Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Role of Basal Ganglia
1. Movement ON/OFF
2. Movement specificity
3. Learning
Role of Cerebellum
1. Movement Error Detection
2. Movement Error Correction
3. Learning
Basal Ganglia and Cerebellar circuits are predominantly ______
Inhibitory
Basal Ganlia and Cerebellar circuits must be ________ to promote movement
disinhibits
____________ is required for normal voluntary movement
Basal Ganglia
_____________ mediates smooth transitions between commands for movement initiation and/or movement termination
Basal Ganglia
The functions of Basal Ganglia are disrupted by _________ ______ and ________ ________
Parkinson’s disease
Huntington’s disease
What is the corpus striatum?
Receives cortical input
Consists of the caudate and putamen
Caudate
Eye/head movement and body movements
sensory input from cortex
Motor input from eye areas in frontal lobe and motor cortex
Putamen
Body movements
Sensory input from cortex
Motor input from premotor and motor cortex
Topological map of body
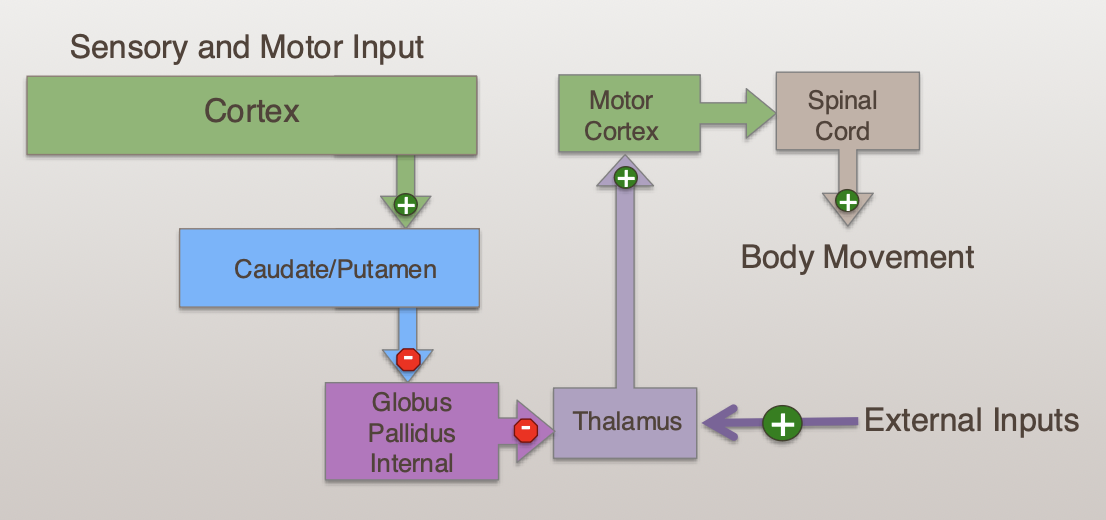
What is the Globus Pallidus
Receives input from the corpus striatum
Inhibits the thalamus
Must be “turned of” for movement
What is the Thalamus?
Relays Basal Gnglia output to motor cortex
Receives inhibition from the internal Globus Pallidus (iGP)
Provides excitatory drive to motor cortex
Must be disinhibited. for movement
What is the Basic Loop (Direct pathway through Basal Ganglia)
1) Cortical Input “Motor Plan”
2) Modulation by Basal Ganglia “Go/Stop”
3) Thalamic integration & relay
4) Cortical integration & execution
_________ ______ ________ in the caudate and putamen receive cortical input
Medium spiny neurons
_________ _________ __________ do NOT fire action potentials easily, require many cortical inputs
GABAergic Inhibitory Neurons
_________ _________ _________ Code a “decision to move toward a goal” rather than movement itself
Basal Ganglia Neurons
A ______ _______ neuron receives input from ~ 100 medium spiny neurons
Globus Pallidus
_______ make a small number of synapses with many globus pallidus neurons (GPNs)
Medium Spiny Neurons (MSNs)
Explain the Basal Nerual Circuit of the Basal Ganglia
1) MSNs of the caudate and putamen receive excitatory input from the cortex
2) MSNs inhibit GPNs
3) GPNs inhibit thalamic neurons
4) GPNs control thalamic responses to excitatory inputs
5) Thalamic neurons excite upper motor neurons
If there is no input from the cortex, there is no (or aberrant) movement because….
1) MSN neurons are inactive
2) GPNs are not inhibited by MSNs
3) GPNs inhibit thalamic neurons
4) Motor cortex is not excited
Cortical input excites the MSNs and there is correct movement because….
