sequences
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
the 3 types of sequence
arithmetic (common difference, e.g., +2)
geometric (common ratio, e.g., x2)
fibonacci (term is sum of the 2 prior terms)
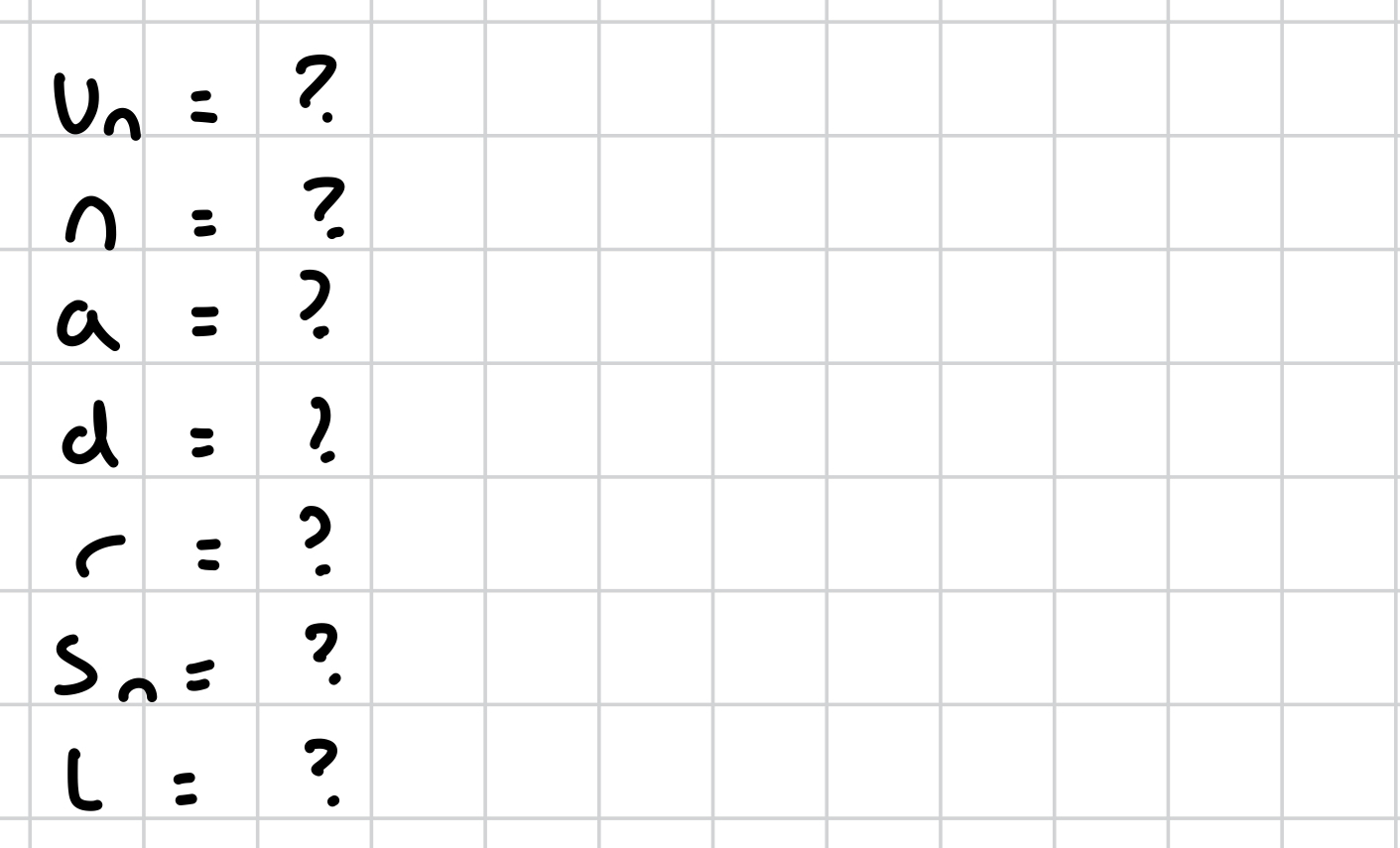
common terminology

Un for arithmetic sequence
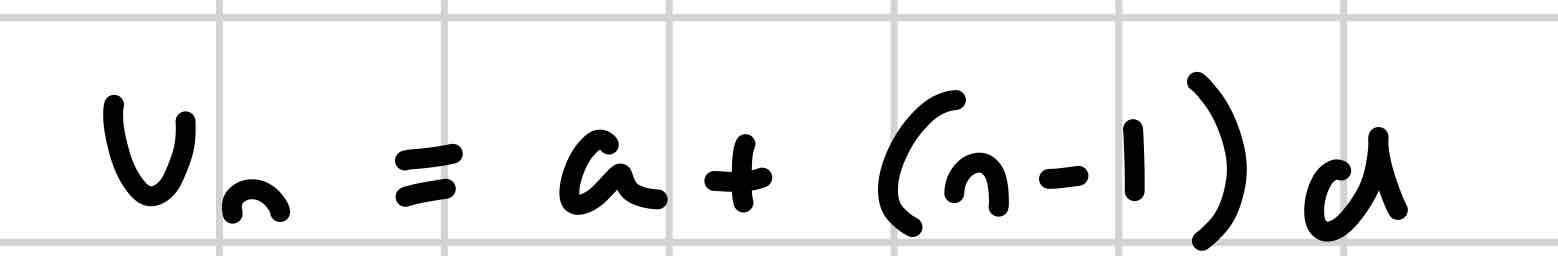
why is nth term formulae (n-1)d rather than nd?
