Miosis, Mitosis, Punnet Squares
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
chromosomes
carries DNA, packaged by histones + proteins
histone
proteins that package chromosomes into chromatin
centromere
connects chromatids together
chromatid
one strand of a chromosome
sister chromatids
two chromatids, a chromosome
homologous chromosomes
two chromosomes with similar genes that sit together
haploid
1 set of chromosomes, gametes (n)
diploid
2 sets of chromosomes, humans (2n)
Interphase
g1, s, g2
G1
cells grows and copies organelles
S
DNA replication (23 pairs, 46 chromosomes double)
G2
More cell growth, organelles, and proteins develop and mature
G0
Not a part of the cell cycle. Quiescent cells perform their functions without ever dividing. They have a particular life function and when they die there is no offspring. Ex: neurons, RBCs
Euchromatin
DNA is less condensed and loosely contained. Has an active form that can be accessed by RNA polymerase for transcription
Heterochromatin
Tightly wrapped, heavily condensed, cannot be transcribed, not active
Prophase
Nucleolus and nuclear envelope disapears
Centromeres move to opposite poles
microtubules extend between centrosomes
Sister chromatids coil tightly and become visable
centrosome
holds miotic spindle
prometaphase
microtubules extend and form miotic spidle
sister chromatids attach to microtubules at centromere
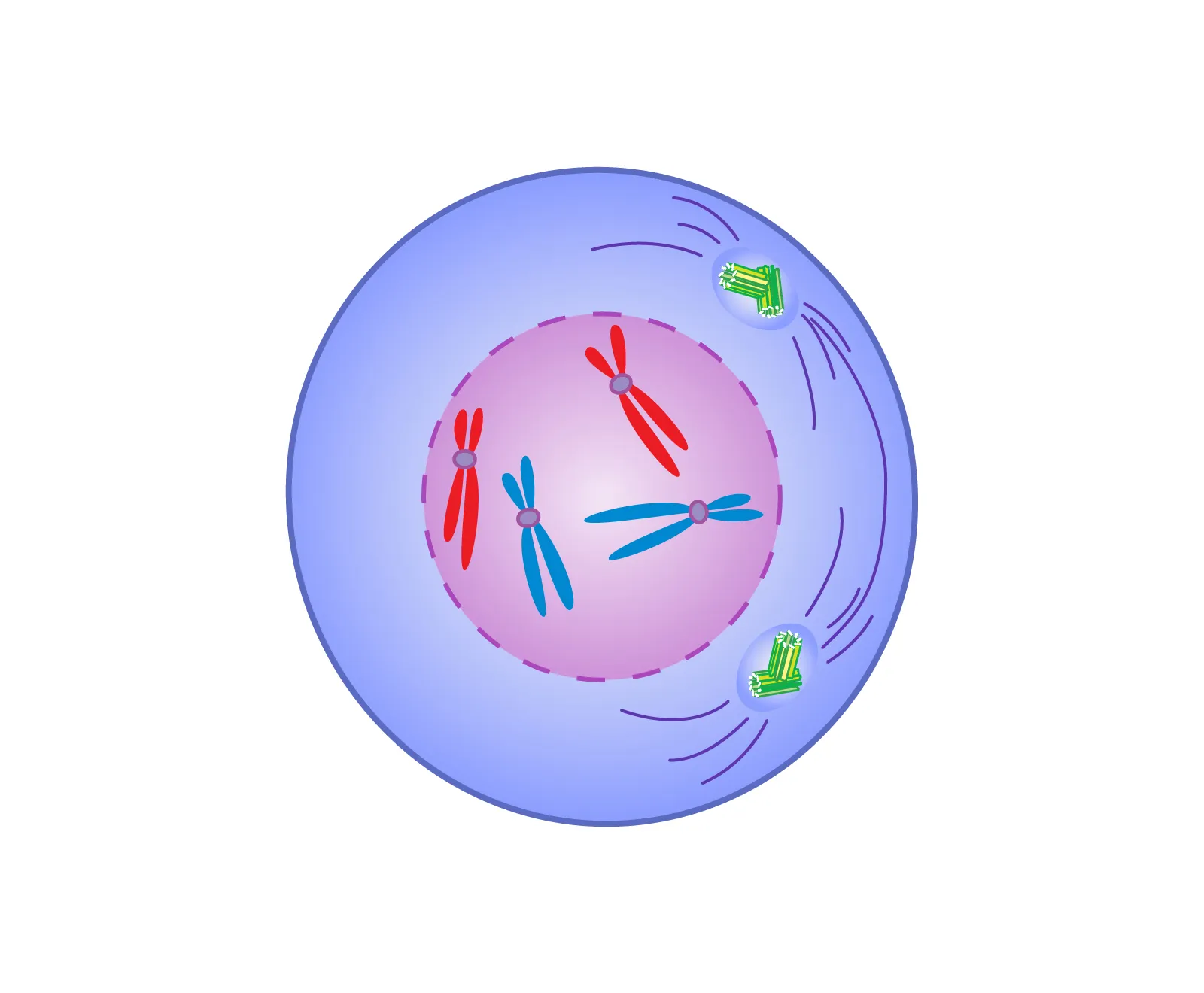
metaphase
chromosomes go to middle of the cell and are their most visable
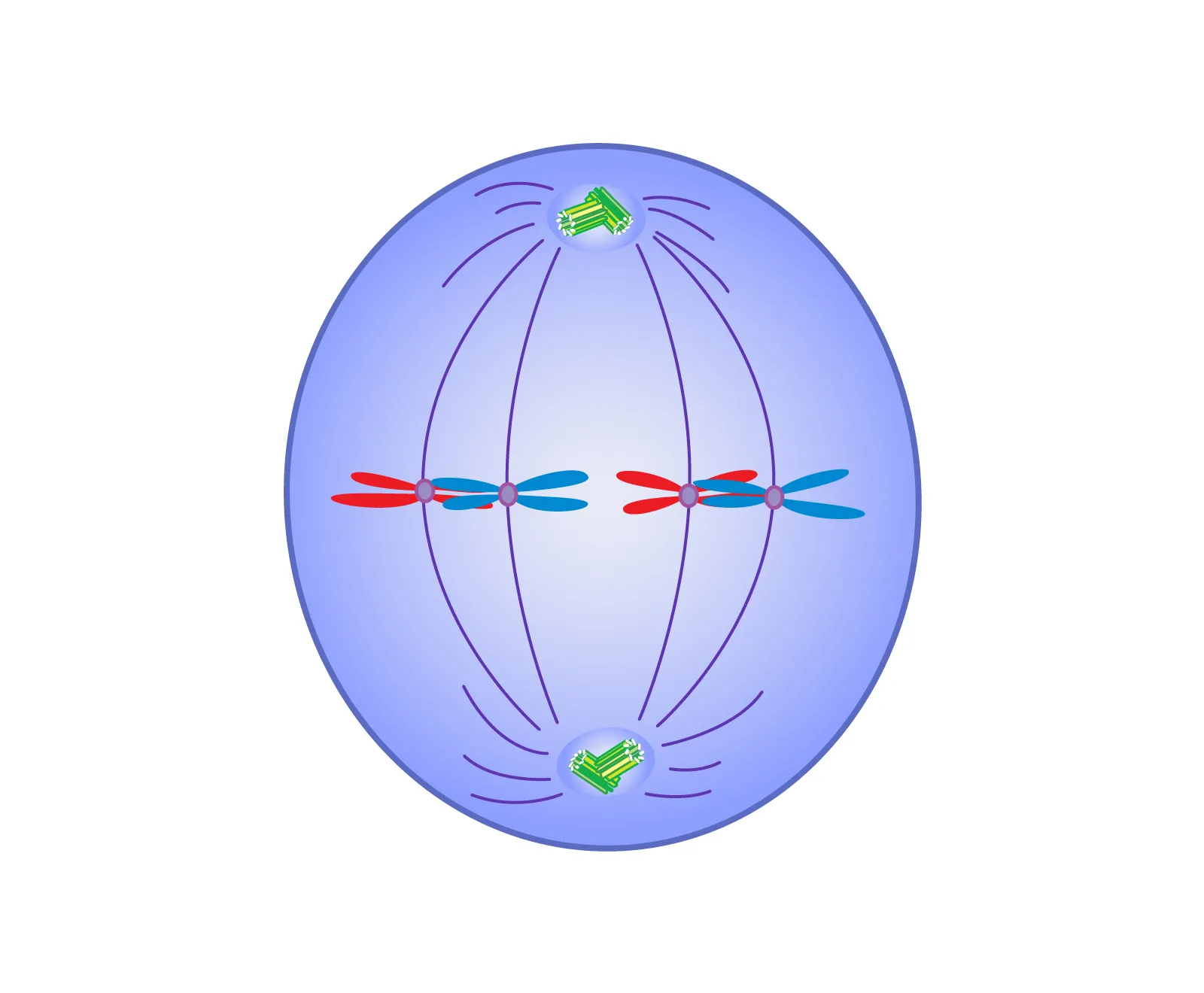
Anaphase
cell elongates
sister chromatids are split at the centromere and pulled towards their centrosome
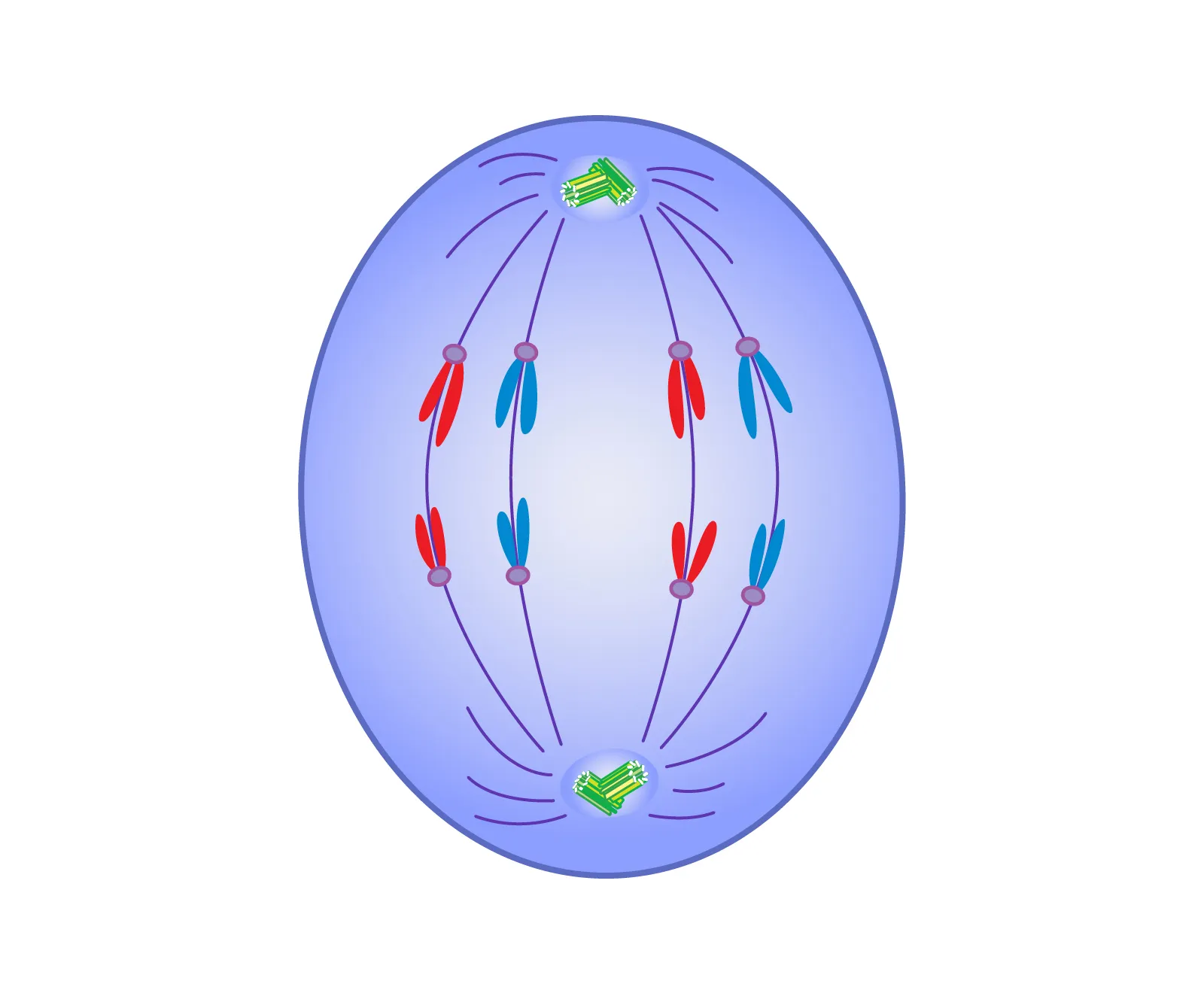
telophase
chromatids decompose at opposite poles
