RADT 142 - Week 9: Electromagnetism & Magnetism
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Who invented the first battery and what was it called?
Alessandro Volta
Voltaic Pile: layers of metal & zinc. When wires were attached, a current would be induced.

Who discovered that electric current produces a magnetic field?
Hans Christian Oersted
What happens to a compass when there is no electric current in a nearby wire?
The compass needle points north, responding only to Earth's magnetic field.
What happens when an electric current flows through a wire near a compass?
The wire produces its own magnetic field, causing the compass needle to move or change direction.
What is electromagnetic induction?
Production of an electric current
What did Michael Faraday discover?
That current is induced by a moving magnetic field
What is Faraday's Law of Magnetism?
A changing magnetic field induces an electric current (or electromotive force) in a nearby conductor
What are the four things that influence the magnitude of the current?
1. Strength of the magnet: If the magnetic field is stronger the current produced is stronger. (I=amperage)
2. Speed of motion: The speed of wire being moved through the magnet influences the current - The faster the speed of the wire rotating, the more current is induced.
3. Direction of motion: Depending on how the wire moves through the magnetic field, it's going to determine its intensity
- The induced current is strongest when the wire moves perpendicular (at 90°) to the magnetic field.
- The induced current is weakest (or zero) when the wire moves parallel to the magnetic field.
4. Shape of conductor:
- Straight wire: Some current
- Medium Coil (loops/turns): More current
- Lots of Coil: More current
***More turns = more loops = more current***
What is the right thumb rule when it comes to the magnetic field produced by Intensity?
Electric current flows from the positive side to the negative side.
When you point your right thumb in the direction of this current (from positive to negative), the way your fingers naturally curl shows the direction of the magnetic field around the wire.

What is a solenoid and helix?
Solenoid: A helix with a current
Helix: a coil of wire
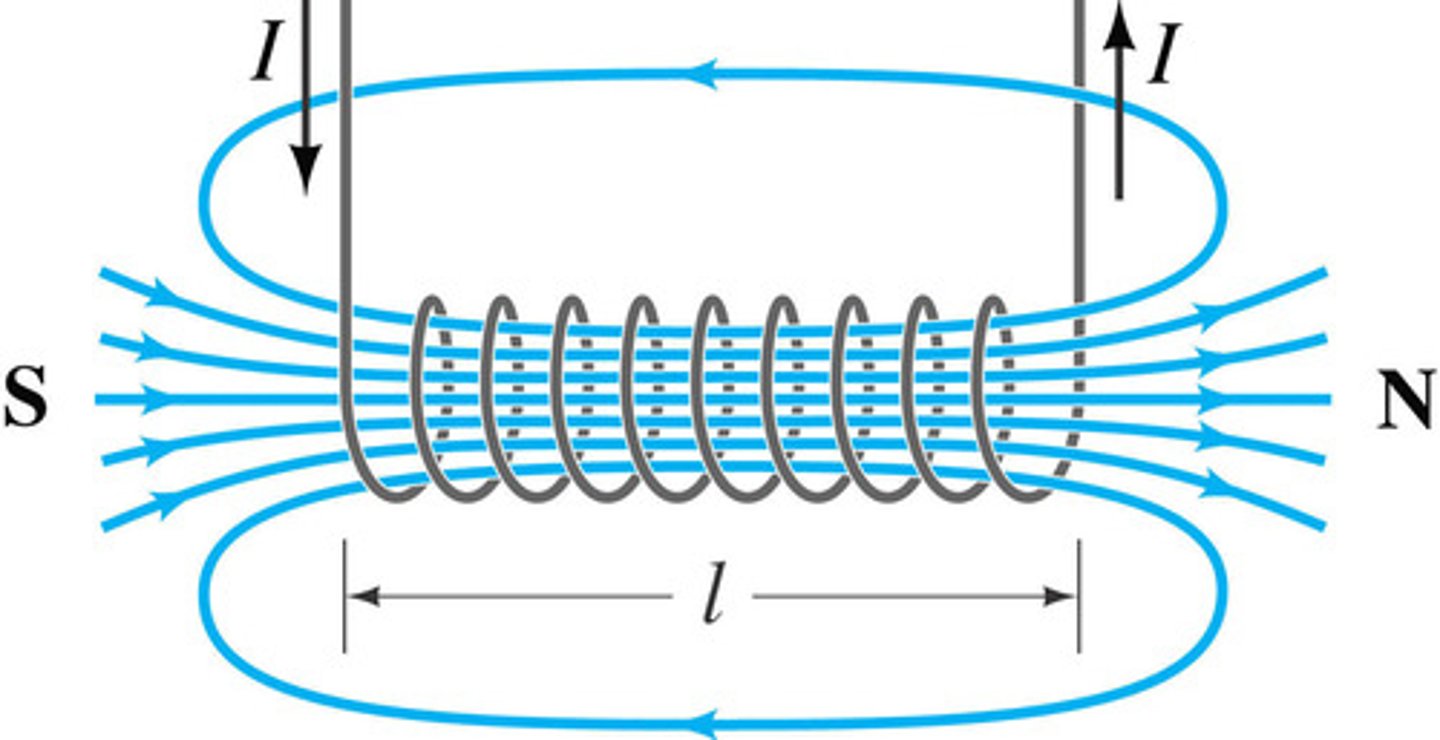
What is an electromagnetic? **
A solenoid with an iron core.