1) MSN neurons are active
2) GPNs are inhibited by MSNs
3) Thalamic neurons are disinhibited
4) Motor cortex is excited
Explain the Basal Ganglia Projections: Direct Pathway
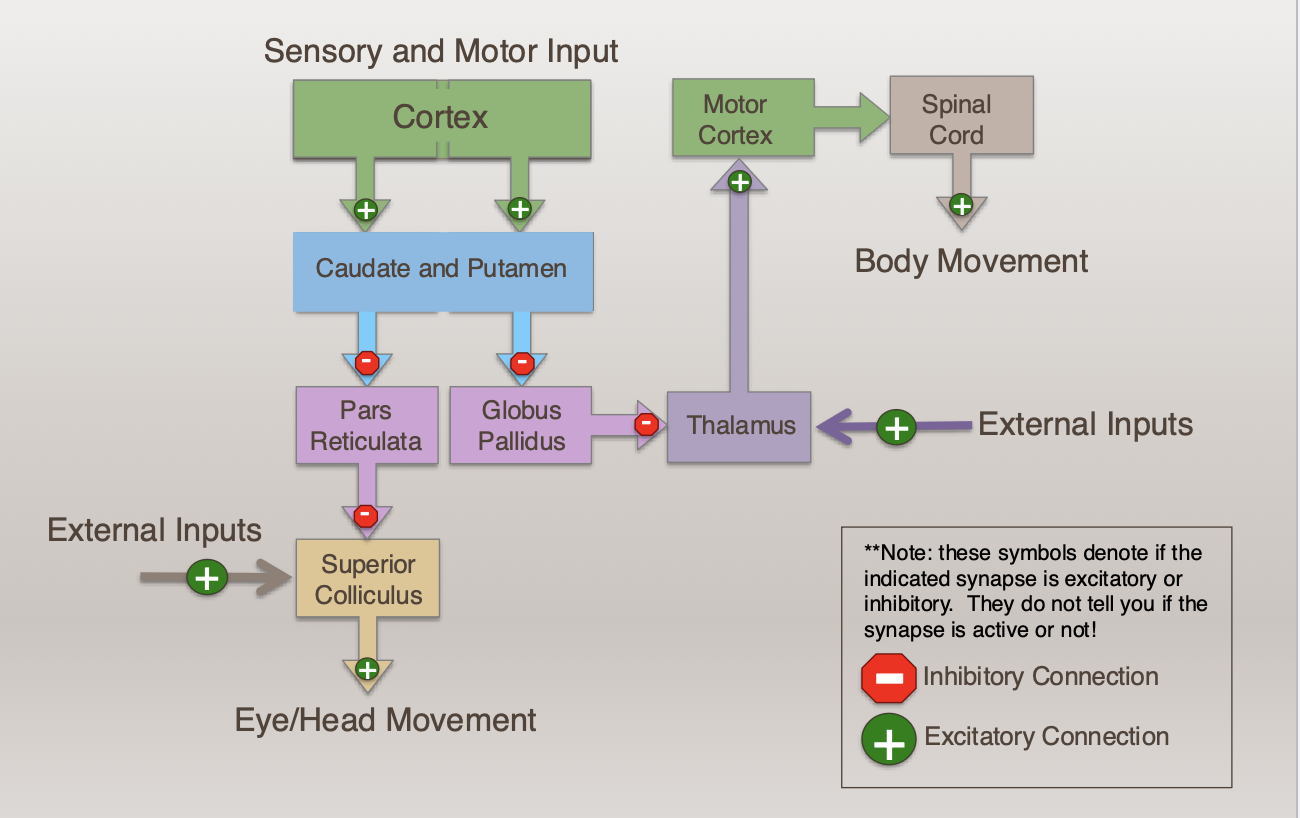
Explain the Basal Ganglia Circuitry: Direct Pathway Movement
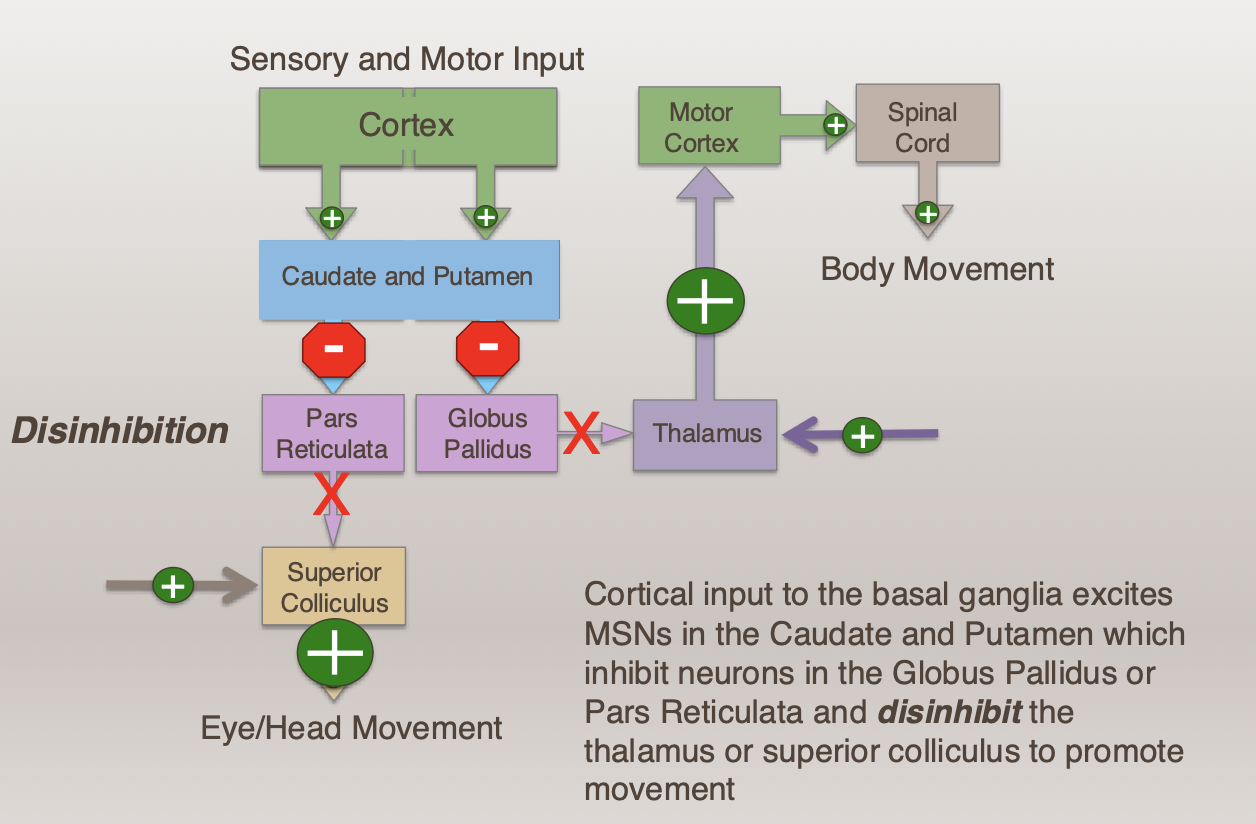
Cortical input to the basal ganglia excites MSNs in the Caudate and Putamen which ______ neurons in the Globus Pallidus or Pars Reticulata and ________ the thalamus or superior colliculus to ________ movement
Cortical input to the basal ganglia excites MSNs in the Caudate and Putamen which inhibit neurons in the Globus Pallidus or Pars Reticulata and disinhibit the thalamus or superior colliculus to promote movement
What does the Motor Nuclei contain?
Caudate
Putamen
Globus Pallidus
Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata
What does the Modulatory Nuclei contain?