because a (first term) doesn’t have a common difference
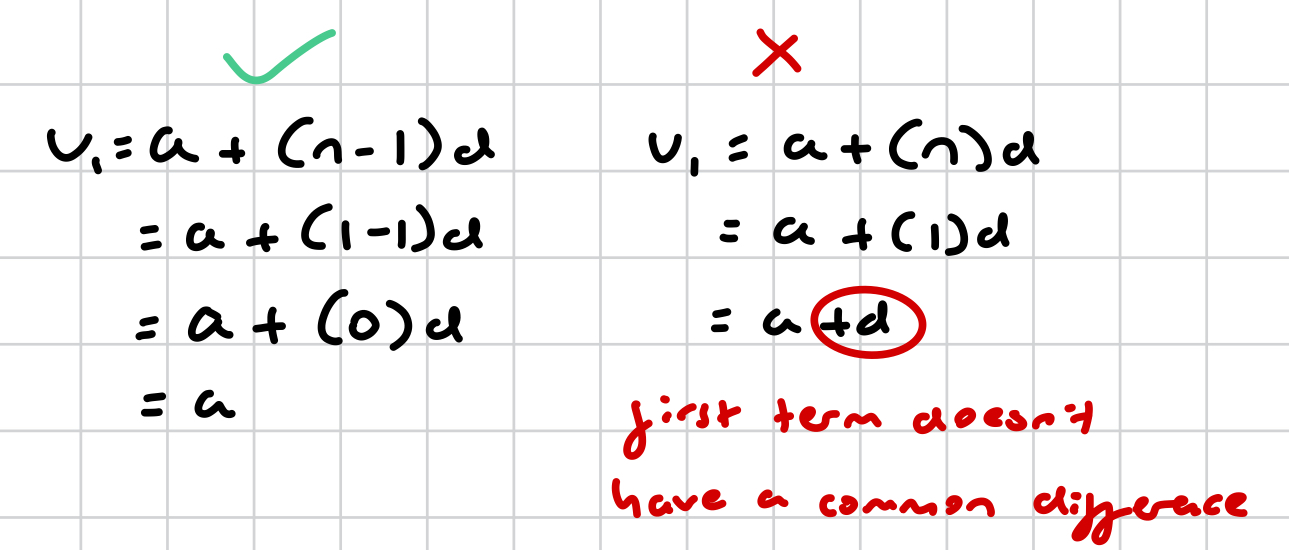
how do you find the first positive / negative term?
set the equation to > / < 0 (respectfully)
rearrange for n or factorise for n. this will tell you at which n value the first positive / negative term is at
find the term using n
what does it mean when d is positive, and when d is negative?
