Lecture 8 - Ceramics and Other Materials
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What are Ceramics, Glasses and Glass Ceramics?
Definition: an ____ , ___ solid
prepared from ____ materials and
fabricated into products through the application
of ___Primarily ___ and ___ bonds
Categories of these materials
____ (bio-resorbable or inert) ceramics
glass, ___,
glass-ceramics, starts as a ____ and ends up as
a ____ ceramics possibly with a
residue ___ matrix.
General properties:
____ bond =>Difficult to ____, very low ____,
high ____ strength, low ____ strength;Low ___ and ___ conductivity
____ and high ___
High ___ → dental materials
Aesthetically pleasing appearance
Definition: an inorganic, nonmetallic solid
prepared from powdered materials and
fabricated into products through the application
of heatPrimarily ionic and covalent bonds
Categories of these materials
crystalline (bio-resorbable or inert) ceramics
glass, amorphous,
glass-ceramics, starts as a glass and ends up as
a polycrystalline ceramics possibly with a
residue glassy matrix.
General properties:
Ionic bond =>Difficult to shear, very low ductility,
high compressive strength, low tensile strength;Low thermal and electrical conductivity
Refractory and high Tm
High hardness dental materials
Aesthetically pleasing appearance
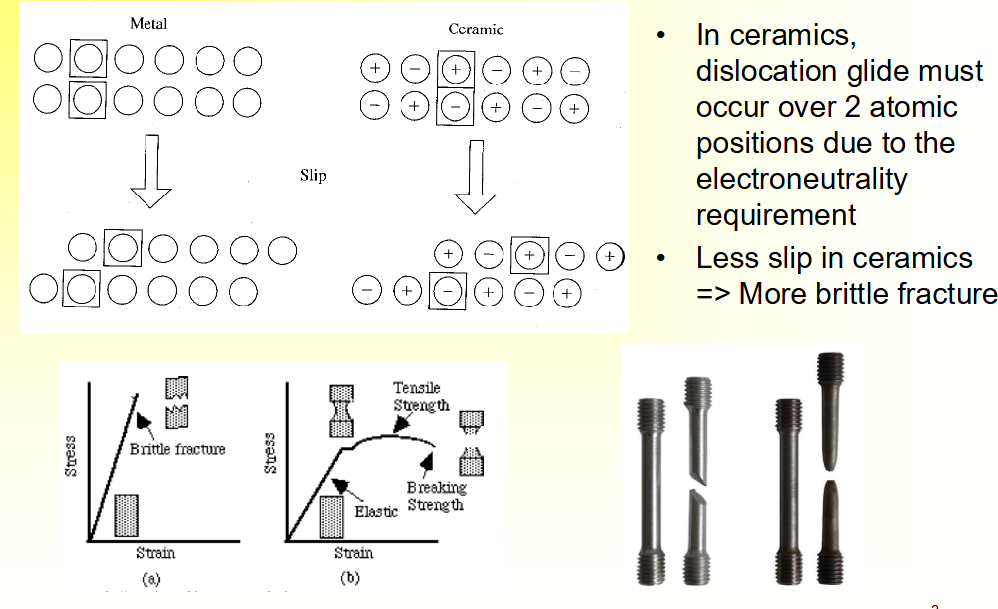
Variation in Slip Between Metal and Ceramics
• In ceramics, dislocation glide must occur over ___ atomic
