Biochem Exam Three Clinical Applications
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
cardiac diet
low sodium, low saturated fat.
who is the cardiac diet used for
heart failure and post-myocardial, hypertensive patients
renal diet
restricted in sodium, potassium, phosphorus. protein may be restricted pre-dialysis or increase during dialysis
consistent carbohydrate diet
consistent amount of carbohydrates at each meal
who is the consistent carbohydrate diet used for
diabetic patients to manage blood glucose
dysphagia diet
texture-modified from pureed to mechanically soft, with thickened liquids to prevent aspiration
who is the dysphagia diet for
patients with difficulty swallowing as determined by a Speech-Language Pathologist
Enteral Nutrition
“tube feeding” delivered into the stomach or small intestines. maintains gut integrity, is safer, and less expensive
Parenteral Nutrition
delivered directly into the blood stream. last resort when the GI tract is non-functional
Obese patients Energy Shortcut: 30-50 BMI
11-14 kcal/kg
Obese patients Energy Shortcut: BMI>50
22-25 kcal/kg
Average Adult (Maintenance) Protein Needs
0.8 g/kg/day
Minor Stress/Post-operative Protein Needs
1.0 -1.2 g/kg/day
Moderate to Severe Stress (sepsis, trauma) Protein Needs
1.2 - 2.0 g/kg/day
severe burns or multi-trauma Protein Needs
up to 2.5 g/kg/day
obese patients (critically ill): BMI 30-40
2.0 g/kg
obese patients (critically ill): BMI > 40
up to 2.5 g/kg
net equation of CAC
acetyl-CoA + 3NAD + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H2O → 2CO2 + 3NADH + FADH2 + GTP + CoA + 3H
put together the steps of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex rxn.
1) decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetaldehyde 2) reoxidation of the dithiol lipoamide cofactor 3) formation of acetyl CoA by thioester exchange 4) regeneration of the oxidized FAD cofactor 5) oxidation of aldehyde to a lipoyl thioester
1) 5) 3) 2) 4)
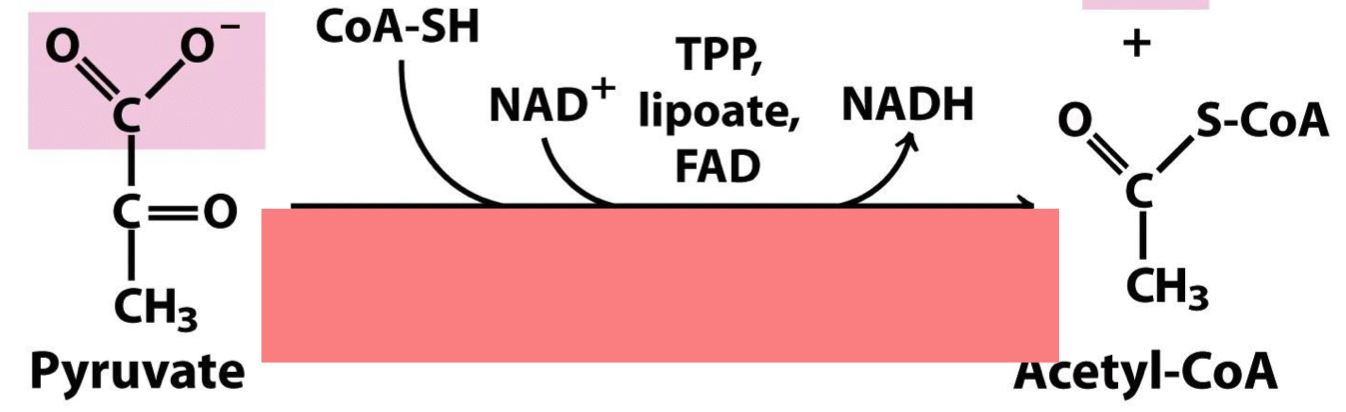
what enzyme converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (E1+E2+E3)
Respiration Stage 1:
Acetyl-CoA produced from glycolysis and generates ATP, NADH, FADH2
Respiration Stage 2:
