PE - skill acquisition
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is a skill?
A learned ability to bring about pre determined results with the minimum outlay of time, energy or both.
What are the required characteristics of a skill?
Aesthetically pleasing
Controlled / coordinated
Efficient
Fluent / smooth
Accurate
Consistent
Economical
What determines it a skill is open or closed? And give examples
Environmental influences. Eg open skill - dribbling past a defender. Closed skill - darts throw.
What determines a skill being gross or fine? And give examples.
Large muscle groups vs small muscle groups. Eg gross skill- rugby tackle. Fine skill- snooker shot.
What decides if a skill is simple or complex? And give examples.
The number of decisions needed to make. Simple skill - split leap in gymnastics. Complex - 10 bounce trampolining routine.
What determines is a skill is self paced or externally paced? And give examples.
If you have to control the skill or react to something else. Self paced - High jump. Externally paced- Block in volleyball
What determines it a shill is low organisation or high organisation? And give examples.
How you break the skill down. Low organisation- discus throw. High organisation - triple jump.
What are discrete, serial and continuous skills? And give examples.
Skills can be discrete (readily identifiable beginning and end), serial (a series of discrete actions), or continuous (no readily identifiable beginning and end). Discrete - snooker shot. Serial - triple jump. Continuous - dribbling in a hockey game.
What is transfer of learning?
When a skill learnt in one activity can affect/ influence / impact skills in another.
What is positive transfer? And give an example.
Learning a skill facilitates the learning of an additional skill. Eg overarm volley in volleyball and a tennis serve.
What is negative transfer? And give an example.
Learning a skill hinders / inhibites the learning of an additional skill. Eg forehand clear in badminton and a forehand drive in tennis.
What is zero transfer? And give an example.
Learning a skill has no effect on learning another skill. Eg a tackle in rugby and a tumble turn in swimming.
What is bilateral transfer? And give an example.
Learning and practicing a skill on one side of the body improves learning on the other side of the body. Eg snooker shot from one hand to another.
How do you ensure positive transfer?
Ensure the skill is over learned
Make practice sessions realistic and relevant to competitive environment
Give praise and positive reinforcement
Coach makes performer aware of possible transfers
Identify elements that may hinder learning
Slow planned progression
Eliminate bad habits
Ensure performer is motivated
What are the different types of practice?
Massed
Distributed
Mental
Varied
What is massed practice?
Continuous practice without rest periods.
Used when the skill is closed, simple and discrete.
Used when a performer is highly motivated, autonomous and physically fit.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of massed practice?
Advantages
Improves fitness
Skill becomes over learned and habitual
Motor programmes are formed and stored
Efficient use of time
Disadvantages
Can cause fatigue
No time for feedback
Might not be physically fit to perform this type of practice
What is distributed practice?
Practice with rest periods included for those that may have low motivation and/or fitness.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of distributed practice?
Advantages
Used for complex skills
Useful for discrete skills
Provides time for mental rehearsal
Helpful for beginners
Disadvantages
Can be time consuming
Breaks can be unnecessary for experienced athletes
What is mental rehearsal?
Going over the skill in the mind without moving. This can be used when the skill is complex or serial.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of mental practice?
Advantages
Can be used for cognitive and autonomous players
Produces clear mental images
Helps with motivation, confidence and anxiety
Muscles are stimulated
Reaction time improves
Disadvantages
Mental images must be accurate
Difficult for cognitive performers
Difficult if environment is not quiet
What is varied practice ?
Practicing skills and drills in a consistently changing environment. Used for open, externally paced and complex skills.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of varied practice ?
Advantages
Increased motivation
Performer gains experience from lots of situations
Positive transfer into gave play
Disadvantages
Time consuming and fatiguing
Risk of negative transfer
What is whole practice?
Practicing the skill in its entirety without breaking it into sub-routines.
What is whole-part-whole practice?
Skill is attempted fully to get initial feel then is broken up to perfect.
What is progressive part practice?
Skill is learnt in parts, broken down into consecutive parts.
What is a cognitive learner?
Beginner
Thinking and working out.
Slow and uncoordinated.
Trying to copy demonstrations.
Motor programmes haven’t developed.
Trial and error.
Extrinsic feedback.
What is an associative learner?
