IB HOTA Topic 8: United States' Civil War (1840-1877)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
US Civil War
(1861- 1865) The violent conflict between Union and Confederate forces over states' rights and slavery.

Cotton Economy
Southern economy depended on slave labor where cash crops like cotton and tobacco were grown on plantations

Slave Resistance
Labor Slowdowns, Breaking Tools, Running Away, Underground Railroad, Songs as communication, playing dumb to get out of working

Argument for slavery
The South thought the North was trying to turn the south into an agricultural colony through economic legislation controlled by a northern congress (In other words, they needed to rely on slavery in order to make an economic profit)

Argument against slavery
Radical view that departs from Locke, War and conquest do not provide the right to kill or enslave the defeated, people own themselves, and no one else, and the US would be stronger united

origins of the US civil war
Souuthern states wanted to exit the union if it meant that they could no longer use slavery for economic purposes
Nullification Crisis
A sectional crisis during the presidency of Andrew Jackson created by the Ordinance of Nullification, an attempt by the state of South Carolina to nullify a federal law - the tariff of 1828 - passed by the United States Congress. (Southerners favored freedom of trade & believed in the authority of states over the fed. gov.)
Sectionalism
Loyalty to one's own region of the country, rather than to the nation as a whole (Different parts of the country developing unique and separate cultures)
Economic differences between the North and South
The North had a diverse economy (many industries)
and abolished slavery. The South had slaves, plantations and mostly grew cotton and tobacco.

