Macro 1st midterm
1/87
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Tourism
short-term movement of people from one place to another for leisure or business purposes.
Christina Frasco
DOT secretary
Department of Tourism
regulation and promotion of tourism activities in a country.
Hospitality
helping people to feel welcome
Hospitality industry
combination of accommodation and food and beverages
-invisible export industry
-supporting goods and services
-fragmented product
-perishable product
-subject to unpredictable external influences
Why tourism is unique
-as a force for peace
-as commodifier
-as cultural homogenizer
-as a world view
Tourism on globalization
Direct
direct contact with tourist
indirect
support sectors
-weather
-scenic attraction
-cultural factors
-accessibility
-amenities
-accommodation
-safety and security
7 elements of tourism
-attraction
-accommodation
-accessibility
-affordability
-accountability
-activities
-amenities
7 components of toursm
-distance
-length of stay
-residence of the traveler
-purpose of travel
4 elements of travel
Distance
the difference between local travel or travelling within a person’s home community ang nonlocal travel and travelling away from home
length of stay
Refers to the duration a traveler spends at a particular destination.
Purpose of the travel
refers to the motivations or reasons behind a traveler’s journey
Residence of the traveler
Refers to the place where the traveler lives before embarking on their journey.
International Air Travel Agency
IATA
Meetings Incentives Conferences Exhibitions
MICE
Hard currency
any globally accepted and traded currency that can easily use for exchange, export, and import.
Soft currency
A currency that is not globally accepted for trade and such.
visitors
may be tourist, excursionist, resident, or non resident that is involved in tourism expenditure
-creates demand
-meets and spreads demand
-requires country to develop
-motivates to reach global standard
-brings numerous economic value and benefits
-helps in building a country’s brand value, image, and identity
-supports economic growth
Importance of tourism
DOT mission
shall be the primary government agency charged with the responsibility to encourage, promote, and develop tourism as a major socioeconomic activity to generate foreign currency and employment to spread the benefits of tourism to both the public nd private sector.
DOT vision
to develop a globally competitive environmentally sustainable and socially responsible tourism industry that promotes inclusive growth, through employment generation and equitable distribution of income thereby contributing to building a foundation for high trusted society.
tourist
visitor that stayed for more than 24 hours
excursionist
visitor that stayed for less than 24 hours
resident
visitor that stayed for more than 12 months
sustainable development goals
Are the blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all.
17 Sustainable development Goals
No Poverty
Zero Hunge
Good Health and Well-being
Quality Education
Gender Equality
Clean Water and Sanitation
Affordable and Clean Energy
Decent Work and Economic Growth
Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
Reduced Inequalities
Sustainable Cities and Communities
Responsible Consumption and Production
Climate Action
Life Below Water
Life on Land
Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
Partnership for the Goals
-intangibility
-inseparability
-inconsistency
-immobility of ownership
-perishability
-people oriented
6 characteristics of tourism
intangibility
a characteristic of tourism that states that they cannot be touched, seen, or experienced before purchase and is a subjective picture.
inseparability
a characteristic of tourism that states that it can only be consumed at supplier’s premise
inconsistency
a characteristic of tourism that states that tourism always differ from time to time
perishability
a characteristic of tourism that states that tourism cannot be stored
immobility of ownership
service are purchase that activity can be enjoyed
a characteristic of tourism that states that refers to the fact that tourism products and services are intrinsically tied to specific locations, making it impossible to relocate them
people oriented
a characteristic of tourism that states that tourism is built entirely upon people
Attraction
a component of tourism that include natural wonders, historical sites, cultural landmarks, amusement parks, and events.
Amenities
a component of tourism that refers to the additional facilities and services that enhance the tourist experience.
Accountability
a component of tourism that pertains to the responsibility of service providers to deliver promised experiences and maintain ethical practices.
Activities
a component of tourism that refers to a wide range of experiences available to tourists, allowing them to engage intimately with the destination.
Accommodation
a component of tourism that includes various lodging options such as hotels, hostels, bed and breakfasts, vacation rentals, and camping sites.
Affordability
a component of tourism that refers to the economic accessibility of tourism products and services.
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Refer to businesses whose personnel and revenue numbers fall below certain thresholds.
Philippine Tourism Promotion Board (TPB)
Promotes the Philippines internationally and domestically
Tourism Promotions Board (TPB)
The Philippine Convention Bureau (PCB) was later reorganized in 1987 to become the Philippine Convention and Visitors Corporation, now known as _____
Philippine Convention and Visitors Corporation
Former name of Tourism Promotions Board
Superstructure
refers to the physical and organizational elements designed to cater directly to tourists. Example of this are lodgings, restaurants, and hotel.
