Ella Kulman Haematology
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What is myeloma?
malignancy of plasma cells leading to progressive bone marrow failure
In order to make a diagnosis of myeloma, there must be evidence of mono-clonality. What is this?
abnormal proliferation of a single clone of plasma cell leading to immunoglobulin secretion and causing organ dysfunction especially to the kidney
Give 3 symptoms of myeloma
1. Tiredness
2. Bone/back pain
3. Infections
Give 4 signs of myeloma
CRAB!
1. Calcium is elevated
2. Renal failure
3. Anaemia
4. Bone lesions
Why is calcium elevated in myeloma?
There is increased bone resorption and decreased formation, so there is more calcium in the blood
Why might someone with myeloma have anaemia?
bone marrow is infiltrated with plasma cells - consequences of this are anaemia, infections and bleeding
Why might someone with myeloma have renal failure?
due to light chain deposition
What investigations might you do in someone who you suspect has myeloma?
1. Blood film
2. Bone marrow aspirate and trephine biopsy
3. Electrophoresis
4. x-ray
5. CT scan
6. MRI scan
7. Chromosomal abnormalities
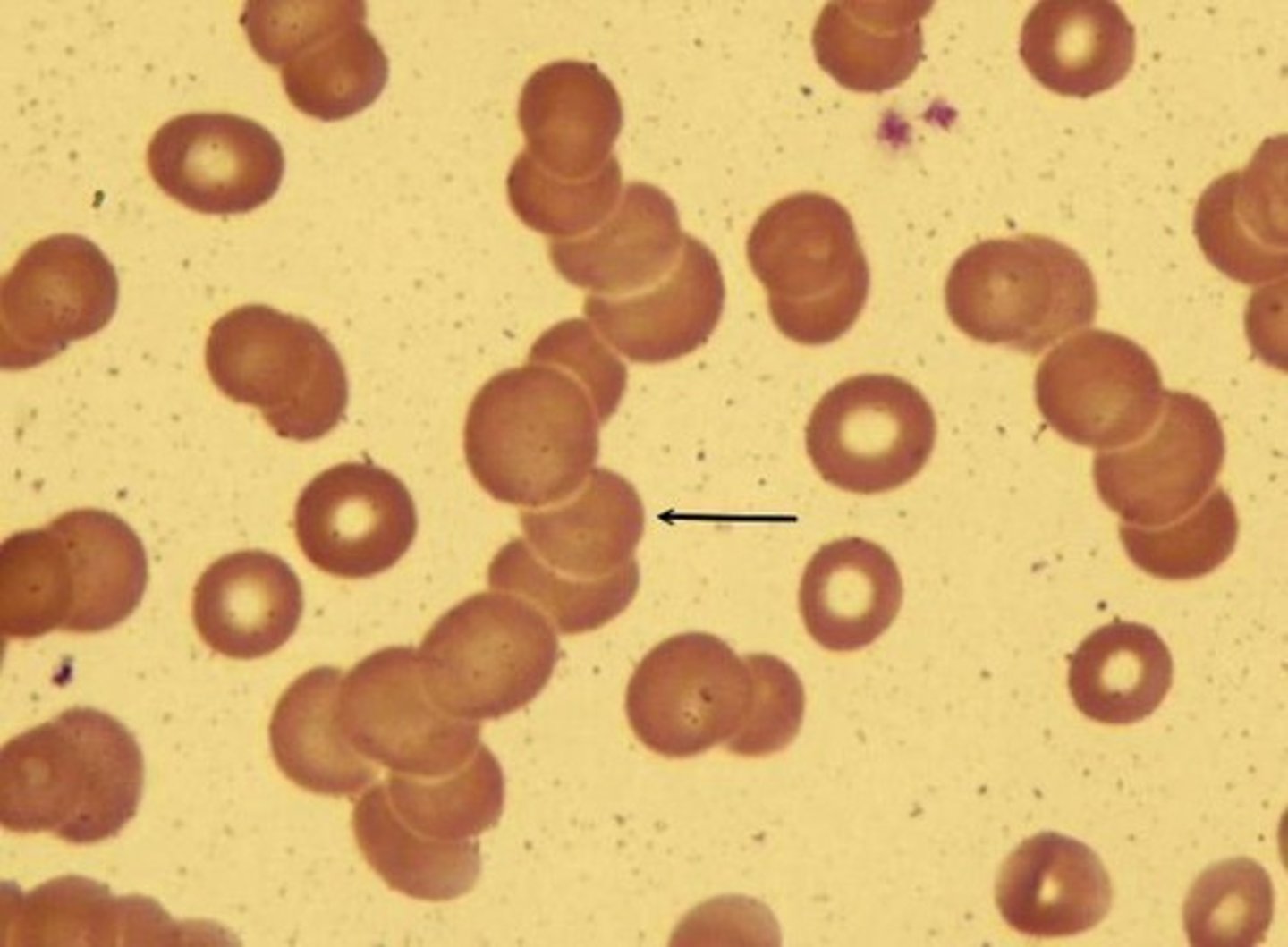
What would you expect to see on the blood film taken from someone with myeloma?
