Physics end of year revision Thursday
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the definition of a wave
things that transfer energy without transferring matter
Features of longitudinal waves
direction of oscillation is parallel to the direction of energy transfer. They have compressions and rarefactions
Features of transverse waves
Direction of oscillation is parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
A wavelength is the length between two of the same points on consecutive waves.
Amplitude symbol, unit and meaning
symbol-A
unit-meters
Meaning-maximum distance from rest
Wavelength symbol, unit and meaning
Symbol- upside down y
unit-meters
Meaning- distance between 2 consecutive identical points in a wave cycle
Frequency symbol, unit and meaning
symbol-f
unit-hertz, Hz
meaning-the number of waves cycles per second
Time period symbol, unit and meaning
symbol-T
Unit-seconds
meaning-time taken for one wave cycle to pass through a point.
What is the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?
The difference between transverse and longitudinal waves is the direction of oscillation in relation to the direction of energy transfer. In a longitudinal wave the direction of oscillation is parallel to the direction of energy transfer. In a transverse wave the direction of oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
Word and symbol equation for time period
Time period(s)= 1/frequency(Hz)
T=1/f
Word and symbol equation for wave speed
Wav speed(m/s) = frequency(Hz) x Wavelength(m)
V=f x upside down y
What is a real image
formed where light rays meet
What is a virtual image
Formed where the brain incorrectly thinks light rays meet
What is a specular reflection
Image formed when light reflects off a smooth surface
What is a diffuse reflection
no image forms, light scatters off a bumpy surface
How does the angle of incidence relate to the angle of reflection
they are equal
what is the normal
a line that is always perpendicular to the reflecting surface
What happens when white light is shining on a blue object
Blue light is reflected and red and green light is absorbed because blue objects only reflect blue light.
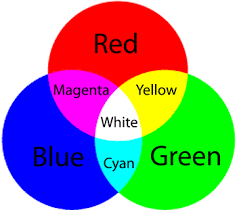
What happens when white light is shining on a yellow object
red and green light is reflected and blue light is absorbed because yellow only reflects red and green.
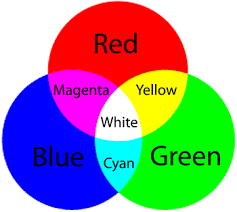
What light is reflected when yellow light shines on a magenta object
Red light is reflected because magenta objects reflect red and blue. yellow contains blue and green. the green is absorbed and the red goes through.
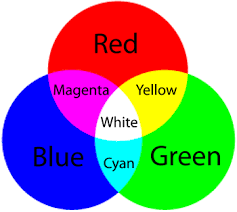
What light is reflected when cyan light is shining on a red object
black because a red object reflects only red. cyan contains green and blue but no red so nothing is reflected.
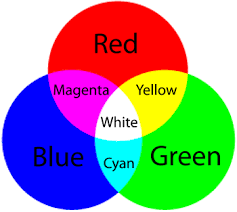
What light goes through when white light is shone on a cyan filter
blue and green light go through because a cyan filter transmits green and blue
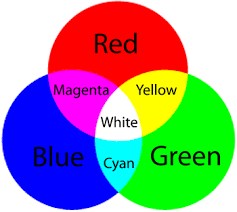
What light goes through when cyan light is shone on a magenta filter
Blue light goes through because a magenta filter only transmits red and blue light so the green in the cyan is absorbed and only the blue goes through.
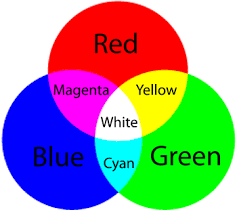
what light is reflected when magenta light shines through a red filter and onto a blue object
Magenta light consists of red and blue wavelengths.
A red filter only transmits red light while absorbing other colors. So, the blue component of magenta is removed, leaving only red light to illuminate the object.
A blue object mainly reflects blue wavelengths and absorbs other colors. Since the red filter removed the blue light, the object doesn't receive any blue to reflect.