+d = positive common difference, sequence is increasing
-d = negative common difference, sequence is decreasing
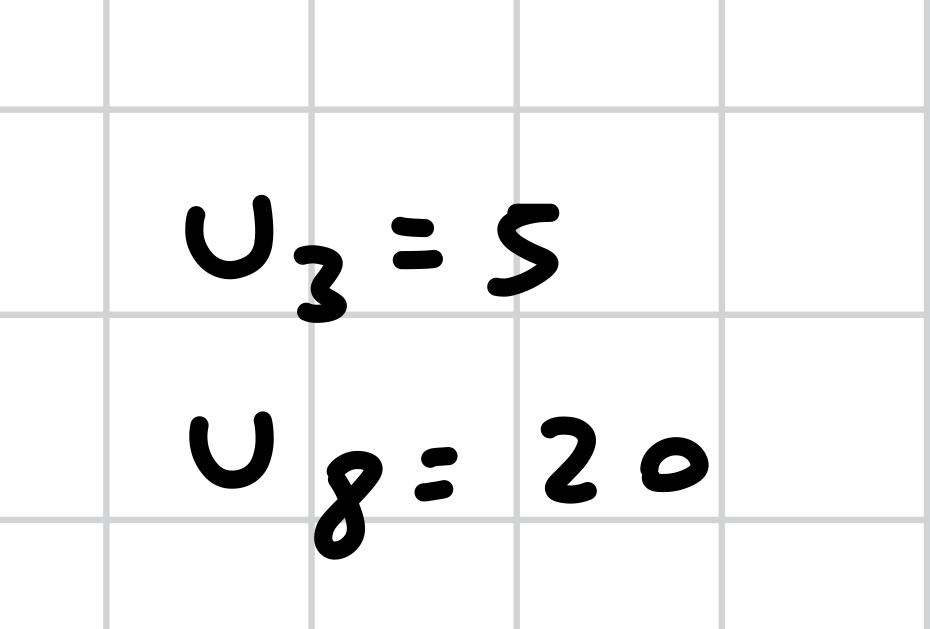
how do you answer this?
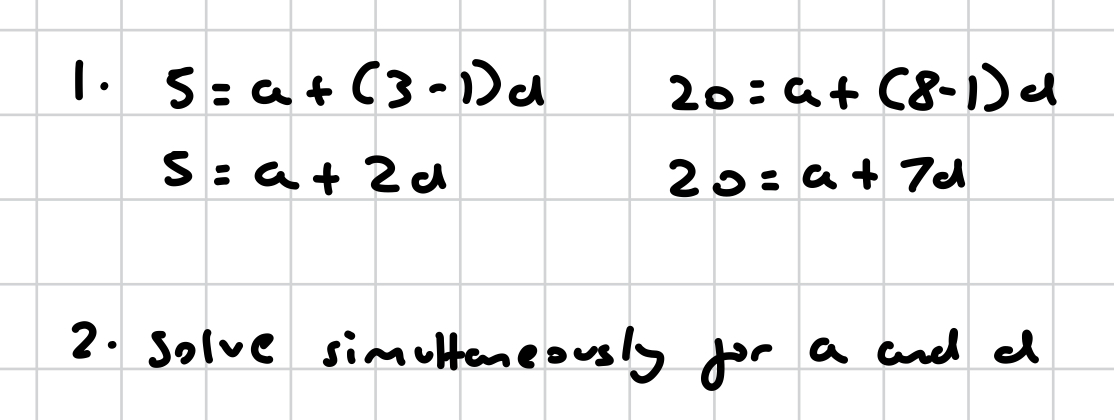

how do you solve this?

when working out a constant, what does it mean when you calculate 2 values as opposed to 1?
IDKJJJ ASK MISS
what is a series?
the sum of terms in a sequence
Sn for arithmetic sequence
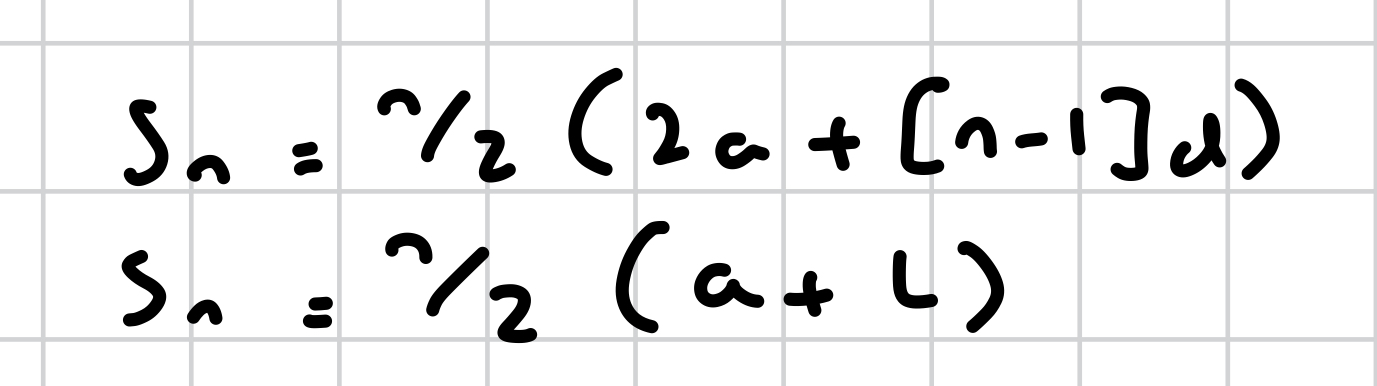
what do you do if you get a decimal for your n value?