aggregation of RBC's - Rouleaux formation
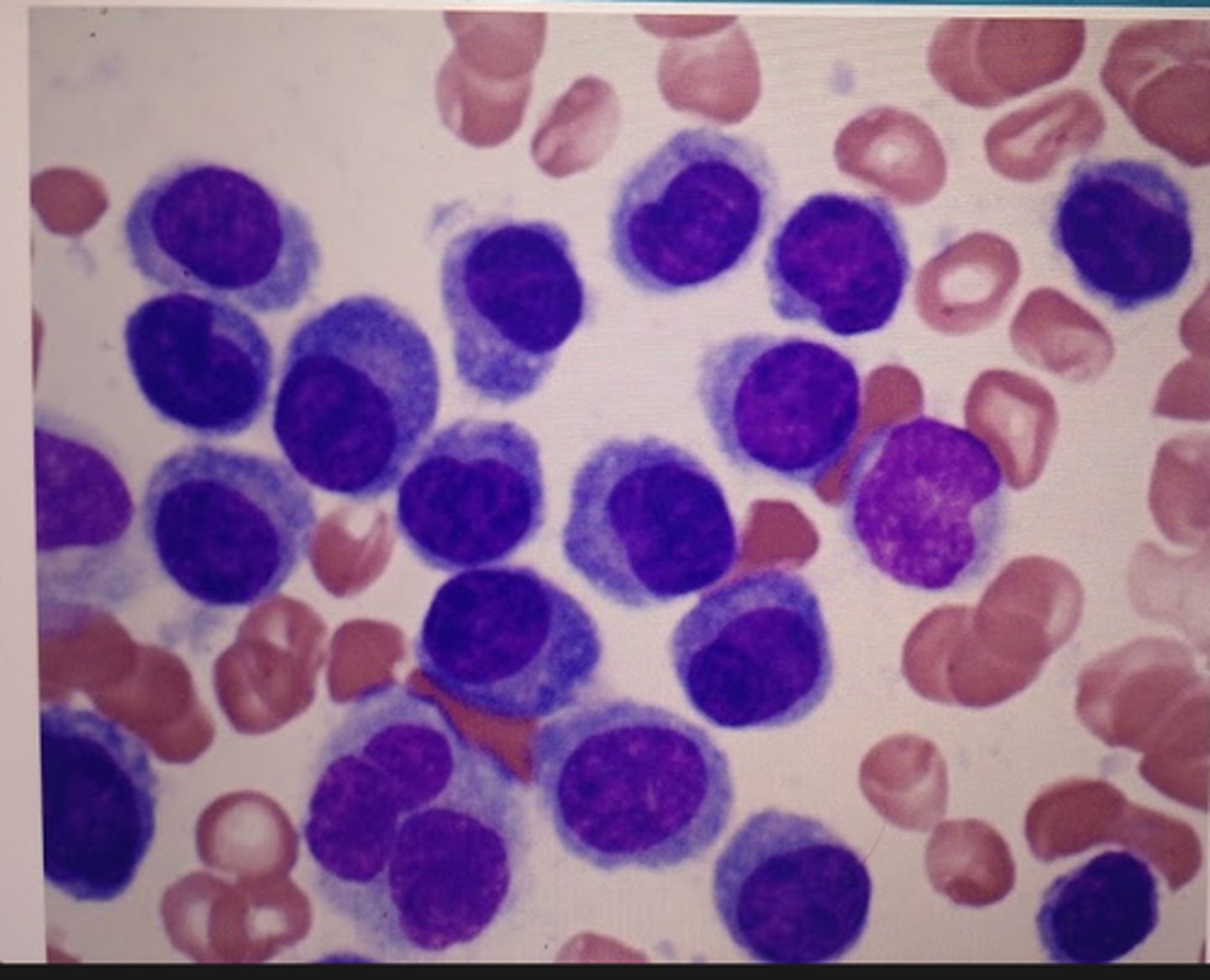
what are you looking for on a bone marrow biopsy taken from someone with myeloma?