Reasons for Westward Expansion
The revolution in transportation and communication, a growing population, and a booming economy propelled the western surge, and the cost of westward expansion was bloody wars with both the native populations and the Spanish in addition to the conflict over where to permit slavery.
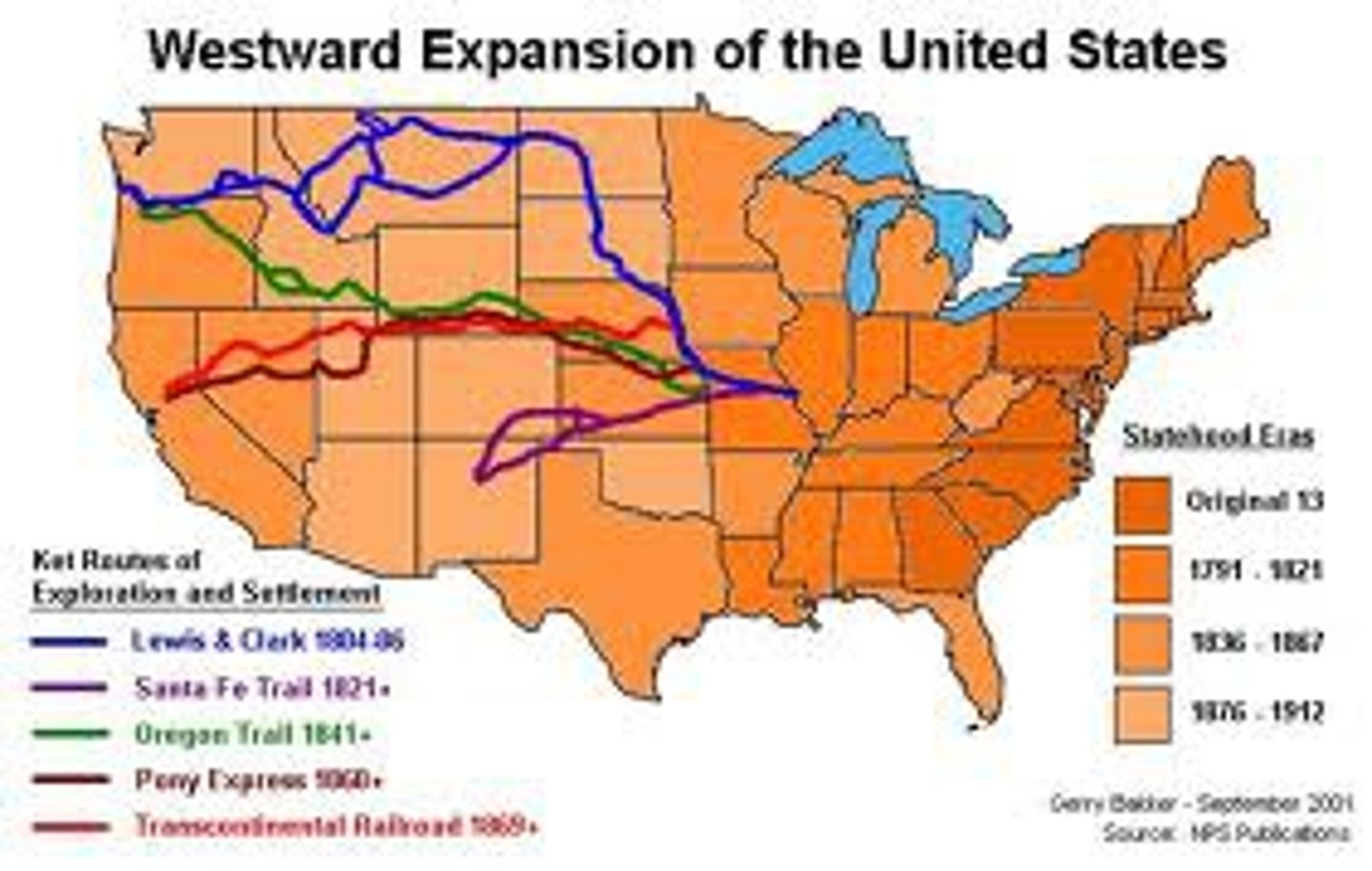
Effects of Western Expansion
Slavery needed to be spread equally across the nation so that southern states are not a minority when it comes to the topic, led to compromise of 1850
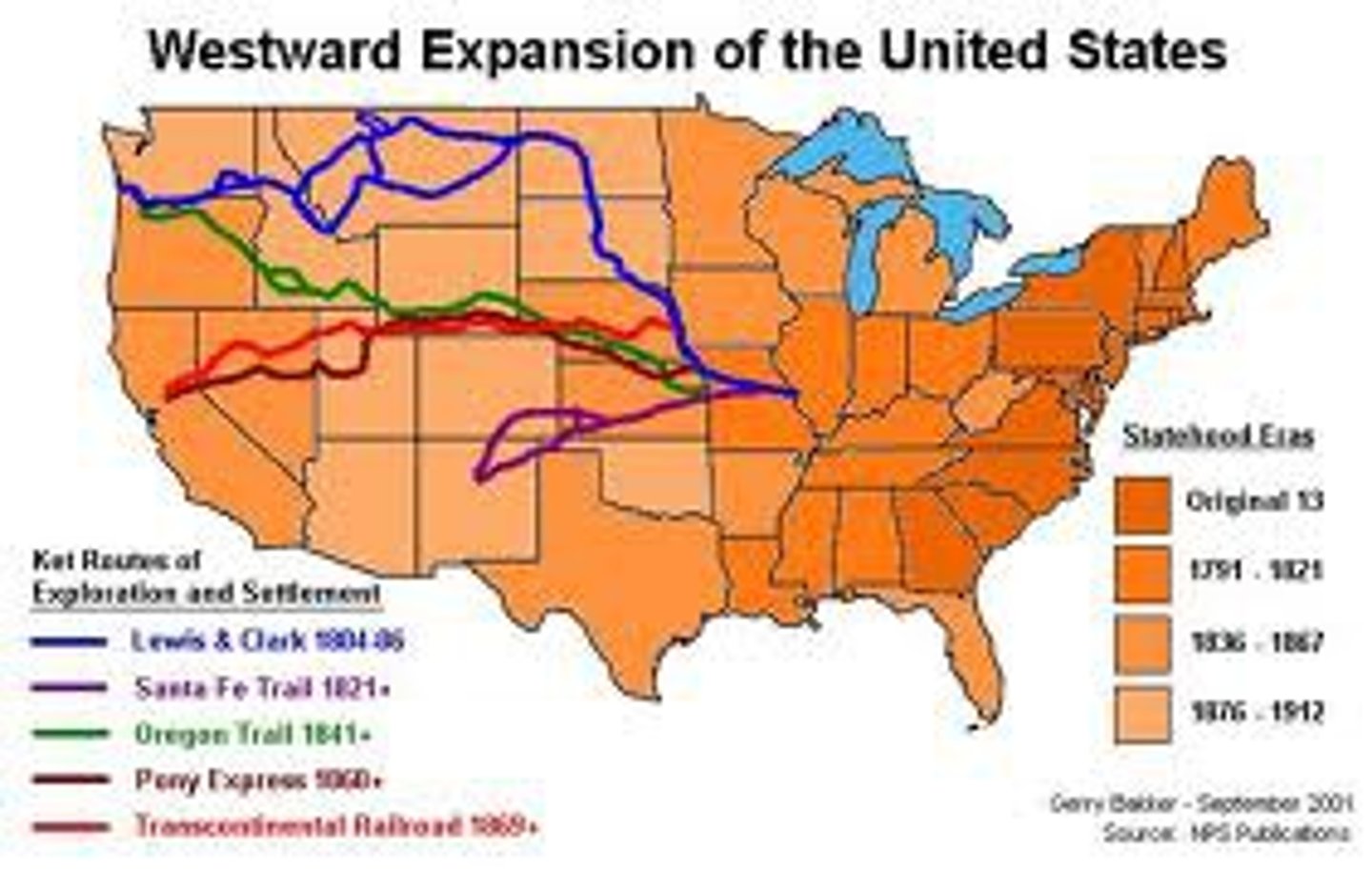
Comprimise of 1850
designed to cool heated north-south tensions. California was admitted as a free state, Texas got cash, but lost land, due to pop. sovereignty, New Mexico and Utah were open to slavery, and a fugitive slave law was strengthened. clearly, senate favored North
Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858)
Senate Debate, Lincoln forced Douglas to debate issue of slavery, Douglas supported pop-sovereignty, Lincoln asserted that slavery should not spread to territories, Lincoln emerged as strong Republican candidate

