Anatomy 338 Exam 1
1/313
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
314 Terms
Anatomical position
Person stands erect with feet flat on the ground, toes pointing forward, and eyes facing forward. Palms face anteriorly with the thumbs pointed away from the body
Coronal (frontal) plane
Bisects the body laterally from side to side, dividing it into front and back halves. Abduction and Adduction movements occur in this plane
Axis: Anterior-posterior
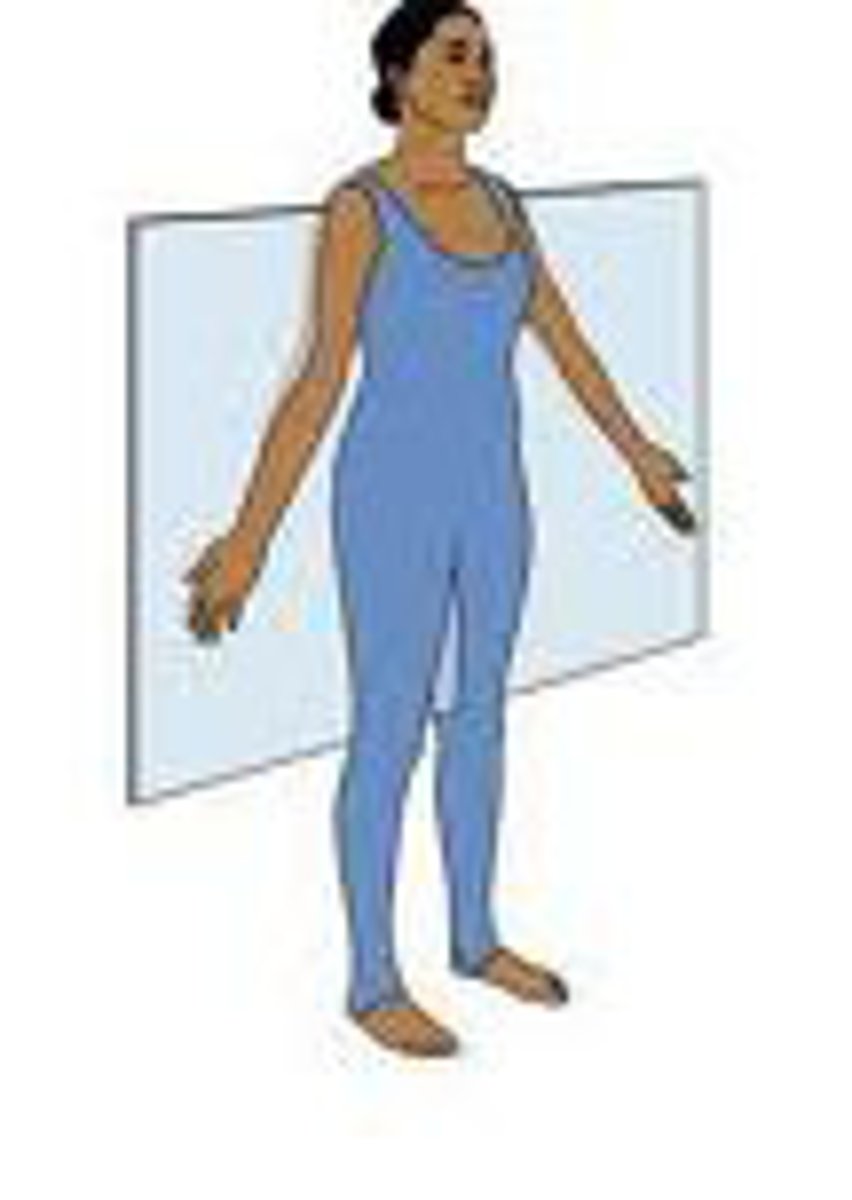

Anterior-posterior axis
What axis is with the coronal plane?
Sagittal plane
Bisects the body from front to back, dividing it into left and right halves. Flexion and Extension movements usually occur in this plane
Axis: Transverse
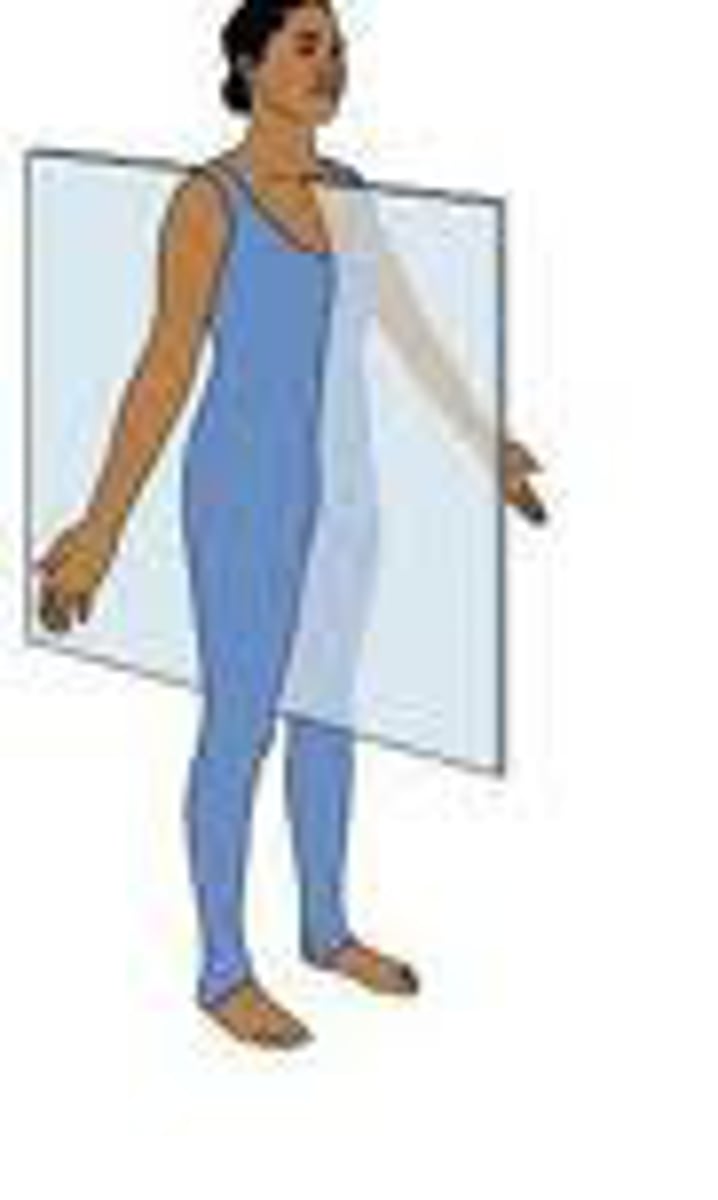
Transverse axis
What is the axis that goes through the sagittal plane?
Transverse (horizontal) plane
Divides the body horizontally into Superior and Inferior halves. Rotational movements usually occur in this plane
Axis: Vertical/ longitudinal
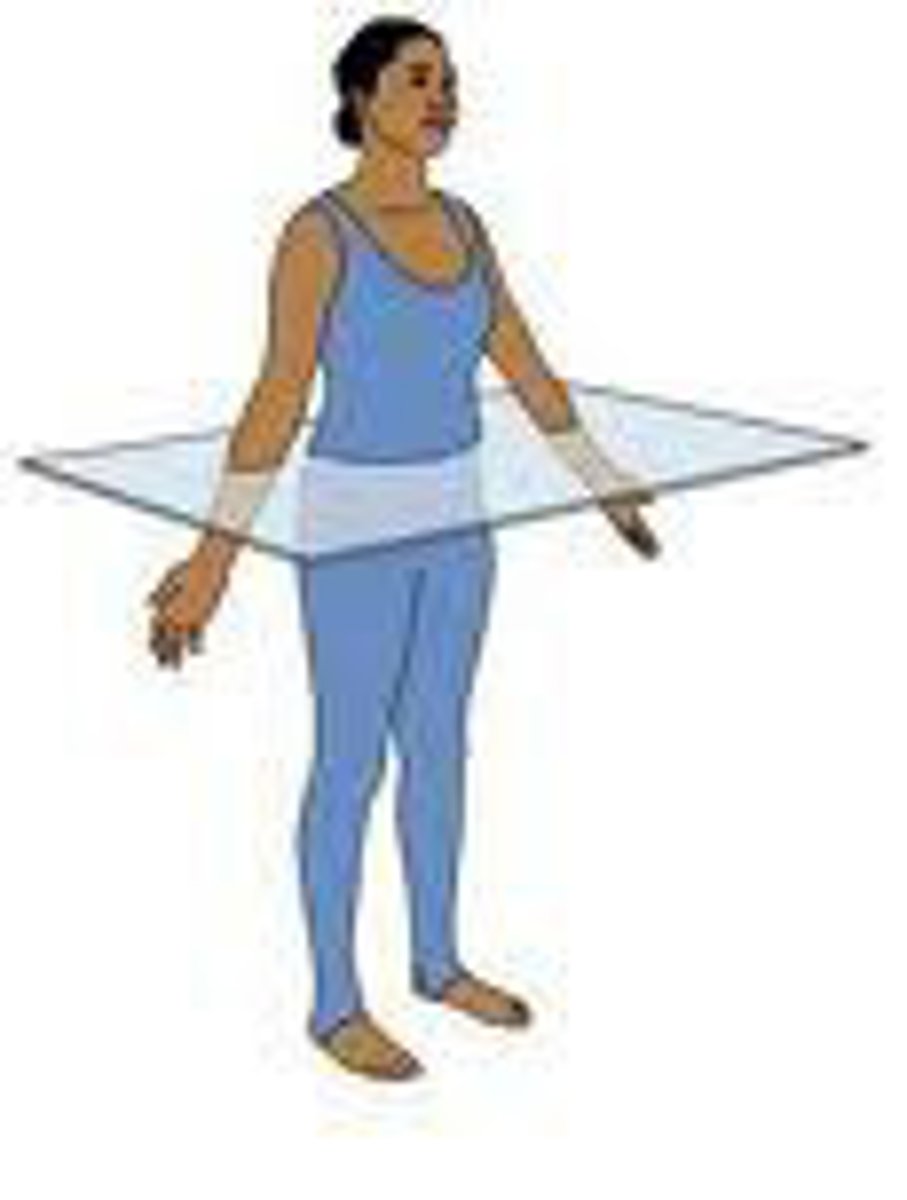
vertical/longitudinal axis
Axis that intersects the transverse plane
Midsagittal (median) plane
The plane passes through the midline, dividing the body in half and separating right and left sides
(parasagittal section misses the midline, separating right and left portions of unequal size)
Prone
Anatomical position laying face down
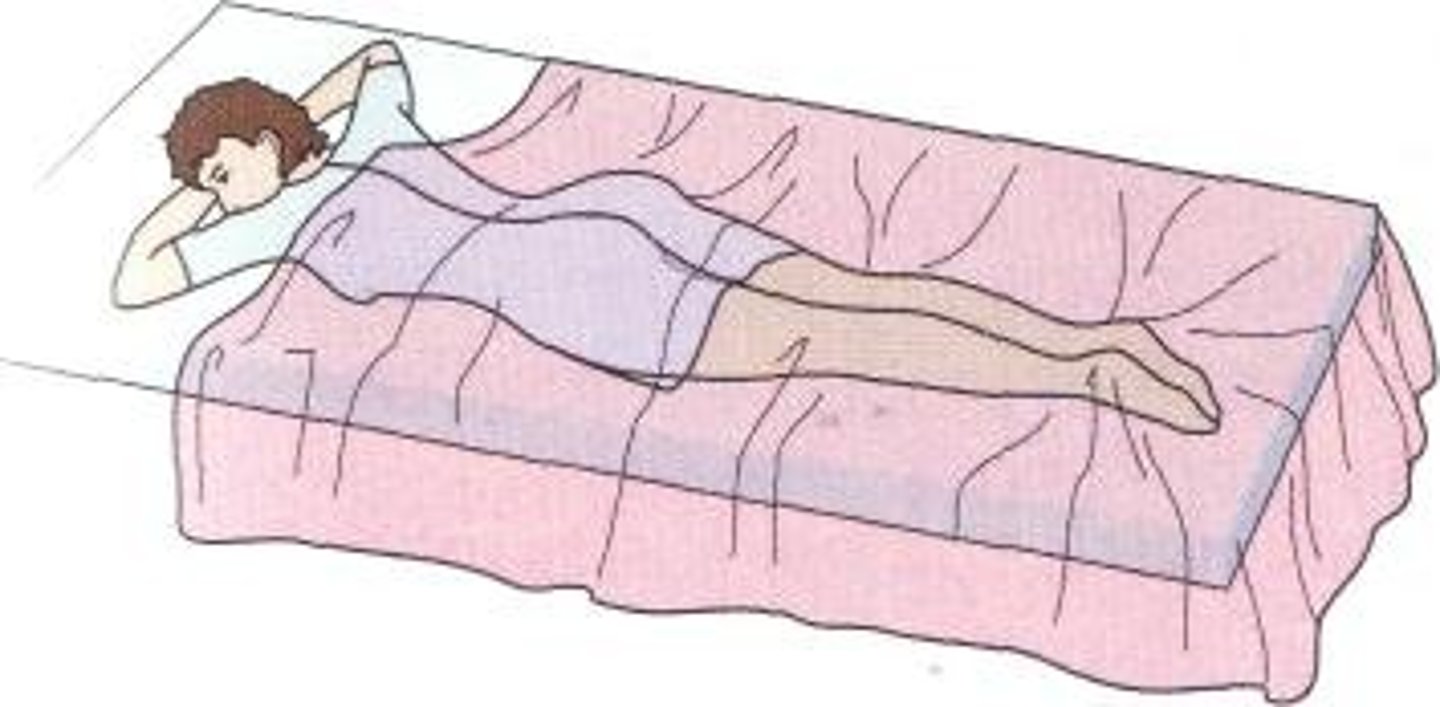
Supine
Anatomical position
Laying face up
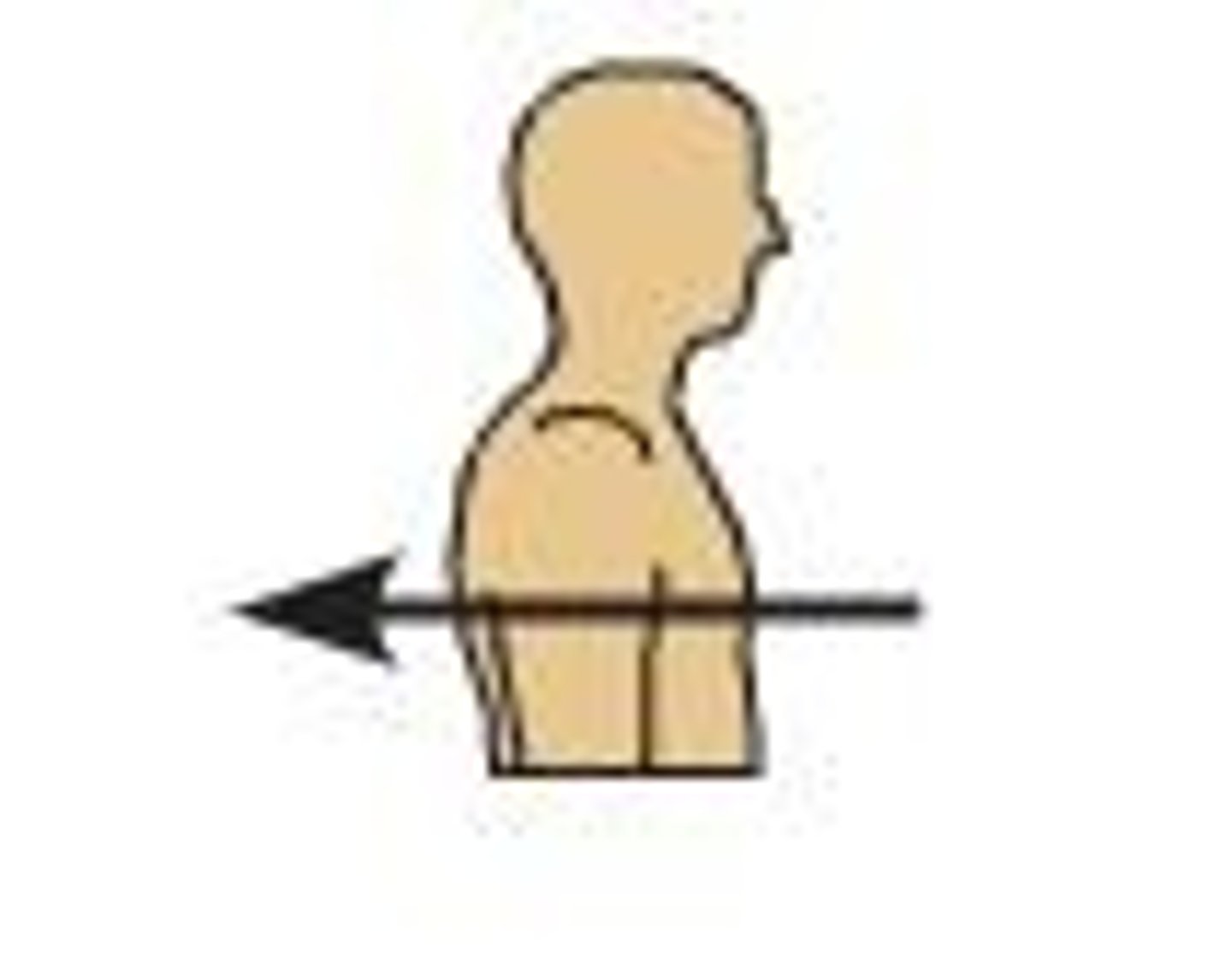
Anterior
On or near the front, or ventral, surface of the body
Posterior
Toward the back; dorsal
Superior
Above, in reference to a portion of the body in the anatomical position.
Inferior
A directional reference meaning below, in reference to a particular structure, with the body in the anatomical position.
Medial
Toward the midline of the body.
