Reconstruction and the Jim Crow Era
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Reconstruction
the period after the Civil War in the United States when the southern states were reorganized and reintegrated into the Union. 1865-1877
Radical Republicans
A group that believed the South should be harshly punished and thought that Lincoln was sometimes too compassionate towards the South. Wanted social and political equality for African Americans.
Solid South
Describes the domination of post-Civil War southern politics by the Democratic Party.
Wade Davis Bill
An 1864 plan for Reconstruction by Radical Republicans that denied the right to vote or hold office for anyone who had fought for the Confederacy...Lincoln refused to sign this bill thinking it was too harsh. It was pocket vetoed.
Freedmen's Bureau
Organization run by the army to care for and protect newly freed people after the Civil War.
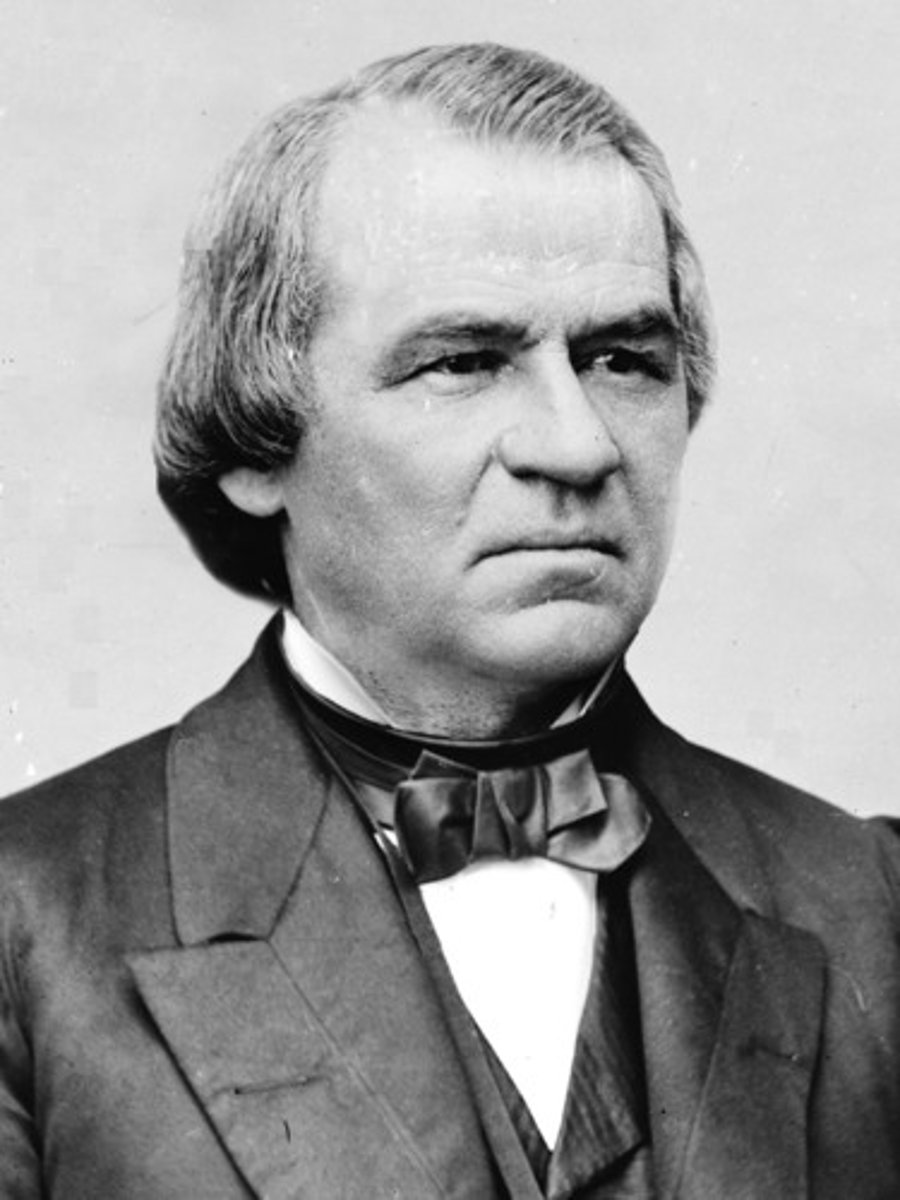
Andrew Johnson
17th president of the United States, came to office after Lincoln's assassination and opposed Radical Republicans; he was impeached.

Black Codes
Laws denying most legal rights to newly freed slaves; passed by southern states following the Civil War. A continuation of slave codes.
14th Amendment
(1) All persons born in the U.S. are citizens; or through naturalization; (2) no person can be deprived of life, liberty or property without DUE PROCESS OF LAW; (3) no state can deprive a person of EQUAL PROTECTION of the laws.
Impeach
To accuse government officials of misconduct.
15th Amendment
Citizens cannot be denied the right to vote because of race, color , or previous condition of servitude.
