Lecture 2 - Molecules and Bonds
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
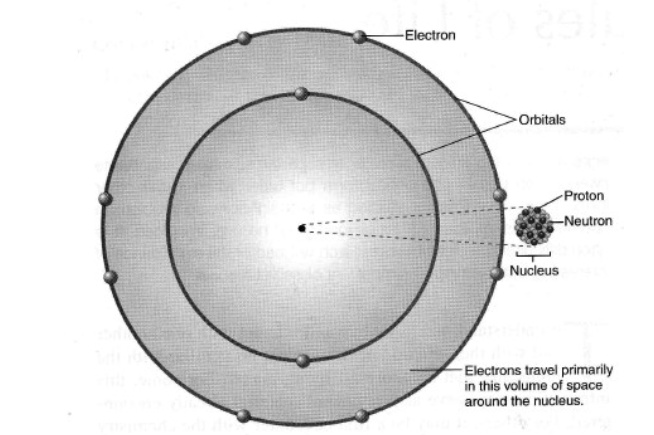
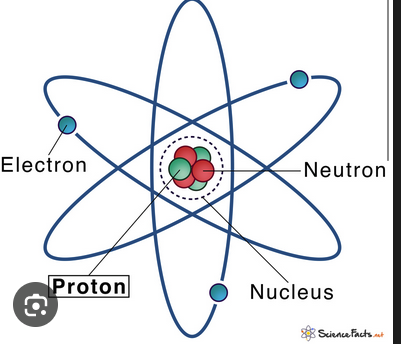
Proton
A subatomic particle with positive charge found in the nucleus.
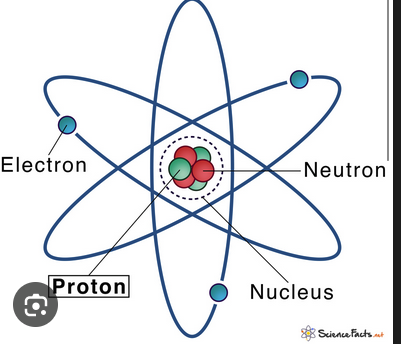
Neutron
A subatomic particle with neutral charge found in the nucleus.
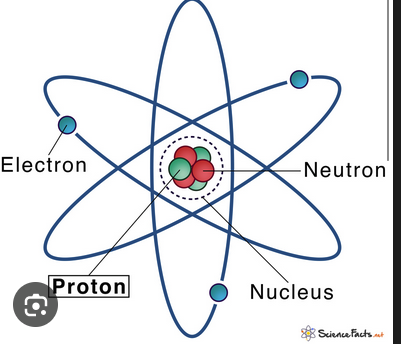
Electron
A subatomic particle with negative charge that orbits the nucleus in orbitals.
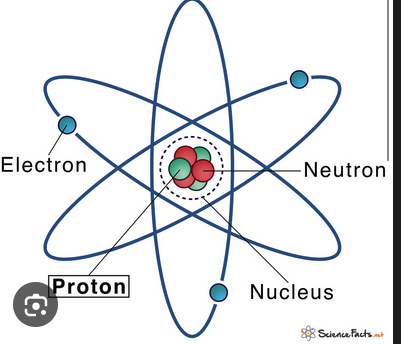
Nucleus
The central core of an atom containing protons and neutrons.
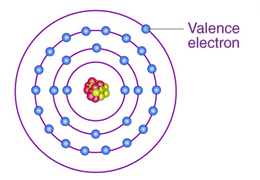
Valence electrons
The electrons in the outermost orbital that participate in chemical bond formation.
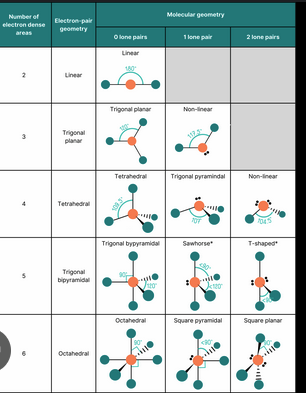
VSEPR
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory describing how electron pairs arrange in three-dimensional space.
