Types of necrosis II (So nice we hit it twice)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
gangrenous necrosis
Not a specific pattern of cell death, but a term that denotes a type of necrosis that develops at the distal aspect of extremities or dependent portion of organs
wet and dry
what are the two forms of gangrenous necrosis
wet gangrene
Necrotic tissue invaded by saprophytic or putrefactive bacteria leads to what?
abundant fluid and warmth
wet gangrene occurs in tissue with abundant what?
with gas producing bacteria (Clostridium)
gas gangrene forms when?
aspiration pneumonia
bacterial infections
torsion, volvulus, incarceration, intussusception
What causes gangrenous necrosis in the lung?
In the mammary tissue?
In the intestine?
presence of both liquefactive and coagulative necrosis
liquefactive
What is characteristic of wet gangrene microscopically?
Which type of necrosis is more prominent?
wet gangrene
what type of necrosis
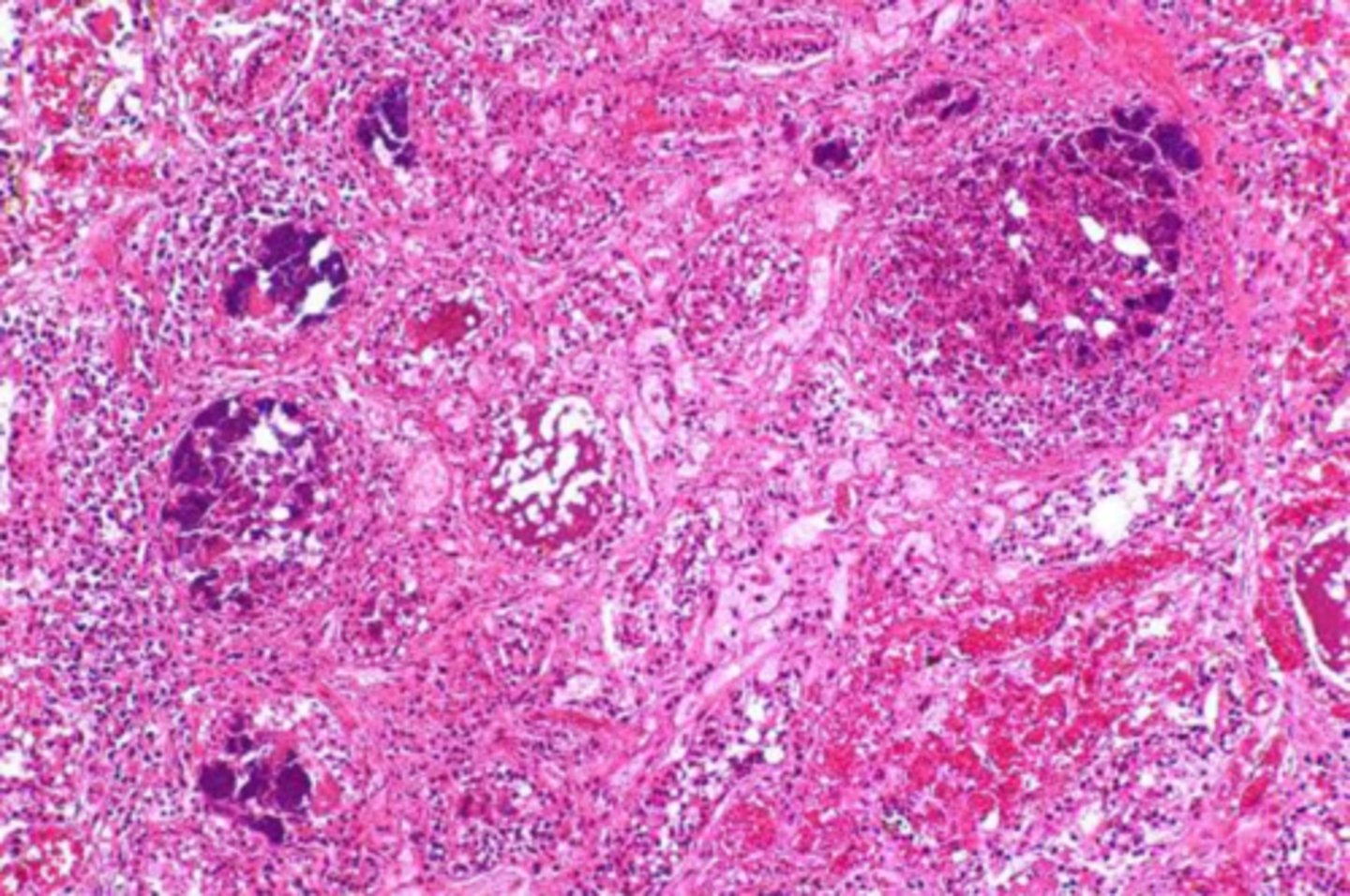
swollen soft tissue, wet, dark red/green, putrid odor, sharp line of demarcation, emphysematous
describe a wet gangrene's gross appearance
hydrogen sulfide + iron = iron sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide gas (smell)
What would turn a wet gangrenous lesion black?
