Anatomy and physiology unit 2 exam study set
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is lymph?
Lymph is fluid that is found in vessels
Characteristics of lymph capillaries & now they compare to blood capillaries
They weave between tissue cells and blood capillaries. Very similar to blood capillaries but more permeable and can take larger molecules and particles.
What are lacteals and where are they found?
Lacteals are specialized lymph capillaries, they absorb digested fat and deliver fatty lymph to the blood. They are found in intestinal mucosa.
Lymph nodes (description/funtion)
Lymph nodes cleanse the lymph
Stroma (description/funtion)
Network-like support that acts as scaffolding for immune cells.
Spleen (description/function)
Blood rich organ located in left side of abdominal cavity, just below the stomach. The spleen is the site of lymphocyte multiplication and immune surveillance and response. Cleanses blood of aged blood cells and platelets.
White pulp (description/function)
Site in the spleen where the immune function occurs.
Red pulp (description/function)
Site in the spleen where old blood cells and bloodborne pathogens are destroyed.
MALT (description/function)
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Lymphoid tissue in mucous membranes around the body , they protect from pathogens trying to enter the body.
Peyer's patches (description/function)
Clusters of lymphoid follicles in wall of distal portion of small intestine, they destroy bacteria trying to breach the intestinal wall
Thymus (description/function)
Bilobod lymphoid organ found in the inferior neck. It’s the site where T-cells mature
Right lymphatic duct
Drains upper right arm and right side of head and thorax.
Thoracic duct
Drains everything that the right lymphatic duct doesn’t
What are the primary lymphoid organs?
The thymus and red bone marrow
What are the secondary lymphoid organs?
Lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, appendix, Peyer'S patches
Lymphangitis
Condition in which lymphatic vessels appear as painful red lines under the skin.
Lymphedema
Severe localized edema
Buboes
Inflamed, swollen, tender lymph nodes that result when nodes are overwhelmed by what they are trying to destroy.
Elephantiasis
Typically tropical disease in which the lymphatics, often in the lower limbs and scrotum, become clogged with parasitic roundworms and infectious condition called filariasis. Swelling reaches enormous proportions.
Hodgkin's lymphoma
A malignancy of lymphoid tissue
What is MALT?
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Lymphoid tissue in mucous membranes throughout the body, the protect from pathogens trying to enter the body. The largest collections of found in the body in the tonsils, Peyer'S patches, and appendix
The mechanisms by which lymph is transported?