positions due to the ____ requirement
• ___ slip in ceramics
=> More ___ fracture
• In ceramics, dislocation glide must occur over 2 atomic positions due to the
electroneutrality requirement
• Less slip in ceramics
=> More brittle fracture
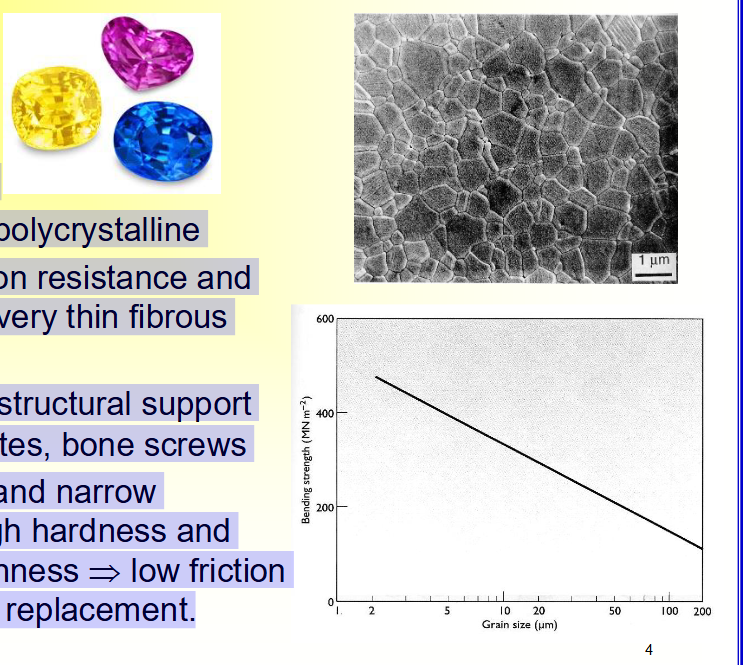
Nearly Inert Bioceramics
• ___ (Al2O3)
• ___ or ___
• ___ crystal or ____
• Excellent ____ resistance and ____ (very ___ fibrous layer)
• ___ strength → structural support such as ___ plates, ____ screws
• ___ grain size and ___ distribution → high ___ and
low surface ___ → low ___ and wear → joint replacement.
• Alumina (Al2O3)
• Sapphire or ruby
• Single crystal or polycrystalline
• Excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility (very thin fibrous layer)
• High strength → structural support such as bone plates, bone screws
• Small grain size and narrow distribution → high hardness and
low surface roughness → low friction and wear → joint replacement.
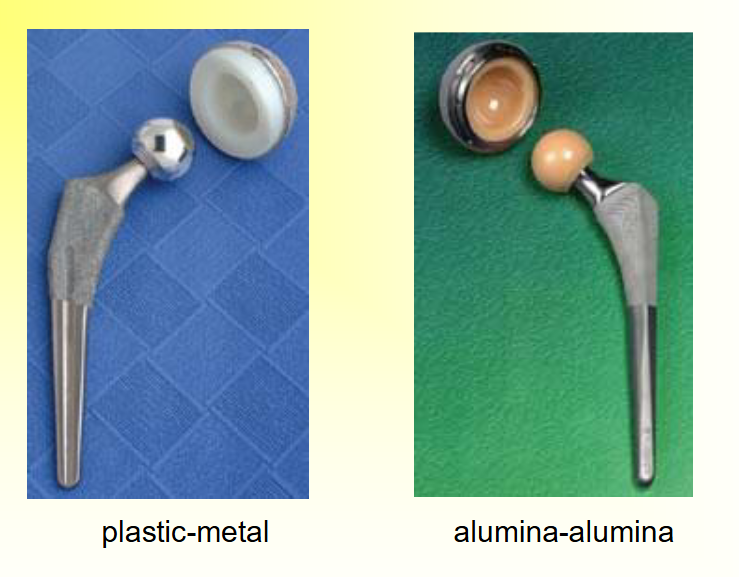
Joint Replacement Applications of Alumina
____ socket and ball, coefficient of friction ___ with time and approaches the value of a ___ joint → wear 10 times ___ than metal-PE surfaces
Alumina socket and ball, coefficient of friction decreases with time and approaches the value of a normal joint wear 10 times slower than metal-PE surfaces
Biodegradable or Resorbable Ceramics:
What causes the biodegradability or resorption?
