Skin Lesions
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Palor
Abnormal color:
white skin--> pale
dark skin --> gray, grayish brown
yellow undertones --> pale gray, greenish brown
Cyanosis
Abnormal color:
white skin --> blue undertones
dark skin --> gray, whitish skin with gray/blue conjunctiva
yellow undertones: greenish- gray
Jaundice
white ski --> yellow
dark skin --> golden to dark olive
Erythema
redness or rash caused by increased blood flow to the capillaries near the skin's surface
red to dark bluish-purple
hyperpigmentation & hypopigmentation
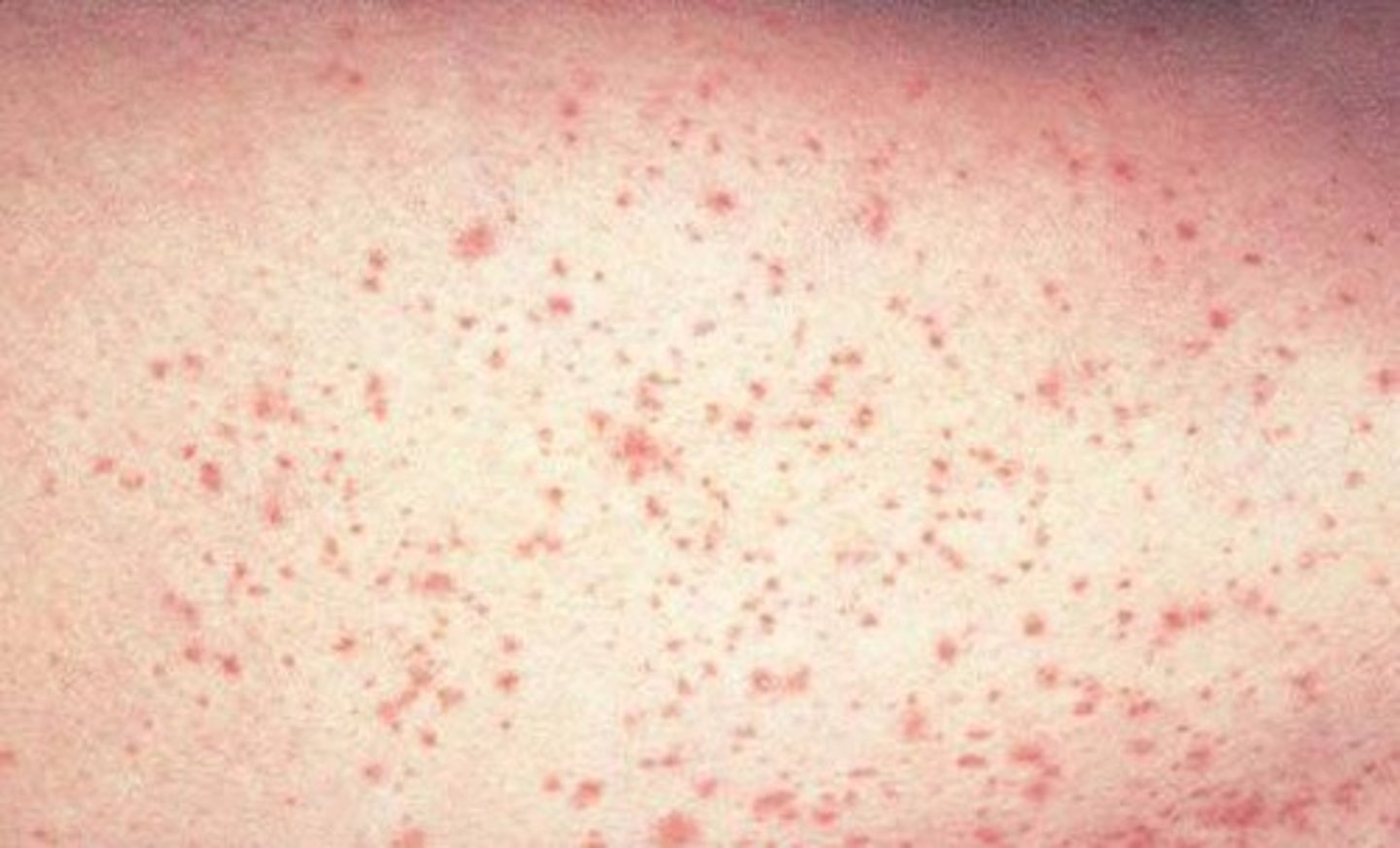
Petechiae
Petechiae are small, pinpoint red or purple spots that appear on the skin, mucous membranes, or eyes due to bleeding from small capillaries under the skin
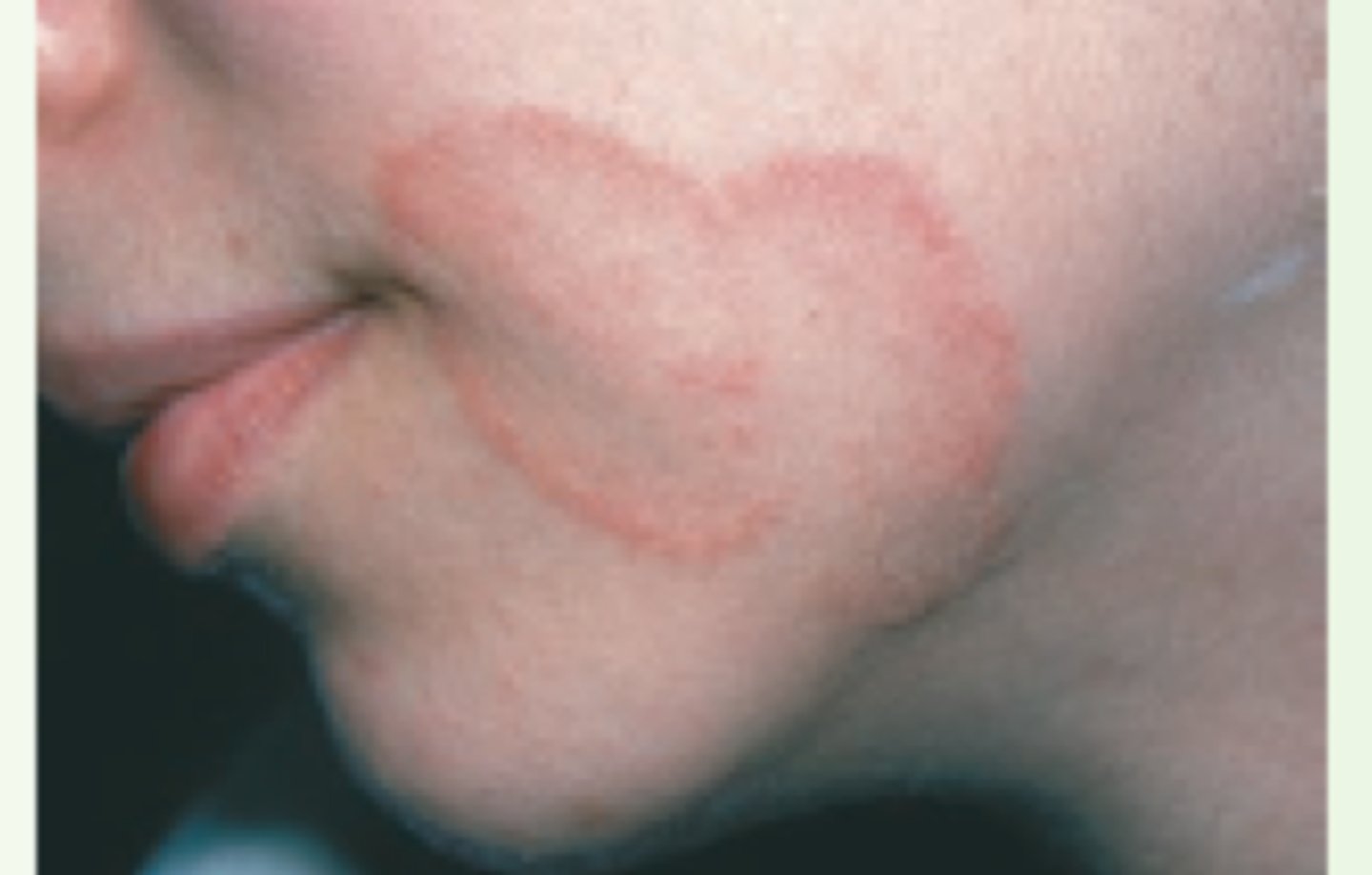
Clustered
Patterns and Shapes
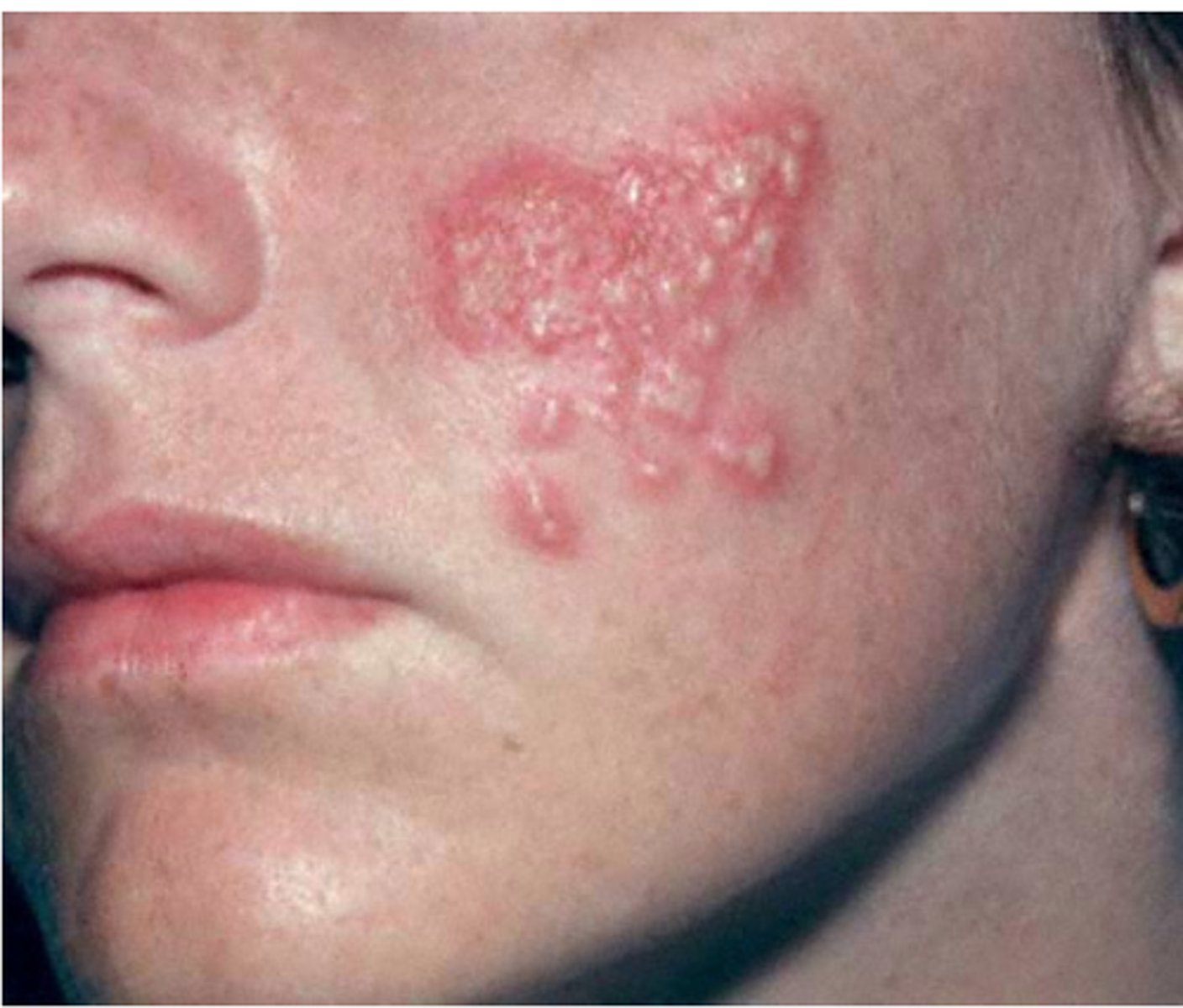
Serpiginous
Patterns and Shapes
