Glencoe Biology - 8.1, 8.2: Cellular Energy and Photosynthesis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
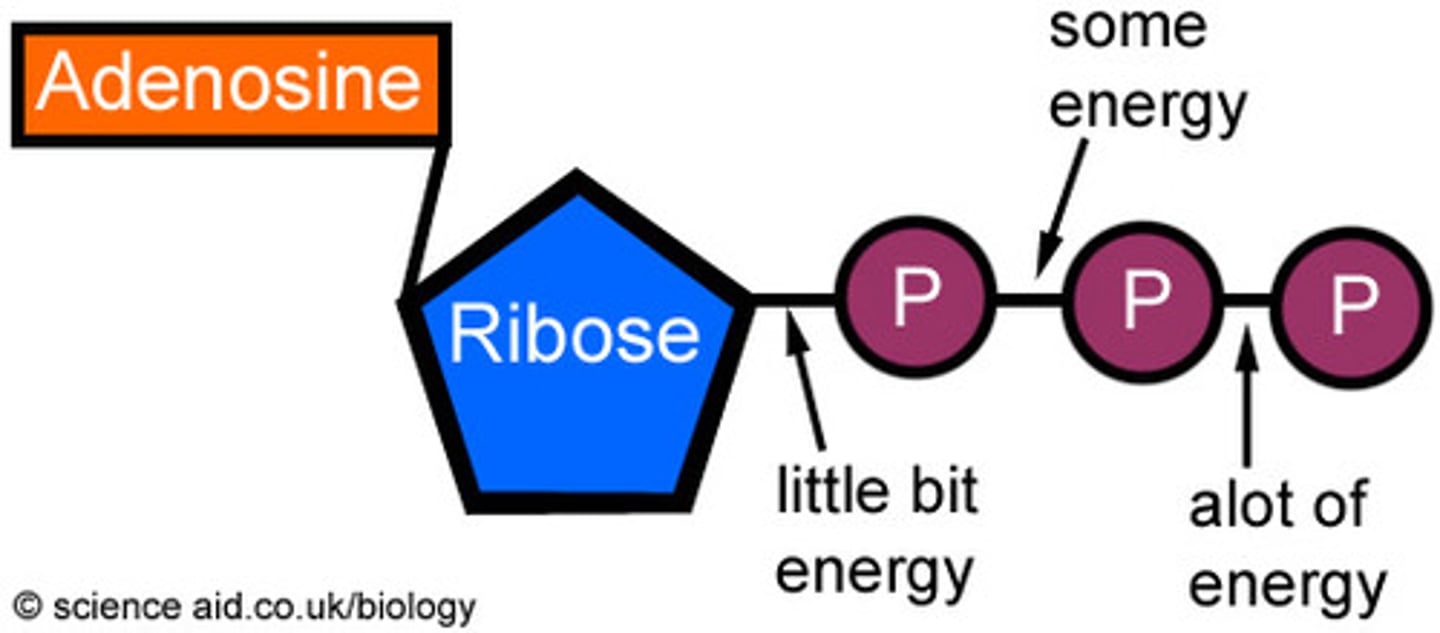
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Energy-carrying biological molecule, which, when broken down, drives cellular activities.