– Physiochemical ____, depending on the ____ of the material and local __
– Physical ___ into small ___ as a result of preferential chemical attack of ___ ____
– Biological factors, such as ___, which also causes a decrease in local ___
– Physiochemical dissolution, depending on the solubility of the material and local pH
– Physical disintegration into small particles as a result of preferential chemical attack of grain boundaries
– Biological factors, such as phagocytosis, which also causes a decrease in local pH
Calcium Phosphate
• The mineral phase of bone and teeth is mainly ___ and
___ ions.
____ CERAMIC
• Solubility and hydrolysis ___ with increasing __/_ ratio.
• Ca/P ratio __ 1 is not suitable for biological implantation.
• The mineral phase of bone and teeth is mainly calcium and
phosphate ions.
bIODEGRADABLE CERAMIC
• Solubility and hydrolysis decrease with increasing Ca/P ratio.
• Ca/P ratio less than or equal to 1 is not suitable for biological implantation.
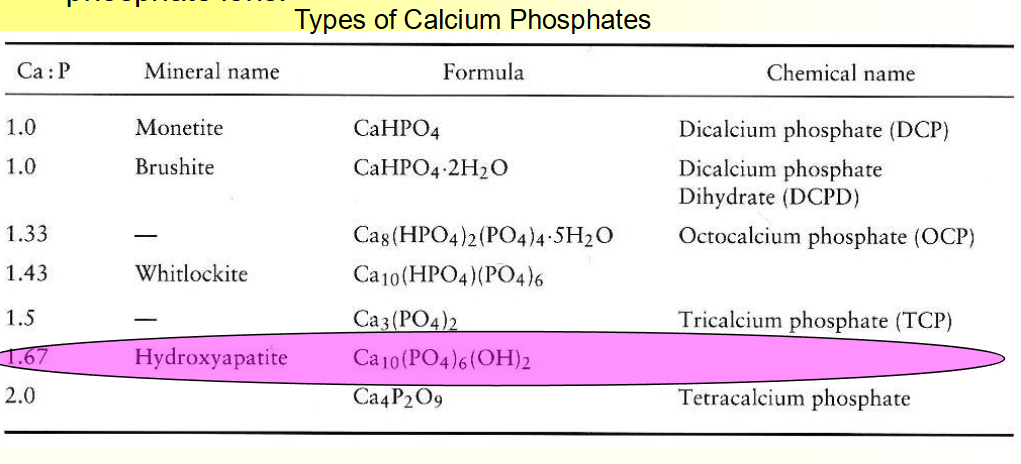
Hydroxyapatite (HA)
Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2,
Hard tissue contain _% HA (mostly carbonate HA), 25% water and 15% organic materials. HA can be converted from ___ or animal __
Manufacturing:
– Ca(NO3)2 + NaH2PO4 → precipitate of HA → drying and filtering → furnace 1150 degrees C → grounding →sieving → pressing in a die → sinteringElastic modulus (__-___ GPa),
– Enamel: 74GPa
– Dentin: 21GPa
– Compact bone: 12-18 GPaHexagonal rhombic crystal
– Substitute of OH- by F-, __ chemical stability
– Defects and impurities can be characterized by __ ___ (crystalline phase), ___ (chemical groups)
Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2,
Hard tissue contain 60% HA (mostly carbonate HA), 25% water and 15% organic materials. HA can be converted from coral or animal bone