Infrastructure
refers to the basic facilities and services that support and enhance tourist activities like transportation, utilities, and communication networks.
Site attraction
refers to the kind of attraction that focuses on the nature
Built attraction
refers to the kind of attraction that focuses in the infrastructure made by human
event attraction
refers to the kind of attraction that draw visitors to a specific location on a specific date.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
refers to the accountability of tourism businesses to a wide range of stakeholders, emphasizing the ethical, social, and environmental implications of their operations.
2012
when was the campaign "It's More Fun in the Philippines" established?
2023
when was the campaign "Love the Philippines" established?
7641
how many islands are in the Philippines?
Holiday Economics
policy that moves the observance of certain public holidays to the nearest weekend to boost tourism.
Torah
tourism derived from a Hebrew word __.
Roman Empire
Ancient Rome
in what era did tourism start?
-travel for business and religious travel
-travel for private purposes
2 forms of early tourism
First journey for peace purposes was made by ____ to the land of Punt
Queen Hatshepsut
barter system
a trade system where a good is exchange for a good
Medieval period
In this period travelling became dangerous and only crusaders and pilgrims are the only travelers
Renaissance Era
In this era, travel for education purpose has started.
19th century
railway and steam power was introduced in this period.
Thomas Cook
He was an English businessman and trade operator known as the father of travel agency
-admire mother nature
-strengthen relationships
-unplug
-gain appreciation for what you have
-get out of your comfort zone
-settle grievances
6 travel motivation
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
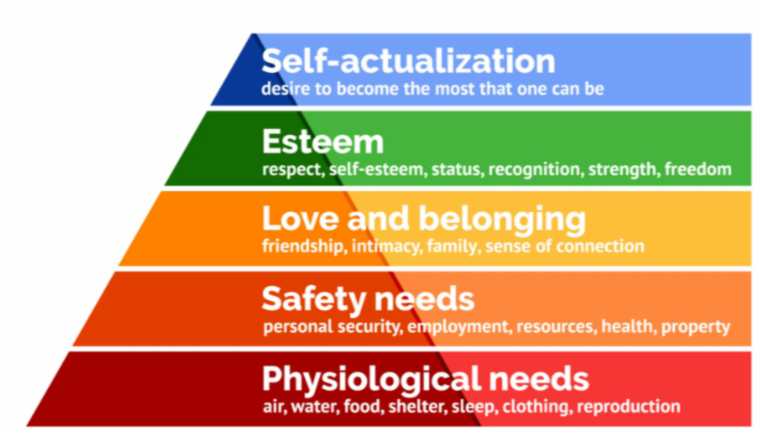
push factors
under Danni’s Theory of Push and Pull, this factor is the personal reason why a person wants to go to a certain place.
pull factors
under Danni’s Theory of Push and Pull, this factor draws a person to a certain place due to the attractions itself.
Travel Career Ladder (TLC)
Motivation to travel changes with its travel experience.
Travel career ladder (TCL)
Motivation to travel changes because of age, physical capabilities, etc.
-lack of money
-lack of time
-health
-family stage
-lack of interest
-fear and safety
Travel demotivators
japayuki
foreign worker in Japan; a female entertainer working in Japan; bargirl. example of drifter
Cohen’s classification of tourist
-Organized mass tourist
-individual mass tourist
-Explorer
-Drifter
Organized mass tourist
a classification of tourist that relies on travel agencies/package deal
individual mass tourist
is similar to the Organised Mass Tourist but enjoys slightly more freedom in their travel choices.
explorer
travels independently and do not adapt culture
drifter
travels with no itinerary, and adapts culture
-Allocentric
-Psychocentric
-Mid-centric
Plog’s classification of tourist
allocentric
a classification of tourist that wants new experience and adventure
psychocentric
a classification of tourist that is more conservative
mid centric
not particularly adventurous
20th century
in this era, travel for pleasure continue to expand
travel motivators
factors that activate direct and sustain goal/directed behavior. Why people travel
4 basic classes of travel motivators
-Physical motivators
-Interpersonal motivators
-Cultural motivators
-Status and prestige motivators
Tourism Carrying Capacity
maximum number of visitors a tourist location can handle at a given time without causing detrimental impacts on its environment, local culture, economy, and without significantly reducing the quality of the visitor experience
Tourism Sectors
Accommodation Sector
Transportation Sector
Food and Beverages Sector
Attraction Sector
Entertainment Sector
Travel Organizers Sector
Destination Organization Sector
Guest opportunities 7 Elements
Recovery
Personalization
Knowledge
Passion
Commitment
Inclusion
Personality