Subthalamic Nucleus
Substantia Nigra
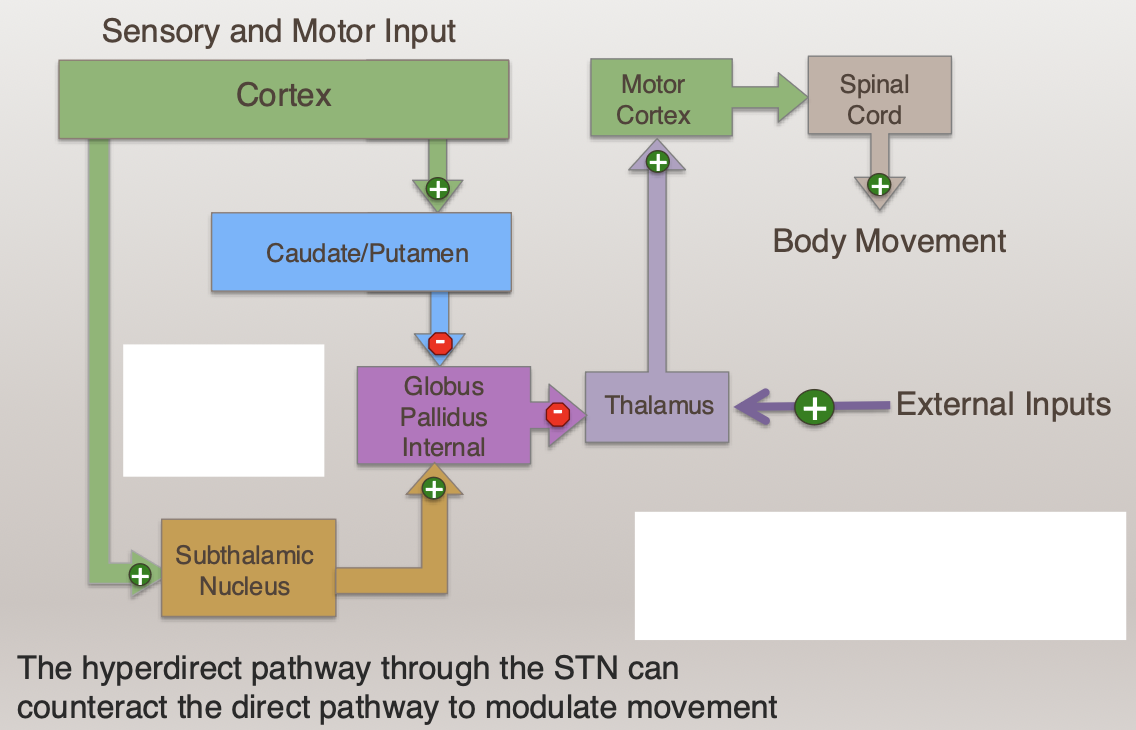
What is the Subthalamic Nucleus (STN)- Hyper-Direct Pathway?
Receives excitation from cortex
Role: Provide excitatory drive globus pallidus internal (GPI)
Must be inhibited for movement
Explain the Direct Pathway in the Basal Ganglia
Explain Hyperdirect pathway in Basal Ganglia Projections
Explain the Indirect pathway in the Basa Ganglia Projections
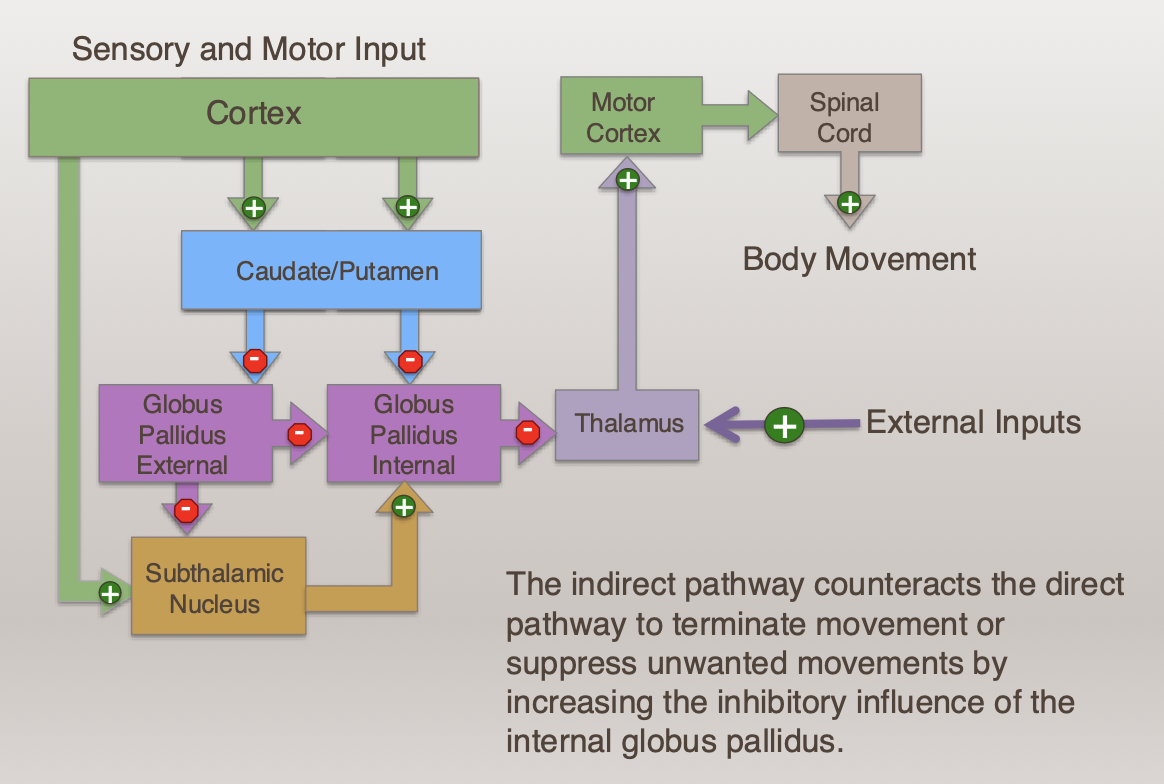
The _______ pathway counteracts the ______ pathway to terminate movement or suppress unwanted movements by ________ the inhibitory influence of the internal globus pallidus.