Why would they smell so bad?
dry gangrene
what type of gangrene results from a local tissue hypoxia or ischemia? (often extremities)
infarction, mechanical constriction, frostbite, fescue foot
what can cause dry gangrene?
coagulative necrosis
What does dry gangrene look like microscopically?
dry leathery texture, cool, shriveled
describe a dry gangrene grossly
wet gangrene is an emergency and leads to septicemia/toxemia/shock,
dry gangrene doesn't lead to toxemia, and dead tissue normally sloughs and heals
compare the end outcomes of wet vs dry gangrene
ulceration
Not a specific pattern of cell death, but a term that denotes a type of necrosis of epithelium
ulcer = full thickness
erosion = partial epithelial loss
What si the difference between an ulcer and an erosion?
trauma, infectious agents, ischemia
What can cause ulceration?
thinning/loss of mucosa; plus or minus crust/exudate
describe the gross apearance of an ulceration
regeneration, fibrosis/scarring, adaptation
What is the ultimate outcome of an ulcer?
fat necrosis
Not a specific pattern of cell death, but a term that denotes focal areas of fat degeneration and death
nutritional, enzymatic, traumatic, idiopathic
what are the 4 causes of fat necrosis?
polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamin E
Nutritional fat necrosis: Diets high in __________________ / low in _____________
pancreatic lipases leaking into the body,
fatty acids, glycerol, soap
Enzymatic fat necrosis is caused by _______________________.
These split triglycerides into _________ and _______.
The first of which can combine with calcium, sodium, and potassium to make _________
blunt trauma or chronic pressure
Traumatic fat necrosis is caused by ________ or _____________
clear, pale eosinophilic, basophilic