Acetyl-CoA is oxidized by 2CO2 by the CAC. this generates more NADH, FADH2 for ATP production and one GTP
Respiration Stage 3:
Electrons from NADH and FADH2 used to reduce O2 to H2O. creates proton gradient that is used to make ATP from ADP and Pi by the enzyme ATP synthase. 15 molecules of ATP are produced per molecule of pyruvate
overall equation for glycolysis
glucose + 2NAD + 2ADP + 2Pi → 2 pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H2O
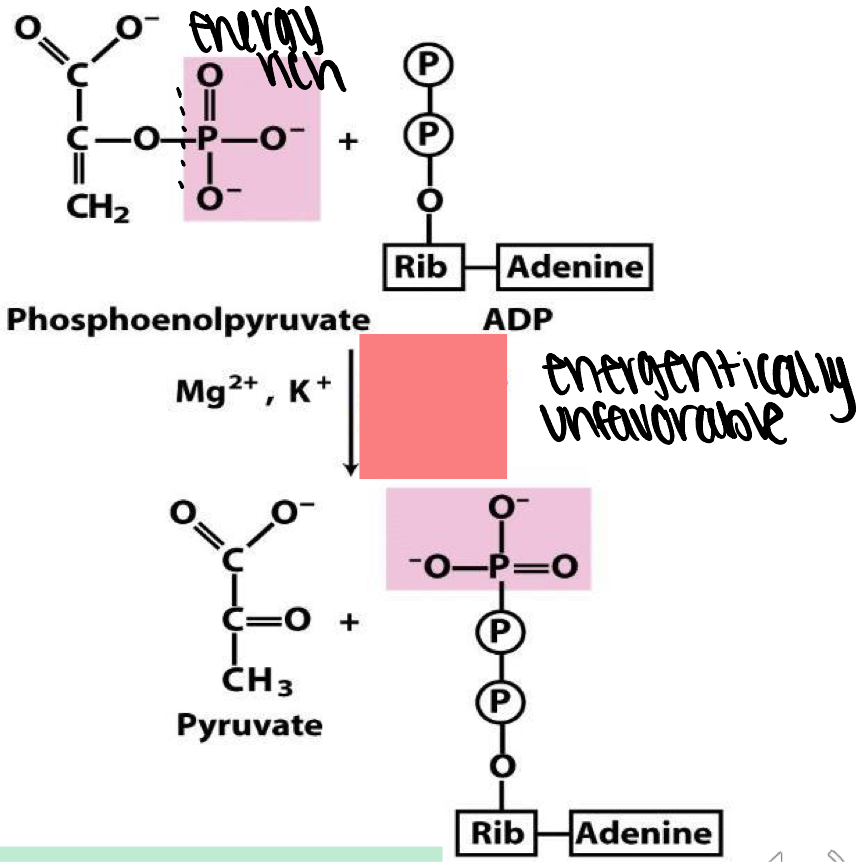
what enzyme catalyzes if energy rich phosphate from PEP to ADP to make ATP
pyruvate phosphate
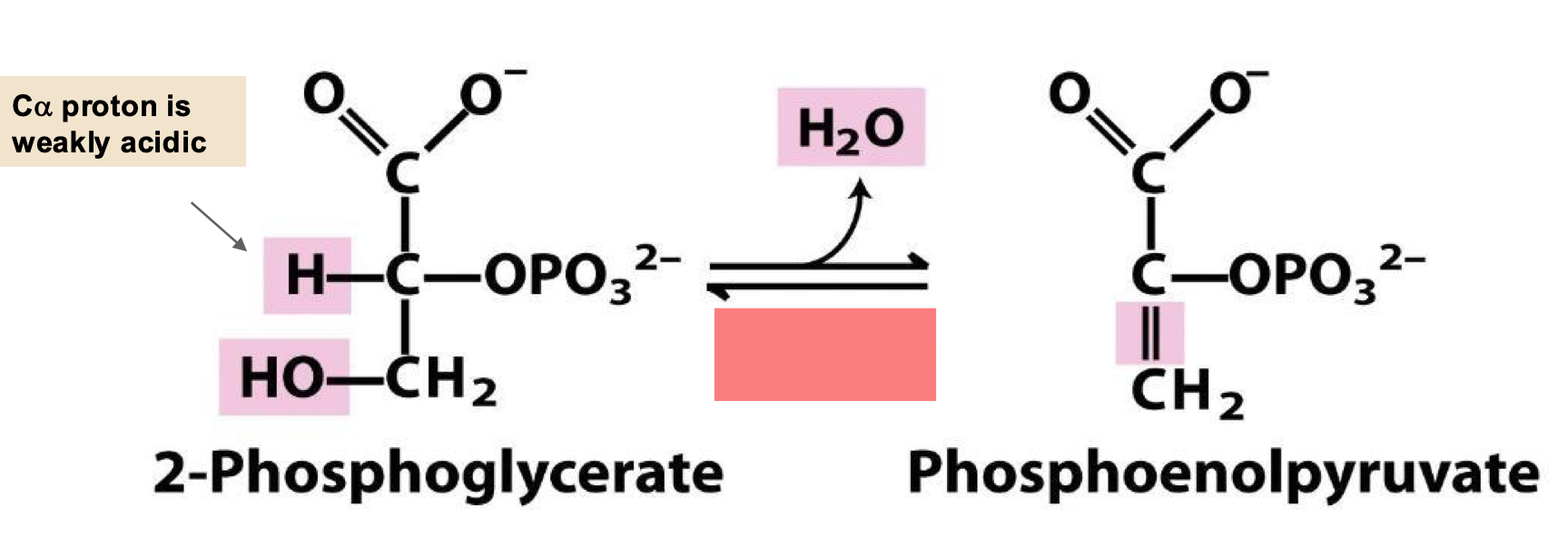
eliminate water from PEP
enolase
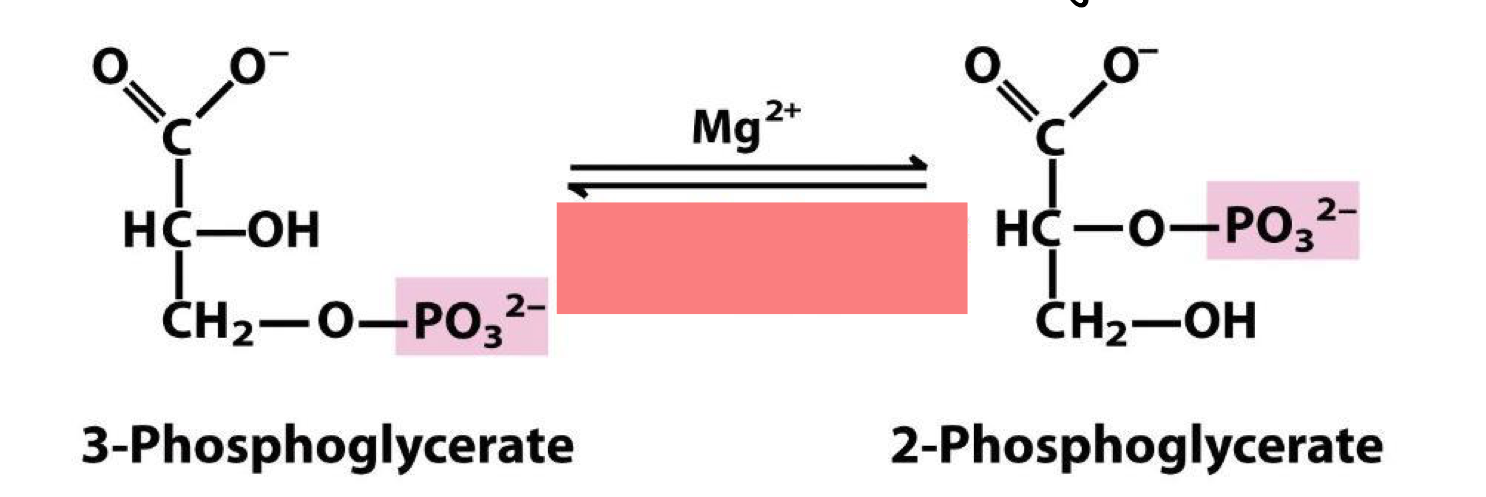
sets stage for phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) formation by rearranging the position of the phosphate so that elimination can give enol phosphate
phosphoglycerate mutase
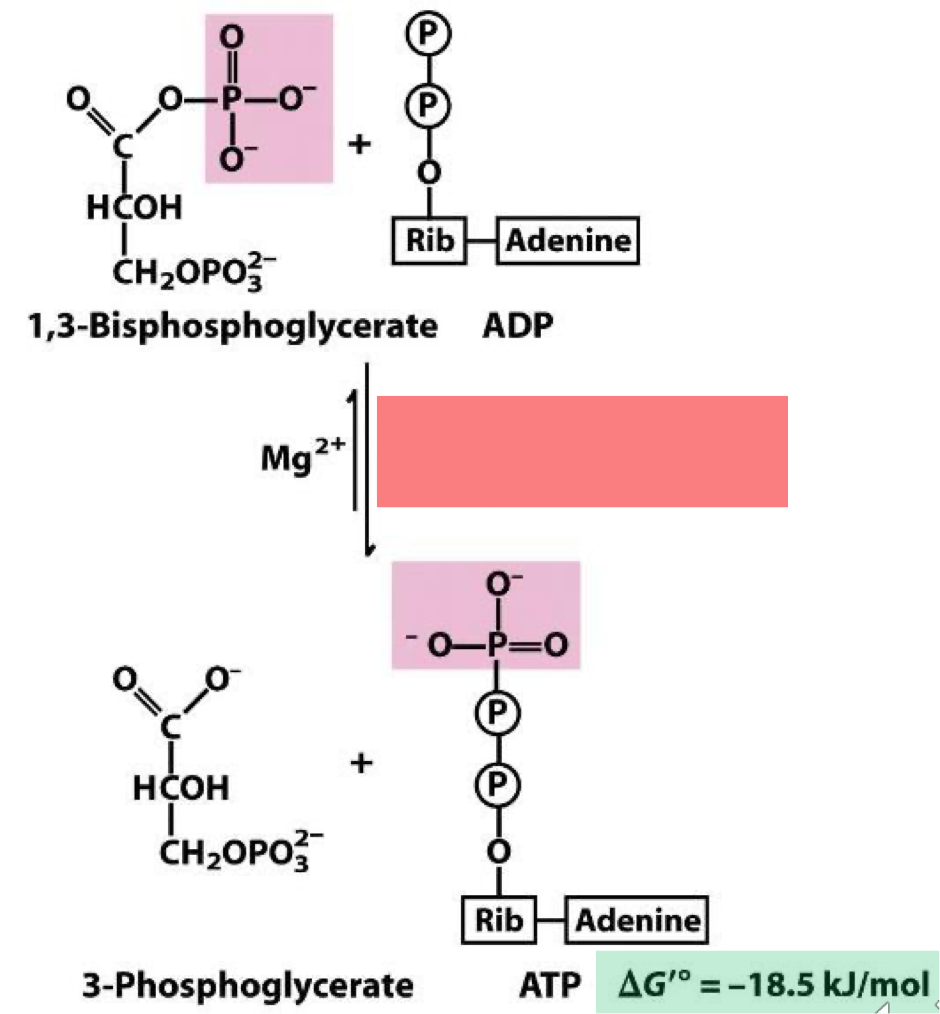
acyl phosphate of 1,3 - bisphosphoglycerate is energy rich enough to enable thermodynamically favorable synthesis of ATP. named for the reverse reaction the energetically unfavorable phosphorylation of the carboxylate of glycerate.