Manufacturing:
– Ca(NO3)2 + NaH2PO4 → precipitate of HA → drying and filtering → furnace 1150 degrees C → grounding →sieving → pressing in a die → sinteringElastic modulus (40-117 GPa),
– Enamel: 74GPa
– Dentin: 21GPa
– Compact bone: 12-18 GPaHexagonal rhombic crystal
– Substitute of OH- by F-, more chemical stability
– Defects and impurities can be characterized by X-ray diffraction (crystalline phase), FTIR (chemical groups)
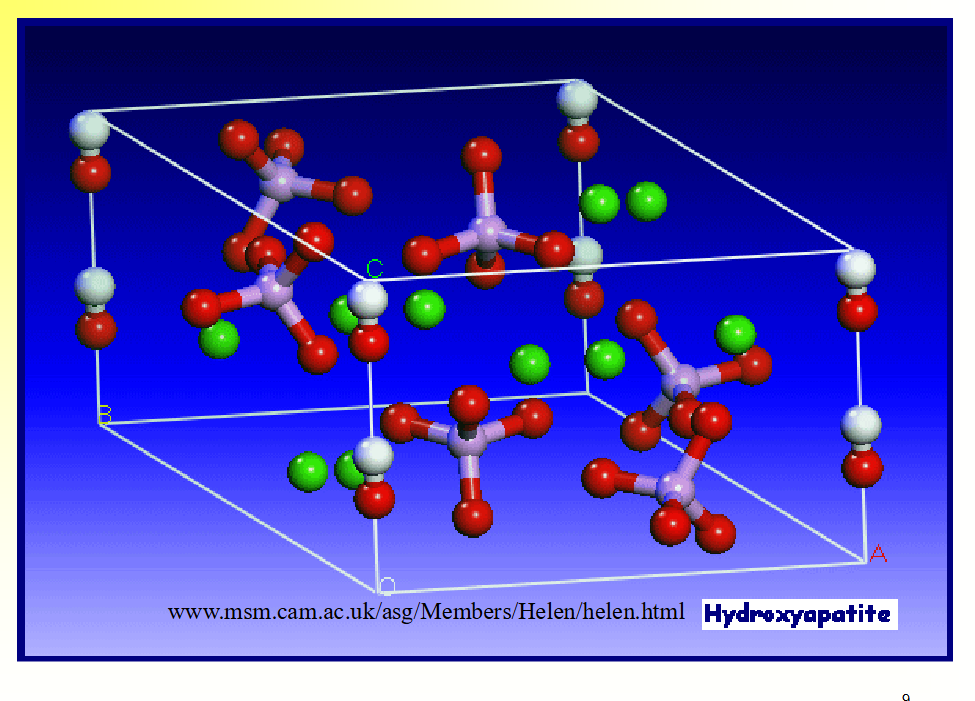
X-Ray Diffraction of HA
Typical FT-IR Spectrum of HA
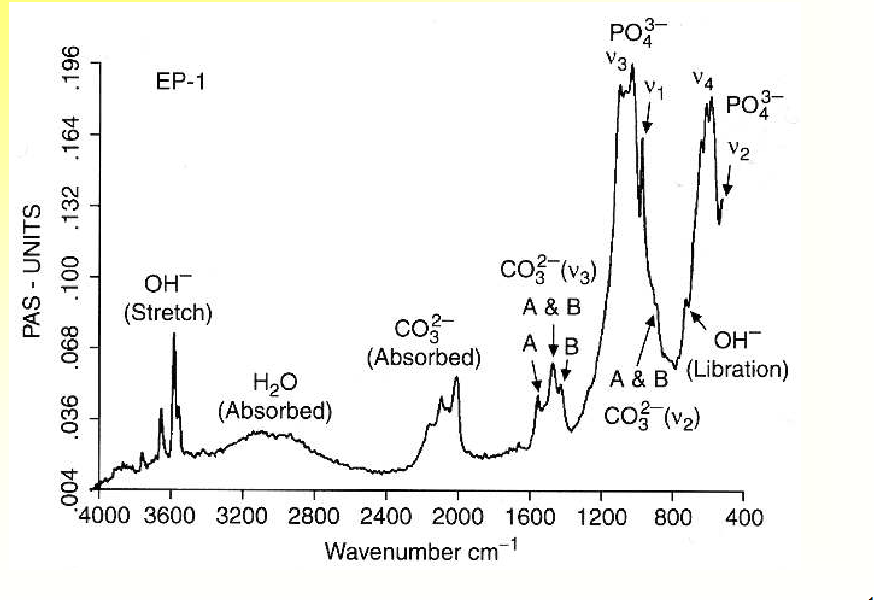
Factors Influence Degradation Rate of Calcium Phosphate
– Rate of degradation increases as
• Chemical susceptibility to dissolution ____
• Surface area ____
• Crystallinity ____
• Crystal perfection ____
• Grain size ____
• F- substitution ____
– Rate of degradation increases as
• Chemical susceptibility to dissolution increases
• Surface area increases
• Crystallinity decreases
• Crystal perfection decreases
• Grain size decreases
• F- substitution decreases
Clinical Application of Calcium Phosphate
• Advantages: ___ and ___
• ___ bonding mechanism
– differentiated osteoblasts produce a cellular bone matrix of 3-5 micrometer layer at the surface → 0.05 to 0.2 micrometer → normal bone ____
through a thin epitaxial bonding layer to the ___ ___
• As dense form:
– small ___ implants such as in the ___
___ implant,
• As porous form
– ____ for filling bony defects in orthopedic
and dental surgery
• As coatings
– with reinforcing ___ posts as in dental
materials,
• As fillers in ____
• Advantages: bioactive and osteoconductive
• Bioactive bonding mechanism
– differentiated osteoblasts produce a cellular
bone matrix of 3-5 micrometer layer at the surface →
0.05 to 0.2 micrometer → normal bone attached