The indirect pathway counteracts the direct pathway to terminate movement or suppress unwanted movements by increasing the inhibitory influence of the internal globus pallidus.
The external segment of the globus pallidus projects to the internal segment and the
_________ in the ___________
pathway.
A. subthalamic nucleus; indirect
B. thalamus; indirect
C. caudate; indirect
D. caudate; direct
E. subthalamic nucleus; direct
E. subthalamic nucleus; direct
Increased activity from the ________ to the subthalamic nucleus increases the
________ input to the thalamus.
A. GP external; excitatory
B. GP internal; inhibitory
C. cortex; excitatory
D. GP internal; excitatory
E. cortex; inhibitory
E. cortex; inhibitory
What is the Substantia Nigra and what does it do?
Receives excitation from the corpus striatum
Provide dopaminergic input tot the corpus striatum
Excites the direct pathway, inhibits the indirect pathway
The substantia nigra pars compacta provides __________ to the MSNs of the __________________. Dopamine increases the activity of the _______ pathway but suppresses the ________ pathway
The substantia nigra pars compacta provides dopamine to the MSNs of the corpus striatum (caudate/putamen). Dopamine increases the activity of the direct pathway but suppresses the indirect pathway
What is the cause of Parkinson’s disease?
Loss of doapmine neurons in the substantia nigra
What happens in the Basal Ganglia projections in Parkinson’s disease?
The loss of dopamine to the MSNs of increases the activity of the indirect pathway but suppresses the direct pathway
What is Huntington’s Disease?
Atrophy of cerebral nerve tissue and Basal Ganglia
Increased inhbition of GP internal
Too much ballistic movement
What occurs in the Basal Ganglia projections in Huntington’s disease?
The connection between the caudate and GP-External is degenerated
What are the inputs to the cerebellum?
Cortex - vid the pons (movement information)
Spinal cord (sensory input)
Vestibular Nuclei (sensory input)
Olive (sensory and modulatory input)
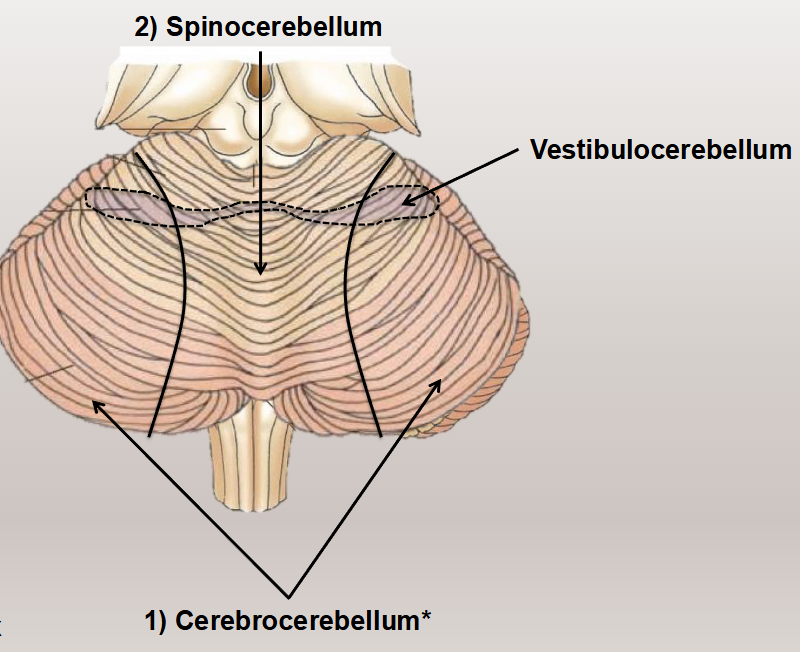
What are the parts of the cerebellar cortex?
