Gene expression - C&M
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
efficiency
regulation maintains ____
energy
expressing all genes would require a massive amount of ____
space
cells are kept to a manageable size
time
genes can be expressed as needed & more rapidly
gene expression
different cell types exhibit differential ____ _______:
eye vs. liver cell
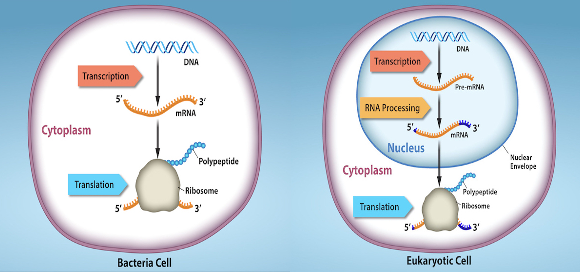
prokaryotic regulation
transcription/translation occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm
regulation occurs at the transcriptional level
eukaryotic regulation
transcription & RNA processing occurs in the nucleus
translation takes place in the cytoplasm
gene expression is regulated during:
transcription
translation
post-translational modification of proteins
prokaryotic DNA
circular chromosome located in nucleoid region of cytoplasm
operons — organized blocks of proteins w/ similar function/in the same biochemical pathway
3 molecules that regulate operons
repressors — suppress transcription
activators — increase transcription
inducers — may suppress/activate transcription depending on cell needs