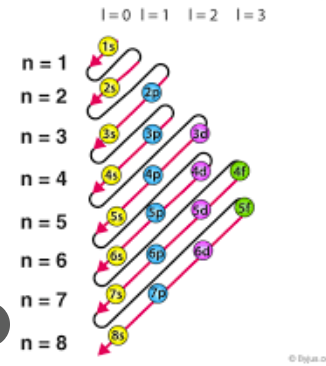
Orbitals
Regions of space around the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found, each with different energy levels.
Covalent bond
A strong bond formed by shared electrons between two atoms.
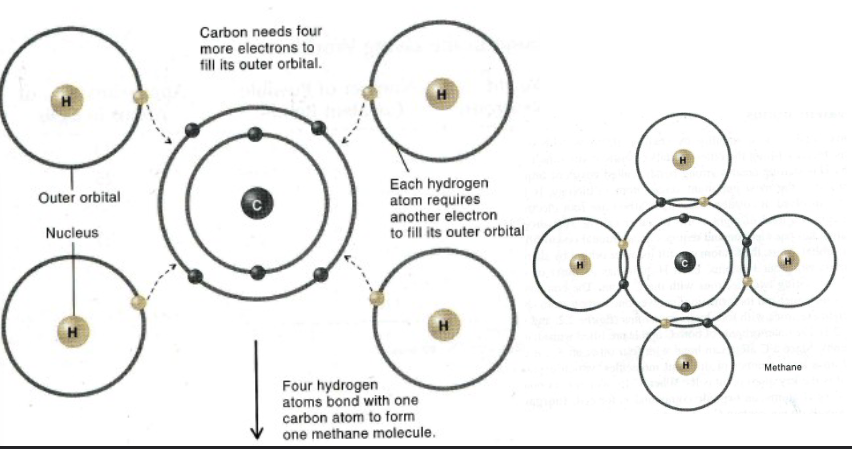
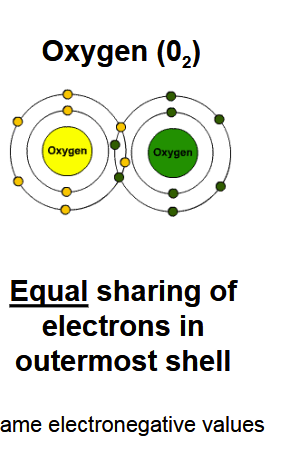
Nonpolar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally between atoms with similar electronegativity values.
Polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are shared unequally between atoms with different electronegativity values, creating partial charges.
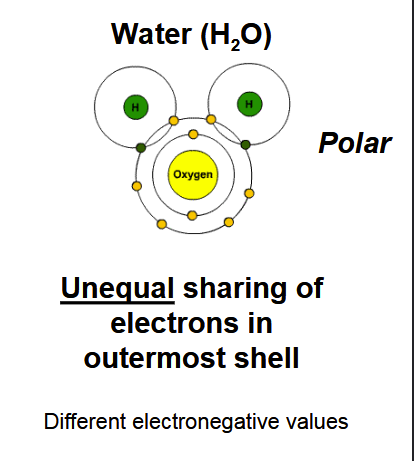
Electronegativity
The attraction of an atom for its electrons, unique to each element.
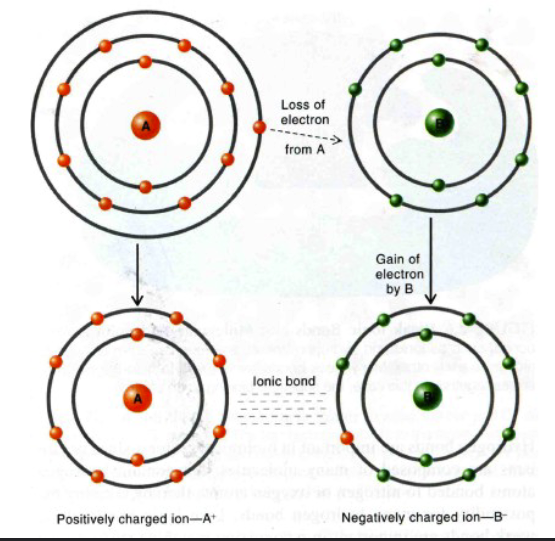
Ionic bond
A weak bond formed between oppositely charged ions through electrostatic attraction.
