pain relief in labour
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
what may be causing pain during the first stage of labour?
ischaemia of cervical wall from contractions
what is ischaemia?
lack of blood suppy to tissues
what does visceral pain mean?
pain that develops from your internal organs
what does somatic pain mean?
pain that develops from your skin, bone, muscle, ligaments, tendons and joints
what is the difference between visceral and somatic pain?
visceral - dull and poorly localised
somatic - sharp and easily localised
what nerve roots usually transmit visceral pain?
T10-L1
what nerve roots usually transmit somatic pain?
S2-S4
what type of pain occurs in the first stage of labour?
visceral pain
what may be causing pain in the second stage of labour?
stretching of pelvic floor, perineum and vagina
what type of pain occurs in the second stage of labour?
somatic pain
what are 4 different types of pain management?
- systemic analgesics
- regional techniques
- pain modulation
- psychological approaches
what are 2 examples of systemic analgesics?
- opioids
- nitrous oxide
how is nitrous oxide administered?
- 50:50 mix with oxygen (entonox)
- inhaled
how quick is the onset/offset of nitric oxide?
rapid - within a few breaths
what are the wanted effects of nitric oxide? (2)
- analgesia
- sedation
what are the negatives of nitrous oxide? (2)
- pollution
- concerns about staff having prolonged exposure
what are 2 examples of opioids?
- diamorphine
- remifentanil
is diamorphine a drug or prodrug?
a prodrug of morphine
how long is the onset of diamorphine?
peaks around 10-20 minutes
what is the half-life of morphine?
2 hours (quite long-lasting)
how long is the onset of remifentanil?
peaks around 2 minutes
what is the half-life of remifentanil?
around 3 minutes
what are some disadvantages of opioids? (4)
- nausea
- respiratory depression
- baby can be sedated
- remifentanil in particular needs intensive monitoring
what are two examples of regional techniques?
epidural and pudendal nerve block
what does epidural mean?
above the dura mater
where is the dura mater located in the spine?
outer layer surrounding the spinal cord
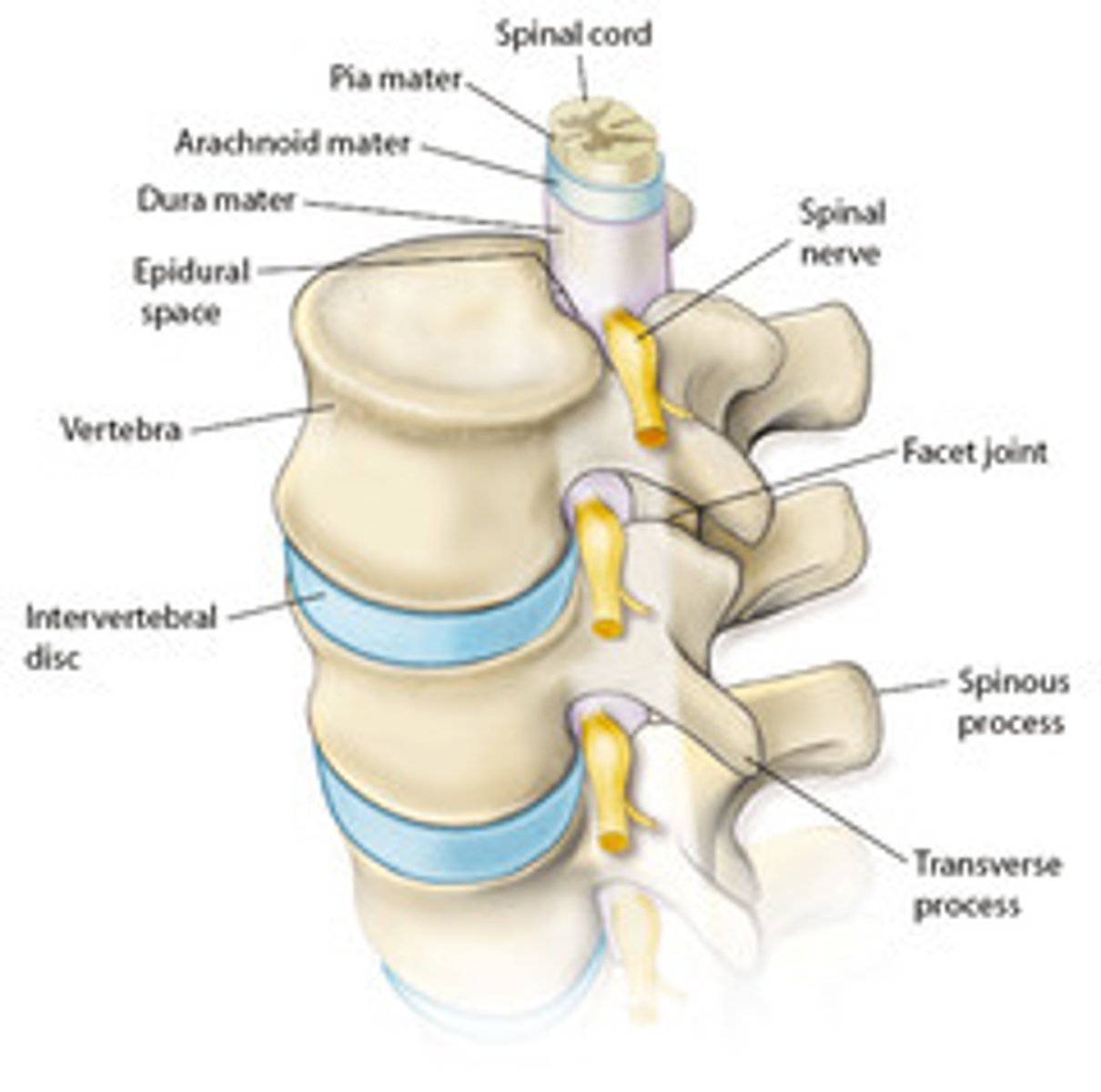
what are the effects of an epidural? (2)
- blocks nerve transmissions
- fairly localised effect
how is an epidural administered? (3)
- local anesthetic is given to numb an area on the back
- a needle is inserted into the lower back near the spinal cord
- a catheter is threaded into the epidural space and medication is injected
what are some disadvantages of epidurals? (4)
- likely to make instrumental delivery more likely (e.g. use of forceps)
- risk of headache
- low blood pressure
- needs intensive monitoring
what is an example of pain modulation?
TENS (neuromodulation)
what are the effects of TENS?
small electrical impulses are delivered to affected area, which can reduce the pain signals going to the brain and spinal cord
how is TENS delivered?
small patches applied to target area and small electrical impulses are sent from machine
is TENS useful in labour and why/why not?
no - not strong enough!
what is an example of a psychological approach?
hypnobirthing
why can hypnobirthing work?
pain and psychology strongly related
what is the pain ladder in labour?
1) non-pharmacological methods
2) nitrous oxide
3) simple analgesia - paracetamol
4) opiate analgesia
5) epidural
6) pudendal nerve block
what are examples of non-pharmacological methods?
- exercise
- heat therapy
- acupuncture
- hypnosis
- massage