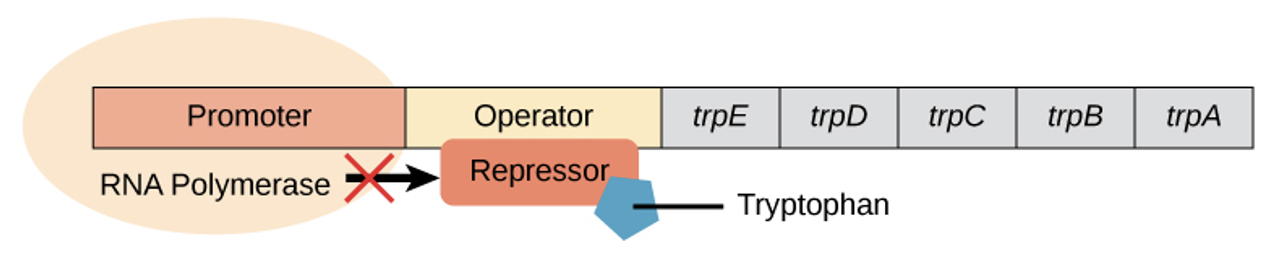
trp repressor operon - when tryptophan is plentiful
2 tryptophan molecules bind the repressor protein at the operator sequence
complex physically blocks the RNA polymerase from transcribing the tryptophan genes by binding to operator
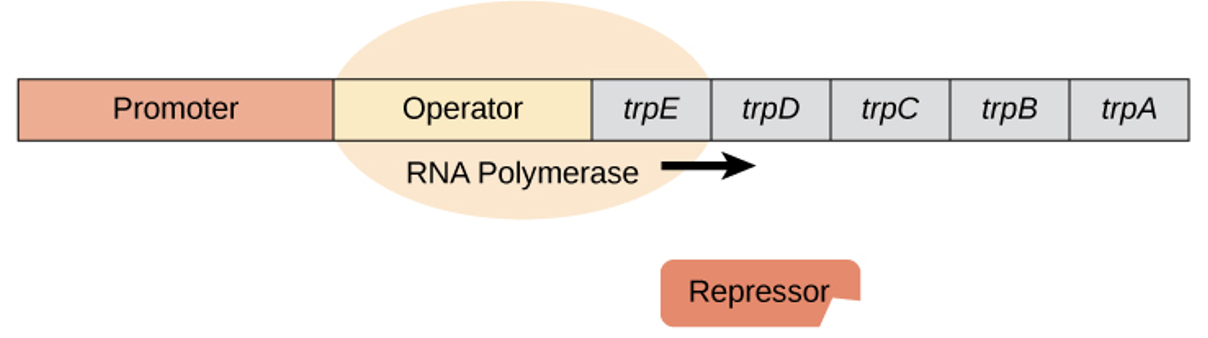
trp repressor operon - when tryptophan is absent
repressor protein doesn’t bind to operator
RNA polymerase can access the operator & the genes are transcribed
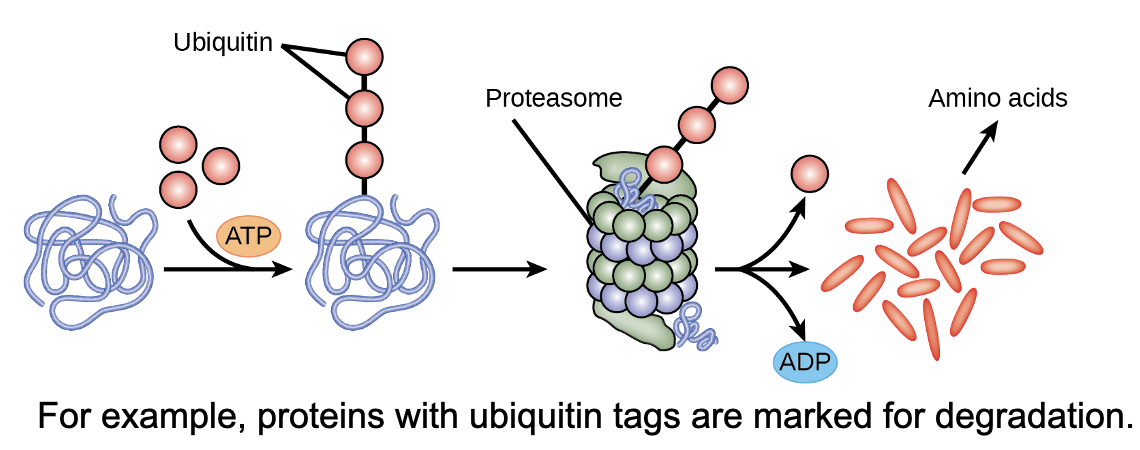
negative regulators
proteins that bind to the operator & silence trp expression
ex. trp repressor operon - tryptophan absent
CAP - positive regulator
glucose supplies become limited in cell:
cAMP levels increase
cAMP binds to the __ protein
cAMP/__ protein complex binds to an operator region upstream of the genes required to use other sugar sources
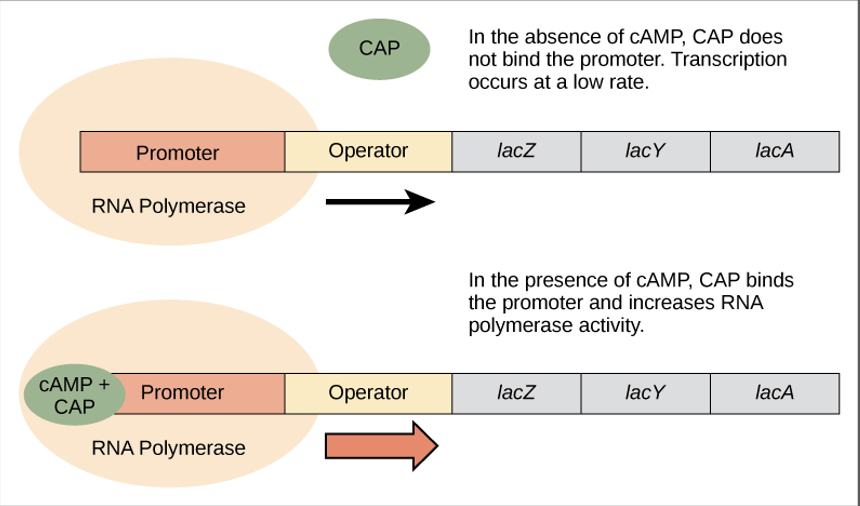
positive regulators
proteins that bind the promoter in order to activate gene expression
ex. CAP protein
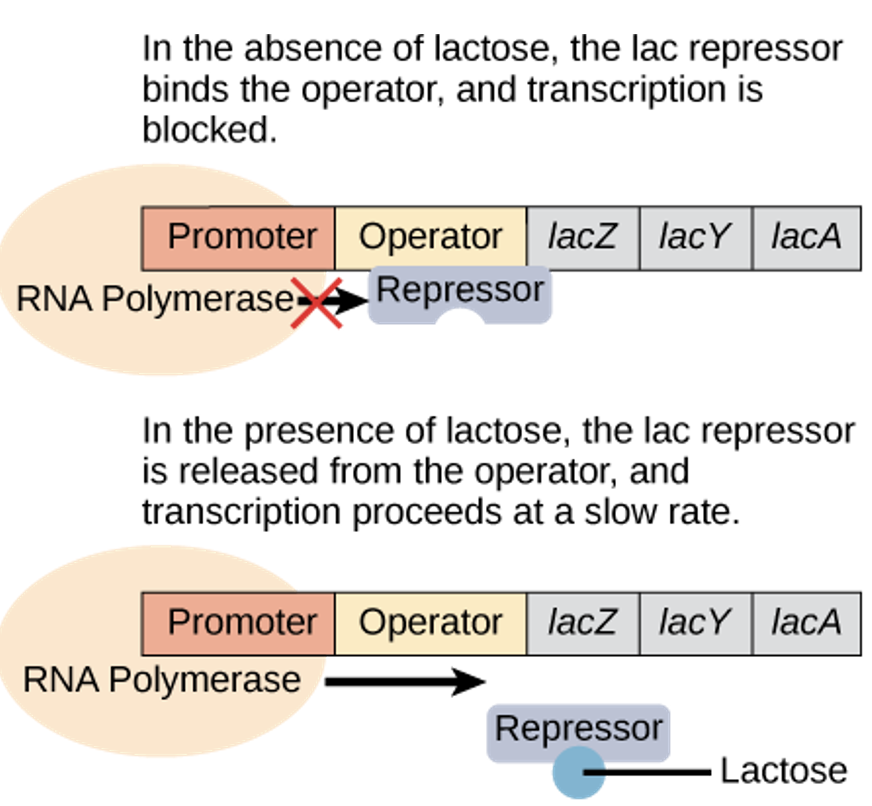