through a thin epitaxial bonding layer to the bulk
implant
• As dense form:
– small unloaded implants such as in the middle
ear implant,
• As porous form
– granules for filling bony defects in orthopedic
and dental surgery
• As coatings
– with reinforcing metal posts as in dental
materials,
• As fillers in composites
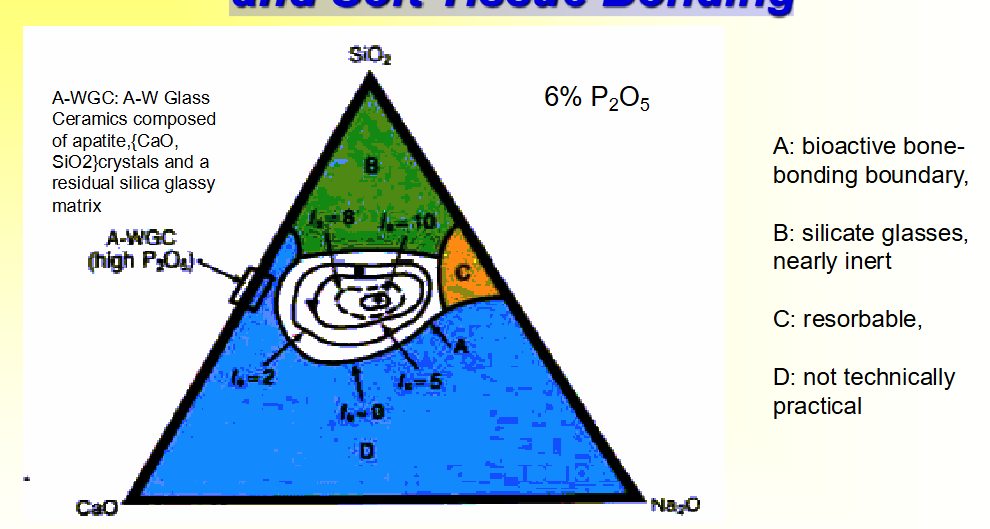
Bioactive Glasses and Glass-ceramics
• Specific composition → highly ____ surface in aqueous medium
– ___ less than or equal to 60%,
– ___ Na2O and CaO,
– ___ CaO/P2O5
• The surface forms a ___ ____ carbonated ___ layer that
provides the bonding ___ with tissue. The ____ strength
greater than or equal to the bulk strength of both the ___ and tissue
• Clinical applications
– 45S5, SiO2 45%, Ca/P=5:1
– Ceravital®, middle ear surgery to replace ___ damaged by chronic infection
– ____ defect repair, maintenance of the alveolar ridge for denture wearers
– Toothpaste ingredient against ____
• Specific composition → highly reactive surface in aqueous medium
– SiO2 greater than or equal to 60%,
– high Na2O and CaO,
– high CaO/P2O5
• The surface forms a biologically active carbonated HA layer that
provides the bonding interface with tissue. The interfacial strength
the bulk strength of both the implant and tissue
• Clinical applications
– 45S5, SiO2 45%, Ca/P=5:1
– Ceravital®, middle ear surgery to replace ossicles damaged by chronic infection
– Periodontal defect repair, maintenance of the alveolar ridge for denture wearers
– Toothpaste ingredient against sensitivity
Compositional Dependence (w%) of Bone and Soft Tissue Bonding
The level of bioactivity of a specific material can be related to the time for more than
50% of the interface to be bonded, (t0.5bb) e.g.: (Index of Bioactivity) IB = (100/t0.5bb).
