abeyes
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
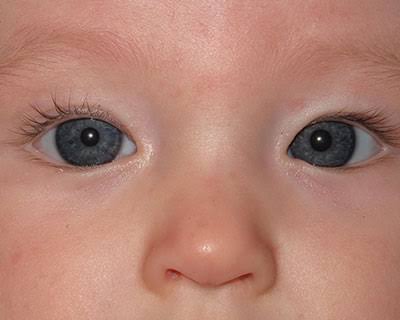
Pseudostrabismus
Normal in young children, the pupils will appear at the inner canthus (due to the epicanthic fold).
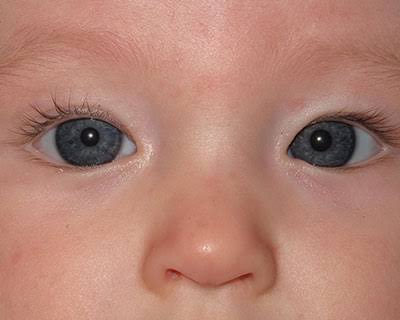
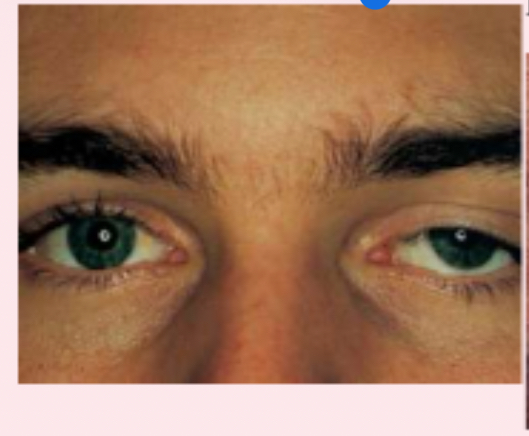
Strabismus (or Tropia)
A constant malalignment of the eye axis, is defined according to the direction toward which the eye drifts and may cause amblyopia.
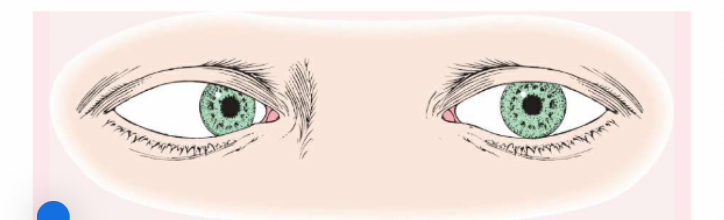
Esotropia
(eye turns inward).
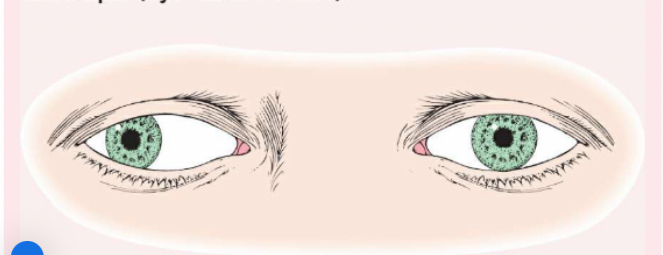
Exotropia
(eye turns outward).

Phoria (Mild Weakness)
Noticeable only with the cover test, is less likely to cause amblyopia than strabismus.