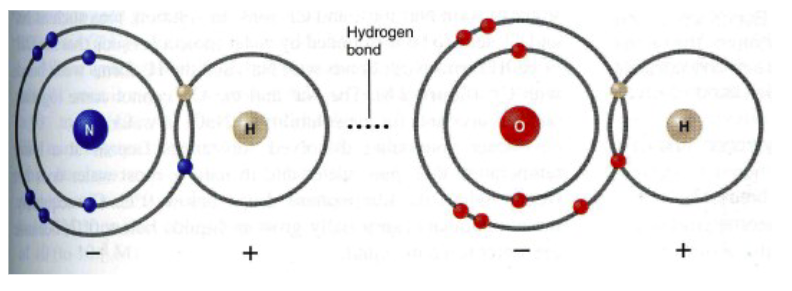
Hydrogen bond
A weak electrostatic interaction between a lone pair of electrons on an electronegative atom (acceptor) and a hydrogen (donor) bonded covalently to another strongly electronegative atom.
H with N or O, NEVER H with C
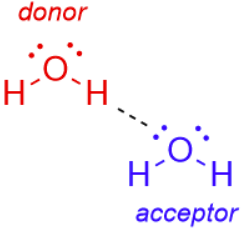
hydrogen bond donor
A strongly electronegative atom (nitrogen or oxygen) covalently bonded to hydrogen that participates in hydrogen bonding.
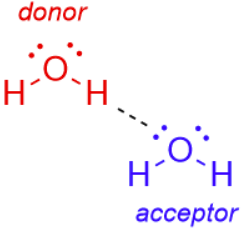
hydrogen bond acceptor
An electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons that accepts a hydrogen bond.
van der Waals interaction
A weak intermolecular force resulting from induced dipoles when atoms or molecules come within 5 nanometers of each other.
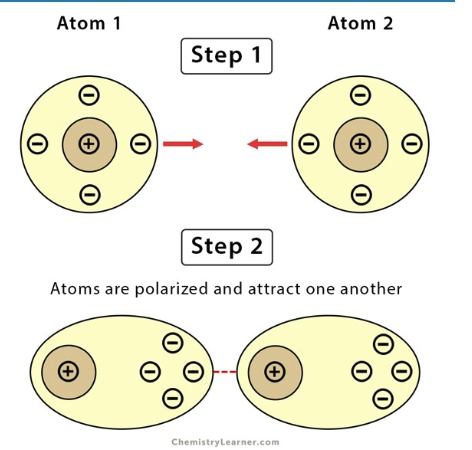
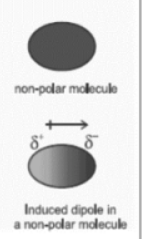
induced dipole
A temporary separation of charge in an atom or molecule caused by a nearby charged particle.
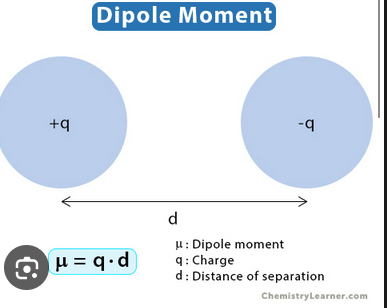
Dipole moment
The measure of separation of positive and negative charge in a molecule.
Cohesion
The tendency of molecules to stick together via hydrogen bonds.
Heat capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a substance, high in water due to hydrogen bonding.
Water of hydration
water that is chemically combined with a substance to form a hydrate and can be expelled by heating
hydrophobic effect
The tendency of nonpolar molecules to aggregate and exclude water by forcing water to form hydrogen bonds with itself around the nonpolar material.
