Organic Chem
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Number of bonds per element
HONC
H - 1
O - 2
N - 3
C - 4
Hydrocarbon
organic molecule composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms
saturated alkanes
have single bonds as the maximum number of atoms per C atom (4)
Homologous series
Must be in same family of organic compounds
each successive member of the group must change by the same unit
General formula of Alkanes
CnH2n+2
Molecular formula
number of each molecule

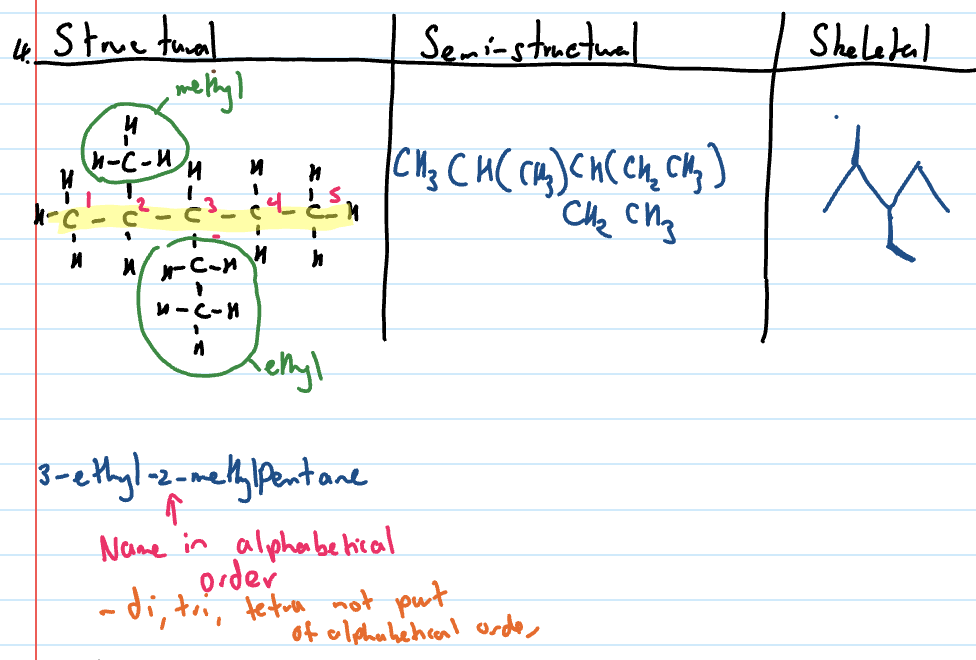
Structural formula
shows all bonds between atoms