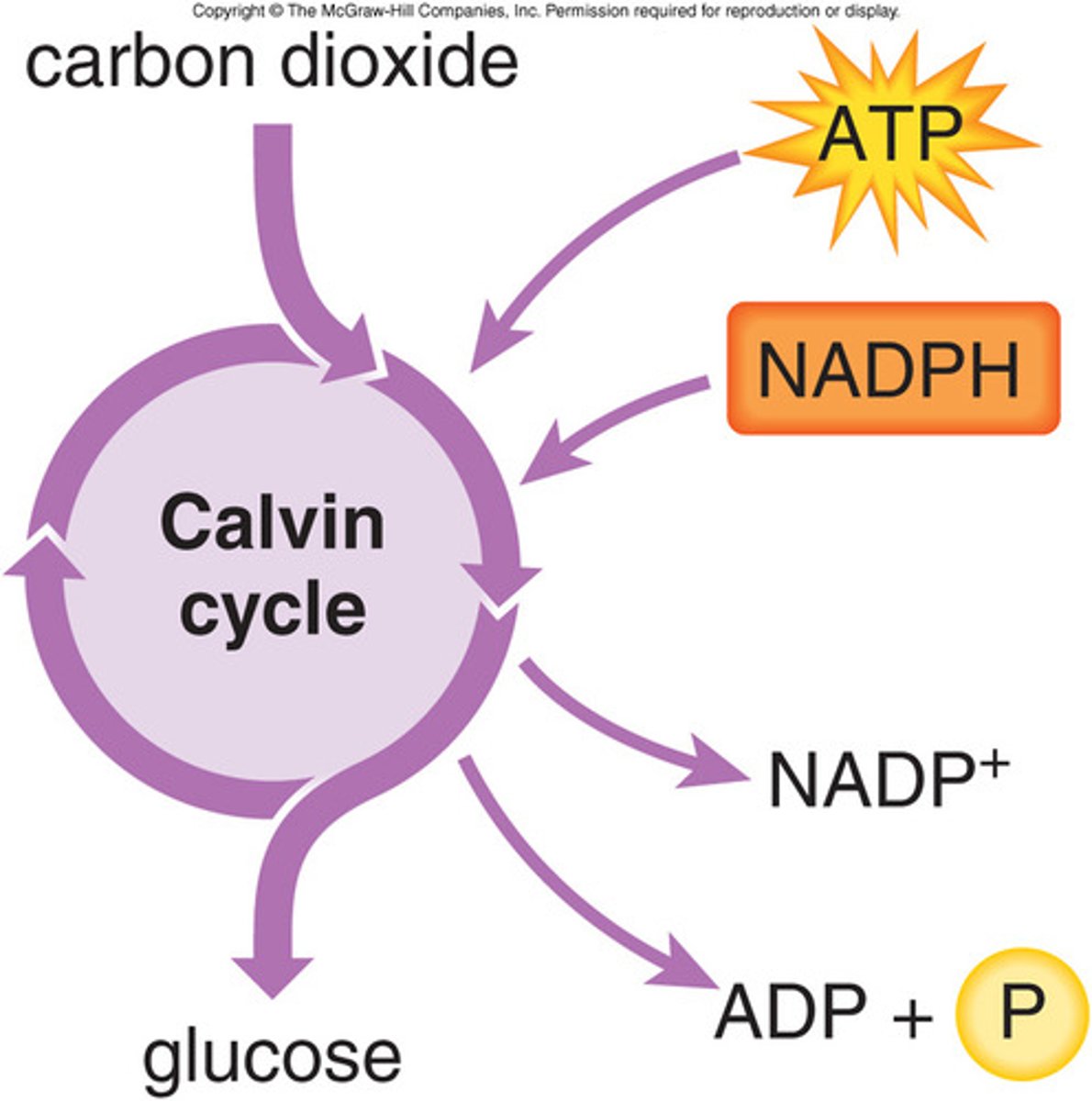
Calvin cycle
Light-independent reactions during phase two of photosynthesis in which energy is stored in organic molecules as glucose.
Energy
Ability to do work; energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
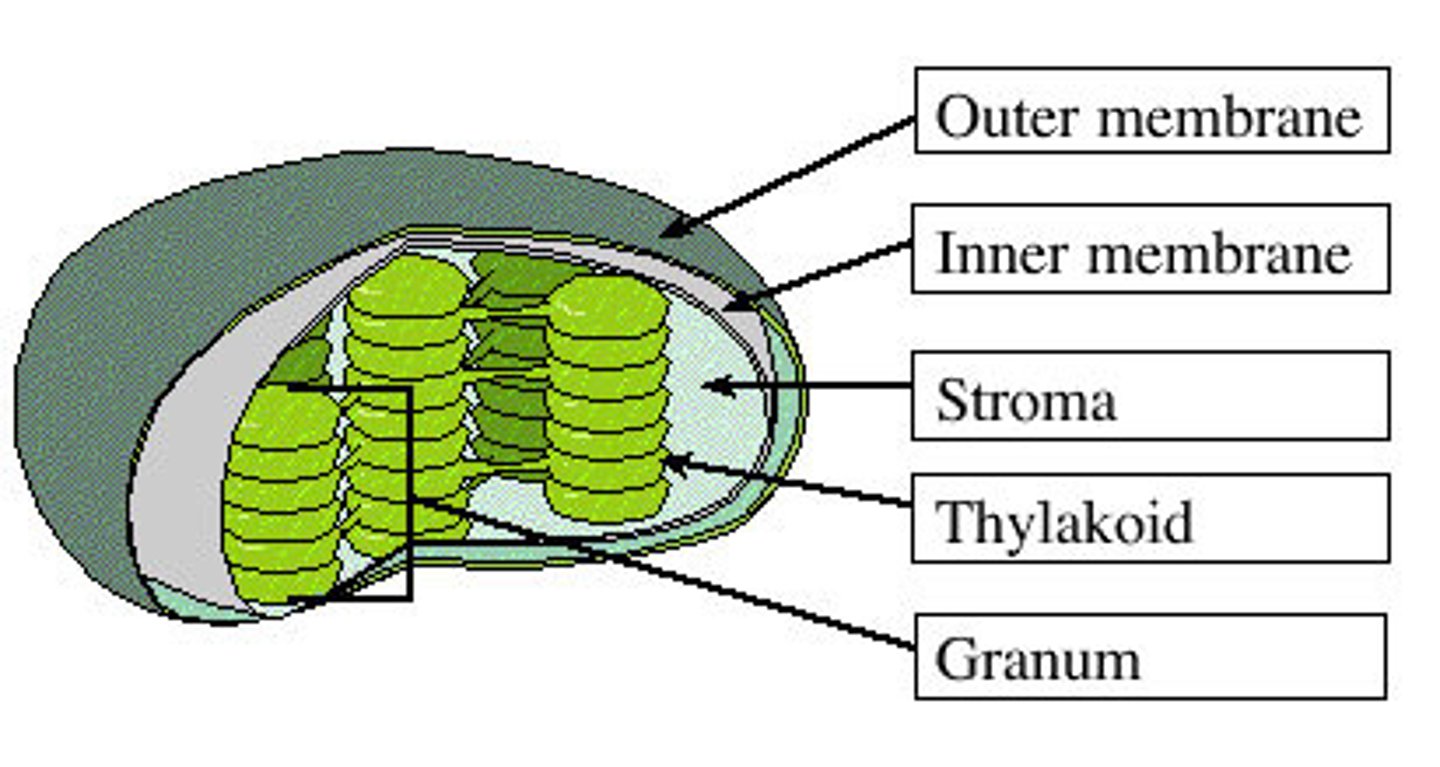
Granum
One of the stacks of pigment-containing thylakoids in a plant's chloroplasts.