Mediocre
Becomes accomplished performer.
Trial and error.
Compares performance to top level
Movements become smooth and coordinated.
Feedback becomes more intrinsic.
What is an autonomous learner?
Expert/pro
Reached after effective practice.
Must continue to practice in order to stay at this level.
Fluent, efficient and automatic.
Basic skills have developed as motor programmes.
Less trail and error.
Intrinsic feedback.
What is a learning plateau?
A period of time during performance where there are no signs of improvement.
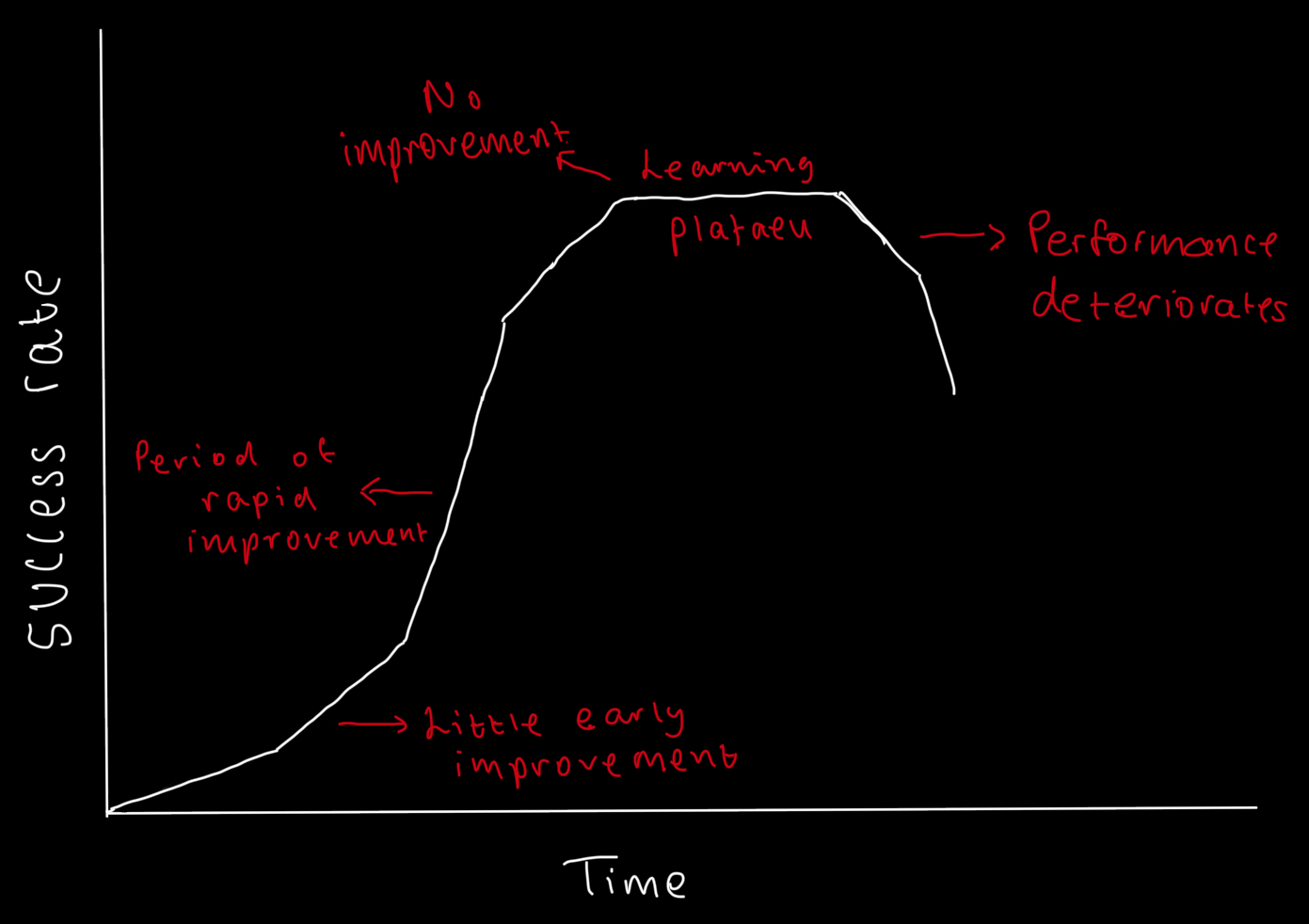
What's the first stage of the learning curve?