Semi-structural formula
does not show single bonds but can show C to C double bonds
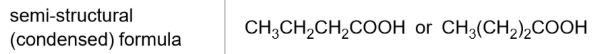
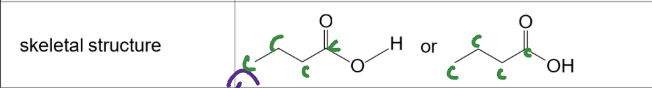
skeletal formula
does not show any atoms unless part of a functional group
never shows carbons
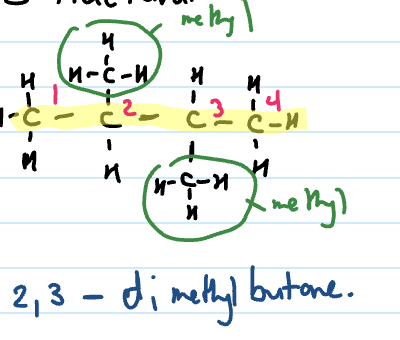
Naming branched chain alkanes
Identify the longest chain
Identify and name side/branched chains (named at front)
Identify position of side chain. Number the carbons from end that gives side chain the lowest number. This is written at front.
Draw structural formula of branched chain alkanes
Draw the number of carbons on parent chain
Identify the position of side chain and draw carbons of the side chain
Add necessary hydrogens
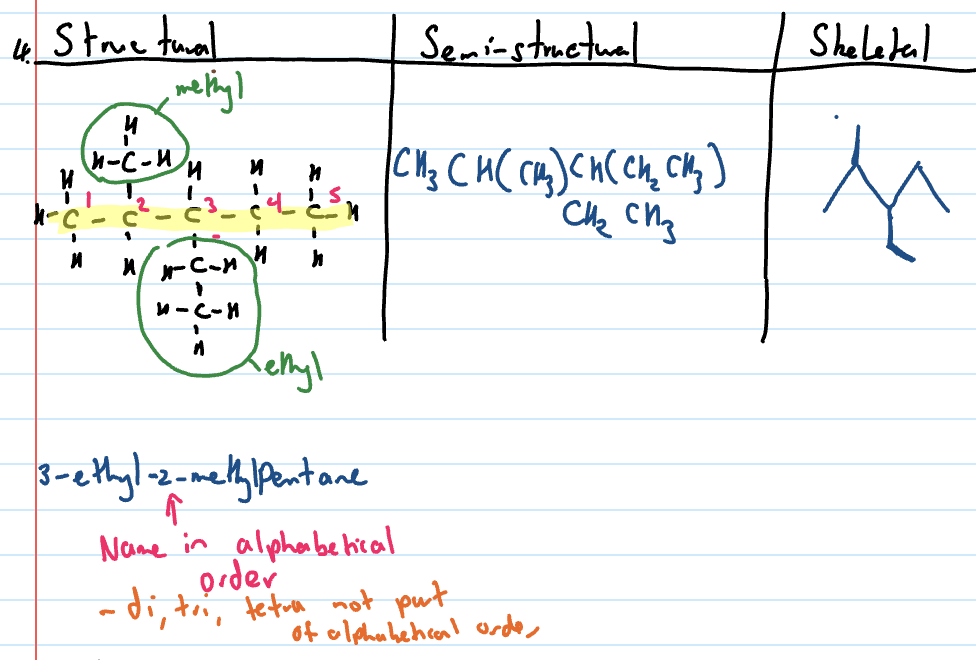
Draw semi-structural formula
Draw structural formula
Side chains will be in brackets
Alkenes
Hydrocarbons with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds and are unsaturated (carbons that form double bonds are not bonded to the maximum number of atoms)
General formula of alkenes
CnH2n
Naming branched chain alkenes
Identify longest chain that contains the C to C double bond (position of double bond must be indicated)
Number the carbons starting from end that gives the double bond the lowest number
Identify side chain and indicate position of side chains
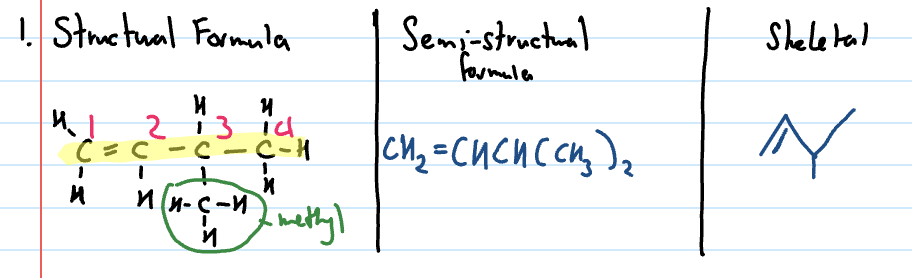
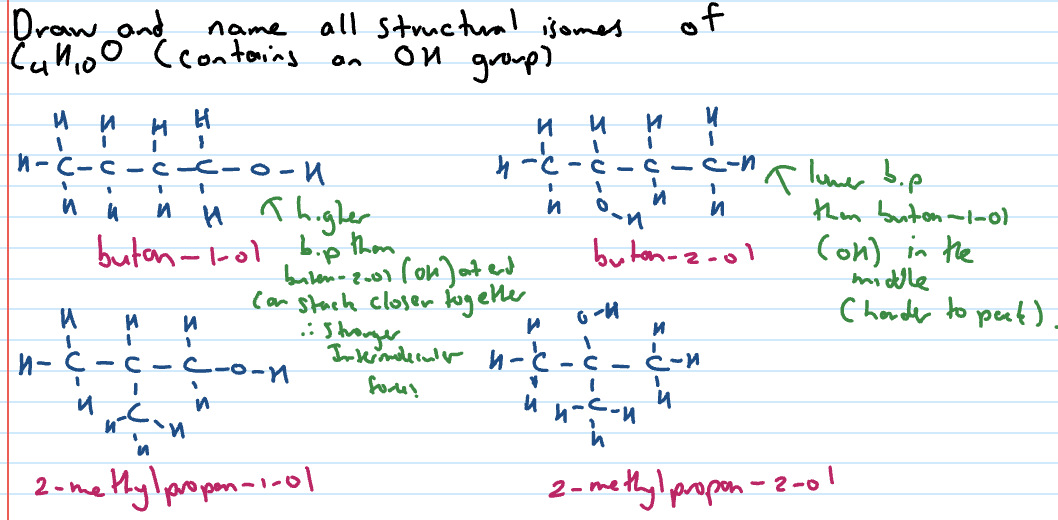
Structural isomers
Same molecular formula (same number and type of atoms) but different structural formula (arranged differently)
Also have different mass and names
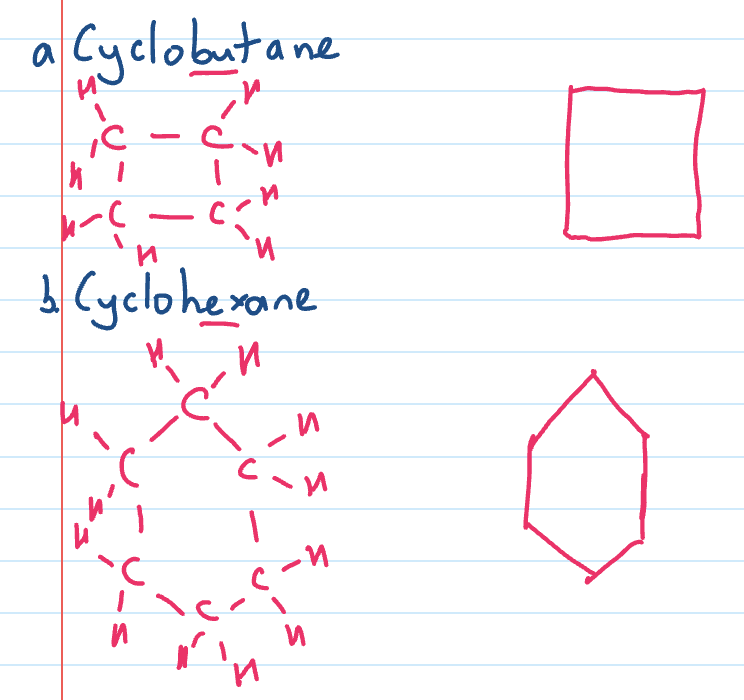
Cyclo alkanes
ring molecules based on an alkane
eg. cyclopropane and cyclopentane