presidential election of 1860
a presidential election that pitted Abraham Lincoln (Republican) against Stephen A. Douglas (Northern Democrat), John Breckinridge (Southern Democrat), and John Bell (Constitutional Union Party); the main issue of the election was the debate over the expansion of slavery; Lincoln won and South Carolina seceded

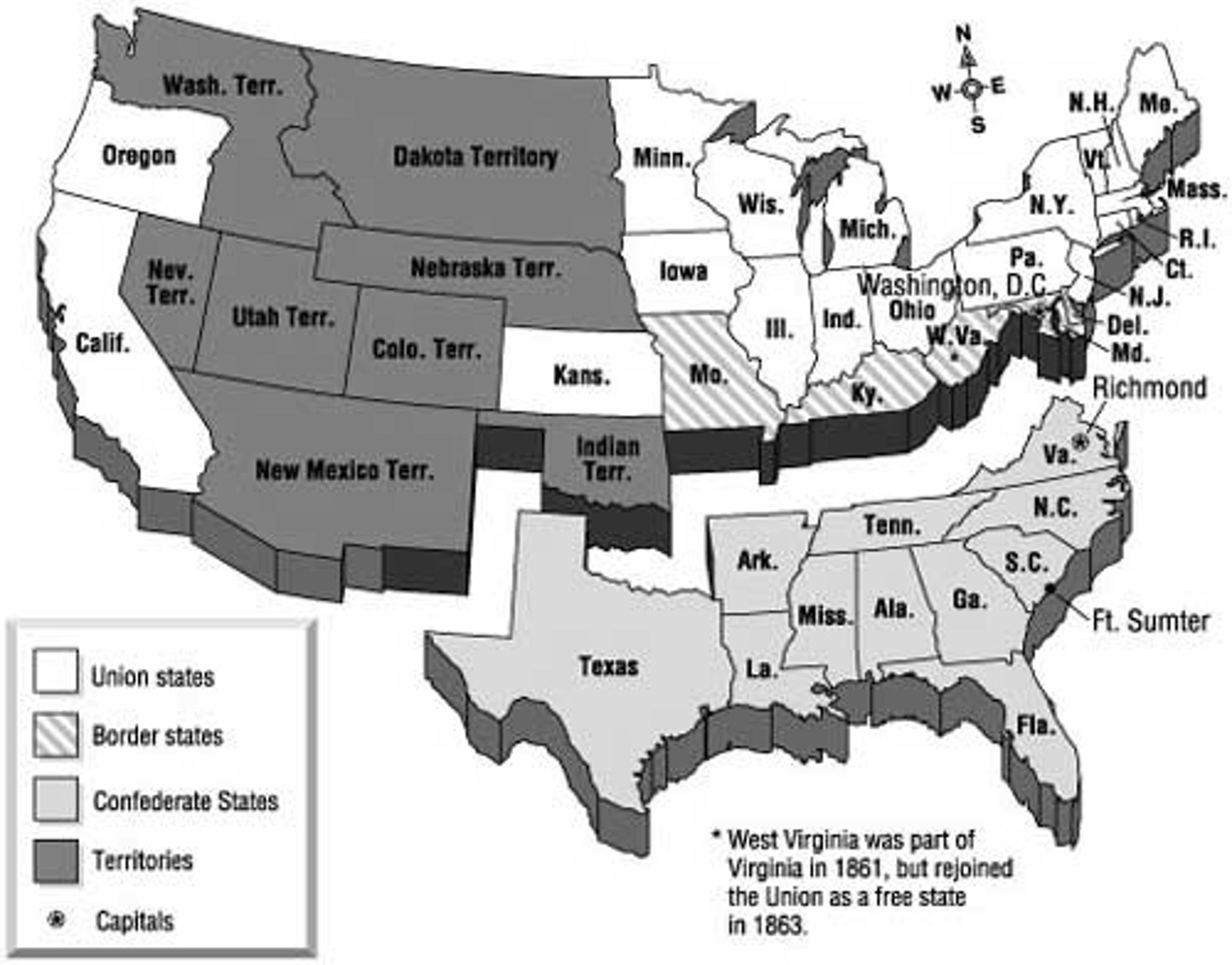
Significant military battles of Civil War
Fort Sumter 1861, 1st Bull Run 1861, Gettysburg 1863, Vicksburg 1863, Sherman's march to the sea 1864