Rates of success are slow and performance is poor
New to the task - cognitive.
Using trial and error.
What's the second stage of the learning curve?
Sharp increase in success rate.
Performer has began to master the task.
Fluency increases and motivation increases.
What's the third stage of the learning curve?
Learning plateau reached.
Progress has been haltered.
Performance levels are maintained.
What the fourth stage of the learning curve?
Reduced success rates.
Drive reduction occurs
Tedium.
New challenge or goal must be set.
What are the causes of a learning plateau?
Loss of motivation
Poor coaching
Reached ability level
Goals set too high or low
Mental / physical fatigue
Tedium
What are some cures for the learning plateau?
Set new goals
Positive feedback
New coach / different methods of coaching
Play against the same ability
Set ‘SMARTER’ goals
Rests to improve fatigue
Varied practice to improve tedium
What are the different types of guidance?
Visual
Verbal
Mechanical
Manual
What is visual guidance?
Allows performer to see how to perform a skill.
Eg demonstrations, images, videos.
Must be within their capability
What is verbal guidance?
Instructions on what to do and how to do it.
Best used in conjunction with visual guidance.
Used more for autonomous players.
What is mechanical guidance?
Use of an artificial device or aid to shape movement.
What is manual guidance?
Physical supporting the performer.
What is operant conditioning?
Psychologist : Skinner (1948)
Uses rewards and punishment to modify behaviour
Rewards - more likely to repeat
Shapes behaviour using reinforcements
What s observational learning?
Psychologist : Albert Bandura (1977)
4 stages :
Stage 1- attention
Grab attention to sell the demonstration
Stage 2- retention
Ability to remember and recall from memory
Stage 3- motor production
Ensure player can recreate the demonstration with their capabilities
Stage 4- motivation
Drive needed to copy the demonstration
What is social development learning?
Learning by association with others influence (MKO - more knowledgeable others).
Inter-psychological learning will take place - the process of learning from others externally.
Constructivism - build on what you know, by interacting with others and copying actions, skills are improved - socialisation.
3 stages of proximal development - 1. Can do alone. 2. Can do with help. 3. Cannot do yet.
What is insight learning?
The performer needs to understand the whole problem before performing the skill correctly.
They base their response on their previous experiences and their current situation.
What is intrinsic feedback?
Feedback that comes from within the performer as a result of their own sensory experience during or after performing a skill.
What is extrinsic feedback?
Feedback provided by an external source, such as a coach or video, to enhance performance and learning.
What is positive feedback?
Feedback that reinforces and encourages a performer by acknowledging their successful actions and efforts.
What is negative feedback?
Feedback that provides information about errors or areas needing improvement, helping the performer to identify mistakes and enhance performance.
What is knowledge of performance?
Feedback related to the quality of movement during a skill execution, focusing on the technique rather than the outcome.
What is knowledge of results?
Knowledge of results is feedback that provides information about the outcome of a performance, indicating whether the goal was achieved.
What is the purpose of feedback?
Reinforces correct actions.
Corrects errors.
Eliminates bad habits.
Acts as a motivator.
Builds confidence.
What does Whiting's information processing model look like?