When there is ferromagnetic material (like iron), the stronger the magnetic strength

What is the Lenz Law of Electromagnetism? **
The induced current flows in the opposite direction of the applied current.
“Lenz Law → Likes things the same.”(Induced current opposes the change that caused it.)
What is self induction?
The induction of an opposing EMF in a single coil by its own changing magnetic field.
*it creates its own opposing magnetic force*
Induction: charged & uncharged objects do not touch
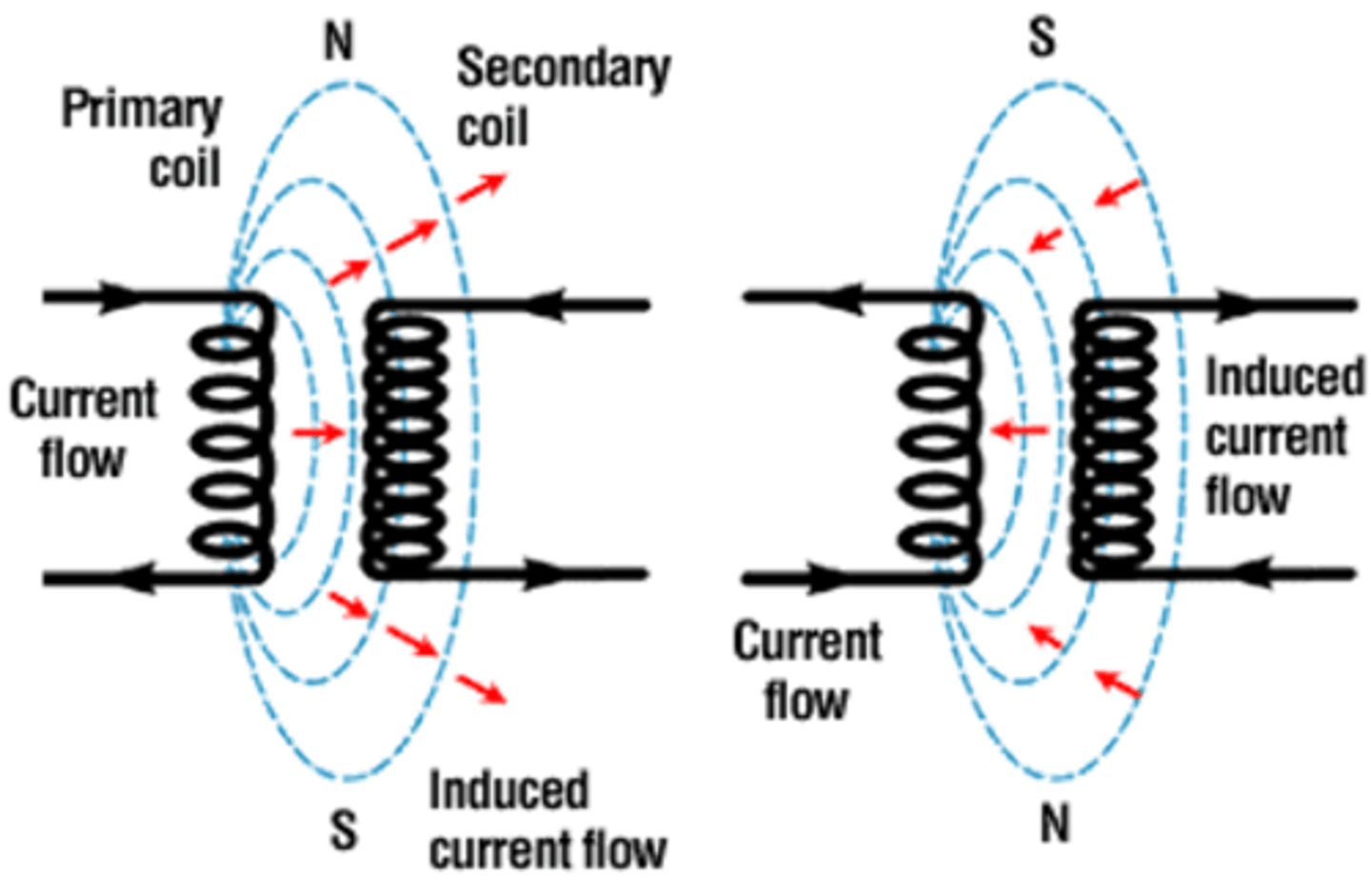
What is mutual induction?