often drawn more simply with just shapes as skeletal and each carbon is a corner
Benzene
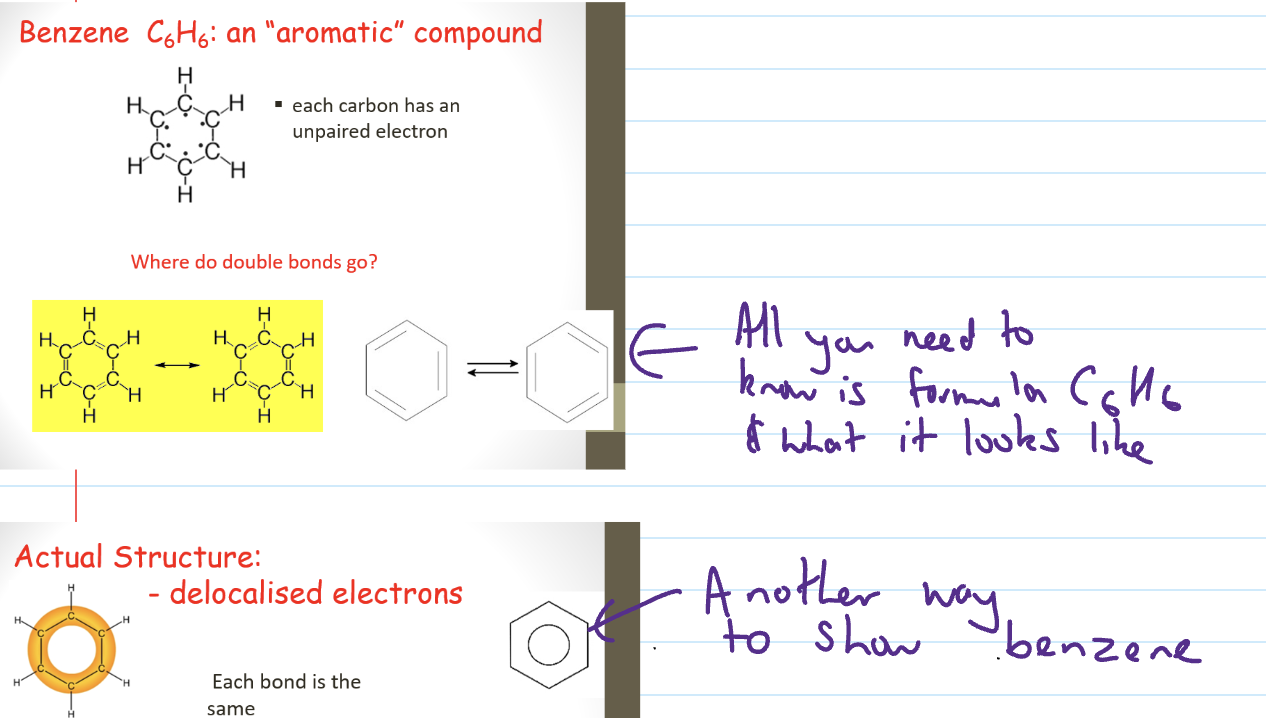
Functional Groups
A functional group is a specific atom or group of atoms within a molecule that gives the molecule characteristic chemical properties
alkanes, side chains NOT functional groups
Haloalkanes
Halo groups have same priority as side chain
When multiple, name halo groups in alphabetical order
In semi structural formula they are in brackets
Same priority as alkyl branches
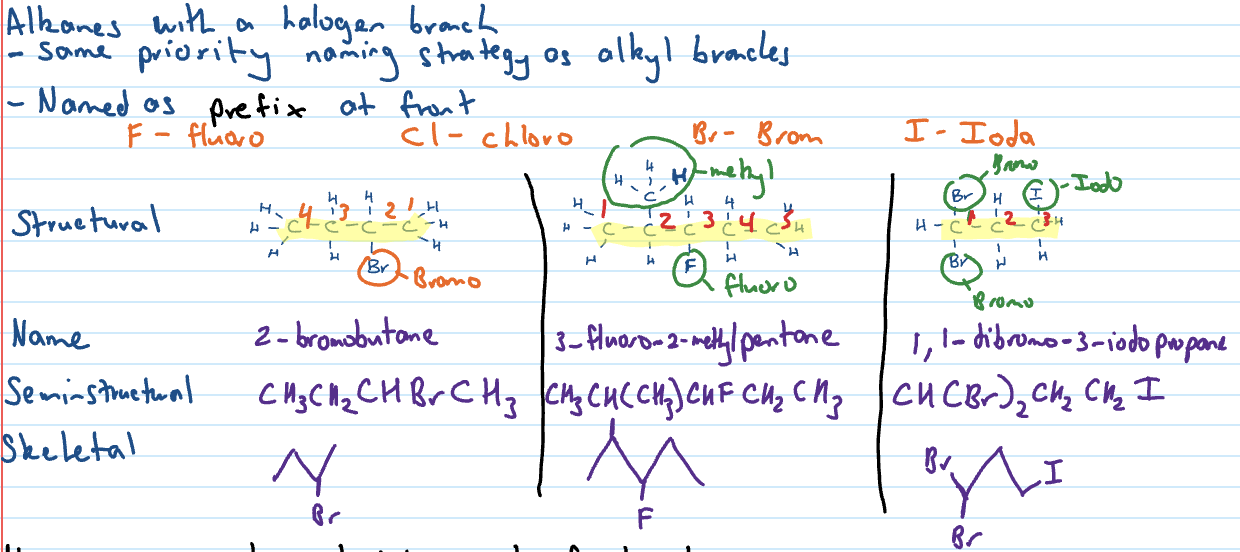
Naming compounds with single functional groups
Functional group has priority over any branches
Number from end closest to functional group
Use functional group suffix
If more than 3 carbons (4 for alkenes), include location
EXCEPT: carboxylic acids, esters and aldehydes which don’t need location
Alcohols
contain a hydroxyl functional group
-ol suffix
family: alcohol
functional group: hydroxyl
when not highest priority: hydroxy
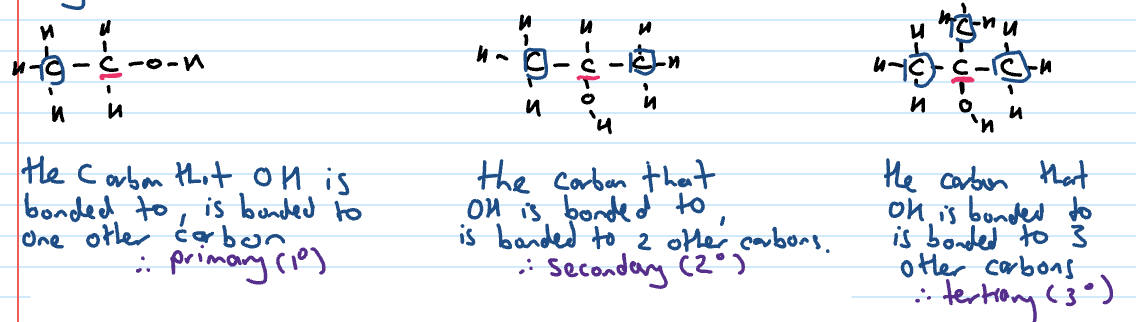
Types of alcohols
Primary, secondary or tertiary tells us how many C’s are bonded to the C that is bonded to the OH
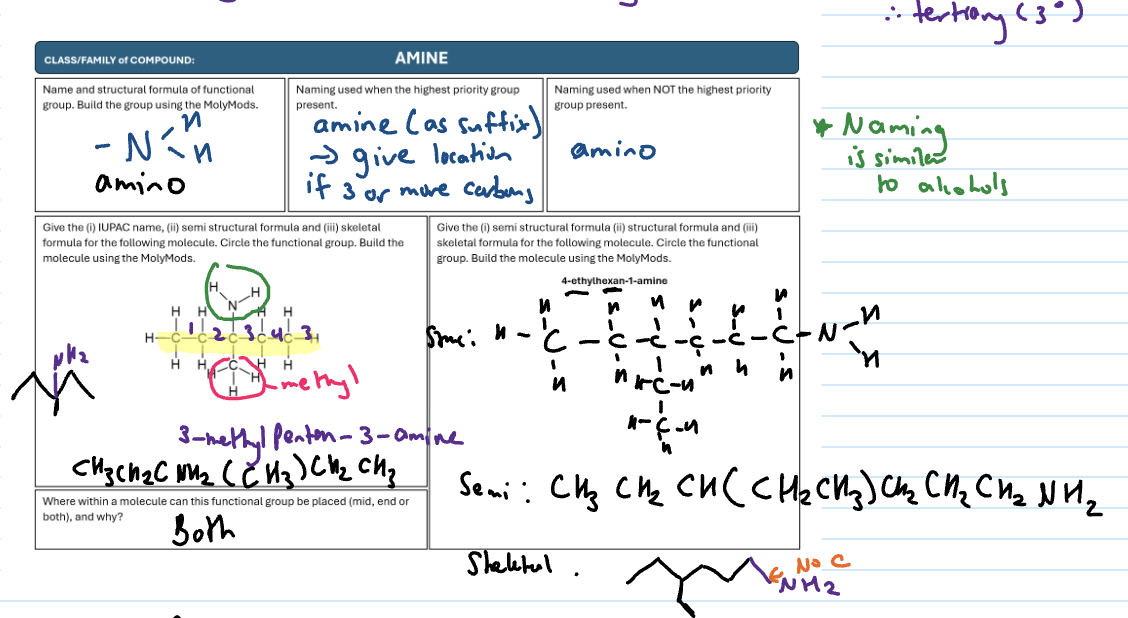
Amine
NH2 (amino) group
-amine suffix (give location)
“amino” is used when not the highest priority functional group
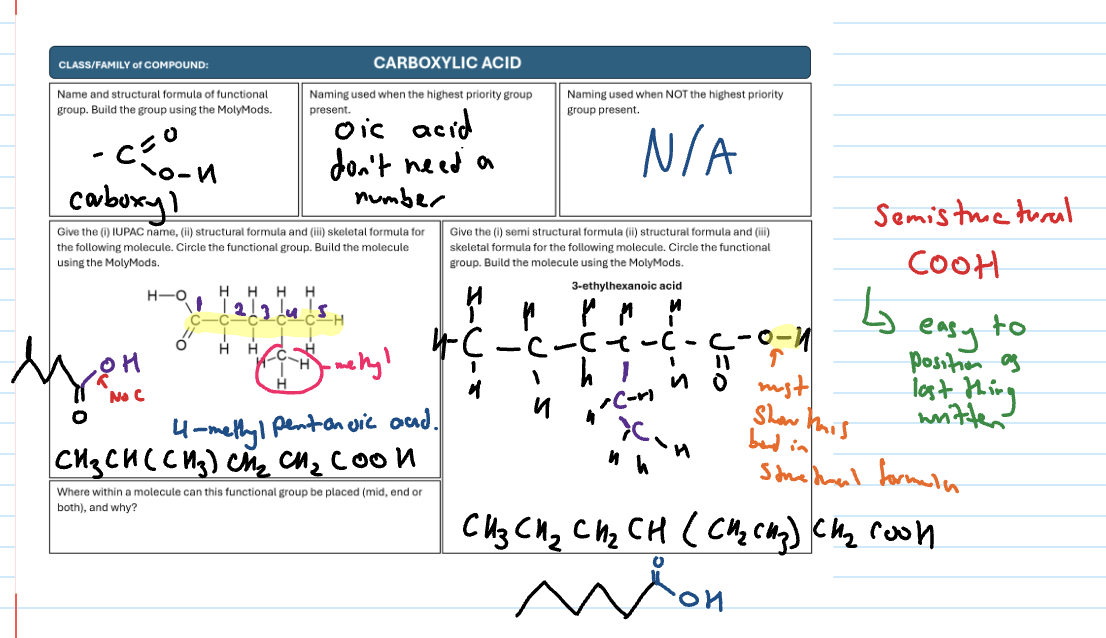
Carboxylic acid
have a carboxyl functional group
-COOH
-oic acid (don’t need location)
highest priority always
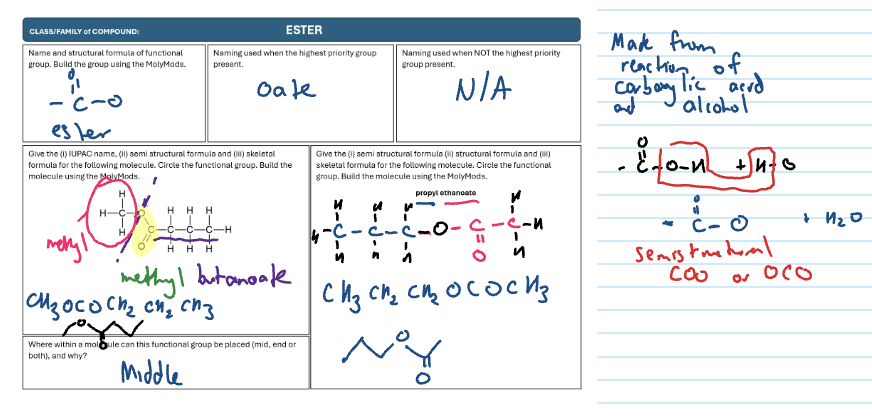
Ester
COO
-oate
“yl” comes from alcohol which is the one without double bond O
“oate” comes from carboxylic acid which is the one with double bond
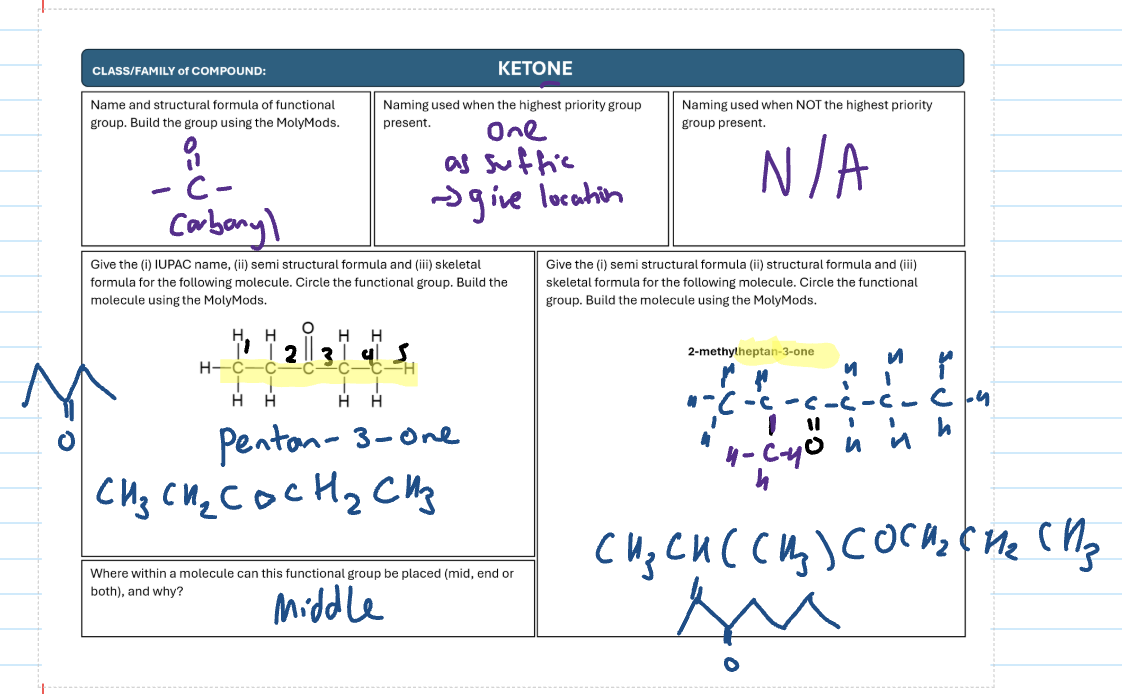
Ketone
CO
-one as suffix
always in middle
Aldehyde
-al as suffix (location not needed)
CHO (NOT COH)