Lateral
away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
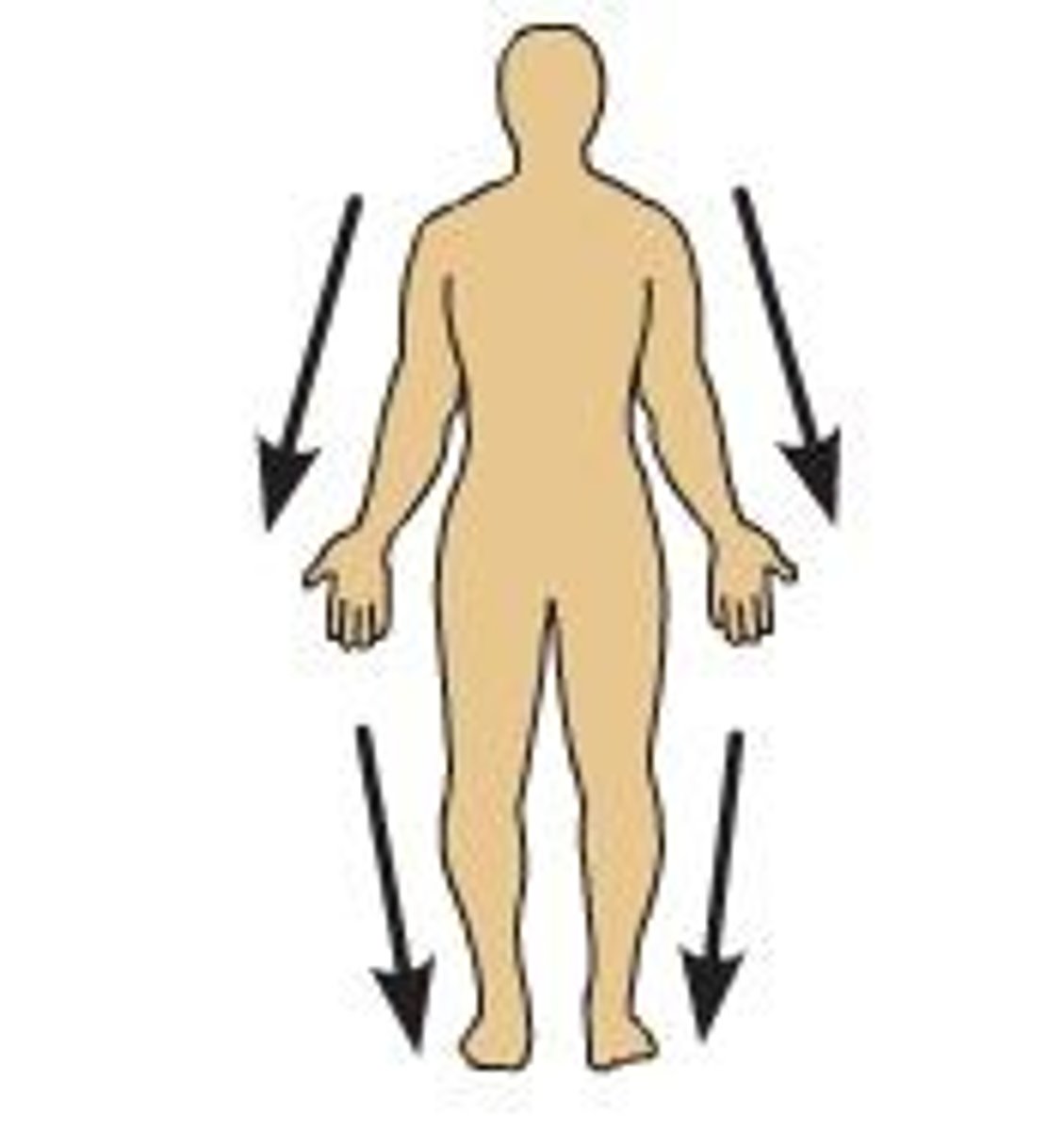
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Dorsiflexion
Upward movement of the foot through flexion at the ankle.
Plantar flexion
Ankle extension; toe pointing.
Flexion
A movement at a joint that reduces the angle between two articulating bones; the opposite of extension.
Extension
An increase in the angle between two articulating bones
Abduction
Movement away from the midline.
Adduction
Movement toward the axis or midline of the body as viewed in the anatomical position.
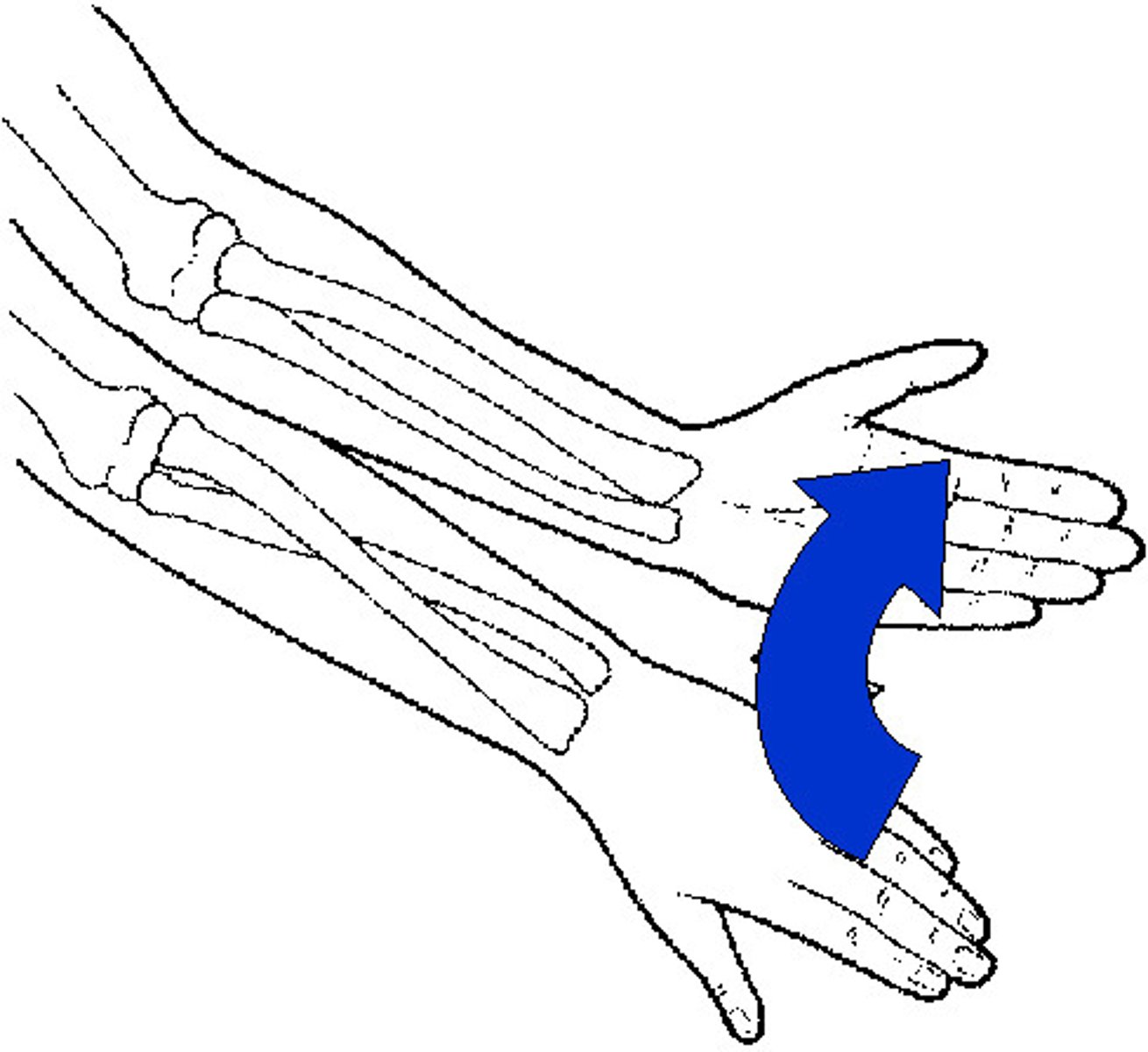
Pronation
Rotation of the forearm that makes the palm face posteriorly.
Supination
Rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces anteriorly.
Denser objects (bones) prevent x-rays from passing through, so they show up white
Why is there clear image of bone on an x-ray, but not of the soft tissue?
Fluoroscopy shows real time and can see actions
What is an advantage of fluoroscopy over x-ray?
Have different views in 3D
Surgical planning- safer and easier
See vasculature
Good for neuroimaging- images patients in a helix and patient is given contrast
What are uses for CT scan reconstructions?
The hydrogen atoms present in the water in the body; and the ability to align them using radiofrequencies
Exciting and relaxing of protons
What is an MRI dependent upon?
-can see soft tissue better
-deeper tissue
-can see CS fluid, disks, vasculature systems, ligaments
Advantages of MRI?
Specialized imaging used with procedure to provide live image during surgery
Subtracted and real time view
More guidance during operation
Advantage of interventional radiology technique (angiogram)?
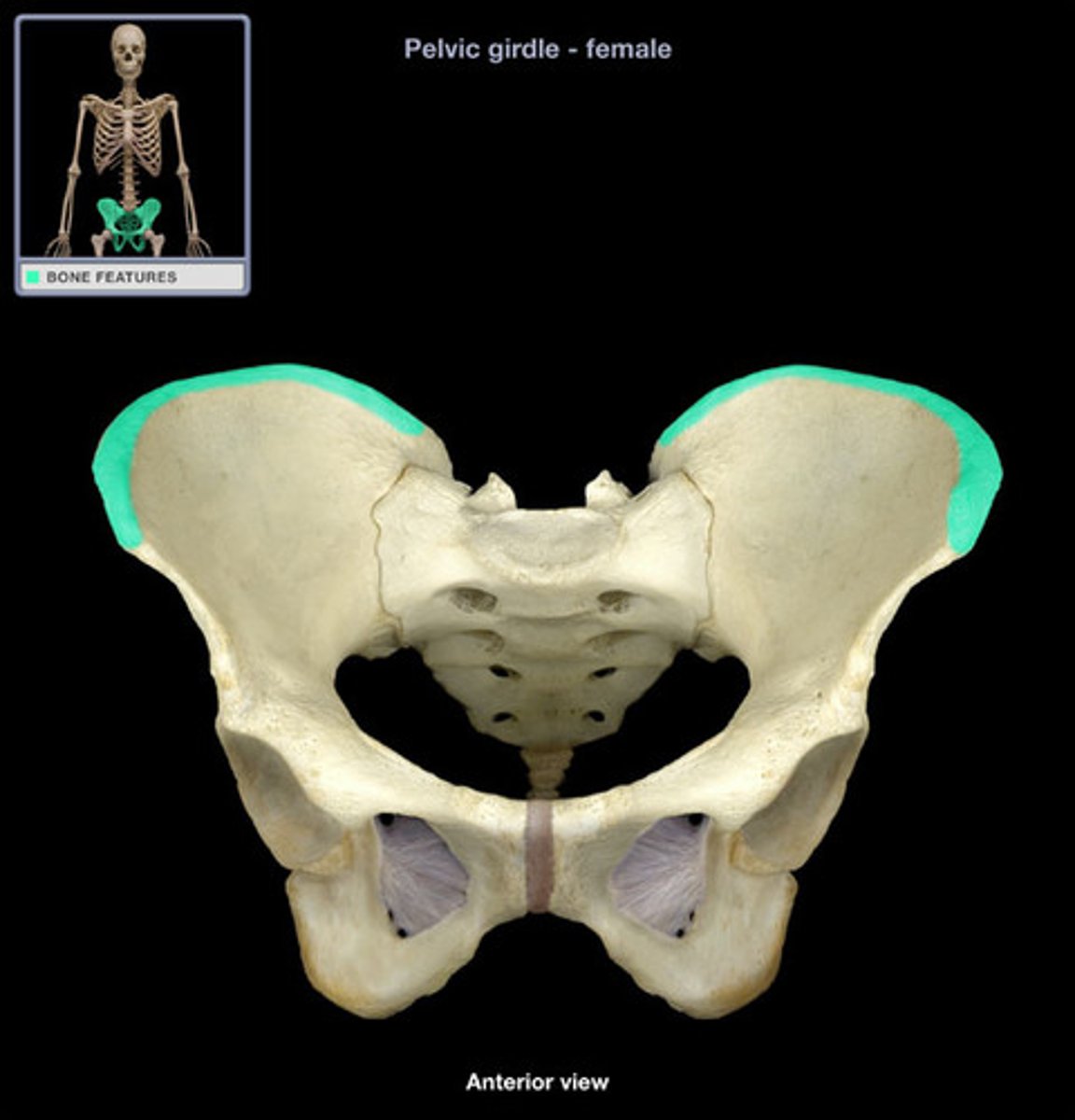
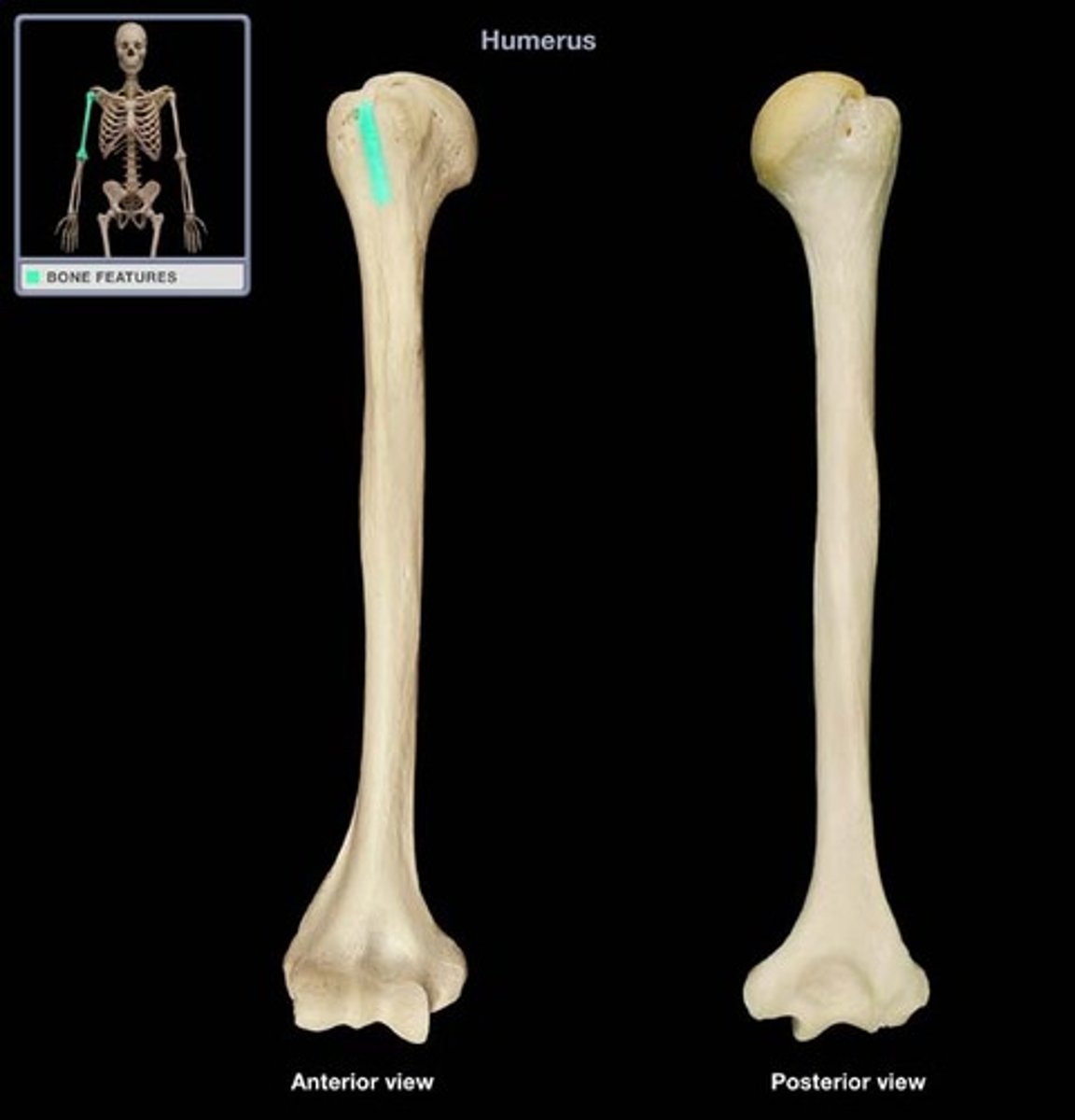
Tuberosity
Large rounded projection; may be roughened. Site of muscle attachment.