round UP to the nearest whole number, as terms can only be whole numbers
what 2 integers can you not have for your n value?
negative numbers
non-whole numbers
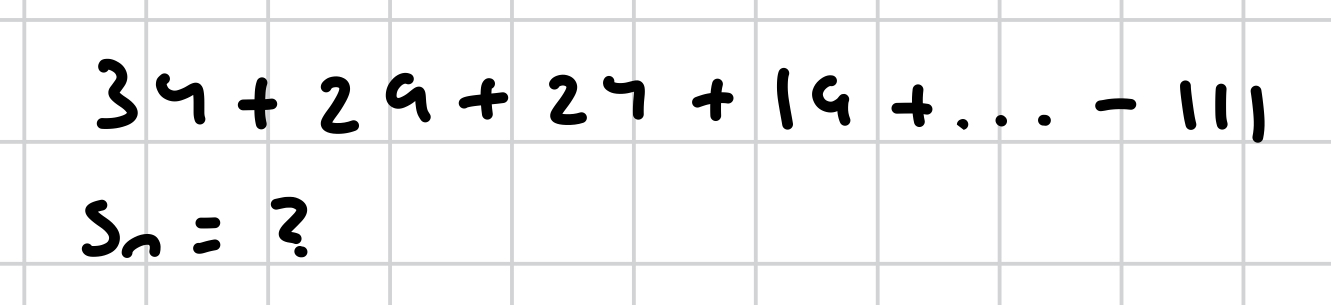
how do you solve this?


how do you solve this?


how do you solve this?
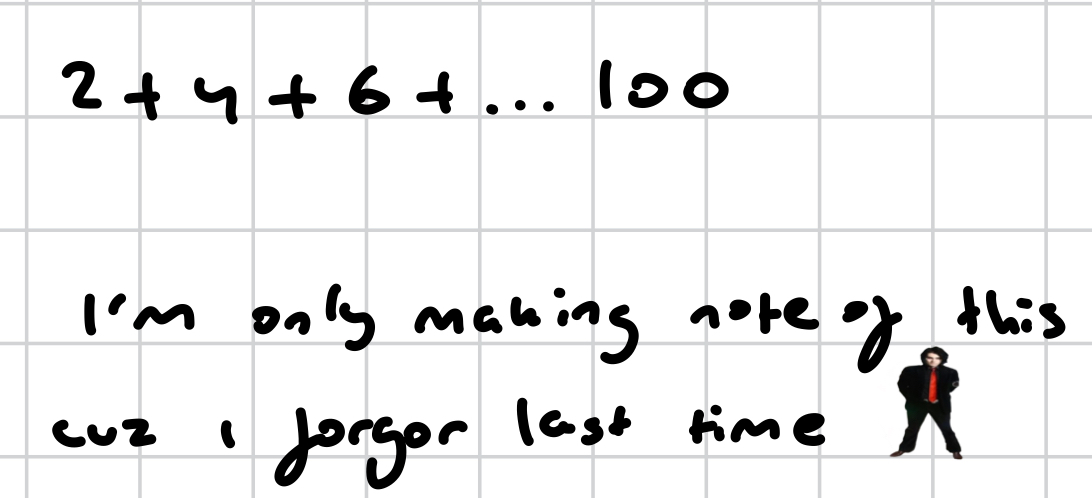

how do you solve this?

Un for geometric sequence

how do you find the common ratio?

is the common ratio multiplication, division, or both?