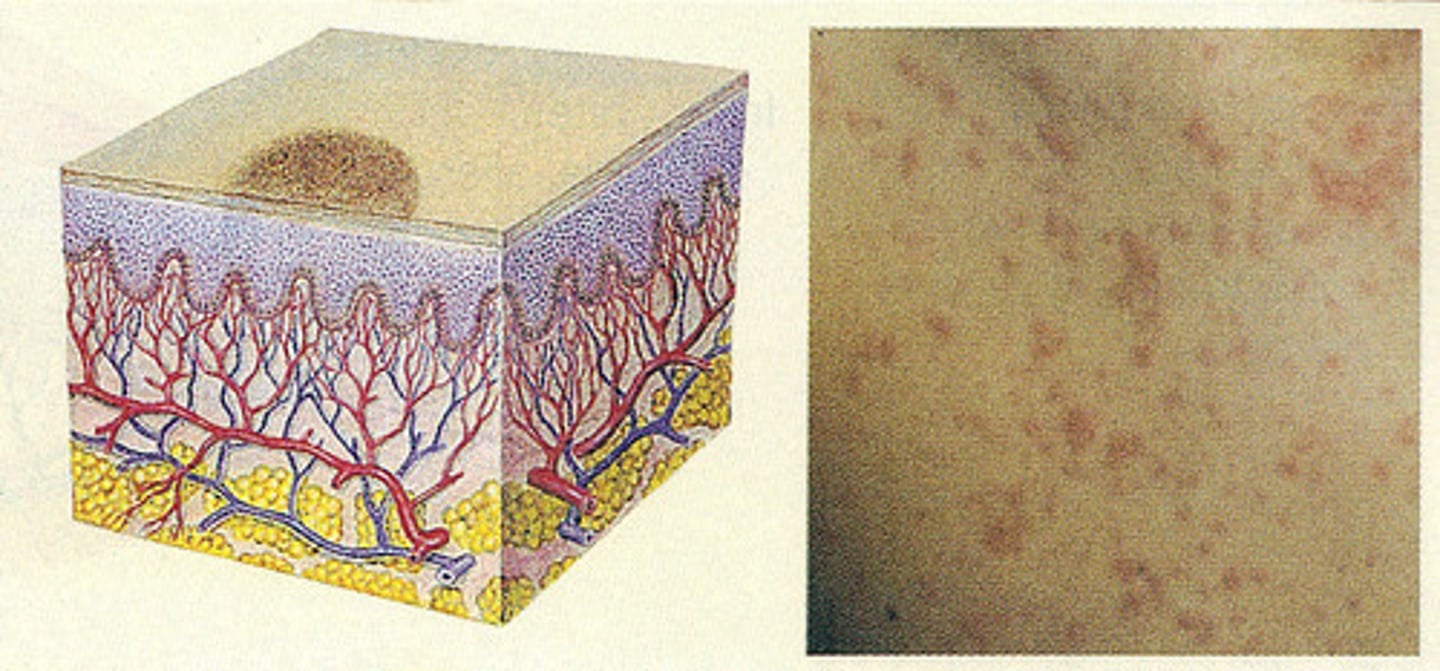
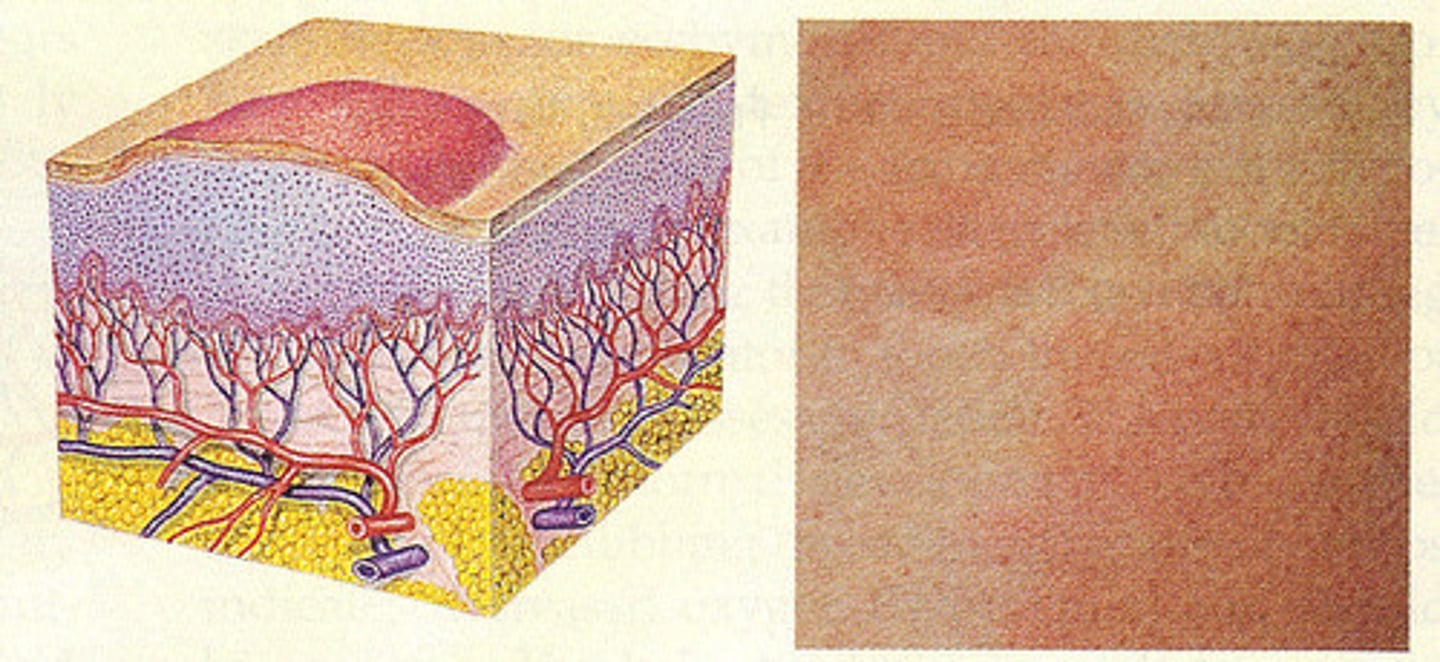
Macule
Primary skin lesion:
less than 1.0 cm
on the surface
non-palpable
local
color changes in skin
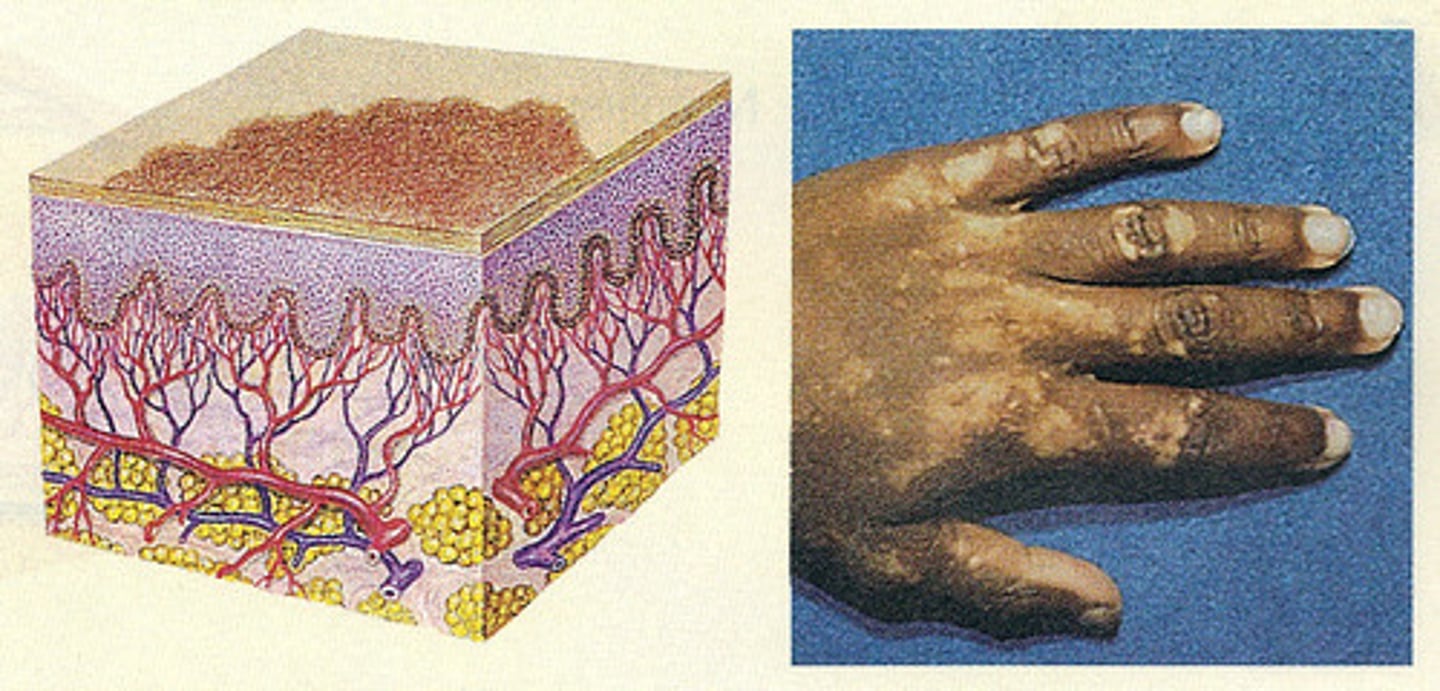
Patch
Primary skin lesion:
more than 1.0 cm
on the surface
non-palpable, local color changes in skin
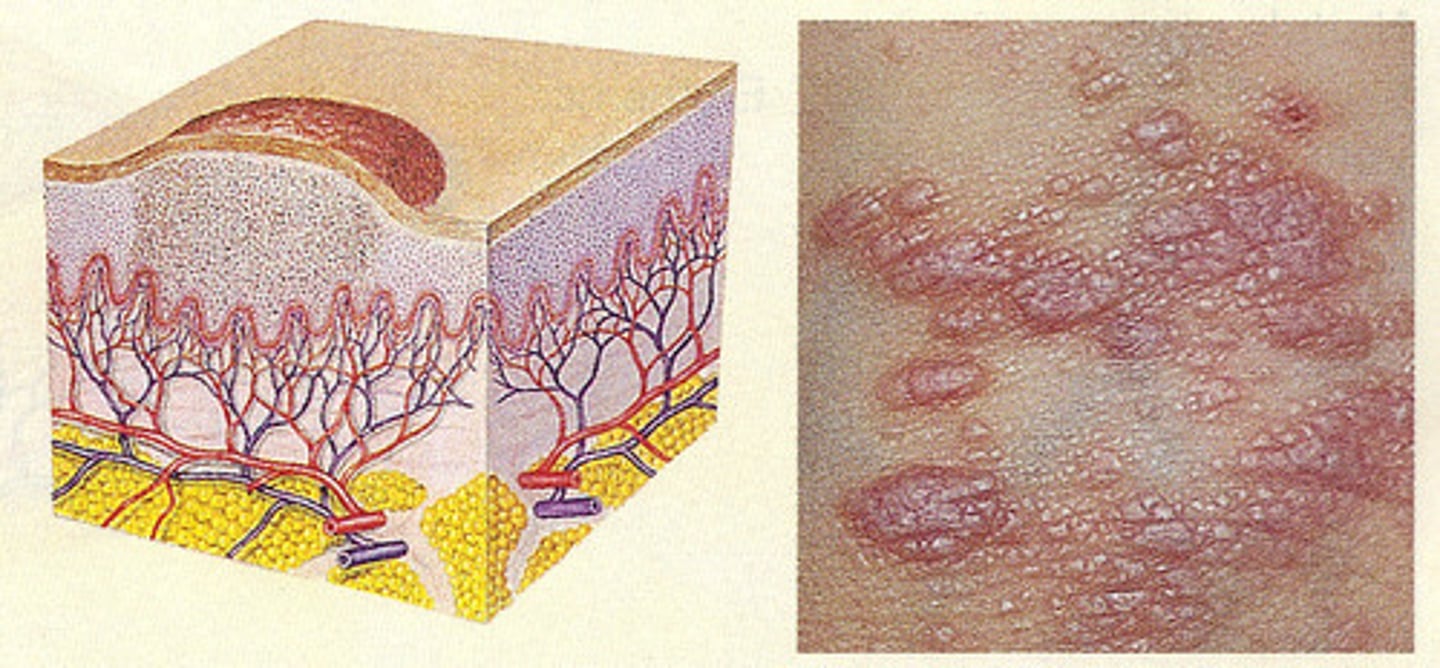
Papule
Primary:
less than 1.0 cm
superficial
elevated
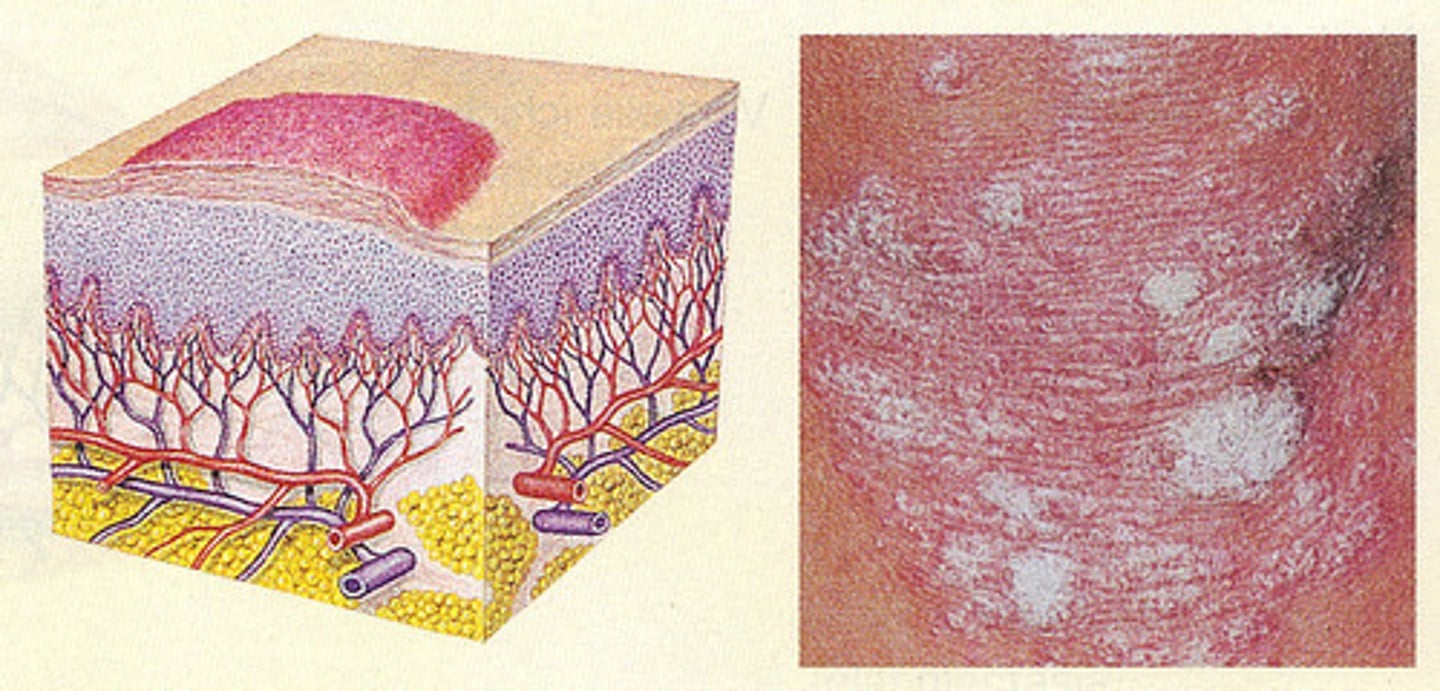
