Observational Study Design/Sources of Bias
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
case report
description of patient clinical experience
case series
multiple case reports
usually no statistical tests used
case series: pros/cons
pros:
- available clinical data
- rapid hypothesis generation
- natural history of presentation
cons:
- cases may not be representative of all cases
- no comparison group
- case identification can be slow
cross-sectional studies
examine a sample of population of interest at given point in time
- usually the present
outcome and exposure of interest determined at the same time
- usually single data point
can provide estimates of prevalence or exposure of a condition
cross-sectional studies: pros/cons
pros:
- rapid analysis if data gathering proceeds quickly
- accurate estimates of population prevalence if sample appropriate
- can generate strong hypotheses
cons:
- unclear temporal direction (causality)
- cannot determine whether exposure occurred before outcome
cohort studies: overview
participants classified as "exposed/unexposed" to a given risk and followed to determine whether exposure status predicts outcome
can be prospective or retrospective
design parallels RCTs but without random assignment to exposure
useful when unethical or impossible to conduct intervention
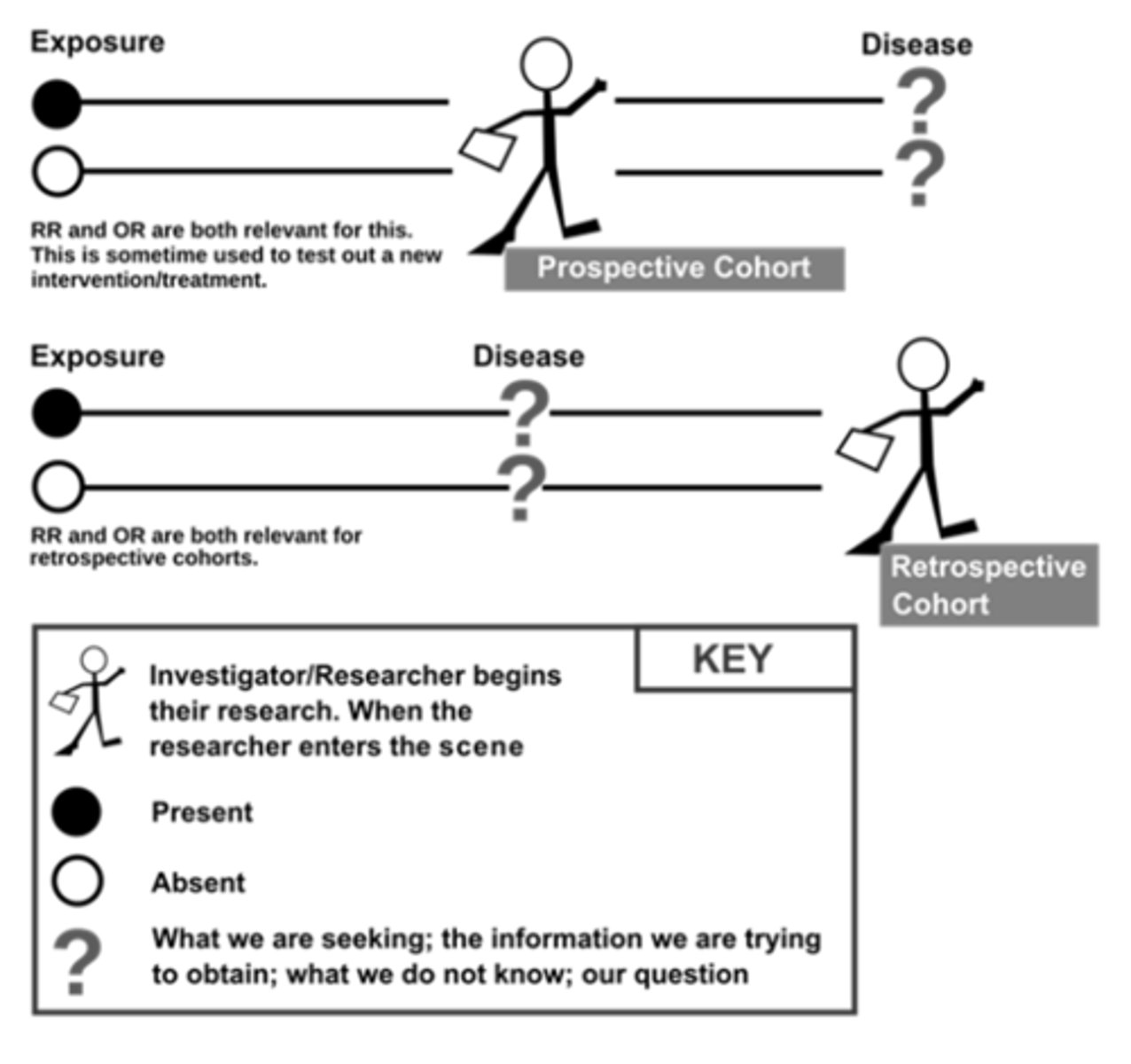
cohort studies vs case control
cohort methodology stronger than case control
- more rigorous observational design
- exposure known to occur before outcome
role of cohort studies
detection associations between health outcomes and exposures
evaluation of interventions in usual practice
estimate risk or rate of some outcome
cohort studies: pros/con
pros:
- clear temporal relationship
- least susceptible to some forms of bias
- allow direct measurement of incidence in exposed and unexposed
cons:
- no control over exposure
- inefficient for rare outcomes
- loss to follow-up threatens validity
- more expensive than other observational designs
cohort studies: variations
retrospective cohort studies
- ascertain historical control
- ascertain historical outcomes status
pros:
- data already collected, no wait
cons:
- not feasible without accurate historical records
case-control studies
participants identified based on outcome
prior exposure determined after outcome status
generate odds ratios (ORs)
main comparison = rates of exposure in case vs control

case control studies: pros/cons
pros:
- fewer resources
- for rare/multiple outcomes
- for outcomes with long latency
cons:
- inefficient for rare exposures
- hard to identify controls
- can be hard to obtain exposure history
- prone to bias
sources of bias in observational research
selection bias
information bias
confounding
selection bias
selection of participants or data such that the sample is not objectively represented in one or more groups
affects internal validity while sampling bias affects external validity
types of selection bias
self-selection
referral bias = referred based on exposure so overstates association between exposure and positive test/diagnosis
controlling for selection bias
-random sampling
- systematically recruiting to prevent self-selection
- increase frequency of contact/communication to minimize loss
- well-defined patient accrual/enrollment procedures
- use propensity scores to match exposed/unexposed groups
information bias
errors in exposure or outcome info collected about study subjects
misclassifying:
- exposed as unexposed
- deceased as living
types of information bias
recall bias = cases more likely to recall exposures than controls
detection bias = exposed participants followed more closely than unexposed
controlling for information bias
- must be handled during design phase
- use blinding if appropriate
- standardize measurement process
- minimize recall bias by using other information sources
confounding bias
"third variable"
confounder:
- has effect on outcome
- associated with exposure
- cannot be an effect of exposure
controlling for confounding
identify potential confounders
design:
- random allocation
- restriction
- matching
analysis:
- stratification
- regression modeling
- propensity scores
- sensitivity analysis
common confounders
- age
- sex
- principal diagnosis and its severity
- extent and severity of comorbidities
- physical functioning status
comorbidities
most common source of difference
all other conditions that exist in a patient in addition to condition under study