always multiplication
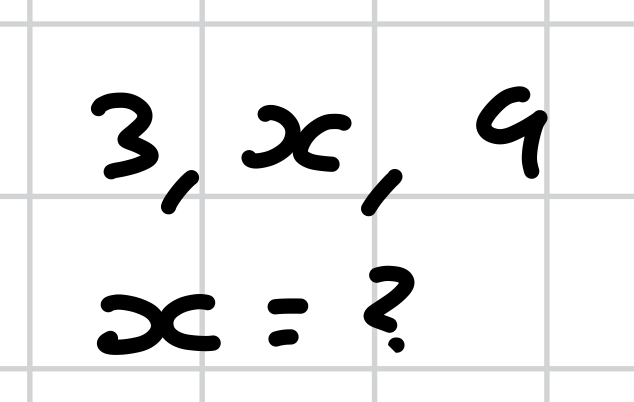
how do you solve this? (geometric)
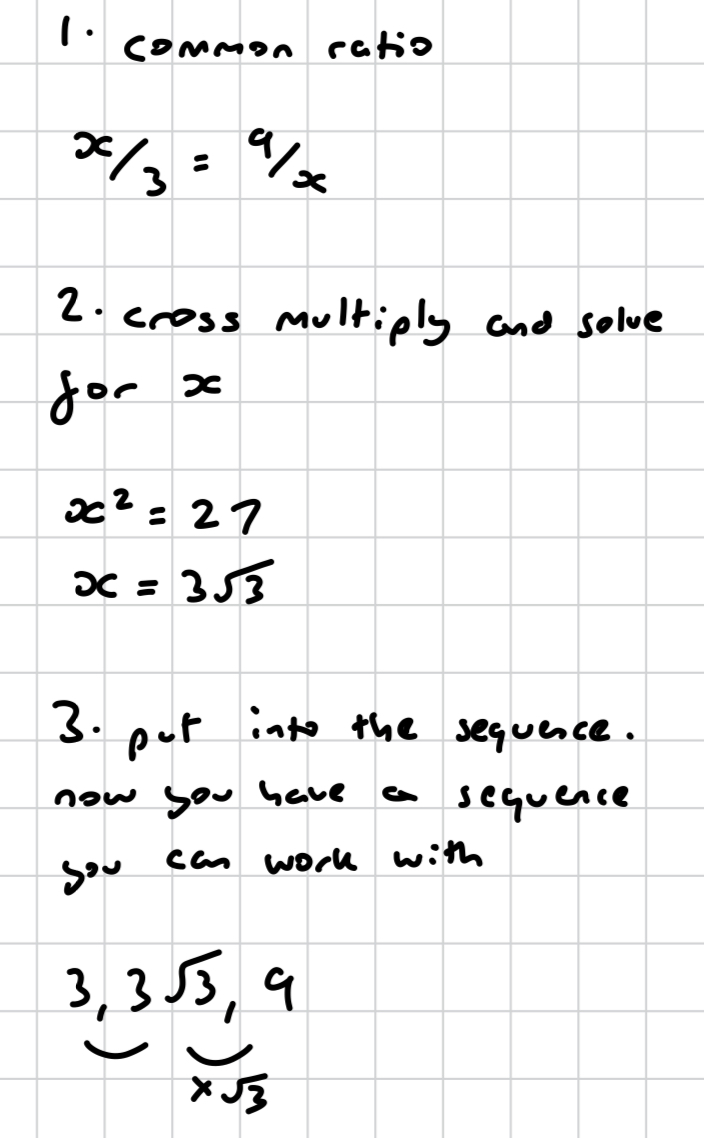
is 0 a natural number?
no
what are sequences also sometimes called?
progressions
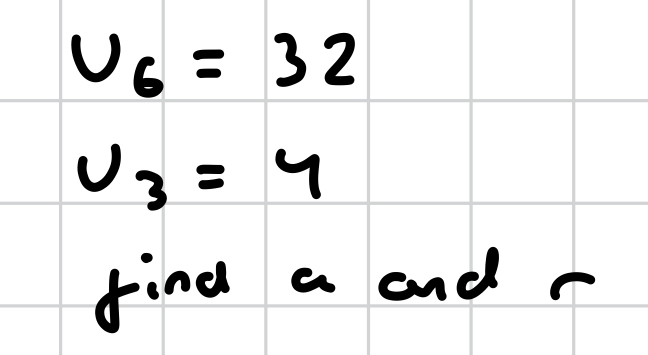
how do you solve this? (geometric)
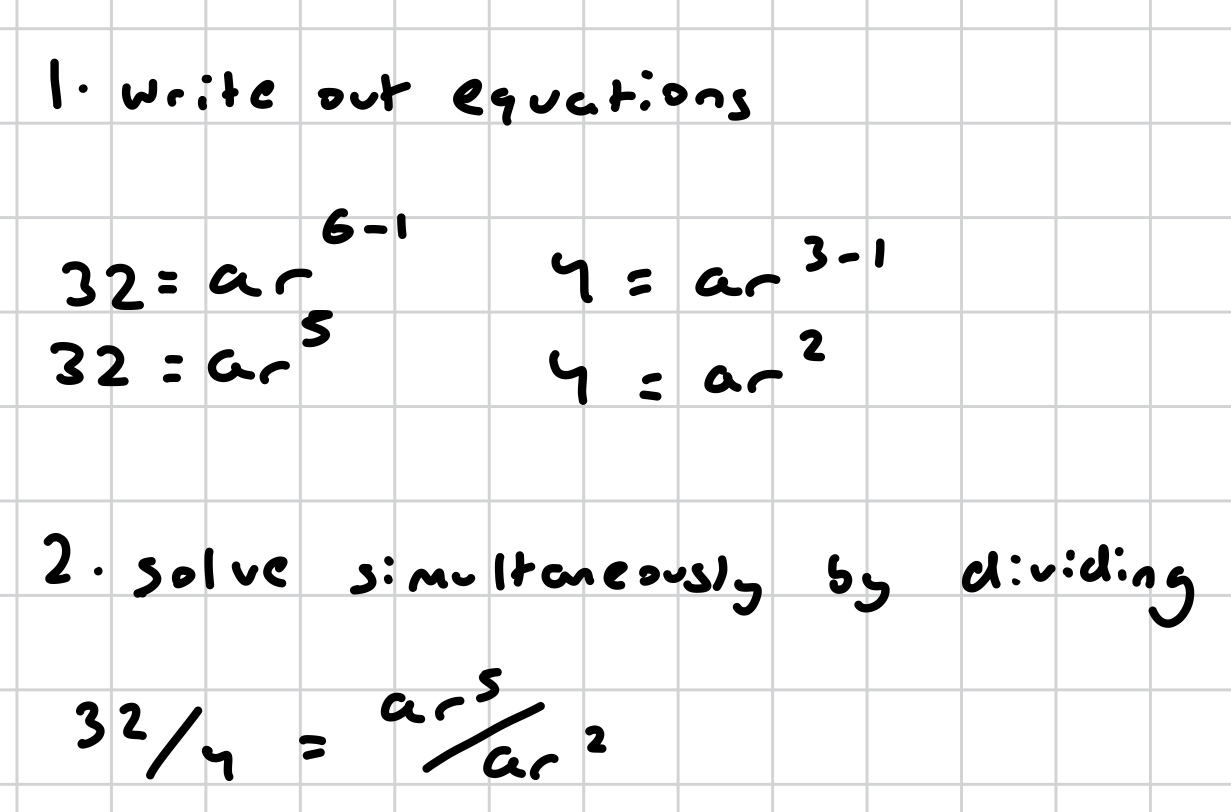