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism.
NADP+
In photosynthesis, the major electron carrier involved in electron transport. 'uncharged' version which is recycled and sent back to the light reaction
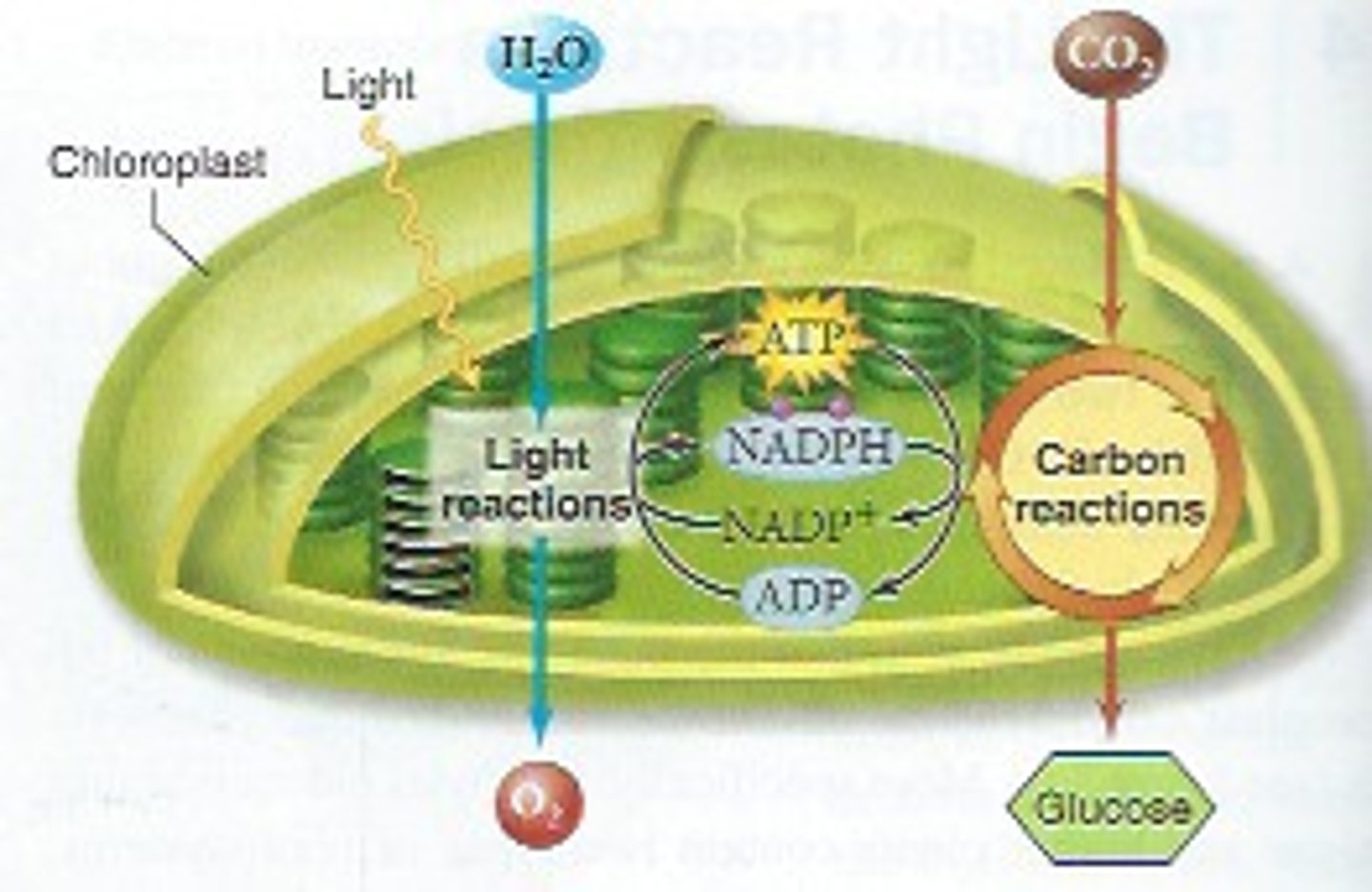
Photosynthesis
Chemical reaction in which the Sun's light energy is converted to chemical energy for use by the cell.
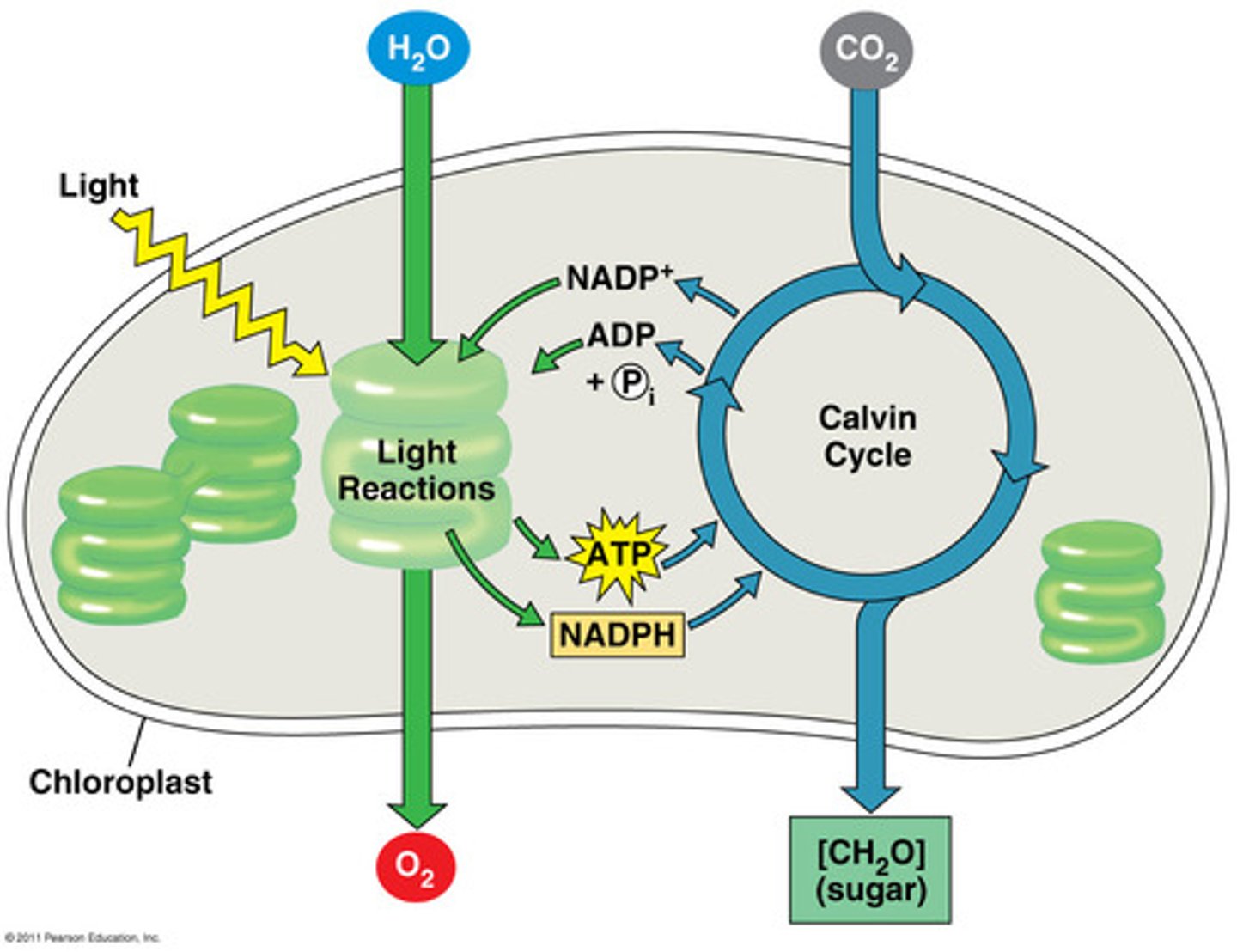