Magnetic field induces a current in a nearby helix
Like poles put together will store energy as _______ energy. When released of one another, the energy will be converted into ______ energy.
Like poles put together will store energy as potential energy.
When released of one another, the energy will be converted into kinetic energy.
changes from potential energy to kinetic energy
Like poles pushed together → store potential energyReleased → convert to kinetic energy
Generator converts _______ energy to _________ energy
Motor converts ___________ energy to _______________ energy.
Generator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. (GEM)
Motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. (MEM)
What are the parts of a generator? *
Armature (coil of wire), brush, and slip ring.
Slip rings are metal rings attached to the armature that rotate with it, allowing current to flow from the spinning coil. Brushes touch the slip rings and transfer the electrical current to the external circuit.
Why does alternating current (AC) reverse direction?
As the coil rotates, the current reverses every half turn, producing an alternating current (AC) that changes direction periodically.
What are the two motor types?
Synchronous: Coil rotates at same frequency as current (60Hz), used in timing circuits in old machines.
Induction: Stator (magnets around rotor) & rotor. Uses electromagnets to create a magnetic field to interact with the current's magnetic field. Used to rotate anode in an X-ray tube.****
What is the difference between the actual focal spot and the effective focal spot?
The actual focal spot is the area on the anode target where the electrons from the cathode actually hit.
The effective focal spot is the projected area of the actual focal spot as seen from the patient’s perspective (the x-ray beam).
What is are the two types of transformers?
Step Up & Step Down: Used to change the magnitude of current & voltage.
Transformers operate on the principle of mutual induction.
Step Up: Found in tube circuit (High Voltage Transformer HVT)
Step Down: Found in filament circuit (used to heat up cathode to boil off electrons
What are the main parts of a transformer and their functions?
1. Primary coil (input side): Receives the incoming voltage.
2. Secondary coil (output side): Delivers the transformed voltage.
3. Core: A metal rod that strengthens the magnetic field between coils.
What is the difference between self-induction and mutual induction?
Self-induction (autotransformer): Uses one coil that acts as both the primary and secondary; voltage changes within the same coil.
Mutual induction: Uses two separate coils; a changing current in the primary coil induces a current in the secondary coil.
Self = Single → One coil does it all (changes its own voltage).
Mutual = Multiple → Two coils help each other (primary affects secondary).
What is the difference between a step-up and step-down transformer?
Step-up transformer: Increases voltage; secondary coil has more turns than the primary.
Step-down transformer: Decreases voltage; secondary coil has fewer turns than the primary.
*mutual induction*
What are the main types of power losses in a transformer?
1. Copper loss: Caused by resistance in the coils (wires heat up as current flows).
2. Hysteresis: Magnetic Lag. When the current changes direction, the magnetic domains in the core flip, causing energy loss that turns into heat.
3. Eddy current: Swirling currents in the metal core that waste energy as heat.
How can transformer power losses be minimized?