Result: The blue object absorbs the red light and reflects little to no visible light, making it appear black
examples of transverse waves
Gamma rays
X-rays
Light
examples of longitudinal waves
Sound
Ultrasound
Name and describe the 8 energy stores
Kinetic-Moving objects have energy in this store
Thermal-Hot objects have energy in this store
Gravitational potential-Objects that are higher up have more energy in this store
Chemical- Energy stored in substances due to the bonds between atoms and molecules. This energy is released during chemical reactions
Elastic potential energy-Stretched or compressed objects have energy in this store
Electrostatic-Refers to the energy stored due to the presence of electric charges.
Magnetic-Magnetic objects have energy in this store
Nuclear-Energy stored in an atoms nucleus. released in nuclear reactions.
Name and describe the 4 energy transfers
Mechanically-An object moving due to a force acting e.g. pushing, pulling, stretching
Electrically-A charge moves through a potential difference e.g. a current flowing around a circuit
By heating-Energy transferred from a hotter object to a colder object
By radiation-Energy transferred by waves e.g. sound, electromagnetic
What is the equation for efficiency
Efficiency(%) = Energy transferred to useful store
Total input energy
X 100
What do Sankey diagrams do
They show how much energy is transferred usefully and how much is wasted
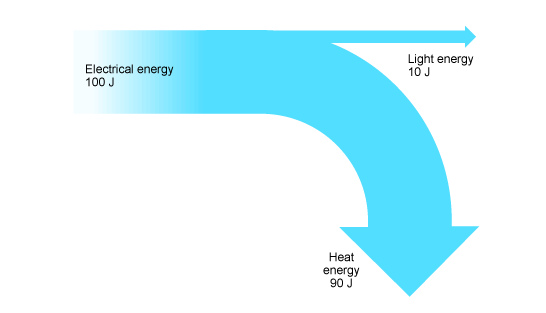
How can waste energy transfers be reduced
Use high quality items to reduce friction between the different objects. Use lubricant to reduce energy lost by friction. Cooling fans can be used to stop over heating.
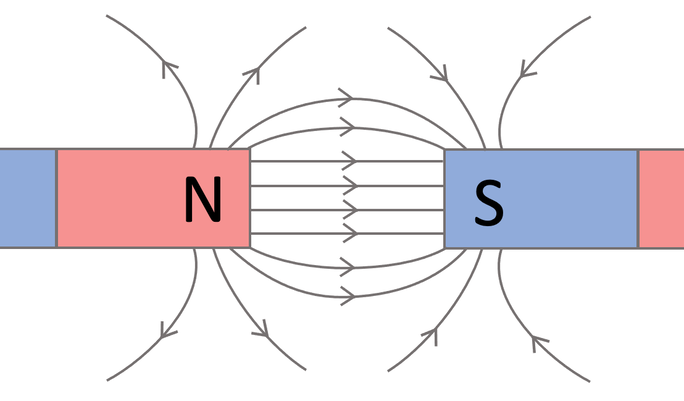
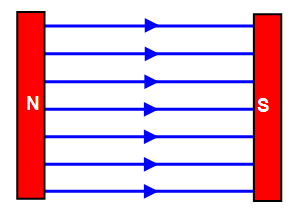
What are the 3 rules of drawing field diagrams for magnets
Filed lines cannot cross
The more dense the field lines, the stronger the field
Field lines point in the direction that a north pole feels force(N to S)
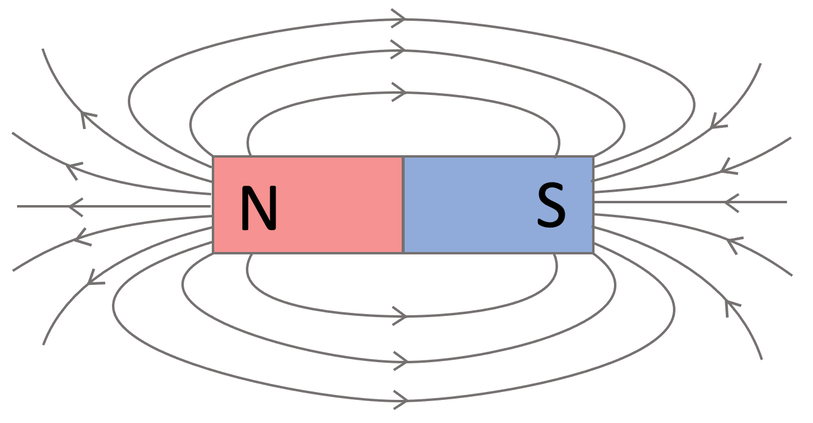
Diagram for like poles

diagram for opposite poles
uniform field diagram
like poles…
repel
opposite poles…
attract
Permanent magnets have their domains…
aligned
something non magnetic has … domains
no
Something magnetic has … domains
If I put a magnet near them then the domains will…
random, align
soft magnetic materials … their magnetism when I take away a magnet. The domains….