phosphoglycerate kinase
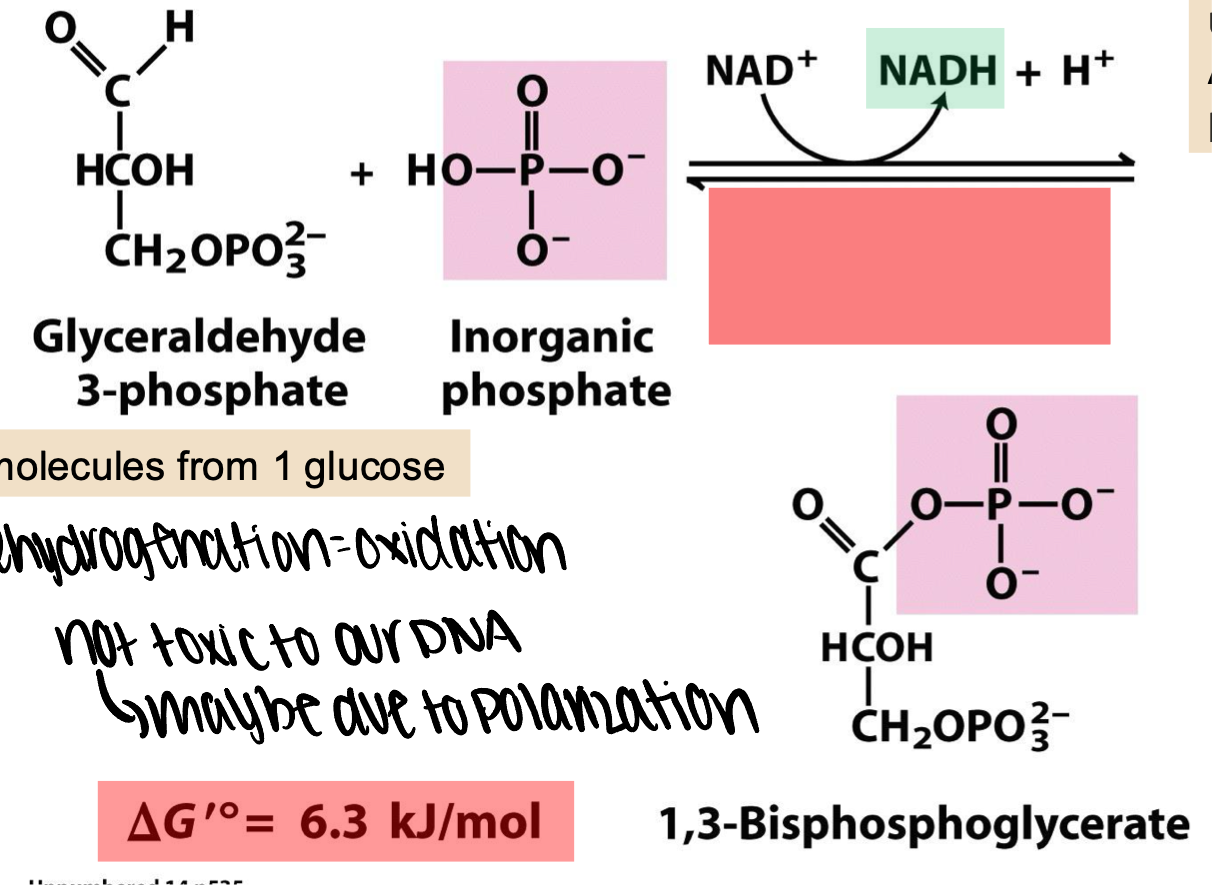
this energy creates an energy rich acyl phosphate from inorganic phosphate
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenasw
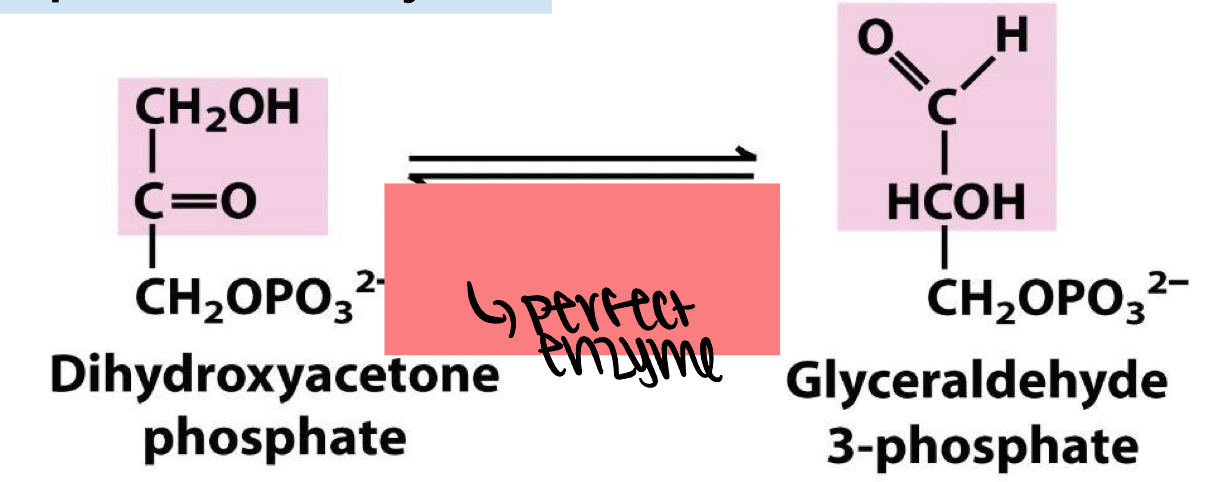
perfect enzyme.