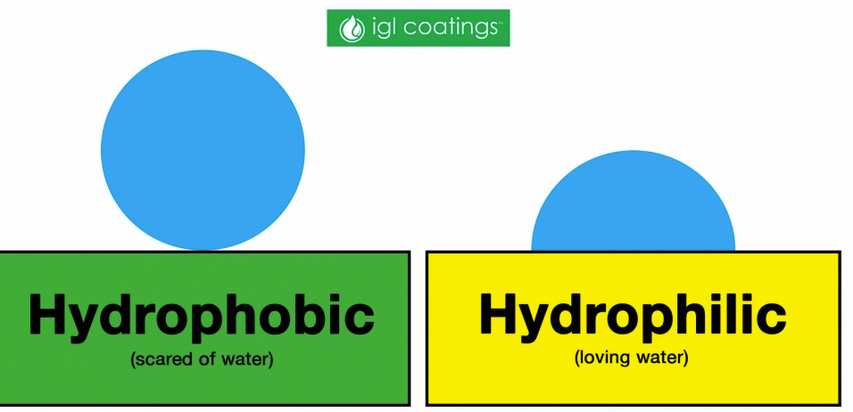
amphipathic
Having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties, as in molecules with a nonpolar tail and polar head group.
micelle
A spherical structure formed by amphipathic molecules with hydrophobic ends pointing inward and hydrophilic ends pointing outward in water.
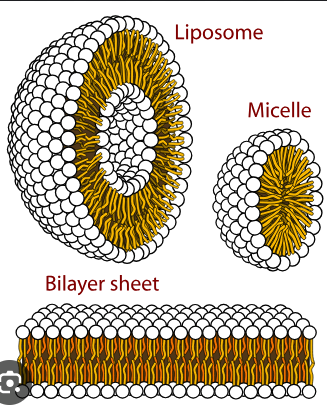
membrane
A structure composed of a phospholipid bilayer and proteins that encloses the cell.
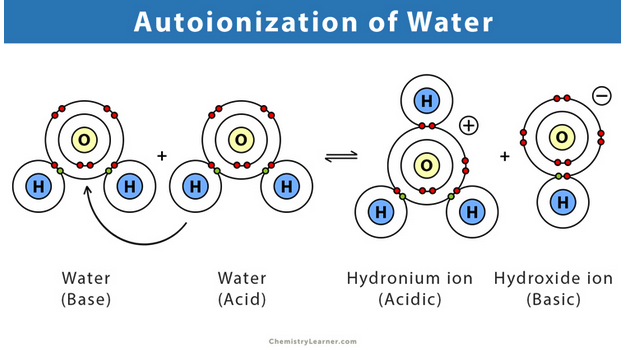
autohydration
The self-ionization of water forming hydronium ion and hydroxide ion.
pH
The negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration that measures acidity or basicity.
pOH
The negative logarithm of hydroxide ion concentration related to pH by pH + pOH = 14.
acid
A chemical that donates hydrogen ions to a solution, lowering pH.
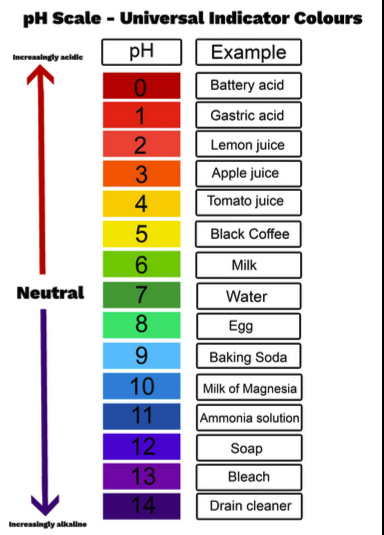
base
A chemical that donates hydroxide ions to a solution, raising pH.
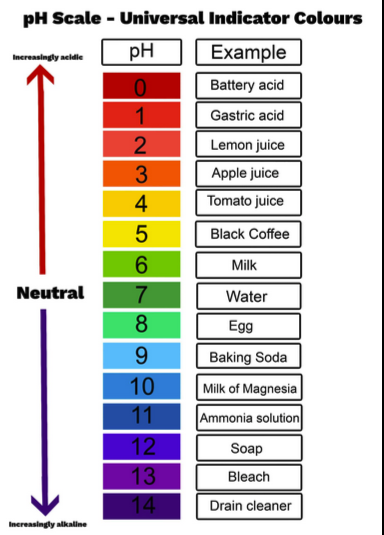
neutral
A solution with pH 7 where hydrogen ion concentration equals hydroxide ion concentration.
Aufbau principle
The principle that electrons fill lower energy orbitals first when building up the electronic configuration of an atom.