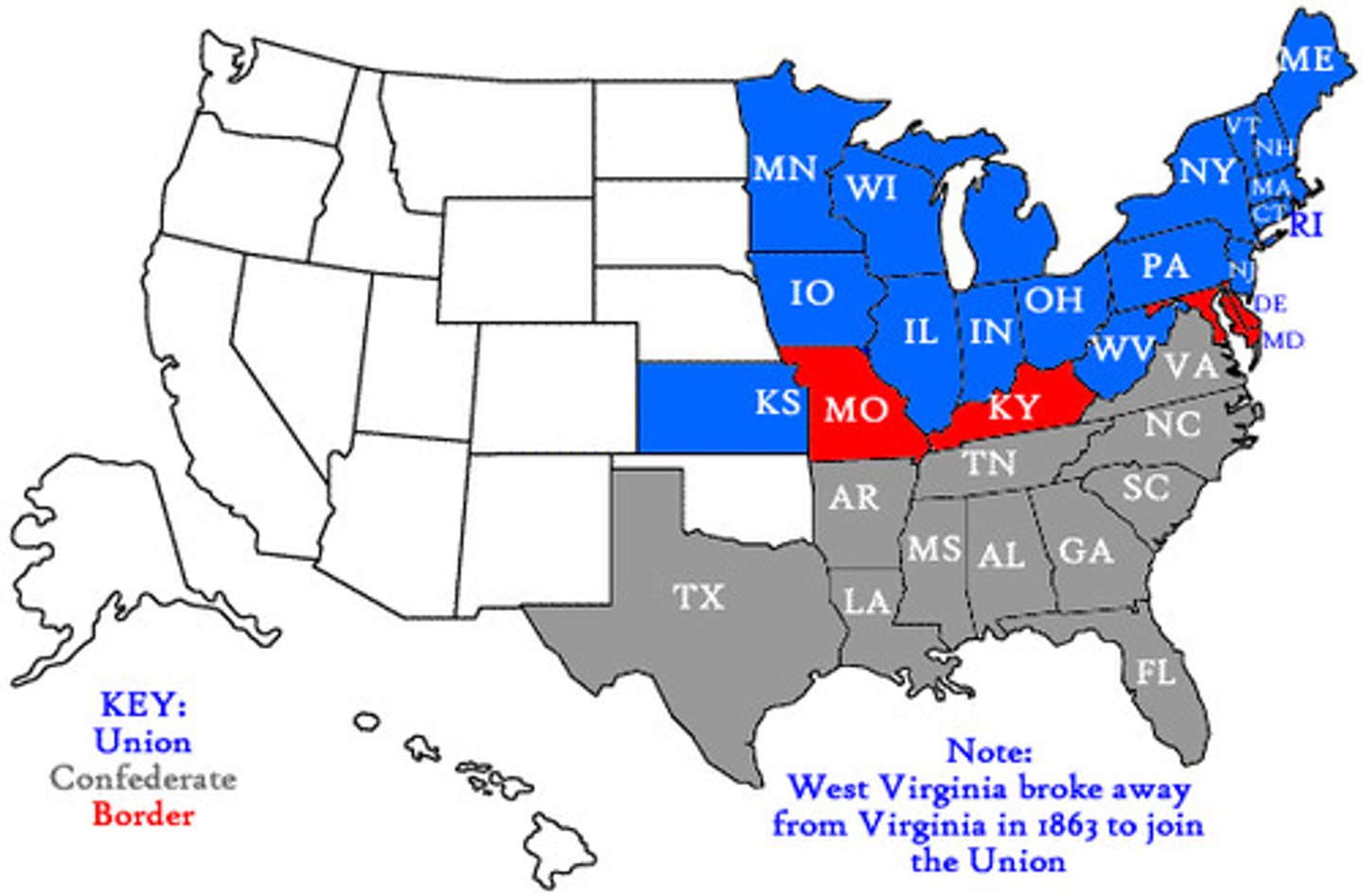
Union vs Confederate strength and weaknesses
Union had more territory, larger population, more factory workers, more railroad track, and gold
Robert E. Lee
Confederate general who had opposed secession but did not believe the Union should be held together by force

Role of Lincoln in Civil War
Lincoln was on the side of uniting the country, he wanted the nation to stay united because they're stronger that way, but he also believed that slaves should be freed

Emancipation Proclamation
(1863) Issued by Abraham Lincoln on September 22, 1862 it declared that all slaves in the confederate states would be free

Factors affecting the outcome of the Civil War
The northerners had more resources and infrastructure, so they had an advantage

