Chapter 22 Cardiovascular Disease
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Explain how atherosclerosis develops
the artery walls become progressively thickened due to an accumulation of fatty deposits, fibrous tissue and smooth muscle cells (collectively known as plaque)
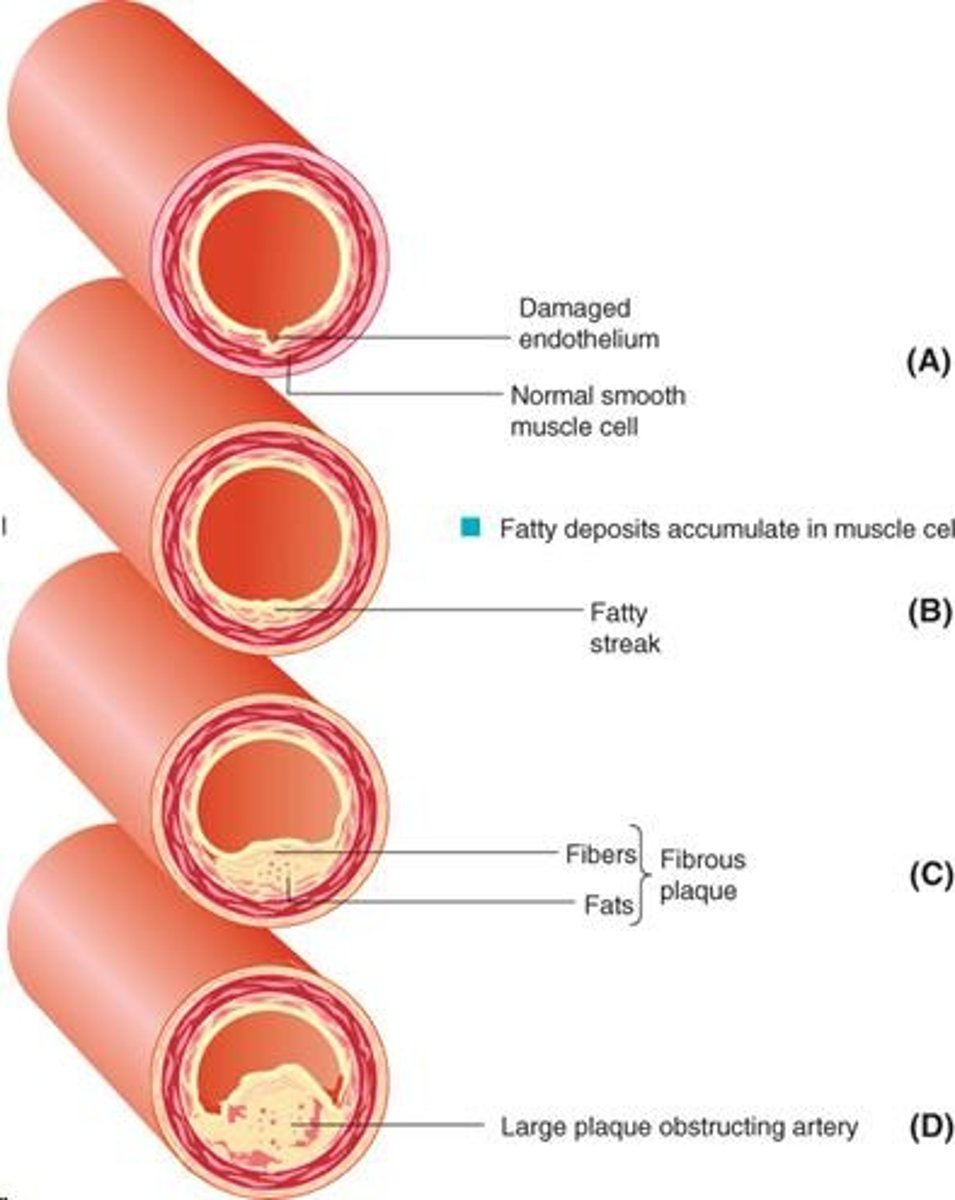
What is atherosclerosis?
a disease of the arteries characterized by the the build up of lipids and fibrous scar tissue on the inner wall of the arteries.
Describe the potential consequences of atherosclerosis
coronary disease (heart attack)
renal disease
cerebral disease (stroke)
peripheral vascular disease (damage to blood circulation in lower limbs)
Discuss the risk factors that contribute to the development of atherosclerosis (hint there are 9)
smoking
high cholesterol
high blood pressure
diabetes
stress
sedentary lifestyle
obesity
aging
Explain an individual's risk for coronary heart disease (CHD)
smoking: toxic chemicals damage endothelial cells (inflammation, vasoconstriction, etc..)