Pigment
Light-absorbing colored molecule, such as chlorophyll and carotenoid, in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
Stroma
Fluid-filled space outside the grana in which light-dependent reactions take place.
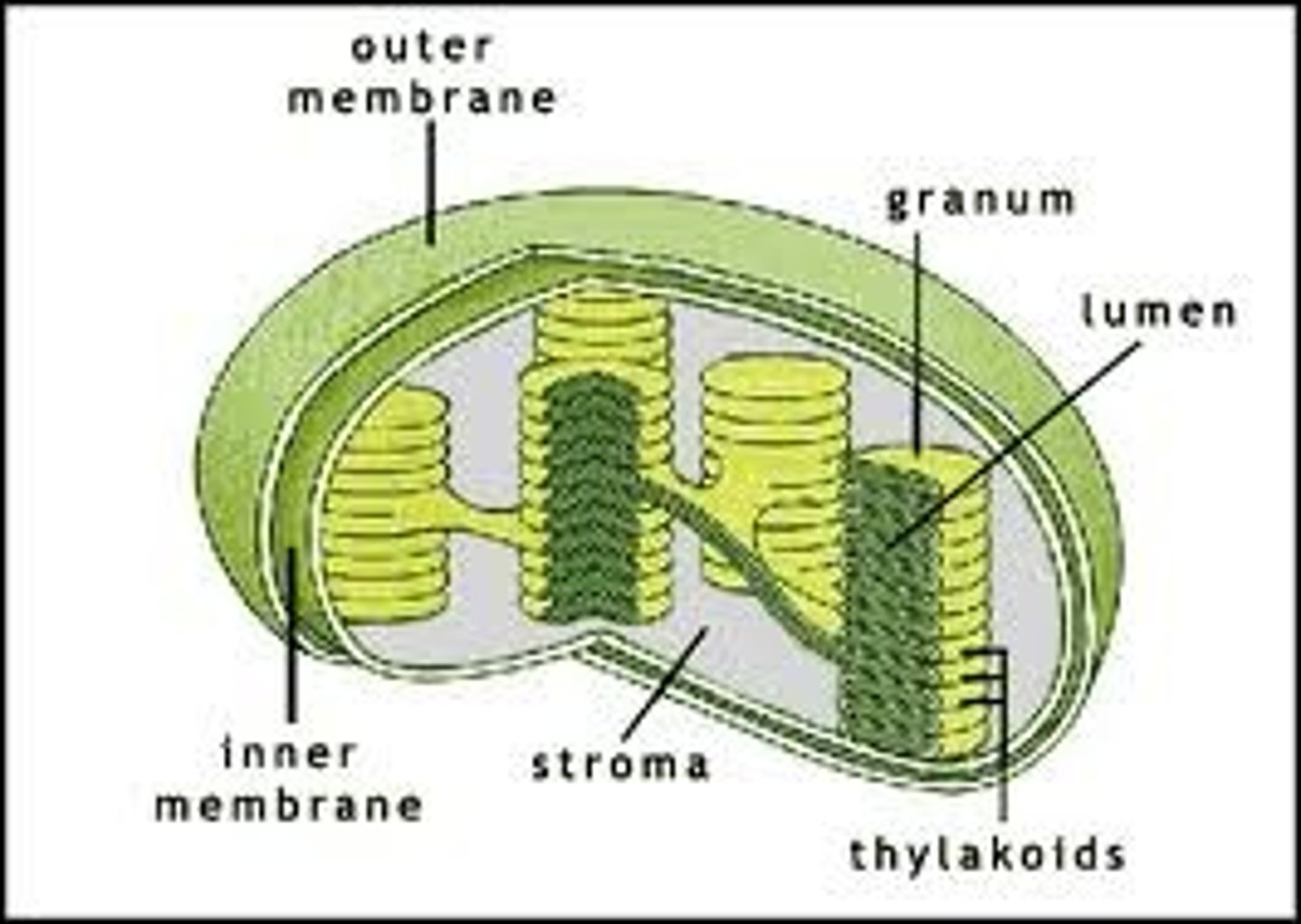
Thylakoid
In chloroplasts, one of the stacked, flattened, pigment-containing membranes in which light-dependent reactions occur.