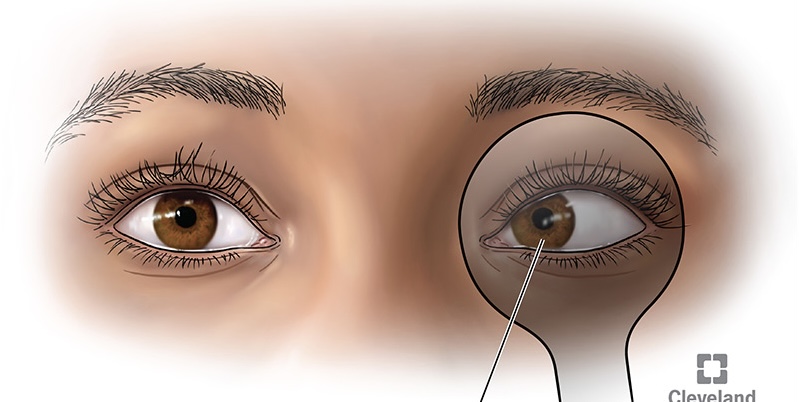
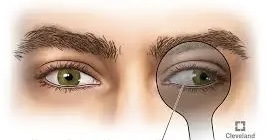
Esophoria
is an inward drift and
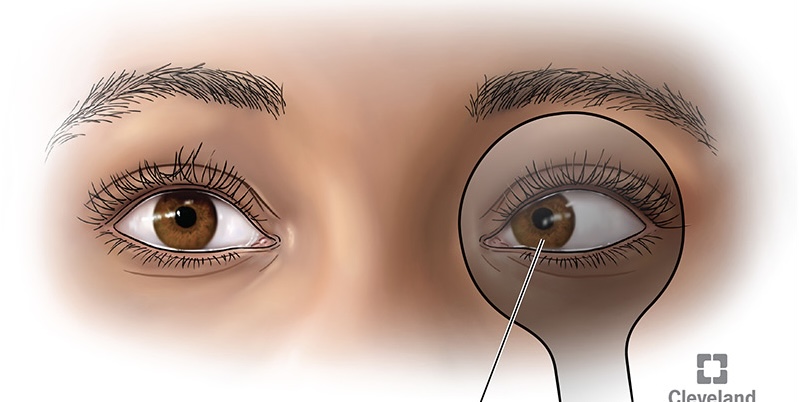
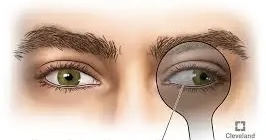
exophoria
an outward drift of the eye.
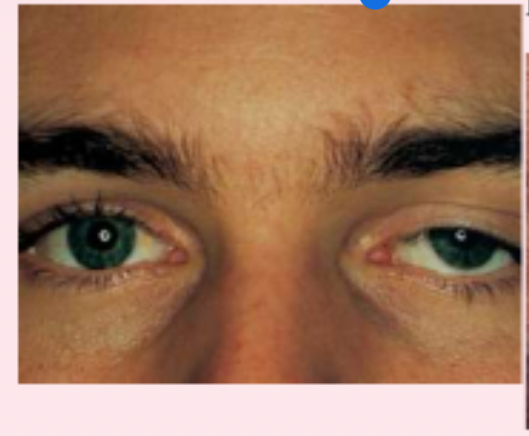
Ptosis
(drooping eye)
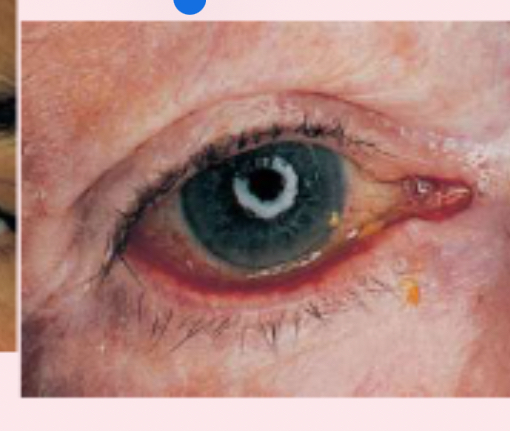
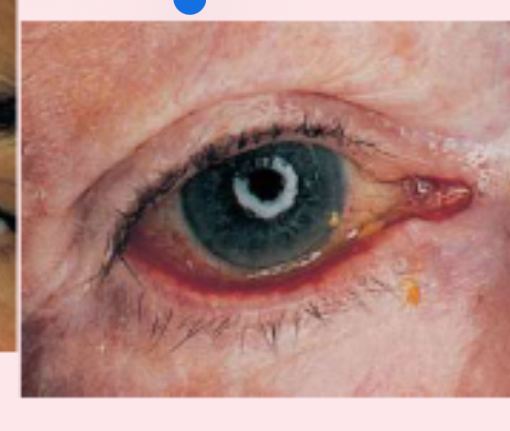