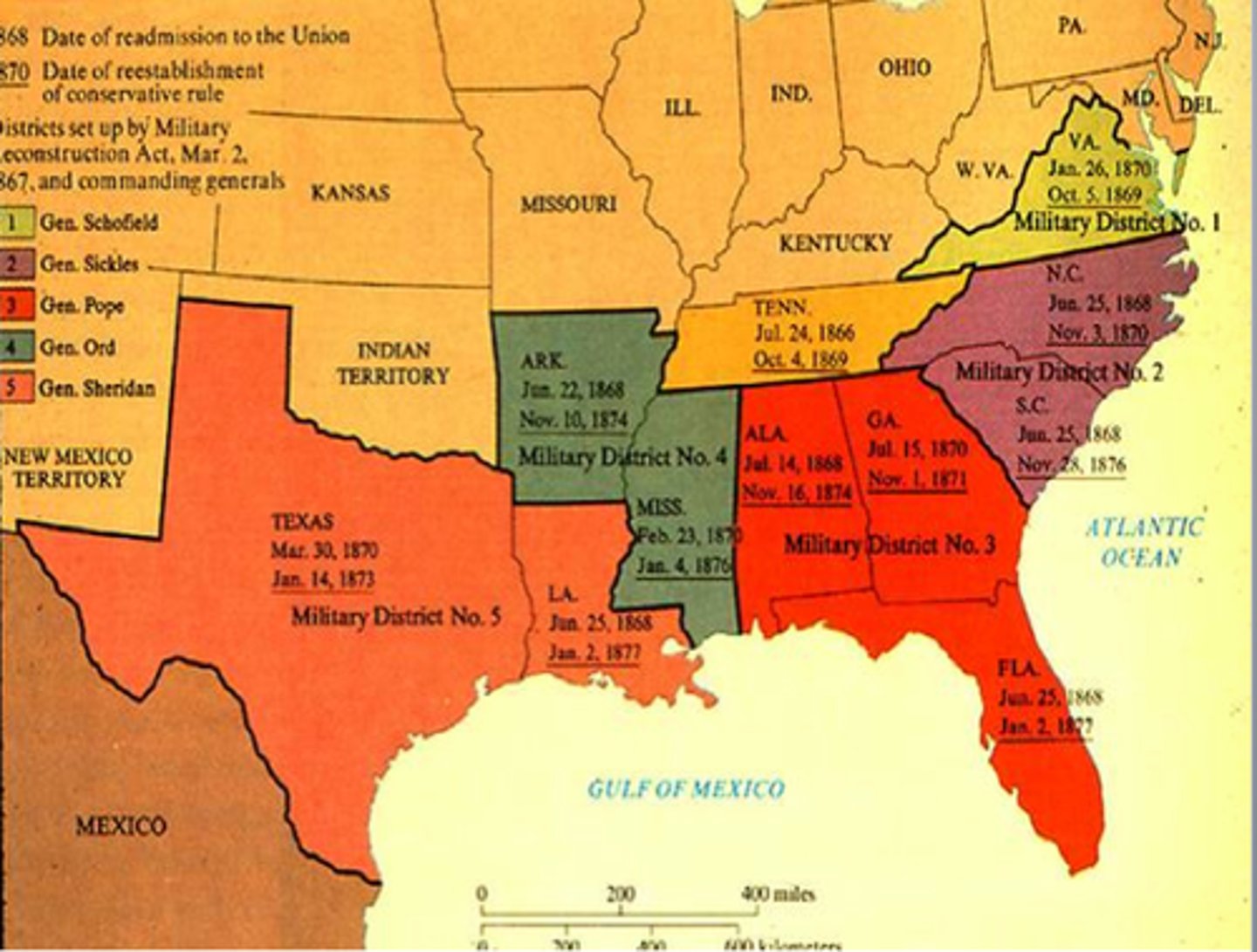
Reconstuction
the reorganization and rebuilding of the former Confederate states after the Civil War (late 1860s)
13th Amendment (1865)
Abolition of slavery w/o compensation for slave-owners