Amides
primary = 2Hs to N
secondary = 1 H to N

Functional group priorities in the data booklet

Naming when multiple functional groups
Functional group with highest priority is assigned the lowest possible number and the suffix for the functional group is the same
the lowest priority functional group is indicated by prefix or alternative name
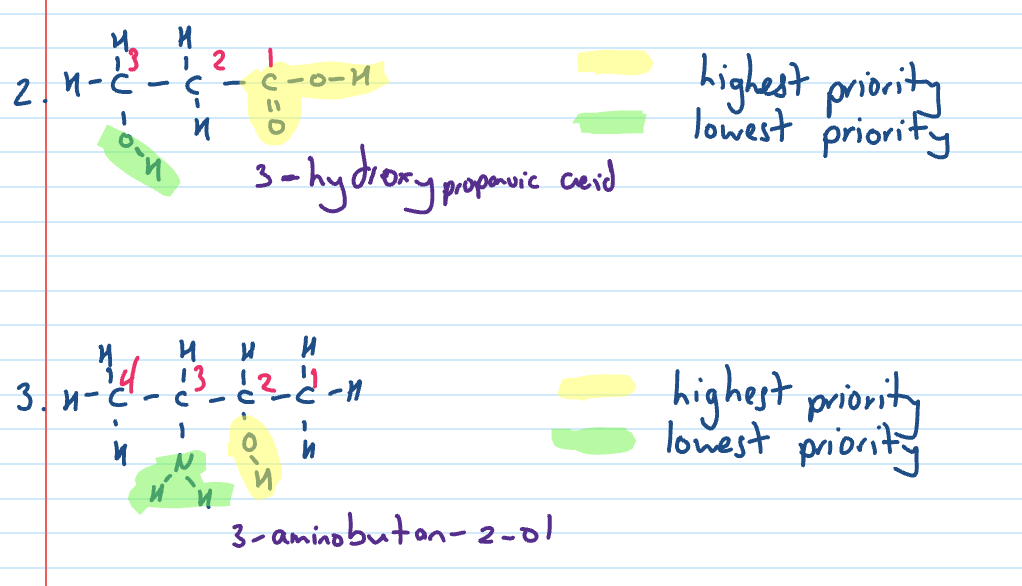
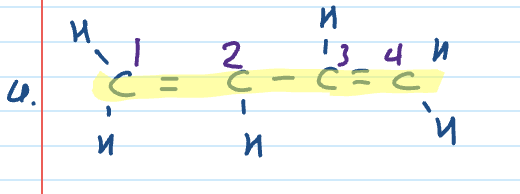
Name