ectropion
outwardly turned lower lid
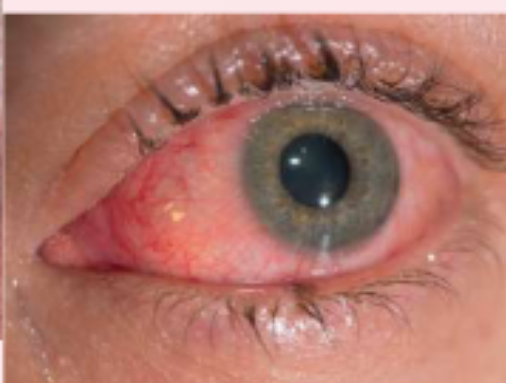
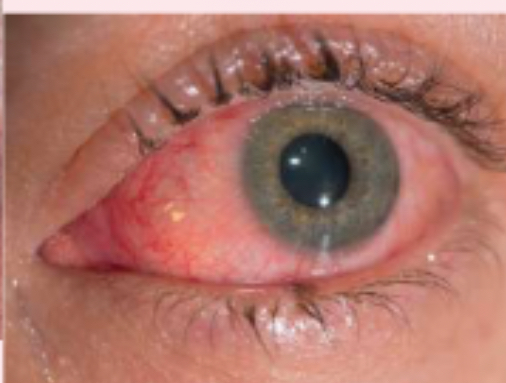
conjunctivitis
generalized inflammation of the conjunctiva
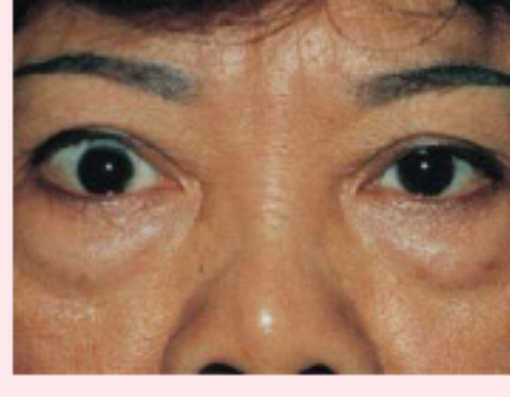
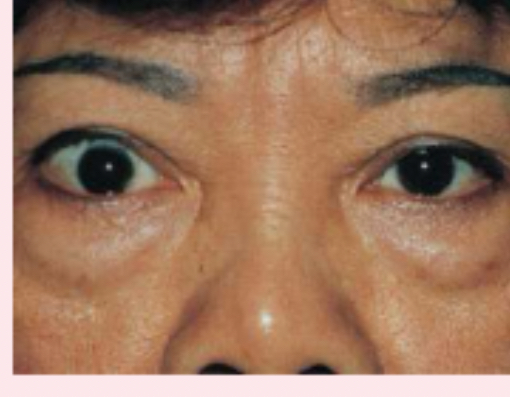
exophthalmos
protruding eyeballs and retracted eyelids
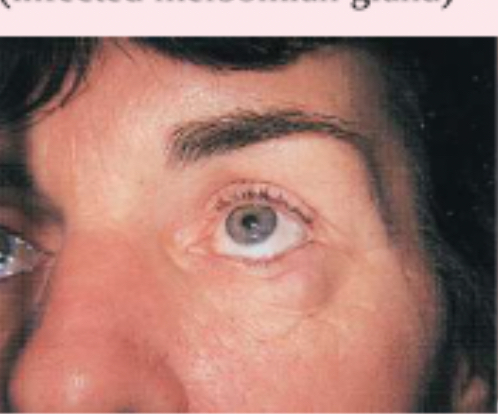
