BIOL430: Nervous System (Organization)
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GMU A/P-1 exam 3 Chapter 11.1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
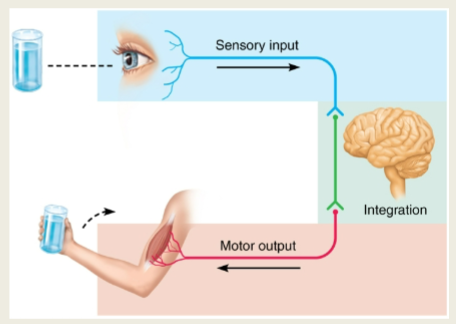
Functions of the Nervous System
Sensory: Detect internal and external stimuli with receptors and send to the CNS
Integrative: Interpretation of sensory input/dictating appropriate response(s)
Motor: Respond to the stimuli by activating muscles and glands (effectors)
Central Nervous System
CNS: Made up of the brain and spinal cord.
Integration of input and determines appropriate output
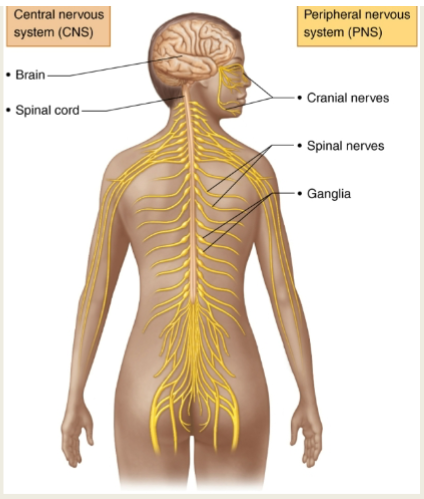
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), 4 parts
Sensory/Afferent Neurons
Efferent/Motor Neurons
Cranial and Spinal Nerves
Enteric Nervous System
Sensory (afferent) Neurons
part of the PNS, provide input to CNS from Receptors
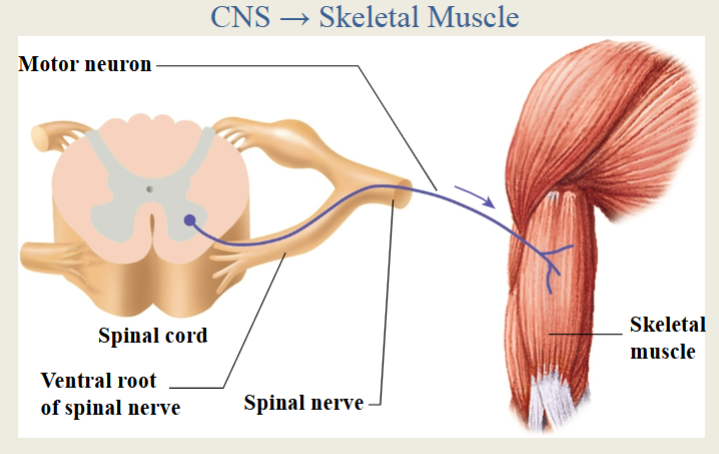
Efferent (motor) Neurons
Part of the PNS, provide output from CNS to effectors
Cranial and Spinal Nerves
Part of the PNS, sensory and motor neurons to and from the brain and spinal cord
Enteric Nervous System
Part of the PNS, “brain of the gut”
Somatic afferent fibers
skin, sensory structures, skeletal muscles, and joints
conscious perception
visceral afferent fibers
visceral organs
unconscious perception
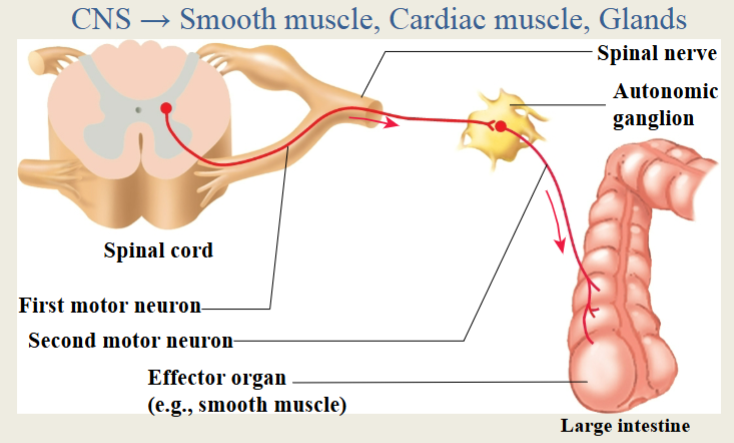
Autonomic Neurons
Sympathetic = fight or flight
Parasympathetic = rest and digest
movement of the Enteric Nervous System
Involuntary sensory and motor neurons that control the GI tract
independent from the autonomic motor division and the CNS