triose phosphate isomerase (TIM)
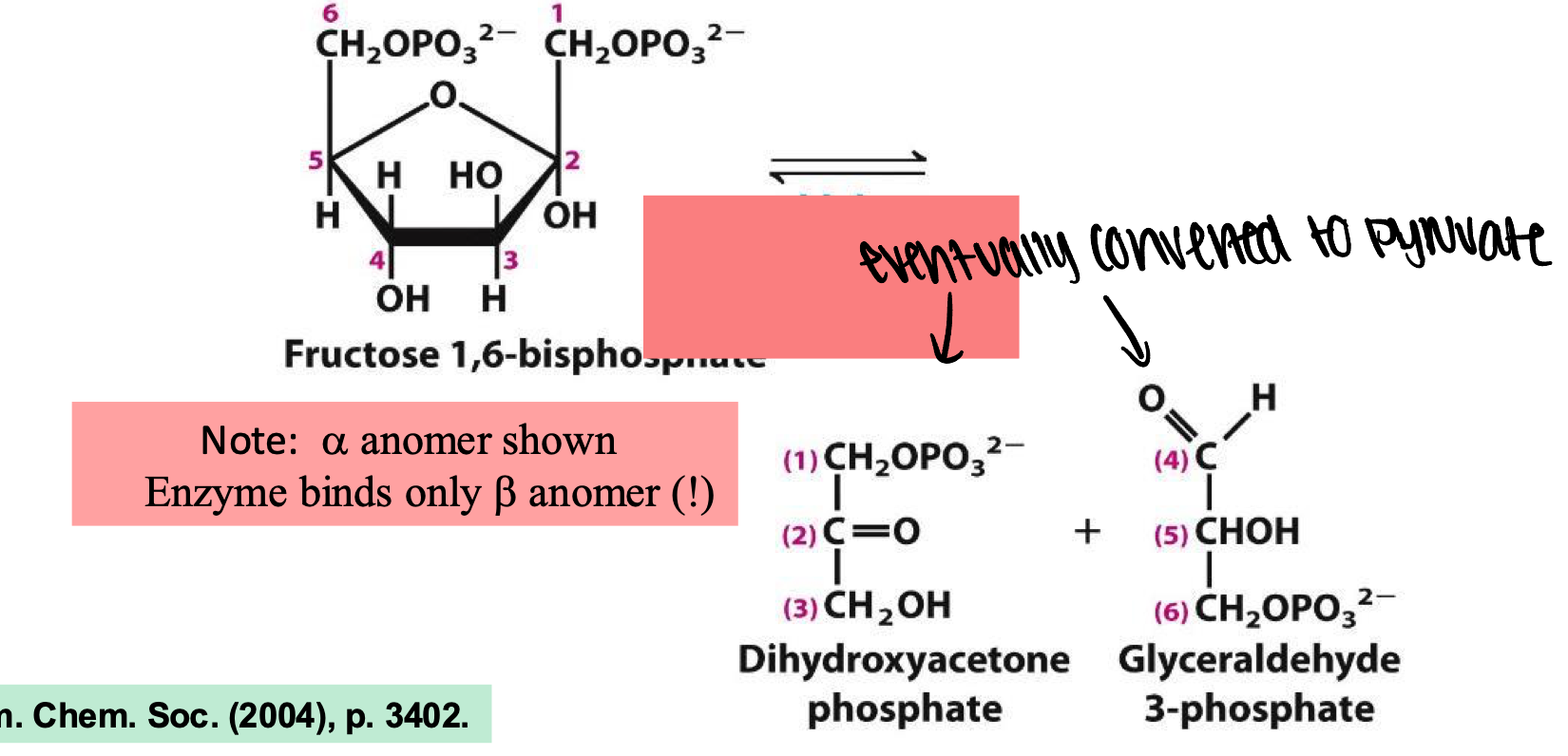
enzyme catalyzes the reversible cleavage of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into two three carbon sugars
aldolase
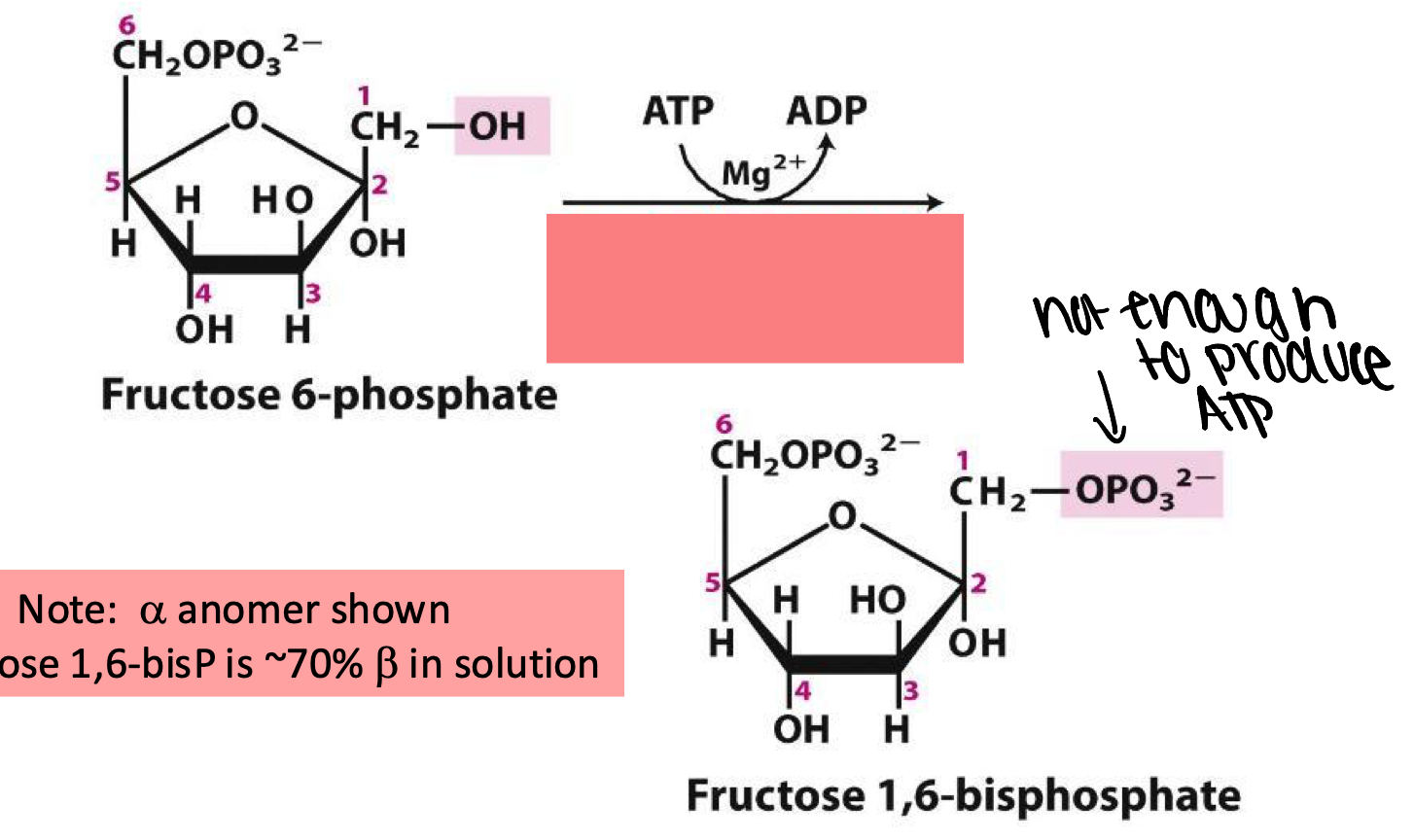
enzyme catalyzes the first committed step in the glycolytic pathway
phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
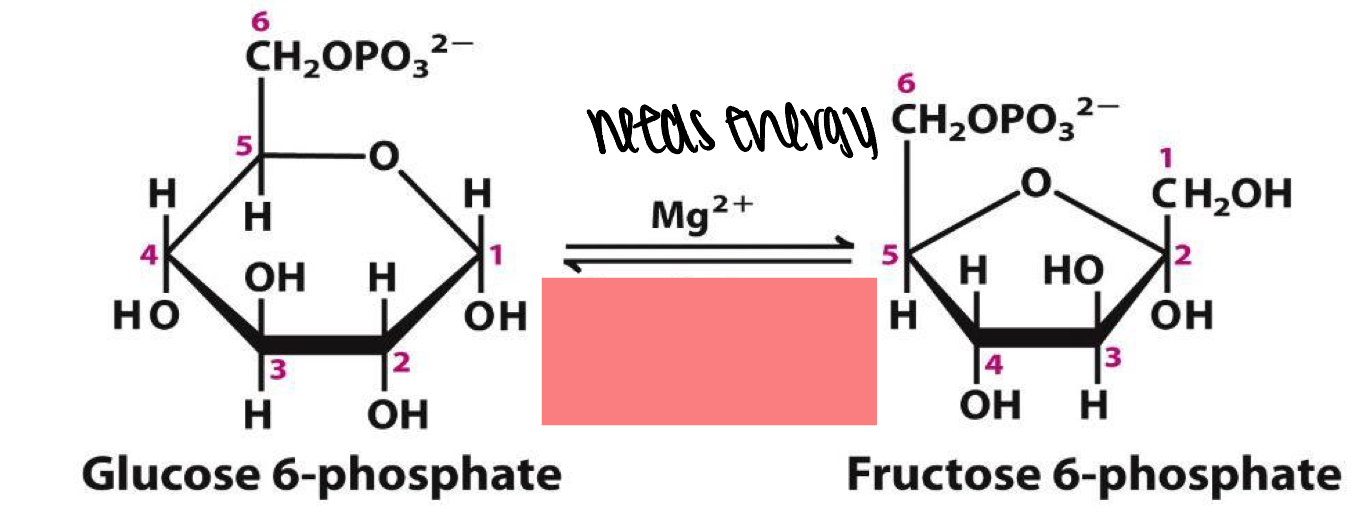
interconverts glucose-6-P and fructase-6-P in a reaction that is nearly energy neutral although the furanose is less stable than the pyranose
phosphohexose isomerase
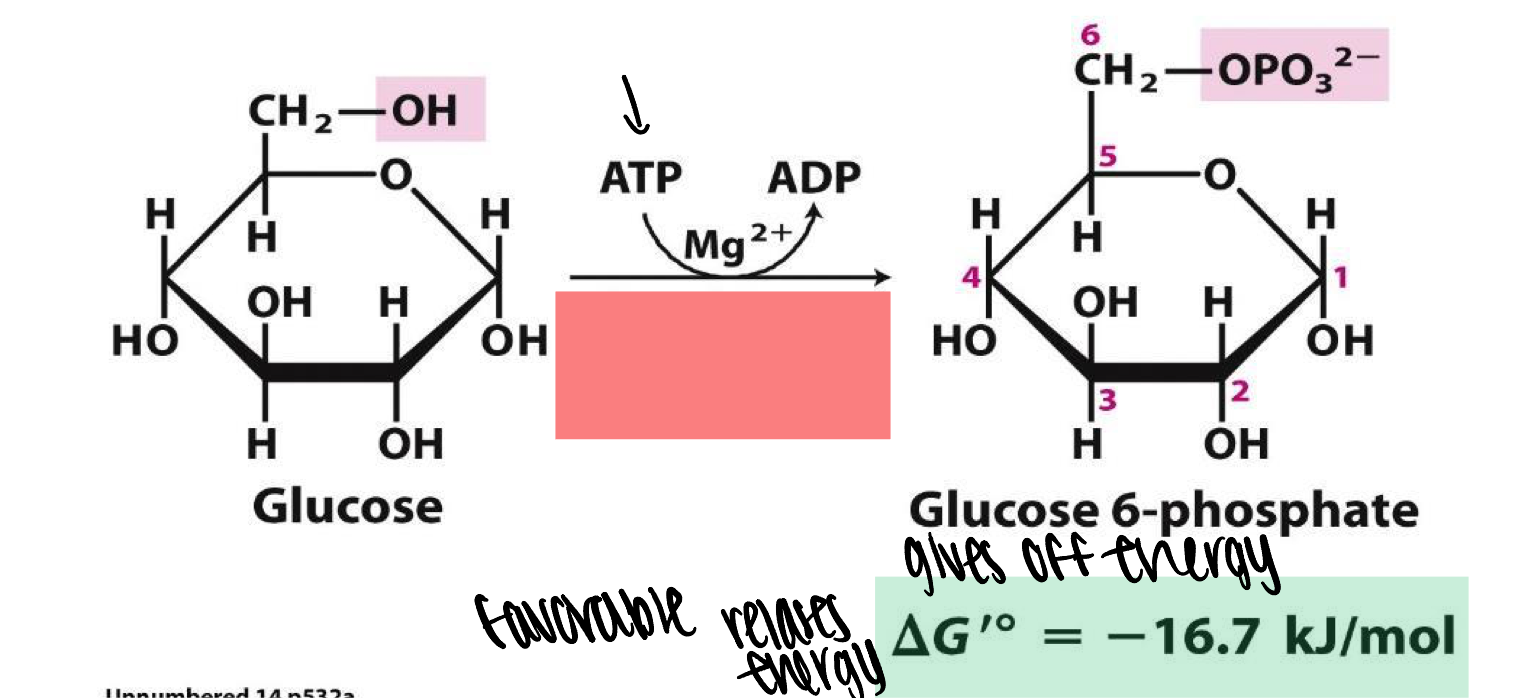
enzyme catalyzes the first step of glycolysis by selectively phosphorlylating glucose at the 6-position using ATP as energetically favorable phosphate donor
hexokinase
what are the products from pyruvate
2 ethanol + 2CO2 + 2acetyl-CoA* + 2 lactate (from 2acetyl-CoA you can also make 4CO2 + 4H2O)
phase I of glycolysis
preparatory phase that consumes 2 ATP
order the steps of Phase I glycolysis: 1) isomerization to furanose fructose 2)cleavage of the furancose to give two interconverting 3-carbon sugars 3) glucose phosphorylation 4) phosphorylation to give a biphosphate
3) 1) 4) 2)
phase II of glycolysis
Payoff phase - produces energy (+4ATP, +2NADH)
order the step of Phase II glycolysis: 1) interconversion of G-3-P and DHAP to give two molecules G-3-P 2) transfer of enol phosphate to ADP to give 2nd ATP 3) oxidation of G-3-P aldehyde to acid with conversion to acyl phosphate and NADH 4) transfer of high energy acyl phosphate to ADP to give first ATP 5) elimination of water to give high energy enol phosphate 6) rearrangement of phosphate to set up elimination
1) 3) 4) 6) 5) 2)
T/F glycolysis was likely developed before photosynthesis, when the atmosphere was still anaerobic