miotic spindle breaks down and nuclear envelope forms
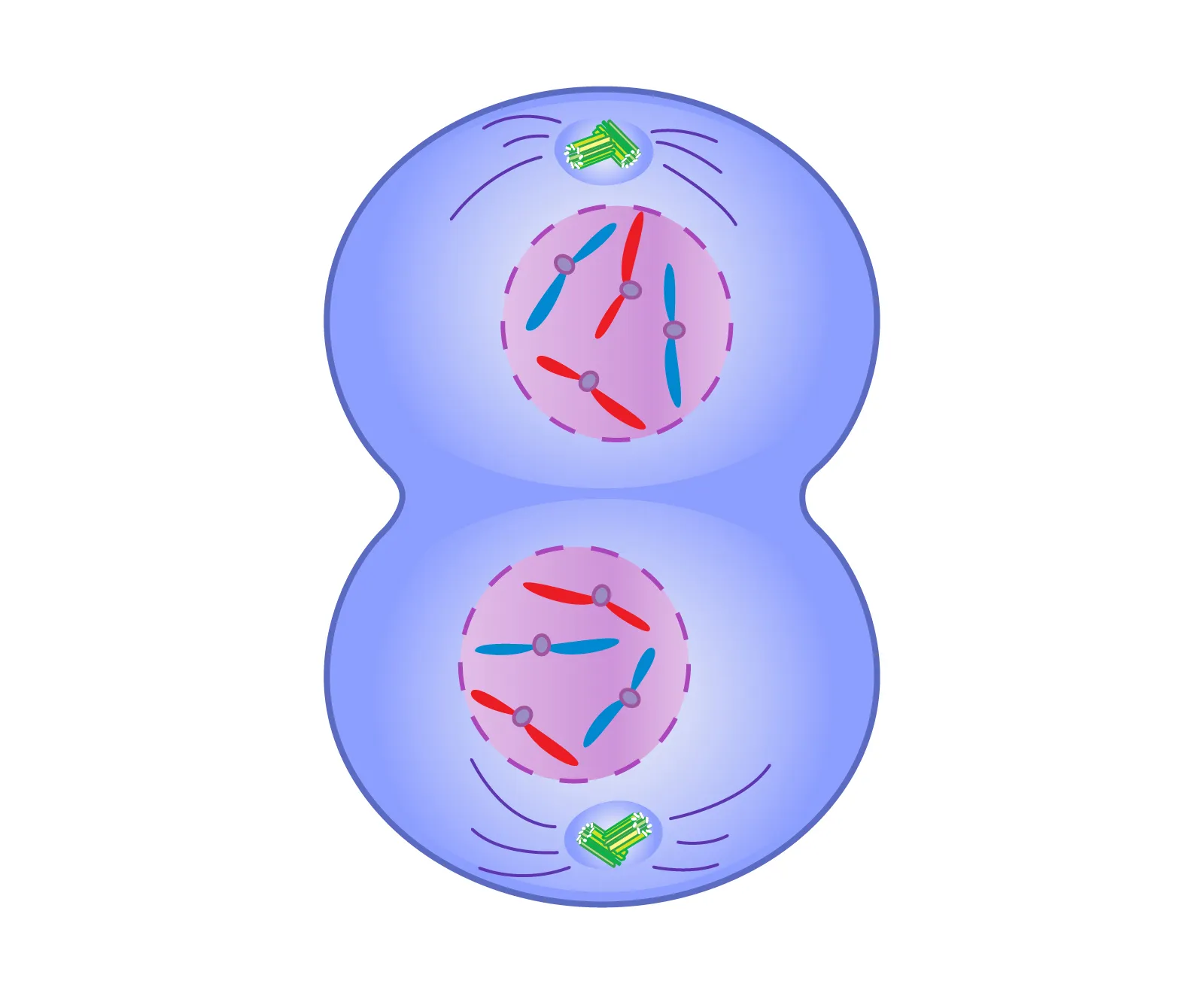
Cytokinesis
Cell physically splits
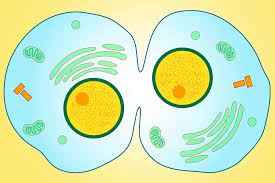
Animal cytokinesis
Actin forms a ring called cleavage furrow and pinches the cell apart
Plant cytokinesis
Golgi apparatus makes vesicles lined up at the middle acting like a cell wall that then splits creating two cells
Mitosis
genetically same cells (2n → 2n)
Miosis
genetically differing gametes (n)(2n → n)
prophase I
miosis: chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope breaks, homologous chromosomes cross over
