Chapter 3.2 - DNA Replication
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
semiconservative
the process of DNA duplication where the original double helix unwinds, and each strand serves as a template for a new, complementary strand
conservative
a hypothetical model of DNA replication where the original parental DNA double helix remains intact, and an entirely new double helix is synthesized separately. This would result in two daughter DNA molecules: one composed of the two original "old" strands, and the other composed of two completely "new" strands
dispersive
a hypothetical model of DNA replication where the original double helix breaks into fragments, and the new double helices are a mixture of both old and new DNA segments interspersed on each strand
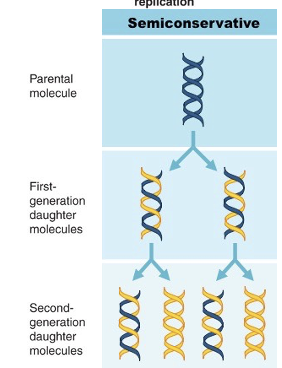
semiconservative
how does DNA replicate? AKA which hypothesis was correct?
helicase
binds to the origin and unwinds the parental double helix to allow an access place for DNA polymerase to bind
binding proteins
make sure the two strands are actually separated and stay apart
primase
makes a short stretch of RNA on the DNA template; primes it for polymerase
DNA polymerase
proofreads activity checks and replaces incorrect bases
okazaki fragment
short DNA sequences synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication because DNA polymerase can only build new DNA in the 5′→3’ direction
because it is being created in 5’ to 3’
why is the leading strand continuous
because it’s going 3’ to 5’ and DNA polymerase can only make DNA in 5’ to 3’; it solves this by making fragments
why is the lagging strands discontinuous
ligase
seals up the sugar phosphate backbone
enzymes
what removes RNA primers?
helicase binds to origin and separates strands
binding proteins keep strands apart
primase makes a short stretch of RNA on the DNA template
DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the RNA primer
DNA polymerase proofreading activity checks and replaces incorrect bases
continuous strands synthesis continues in a 5’ to 3’ direction
discontinuous synthesis produces Okazaki fragments on the 5’ to 3’ template
Enzymes remove RNA primers and Ligase seals sugar-phosphate backbone
What are the steps to DNA replication? (8)
transcription, RNA processing, translation
what are the steps of protein synthesis?
transcription
production of mRNA
translation
production of protein using mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
gene expression
taking the sequence of the purines and puramadines on DNA and using the info to synthesize a protein
nucleus
where is DNA replicated?
nucleus
where does transcription take place?
cytoplasm
where does translation take place?
RNA: single stranded, uses ribose, uses uracil
DNA: double stranded, uses deoxyribose, uses thymine
what are the three main differences between RNA and DNA
mRNA
carries information from DNA to ribosome
nucleus
where is mRNA produced?
ribosome
where is mRNA transported to?
codon
a three nucleotide ____ specifies a particular amino acid
rRNA
with associated proteins to make up ribosome; provide structural support
two
how many subunits does rRNA have?
tRNA
used to transfer amino acids to the ribosome to create the amino acid polypeptide chain
cloverleaf
what shape is tRNA
anticodon binding site
the site of tRNA that forms hydrogen bonds with the mRNA codon
thanks!
Here’s a picture showing the difference between mRNA and tRNA and how they interact with each other
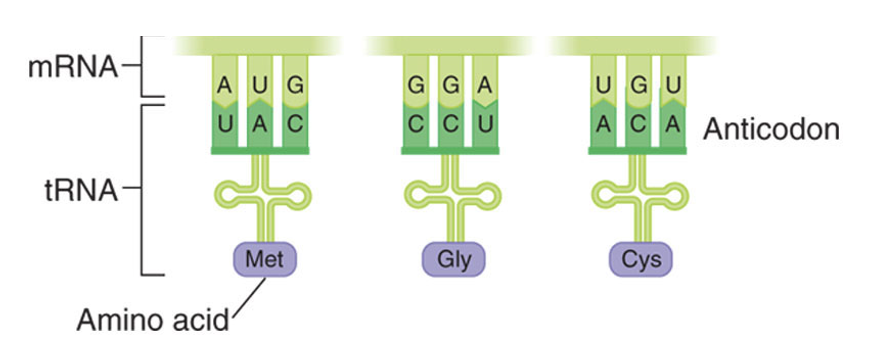
RNA
____ is the bridge from DNA to protein
mRNA
____ is synthesized from the template strand of DNA
complementary strand
which strand of DNA is the coding strand?
RNa polymerase and transcription factors
what enzymes are required for transcription?
operons
in bacteria, these control gene expression
transcription factors
transcription factors
over 2,000
how many kinds of transcription factors exist?
True
True or False: there can be mutations in transcription factors
they bind to specific regions of DNA
what is the thing that is common between all types of transcription factors?
helix-turn-helix, zinc finger, leucine zipper
give 3 examples of transcription factors
initiation
promoter attracts transcription factors and RNA polymerase
elongation
RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to growing RNA
termination
sequences in the DNA prompt the RNA polymerase to fall off, ending the transcript
initiation, elongation, termination
what are the three steps of transcription in order?
promoter
a segment of DNA that binds to RNA polymerase to initiate the process of transcription
5’ to 3’
direction of transcription
False
True or False: you can only have one RNA polymerase on DNA at a time