Increased plasma calls
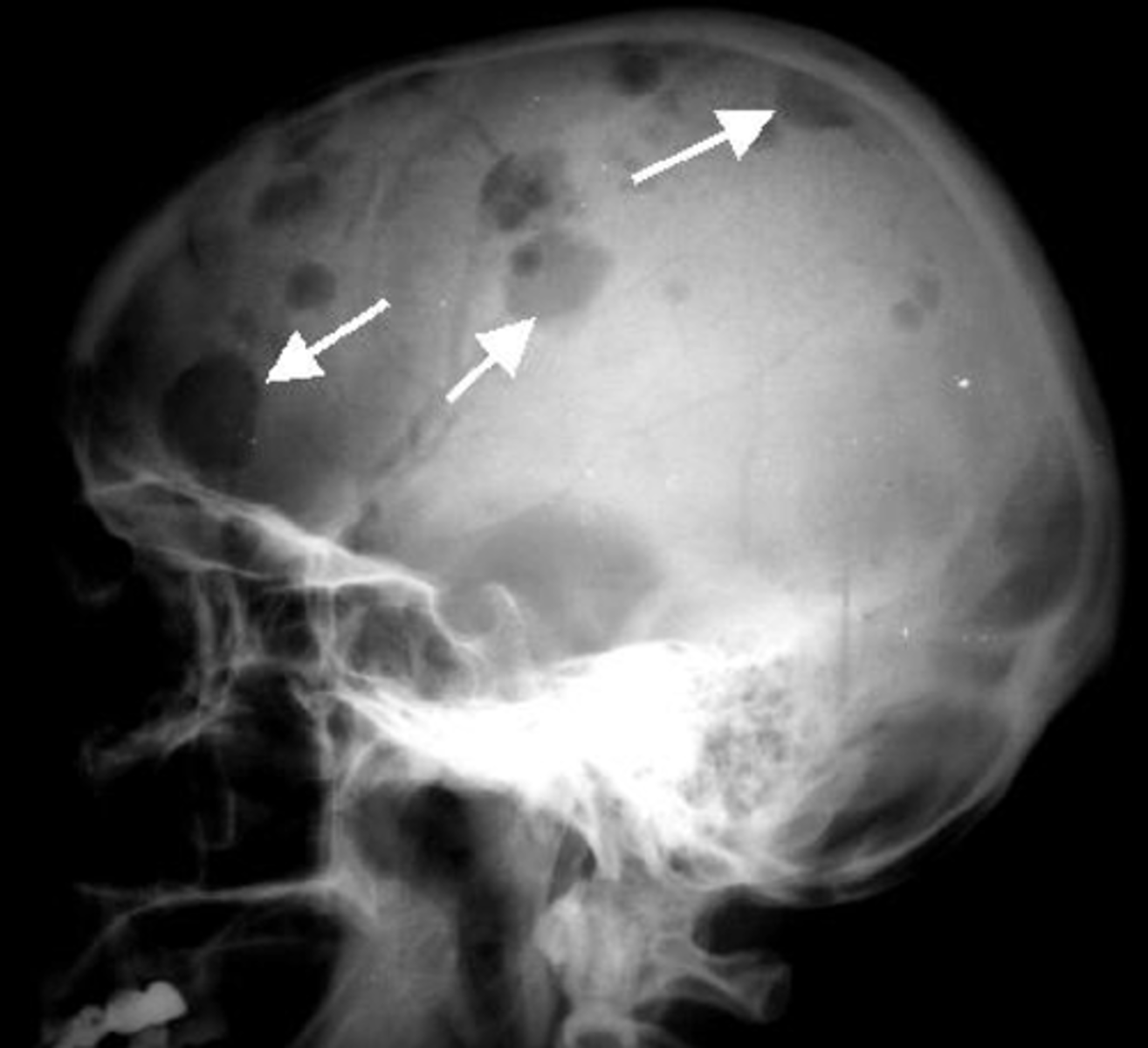
what are you for on an X-ray taken from someone with myeloma?