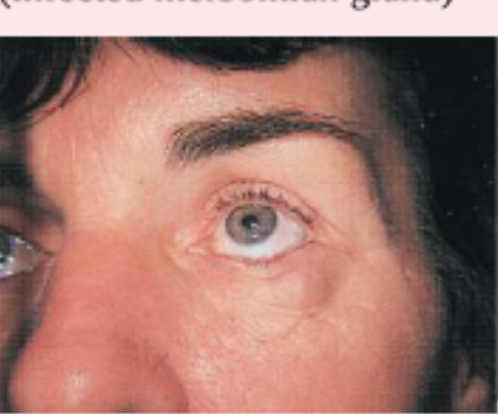
chalazion
infected meibomian gland
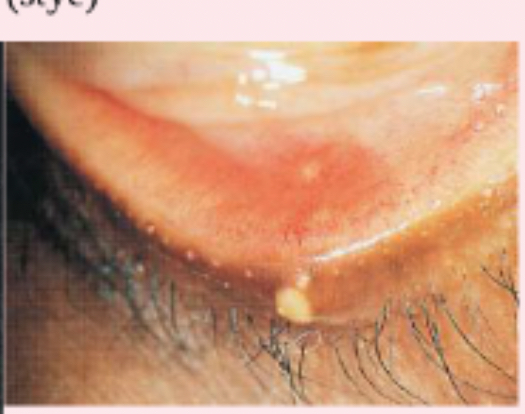
hordeolum (stye)
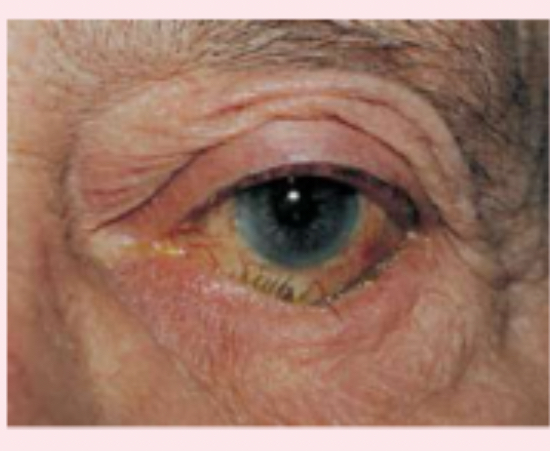
entropion
inwardly turned lower eye lid
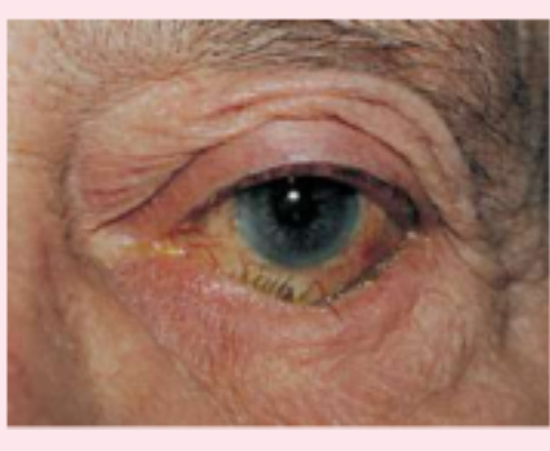
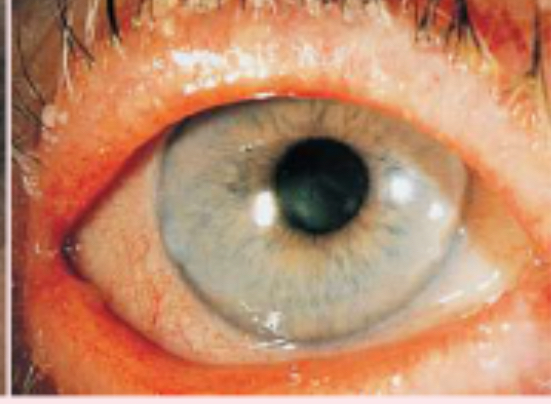
blepharitis
staphylococcal infection of the eyelid
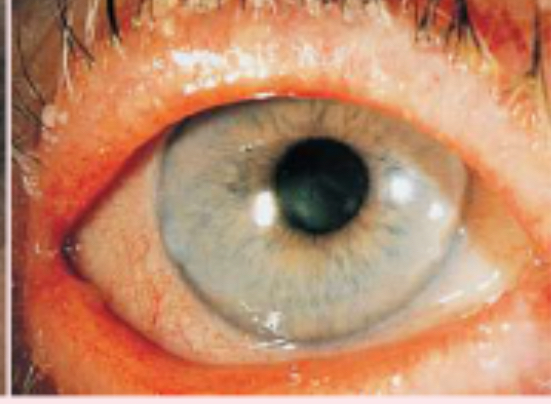