Sequence of Interfacial Reactions Involved in Forming a Bond Between Tissue and Bioactive Glass

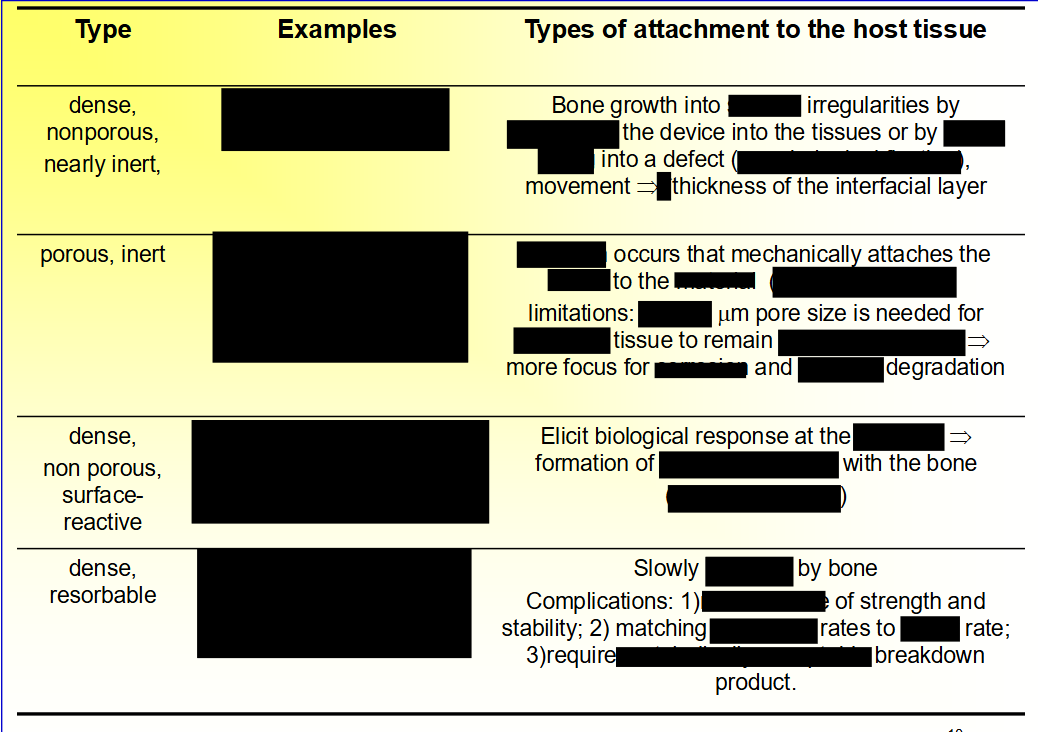
Fill out this chart
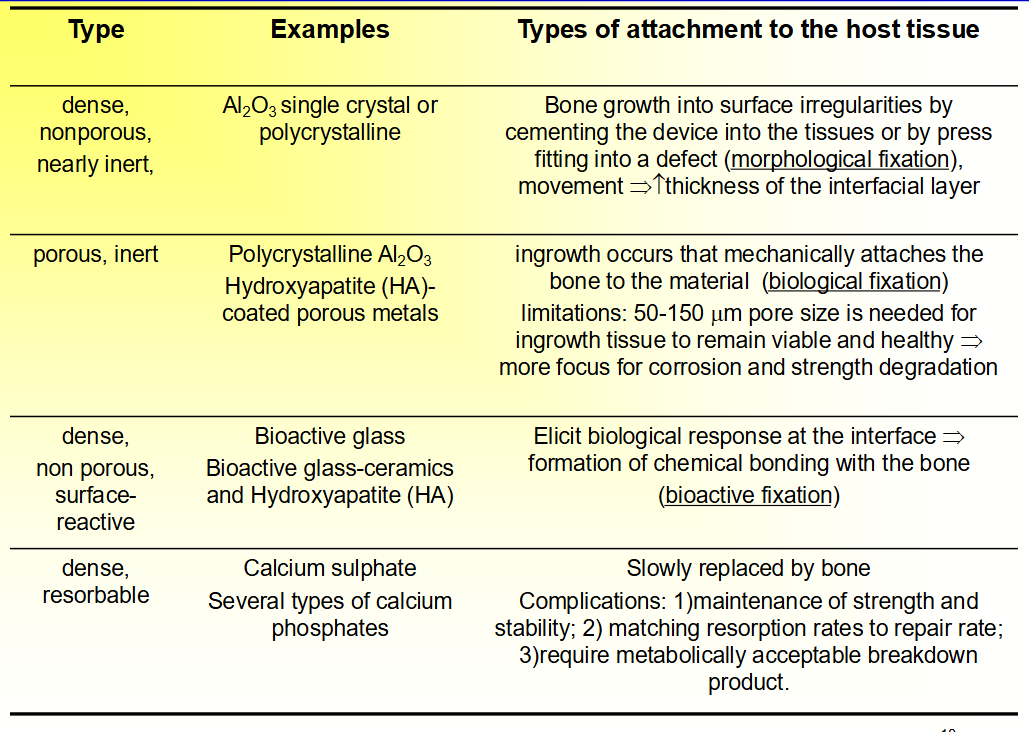
Crystalline Carbon Materials
• Crystalline: diamond, graphite, and fullerene
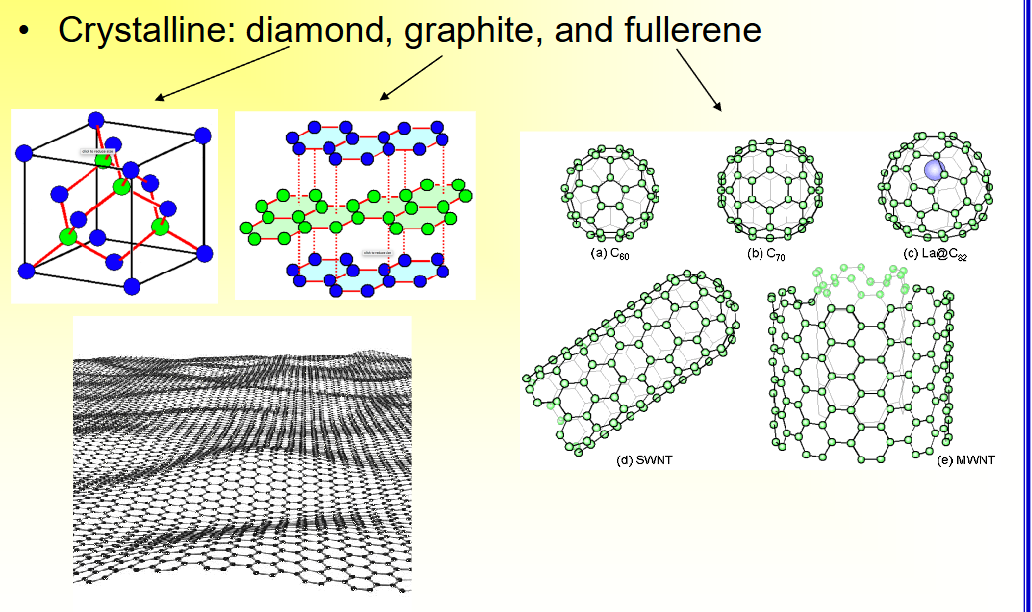
Quasicrystalline Carbon Materials
• Quasicrystalline,
– ____ carbon, extremely ___, used as ____ in electrochemistry or ____
– ____ carbon as implant surface coating, has ____ mechanical strength than glassy and graphite carbon, ____ tissue and blood compatibility,
used in ___ valves and finger joint ____
• Quasicrystalline,
– glassy carbon, extremely inert, used as electrodes in electrochemistry or prosthetics