Autotrophs
Organisms that make their own food. Usually w/ photosynthesis. could be chemosynthesis

Heterotrophs
Organisms that need to ingest food for energy. Includes Animals, fungi, protists and some bacteria.

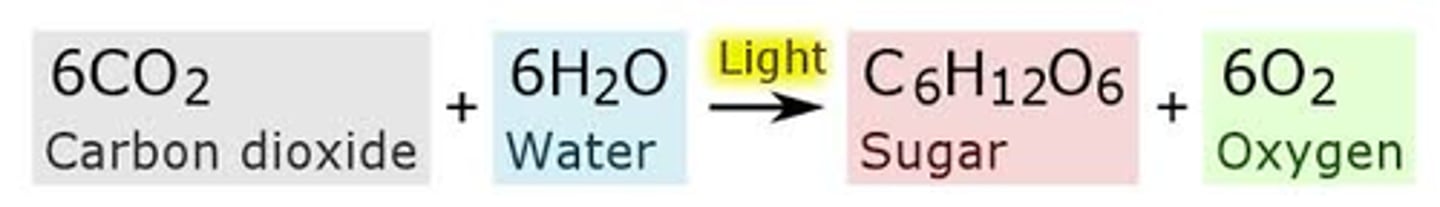
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2+ 6H2O=> C6H12O6+ 6O2
ADP