Bone lesions
what is the treatment for asymptomatic myeloma?
active watch + wait
Describe the treatment for symptomatic myeloma
Chemo, analgesia and bisphosphonates.
radiotherapy and bone marrow transplant can also be done
What is a lymphoma?
malignant growth of WBC's predominantly in the lymph nodes
Athough predominantly in the lymph modes, lymphoma is systemic. What other organs might it effect?
1. Blood
2. Liver
3. Spleen
4. Bone marrow
Give 4 risk factors for lymphoma
1. Primary immunodeficiency (syndromes)
2. Secondary immunodeficiency (e g. HIV)
3. Infection
4. Autoimmune disorders e.g. RA
Give 4 symptoms of lymphoma
1. Enlarged lymph nodes in arm/neck
2. Symptoms of compression symptoms
3. General systemic 'B' symptoms - weight loss, night sweats, fever
4. Liver and spleen enlargement
What investigations might you do in someone who you suspect has lymphoma?
1. Blood film
2. Bone marrow biopsy
3. Lymph node biopsy
4. Immunophenotyping
5. Cytogenetics
What are the 2 sub-types of lymphoma?
Non/Hodgkins
What are the symptoms of Hodgkins lymphoma?
1. Painless lymphadenopathy
2. Presence of 'B' symptoms - fever, night sweats, weight loss
What is needed for a diagnosis of Hodgkins lymphoma?
Presence of Reed-sternberg cells
What are the possible complications of treatment for Hodgkins lymphoma?
1. Secondary malignancies
2. IHD
3. Infertility
4. Nausea
5. Alopecia
Describe low grade/indolent non-hodgkins lymphoma
slow growing, advanced at presentation, often incurable - median survival 10 years
Describe high grade non-hodgkins lymphoma
aggressive. Nodal presentation, patient unwell. Often incurable
What is leukaemia?
malignant proliferation of haemopoietic stem calls
4 sub-types of leukaemia
1. AML- acute myeloid leukaemia
2. CML - chronic myeloid leukaemia
3. ALL- acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
4. CLL- chronic lymphoblastic leukaemia
What is acute lymphoblastic leukaemia?
Neoplastic proliferation of blast cells
What can increase the risk of developing AML?
1. Preceding haematological disorders
2. Prior chemotherapy
3. Exposure to ionising radiation
Give 5 symptoms of leukaemia
1. Anaemia
2. Infection
3. Bleeding
4. Hepatomegaly
5. Splenomegaly
Why are anaemia, infection and bleeding symptoms of Leukaemia?
due to bone marrow failure
Why are hepatomegaly and splenomegaly symptoms of leukaemia?
because of tissue infiltration
What investigations might you do on someone you suspect has Leukaemia?
1. Blood film
2. Bone marrow biopsy
3. Lymph node biopsy
4. Immunophenotyping
5. Cytogenetics
Treatment for AML
1. Supportive care
2. Chemotherapy (palliative - local)
3. Bone marrow transplant
What is CML?
chronic myeloid leukemia - uncontrolled clonal proliferation of basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils
what would the FBC from someone with CML look like?
High WBC's
What is ALL?
acute lymphoid leukemia - uncontrolled proliferation of immature lymphoblast calls
What is the treatment for ALL?
CNS directed therapy and stem cell transplant
What is CLL?
chronic lymphoid leukemia - proliferation of B lymphocytes leads to accumulation of mature B calls that have escaped apoptosis
3 broad categories of RBC disorders
1. Haemoglobinopathies
2. Membranopathies
3. Enzymopathies
What is normal adult Hb made of?
2 alpha and 2 beta chains
What is foetal Hb made of?
2 alpha and 2 gamma chains
What is sickle cell disease?