Plaque
primary skin lesion:
more than 1.0 cm
elevates superficial
often formed by coalesces of papules
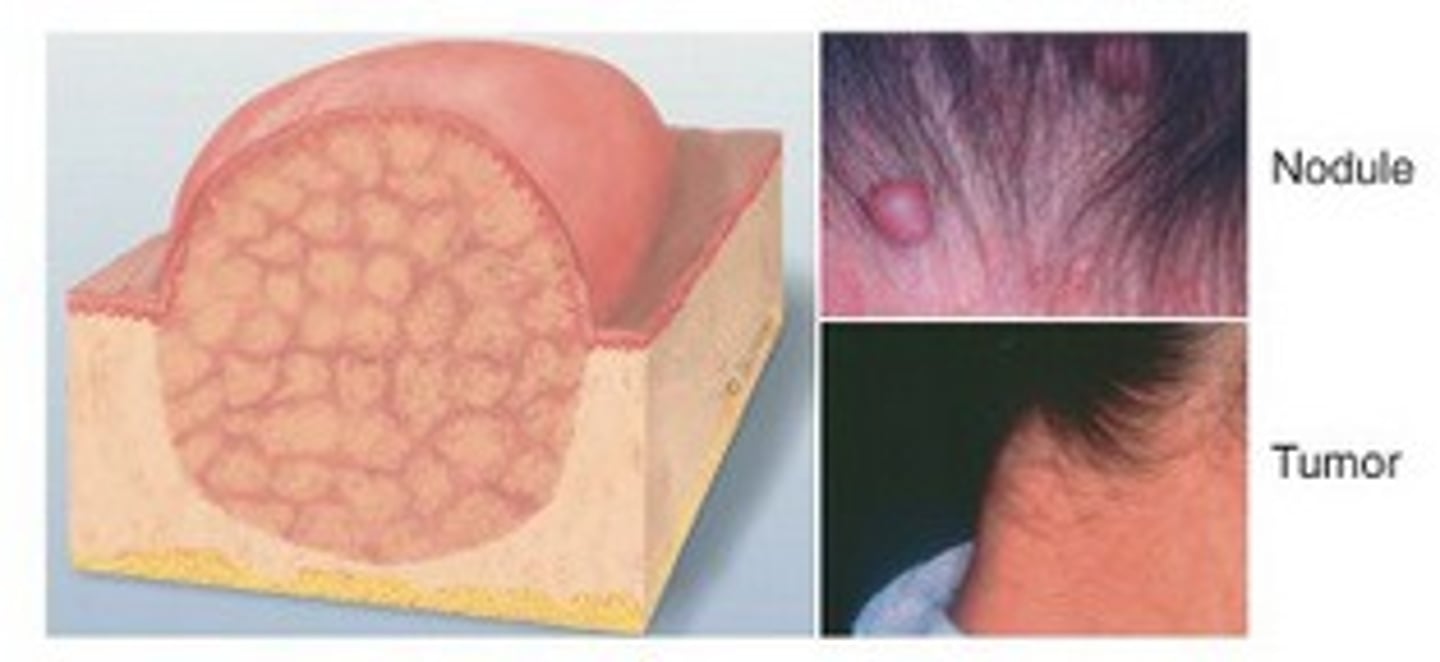
Nodule
Primary skin leison:
more than 0.5 cm marble like deeper and firmer than papule
under the skin
Wheal
hives
superficial often reddish or deeper brown
localized skin edema
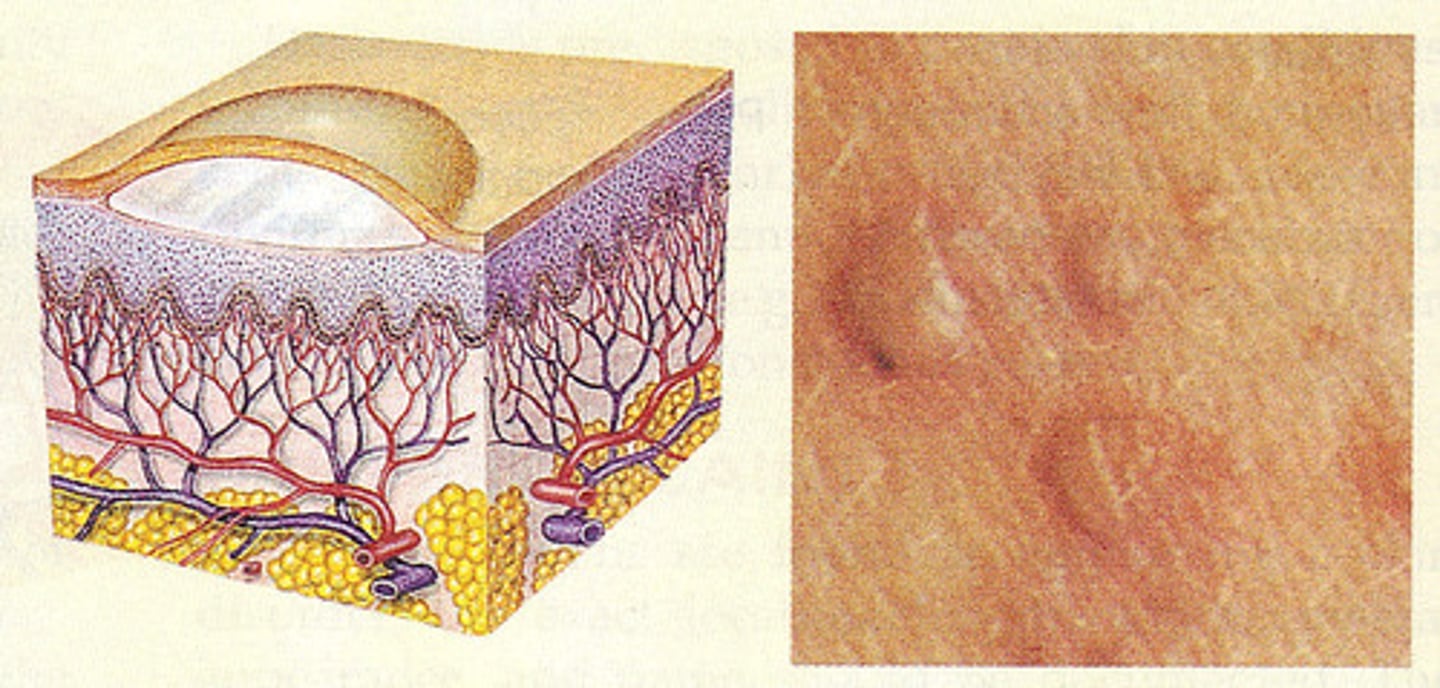
Vesicle
Primary:
less than 1.0 cm
palpable serous fluid
round/oval lesions
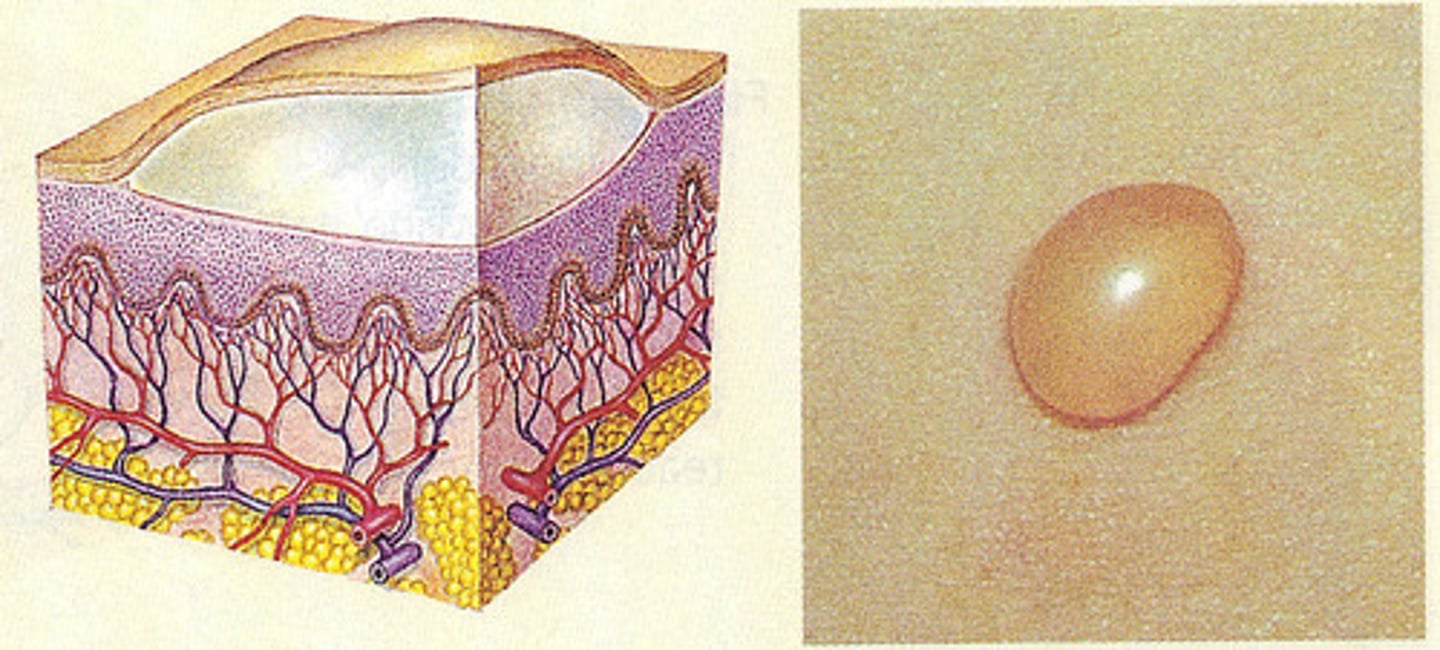