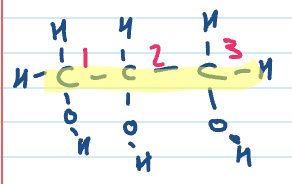
Name

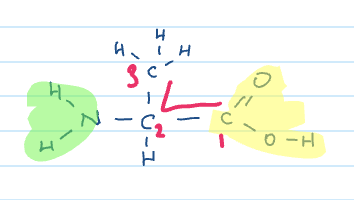
Name

If next consonant next to consonant
put in e

Properties of alkanes
-non-polar
-insoluble in water
-relatively malleable as dispersion forces are weak
-relatively low m.p and b.p
Melting and boiling point of alkanes
As no. of carbons increases, the melting and boiling point increases
Alkanes are non-polar so only have dispersion forces
As molecule gets larger, no. of electrons also increases so stronger dispersion forces
more heat energy is required to break them so higher b.p and m.p
Melting and boiling point between branched chain and straight chain alkanes
All alkanes are non polar so only dispersion forces
Straight chain alkanes can pack closely together so stronger dispersion forces and more heat energy required to break the forces, so higher m.p b.p
Branched chain alkanes cannot pack closely together so weaker dispersion forces and amount of heat energy required is less so lower b.p
Organic molecules in order of increasing b.p and m.p when similar in size
Alkenes and alkanes - non polar - dispersion forces only
Haloalkanes - polar - dipole-dipole
Alcohols - polar - H-bonding
Carboxylic acids - polar - H bonding
can also form dimers so stronger than alcohols
Intramolecular forces
bonds within molecule
covalent
strong
hard to break
Intermolecular forces
Between molecules
broken when states change
weak
Hydrogen bonding
occurs between polar molecules
strongest IMF
occurs when H is bonded to N,O,F covalently and directly
Dispersion forces
all molecules have dispersion forces
due to formation of instantaneous dipole
large molecules have greater d.f as they have larger molar mass, meaning more e-
m.p and d.p dispersion forces
Larger molecule, higher Mr, more e-, stronger d.f, more heat energy required to break, higher m.p and b.p
Who undergoes addition reactions?
alkenes
Addition reactions
C to C double bond in alkene breaks and more atoms can be added to the carbons with the double bond
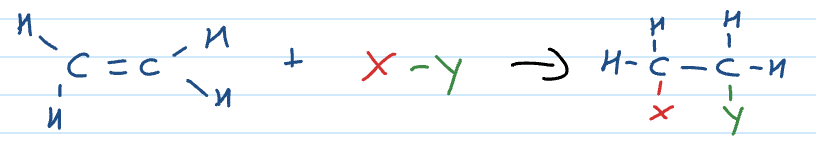
Addition reaction: adding halogens (eg. Cl2)
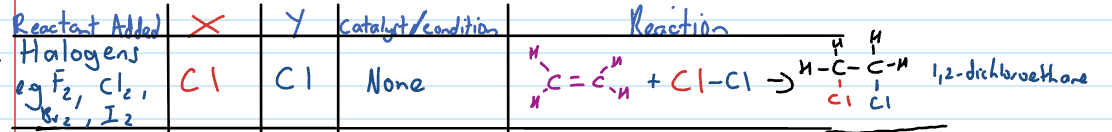
Addition reaction: adding hydrogen halides (eg. HCl or HF)

Addition reaction: adding hydrogen (H2)
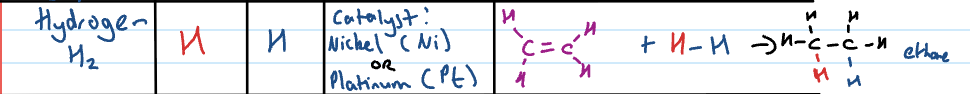
Addition reaction: water (H20)
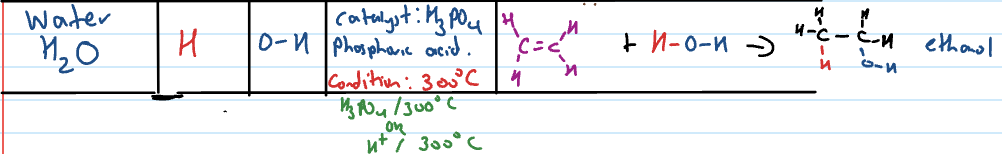
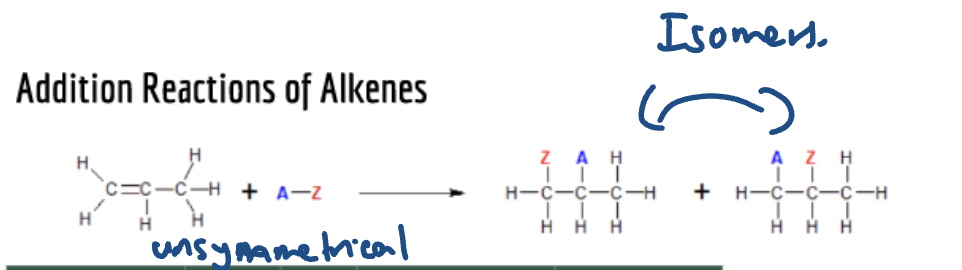
If alkene is unsymmetrical and 2 diff atoms/ groups added (eg. HCl, H20)
then you will get isomers
Substitution reaction
occurs when an atom or a functional group in a molecule is replaced or substituted by another atom or group
ALWAYS GET A SIDE PRODUCT
Substitution reactions of alkenes
Alkanes react with halogens
One H swaps places with a halogen atom (we only learn about ones at end)
CONDITION: REQUIRES UV LIGHT

