Sight/Vision
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
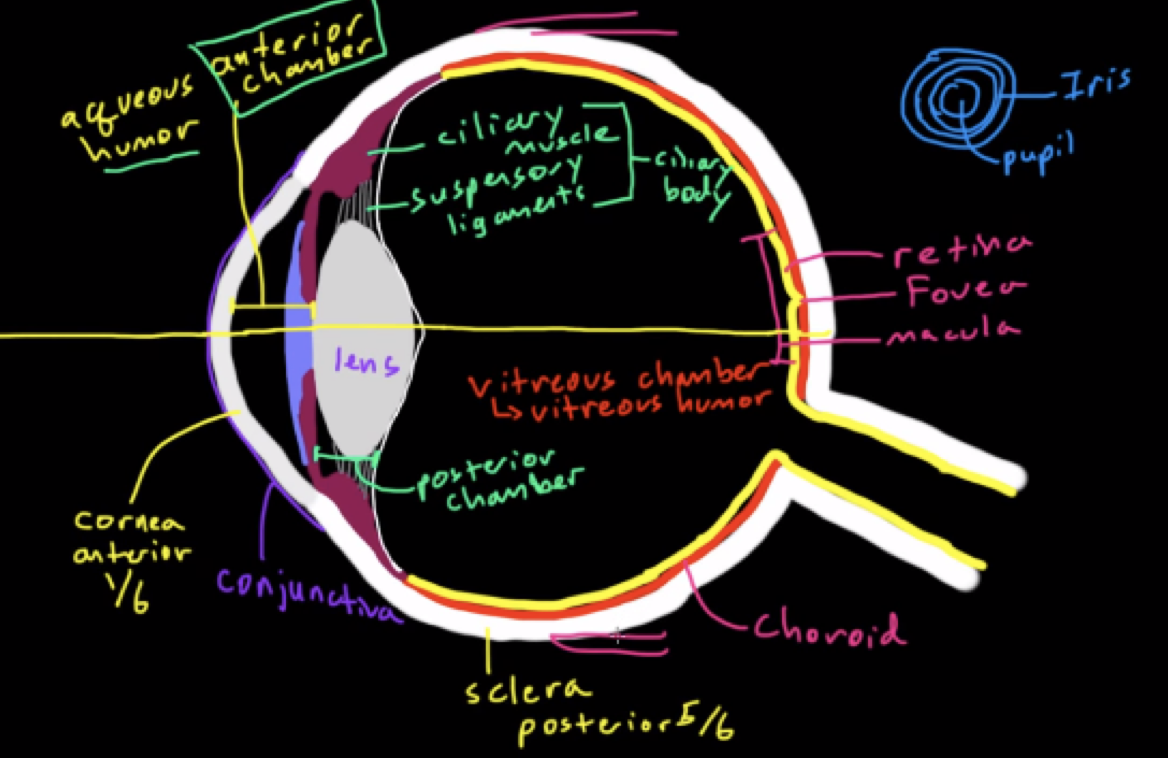
Conjunctiva
Thin layer of cells that lines the inside of your eyelids from the eye
Cornea
Transparent thick sheet of fibrous tissue, anterior 1/6th; starts to bend light, first part of eye that light hits
Anterior chamber
space filled with aqueous humor
provides pressure to maintain shape of eyeball; allows nutrients and minerals to supply cells of cornea/iris
Pupil
The opening in the middle of the iris
can get smaller/larger based on the iris relaxing/contracting respectively to modulate the amount of light able to enter the eyeball
Iris
Gives eye color
is the muscle that constricts/relaxes to change the size of the pupil L
Lens
Bends the light so it goes to the back of the eyeball
focuses light specifically on the fovea of the retina
adjusts how much it bends the light by changing its shape using suspensory ligaments
Suspensory ligaments
Attached to the ciliary muscle
ciliary muscle + suspensory ligaments = ciliary body which secretes aqueous humor
Posterior chamber
area behind iris to the back of the lens
filled with aqueous humor
Vitreous chamber
Filled with vitreous humor (jelly like substance to provide pressure to eyeball and give nutrients to the inside of the eyeball
Retina
Inside, back area filled with photoreceptors, where the ray of light is converted from a physical waveform to an electrochemical; impulse the brain can interpret
Macula
Special part of a retina rich in cones
also has some rods
Fovea
Special part of macula completely covered in cones, no rods
Cones
Detect color and discern high level of detail in what you are observing
6-7 million cones
Types: red, green, blue
detect color primarily but also some light
fast recovery time: easy to detect changes in color
Rods
detect light
120 million rods for night vision
Normally rods are turned on, but when light enters the pupil, it his the rod and light turns the rod off
When the rod is off, it turns on a bipolar cell → on a national ganglion cell → optic nerve → enters the brain
More rods than cones: more important to detect light than detail
1000x more sensitive to light than cones
slow recovery time: longer time to detect changes in light
Choroid
pigmented black in humans
network of blood vessels that helps nourish the retina
all light is absorbed
some animals have a different color choroid which gives them better night vision
Sclera
The whites of the eyes, thick fibers tissue that covers 5/6th of eyeball
attachment point for muscles
extra layer of protection and structure of eyeball
lines with conjunctivia
Anatomy of the eye
Transmission
The electrical activation of one neuron by another neuron
Perception
Conscious sensory experience of neural processing P
processing
The neural transformation of multiple neural signals into one perception T