Bulla
Primary:
1.0 cm or larger
palpable serous-filled
round/oval lesions
bug bite
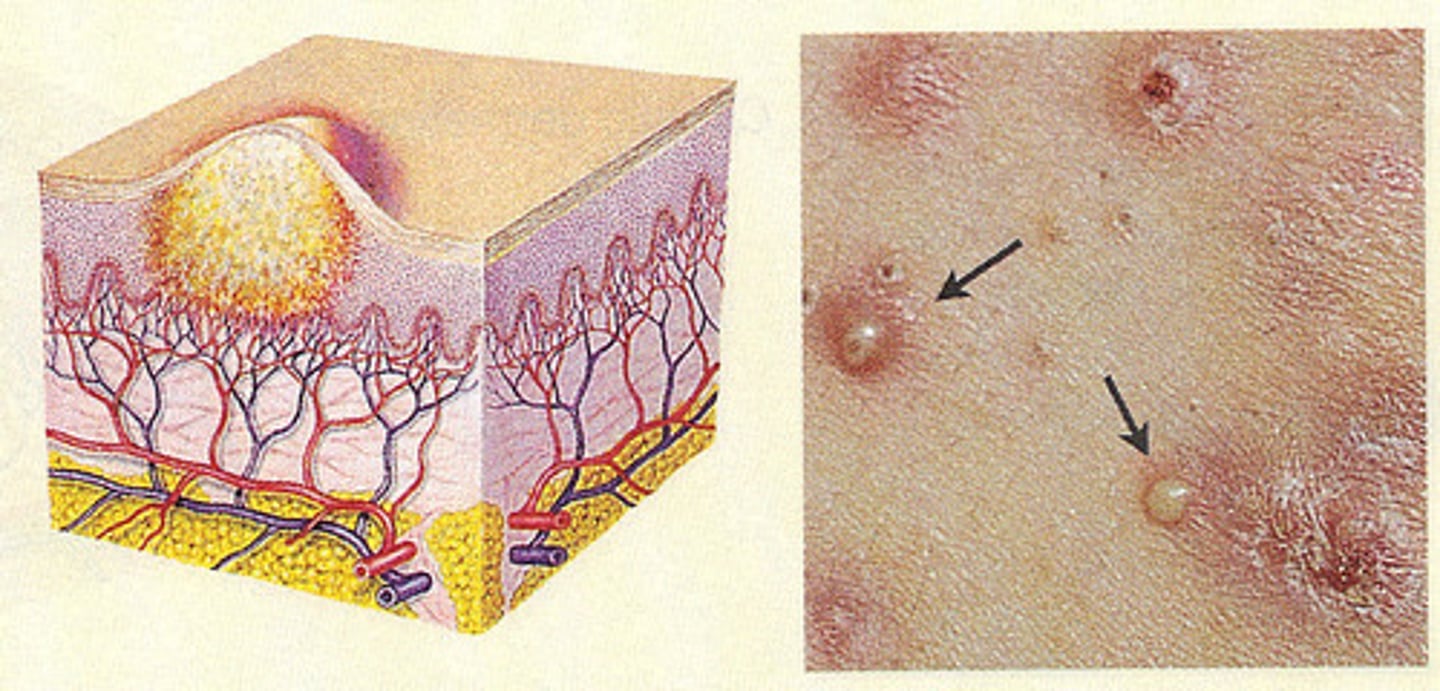
Pustule
Primary:
filled with puss
inflammatory cells
acne
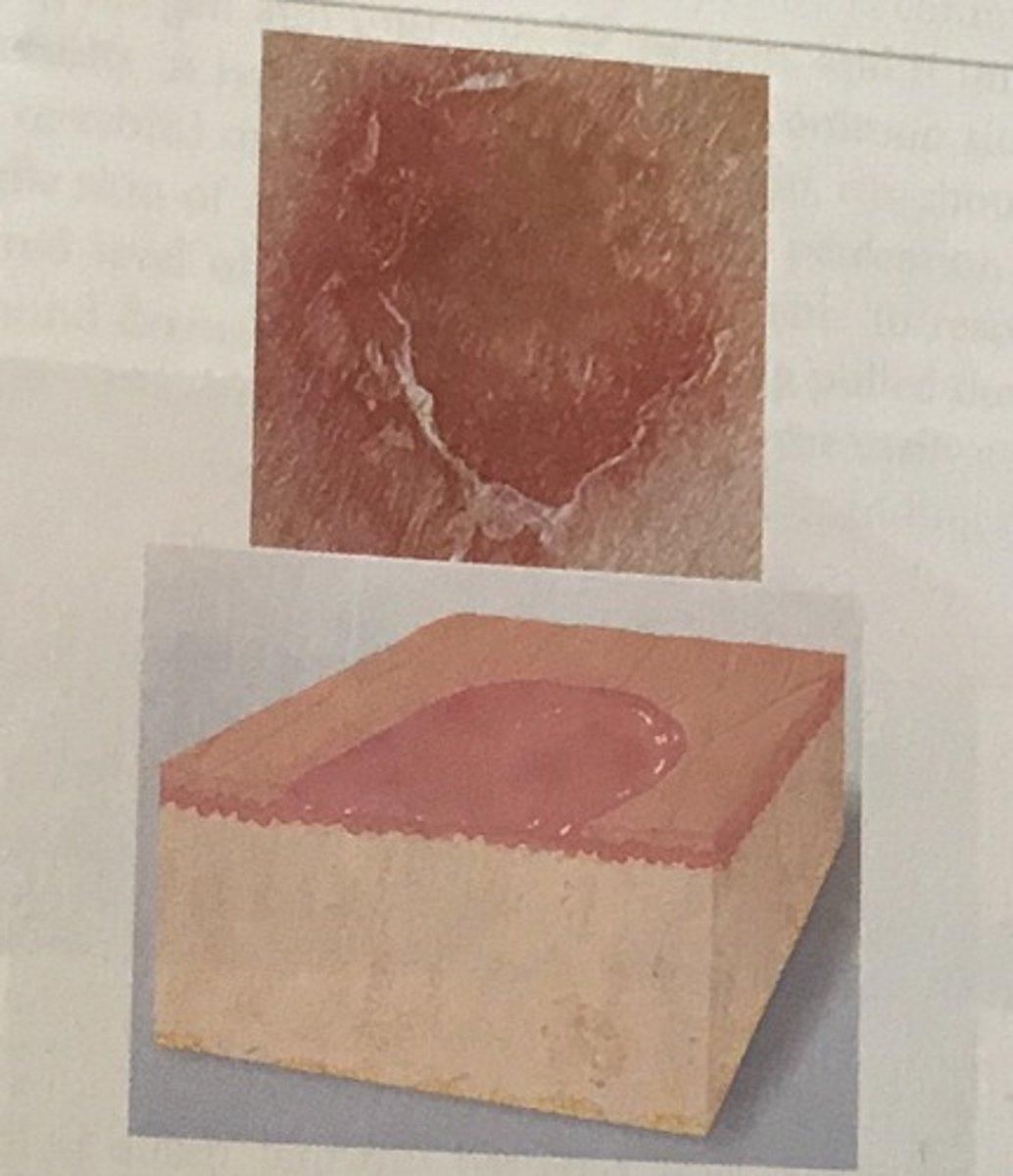
Erosion
Secondary skin lesions
non-scarring wearing away of superficial epidermis
surface is moise but does not bleed, one healed no scar
ex: canker sore and blister
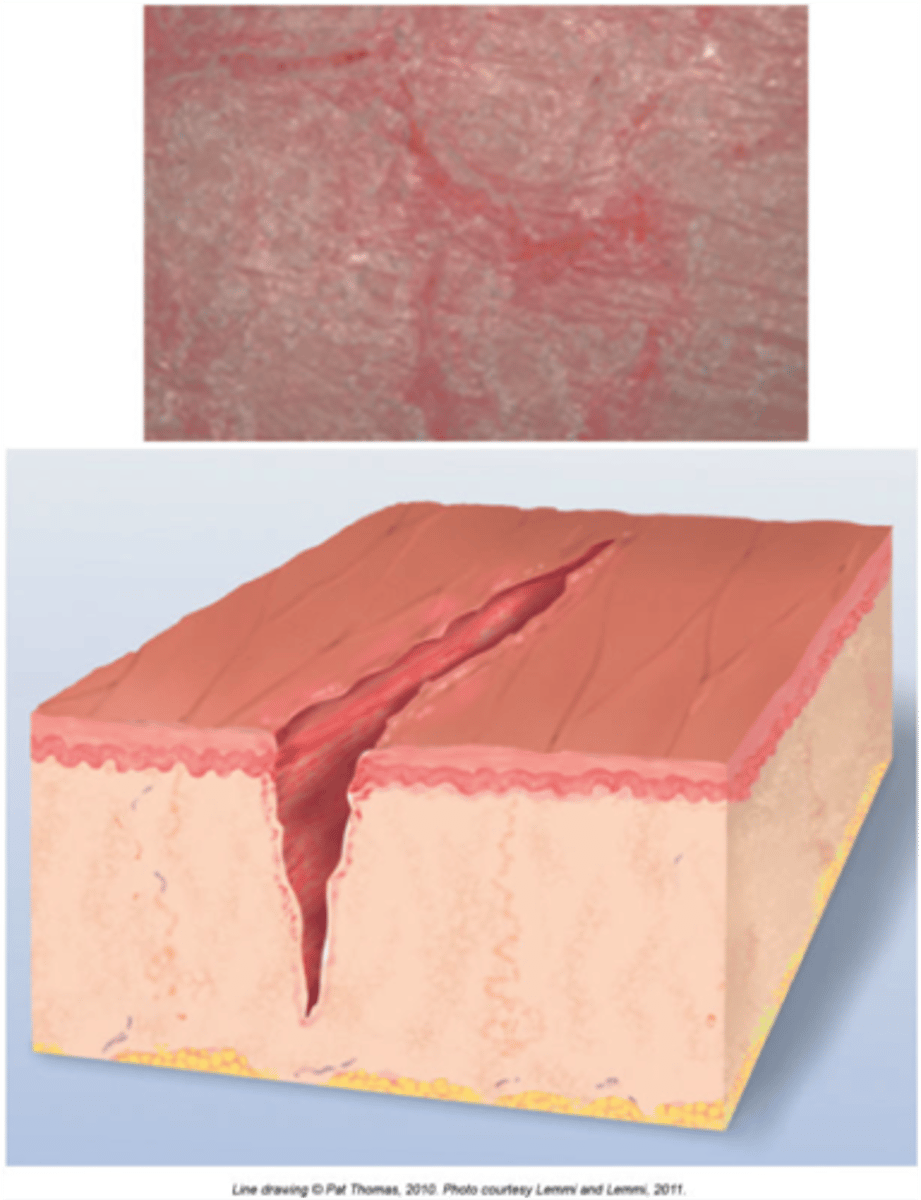
Fissure