Sn for geometric sequence
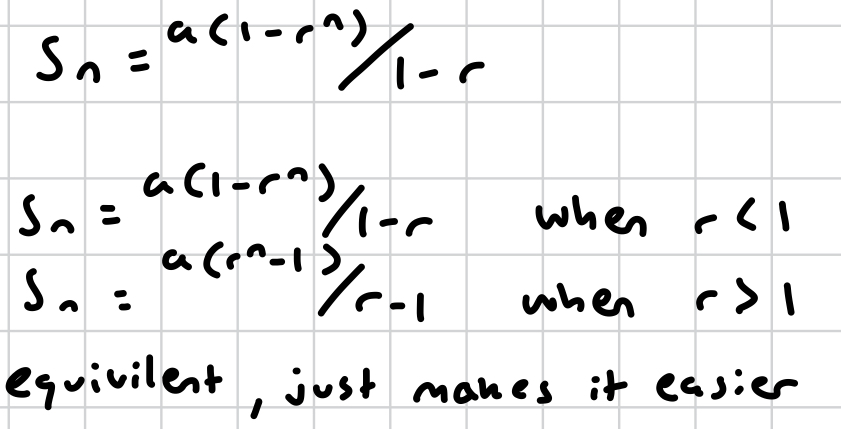
if you flip the signs (+ve and -ve), what must you also flip?
the inequality
what mathematical technique must you implement when finding the sum of geometric sequences?
logs
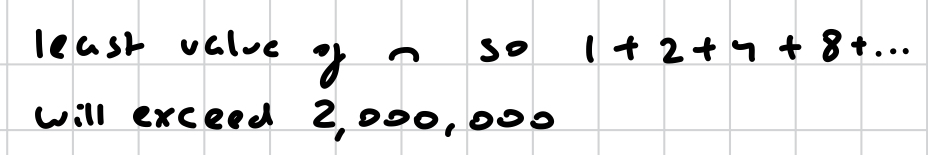
how do you solve this?