Crest
Site of muscle attachment
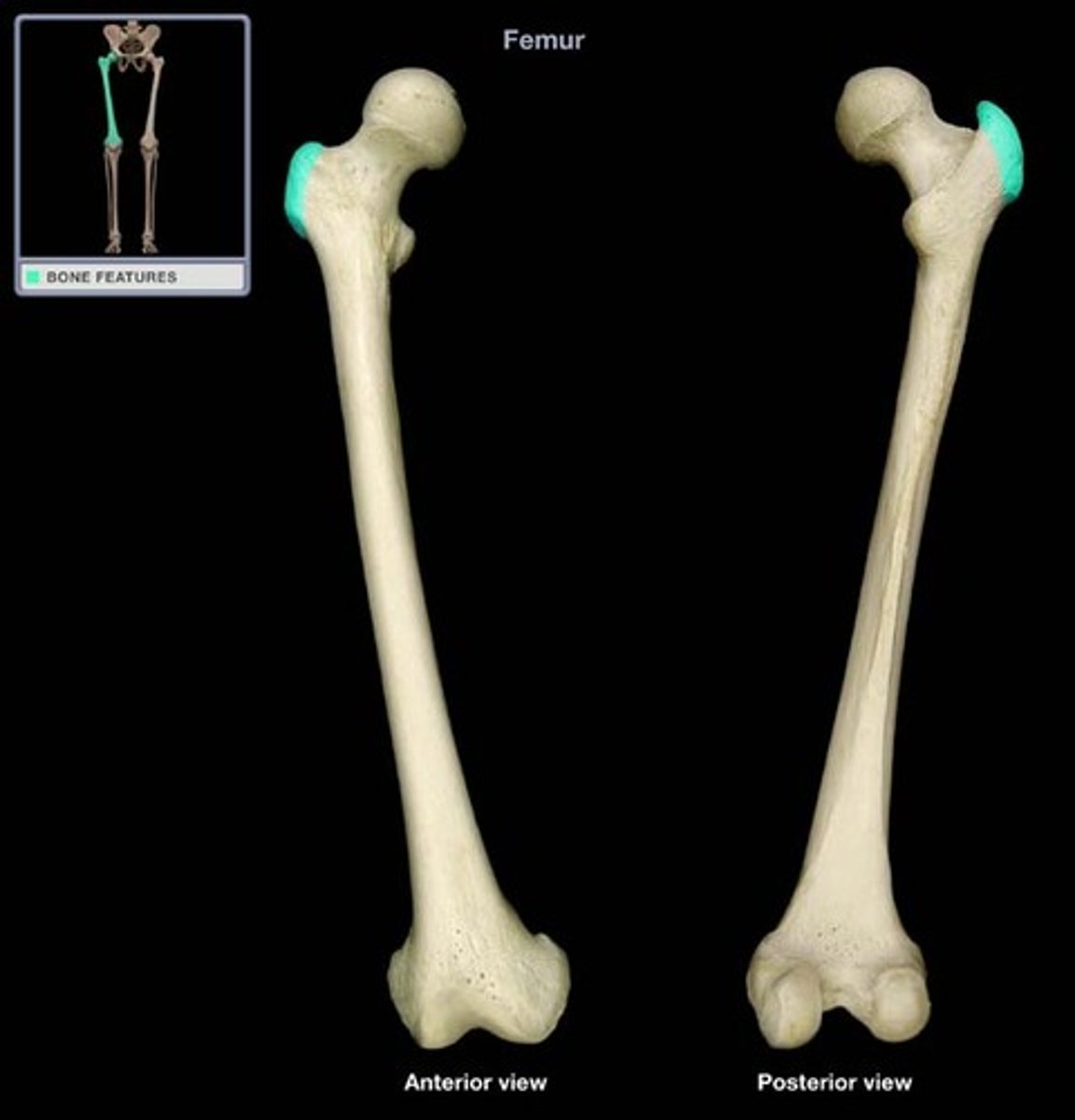
Trochanter
Large, rough projection (femur)
Site of muscle attachment
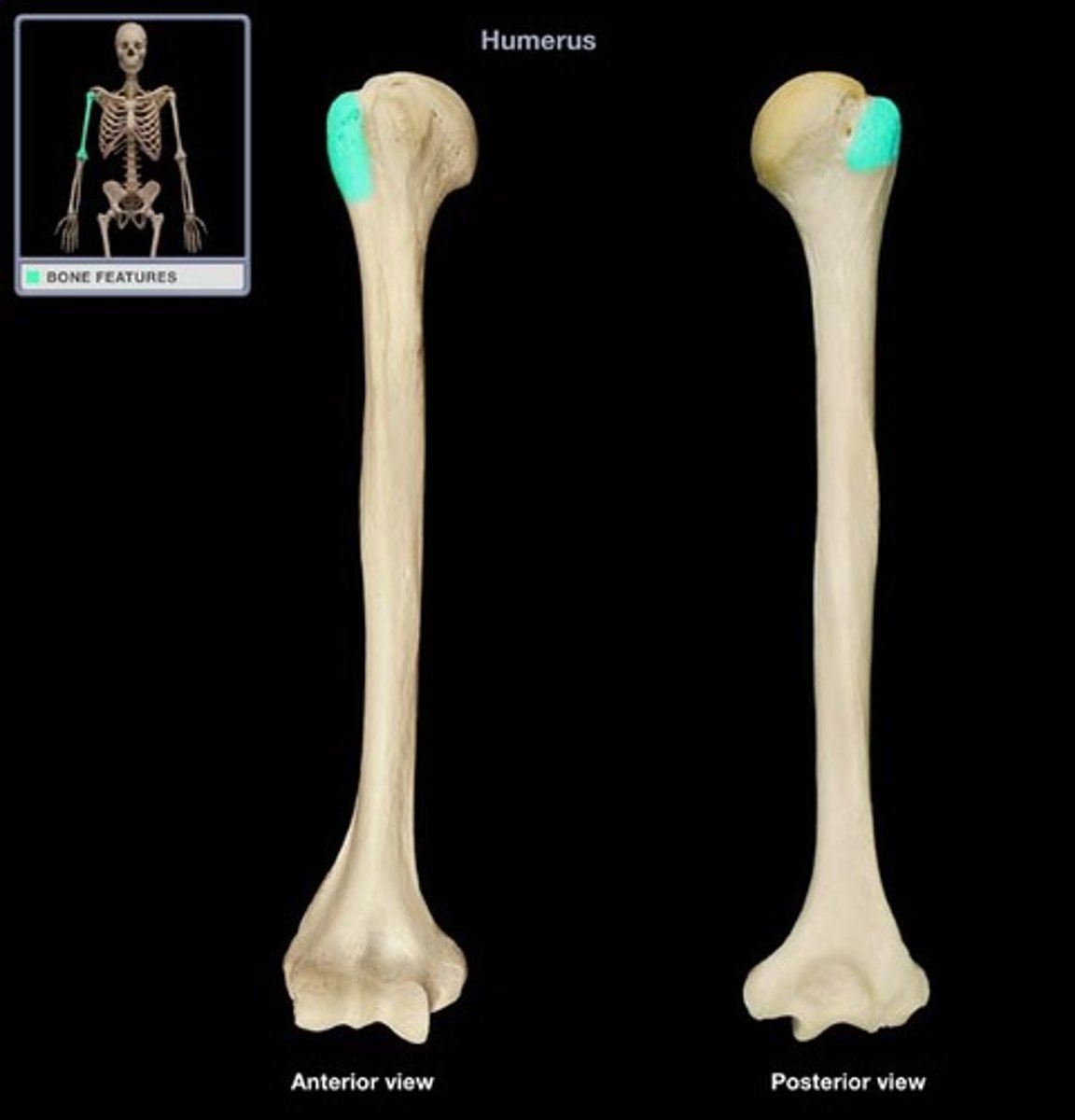
Line
Narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest
Site of muscle attachment
Tubercle
Small rounded projection or process
Site of muscle attachment
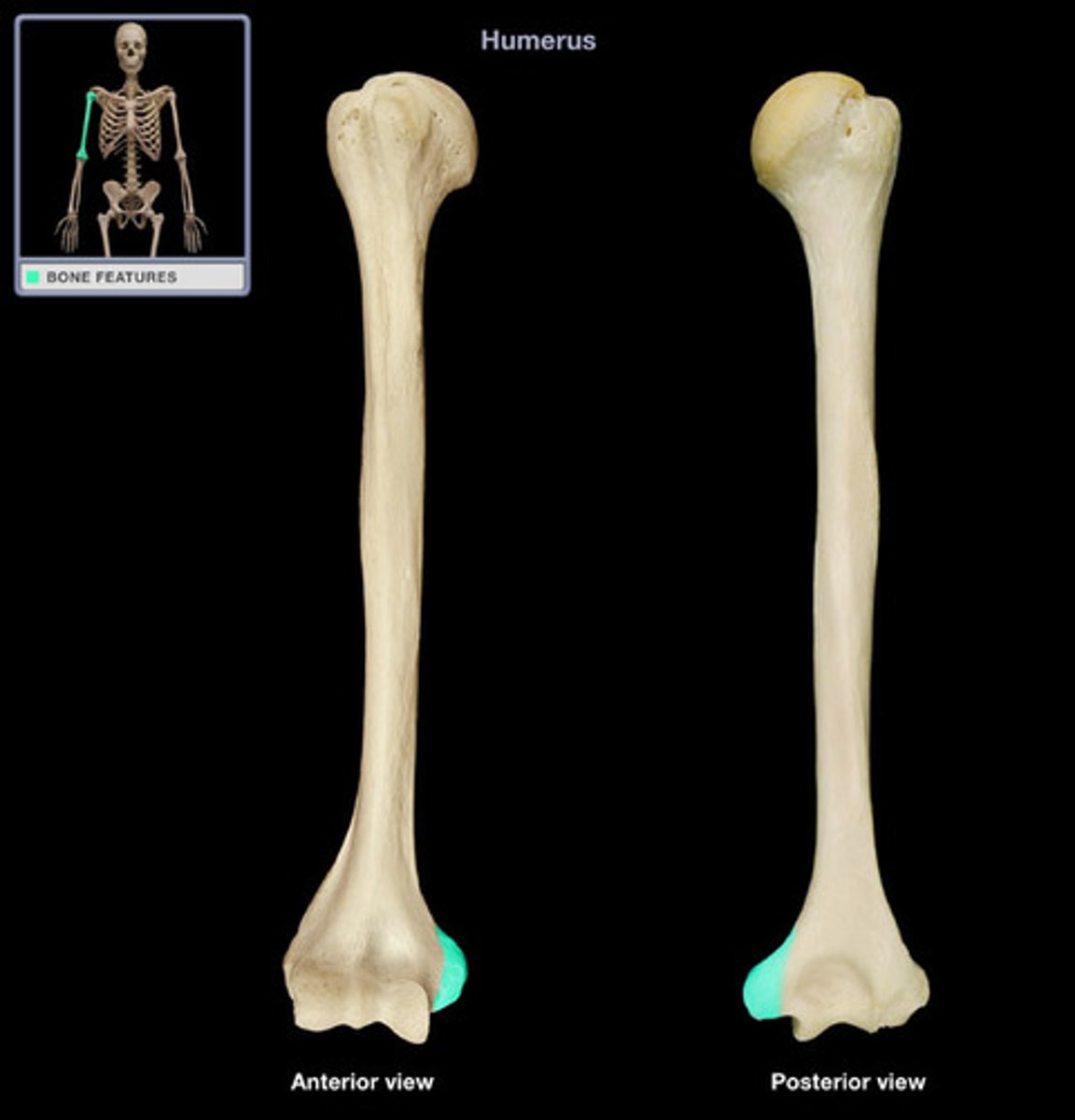
Epicondyle
raised area on or above condyle; site of muscle attachment
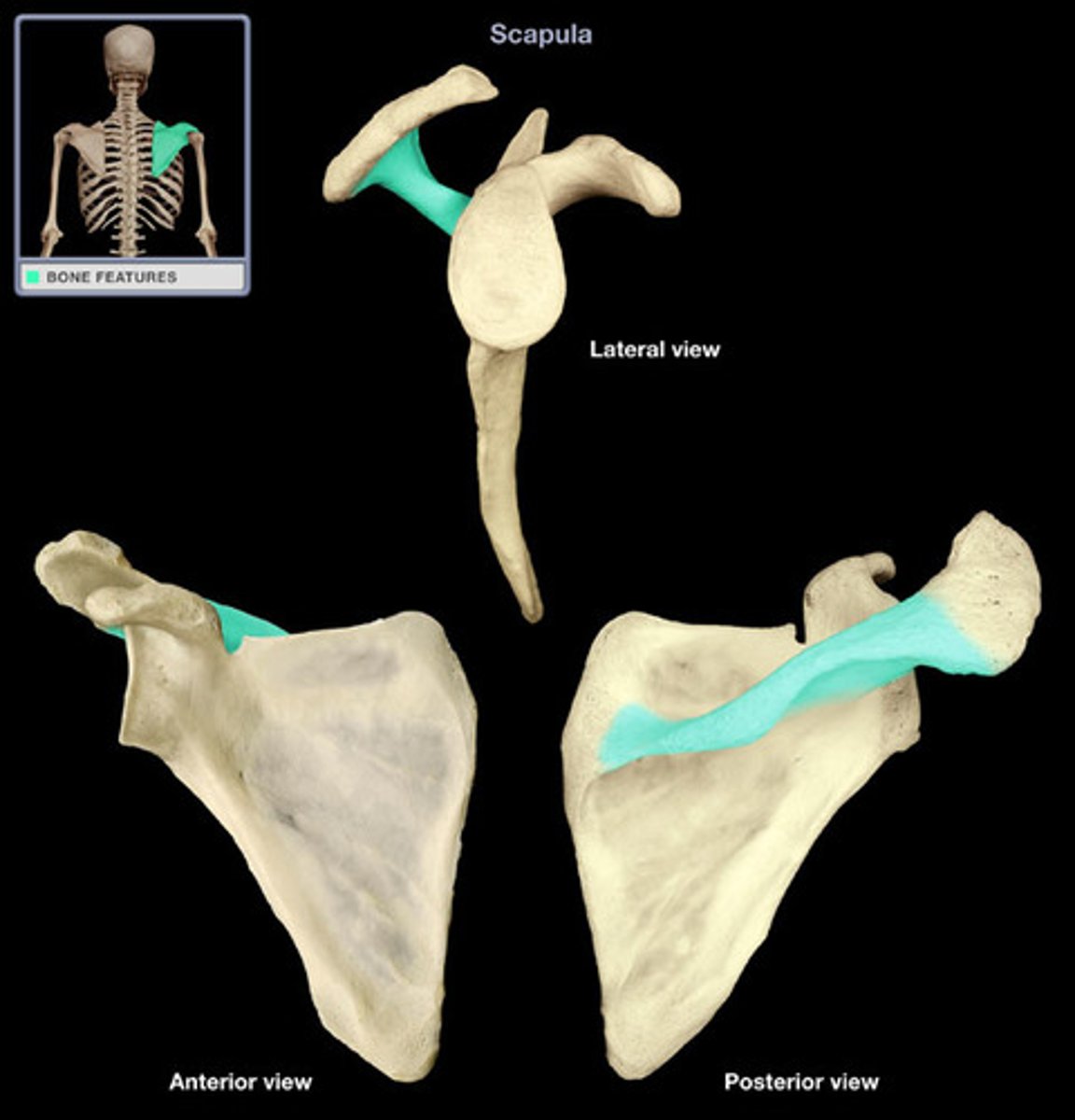
Spine (scapular spine)
sharp, slender, often pointed projection; site of muscle attachment
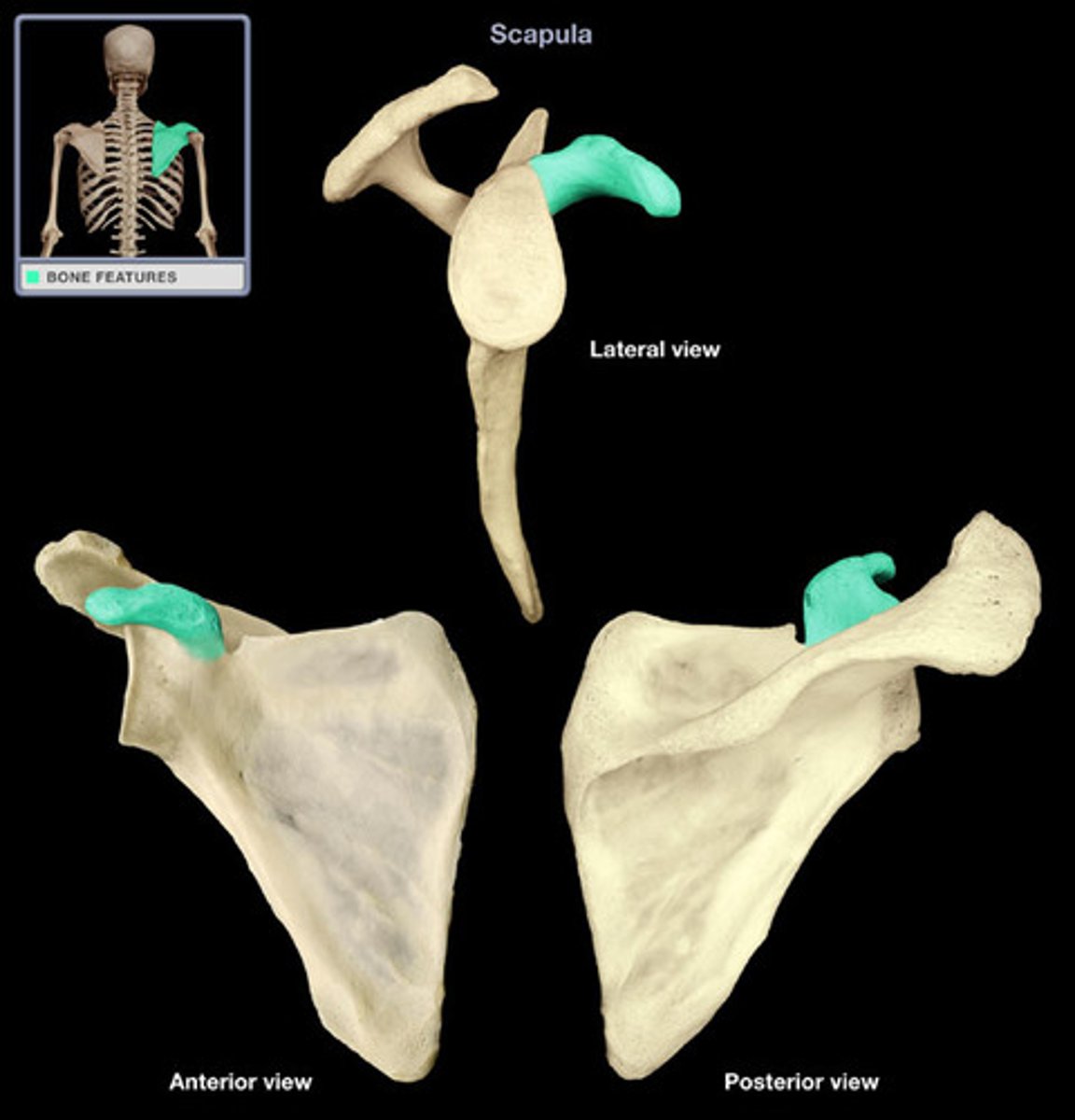
Process
A prominent projection on a bone
Site of muscular and ligament attachment
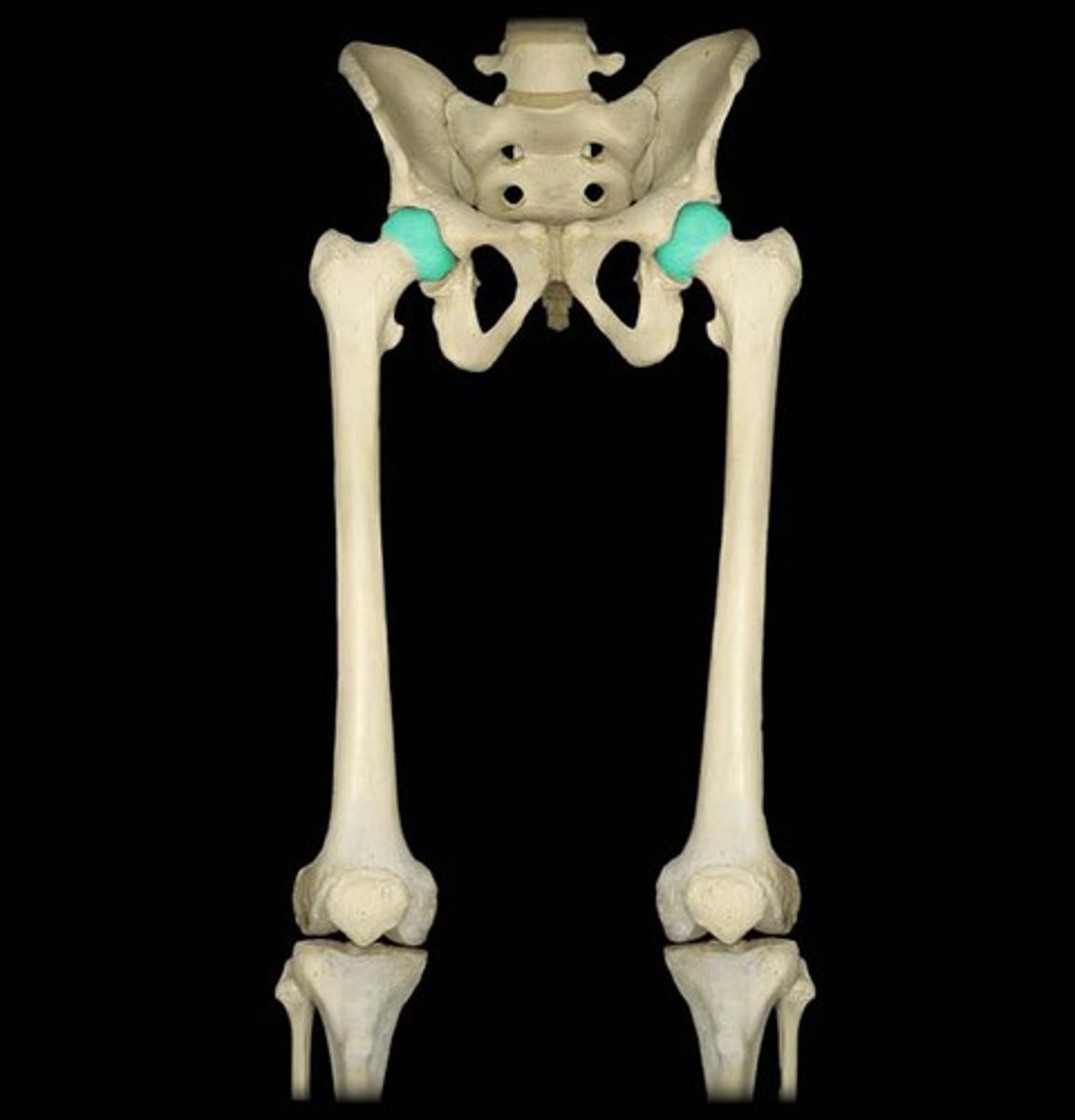
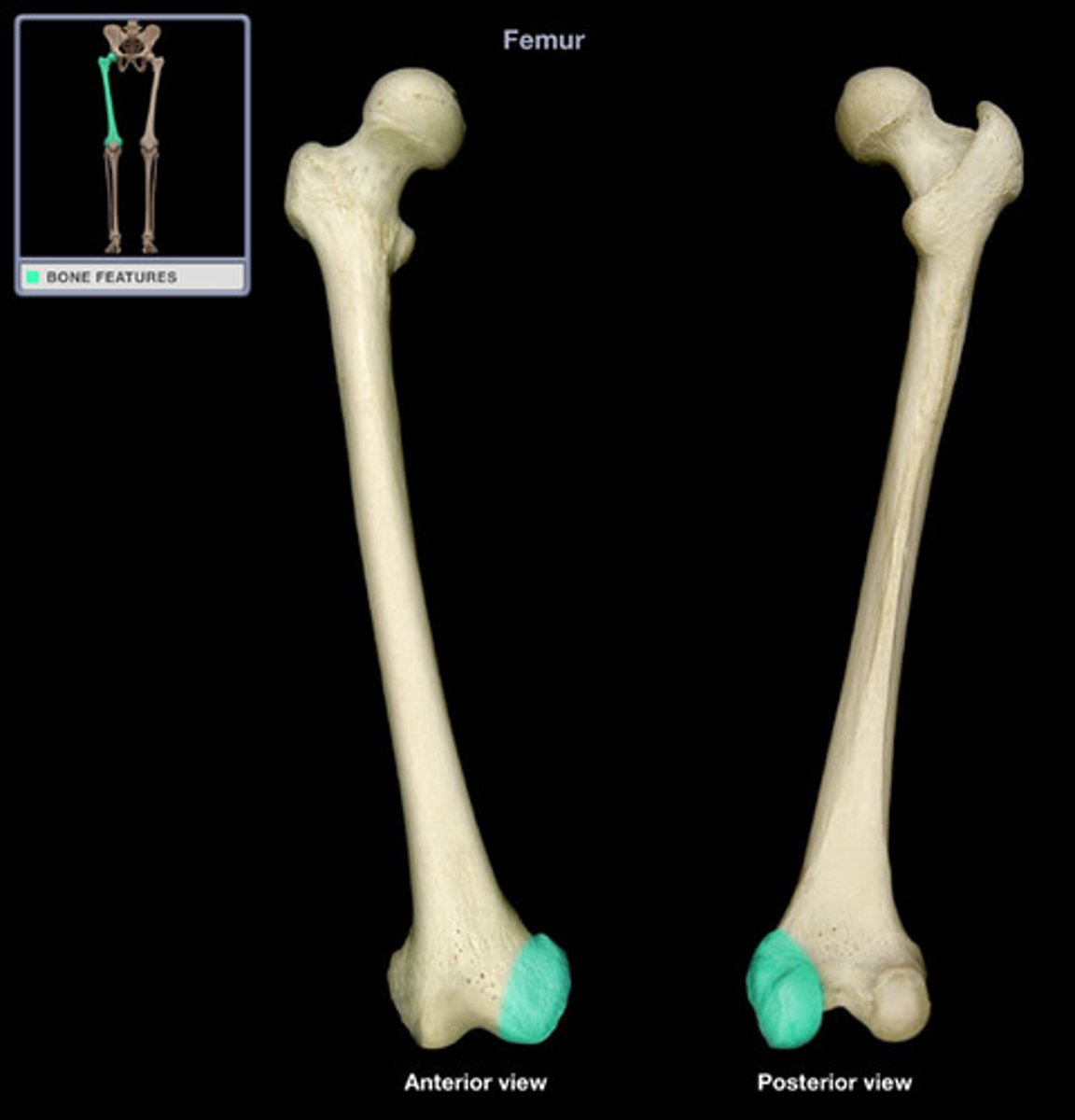
Head (femoral head)
Big smooth surface of a bone that articulates in ball and socket joints that allows for more movement
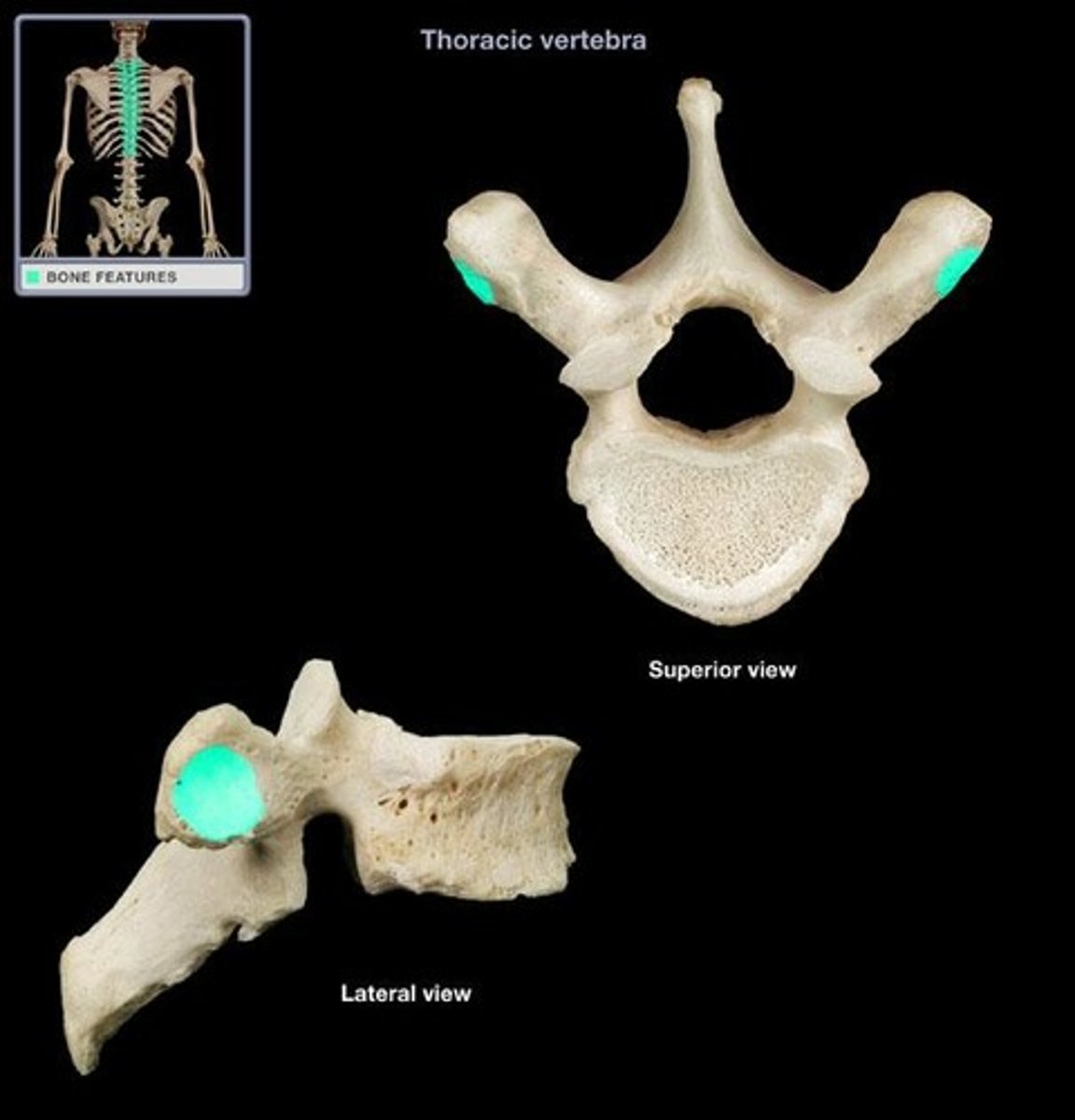
Facet
Smooth, nearly flat articular surface