Substitution reactions of haloalkanes
can occur with OH- base or ammonia (NH3)
Substitution reactions of haloalkanes with OH-
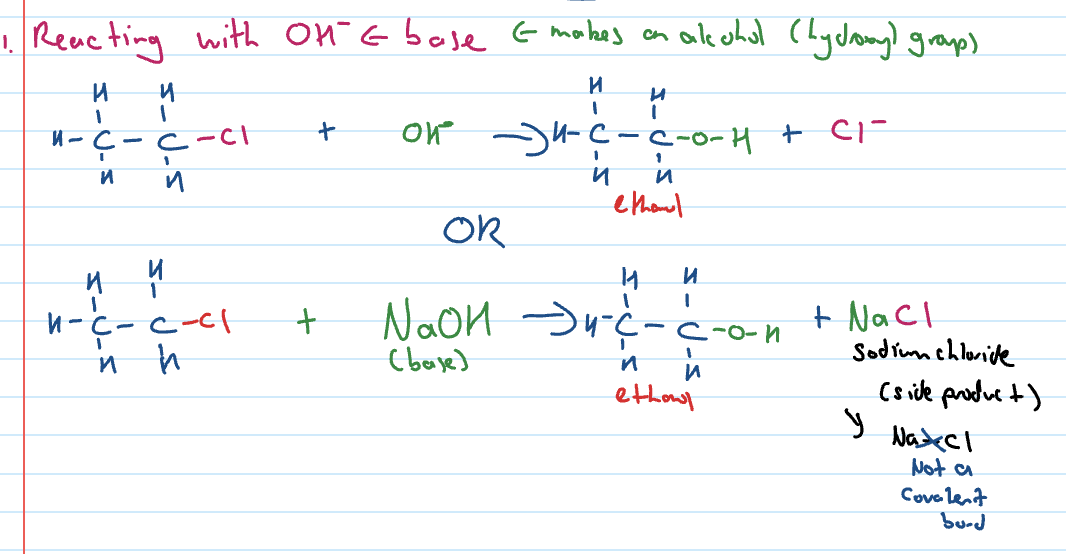
Substitution reactions of haloalkanes with ammonia (NH3)
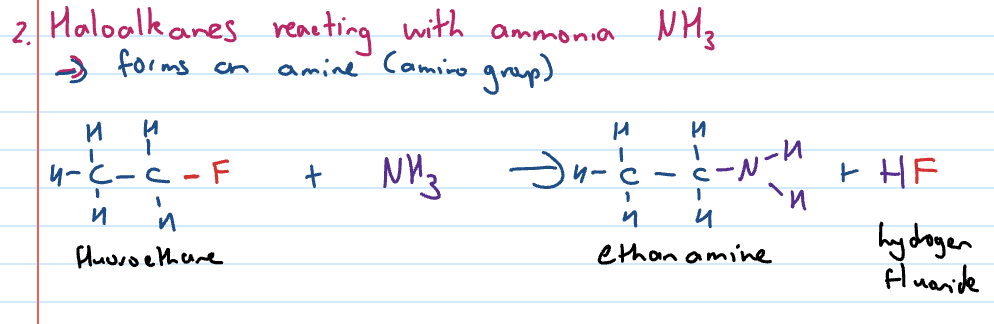
Oxidation reactions
Alcohols undergo oxidation reactions when they react with an oxidant
remember the gain of oxygen, loss of hydrogen part of oxidation
Oxidising agents for alcohol oxidation reactions
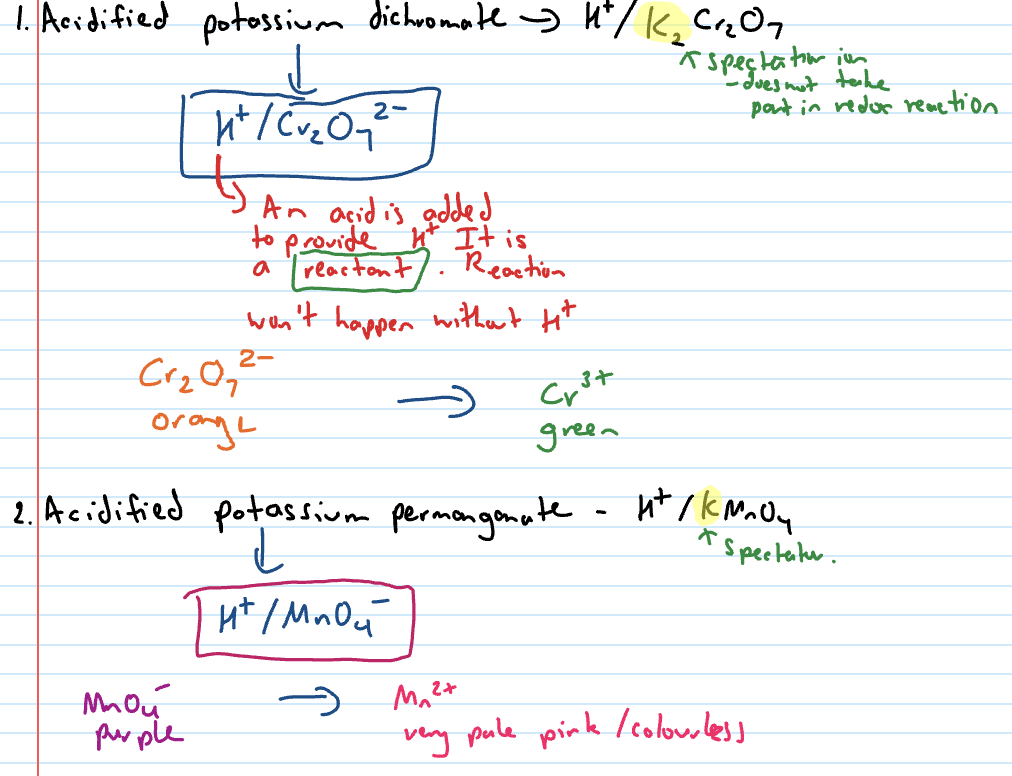
Oxidation of primary alcohols
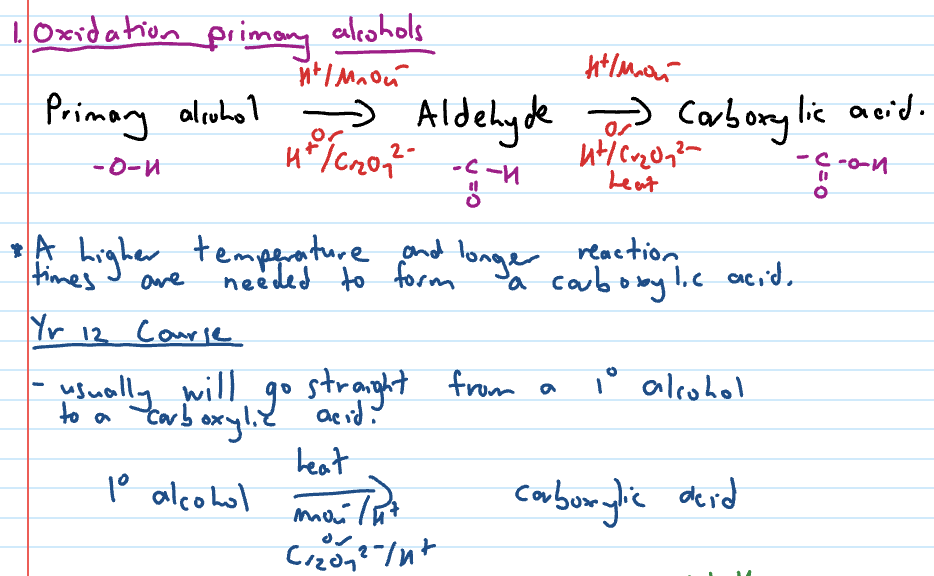
Oxidation of secondary alcohol
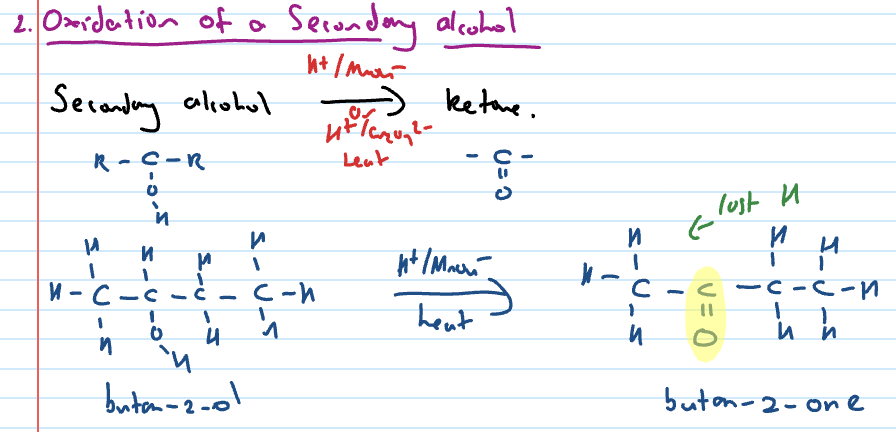
Oxidation of tertiary alcohol
Do not undergo oxidation
write like redox reactions ig
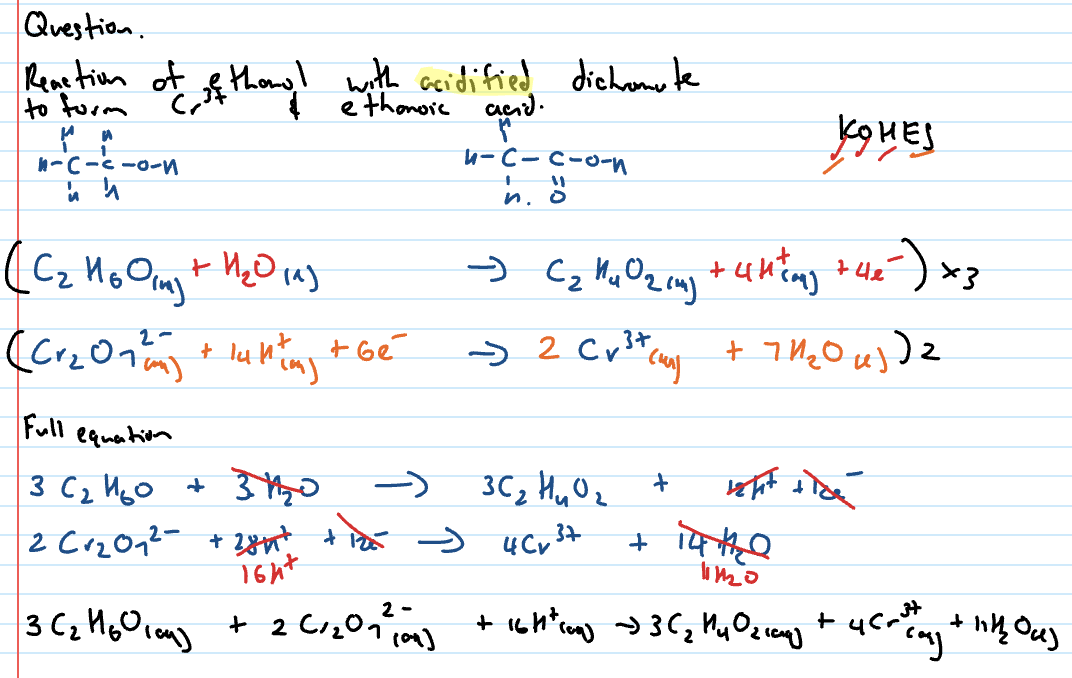
Condensation reactions
Reactions in which two molecules combine, usually in the presence of a catalyst, with elimination of water or some other simple molecule. A new covalent bond is formed.
3 types
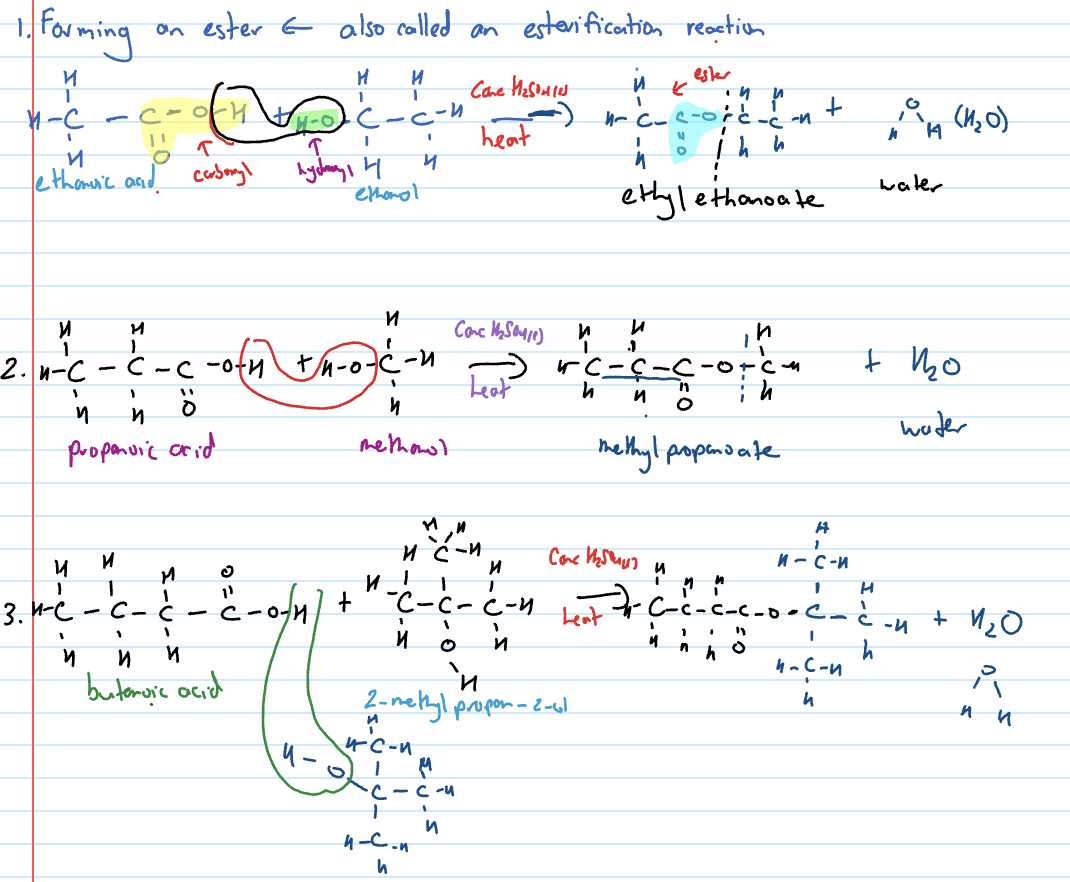
3 Types of condensation reactions