transduction
Occurs when energy is transformed from one form to another
Light energy is transformed to electrical energy by rods and cones
Sensation
Requires a physical stimulus to be converted into a neural impulse
in the eye, light is being converted to a neural impulse by a photoreceptor
Light
An electromagnetic wave that is in the middle of the electromagnetic spectrum
Phototransduction cascade (PTC)
What happens when light hits rod/cone
Light hits rod → rod turns off → turns on bipolar cell → turns on retinal ganglion cells → optic nerve → brain
Makes the brain recognize there is light entering the eyeball
takes light and converts to a neural impulse
More detailed PTC
Rods are made up of optic disk stacks
Proteins on disk stacks like rhodopsin which contains retinal (11-cis) that changes to 11-trans retinal when hit by light, changing the shape of rhodopsin
Transducin, which is attached to rhodopsin has 3 parts, alpha, beta, gamma
When rhodopsin changes shape, transducin breaks off and the alpha subunit binds to phosphodiesterase (PDE)
PDE takes cGMP → regular GMP
cGMP concentration decreases, which closes Na+ channels (cGMP is bound to Na+ and keeps channels open) → hyper polarizes cell, turning rod “off”
Bipolar cells (ON center and OFF center)
When light hits rod → ON center bipolar cells activate and OFF center bipolar cells inactivate → activates ON center retinal ganglion cell → sends signal to optic nerve → brain
What happens with rods when it is dark
Rod turns on
ON center bipolar cells inactivate and off center bipolar cells active
Off center bipolar cells turn on, activates off center retinal ganglion cell
Signals optic nerve → brain
Photopic vison
Occurs at levels of high light
Mesopic vision
Occurs at dawn/dusk and involves both rods and cones
Scotopic vision
Occurs at levels of very low light
Photoreceptor distribution in retina
Optic nerve connects to retina: blind spot ( no cones/rods)
Rods are found mostly in periphery
Cones are found primarily in fovea, few dispersed throughout the eye
Visual processing field
all right visual field goes to the left side of our brain, vice versa
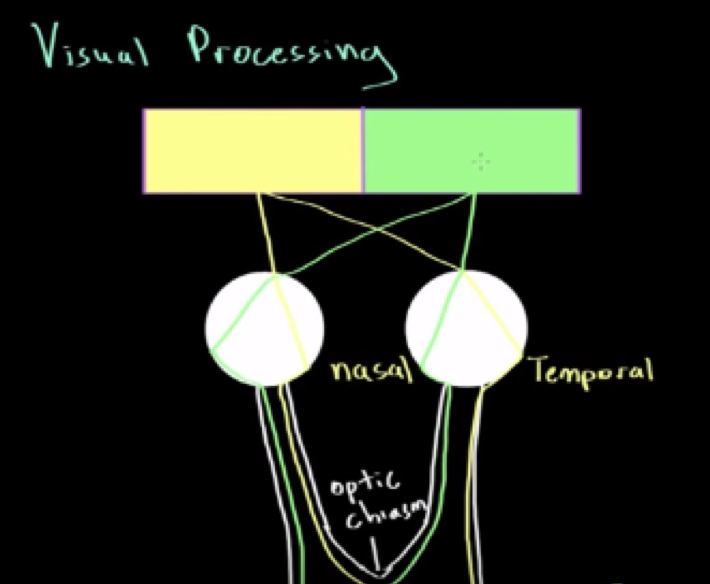
Ray of light from left visual filed his nasal of left eye and temporal of of left eye
Feature detection
Broken down into color, form, and motion to identify what is being looked at
Color
Cones
Trichromatic theory: 3 cones
ex: red object reflects red → red hits red cone → fire axon potential → brain identifies red
Form
We need to figure out boundaries of the object and the shape of the object
Parvocellular pathway: good at detecting boundaries, shapes, and color but not motion
Cones are responsible
Motion
Magnocellular pathway: high temporal resolution (time and motion)
no color and rods are responsible
Parallel processing
detects/focus all information (color, form, motion) at same time