B6- Inheritance, variation and Evolution
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
What does DNA stand for
deoxyribonucleic acid
2
New cards
What is a chromosome
Long structure of DNA which usually comes in pairs
3
New cards
What is a gene
A small section of DNA found on a chromosome which codes for a particular sequence of amino acids
4
New cards
What is a Genome
An entire set of genetic material in an organism
5
New cards
Why is researching the human genome important?
* allows scientists to identify genes in the genome that are linked to different types of disease
* Knowing which genes are linked to inherited disease to help treat them
* Can help to trace migration of certain populations and identify when theses populations split off from each other a developed different characteristics
* Knowing which genes are linked to inherited disease to help treat them
* Can help to trace migration of certain populations and identify when theses populations split off from each other a developed different characteristics
6
New cards
What is sexual reproduction?
Where genetic info from two organisms (male and female) combine to produce offspring which are genetically different to either parent.
7
New cards
What combines to create an embryo in sexual reproduction
Male (sperm) and female (eggs) gametes
8
New cards
How many chromosomes does a normal cell contain
46 (23 from each gamete)
9
New cards
What is term for the fusion between mother and father gametes
fertilisation
10
New cards
What is the term for a mixture of genetic information
Variation
11
New cards
What plants also reproduce sexually
Flowering plants which contain egg cells but have pollen instead of sperm
12
New cards
What is asexual reproduction
reproduction involving only one parent meaning the offspring are genetically identical and occurs through mitosis only
13
New cards
Is offspring similar to its parent if they are produced from asexual reproduction
Yes they are clones of their parent
14
New cards
What produces offspring are reproduced asexually
Bacteria, some plants and some animals
15
New cards
What is meiosis
In order to ensure gametes only have one copy of each chromosome so that gamete fusion takes place with the right amount of chromosomes at the end. In humans this only occurs in the reproductive organs.
16
New cards
how many cell divisions occur in meiosis
2
17
New cards
In sexual reproduction how do the cells grow after gamete fusion
Mitosis
18
New cards
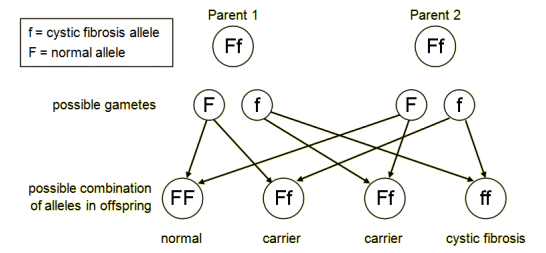
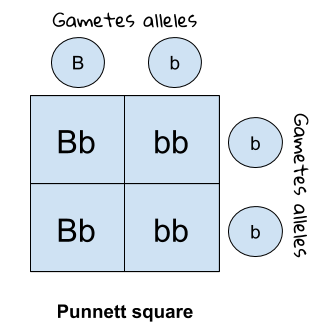
How can you find the probability of genetic outcomes e.g. whether you are going to have a boy or a girl
Genetic diagrams
19
New cards
What controls you’re characteristics
Genes inherited from parents
20
New cards
What are different versions of genes
alleles
21
New cards
What is the term for having two of the same alleles
homozygous
22
New cards
What is the term for having two different alleles for a gene
heterozygous meaning there is recessive and dominant gene
23
New cards
How can an organism display a recessive characteristic
if both allele are recessive
24
New cards
What is a genotype
The combination of alleles you have
25
New cards
What is Cystic Fibrosis
A recessive genetic disorder of the cell membranes. It results in the body producing a lot of thick sticky mucus in the air passages and in the pancreas.
There’s a 1 in 4 chance of a child having the disorder if both parents have or carry it
There’s a 1 in 4 chance of a child having the disorder if both parents have or carry it
26
New cards
What is Polydactyl
A dominant genetic disorder where a person is born with extra fingers or toes. There’s a 50% chance if the baby’s parent has the disorder.
27
New cards
what is screening genetic disorders?
Looking at embryos in IVF to detect disorders or defects if it is the case so they can be terminated before being inserted into the womb
or
In natural pregnancy x rays which occur in the window for abortion if the parents choose to.
or
In natural pregnancy x rays which occur in the window for abortion if the parents choose to.
28
New cards
What is a phenotype
A physical characteristic.
29
New cards
Evolution
Charles Darwin’s discoveries
30
New cards
Evolution definition
Change of inherited characteristics of certain population over time via natural selection
31
New cards
Selective Breeding
* Animals that produces more meat
* Crops with disease resistance
* Dogs with a good, gentle temperament
* Decorative plants with big or unusual or unusual flowers
* Crops with disease resistance
* Dogs with a good, gentle temperament
* Decorative plants with big or unusual or unusual flowers
32
New cards
Genetic engineering
Modifying a genome and adding a gene responsible for a desirable characteristic
33
New cards
What is modified to make human insulin
bacteria
34
New cards
GM crops
\-Kills wild flowers and insects and educes farmland biodiversity
\-Some concerned of GMs effects on human consumption
\-A big concern is transplanted genes may get out into the natural environment e.g. causing super weeds resistant to herbicides being created
\-GM crops increase yield making more food
\-Golden rice is an example of a GM crop which helps prevent blindness (beta-carotene ) Helping devoloping countries with their lack in nutrients
\-Some concerned of GMs effects on human consumption
\-A big concern is transplanted genes may get out into the natural environment e.g. causing super weeds resistant to herbicides being created
\-GM crops increase yield making more food
\-Golden rice is an example of a GM crop which helps prevent blindness (beta-carotene ) Helping devoloping countries with their lack in nutrients
35
New cards
Genetic engineering
A useful gene is isolated from one organism’s genome using enzymes and is inserted into a vector
the vector is usually a virus or a bacterial plasmid ( a fancy piece of circular DNA found in bacterial cells) depending on type of organism
when the vector is introduced to the target organism, the useful gene is inserted into its cells
\
the vector is usually a virus or a bacterial plasmid ( a fancy piece of circular DNA found in bacterial cells) depending on type of organism
when the vector is introduced to the target organism, the useful gene is inserted into its cells
\
36
New cards
Uses for GE
Bacteria can be modified to produce human insulin
Genetically modified (GM) crops have had their genes modified, e.g. to improve size and quality of fruit, or make them resistant to disease, insects and herbicides
Sheep have been genetically engineered to produce substances like drugs, in their milk that can be used to treat human diseases
Research is happening for treatments to inherited disease caused by faulty genes by inserting working genes (Gene Therapy)
Genetically modified (GM) crops have had their genes modified, e.g. to improve size and quality of fruit, or make them resistant to disease, insects and herbicides
Sheep have been genetically engineered to produce substances like drugs, in their milk that can be used to treat human diseases
Research is happening for treatments to inherited disease caused by faulty genes by inserting working genes (Gene Therapy)
37
New cards
Antibiotic resistance
MRSA- super bug hard to get rid of and can be fatal
38
New cards
Fossils
Remains of organisms thousands of years ago
\-Gradual replacement of minerals- Teeth, bones and shells replaced by minerals to form a rock like substance. Surrounding sediment turns to rock but leaves the fossil distinct
\-From casts and impressions- organisms leaves an imprint in hardened clay. Animal burrow or plants roots or footprints
\-from preservation in places where no decay happens
Glaciers
\-Gradual replacement of minerals- Teeth, bones and shells replaced by minerals to form a rock like substance. Surrounding sediment turns to rock but leaves the fossil distinct
\-From casts and impressions- organisms leaves an imprint in hardened clay. Animal burrow or plants roots or footprints
\-from preservation in places where no decay happens
Glaciers