Secondary
linear crack in skin
often from excessive dryness of skin
ex: athletes foot
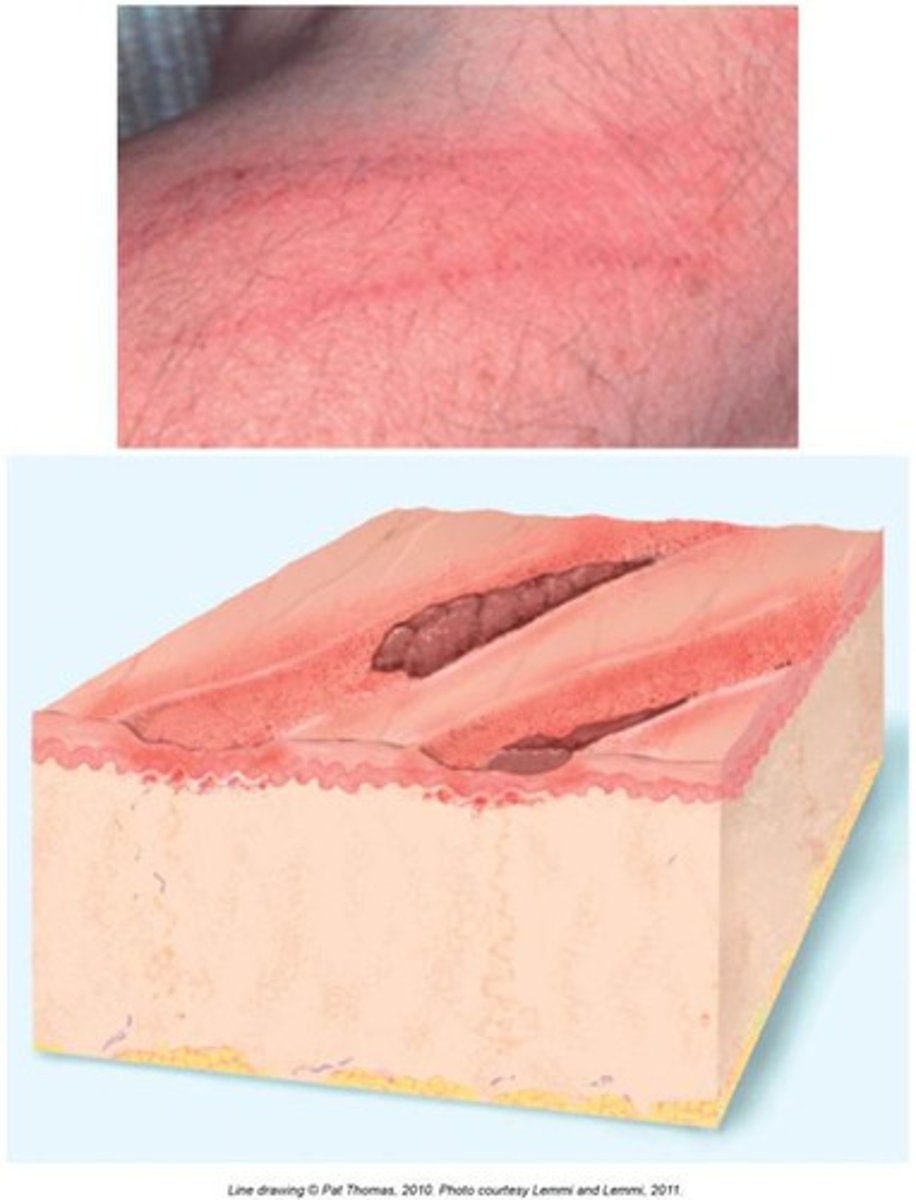
Excoriation
Secondary:
linear or punctate
erosions caused by scratching
ex: cat scratch
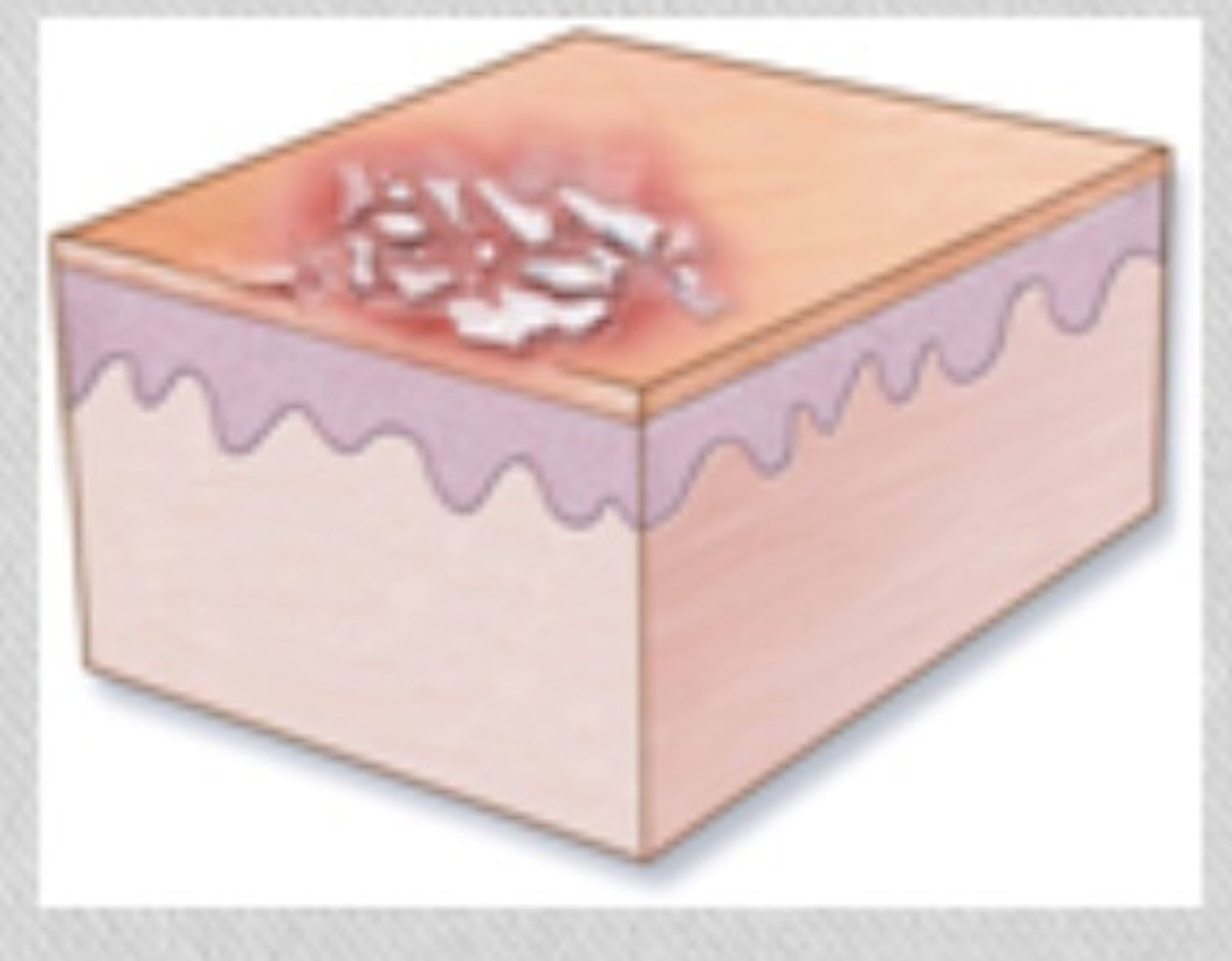
Crust
Secondary:
dried exudate, such as serum, blood, or pus, accumulates on surface of the skin.
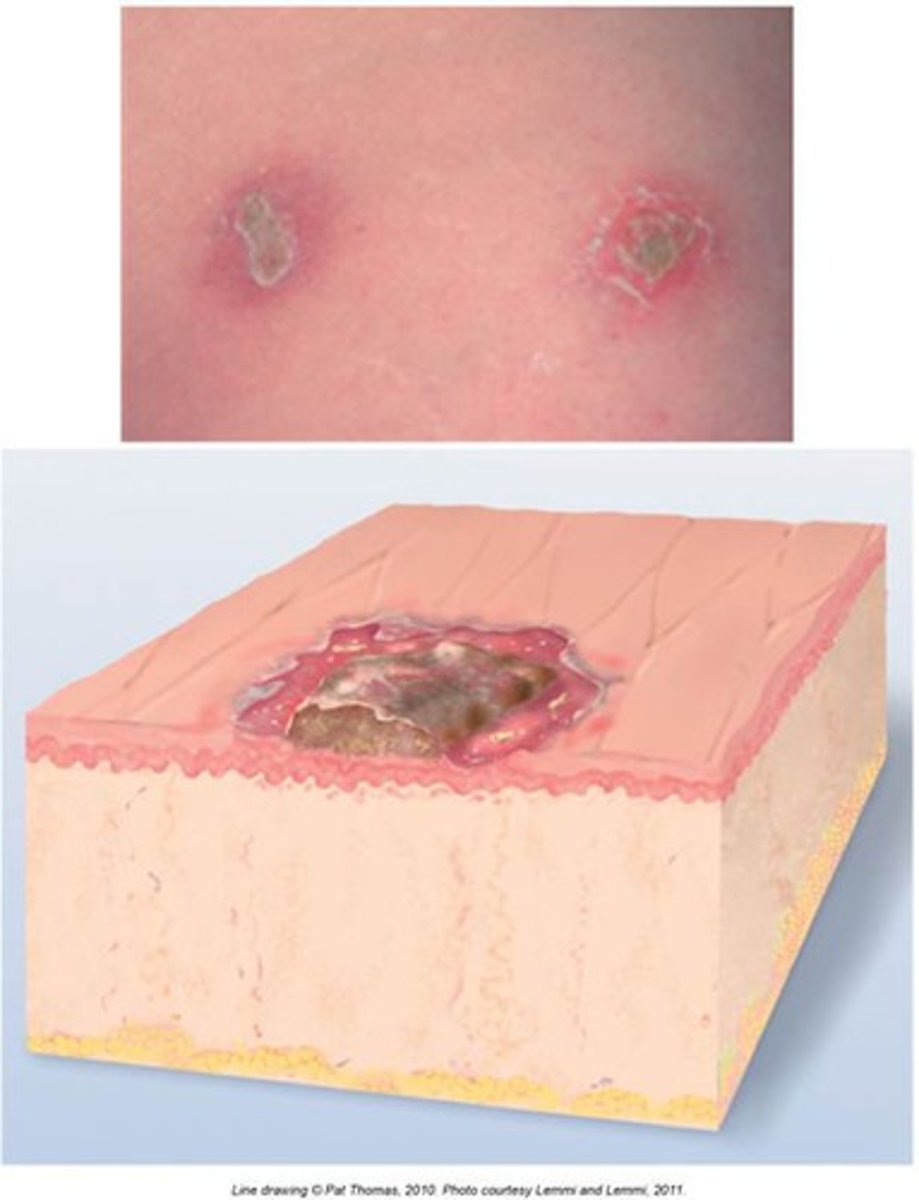
Scale
Secondary:
Shedding or accumulation of dead epidermal cells.