diffuse episcleritis
inflammation of the sclera
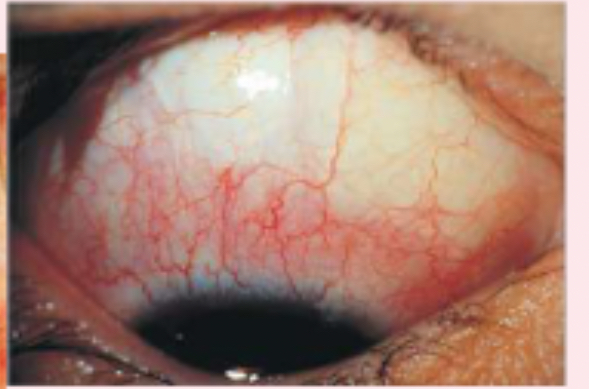
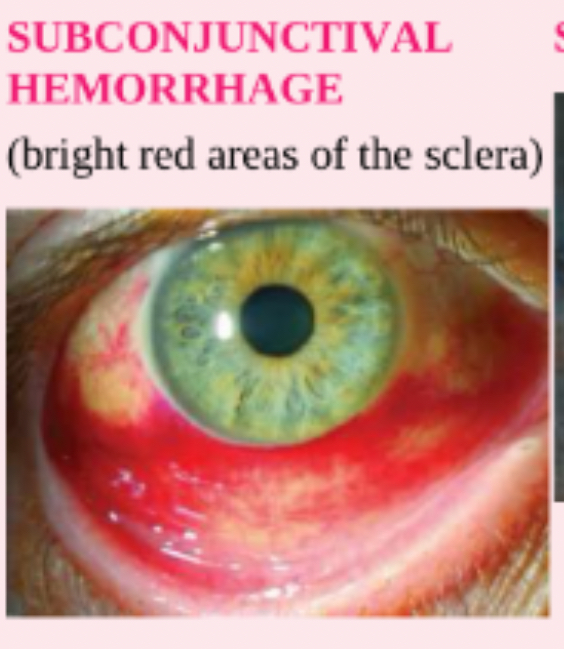
subconjunctival hemorrhage
bright red areas of the sclera
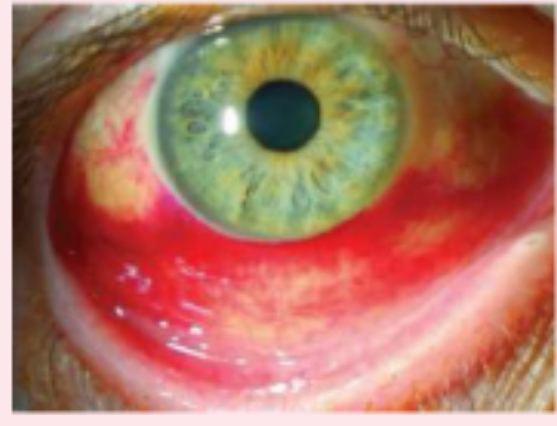
scleral jaundice
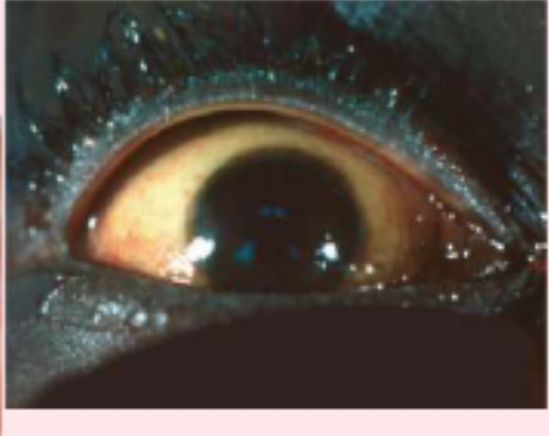
corneal scar
which appears grayish white, may be due to inflammation or an old injury.