true
which enzymes of glycolysis phase I are in order
hexokinase, phosphohexose isomerase, phosphofructosekinase-1, aldolase, triose phosphate isomerase
which enzymes of glycolysis phase II are in order
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerate kinase, phosphoglycerate mutase, enolase, pyruvate kinase
type 1 diabetes stage 1
multiple autoantibodies, blood glucose normal, no symptoms
type 1 diabetes stage 2
autoantibodies present (usually multiple), blood glucose abnormal (dysglycemia), no symptoms
type 1 diabetes stage 3
autoantibodies present, blood glucose elevated (hyperglycemia), often symptomatic
Hyperglycemia drivers: T1DM & T2DM
pancreatic insufficiency/eleven “defects”
what does insulin NOT inhibit
glycogenesis(liver)
sulfonylureas & meglitinides
increase pancreatic insulin secretion
sulfonylureas
decrease blood glucose overall
meglitinides
decrease blood glucose after meals
metformin
decreases hepatic gluconeogenesis
increases insulin sensitivity
decrease blood glucose, especially in the morning
heart protection (long-term)
thiazolidinediones (glitzones, TZDs)
PPAR-y activation → improved lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity
decreases blood glucose overall
secondary ASCVD (heart attack/stroke) prevention
alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs) MOA
reversible inhibition of intestinal alpha-glucosidase
alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs) Outcomes
delays breakdown of complex carbohydrates → slows glucose adsorption
elevated postprandial glucose (to prevent high glucose blood peaks after meals)
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors MOA
inhibits enzyme to increase serum concentrations of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors outcomes