Condyle (medial condyle)
Rounded process that usually articulates with another bone
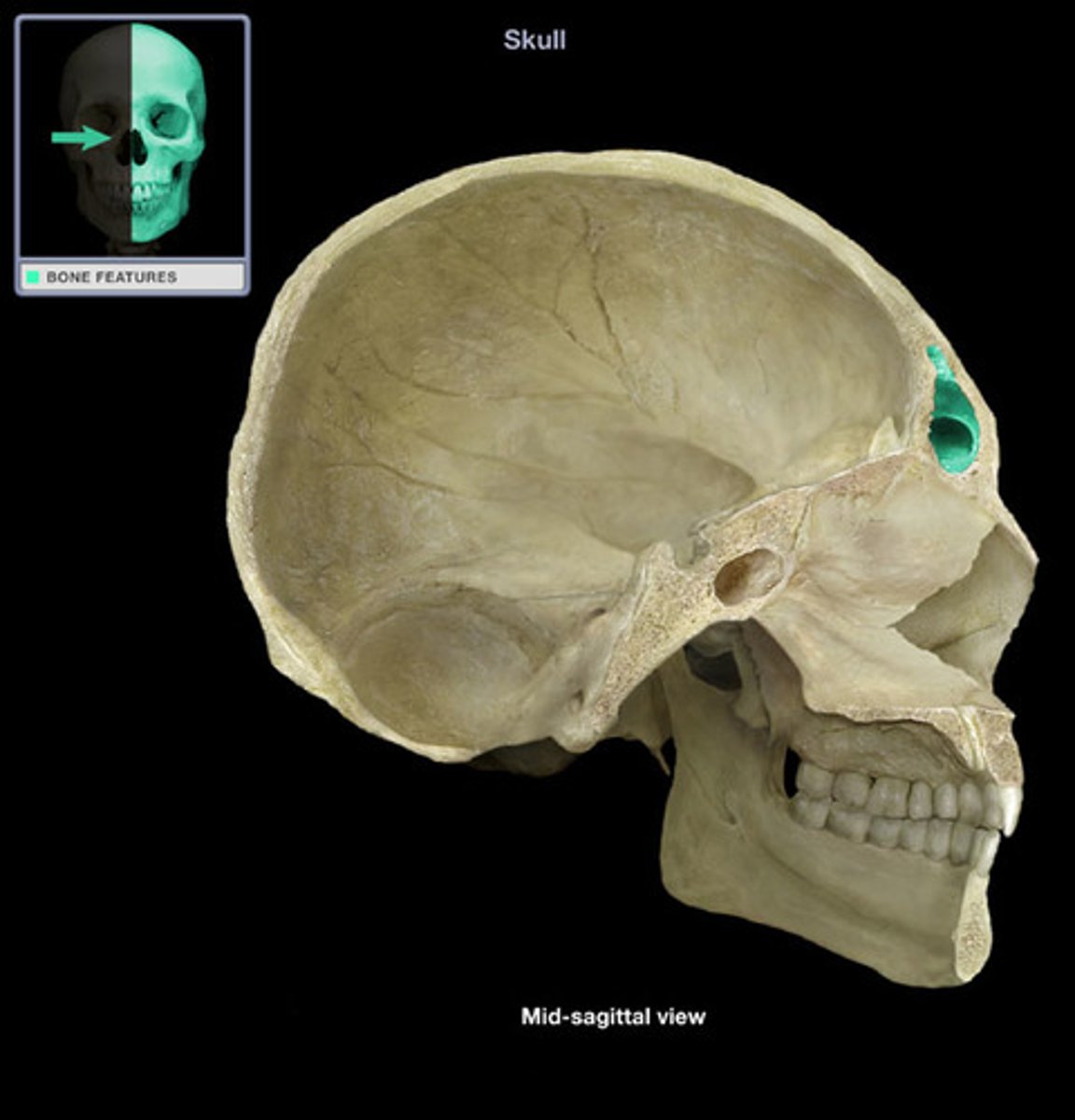
Foramen (foramen magnum)
Round or oval opening through a bone
Groove (bicipital groove)
Depression in bone that is a passageway for nerves and blood vessels
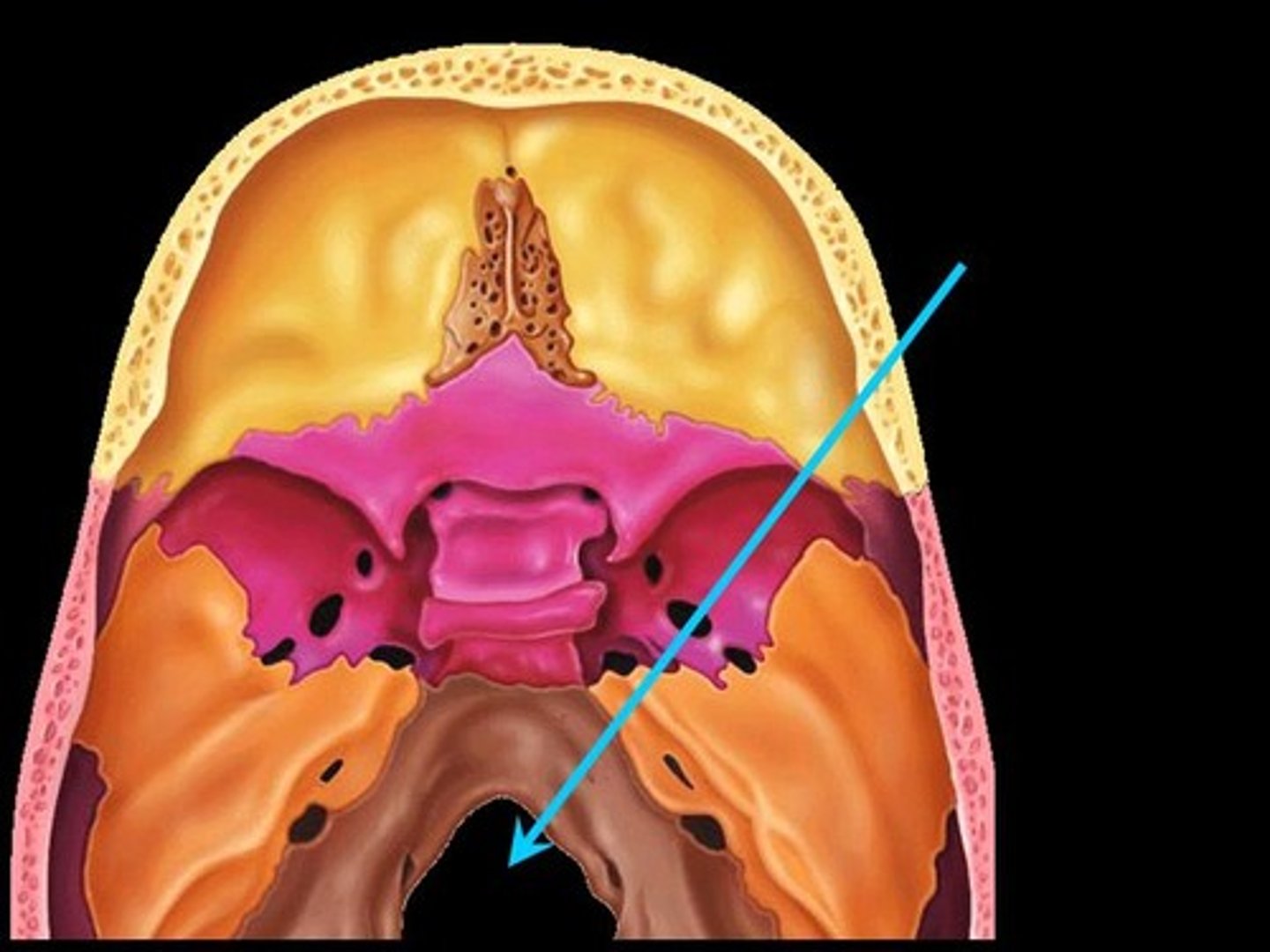
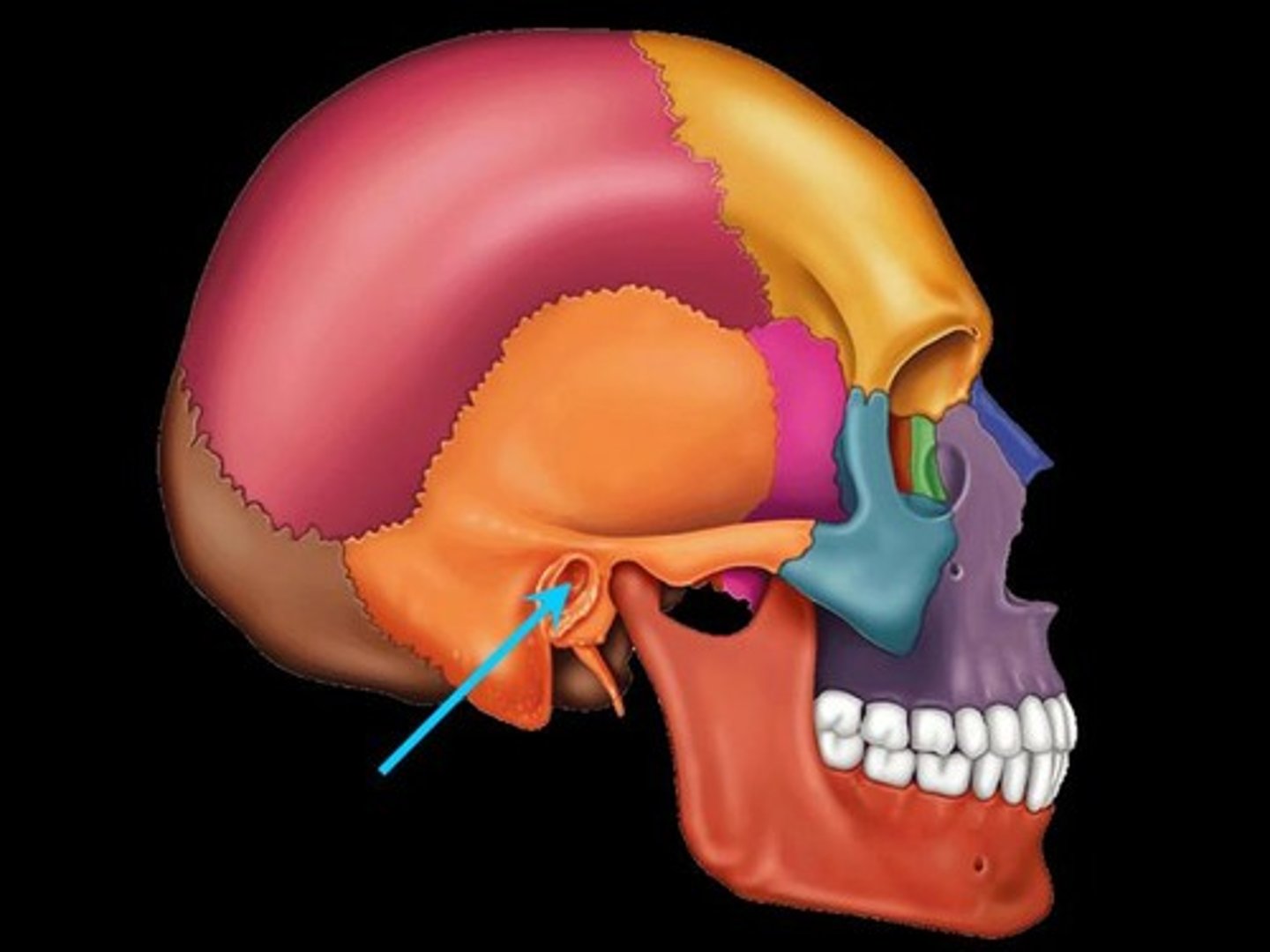
Fissure
Narrow, slitlike opening, oculomotor nerves pass through
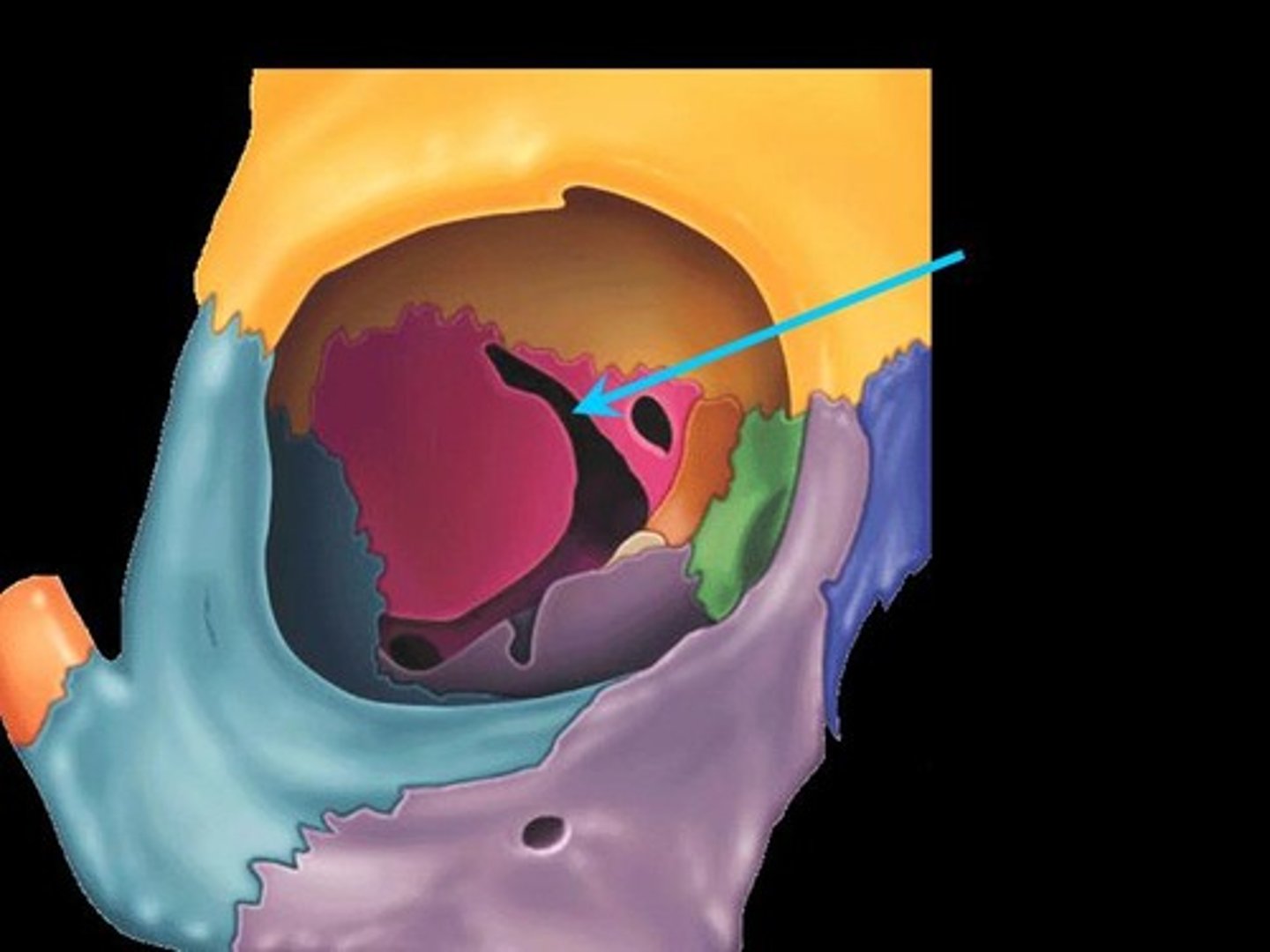
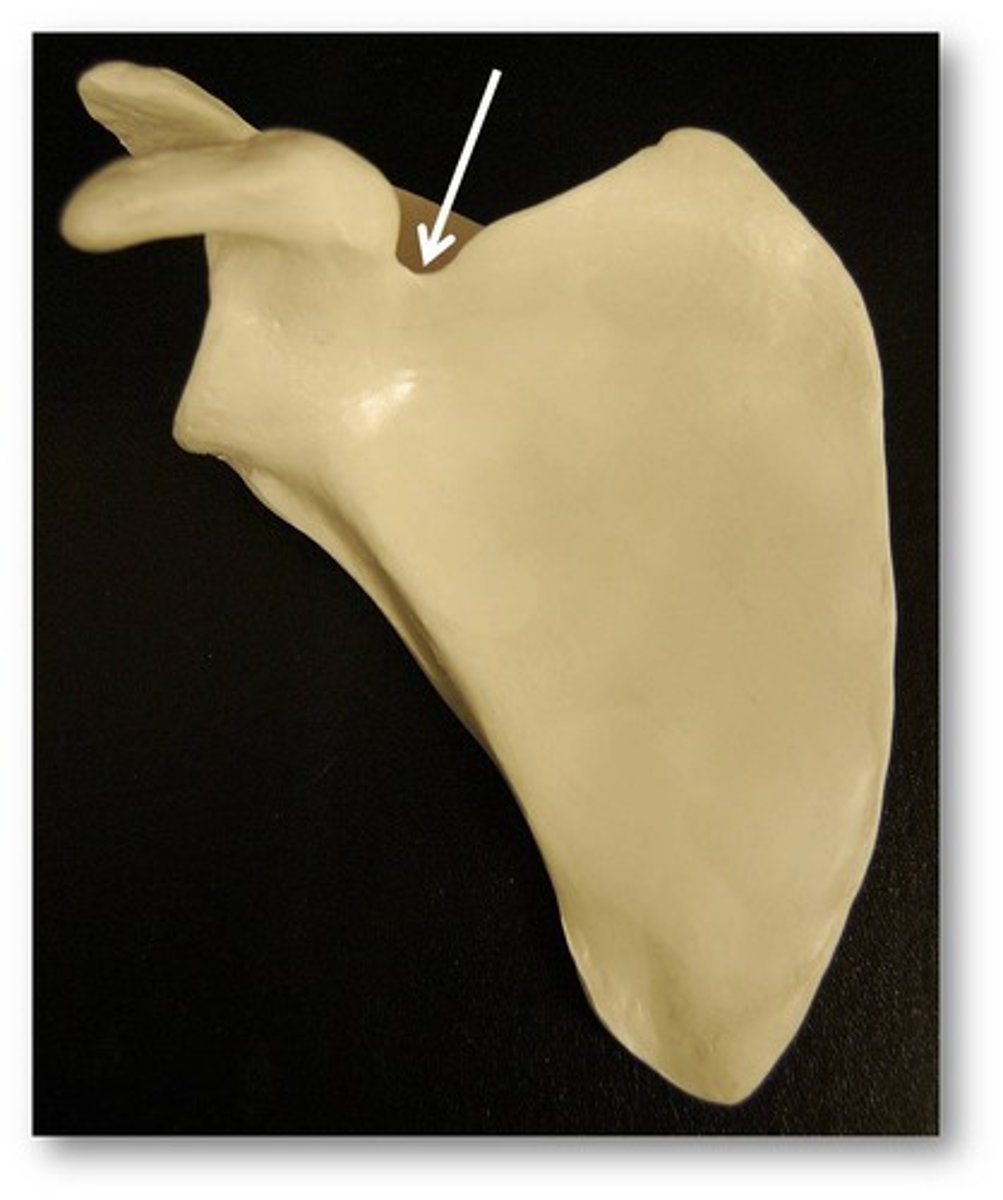
Notch
Depression in the margin of a bone
Passageway of suprascapular nerve
Fossa
Shallow, basinlike depression in a bone, holds muscle or brain
Meatus
Tubelike passageway within a bone
Opening
Sinus
Cavity within a bone, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
Bumpy
Sites of muscle attachment on bones are ____
Surface anatomy
The most common way you will interact with anatomy in the clinic
The anatomy that we can see from the surface of the body
Within
Around
You move _____ a plane and ____ an axis
