KINE 2p05 - Lecture 7
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on key terms and concepts from the Motor Learning lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Motor Performance
Observable behavior at a particular moment in time, subject to influence by performance variables.
Motor Learning
Relatively permanent change in motor performance due to practice and experience, inferred from performance.
Neuroplasticity
The ability of the brain to show modification, involves changes in synaptic strength and organizational connections between neurons.
Short-term Functional Plasticity
Changes in the strength of connections between nerve cells occurring with practice.
Long-term Memory (LTM)
A relatively permanent store of information, can be declarative or procedural.
Declarative Memory
Memory for facts (semantic) and events (episodic); knowing what to do in a particular movement situation.
Procedural Memory
Memory for skills and actions; knowing how to perform a particular motor skill.
Retention Test
Test of a practiced skill performed following an interval of time, used to assess persistence in motor learning.
Transfer Test
Test that measures the amount of learning that can be transferred to a new context or a different skill.
Improvement
One of the four performance characteristics seen in motor learning, indicating better performance over time.
Consistency
Stability of performance outcomes across trials, an indicator of learning.
Persistence
The ability to perform a learned skill over time, maintaining performance levels after a retention interval.
Adaptability
The ability to apply learned skills to varied contexts or novel situations, assessed during transfer tests.
Performance Variables
Factors that can influence observable performance, including learner attributes, learning context, and performance environment.
Warm-up Decrement
Temporary reduction in performance due to a period of inactivity prior to a retention test, can affect retrieved performance.
Positive Transfer
Facilitation of learning a new skill as a result of previous learning on another skill.
Negative Transfer
Inhibition of learning a new skill due to interference from previous learning.
Zero Transfer
No benefit between learning a previous skill and learning a new skill.
Performance Curve
Graphical representation of performance improvement over practice sessions, illustrating different types of learning curves.
S-shaped Learning Curve
A pattern of learning that initially shows slow improvement, followed by rapid gains and plateaus.
Ceiling Effect
A situation where performance measurement cannot exceed a certain level, potentially misrepresenting actual learning.
Floor Effect
A situation where a performance measure cannot fall below a certain level, limiting assessment of skill gains.
Encoding Specificity Principle
Maximizing similarity between practice and performance conditions to enhance encoding and retrieval.
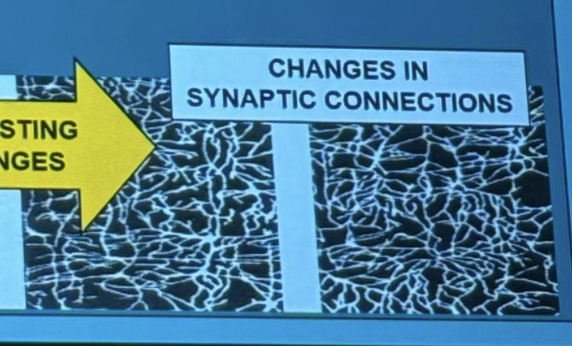
What does structural plasticity mean?
Structural plasticity refers to changes in the organization and numbers of connections between cells in the brain, allowing it to adapt in response to learning, experiences, or environmental changes.
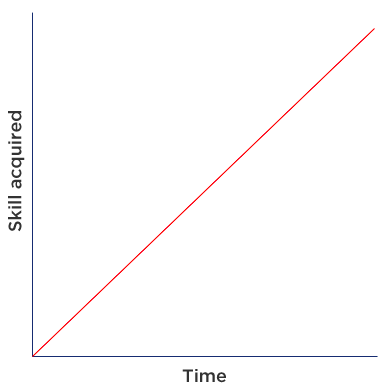
linear performance curves
Direct relationship between practice and performance, showing consistent improvement over time.
Encoding
motor memory is formed
Consolidation
motor memory becomes more stable over time
Retrieval
Motor memory is accessed for performance or recall in task execution.
Performance curve does not
equal learning curve

Positive accelerating performance curve
At first it takes you longer to show improvement then suddenly you start to quickly improve
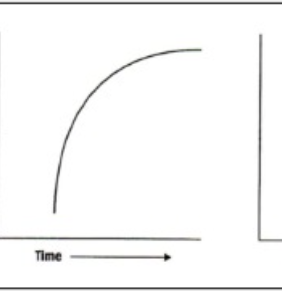
Negatively accelerating performance curve
Reflects the power law of practice
When learning a new skill there tends to be a large improvement in performance early in progress which slows later in practice
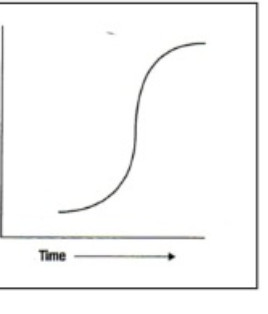
S shaped performance curve
Represents a learning pattern where initial progress is slow, followed by rapid improvement, and then plateaus over time as skill levels off.