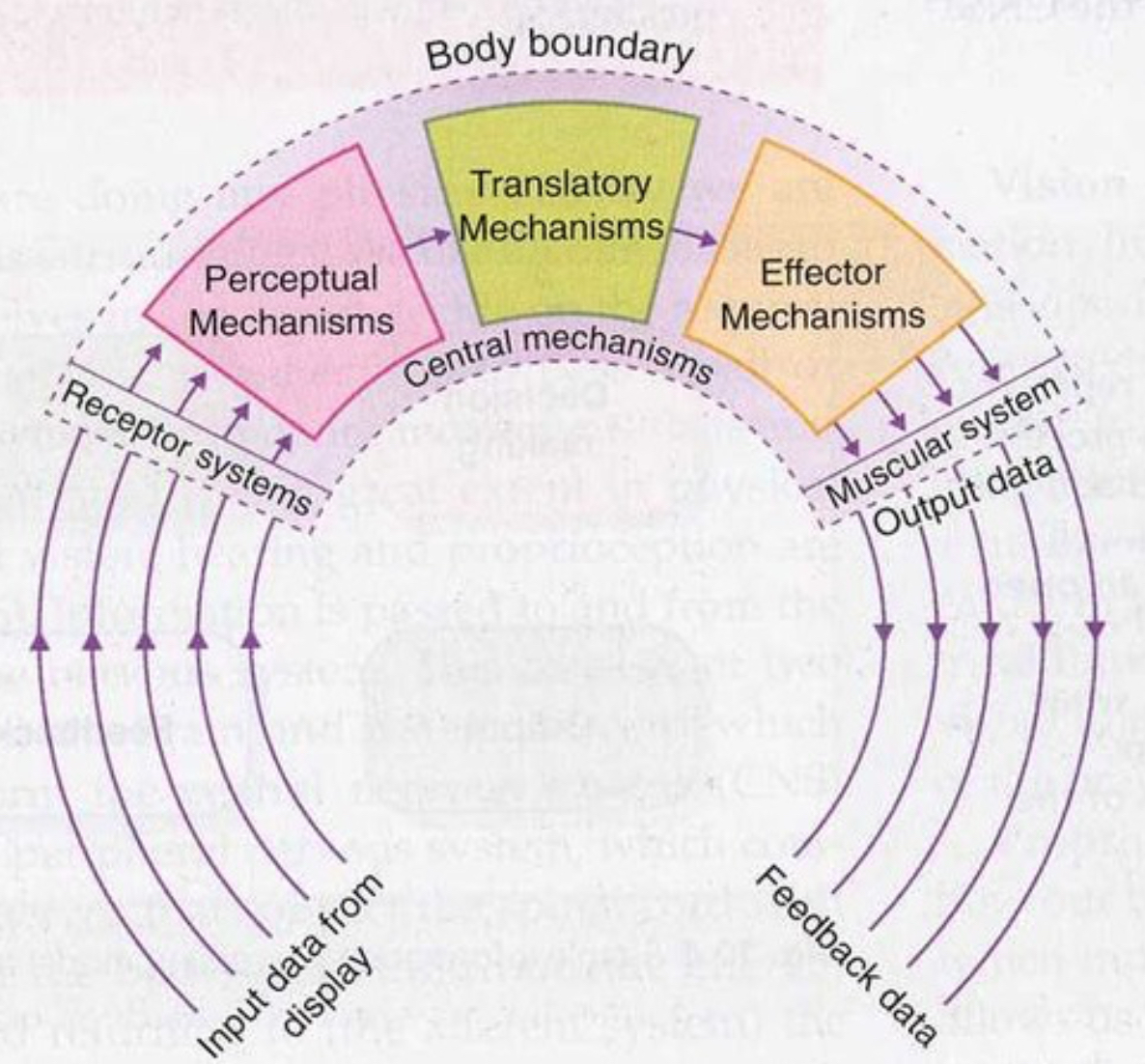
What is the input data from display in Whiting's information processing model?
The information available to the performer- relevant or irrelevant.
What do the 5 arrows represent in Whiting's model ?
The 5 senses -internal and external.
Internal
Touch
Balance
Kinaesthesias
External
Vision
Hearing
What are perceptual mechanisms in Whiting's model?
Interprets information from the display
Uses DCR process.
Detection - receive cues.
Comparison - compare to cues stored in memory systems.
Recognition - what response is needed
What are the translators mechanisms Whiting's model ?
Uses gathered information to make a decision - decision making.
Corrects response selected in form of a motor programme.
What are the effector mechanisms in Whiting's model ?
Transfers decision via nervous system to complete the action.
Impulses are sent to relevant working muscles.
What is selective attention?
The process of focusing on specific stimuli or information while ignoring others, allowing for improved processing of relevant information.
What is the importance of selective attention?
Aids concentration
Improves reaction time
Filters out distractions
Control arousal levels
Reduces chance of information overload in the short term memory
How do you improve selective attention?
Increase stimulus intensity
Relevant practice / learn to ignore irrelevant stimuli
Practice with distractions
Mental rehearsal / imagery
Make stimuli unique / memorable
Highlight specific cues
Optimum arousal levels