CHEM 202 chapter 11: intermolecular forces, liquids, and solids
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Large intermolecular forces in a substance are manifested by __________.
low vapor pressure, high boiling point, high heats of fusion and vaporization, high critical temperatures and pressures
Of the following, __________ is an exothermic process.
freezing
The vapor pressure of any substance at its normal boiling point is________________.
1atm or 760 mmHg
The property responsible for the "beading up" of water is __________.
surface tension
viscosity
the resistance to flow
How high a liquid will rise up a narrow tube as a result of capillary action depends on __________.
the magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube, and gravity
The shape of a liquid's meniscus is determined by __________.
the relative magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and its container
characteristics of gas
assumes the volume and shape of container and has rapid diffusion
characteristic of liquid
takes the shape of container but not the volume of the container, readily and slow diffusion
characterisitc of solids
retains the shape of its container and has a definite volume, with very slow diffusion.
intermolecular forces
forces between molecules that determine the physical properties of substances, including boiling and melting points.
dipole-dipole force
attractive forces between polar molecules due to the positive end of one molecule being attracted to the negative end of another.
hydrogen bonding force
a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs between molecules containing hydrogen bonded to highly electronegative atoms like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
london dispersion force
a weak intermolecular force arising from temporary dipoles in nonpolar molecules.
ion-ion interactions
attractive forces between charged ions in an ionic compound, resulting from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
ion-dipole forces
interactions between an ion and a polar molecule, where the charge of the ion is attracted to the partial charges of the polar molecule.
viscosity
the resistance to flow which increases with stronger intermolecular forces and larger molecular size.
surface tension
the energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid, resulting from cohesive forces between liquid molecules.
capillary action
the ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of external forces, caused by adhesive and cohesive forces.
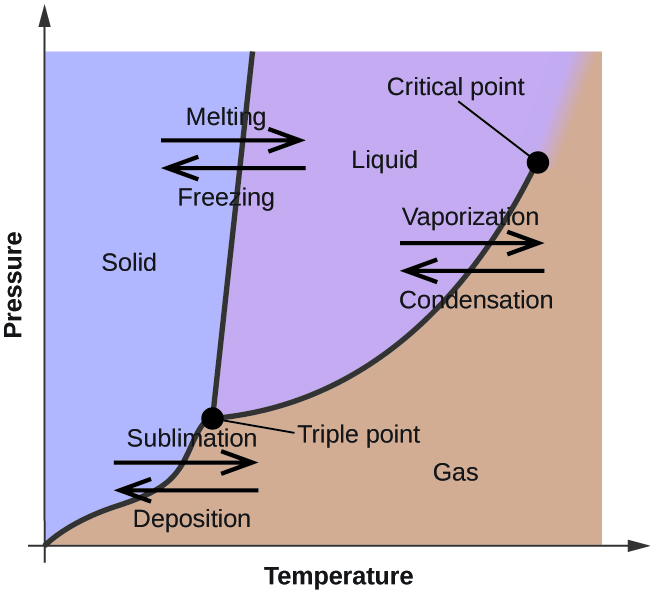
phase change
the transformation of the three states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) due to changes in temperature or pressure.
heat of vaporization
liquid to gas
heat of fussion
solid to liquid
sublimation
solid to gas
heating curve
used to illustrate phase changes and energy changes accompanying them
critical tempature
highest tempature at which substance can exist as a liquid
critical pressure
the pressure required for liquification of a gas at a critical temperature
dynamic equilibrium
rate of gas molecules condensing equaling rate of liquids evaporating
volatile liquids
liquids that evaporate easily
normal boiling point
1 atm or 760 mmHg
point T of phase change
triple point where all three states exist
Line TC of phase change
boiling point of the substance at that pressure
Point C of phase change
critical point where the highest tempature and pressure exist
Segment TA of phase change
The line represents the melting point of a solid at any given pressure
Segment of TB of phase change
sublimation point line which represents a solid and gase phase in equilibrium.
Which of the following is NOT a type of van der Waals force?
covalent bonding
Which type of intermolecular force is present in all molecular substances, regardless of polarity?
London Dispersion Forces
Which of the following substances exhibits hydrogen bonding?
NH3
What happens to the viscosity of a liquid as temperature increases?
decreases
Which of the following factors affects London Dispersion Forces?
Molecular size, Molecular shape, Electron cloud polarizability
Which of the following intermolecular forces is the strongest?
ion-ion interactions
Which of the following statements about hydrogen bonding is TRUE?
It occurs when hydrogen is bonded to N, O, or F.
Which of the following factors increases the strength of London dispersion forces?
increased molecular weight
Which of the following factors affects the viscosity of a liquid?
temperature, intermolecular forces, molecular size
What is the primary reason water exhibits a concave meniscus in a glass tube?
Strong adhesive forces
Which property of liquids is responsible for the formation of spherical droplets?
Surface tension
What happens to the surface tension of a liquid as temperature increases?
it decreases
What happens to the boiling point of a liquid when external pressure is decreased?
decreases
Which phase change occurs when a solid directly transforms into a gas
sublimation
Which of the following phase changes is exothermic
condensation
What is the name of the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure
boiling point
What is the significance of a substance’s critical temperature?
It is the temperature at which a gas becomes a supercritical fluid
Which of the following statements is TRUE about phase diagrams?
The slope of the solid-liquid boundary in water's phase diagram is negative.
Which of the following molecules would exhibit hydrogen bonding?
NH₃ (Hydrogen bonding occurs when H is directly bonded to N, O, or F. NH₃ (ammonia) contains N-H bonds, allowing for hydrogen bonding.)