adenosine diphosphate; molecule that ATP becomes when it gives up one of its three phosphate groups. 'uncharged battery'
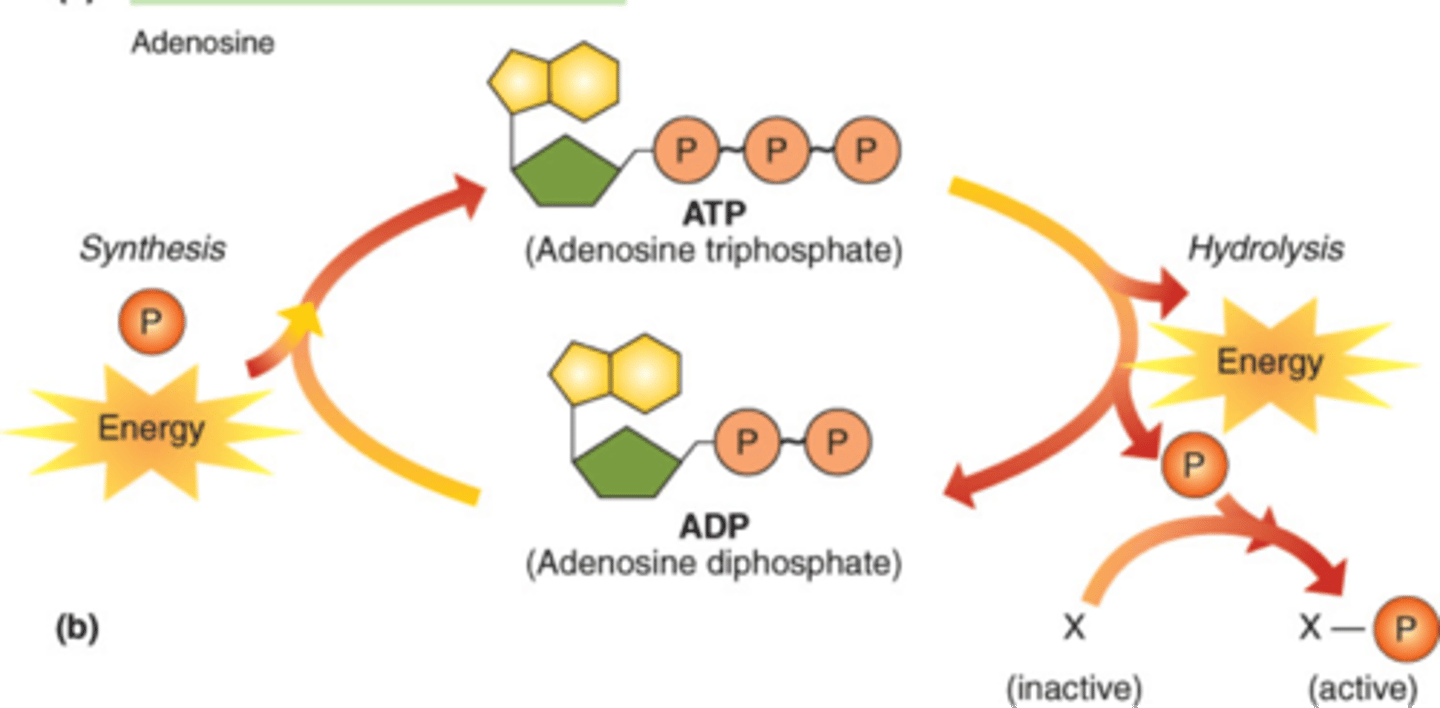
NADPH
An electron carrier involved in photosynthesis. (Light drives electrons from chlorophyll to NADP+, forming NADPH, which provides the high-energy electrons for Calvin cycle.)
catabolism
break down of larger more complex molecules into simper ones, when this