"40 acres and a mule"
A promise made by General Sherman during the war to freed slaves who followed his army. Did not happen because of property rights.
Pocket veto
If a bill is proposed within 10 days of Congress going on recess and the president does not sign it , it will die (un-overrideable veto). Lincoln pocket vetoed the Wade Davis Bill.
Scalawags
Southern whites who supported Republicans.

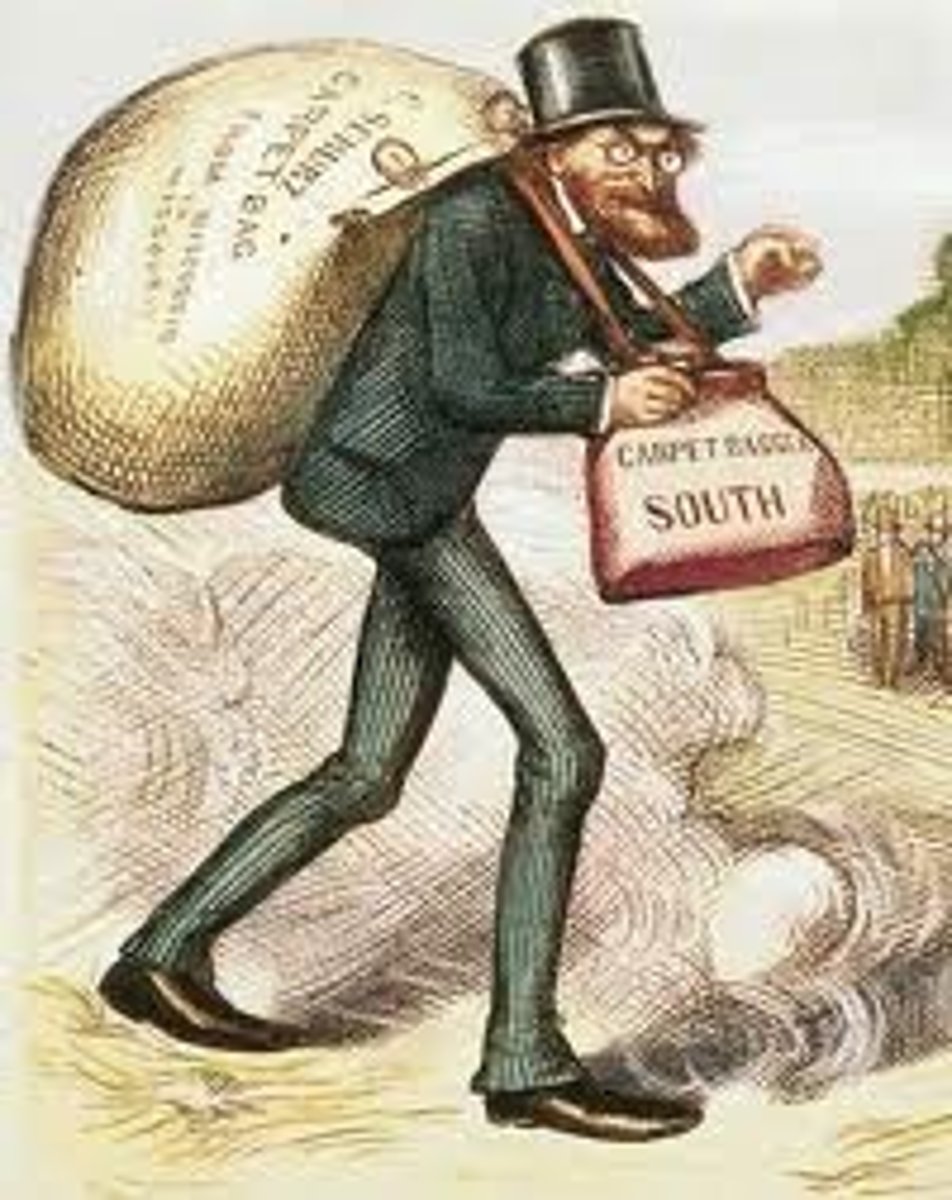
Carpetbaggers
A northerner who went to the South immediately after the Civil War; especially one who tried to gain political advantage or other advantages from the disorganized situation in southern states

Segregation
Separation of people based on racial, ethnic, or other differences
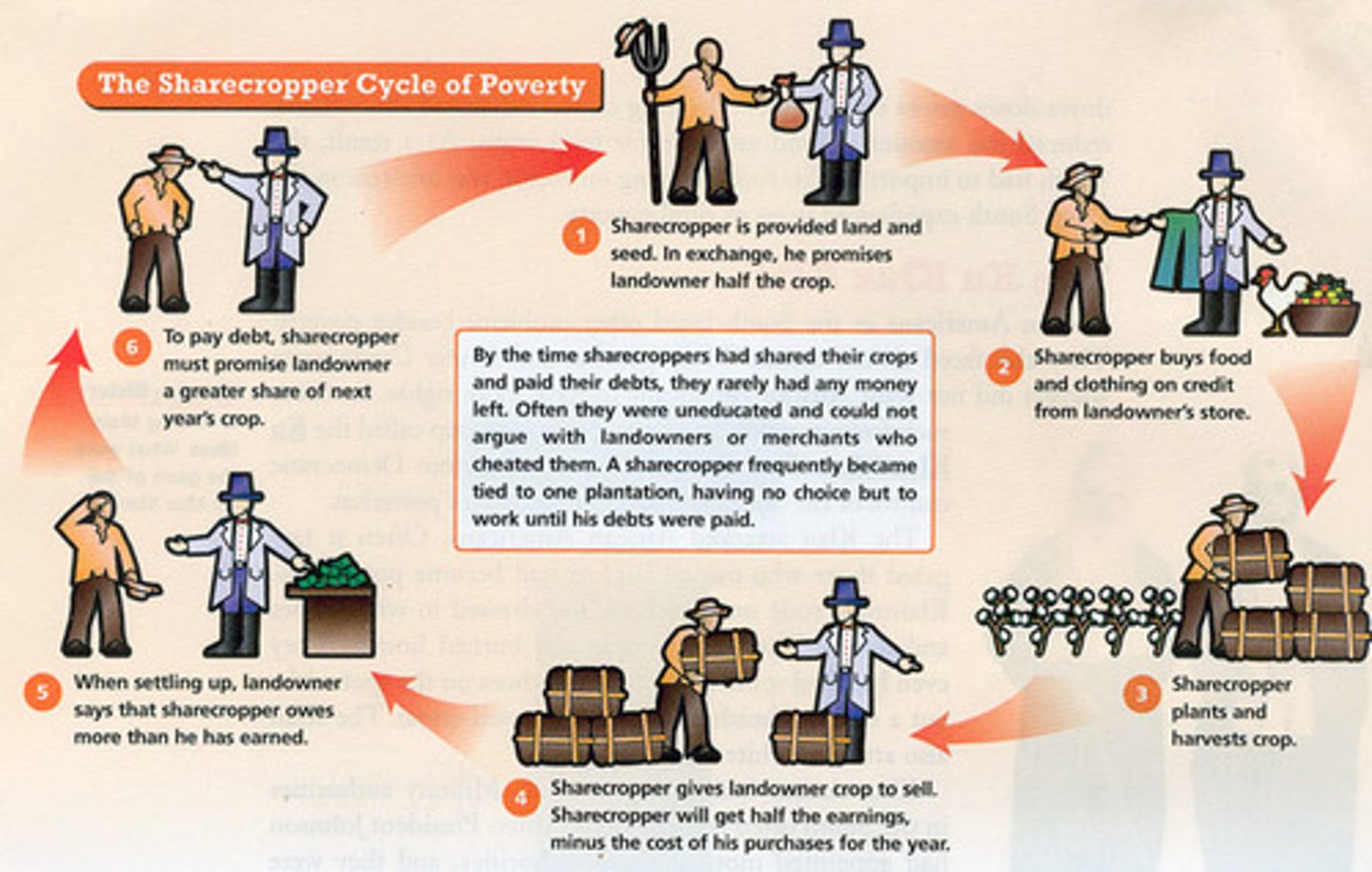
Sharecropping
A system used on southern farms after the Civil War in which a landowner allows a tenant to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on the land.
Tenant farming
The most independent arrangement. The tenant paid cash rent to a landowner and then was free to choose and manage his own crop
Ku Klux Klan
A secret society created by white southerners in 1866 that used terror and violence to keep African Americans from obtaining civil rights.
Redeemers
Former slave owners who were the most bitter opponents of the Republican Reconstruction program in the South. Staged a major counterrevolution to "redeem" the South by taking back southern state governments from the Republicans.
Compromise of 1877
The compromise ended Reconstruction.
Jim Crow Laws
Laws designed to enforce segregation of races. The Jim Crow Era lasted from the 1870s-1960s
Poll tax
Tax on voting. Used to discourage African Americans from voting during the Jim Crow era. Also used to exclude poor whites. Declared unconstitutional by the 24th Amendment.
Literacy tests
Method used to deny African-Americans the right vote in the South that tested a person's ability to read and write - they were done very unfairly so even though most African-Americans could read and write by the 1950's they still failed.
Grandfather clauses
Law that excused any voter from the literacy test if his grandfather had been eligible to vote on January 1, 1867
13th Amendment
Abolition of slavery
New South
Idea that The South should industrialize after the Civil War.
Thomas Nast
A famous caricaturist and editorial cartoonist in the 19th century and is considered to be the father of American political cartooning. His artwork was primarily based on political corruption. He helped people realize the corruption of some politicians
William "Boss" Tweed
Democrat leader of Tammany Hall. This New York City politician, arranged schemes that allowed him and his cronies to steal about $200 million dollars from New York. He also rewarded immigrants with favors if they voted for him or anyone from his political machine. He was eventually sentenced to prison in 1871.