ex. dandruff
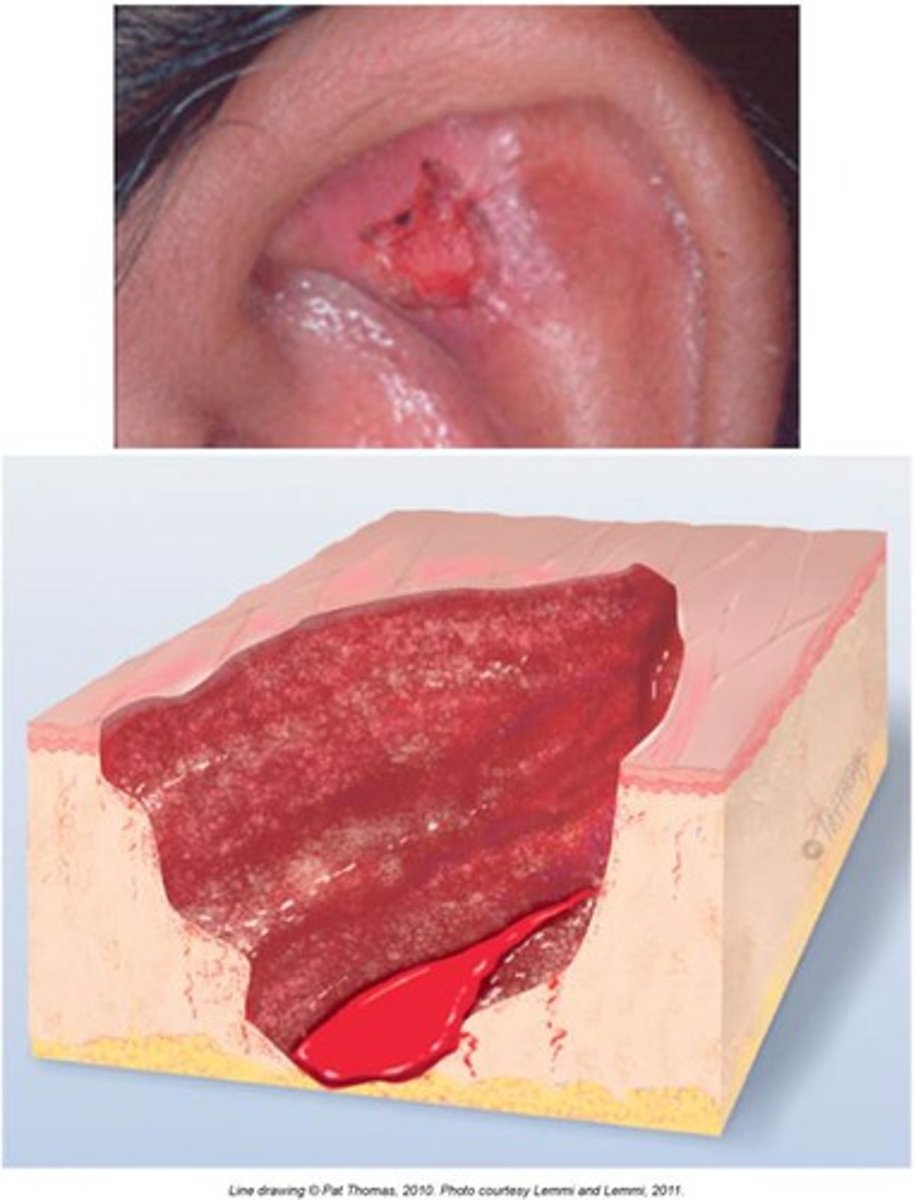
Ulcer
Secondary:
an open sore or wound on the skin that can be painful and may result in tissue breakdown.
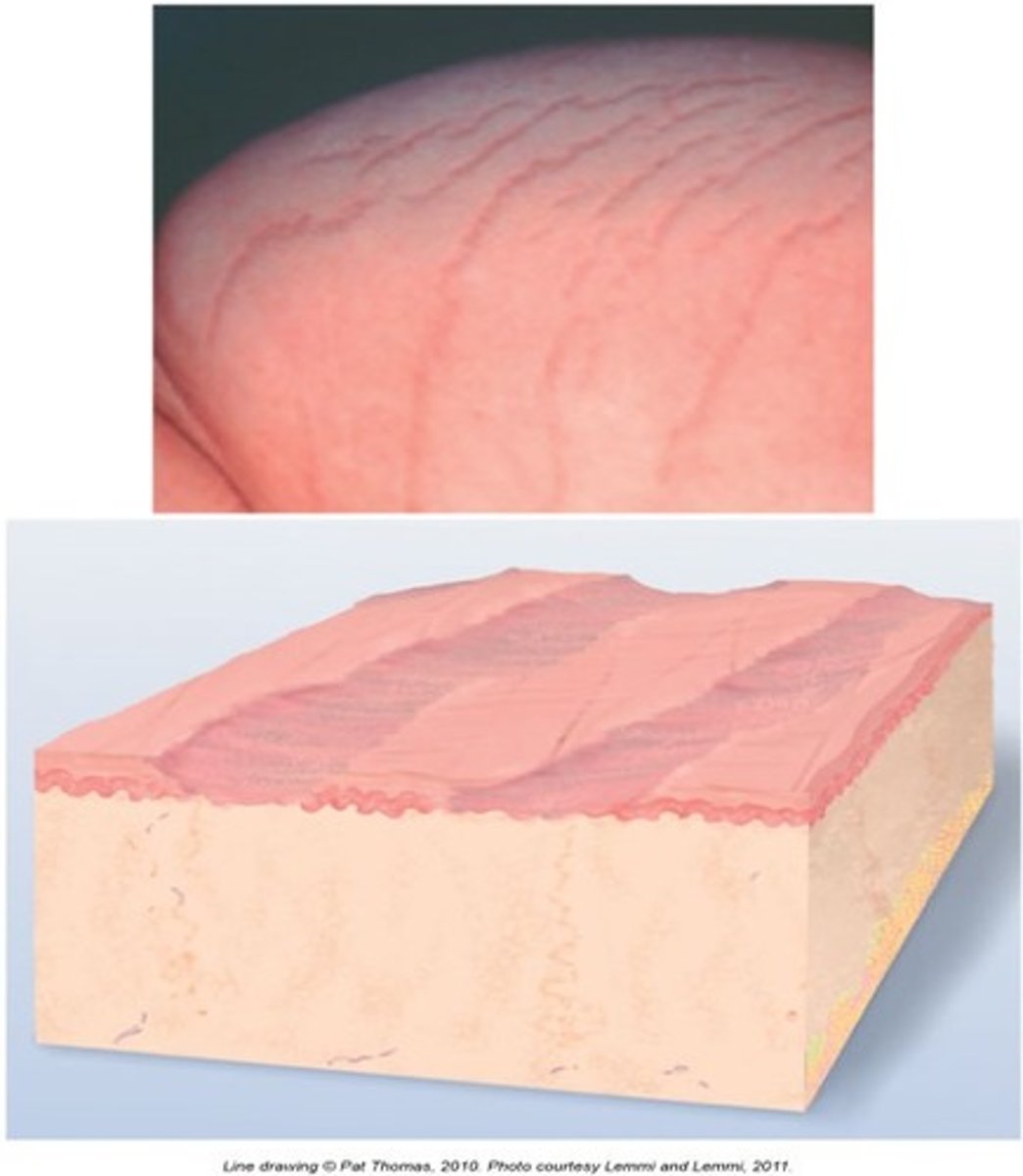
Atrophic Scar
Secondary skin lesion:
resulting skin level is depressed with loss of tissue. a thinning of the epidermis
ex: stretch marks
Lichenification
Secondary:
skin has become thickened and leathery.