high cholesterol: too much animal fat leads to build up of fat in arteries
high blood pressure: causes stiffening of arteries
diabetes: causes damage to blood vessels
high saturated fat diet: leads to narrowing of blood vessels
stress: stress hormones damage blood vessels
sedentary lifestyle: lack of exercise leads to weakening of muscles
obesity: puts stress on heart
aging: normal wear and tear on heart
which of the atherosclerosis risk factors is the only one that is not modifiable
aging
thrombosis
when build up of plaque breaks off and blocks the blood vessel flow (i.e. blood clot)
Define Cardiovascular Disease
general term for disease of the heart and blood vessels
Discuss appropriate dietary and lifestyle changes for individual with mild to severe hypertriglyceridemia
mild hypertriglyceridemia: controlling body weight,
physical activity, restrict alcohol, limit intake of refined carbohydrates
severe hypertriglyceridemia: same dietary and lifestyle change plus medication
Explain the development of congestive heart failure (CHF)
-Major complication from high blood pressure (aka weak heart)
What is CHF
Hearts inability to pump adequate blood to meet the needs of the body due to prolonged high blood pressure
-heart muscles enlarge and then weakens (aka hypertrophy)
what are the symptoms and treatment for CHF
symptoms: fatigue, shortness of breath, and leg swelling
treatment: low sodium diet (this lowers blood volume which cause less strain on heart)
True or False ? Hypertrophy of the heart muscle is reversable.
False
Describe nutrition therapy for clients with CHF
-treatment of underlying diseases (high blood pressure, diabetes, or atherosclerosis)
-nutrition therapy include sodium, fluid, and alcohol restrictions and nutrient supplementation
Describe blood pressure measurements
systolic blood pressure measure ventricular systole (contraction)
diastolic blood pressure measures ventricular diastole (relaxation)
normal= 120/80
Identify the factors that influence blood pressure
-cardiac output and peripheral resistance influence blood pressure
-and heart rate (HR) and stroke volume (SV) can influence cardiac output (CO)
CO = HR * SV
Identify the risk factors for hypertension
Aging
Genetic Factors
Obesity
Salt Sensitivity
Alcohol
Dietary Factors
Discuss the DASH eating plan for hypertensive clients
adopt a diet that emphasizes vegetables, fruits, and whole grains; includes low fat milk products; and limits sugars and red meats
Describe medical treatment options for clients with hypertension
common medications used to treat hypertension include:
-diuretics
-calcium channel blockers
-ACE inhibitors
-angiotensin-receptor blockers
Name the different forms of stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke:
-blood vessels burst
-blood leaks into brain tissue
Ischemic stroke:
-plaque forms thrombosis and gets lodged in blood vessel of brain
-blood clot stop blood supply to are of the brain
(tissue dies)
Discuss risk factors for stroke
risk factors:
-pre-existing conditions like hypertension, diabetes, cholesterol
-high LDL levels
-smoking
Define metabolic syndrome and discuss the medical significance of this disorder
a cluster of interrelated disorders, including abnormal obesity, insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and abnormal blood lipids
Describe dietary and lifestyle changes for an individual with metabolic syndrome
-weight loss
-reduce intake of added sugars and refined grains
-increase servings of whole grains and high-fiber foods
Ischemia in the coronary arteries is a frequent cause of:
A. Angina pectoris
B. Hemorrhagic stroke
C. aneurysm
D. hypertension
A. Angina pectoris
Risk factors for atherosclerosis include all of the following except:
A. smoking
B. hypertension
C. diabetes mellitus
D. elevated HDL cholesterol
D. elevated HDL cholesterol
Which clinical test can help to diagnose peripheral artery disease?
A. Lipoprotein profile
B. Coronary artery calcium score
C. Ankle brachial
D. C reactive protein levels
C. Ankle brachial
Dietary lipids with the strongest LDL cholesterol raising effects are:
A. monounsaturated fats
B. polyunsaturated fats
C. saturated fats
D. plants sterols
C. saturated fats
Moderate alcohol consumption can improve heart disease risk, in part, because it:
A. lowers blood pressure
B. increases HDL cholesterol levels
C. offset the damage from smoking
D. improves nutrition status
B. increases HDL cholesterol levels
Patients with hypertriglyceridemia may improve their triglyceride levels by:
A. reducing sodium intake
B. reducing cholesterol intake
C. consuming moderate amounts of alcohol
D. limiting intakes of refined carbohydrates
D. limiting intakes of refined carbohydrates
Which medications reduce cholesterol synthesis in the liver?
A. Bile acid sequestrants
B. Statins
C. ACE inhibitors
C. Fibrates
B. Statins
Hemorrhagic stroke:
A. is the most common type of stroke
B. results from obstructed blood flow within brain tissue
C. comes on suddenly and usually lasts for up to 30 minutes
D. results from bleeding within the brain, which damages brain tissue
D. results from bleeding within the brain, which damages brain tissue
Hypertensive patients can benefit from all of the following dietary and lifestyle modifications except:
A. including fat free or low fat milk products in the diet
B. reducing total fat intake
C. consuming generous amounts of fruit, veggies, legumes and nuts
D. reducing sodium intake
B. reducing total fat intake
Nutrition therapy for a patient with heart failure usually includes:
A. weight loss
B. reducing total fat intake
C. sodium restriction
D. cholestrol restriction
C. sodium restriction