esterification (condensation reaction that forms an ester)
Condensation reaction of carboxylic acid with ammonia
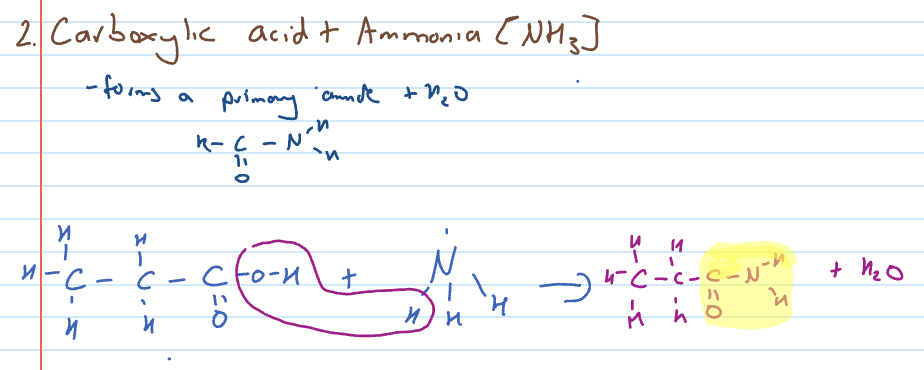
Carboxylic acid and amine