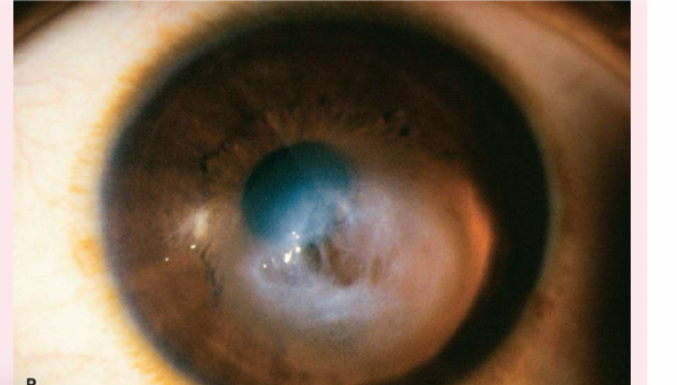
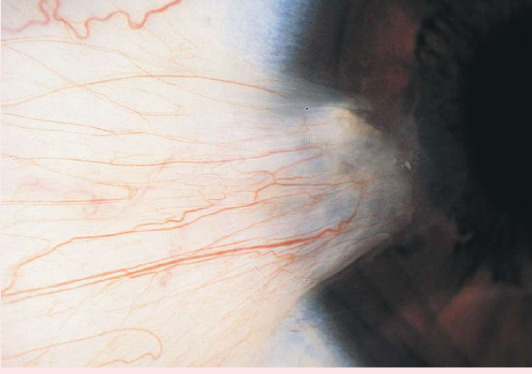
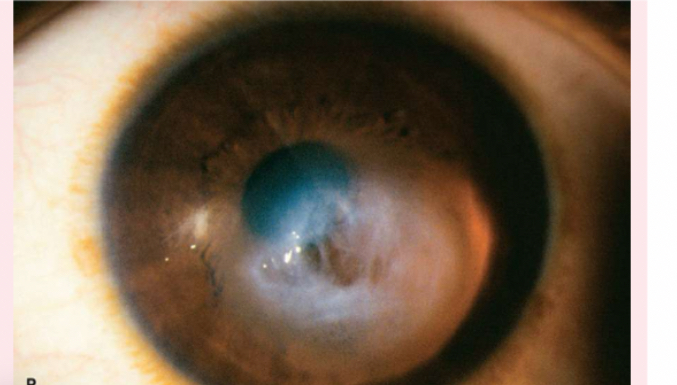
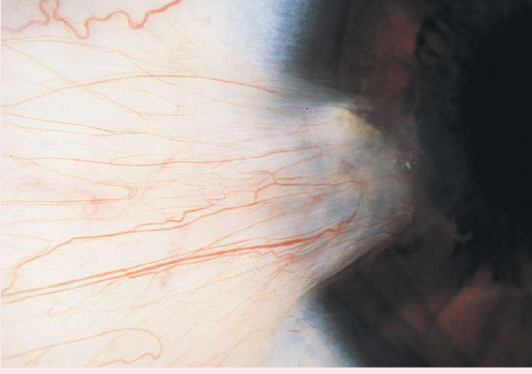
pterygium
a thickening of the bulbar conjunctiva that extends across the nasal side.
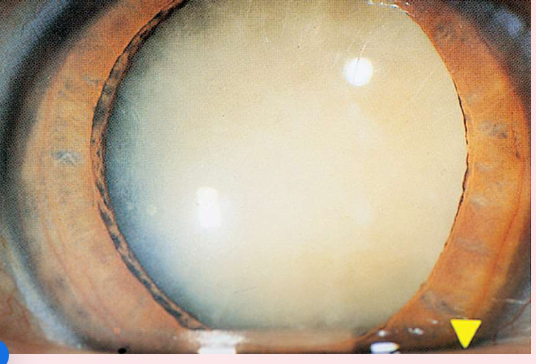
Nuclear cataracts
appear gray when seen with a flashlight; they appear as a black spot against the red reflex
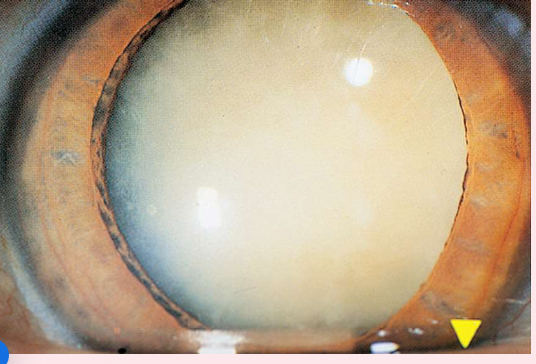
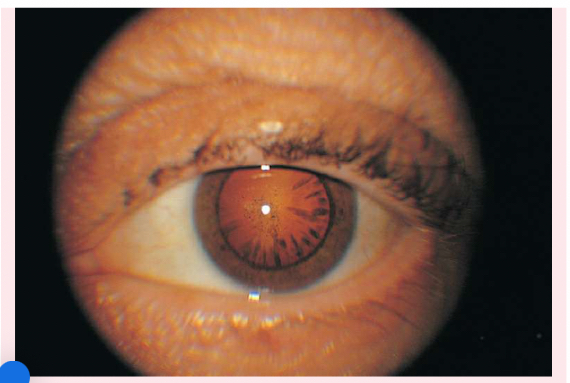
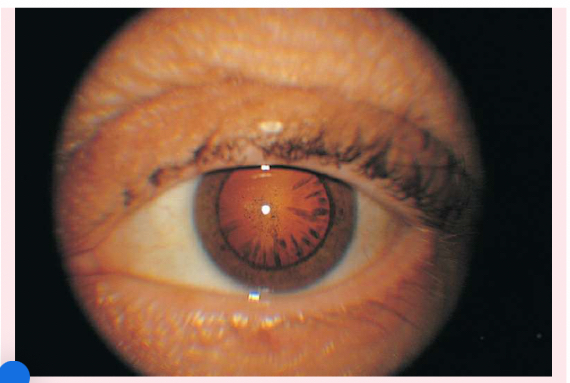
Peripheral cataracts
look like gray spokes that point inward when seen with a flashlight; they look like black spokes that point inward against the red reflex when seen through an ophthalmoscope.