– pyrolytic carbon as implant surface coating, has high mechanical strength than glassy and graphite carbon, excellent tissue and blood compatibility,
used in heart valves and finger joint implants
Composite Materials
• Consisting of ___ or more chemically distinct parts in the ___-scale, having a distinct ____ separating them
• Fiber or particulate composites usually consists of one or more
_____ phases (usually ____, called reinforcing materials)
embedded in a _____phase (called matrix)
• The property of the composite material depends on
– Properties of each ____
– ___ of the heterogeneities
– ____ fraction
– ___
• Natural tissue such as bone and tendon or vessel are ____.
• Consisting of 2 or more chemically distinct parts in the macro-scale, having a distinct interfaces separating them
• Fiber or particulate composites usually consists of one or more
discontinuous phases (usually stronger, called reinforcing materials)
embedded in a continuous phase (called matrix)
• The property of the composite material depends on
– Properties of each constituent
– Shape of the heterogeneities
– Volume fraction
– Interface
• Natural tissue such as bone and tendon or vessel are composites.
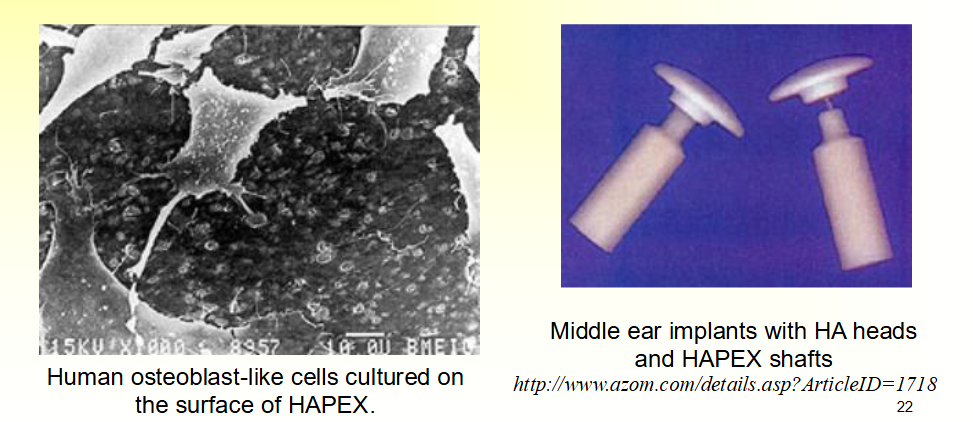
HAPEXTM
• Composite of hydroxyapatite in a polyethylene matrix
• Stiffness similar to cortical bone
• High toughness
• Bone bonding in vivo
• Orbital implant and middle ear implants