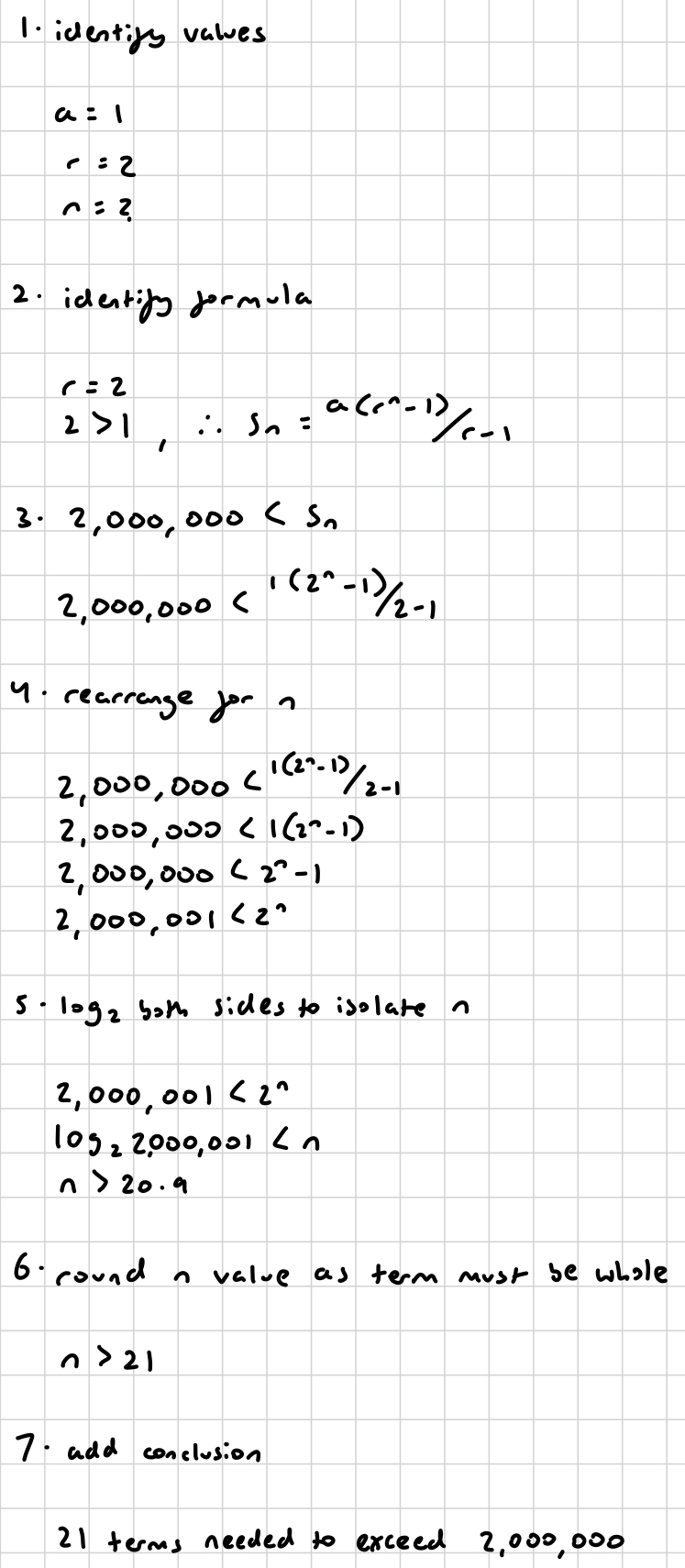

how would you find n given a geometric sum like this, with the last term given?
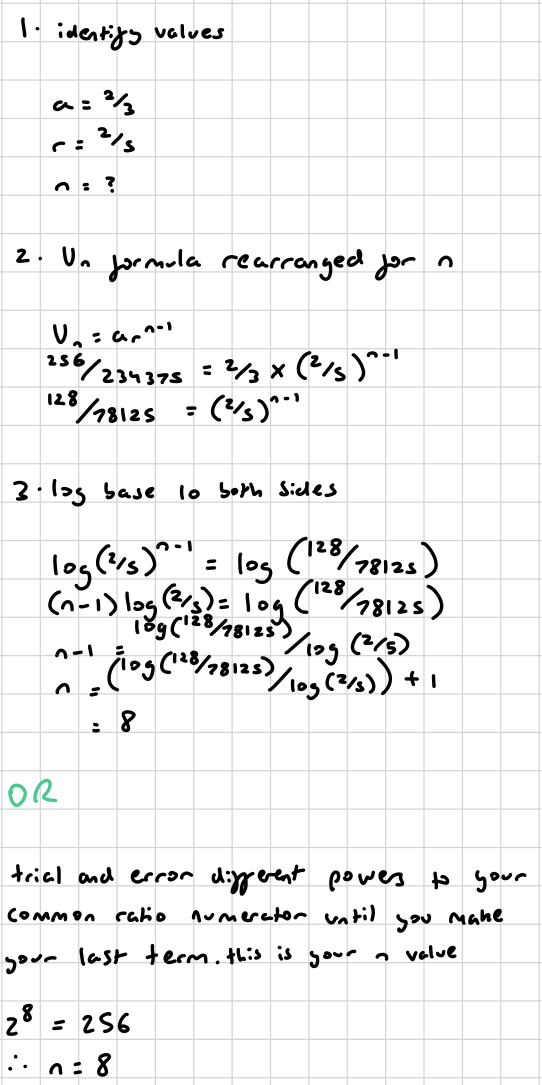
what is an alternating sequence?
a sequence in which terms are alternately positive and negative
do alternating sequences occur in arithmetic or geometric sequences?
geometric

how do you solve this?