By lamination of plates that are wrapped around the wires to reduce eddy current
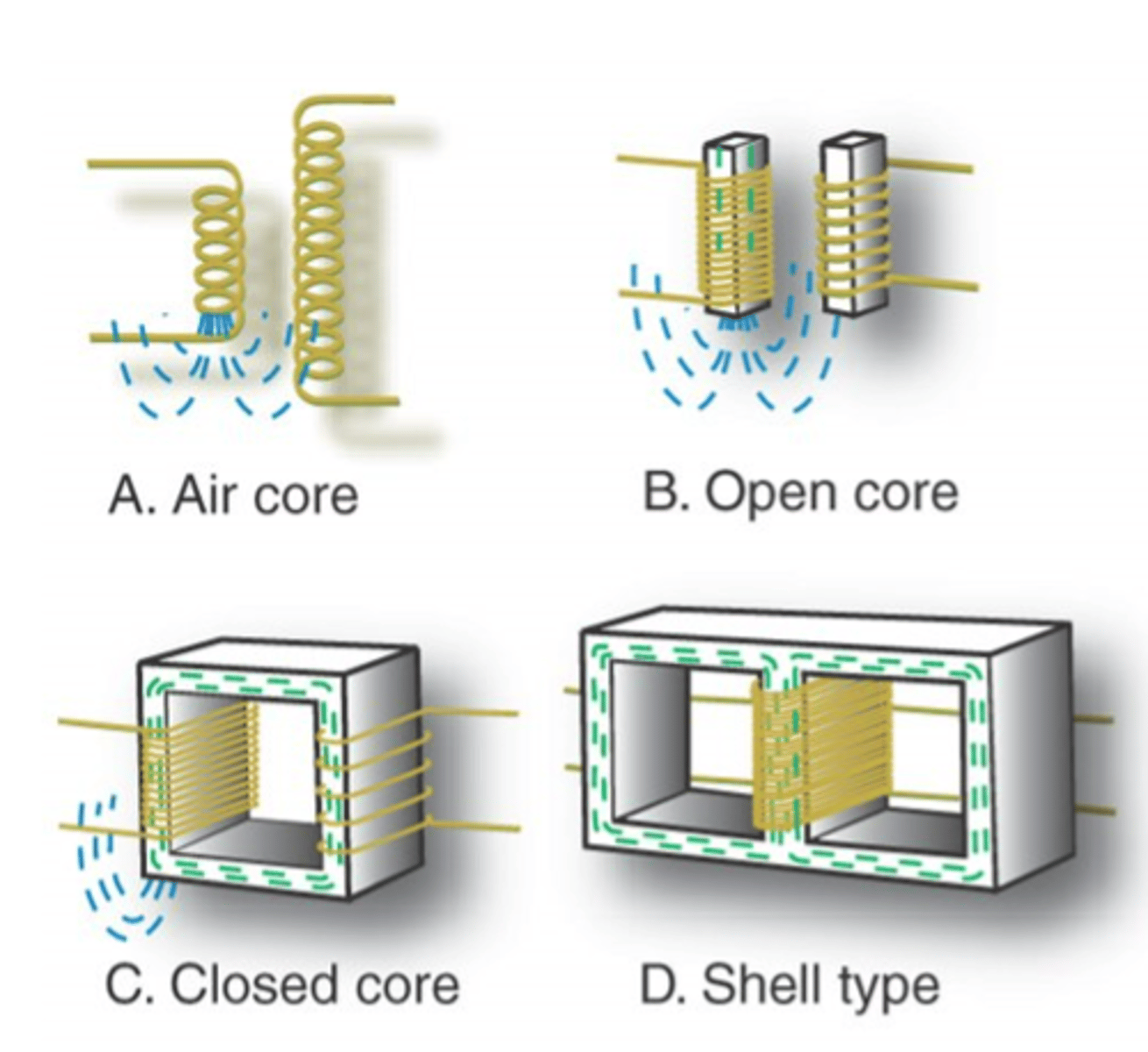
What are the four types of transformer core constructions?
Air core: Has no iron core — coils are surrounded by air; weak magnetic field and low efficiency. Most leakage.
Open core: Uses an iron core that doesn’t fully enclose the coils; some magnetic flux is lost. Some leakage
Closed core: Core forms a continuous magnetic path, keeping magnetic flux contained with minimal leakage; core is laminated to reduce eddy current loss.
Shell type: Most advanced, winding are insulated. Common in modern x-ray systems. Most efficient
Air = weakest → Shell = strongest (each step improves magnetic efficiency)
What is an autotransformer and how does it work?
An autotransformer uses one coil with multiple tap points to vary voltage through self-induction. It adjusts the incoming voltage before it reaches the main step-up transformer.
In x-ray machines, it’s used to adjust and control the kilovoltage (kVp) that determines the energy and penetration power of the x-ray beam before the voltage enters the step-up transformer.
“Auto = one coil, self-induction.”