Nervous System Structure part 1 more notes
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards covering key concepts of the structure and function of the nervous system, including neurons, neuroglial cells, membrane potential, and their roles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are the basic functions of the nervous system?
1.Sensory input (receptors)
2. Integration (thoughts, memories, decisions)
3. Response (motor output, muscle & glands of effectors organs)
What are the functional classes of neurons?
- Sensory (afferent) 2. Interneurons 3. Motor (efferent)
What is the role of sensory (afferent) neurons?
They conduct signals from receptors to the CNS.
What is the function of motor (efferent) neurons?
They conduct signals from the CNS to effectors such as muscles and glands.
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (CNS): spinal cord and brain
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): outside CNS, spinal & cranial nerves
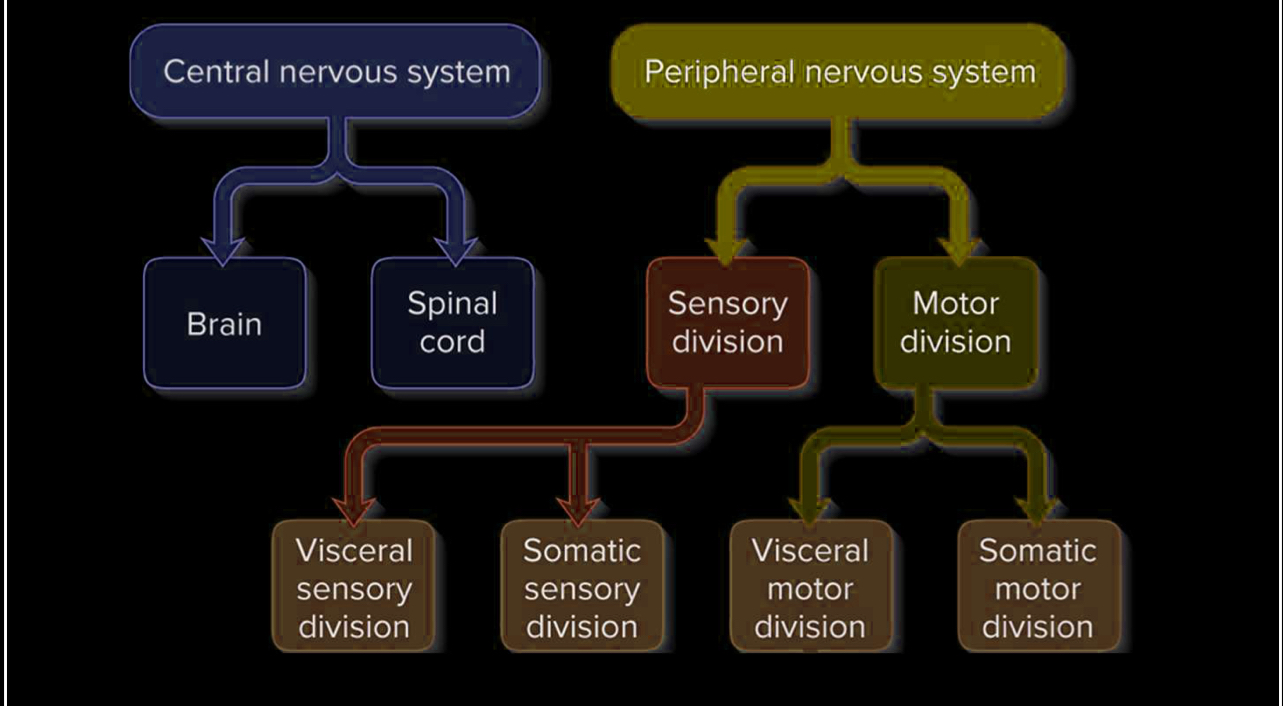
What components are included in the Central Nervous System (CNS)?
The brain and spinal cord.
What are neuroglial cells?
Support cells in the nervous system that outnumber neurons.
PNS Neuroglial cells
Satellite cells
-similar functions astrocytes
-surround somas in ganglia of PNS
Schwann cells
-myelin sheaths
-aid in fiber regeneration
-unmyelinated axons (gray matter)
What are the types of neuroglia found in the Central Nervous System?
Ependymal cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia.
Astrocytes
Most abundant
Wide variety of functions
-guide developing neurons
-facilitate synapse formation
-form scar tissue
-chemical environment around cells
-Leaked k+
-neurotransmitter cleanup
Microglial cells
Long, dendritic branches (thorny)
Monitor health
Sense trouble (damaged neurons and pathogens
Macrophages > phagocytes
Ependymal cells
Cavities of brain, spinal cord
Cerebral spinal fluid production
Oligodendrocytes
Bulbous body, 15 arms
Each arm reaches out to an axon and spirals,
electrical tape wrapped around wire
What is the function of myelin sheath?
It electrically insulates axons and increases transmission speed.
Describe the structure of a neuron.
A neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites, an axon, and axon terminals.
What is resting membrane potential?
Typically -70 millivolts (mV) in an unstimulated neuron due to different charges inside and outside the membrane.
What does the sodium-potassium pump do?
It moves 3 Na+ ions out of the cell and 2 K+ ions into the cell, maintaining the resting membrane potential.
What are the differences in the structure of multipolar, bipolar, and unipolar neurons?
Multipolar neurons have one axon and multiple dendrites,
bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite,
unipolar neurons have a single process that splits into two.
What are the anatomical features of ganglia?
Ganglia are concentrations of cell bodies, appearing as knot-like swellings.
What types of information do interneurons process?
They process and integrate information within the CNS, functioning mainly in reflexes.
What is the importance of the myelin sheath gap (node of Ranvier)?
It facilitates rapid signal transmission as the action potential jumps between nodes.
What are the main functions of astrocytes?
Support neurons, maintain chemical environment, guide development, and form scar tissue.
How do microglia respond to damage in the CNS?
They act as macrophages, traveling toward damaged areas to perform phagocytosis.