The milking action of skeletal muscle, pressure changes in thorax during breathing, valves that prevent back flow, pulsations of nearby arteries, contraction of smooth muscle in walls of lymphatics.
Where in the body are lymph nodes commonly found?
Cervical region, maxillary region, inguinal region
The cortex of a lymph node
Contains follicles with germinal centers that are heavy with dividing B cells
The medulla of a lymph node
The medulla cords extend inward from the cortex and contains B cells,T cells, and plasma cells.
Lymphatic sinuses
Found throughout the lymph node, consists of large lymphatic capillaries.
Diagram of a lymph node
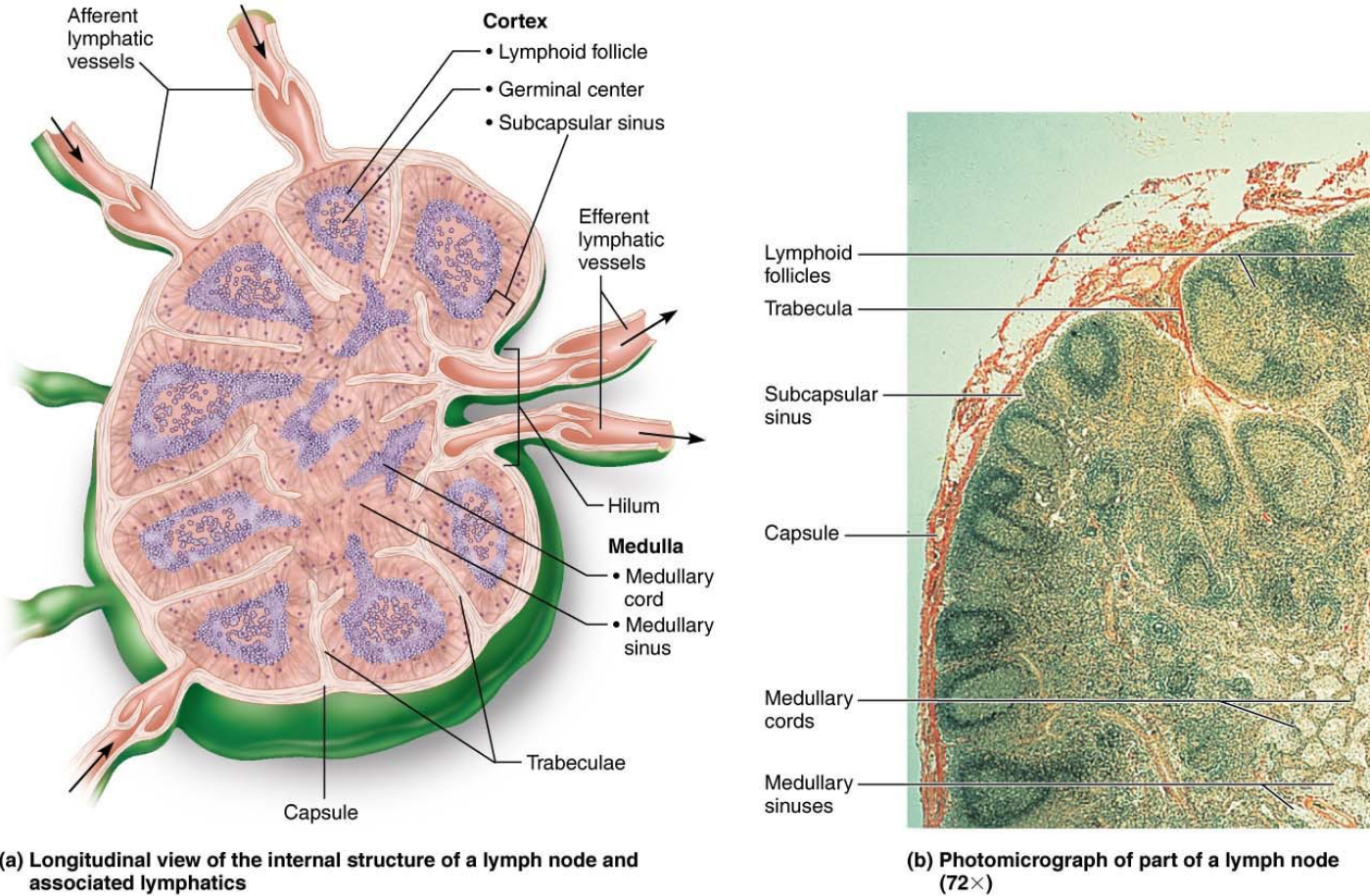
Which vessels does the lymph enter the lymph node through?
The afferent lymphatic vessels.
Which vessel does the lymph exit the node from?
The efferent lymphatic vessels.
What is the first line of defense?
Surface barriers such as the skin and mucous membranes
What is the second line of defense?
Cells and chemicals such as phagocytes, natural killer cells, inflammatory response.
What defenses make up the innate defenses?
Surface barriers
What defenses make up the adaptive defenses?
Humoral immunity (B cells) and cellular immunity (T cells)
What is the disadvantage of the adaptive immune system?
Must be primed by initial exposure to the specific foreign substance. Priming take time.
What is opsonization and what is it used for?
The immune system uses antibodies or complement proteins as opsonins that coat pathogens. It is used in phagocytosis
What is respiratory burst and when is it used?
Helper T cells trigger macrophage to produce respiratory burst, which kills pathogens resistant to lysosomal enzymes.
What are natural killer cells?
Large granular lymphocytes that police the blood and lymph. They kill cancer cells and virus infected cells.
What is the difference between NK cells and cytotoxic T cells?
NK cello are in the innate defenses and cytotoxic T cells are from the adaptive defenses.
Names of inflammatory cells
Histamine, kinins, prostaglandins (PGs), cytokines, and complement chemicals.
Inflammatory chemical response (first step of inflammation)
Chemicals are released into ECF by injured tissues or immune cells.
Vasodilation and increased vascular permeability (second step of inflammation)
Vasodilation causes hyperemia - congestion with blood - which heads to redness and heat.
Increased capillary permeability causes exudate - fluid containing clotting factors and antibodies - to leak into tissue.
What is interferon and what does it defend the body against?
His an antimicrobial protein that indirectly fights cancer.
What is complement
It enhances the ability of antibodies and phagocytes cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism promote inflammation, and attack the pathogen's cell membrane.
Describe Fever and how it affects the body
Abnormally high body temperature that is a systemic response to invading microorganisms.