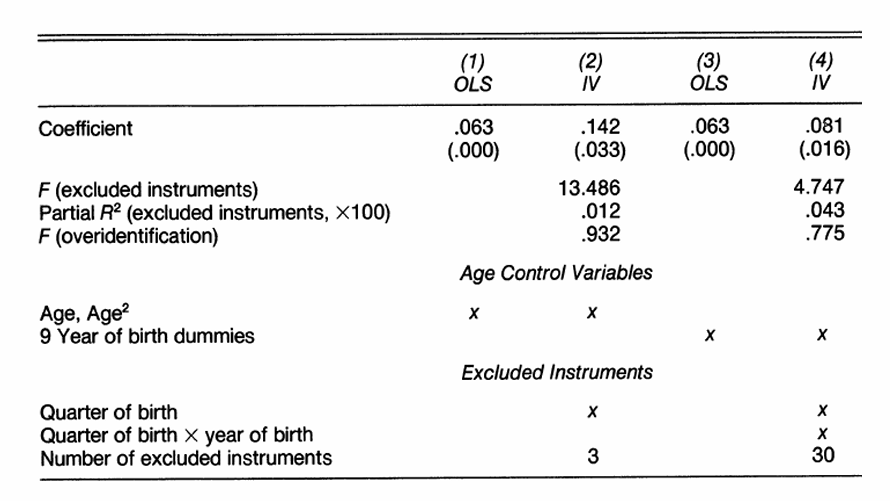
What can we interpret about adding extra instruments in Angrist and Krueger?
Adding more weak instruments reduced the first stage F-statistic and increases the bias of 2SLS. It also moved closer to OLS.
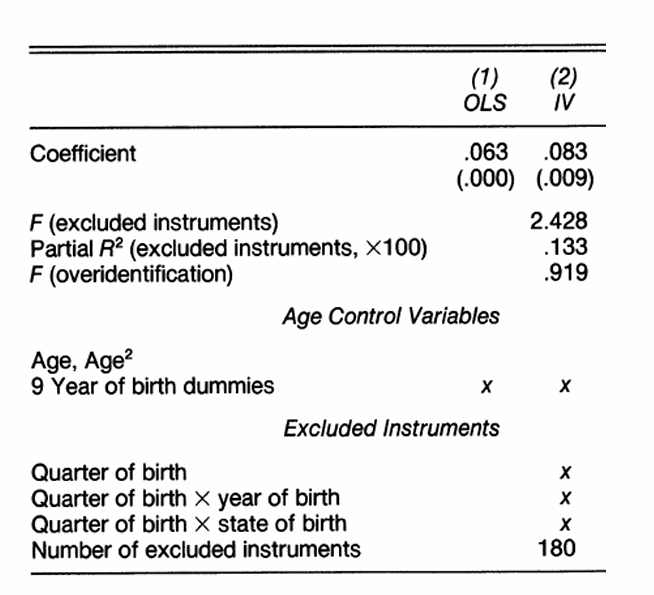
What can we interpret here?
More instruments increase precision, but drive down F, therefore we know the problem has gotten worse
What type of treatment effects have we assumed so far?

What are heterogenous treatment effects?
Individuals respond to treatment differently; may be more realistic
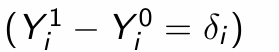
Using the Potential Outcomes Framework, what is the treatment status when the instrument is/isn’t assigned to an individual?

How do we present outcomes with treatment and instrument status?

How do we represent treatment status for an individual?
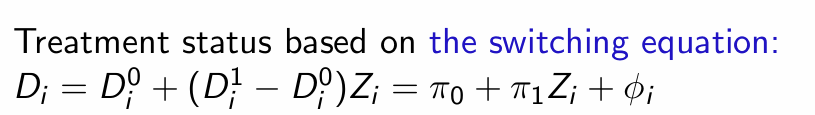
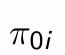
What is this equal to?
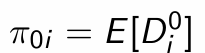
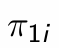
What is this equal to?

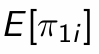
What is this representing?

What assumptions are required to identify heterogenous treatment effects?


And what is the instrument?

What does SUTVA represent in the context of IV?


Why is this the case?
This means the potential outcome is not based on other’s assignment and it means there’s no hidden variation in the instrument
What is an example of a SUTVA violation in the context of Angrist (1990)?

What is the independence assumption for IV?
Instruments are assigned independent of potential treatment status and potential outcomes
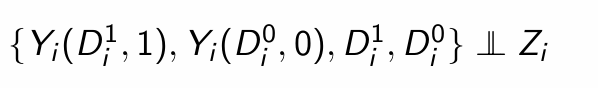
What is an example of the independence assumption for Angrist (1990)?
Random draft numbers generated by a random number generator, independent of potential earnings or potential military service
What does the independence assumption imply for the first stage?
