Human Factors 1
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Breathing
All cells of human body require oxygen (O2) to function
Body stores very little O2, continuous breathing required to oxygenate blood
Cells remove O2 from blood “burn” along with fuel to produce energy, return Carbon Dioxide (CO2) to blood
Lungs exchange CO2 from blood incoming O2
Level of CO2 in blood controls breathing rate
Circulation
Heart pumps blood to lungs to oxygenate, then around body, back to lungs to remove CO2
Heart rate is dependent on number of factors
Age
Physical fitness
Stress
Ears
Primarily used for hearing
Ear drum creates a sealed air cavity in the middle ear
Eustachian tube connects middle ear to back of throat
Normally closes
Opens to equalise pressure between middle and outer ear
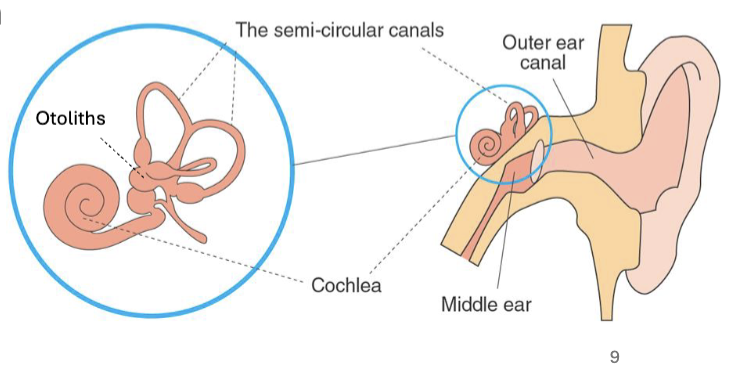
Vestibular system
Inner-ear function
Maintains balance and spatial awareness
Made up of
Semicircular canals - detect rotational motion
Otoliths - detect linear acceleration
Eyes
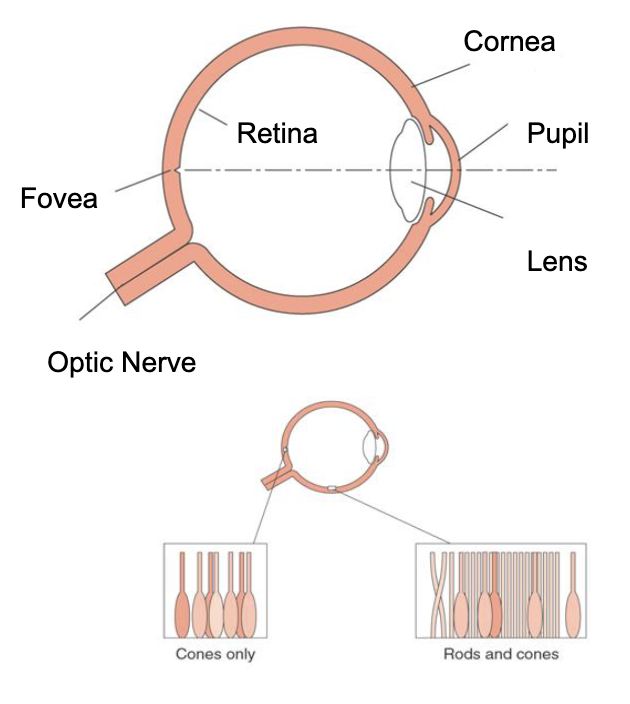
Cornea focuses light on retina via pupil (aperture) and lens
Retina has 2 types of cells
Rods: high sensitivity, but monochrome
Cones: low sensitivity, detect colour
Centre of eye (fovea) has only cones, periphery has a mixture (mostly rods)
Optic nerve transmits signals to brain but also creates a blind spot
Hypoxia
Not enough oxygen getting to cells, mainly the brain
Caused by
Not enough oxygen in the air being breathed in
Ineffective exchange of carbon dioxide with oxygen
Hyperventilation
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Lack of blood flow to the brain
“g”-effects
Common symptoms
Impaired judgement
Confusion
Headache
Unconsciousness
Hypoxia at altitude
Percentage of oxygen in the air remains approximately constant throughout the troposphere
Air press reduces with altitude which reduces partial pressure of oxygen in the lungs
PO2 = 0.21*Pair
Sea level: 213hPa
As partial pressure drops less oxygen is transferred into the blood
A healthy person will have no issues below 10,000ft
Above this supplementary oxygen is required
Hyperventilation
Breathing deeper and more rapidly than required
Caused by
Stress
Anxiety
Symptoms
Dizziness
Tingling sensation in extremities
Vision impairment
Unconsciousness
Treatment - rebreathe exhaled air
“g”-effects
Heart pumps blood to the brain against force of gravity
Upward acceleration increases apparent weight of body
“g”-force
Blood appears “heavier” to the heart, making it harder to pump
Pools in legs, reducing supply to brain
Symptoms
Greying of vision
Tunnel vision
Unconsciousness: g -LOC
Treatment: reduce g-load
Decompression sickness
Nitrogen bubbles escaping from blood due to low air pressure
“The bends”
Symptoms
Headache
Nausea
Unconsciousness
Usually not an issue below 18,000ft
However, diving underwater increases nitrogen pressure in blood increasing likelihood of DCS
Do not fly within 12 hours of any diving activity
Increase to 24 hours if diving below 10m
Illness
Any illness is likely to impair your ability to fly safely
Cold/flu can block Eustachian tubes leading to barotrauma
Any heart or lung issues increase susceptibility to hypoxia and g-effects
Any stomach problems can become rapidly debilitating in flight
Most common cause of pilot incapacitation
Generally, if you’re taking any medication you shouldn’t fly without first consulting an Aeromedical Examiner
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Aircraft heaters typically utilise waste heat from the exhaust system
Cracks in exhausts can leak carbon monoxide into the cabin
Carbon monoxide displaces oxygen in the blood leading to hypoxia
Additional symptom: bright pink skin colour
If suspected shut off heater and ventilate cabin
Alcohol
Alcohol both impairs judgement and increases susceptibility to other conditions
Flying blood alcohol limit is 200mg/L
This is 4 times stricter than UK drink driving limit
Effectively zero in practice
Traditional advice was "Eight hours bottle to throttle”
This is the absolute minimum
Smoking
Smoking reduces lung capacity increasing susceptibility to hypoxia, “g”-effects and carbon monoxide poisoning
Moderate smoking can mimic the effects associated with an altitude of 6,000ft
Thereby reducing tolerance to higher altitudes
Usually banned anywhere on an airfield as well as in the sircraft