miosis
Also known as pinpoint pupils, is characterized by constricted and fixed pupils possibly a result of narcotic drugs or brain damage.
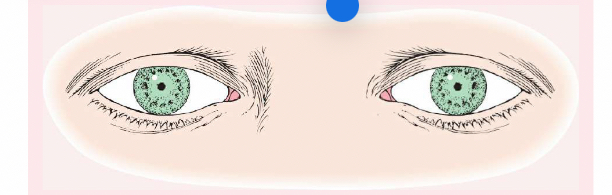
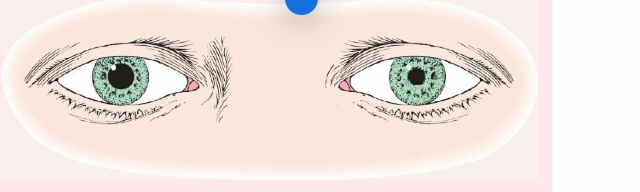
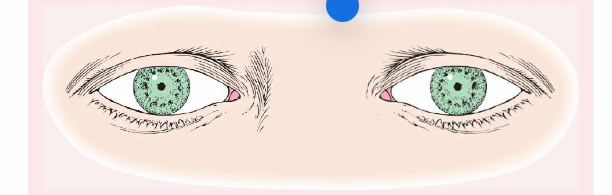
anisocoria
is pupils of unequal size. In some cases, the condition is normal; in other cases, it is abnormal. For example, if is greater in bright light compared with dim light, the cause may be trauma, tonic pupil (caused by impaired parasympathetic nerve supply to iris, and oculomotor nerve paralysis.
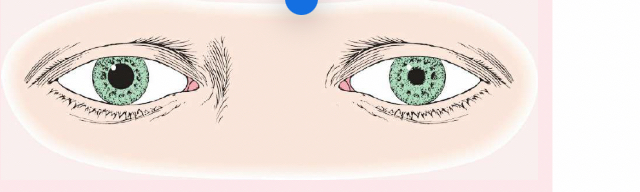
Mydriasis
Dilated and fixed pupils, typically resulting from central nervous system injury, circulatory collapse, or deep anesthesia.