lac operon - inducer operon
proteins that activate/repress transcription:
activation/repression depends on the local environment & cell needs
eukaryotic epigenetic regulation
first level begins w/ control of access to DNA & occurs before TRANSCRIPTION begins
transcription factors
proteins that control the transcription of genetic information from DNA —> RNA
human genome
20,000 genes
23 chromosomes
DNA is compacted w/ histones
expressed genes must be unwound & made available to polymerases
nucleosomes
these control access to DNA:
when spaced closely together
transcription factors cannot bind
gene expression = OFF
when spaced far apart, the DNA is exposed
transcription factors can bind
gene expression = ON
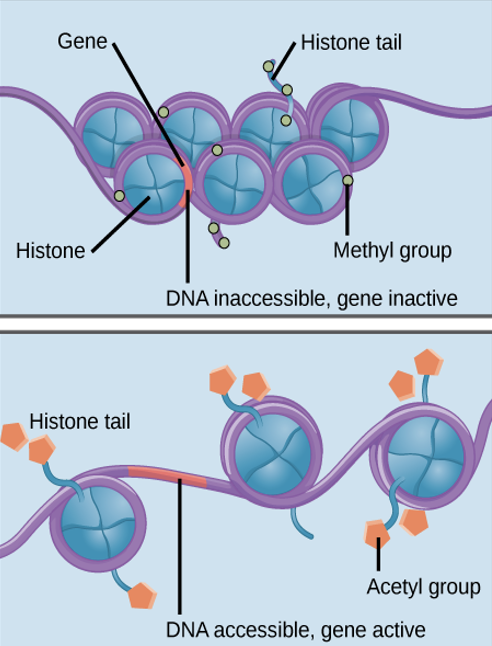
epigenetic regulation
“around genetics” temporary changes to nuclear proteins & DNA that don’t alter nucleotide sequence but do alter gene expression
chemical tags
these are added to histones & DNA:
phosphate, methyl, acetyl groups
not permanent — can be added/removed
acts as signals to tell histones if region of chromosome should be open or closed.