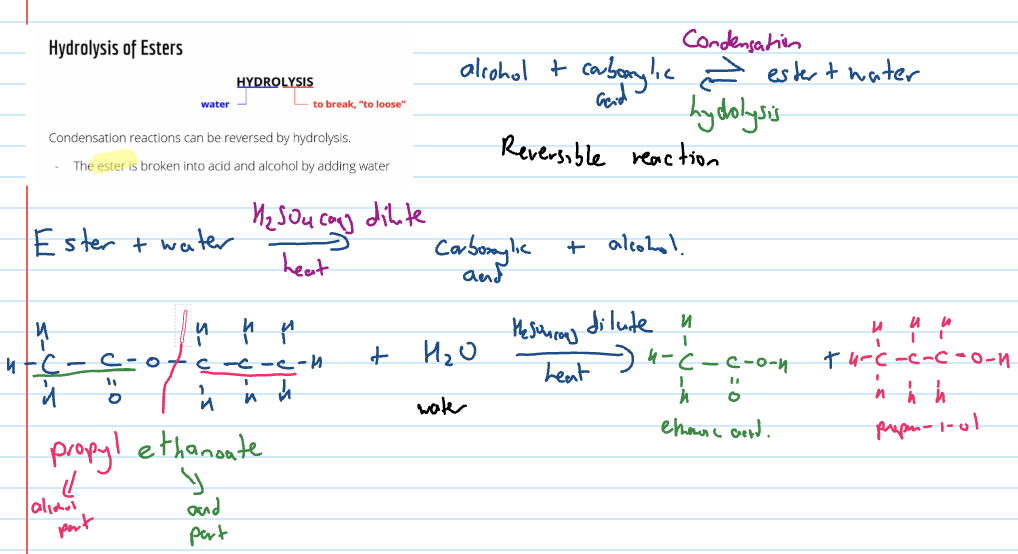
Hydrolysis of esters
condensation reactions can be reversed by hydrolysis
ester broken down into acid and alcohol by adding water
What do percentage efficiency and atom economy tell you?
efficiency of reactions



Calculating percentage yield of multistep reaction
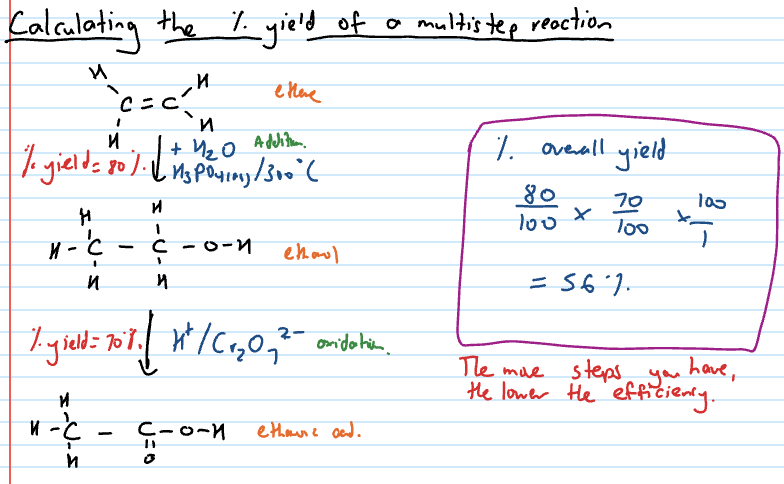
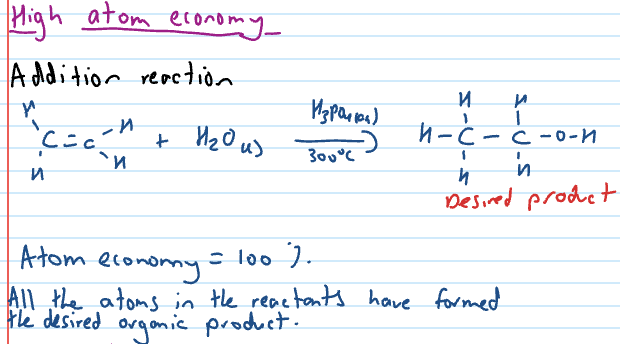
Atom economy
Atom economy for a chemical reaction is a measure of how many atoms in the reactant end up in the desired product
High atom economy?
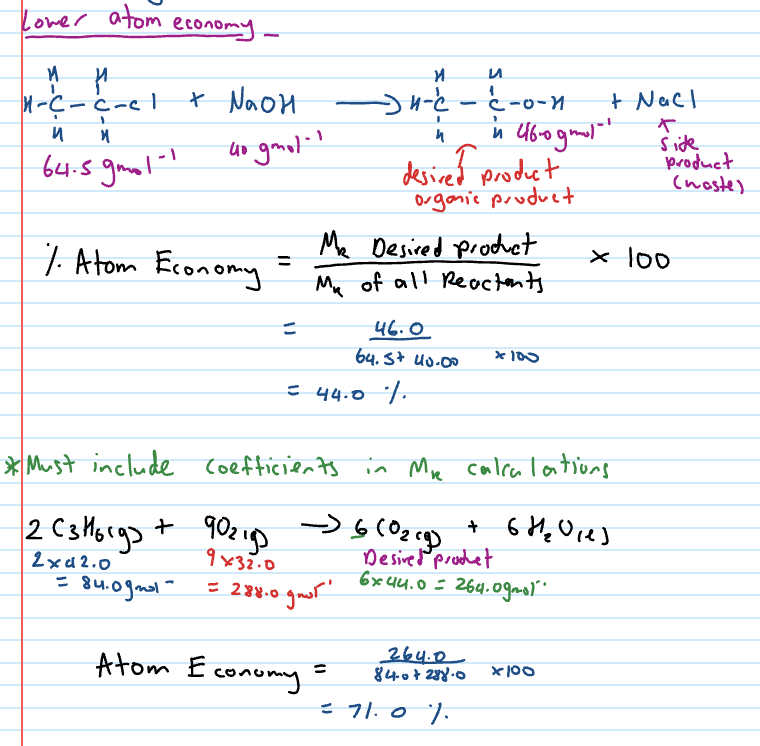
Atom economy formula

Lower atom economy
High atom economy
Less environmental impact
fewer by-products so less waste generated
Better safety
by-products can be toxic and handling waste after is a hazard, so fewer by-products is safer
Reduced cost
less waste, less disposal and maintenance, may reduce overall cost
Better quality of product
fewer by-products means simpler seperation process so maybe higher purity
Sustainable chemical process
one that minimises environmental impact and consumption of non-renewable resources while maintaining or improving the economic and social benefits associated with the product
Renewable feedstocks

Catalysis

Designing safer chemicals