is done energy is released. Essentially eating. Done by heterotrophs.
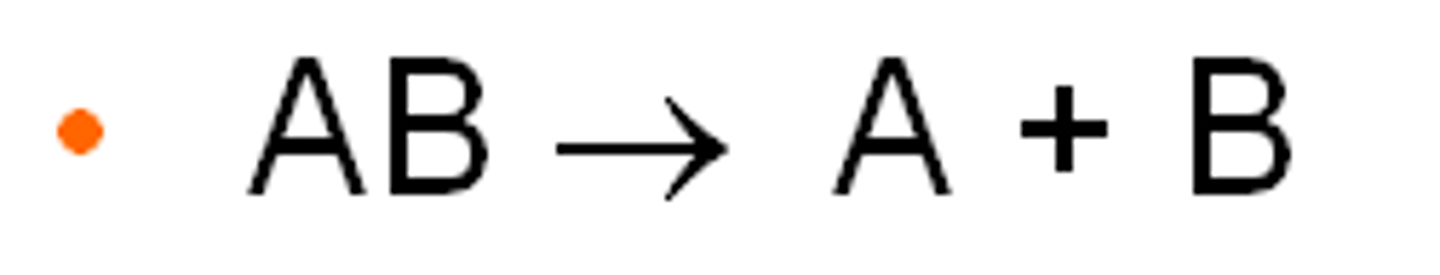
Anabolism
Metabolic pathways that build molecules, requiring energy. Photosynthesis is an example. Done by Autotrophs

Glucose
C6H12O6. An energy molecule, food, carbohydrate, sugar

CO2
Used in the Calvin Cycle or light independent reaction as a source of Carbon to create sugars.