increased insulin release from pancreas beta cells
lowers glucagon secretion from the pancreas alpha cells → reduces liver glucose production
overall reduced fasting & postprandial blood glucose concentrations ; glucose dependent
decreases blood glucose, especially after meals
sodium-glucose transport 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i)
reduce kidney glucose reabsorption into blood
decrease kidney damage from diabetes
protect heart, brain, blood vessels
decreases blood glucose
kidney protection: elevated ACR, decreased eGFR
secondary ASCVD prevention, high risk of primary ASCVD
glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA, GLP1RA) MOA
mimics actions: 1) spur insulin production after a meal but only when blood glucose is elevated 2) suppress inappropriately elevated postprandial glucagon levels 3) promotes satiety & reduces food intake 4) slows gastric emptying 5) and more
glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA, GLP1RA) Outcomes
lower blood glucose overall and especially after meals
kidney protection: elevated AC, decreased eGFR
secondary ASCVD prevention, high risk of primary ASCVD
weight loss
leptin
hormone regulating long-term hypothalamic control of appetite secreted in adipose tissues
what is the best diet for weight loss
no single best diet
which system level intervention is NOT included on the slides: increase access to healthy foods, improve infrastructure for physical activity, encourage workplace and instituitional changes, reduce access to low-nutrient, high calorie foods, set SMART goals, decrease barriers to access to healthcare, enhance community support
set SMART goals
why do GLP-1s help with obesity
target underlying hormonal dysregulation
phentermine/topiramate (Qsymia)