normal adipocytes stain ________
Necrotic adipocytes stain ____________ and have _______ mineral soap deposits
true
true/false: whatever stimulates fat necrosis can stimule a robust immune response leading to fat-filled macrophages (and some neutrophils)
saponification
"soap formation"
firm, nodular, yellow/white, granular, soapy/chalky fat
describe fat necrosis grossly
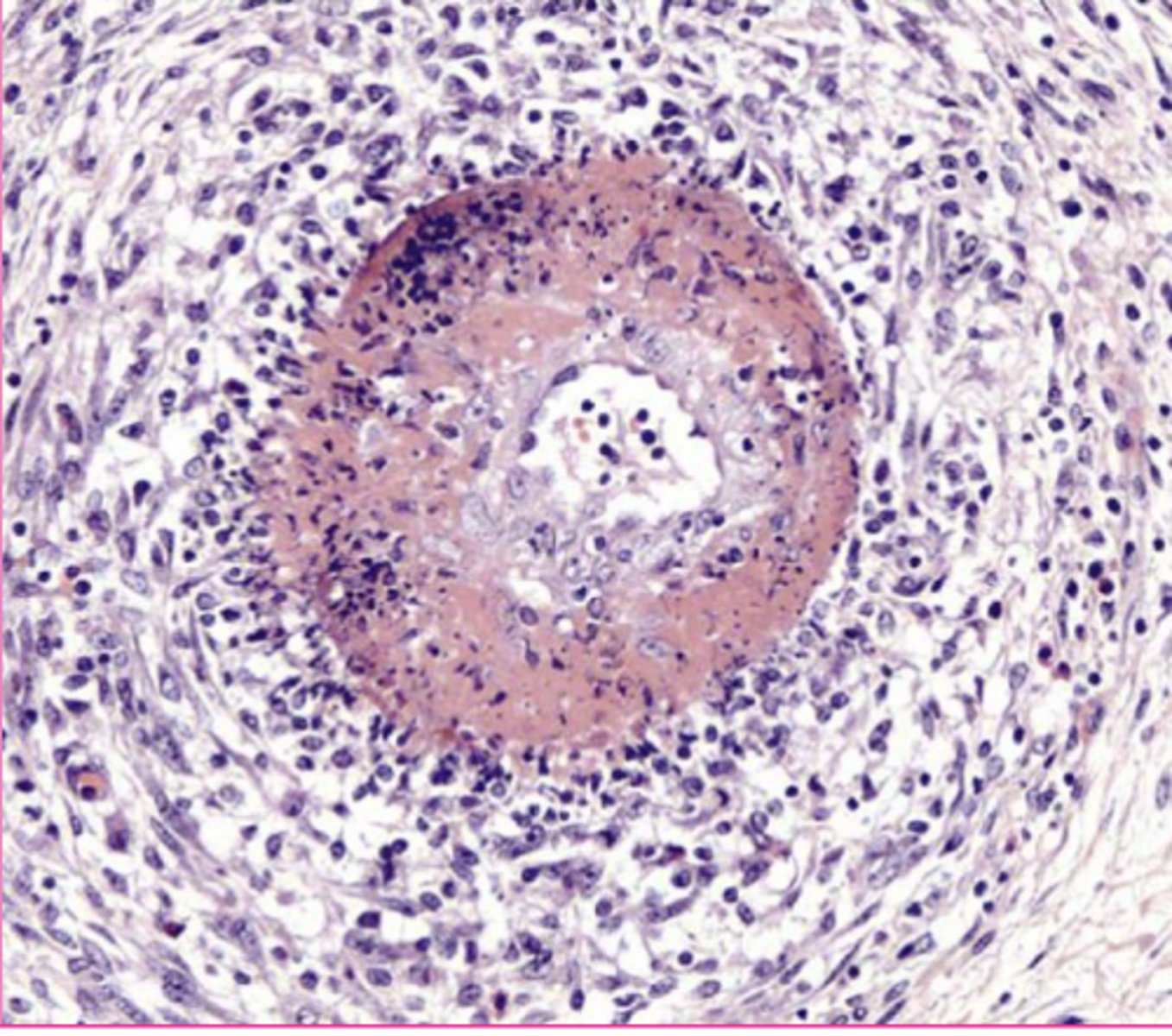
fibrinoid necrosis
Not a specific pattern of cell death, but a term that denotes a
microscopic change seen in blood vessels, where the vessel wall is bright pink, homogenous, and amorphous
Leakage of plasma proteins into the vessel wall
what causes fibrinoid necrosis?
bright pink, homogenous, amorphous
what do the vessel walls look like again? In fibrinoid necrosis...
fibrinoid
What type of necrosis?
true... duh
True/false: the appearance of a necrosis depends on the type of necrosis, tissue involved, cause of cell death and time elapsed
type, location and number of cells affected. Rate at which they are affected
what does the outcome of necrosis depend on?
regeneration, recruitment of inflammatory response (liquefaction, encapsulation, sequestration), replacement by scarring (mineralization), adaptation (hyperplasia, hypertrophy, metaplasia, atrophy)
What are some possible outcomes of necrosis?
4 general things (with specifics in parenthesis)
gangrenous
type of necrosis
caseous
type of necrosis
coagulative (see outline of cells)
Type of necrosis
hepatic coagulative necrosis
give me a morphological diagnosis. Heres a zoomed out pi and a closer view of the lesion
liquefactive
type of necrosis
cerebral liquefactive necrosis OR cerebral abscess
morphological diagnosis?
fat necrosis
type of necrosis?
renal coagulative necrosis
morphological diagnosis