Superficial
Near the surface
Deep
Away from the body surface; more internal
Transverse plane
Horizontal abduction and adduction of the shoulder takes place in what plane
Transverse plane
Trunk rotation takes place in what plane
Transverse plane (think of it with bent elbow)
What plane does internal and external rotation of the glenohumeral joint (shoulder) take place in?
Transverse plane
What plane does cervical rotation to the right take place in?
Transverse plane (knee bent)
Hip internal rotation (standing) takes place in what plane?
Horizontal adduction in transverse plane
What movement is the right shoulder doing when swinging a bat? What plane?
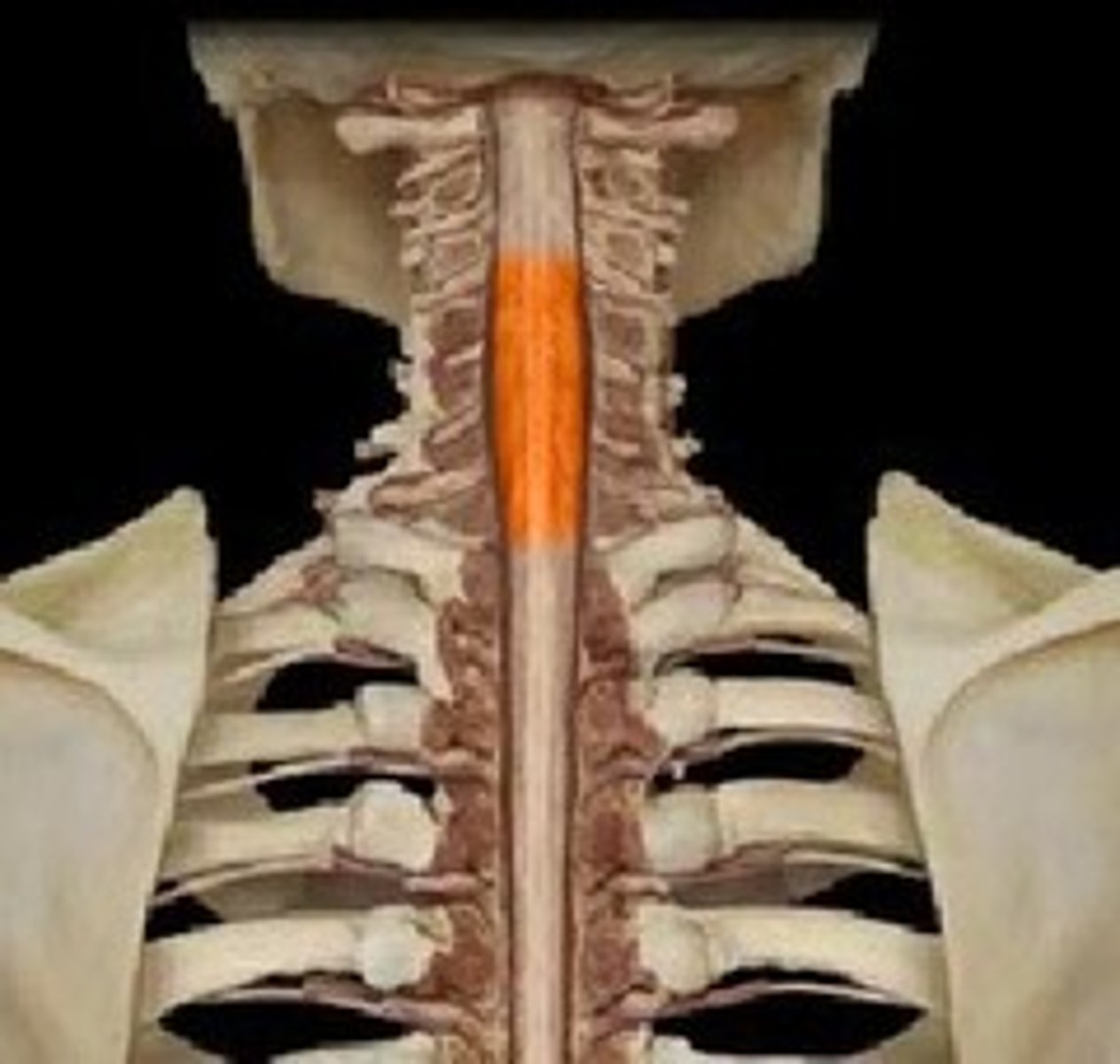
Cervical enlargement
Relative enlargement of the spinal cord which supplies nerves to the pectoral girdle and upper limbs
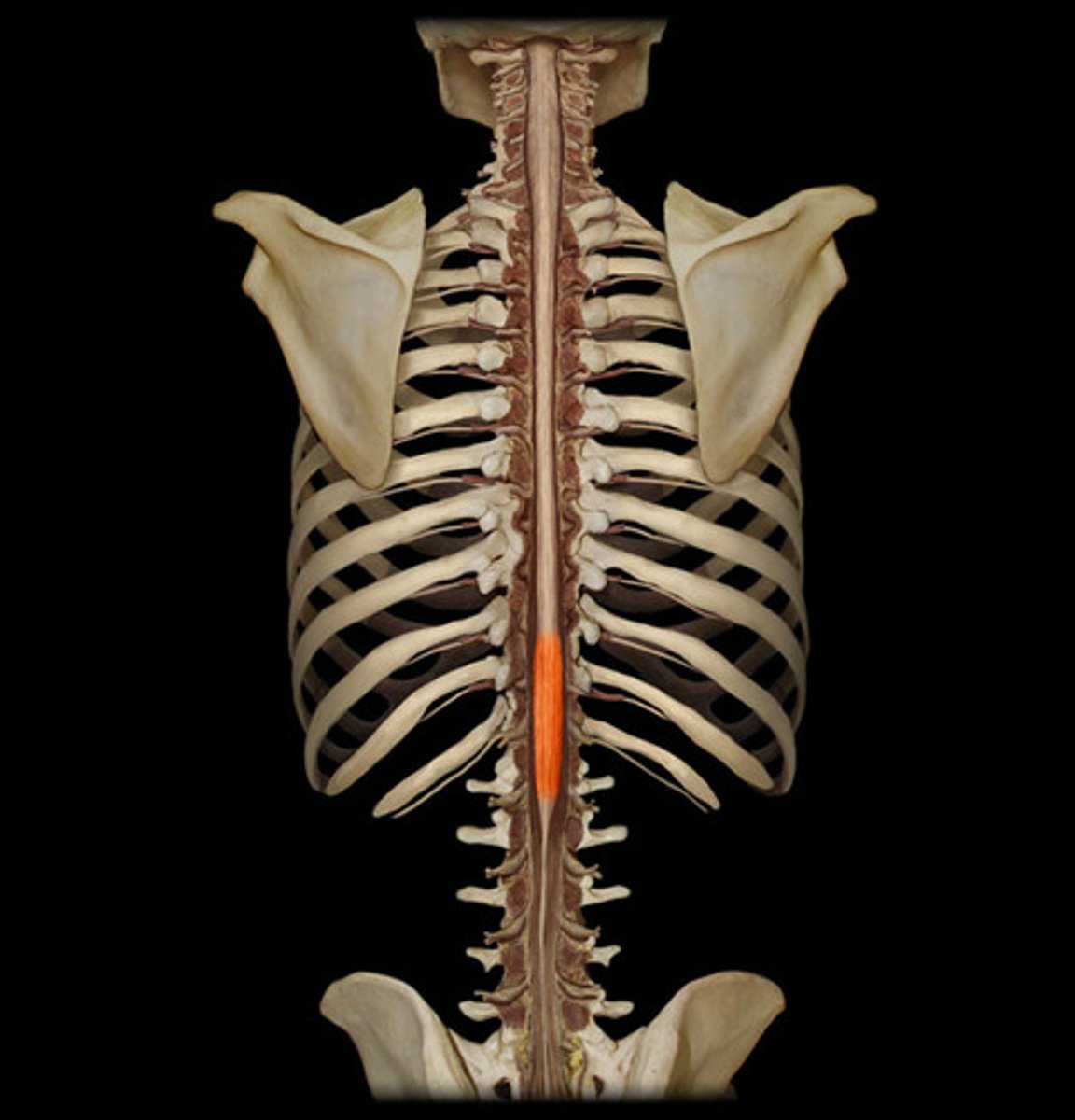
Lumbar enlargement
Enlargement of the spinal cord in the lumbar region. Location where nerves serving the pelvis and lower limbs arise.