increases norepinephrine→suppresses hunger signals / enhances GABA and inhibits excitatory pathways→reduces appetite and cravings
why does phentermine/topiramate (Qsymia) help with obesity
influence neurotransmitters
bupropion/naltrexone (Contrave)
increases dopamine and norepinephrine→decreases appetite / synergistically when combined with bupropion to dampen the “reward response”→reduces cravings
why does bupropion/naltrexone (Contrave) help with obesity
influences neurotransmitters
alli/xenical (orlistat)
inhibits pancreatic and gastric lipase→reduces breakdown and absorption of dietary fats
unabsorbed fat is excreted instead of stored
why does alli/xenical (orlistat) help with obesity
targets energy intake by directly reducing caloric intake by blocking fat digestion. deters individuals from eating high-fat foods because of the side effects
imcivree (setmelanotide)
MC4R agonist→reduces appetite and increase energy expenditure in individuals with rare genetic conditions that impact the MC4R pathway
why does imcivree help with obesity
addresses the genetic disruption that leads to obesity and increases energy expenditure
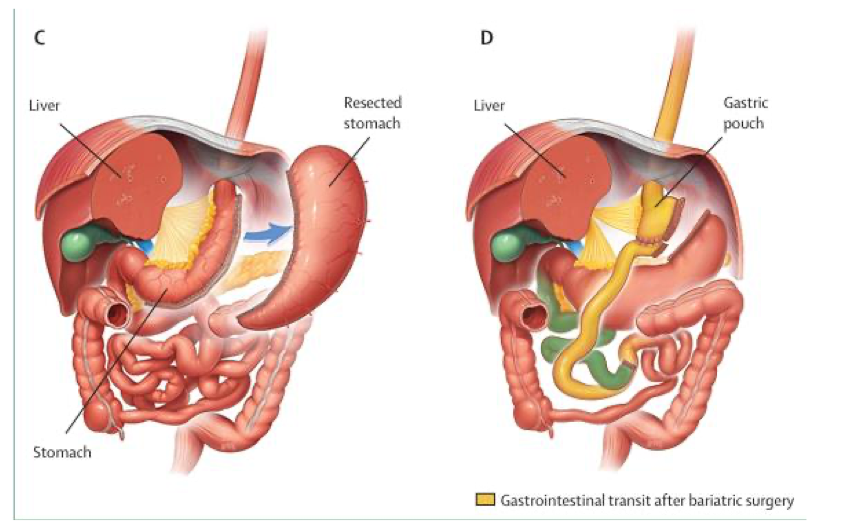
restrictive endoscopic bariatric options
reduce gastric volume to delay gastric emptying by endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty or intragastric ballon
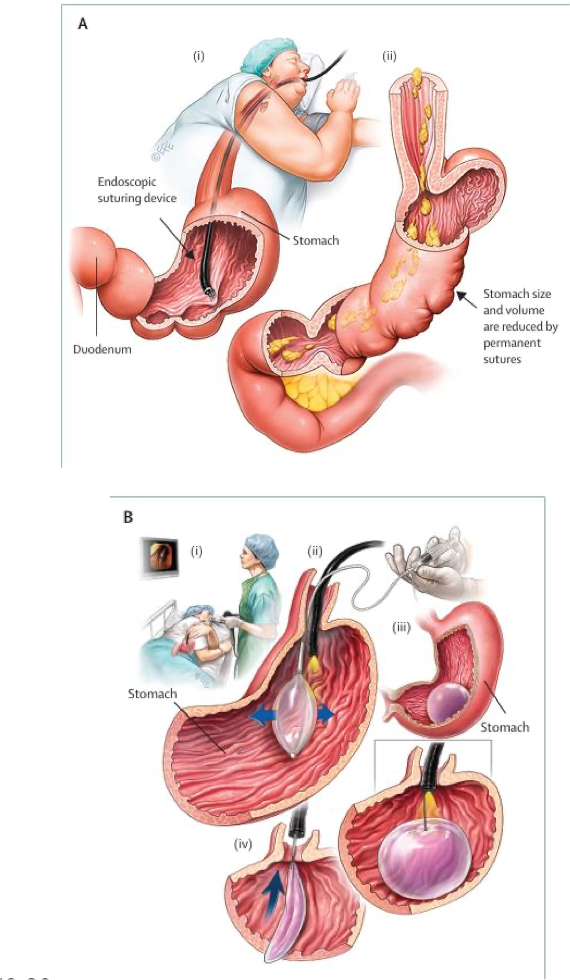
metabolic bariatric surgery options
reduces calorie and nutrient absorption by altering digestive tract by laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (restrictive) or roux-en Y gastric bypass (restrictive and malabsorptive)
which of the following environmental factors contributes most directly to obesity
increased availability of high-calories, ultra-processed foods