unwinding & opening
_____ & _____ of DNA allows transcription factors to:
bind promoters & other upstream regions
initiate transcription
eukaryotic transcription
requires RNA polymerases, which also require transcription factors:
these factors bind the promoter sequence & other DNA regulatory sequences
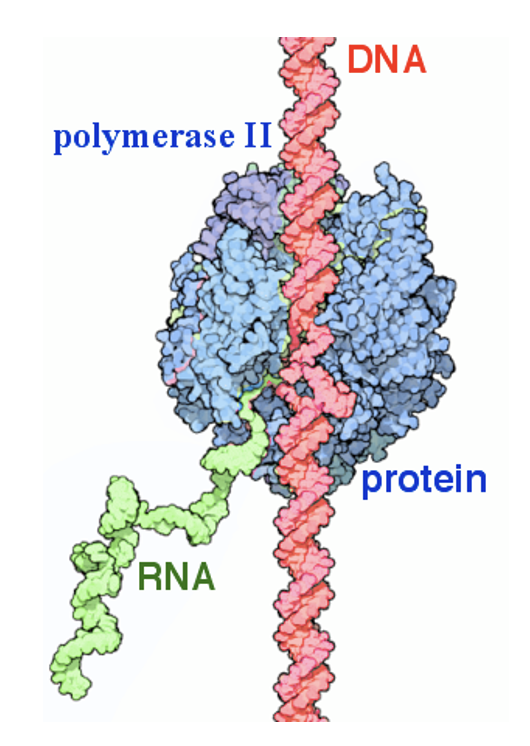
promoter
region of DNA upstream of coding sequence (a few nucleotide to 100’s of nucleotides long)
TATA box
a series of thymine & adenine dinucleotides w/in the promoter just upstream of the transcriptional start site
TFIID
a transcription factor that binds the TATA box:
recruits additional transcription factors to form a complex here
RNA polymerase can bind to upstream sequence:
phosphorylated & part of protein is released from DNA
in proper orientation for TRANSCRIPTION
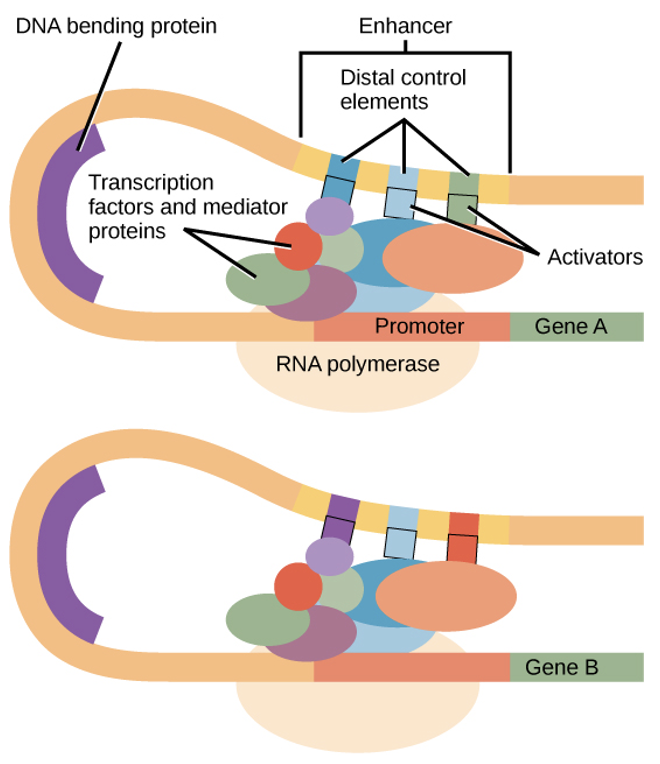
enhancer
a DNA seuqence that promotes transcription:
made of distal control elements — short DNA sequences
activators bind to those & interact w/ mediator proteins & transcription factors
eukaryotic post-transcription
in eukaryotes…
RNA transcripts must be processed into final form before translation can begin modification:
this step can be regulated to control gene expression
evolution of alternative splicing
splicing requires proper ID of introns
errors could lead to splicing out of an intervening exon
usually would be deleterious to organism…
but could produce a protein variant w/o loss of original protein
new variant might’ve had an adaptive advantage
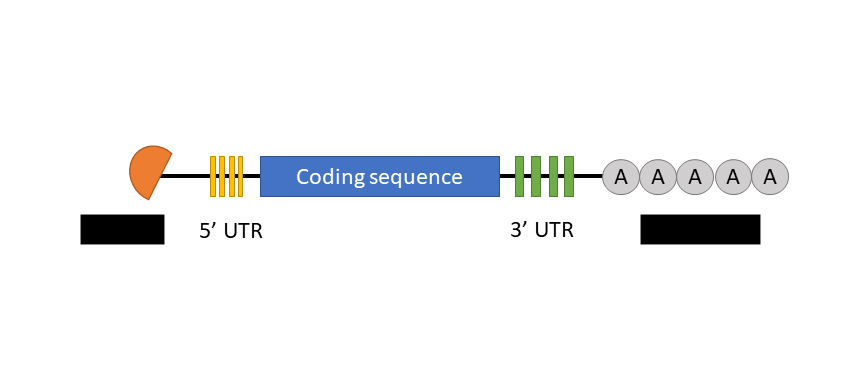
untranslated regions (UTRs)
the protein-coding region of mRNA is flanked by 5’ & 3’ _______ ____.