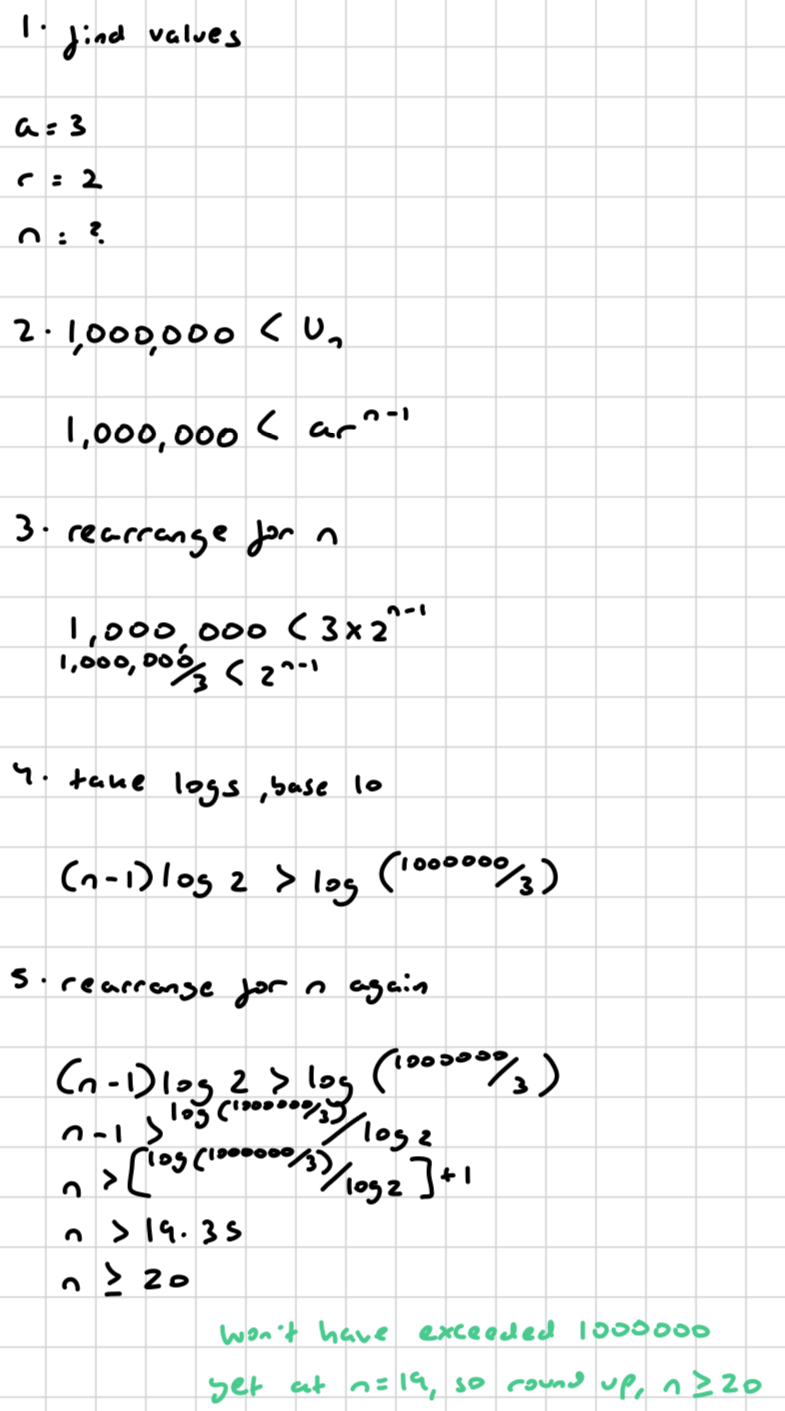
when working out n, how do you round?
always round up because n must be an integer, and the rounded down integer will not yet be the term that exceeds the value
if you’ve had to round up your value for n, how should you present the inequality?
n ≥ value, because the true n value is less than you’re rounded integer, so you include the integer as a possible value n could equal