A haemoglobin disorder of quality - HbS polymerises → sickle shaped RBC
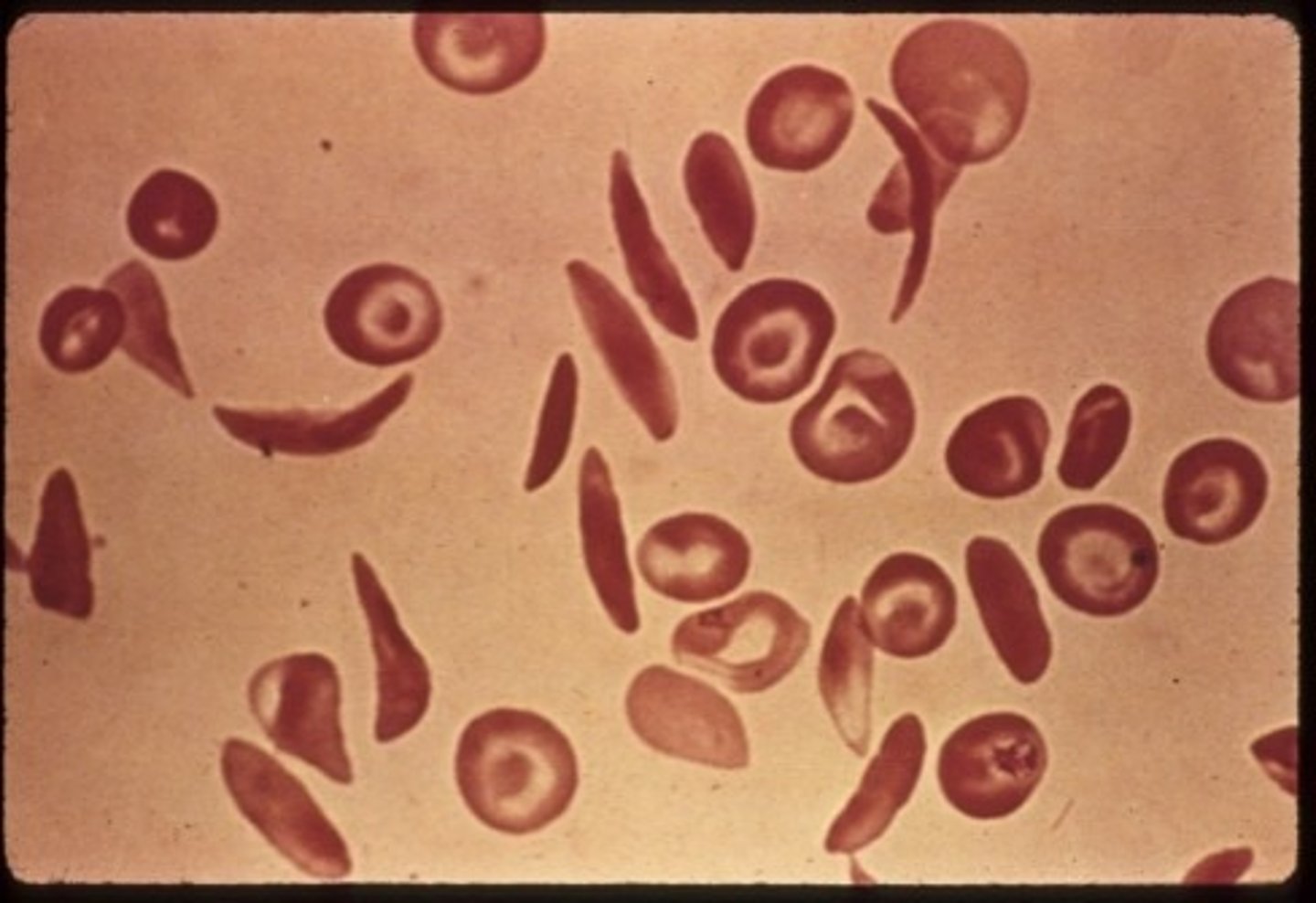
What is an advantage of being a carrier of sickle cell?
offers protection against falciparum malaria
Inheritance pattern of sickle cell
autosomal recessive -homozygous SS
Offspring have 25% chance of affectation, 50% chance of carrier
How long do sickle cells last for?
5-10 days → hence why it is described as haemolytic
Give 4 acute complications of sickle cell disease
1. Very painful crisis
2. stroke in children
3. Cognitive impairment
4. Infections
Treatment for sickle cell
1. Transfusion
2. Hydroxycarbamide
3. Stem cell transplant
what is thalassaemia?
Hb disorder of quantity. Reduced synthesis of one or more globin chains leading to a reduction in Hb → anaemia
What is the significance of parvovirus for someone with sickle cell?
common infection in childen, leads to deceased RBC production → bad as they already have reduced RBC lifespan
What forms the differential diagnosis for a DVT?
Cellulitis
What are enzymopathies?
enzyme deficiencies lead to a shortened RBC Lifespan
What is anaemia?
decrease in the amount of Hb in the blood below the reference range
What organs are responsible for removal of RBC's?
1. Spleen
2. Liver
3. Bone marrow
4. Blood loss
What is microcytic anaemia?