Cerebrocerebellar
Spinocerebellar
Vestibulocerebellum
What is the fucntional organization of cerebellar outputs? (from Cerebellar cortex to Pathways to upper motor neurons)
What is the Cerebrocerebellum?
Gets input from cerebral cortex
Skilled movements
Planning and execution of movement sequences in time and space
What is Dysmetria?
Errors in smoothness and direction of targeting movements due to cerebro-cerebellar pathway
Patients tend to over or undershoot objections
The closer the movement gets to the target, the more irregular the movement (intention tremor)
What is the Spinocerebellum?
Gets input from the spinal cord
Sensory
Has somatotopic maps
Two zones
Median
Paramedian
What is the Vestibulocerebellum?
Input from Vestibular Nuclei
Coordinate Posture, Balance
Coordinate eye-body movements- i.e. Vestibular ocular reflex (VOR)
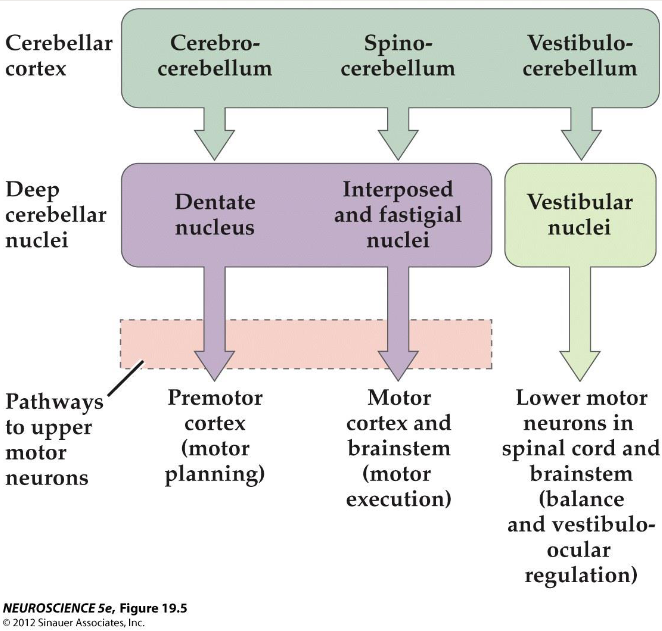
What are Cerebellar Nuclei?
Receive inhibitory input
from the cerebellar cortex
Sole source of output from the cerebellum
Project to the thalamus (which projects to motor cortex)
Project to the brainstem upper motor neurons
What is the Motor Planning Pathway?
Cerebrocerebellum > Dentate Nucleus > Thalamus/Premotor Cortex
What is the Motor Execution Pathway?
Spinocerebellum > Fastigial/Interposed Nuclei > Thalamus/Brainstem
Explain the following in the Vestibulo-verebellar, Spino-cerebellar, and Cerebro-cerebellar pathways:
Input From
Region of Cerebellar Cortex
Deep nuclei
Function(s)
Vestibulo-cerebellar Pathway
Input from: Vestibular system
Region of Cerebellar cortex: Vestibulo-cerebellum
Deep Nuclei: Vestibular nuclei
Function(s): Balance and reflexive eye movements
Spinocerebellar pathway
Spinal Cord
Spinocerebellum
Fastigial nuclei/interposed nuclei
Error Correction for movements
Cerebro-cerebellar Pathway
Cerebral cortex
Lateral hemisphere
Dentate Nuclei
Motor planning
Crossing over Coordinates ________ input from the cortex and ________ input from the spinal cord and brainstem. In the cortex, ipsilateral muscle movements are represented in the _________ hemisphere. At the spinal cord, the muscle movements are driven by _______ neurons. The cerebellum has an _______ representation of muscle movement (like the spinal cord).
Crossing over coordinates descending input from the cortex and ascending input from the spinal cord and brainstem. In the cortex ipsilateral muscle movements are represented in the contralateral hemisphere. At the spinal cord, the muscle movements are driven by ipsilateral neurons. The cerebellum has an ipsilateral representation of muscle movement (like the spinal cord).
What is Ataxia? What are the causes?
A neurological disorder consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements
Causes
Cerebrellar Dysfunction
Could be due to environmental factors (alcohol, trauma)
Also caused by genetic disorders (e.g. spinocerebellar ataxia)
What are the effects of alcohol (short term & long term)
Short term
Lack of coordination
Unsteady gait
Slurred speech
Long term
Damage to anterior portion of cerebellar cortex (anterior vermis in fig) affects movement in lower limbs
Wide and staggering gait
Little impairment of arm or hand movements
No disruption of speech