Right above the conus medullaris
Conus medullaris
Cone-shaped inferior end of the spinal cord
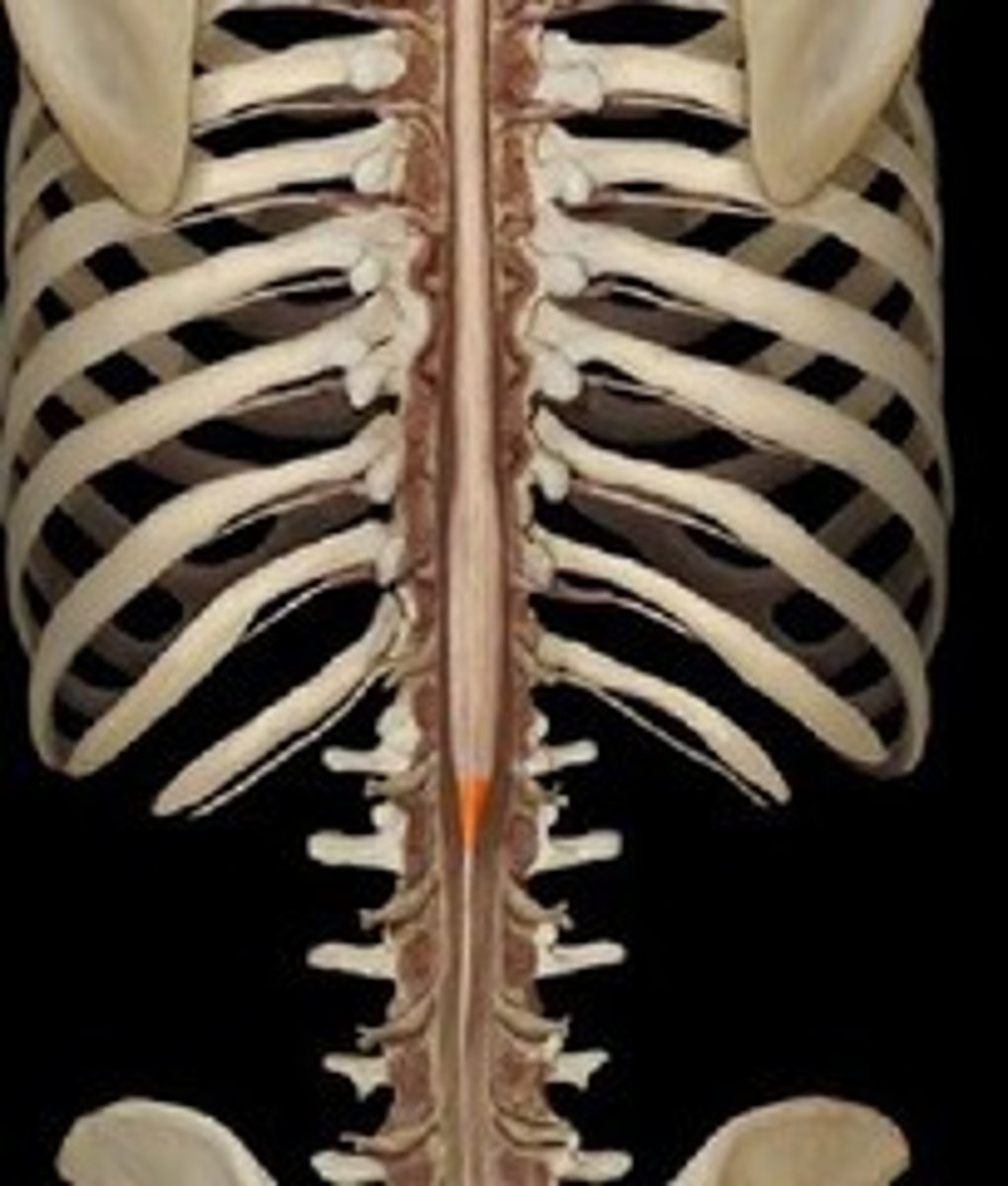
L1
Because of this there is the cauda equina, injections lower on the spine
Where does the spinal cord end?
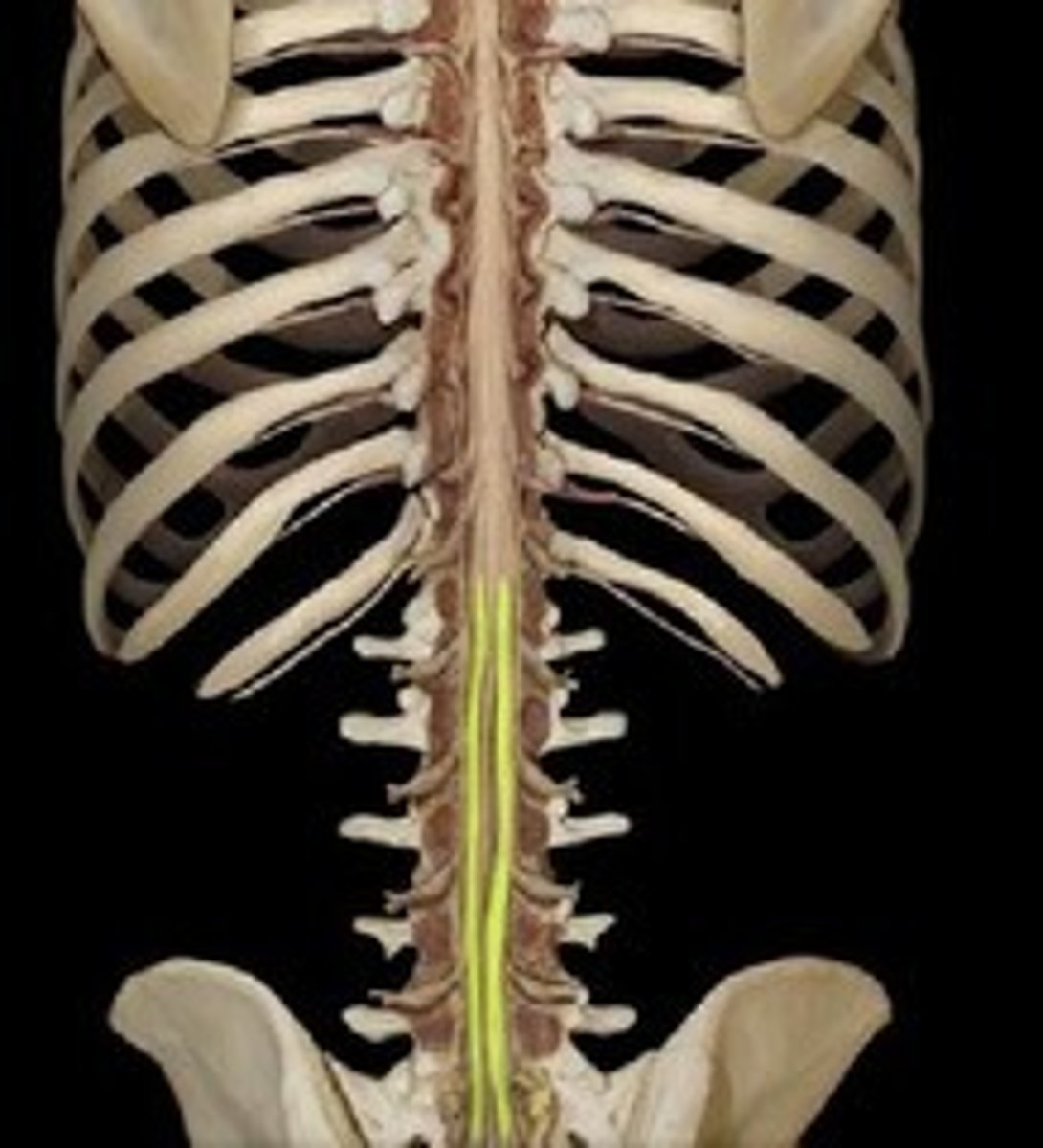
Cauda equina
Collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
Meninges
Three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
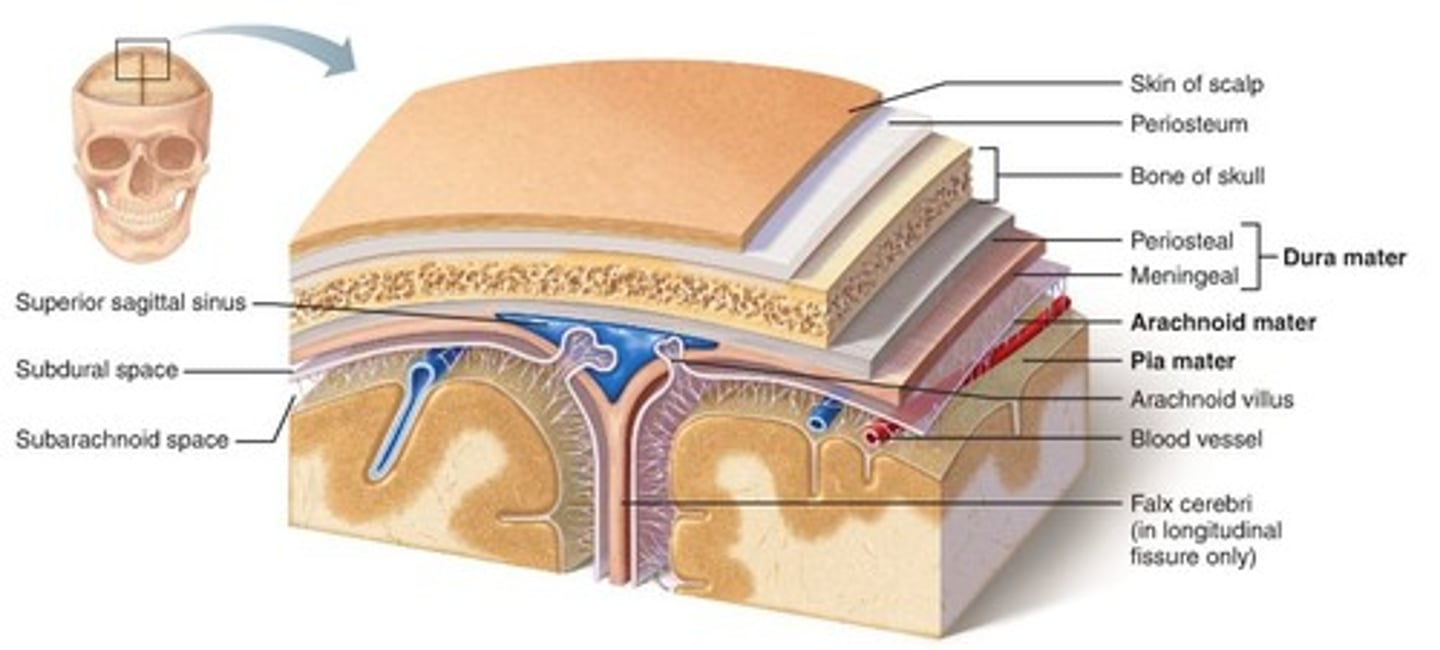
Dura mater
Thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
Arachnoid mater
Thin, transparent layer of meninges deep to the dura mater
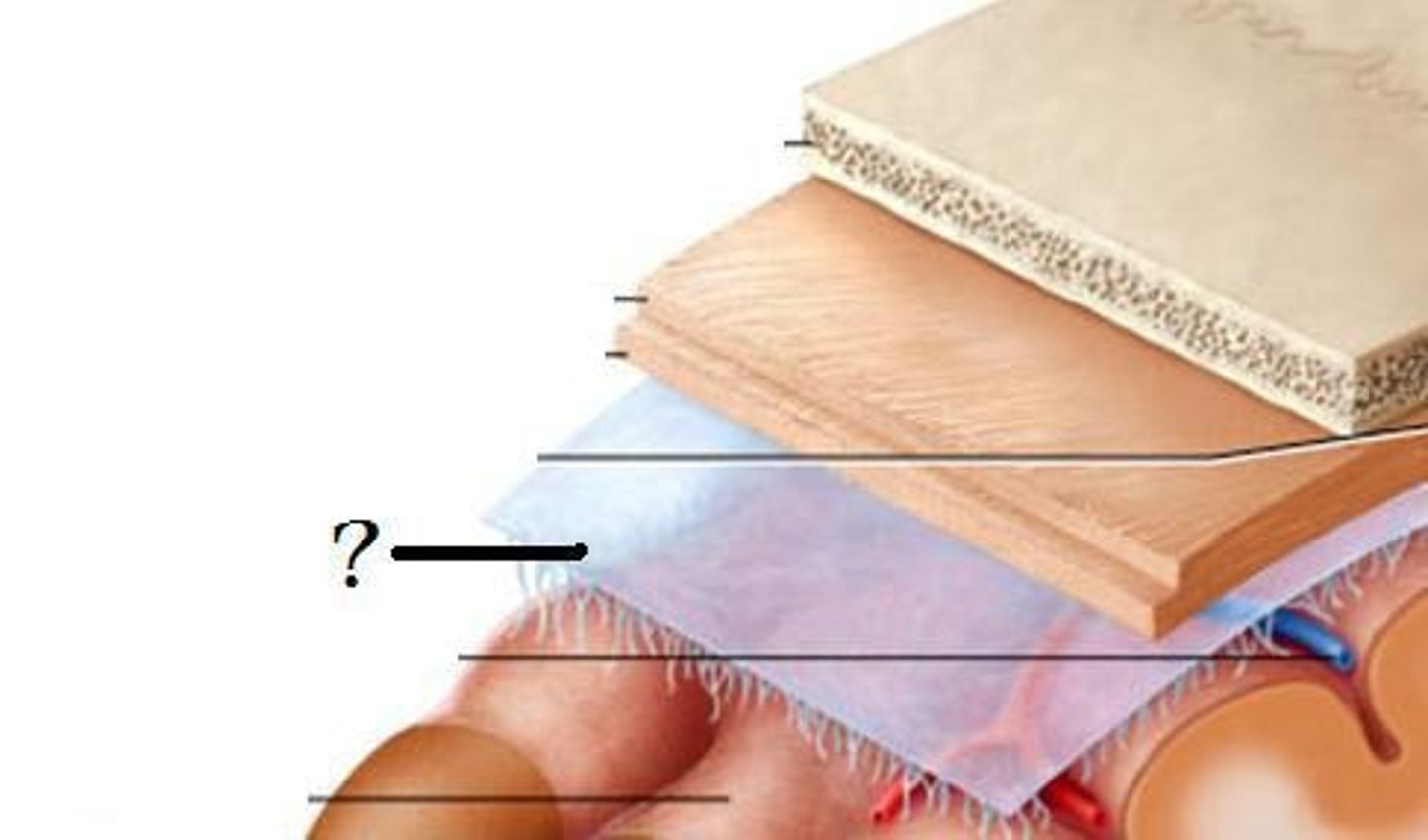
Pia mater
The third layer of the meninges, touching the spinal cord
You cannot see it directly because it is too thin
Filum terminale
Fibrous extension of the pia mater; anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx
Under the nerve roots of the cauda equina
String-like projection off the conus medullaris that is lighter in color than the nerve roots of the cauda equina
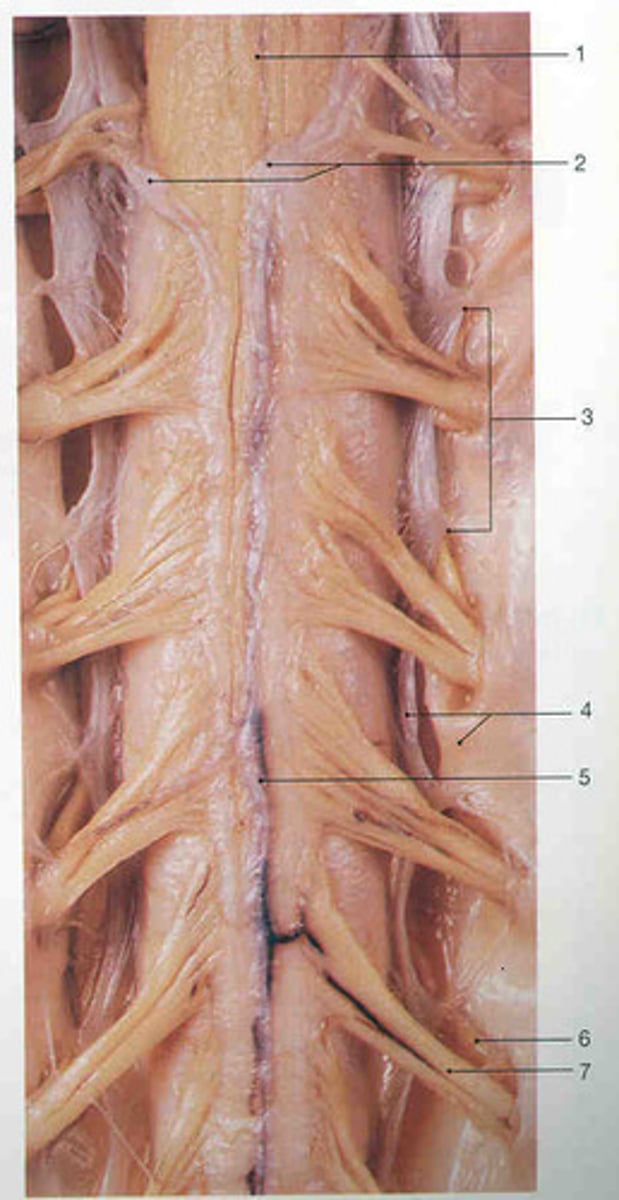
Denticulate ligaments
Extensions of pia mater that secure cord to dura mater, anchor the spinal cord laterally and keep it centrally located within the vertebral column
Triangular-shaped sections of tissue, base is coming from the spinal cord and tip is connecting to the dura mater
White mater
Composed of myelinated axons, outside of the spinal cord
Ventral column
The ventral section of white matter in the spinal cord between the ventral horns.