Any type of anaemia characterised by abnormally small erythrocytes, because they don't have enough Hb
Give 3 causes of microcytic anaemia
1. Iron deficiency
2. Anaemia of chronic disease
3. Thalassaemia
What is thalassaemia?
inherited blood disorders characterised by deceased Hb production
what is normocytic anaemia?
fewer RBC than normal, and they don't have the normal amount of Hb
Give 3 causes of normocytic anaemia
1. Acute blood loss
2. Anaemia of chronic disease
3. Combined haematinic deficiency
What is macrocytic anaemia?
bone marrow produces abnormally large RBC
Give 3 causes of macrocytic anaemia
1. B12/ folate deficiency
2. Alcohol excess /liver disease
3. Hypothyroid
Give 5 potential causes of iron deficiency
1. Blood loss
2. Poor absorption
3. Decreased intake in diet
4. Hook worm!
5. Breastfeeding, low iron in breast milk
Treatment for anaemia
treat the underlying cause
What is polycythaemia?
too many RBCs - increase in Hb
What hormone is responsible for regulating RBC production?
erythropoietin
Name a primary cause of polycythaemia
polycythaemia rubra vera- over reactive bone marrow
Give 3 secondary causes of polycythaemia
1. Heavy smoking
2. Lung disease
3. cyanotic heart disease
4. High altitude
What is neutrophilia?
too many neutrophilia
Give 3 causes of neutrophilia
1. Infection
2. Inflammation
3. CML
4. Cancer
What is lymphocytosis?
too many lymphocytes
Give 3 causes of lymphocytosis
1. Viral infections
2. Inflammation
3. Malignancy
4. CLL
What is thrombocytopenia?
not enough platelets
What is thrombocytosis?
too many platelets
What is neutropenia?
not enough neutrophils
What is the major risk associated with being neutropenic?
susceptible to infection
Give 3 causes of neutropenia
1. Marrow failure
2. Marrow infiltration
3. Marrow toxicity
Where are platelets produced?
bone marrow
What hormone regulates platelet production?
thrombopoietin - produced mainly in the liver
platelet lifespan
7-10 days
Organ responsible for platelet removal?
spleen
what can cause deceased platelet production?
1. congenital causes
2. Infiltration of bone marrow e.g. leukaemia
3. Alcohol
4. Infection e.g. HIV/TB
Give 3 symptoms of platelet dysfunction
1. Mucosal bleeding
2. Easy bruising
3. Petechiae/purpura
Describe the presentation of spinal cord compression
1. Back pain
2. Weakness in legs
3. Inability to control bladder
4. Spastic paresis
5. Sensory level
What is tumour lysis syndrome?
breakdown of malignant calls→ content release can cause electrolyte disturbances
What is hyperviscosity syndrome?
increase in blood viscosity usually due to high levels of immunoglobulins
Describe the presentation of hyperviscosity syndrome
1. Mucosal bleeding
2. Visual change
3. Neurological disorders
4. Breathlessness
5. Fatigue
What do you avoid in the treatment of hyperviscosity syndrome?
blood transfusion - do so cautiously as it could increase serum viscosity
Give 5 signs/symptoms of hypercalcaemia
1. Confusion
2. Bone pain
3. Constipation
4. Nausea
5. Abdominal pain
What might you see on an ECG taken from someone with hypercalcaemia?
shortened QT interval
hypercalcaemia= risk of MI
Treatment for hypercalcaemia
IV hydration and bisphosphonates
How is myeloma bone disease usually assessed?
X-ray
What clotting factors depend on vitamin k?
2, 7, 9, 10
Give 4 symptoms of ALL
1. Bone pain
2. Recurrent infections (neutropenia)
3. Pale and tired (anaemia)
4. Bruising (low platelets)
Is ALL more common in adults or children?
children
Give 3 signs of haemolytic anaemia
1. Pallor
2. Jaundice
3. Splenomegaly
Give 3 things that can cause coagulation disorders
1. Vitamin K deficiency
2. Liver disease
3. Congenital e.g. haemophilia
How does warfarin work?
antagonises vitamin k and so you get a reduction in clotting factors 2,7,9 and 10
How does Heparin work?
activates antithrombin which then inhibits thrombin and factor Xa
Give 7 risk factors for DVT
1. Increasing age
2. Obesity
3. Pregnancy
4. OCP (hyper-coagulability)
5. Major surgery
6. Immobility
7. Past DVT
Give 3 symptoms of DVT
unilateral warm, tender, painful swollen leg
Where would you normally take a bone marrow biopsy from?
posterior iliac crest