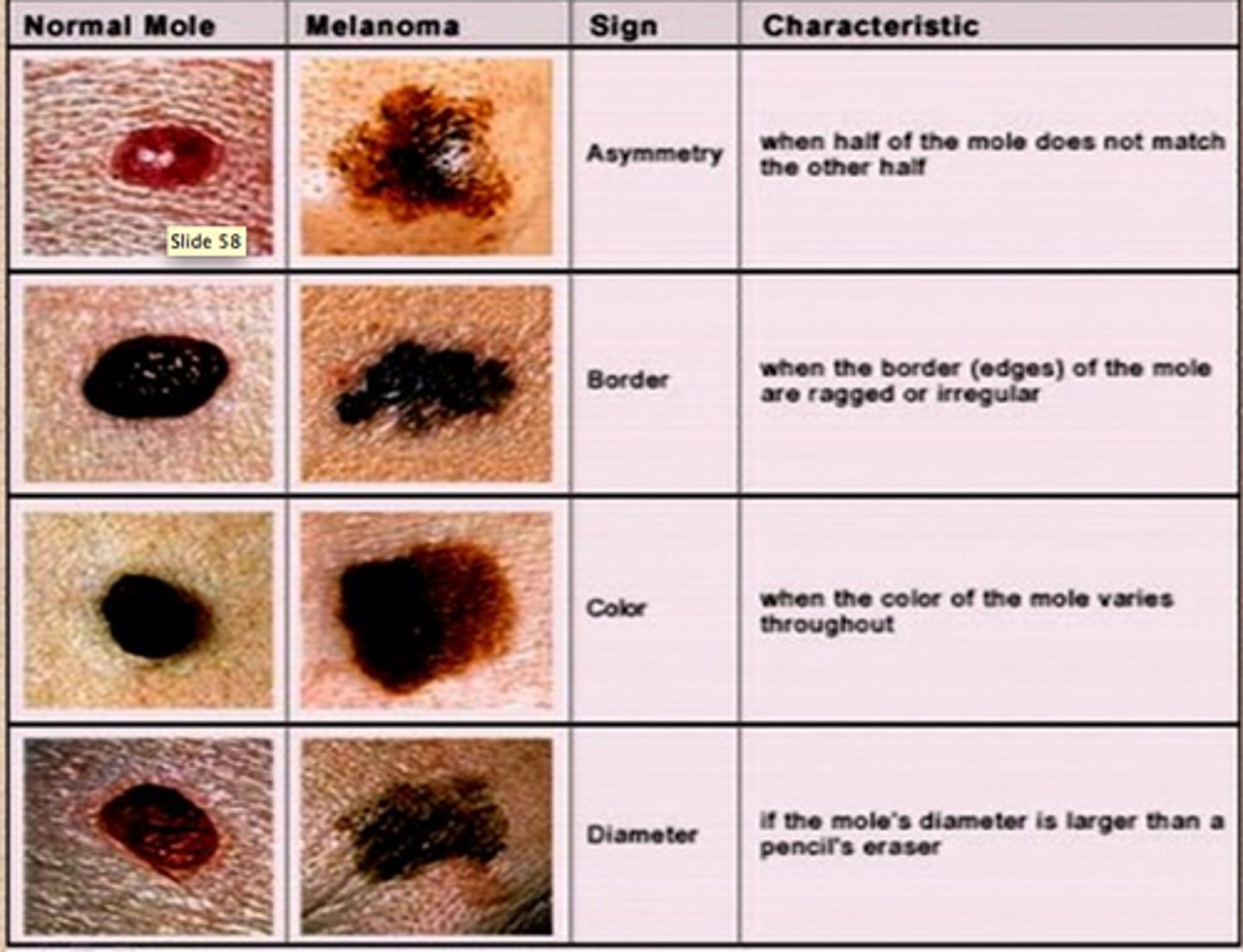
ABCDE of Skin Cancer
asymmetry
border
color
diameter
evolving
Color
Inspection and documentation:
either skin colored or state the discoloration
Size
Inspection and documentation: Measure in mm or cm; for oval measure long axis and perpendicular
Elevation
Inspection and documentation:
flat (cannot palpate or feel), raised, or pedunculated (attached by trunk like a skin tag)
Number
Inspection and documentation:
solitary, multiple or an actual number
Texture
Inspection and documentation:
Smooth
Fleshy
Scaling
Anatomic location and descriptioin
Inspection and documentation:
generalized, localized, skin-fold areas, extensor or flexor areas
Linear
Patterns:
straight line
Geographic
Paterns
areas of one color, with variably scalloped borders of additional color
Confluent
Patterns:
lesions run together
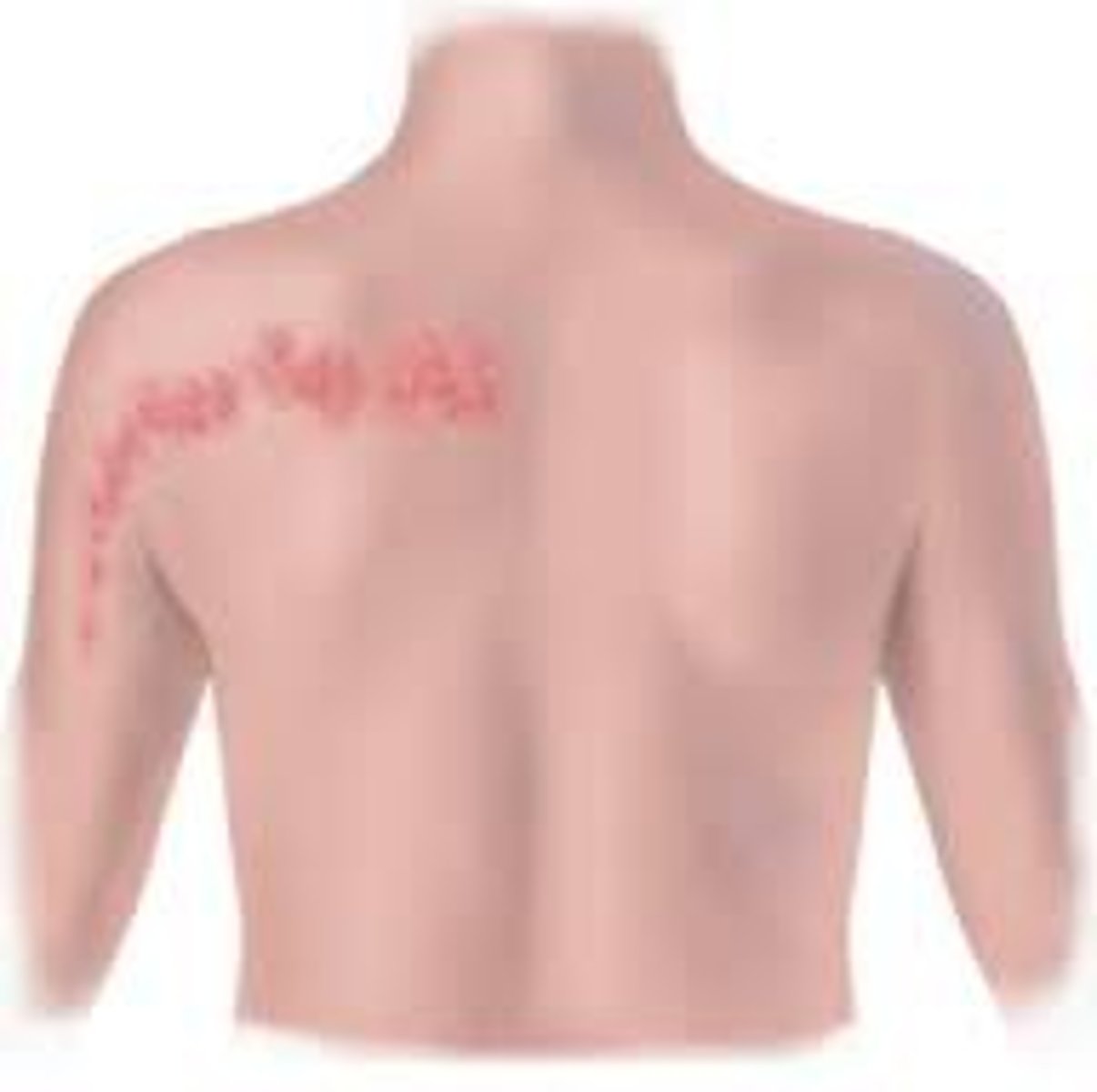
Zosteriform
Patterns:
lesions that follow a nerve dermatome
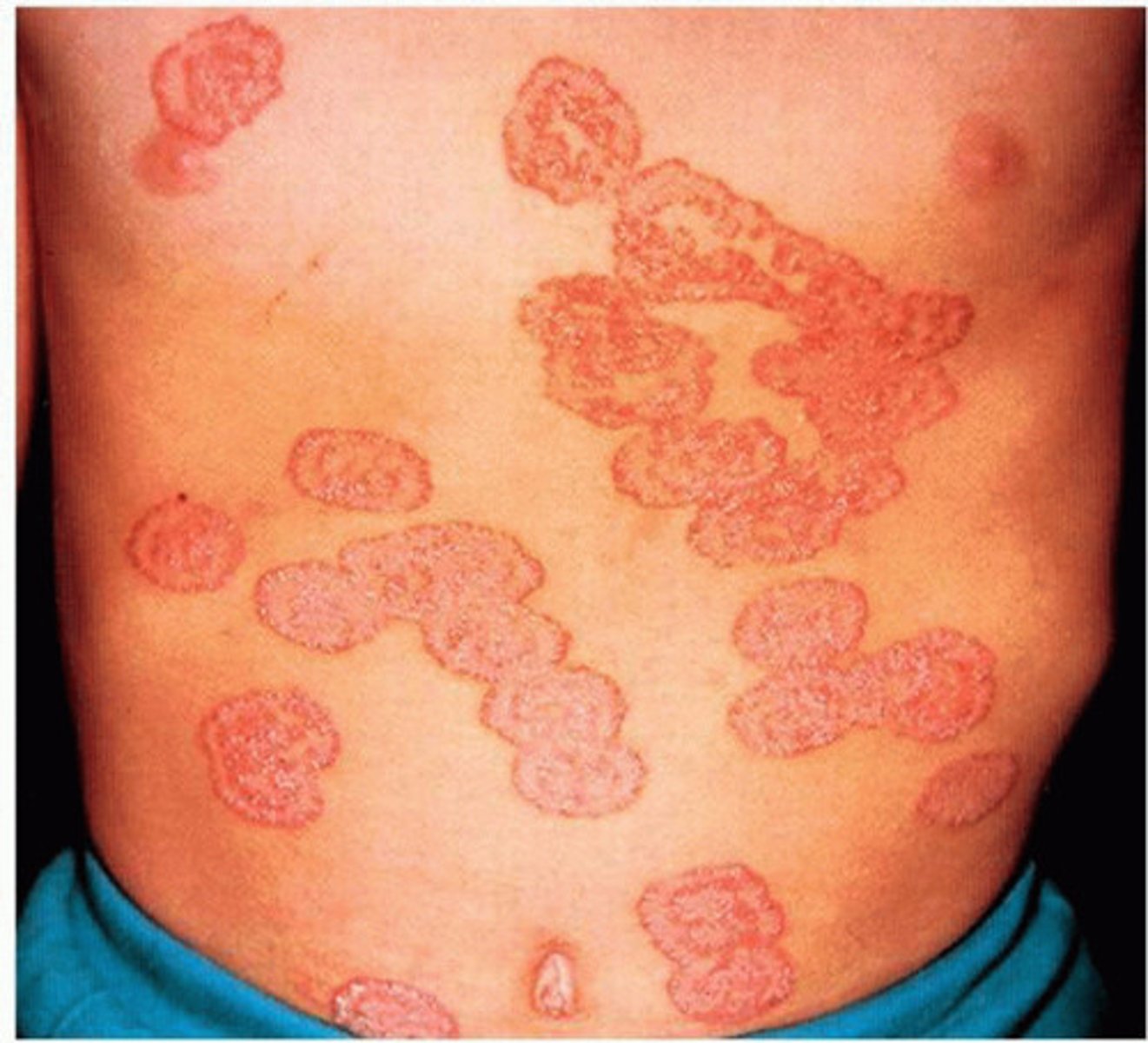
Annular, Acriform
Shape:
have a circular shape