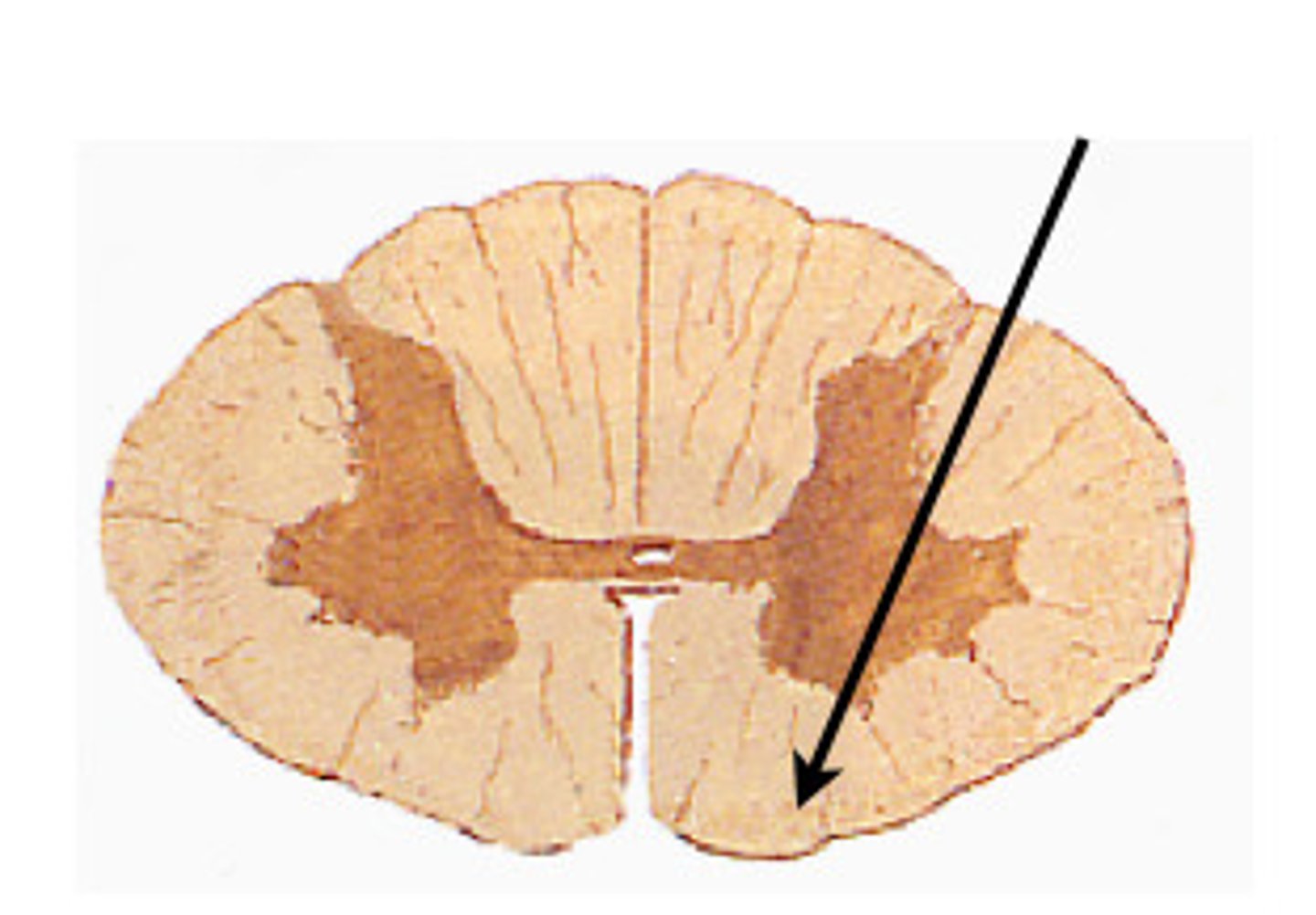
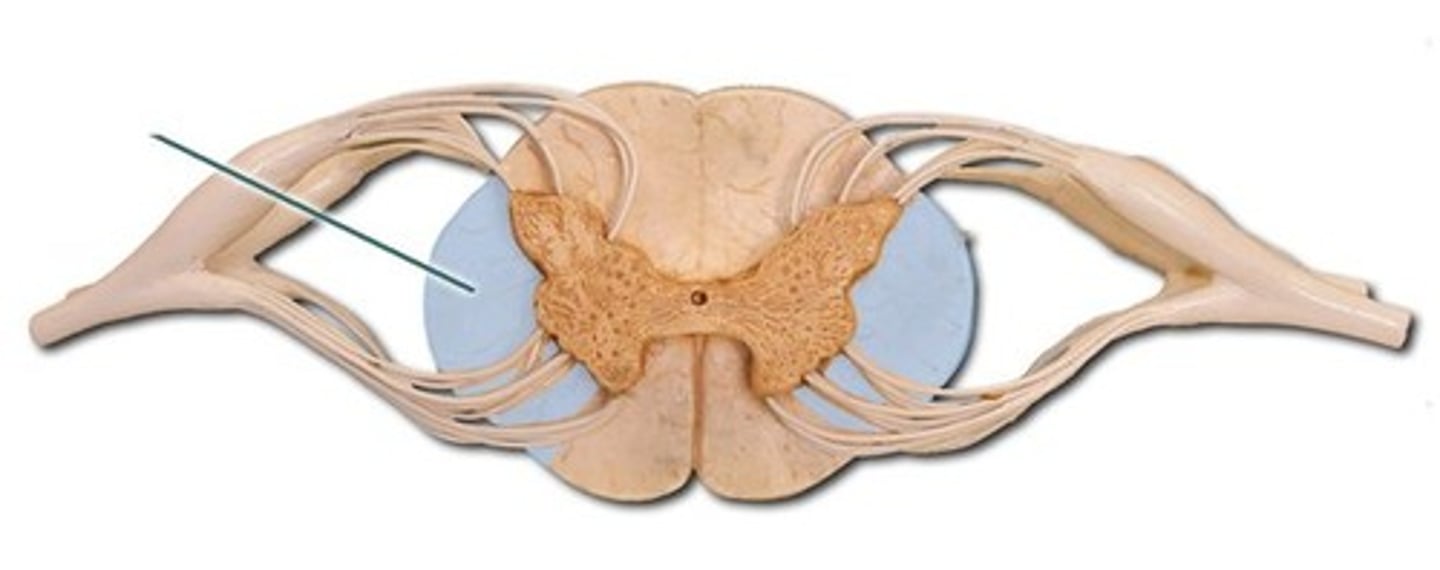
Lateral column
The white matter of the spinal cord lying on either side between the anterior median fissure and the ventral root.
Gray matter
Brain and spinal cord that consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) and unmyelinated axons.
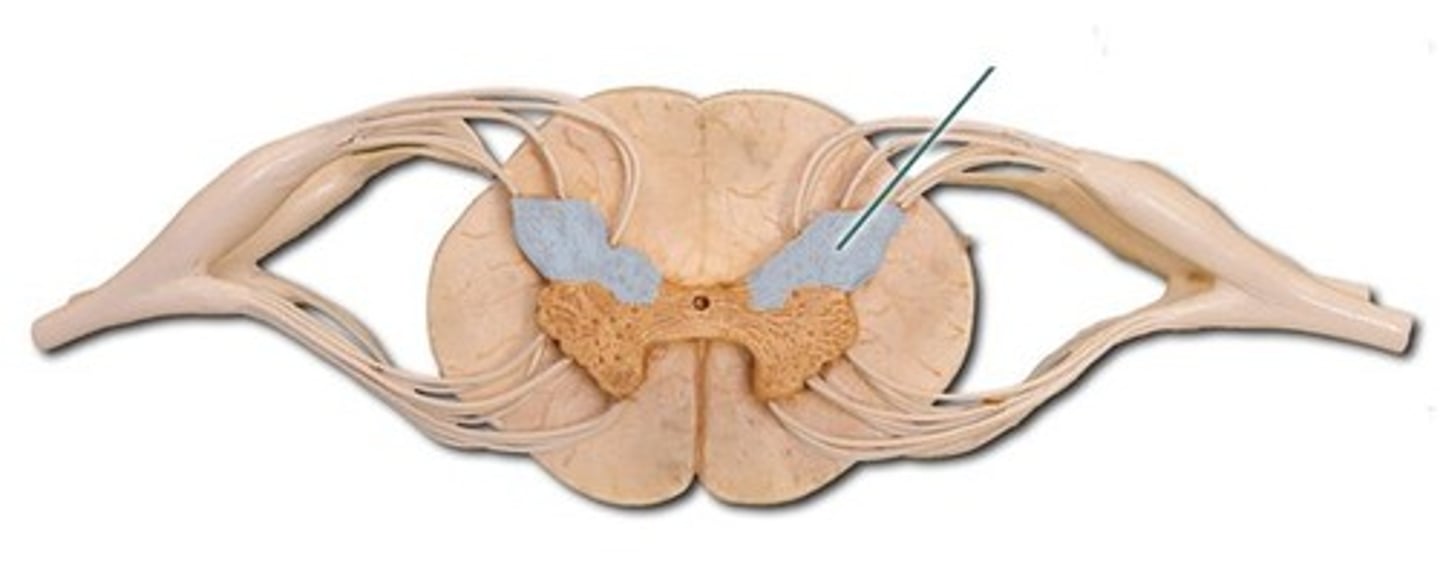
Posterior horn
Gray matter that contains somatic and visceral sensory nuclei
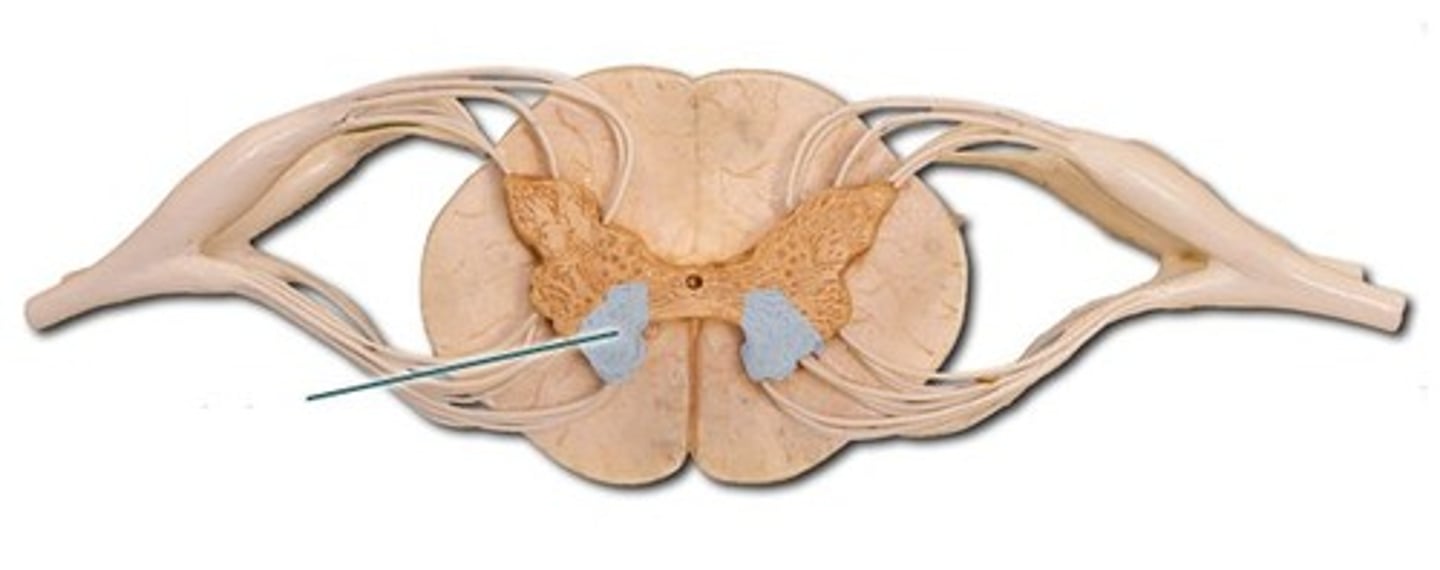
Anterior horn
Somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots
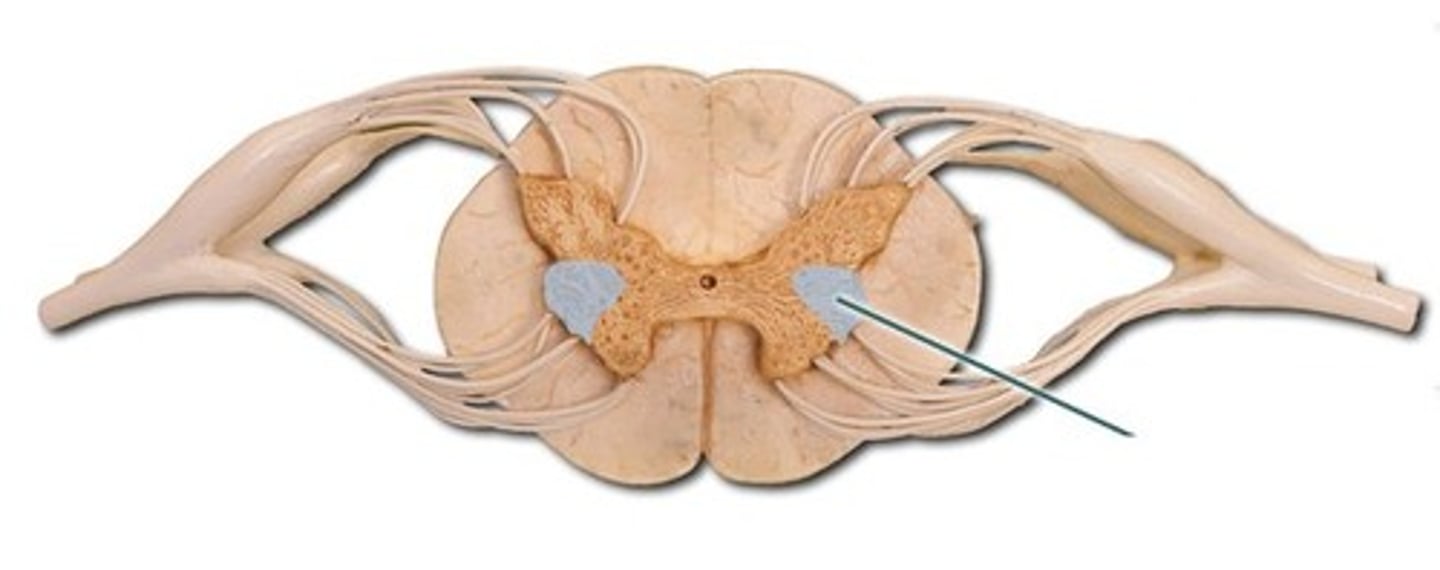
Lateral horns
Only found in the T1-L2 portion of the spinal cord
Contain visceral motor neurons
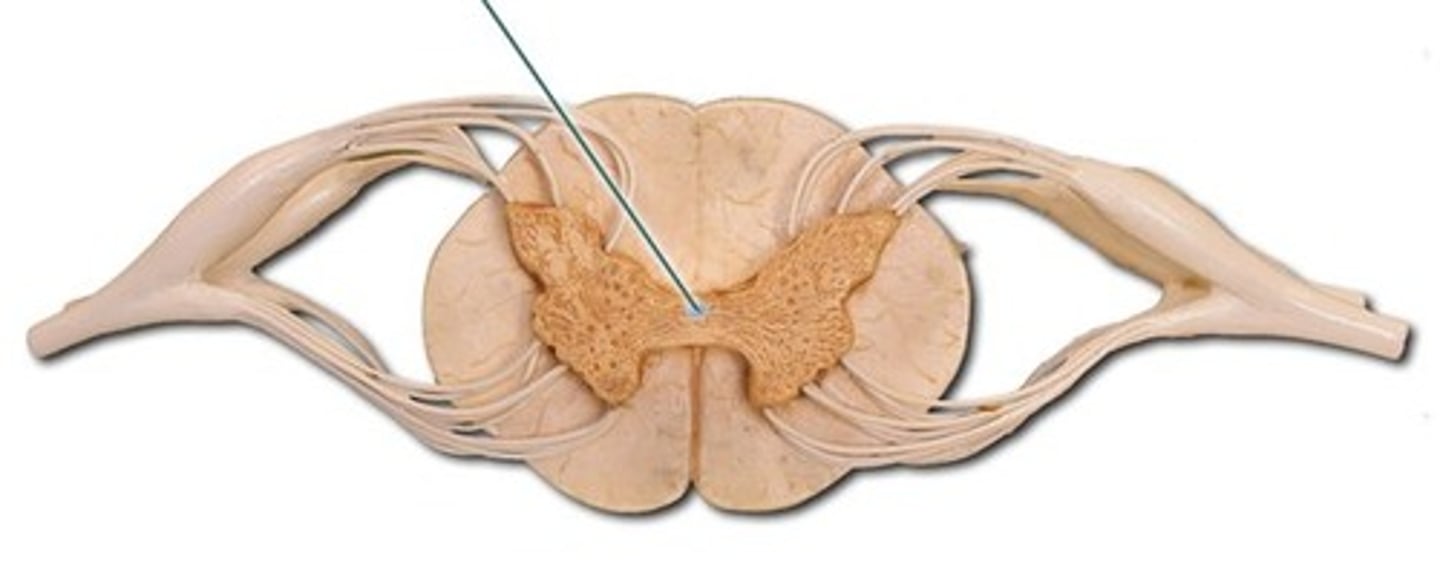
Central canal
A tiny channel found within the spinal cord and inferior medulla oblongata
In the horizontal bar of the H surrounded by gray matter
Longitudinal canal in the center of an osteon that contains blood vessels and nerves, a passageway along the longitudinal axis of the spinal cord that contains cerebrospinal fluid.