RNA stability
RNA-binding proteins at UTRs influence ___ _____:
can increase/decrease length of time mRNA is present in cytoplasm
regulate mRNA localization & protein translation
5’ cap & poly-A tail
a GTP molecule that prevents degradation of transcript
other does the same thing
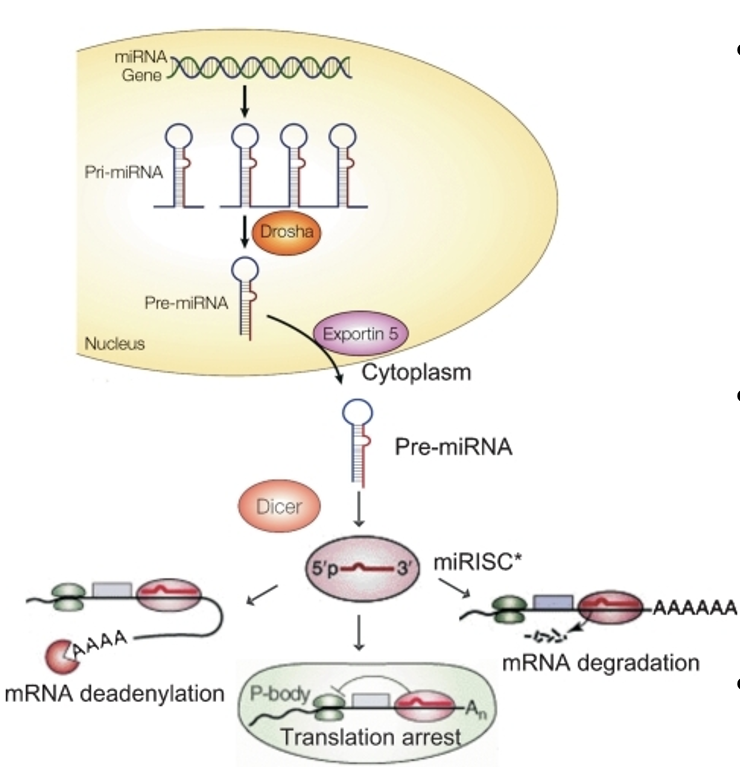
microRNAs (miRNAs)
short RNA molecules (21-24 nucleotides) that recognize specific sequences of mRNA:
associate w/ ribonucleoprotein complex — RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)
RISC/miRNA bind to & degrade the mRNA
initiation complex & translation rate
translation controlled by proteins that bind & initiate process (formation of this complex)
eukaryotic initiation factor-2 (eIF-2) — first protein to bind & form complex
(she said not to go through whole process; slide 30)
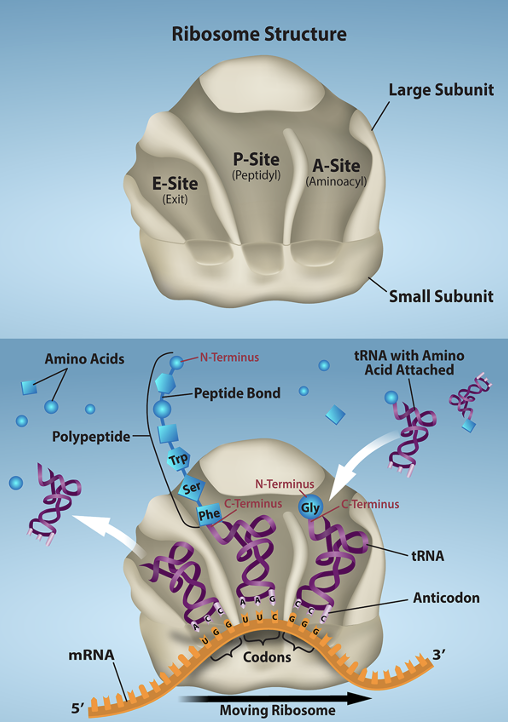
3 tRNA binding sites
A-site (acceptor) — charged tRNAs enter here
P-site
E-site
chemical modifications
these affect protein activity:
can be added/removed
also length of time they exist in cell
can alter epigenetic accessibility, transcription, mRNA stability, or translation
all resulting in changes in expression of various genes