prometaphase I
miosis: microtubules spread across the cell, centrosomes go to opposite sides of the cell
metaphase I
miosis: tetrads (4 chromosomes) moves to mid line with homologous pairs randomly orientating themselves
anaphase I
miosis: microtubules pull apart chromosomes
telophase I
miosis: chromosomes at opposite poles, everything reverses, physical seperation, haploid daughter cells
prophase II
miosis II: chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope breaks, centrosomes move to opposite poles
prometaphase II
miosis II: nuclear envelope is gone, microtubules attach to centromere of sister chromatids
metaphase II
miosis II: sister chromatids are condensed and at the midline of the cell
anaphase II
miosis II: sister chromatids are pulled apart and at opposite sides of the cell
telophase II
miosis II: chromatids decondense, nuclear envelope is back, cells seperates into four haploid cells (n)
Gregor Monk
studied pea plants, founding father of genetics
Principal of Segregation
people have two alleles and passes one to their offspring
dominant and recessive genes
homozygous, heterozygous, homozygous
genotyoe
phenotype
genotype
homozygous dominant and recessive, heterozygous
phenotype
observable traits (color, size, etc…)
Law of individual assortment
inheritance of a gene is independent of inheritance of another
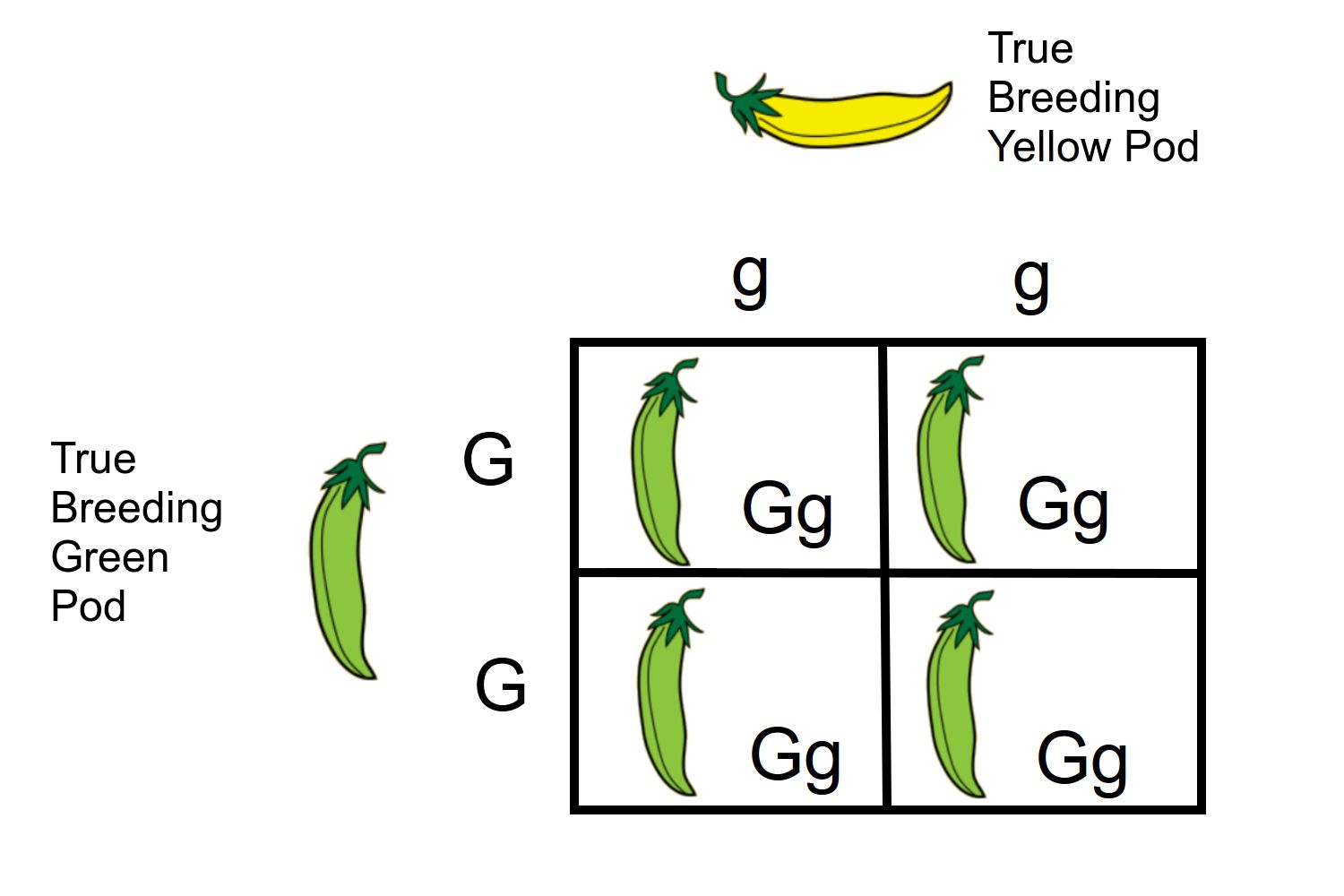
monohybrid square
one trait
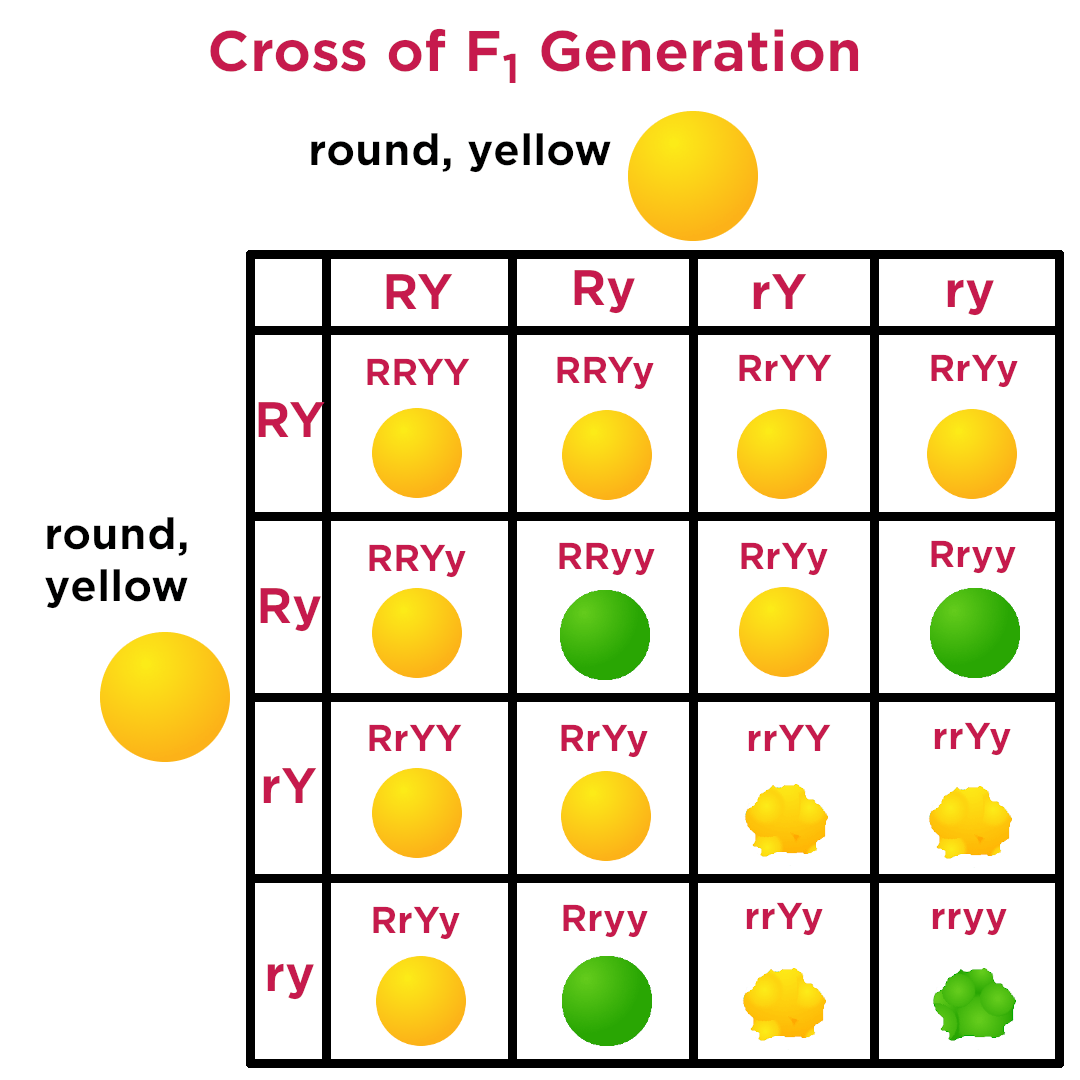
dihybrid square
two traits
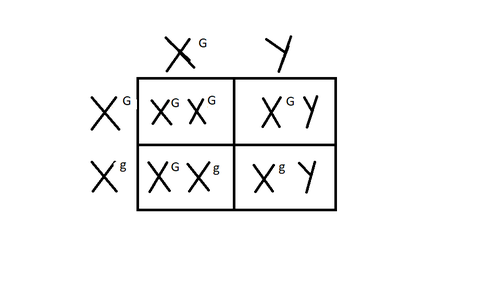
sex linked
Alleles is only on x chromosome
incomplete dominance
two dominant alleles resulting in mixed phenotype (black + white → gray)
codominance
dominant alleles expressed at the same time (black and white feathers)