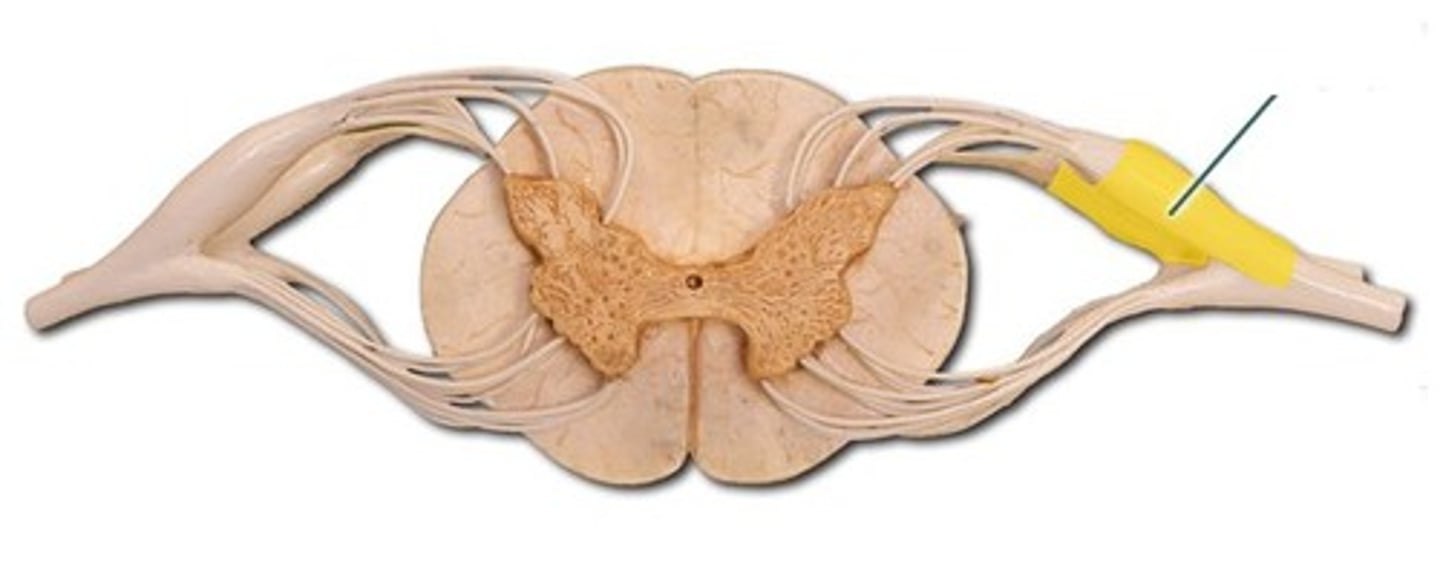
Dorsal root ganglia
Contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons traveling through the dorsal root
Every spinal segment is associated with a pair
Near the intervertebral foramen
Rootlets
Roots
The smaller branches immediately leaving the spinal cord are called ___ that merge to form ___
Ventral roots/ rootlets
Most easily seen exiting the spinal cord
Carry motor information from the spinal cord out to the muscles
Contains efferent axons of somatic motor neurons and at some levels efferent visceral motor neurons
Dorsal roots/ rootlets
Carry sensory information, including fine touch, pain, and proprioception from the periphery to the spinal cord (afferent axons of sensory neurons)
Move dura mater to observe
Thicker than other
Between adjacent vertebrae at the intervertebral foramina
Where do dorsal and ventral roots of each segment enter and leave the vertebral canal?
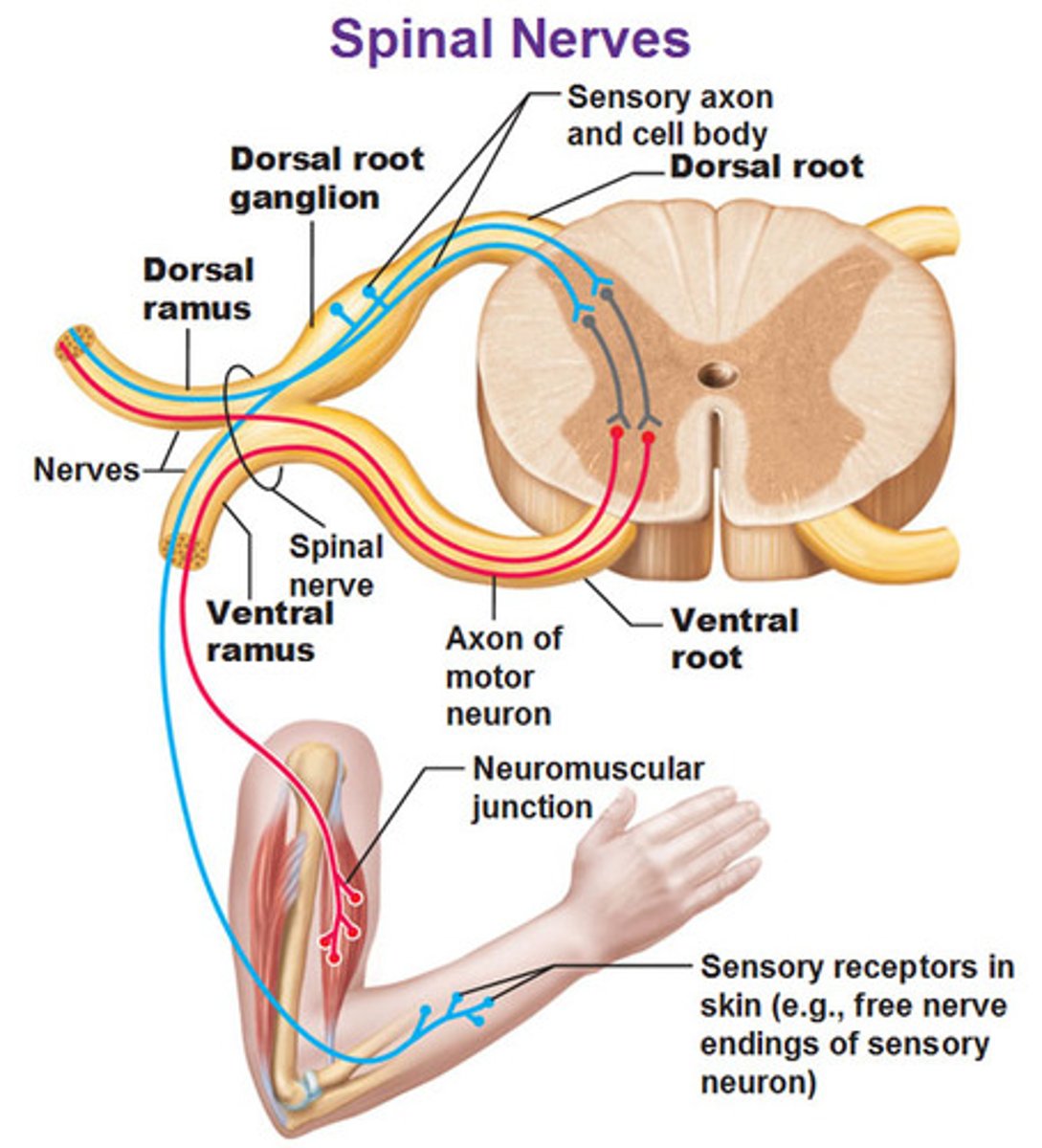
Spinal nerve
Exits from the intervertebral foramina
Dorsal and ventral roots merge for a short distance
Motor and sensory information mixes and then two branches extend out (rami)
Dorsal ramus
Branch off of spinal nerve that innervates the muscles and skin of the back
Ventral ramus
Branch off of the spinal nerve that runs anteriorly to innervate the muscles and skin of the extremities and anterior trunk
There is more gray matter as you go from superior to inferior because more myelinated neurons exit
How does white and gray matter change in cross section from superior to inferior?
Thoracic region of spinal cord
Only region of the spinal cord that has lateral horn
Thoracic region of spinal cord
Supplies thoracic cage, T1-12
Laminectomy
The surgical removal of a lamina, or posterior portion, of a vertebra
Allows you to see the spinal cord within the vertebral foramen
Horizontally
Downward
Dorsal and ventral roots run more ____ in the cervical region but tend to leave the spinal cord and run ____ at the lower thoracic and lumbar levels
Dorsal column
A white matter tract on the dorsal side of the spinal cord, carrying pressure, vibration, and discriminative touch; highly localized
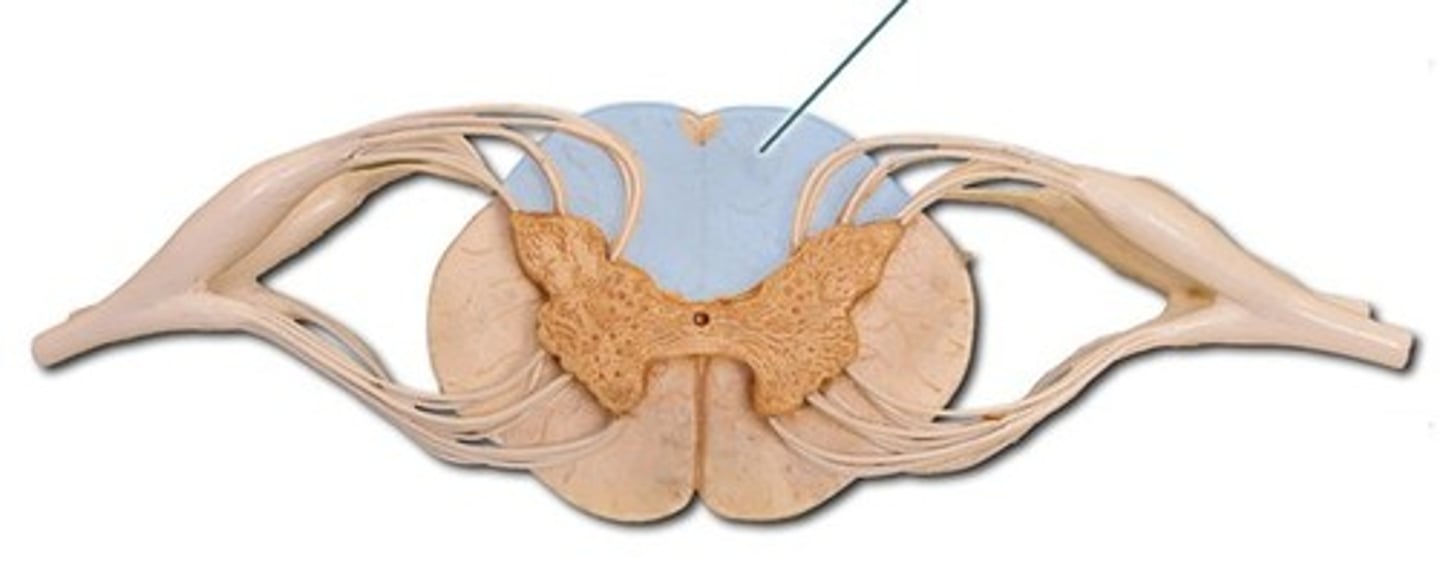
Dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway
Carries: pressure, vibration, and discriminative (fine) touch
Highly localized
Incoming sensory information enters the spinal cord at the dorsal horn (from dorsal root), to the dorsal column, passes superiorly through the dorsal column of the thoracic, cervical enlargement, and high cervical levels, and decussates at the level of the brainstem
Anterolateral system (spinothalamic tract)
Carries pain, temperature, crude (non-discriminative) touch, deep pressure
Sensory information comes in from the dorsal root into the dorsal horn at the lumbar spinal cord, then decussates at the level that it enters the spinal cord through the center of the lumbar spinal cord to the anterolateral anterior horn, then passes superiorly through the anterior horns
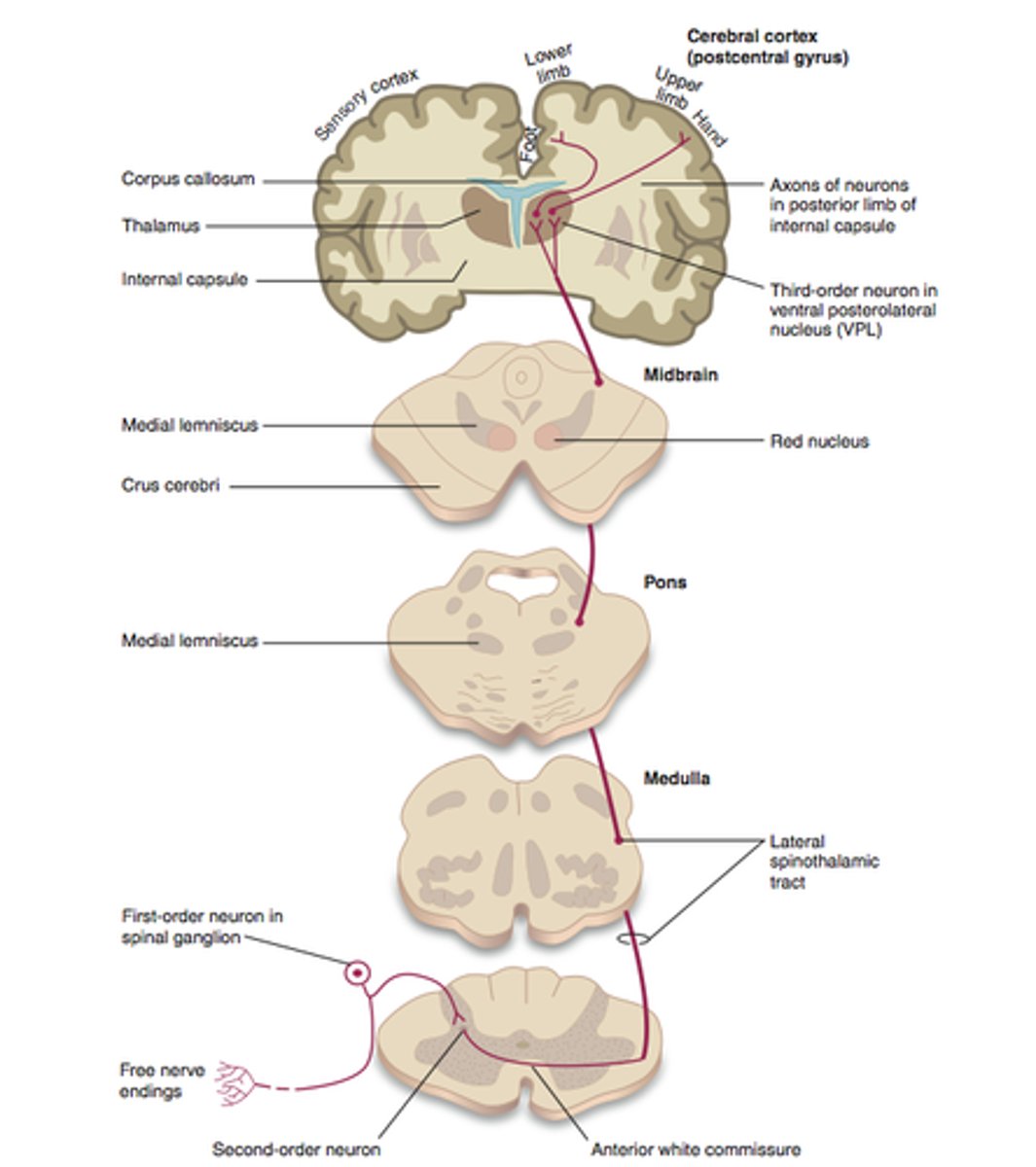
At the brainstem
Where does the dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway decussate?
At the level that it enters the spinal cord
Where does the anterolateral system (spinothalamic tract) decussate?
Corticospinal tract
Executes voluntary motor activity
Spinal cord pathway that starts at the brain, decussates in the brainstem, descends in the lateral column at the high cervical, cervical enlargement, and thoracic levels, at the lumbar level the pathway the pathway passes through the anterior horn that sends the signal through ventral roots to skeletal muscles
Corticospinal tract
Carries orders from the brain to the motor neurons in the anterior horn of the spinal cord