This is called demagnetism.
lose, un-align
Hard magnetic materials become …. magnetised.
permanently
How are the field linesdrawn in a diagram of electromagnetism
the field lines are in concentric circles that get further apart as you move further away.
Are electromagnets made of hard or soft magnets
soft magnets so the can be turned on and off
What is a common type of electromagnet
solenoid. An electromagnet arrange in a coil which has a field similar to a bar magnet
What 3 things can you do to increase the strength of an electromagnet
Add voltage
increase the number of coils on the solenoid
use a coil that is made from a magnetic material
What does a dot mean on a diagram for electromagnets
that the current is coming outward towards you.
What does it mean if there is an X on a diagram for electromagnets
that the current is going into the page away from you.
What is temperature roughly a measure of
the average kinetic energy in the molecules of a substance
What is radiation
Energy transferred by EM waves such as light. The hotter an object the more radiation it emits
What types of objects are good absorbers of radiation
Dark coloured and Matte object absorb radiation well
What types of objects are bad absorbers of radiation
Light coloured and shiny objects reflect most light
What types of objects are good emitters of radiation
Dark coloured and matte objects are good emitters
What are the 3 ways of heat transfer and how do they work
Radiation- energy transferred by EM waves such as light. the hotter and object the more radiation it emits.
Convection-When a fluid is heated the particles gain energy causing them to move faster and collide more often. the particles move further apart and the fluid becomes less dense and it rise carrying energy with it. The cooler denser part of the fluid sinks and is then heated and the process continues. This can happen in liquid and gas.
Conduction-The heated particle will gain energy and vibrate faster. This makes them collide with neighbouring particles and energy is transferred to the slower particles. This repeats until all particles vibrate equally.
What are the 6 ways of home insulation that we learnt about
Cavity wall-Air gap between two layers of wall. can also have foam between the two wall layers.
Attic insulation foam- Foam is a bad conductor, this reduces energy loss.
Thickness of wall-The thicker the wall, the lower the rate of energy loss will be.
Rubber seals-Go on doors and windows to block air. Warm air can’t escape so less energy is lost.
Double glazed windows-Air gap between to layers of glass because air is a bad conductor.
Aluminium sheeting-Reflects radiation back into the home.
What is a blackbody
A theoretical object that is a perfect emitter and absorber of radiation.
Rules for blackbody spectra
Hot objects emit radiation across a range of wavelengths
The hotter the object, the shorter the peak wavelength
The hotter the object, the more radiation is emitted across all wavelengths
What is the equation for speed
speed = distance/time
V = S/T
How can you find the speed on a distance-time graph
The speed is the gradient
What does velocity mean
speed in a particular direction
What is stopping distance made up of and what is each part.
Braking distance- distance travelled while the brakes are applied
Thinking distance- distance travelled while reacting
What factors affect the braking distance
Road surface
quality of brakes
speed and mass of vehicle
What factors affect thinking distance
age
tiredness
intoxication
Describe charging by friction
When we rub objects together, the force of friction can cause electrons to be transferred from one object to another.
Describe charging by induction
A strong charge can attract or repel the electrons in another object. Even though electrons aren’t transferred to a new object, they are re-arranged causing a charge build up.