Positive and negative together
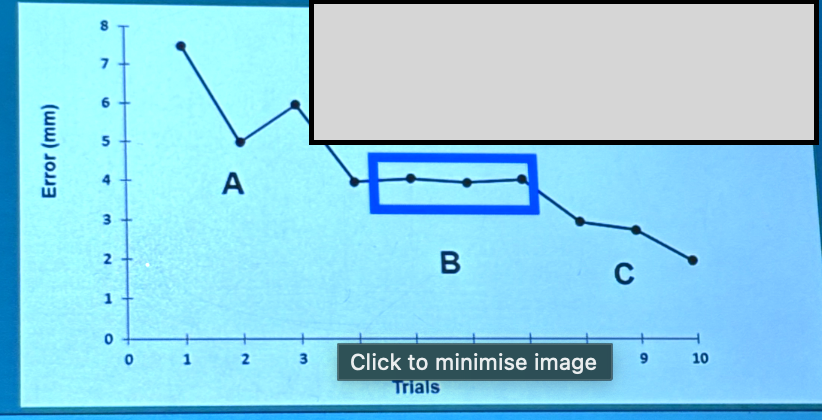
Mis interpreting learning: interpreting plateau
Reflects consistency = skill learned OR
“Learning may still occur in a plateau its just not observable
Mis interpreting learning eg performance plateau
The phenomenon where learners may wrongly assume they have stopped improving, when in fact, learning can occur without visible performance changes. Educationally, this indicates that progress isn't always linear or easily measured.
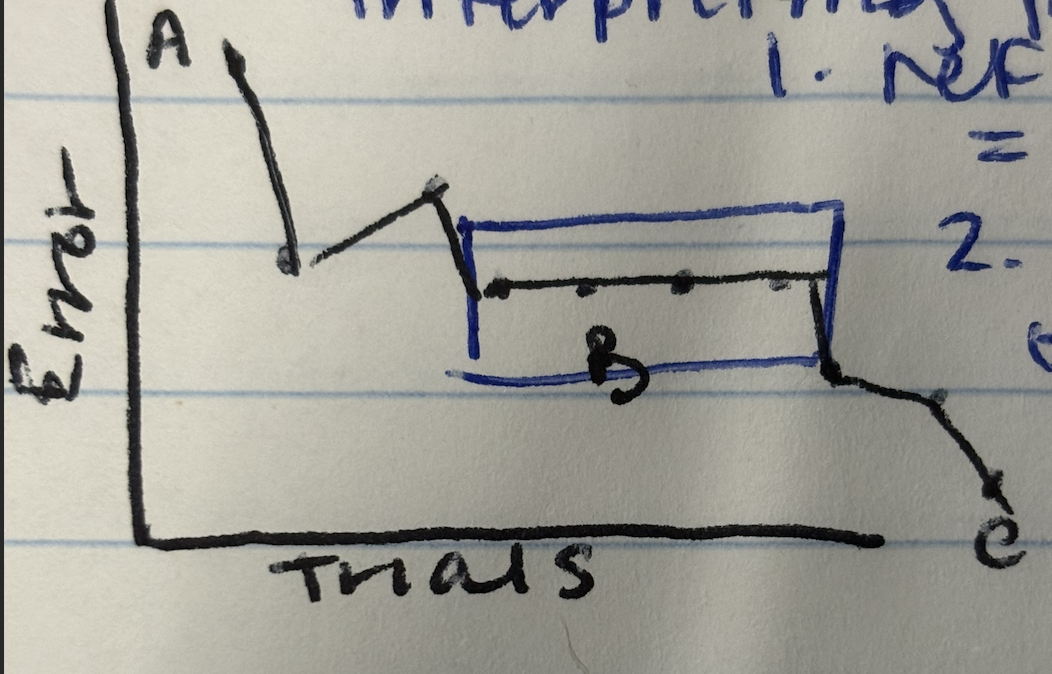
Performance plateau
A) learner experiences constant improvement
B) Learner experiences no improvement (PLATEAU)
C) Learner experiences further improvement
What is a better indicator of learning?
Retention tests
What do retention tests reflect?
Strength of memory over time
What can performance during practice be?
Performance during practice can be temporary. That is why we use retention tests
Motor performance on retention test assesses
the long-term acquisition and retention of skills. (relatively permanent change)
Persistence
Performance lasts over increasing periods of time
warm up decrement
temporary reduction in performance due to a period of inactivity. Therefore need to provide practice trials
Why do we need to perform practice trials
Due to warm up decrement
What causes performance plateaus?
Motivation
Attention
Arousal
Fatigue
New strategy
Measurement techniques
“ceiling” or “floor” effects
Adaptability definition
Even though a relatively permanent change might be observed. can motor skill performance adapt to changes in environmental conditions or task demands.
adaptability during transfer
motor performance on transfer test assesses adaptations to changes in context
transfer test
test measures the amount of learning that can be transferred to a different or similar skill or the original skill in a new context
far transfer
type of transfer of learning that occurs from one task to a different task that is not closely related.
Near transfer or generalization
type of transfer of learning that occurs between tasks that are similar or closely related.
zero transfer (type of transfer)
(Neutral) No transfer between skills
positive transfer (type of transfer)
Facilitation of learning a new skill as a result of previous learning on another skill
Negative transfer (type of transfer)
inhibition of learning a new skill as a result of previous learning on another skill.
Movement elements (parts that can transfer)
Motor patterns leading to a correct performance
Perceptual Elements (Parts that can transfer)
Interpretation of stimuli leading to correct performance
Conceptual Elements (Parts that can transfer)
Guidelines on strategies leading to correct performance
Taking advantage of transfer - Goal: promote positive transfer
Analyze the skill (ie movement, perceptual, conceptual)
Get to know the learner
Make sure the skills you refer to are well learned
Determine the cost benefit trade off (any + or - transfer)
Point out similarities and differences
Maximize similarities between practice (ie encoding) and performance or competition (ie retrieval) - encoding specificity principal