Southern Resistance to Reconstruction
Southern opponents of Reconstruction to undermine republican rule - Klu Klux Klan
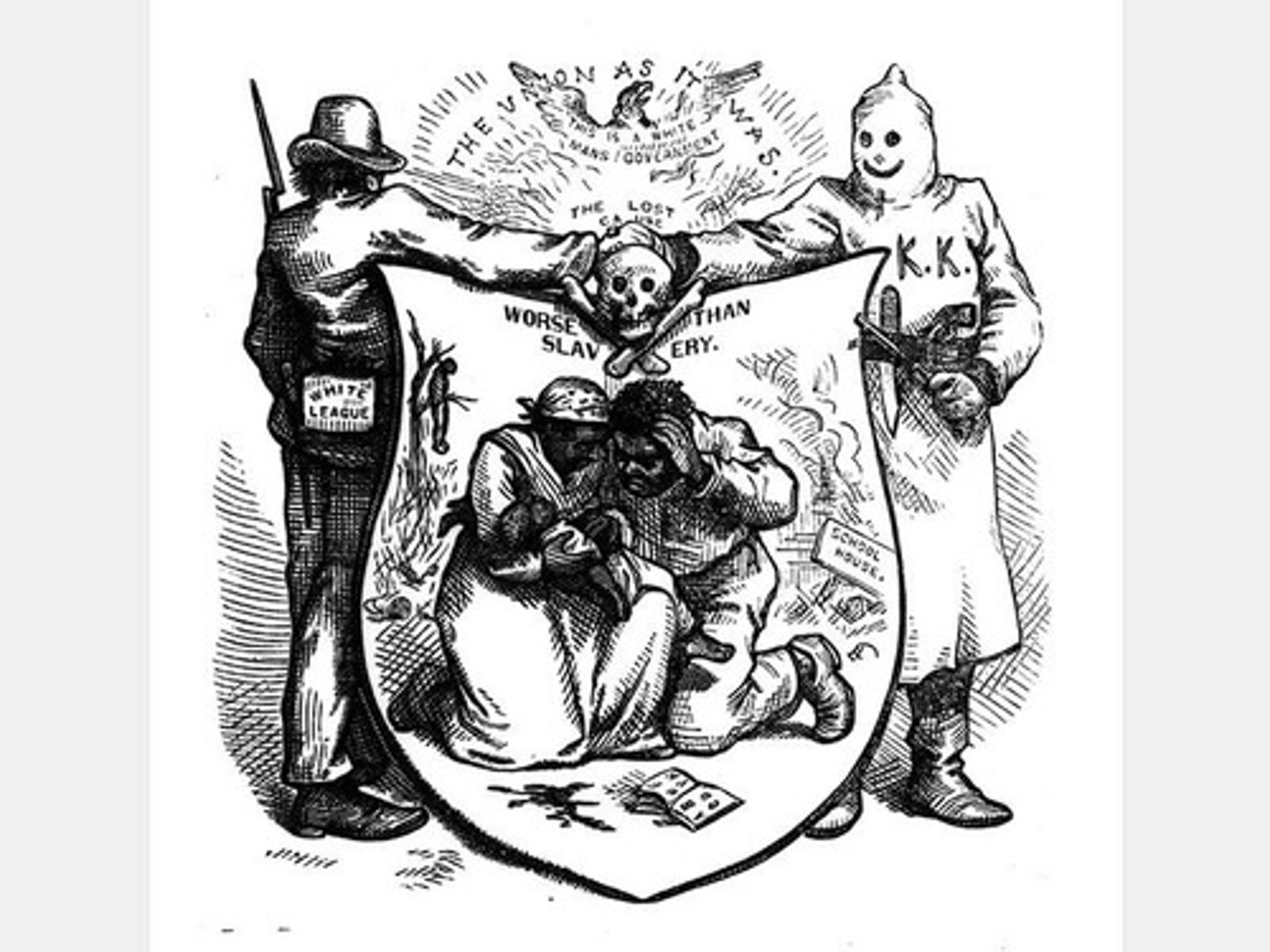

Reconstruction
the period after the Civil War in the United States when the southern states were reorganized and reintegrated into the Union

Legal issues of African Americans in the New South
Voter suppression, poll tax, literacy tests, grandfather clause

Black Codes (1865-1866)
Laws passed throughout the South to restrict the rights of emancipated blacks, particularly with respect to negotiating labor contracts. Increased Northerners' criticisms of President Andrew Johnson's lenient Reconstruction policies.

Jim Crow Laws
Limited rights of blacks. Literacy tests, grandfather clauses and poll taxes limited black voting rights

Failures of Reconstruction
KKK, Black Codes, Radical Republicans had too much power, Weak Presidents, ineffective government, Freedmen's Bureau ended, racism, Lincoln died, expensive

voter suppression
a strategy to influence the outcome of an election by discouraging or preventing people from exercising the right to vote