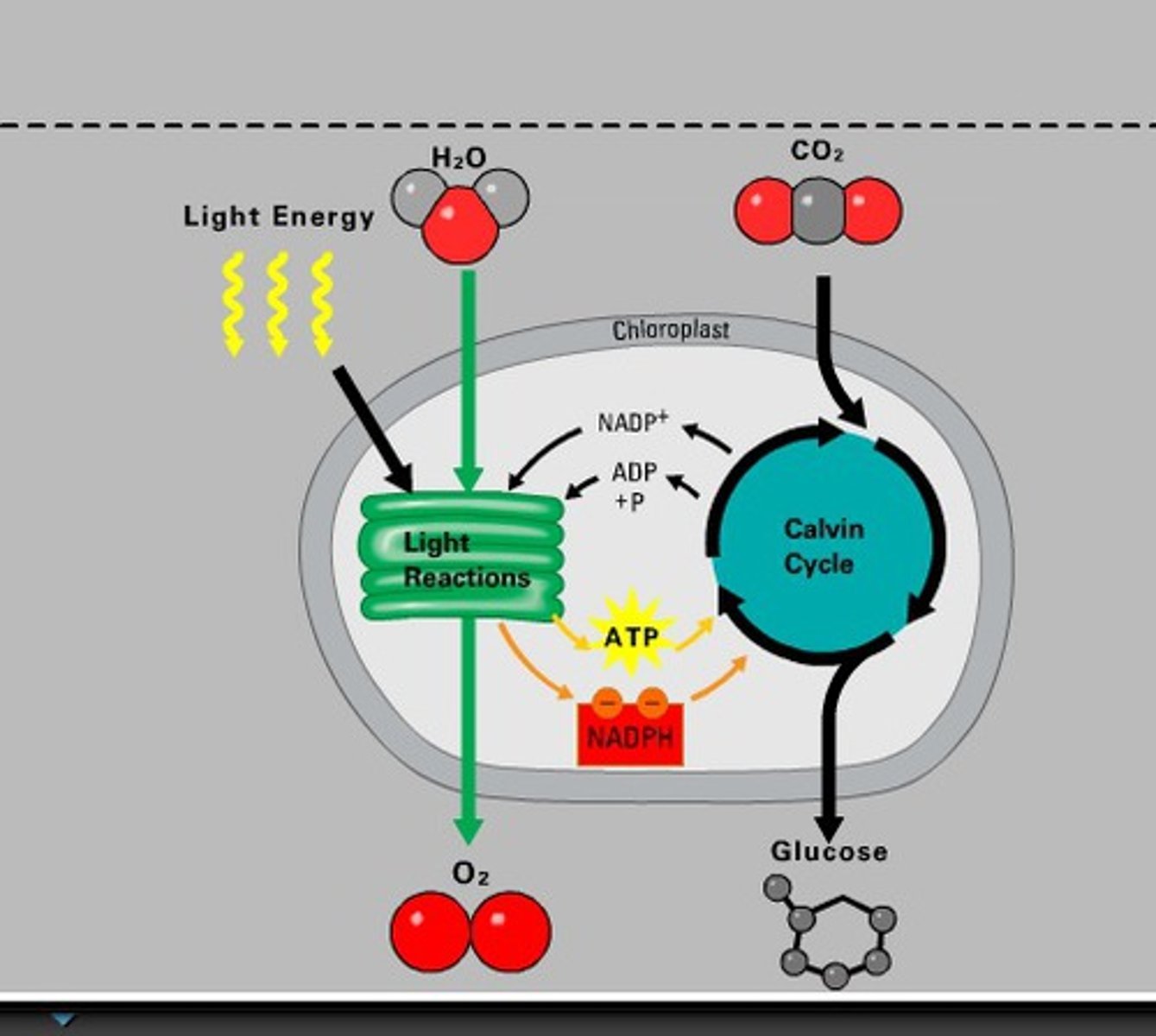
Water
An input in the light reaction of PS. Supplies H+ to help create ATP. Also is source of waste product O2