PAPILLEDEMA
Swollen optic disc
Blurred margins
Hyperemic appearance from accumulation of excess blood
Visible and numerous disc vessels
Lack of visible physiologic cup
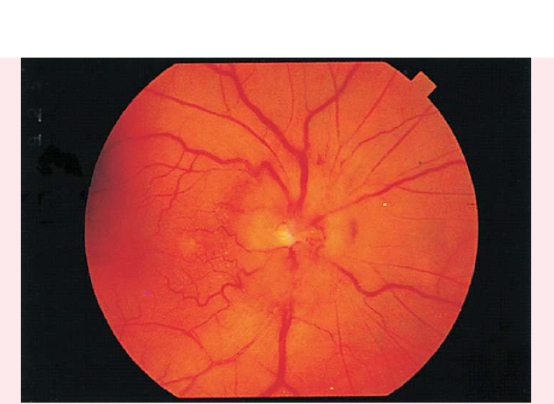
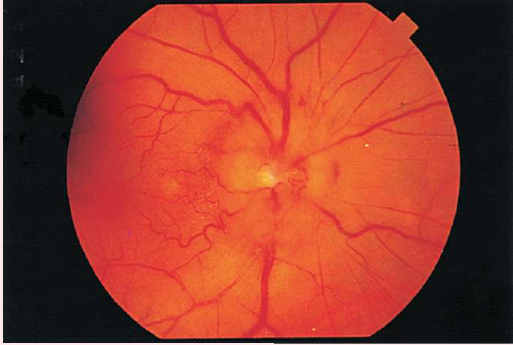
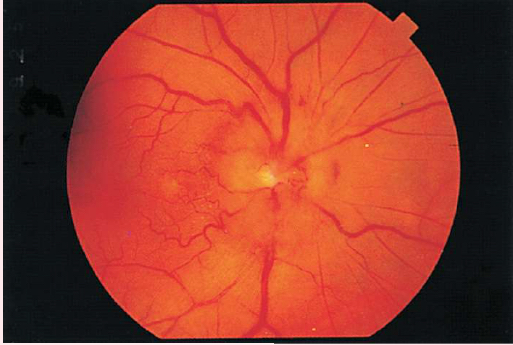
GLAUCOMA
• Enlarged physiologic cup occupying more than half of the disc's diameter
• Pale base of enlarged physiologic cup
• Obscured and/or displaced retina vessels
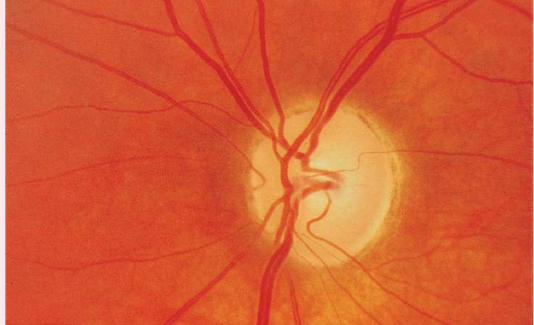
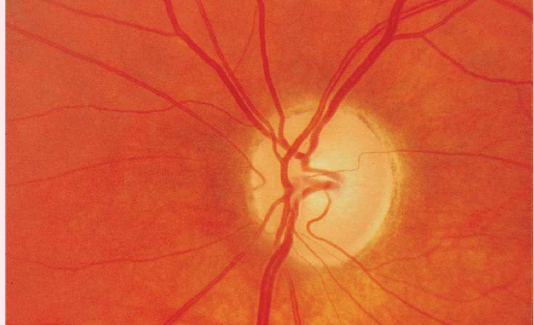
optic atrophy
• white optic disc
• lack of disc vessels
constricted arteriole
• narrowing of the arterials
• occurs with hypertension
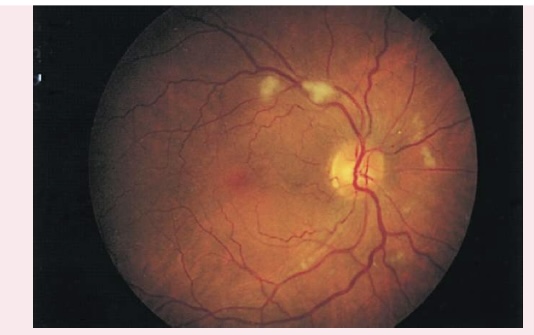
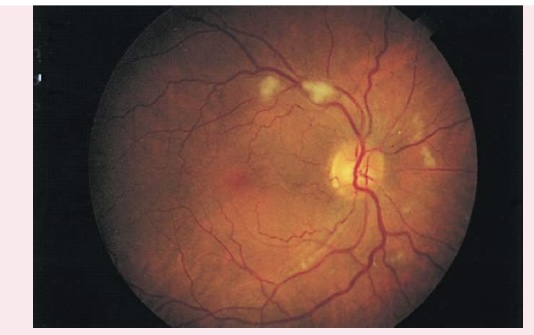
COTTON WOOL PATCHES
Also known as soft exudates, cotton wool patches have a fluffy cotton ball appearance, with irregular edges.
Appear as white or gray moderately-sized spots on retinal background
Caused by arteriole microinfarction
Associated with diabetes mellitus and hypertension