6. Politician Selection and Incentives
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
MVT and Politician Identity
according the MV model, politicians aim to maximize election probability by appealing to the median voter → politician identity should not matter
this is a major appeal of elections → voter preferences (no politicians) matter
otherwise MVT won’t hold if candidates policy preferences differ from MV and care about their own policies
which characteristics matter: age, business experience, ethnicity, gender, socioeconomic background, tenure)
Politician Quality
politician quality: Quality is a valence issue or something most voters agree with and want more of. (ex. competence of a candidate is not a policy preference)
What can politician quality include? ALL valence issues
leadership skills: ability to look for agreement and common goal
analytical skills: problem-solving skills
public service motivation: honesty, not corrupt
How can we provide causal evidence on whether political leaders matter?
look at how growth was impacted right before the natural/accidental death of a leader and right after new leader takes power
main result: sustained change in growth patterns after leadership change → replacing a median leader with a top leader leads to more growth
Does this result of leadership change just before and after death depend on the type of regime?
democracy → constraints due to checks and balances which can be a good or bad thing
autocracy → ruler has more power and control
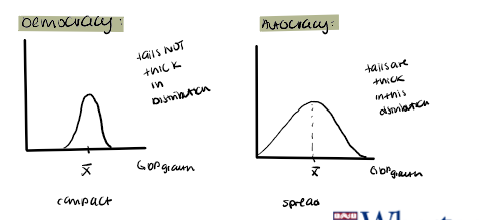
What drives the result?
death of an autocratic leader affects growth, death of a democratic leader does not.
because leader matter more when there are less constraints on the executive
what are the rewards politicians get from office?
wages
public service motivation
rents
Can we recruit better politicians (improve politician selection) by increasing wages?
solution #1: decreased public service motivation
as you increase wages, may attract candidates with lower public service motivation
if public service motivation is important for gov. tasks then this will lead to worse outcome
solution #2: attract people with higher opportunity costs (higher private sector wage) → could be more skilled
higher wages may help recruit more competent politicians if:
private sector wages reflect private sector skills and,
private sector and public office skills are positively correlated
How to improve politician performance?
elections shape incentives politicians face. How?
politician that engages in corruption should have lower re-election changes than a politician that conducts an honest administration
electoral accountability
electoral accountability
keeping politicians honest via electoral rewards and punishments
Support of term limits
incumbency advantage
rotation
political environment
incumbency advantage
electoral advantage derived from being an incumbent through name recognition or access to certain resources available only to them, seeking reelection or to continue serving their term
is incumbency advantage strong in the US? how can you provide casual evidence on this?
The comparison in the graph is between Democratic candidates who barely win and Democratic candidates who barely lose in an election.
find that there is a discontinuity meaning that incumbency advantage is strong
A Democrat who barely wins has a much higher probability of winning re-election compared to a Democrat who barely loses.
allows for rotation
politicians who have been in power for many years will be captured by lobbyists or form corrupt relations, not capturing the voters or MV
term limits allows for rotation
Coviello and Gagliarducci 2017 evidence
compared italian municipalities where rookie mayor was barely elected vs municipalities where the incumbent was barely re-elected
main result: political entrenchment - one more term in office reduces bidders for public work and increases cost of public works
cons of term limits
worse politician selection
kick out experienced politicians
kick out competent politicians who have won past elections
limits electoral accountability
remove the incentive for politicians to work hard for voters once they know they cannot run for re-election
what does evidence say regarding term limits and overall economic performance?
evidence that term limits affect economic policy:
per capita spending and taxes higher under term-limited governors → led to lower state income
higher economic growth under re-election eligible incumbent governors vs. term-limited incumbents
Lecture 6 Summary
difference in leader qualities matter for economic outcomes
higher politician wages may draw better politicians but displace candidates with high public service motivation
electoral accountability can help improve politician performance. However, term limits may be useful in certain cases