DNA transcription - L4
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Differnet types of RNA
Ribosomal RNA
tRNA
mRNA
all made using different RNA polymerases
Differnet types of RNA polymerase
1—> Pre ribosomal RNA —> used to make ribosme components which ae used in portein sytheiss
2—> siRNA, miRNA —> regulatory RNA e.g. in splicing
3—> tRNA —> protein synthesis
what is mRNA made form
Formed form replication bubble of DNA separating out DNA into single stands
It exposes template stand - which mRNA is generated form (primary RNA trascript)
mRNA will be the same as coding strand - except have U instead of T
How RNA polymerase binds to mrna in prok
site of where tarscription starts is known as +1
coding region is downstream/ comes after +1
there is also a promotor region upstream of +1 site this is where RNA polymerase binds as recognises sequnce to then start trascription - so tarscription starts form +1 and to the right until reaches stop codon
mRNA has sequence to show the start of translation AUG
what are at the begining and end of teh mRNA
beginning have leader - 5’ UTR
at the end have trailer region - 3’ UTR
they are regulatory for ribosome, act as signal for ribosomes to translate sequence int o proteins
what is added ONLY to Euk mRNA
have 5’ Cap and at 3’ position get Polyateal
5’ cap helps against degradation and used as signals for when ribsome comes along
Gene promoter region in Prok:
in promoter region have specific sequences that are recognized by RNA polymerase
these are -35 sewynec and -10 sequence
RNA polymerase recognized these and binds knowing there is a gene to transcribe
these sequences are consensus sequences (just means most commonly occurring sequence in all examples that have been studied)
Gene promotor in Euk:
in promotor region have a TATA box and further upstream have CAAT box and GC box
proetin that bids to these boxes are TF (DNA bidning proetins)
these boxes are recognised by RNA polymerase that its the start fo a gene
different gene have different boxes its a way to help regulate gene activity
The immature mRNA produces contains; 5’ cap, leader region, trailer region, Poly(A), exons and introns
later modified to then get mature mRNA
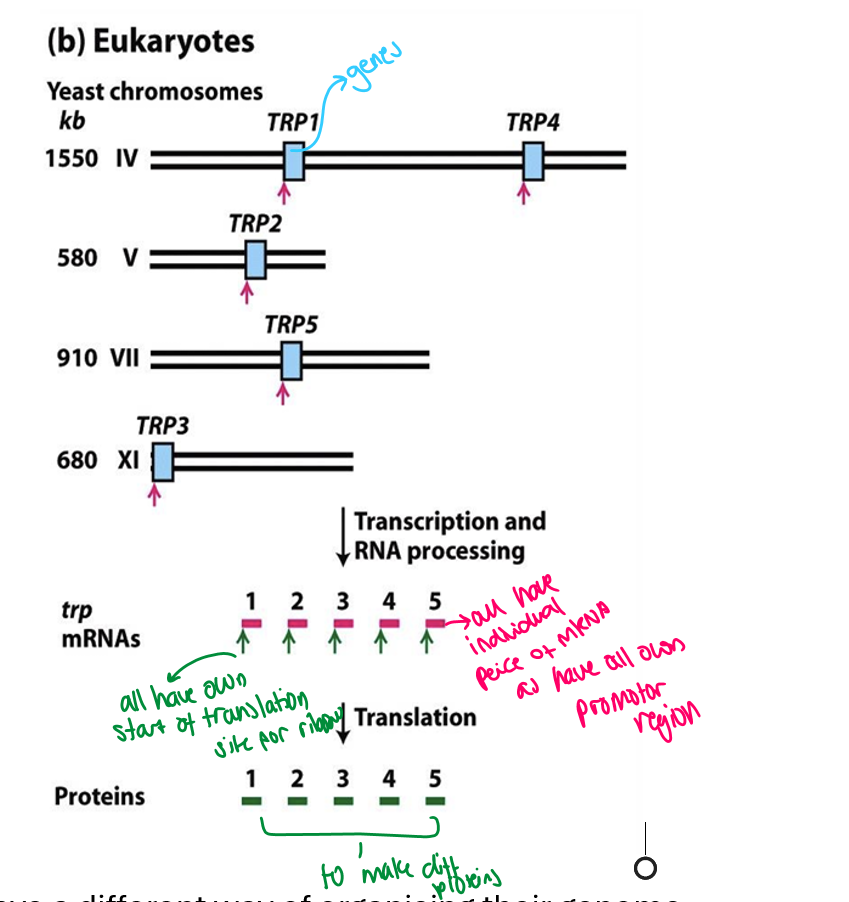
In eukaryotes genome gene structure
each gene has its own promoter region
this is called monocistronic gene organisation
so each gene has its own mRNA sequence and its start site for translation
at the end makes proteins
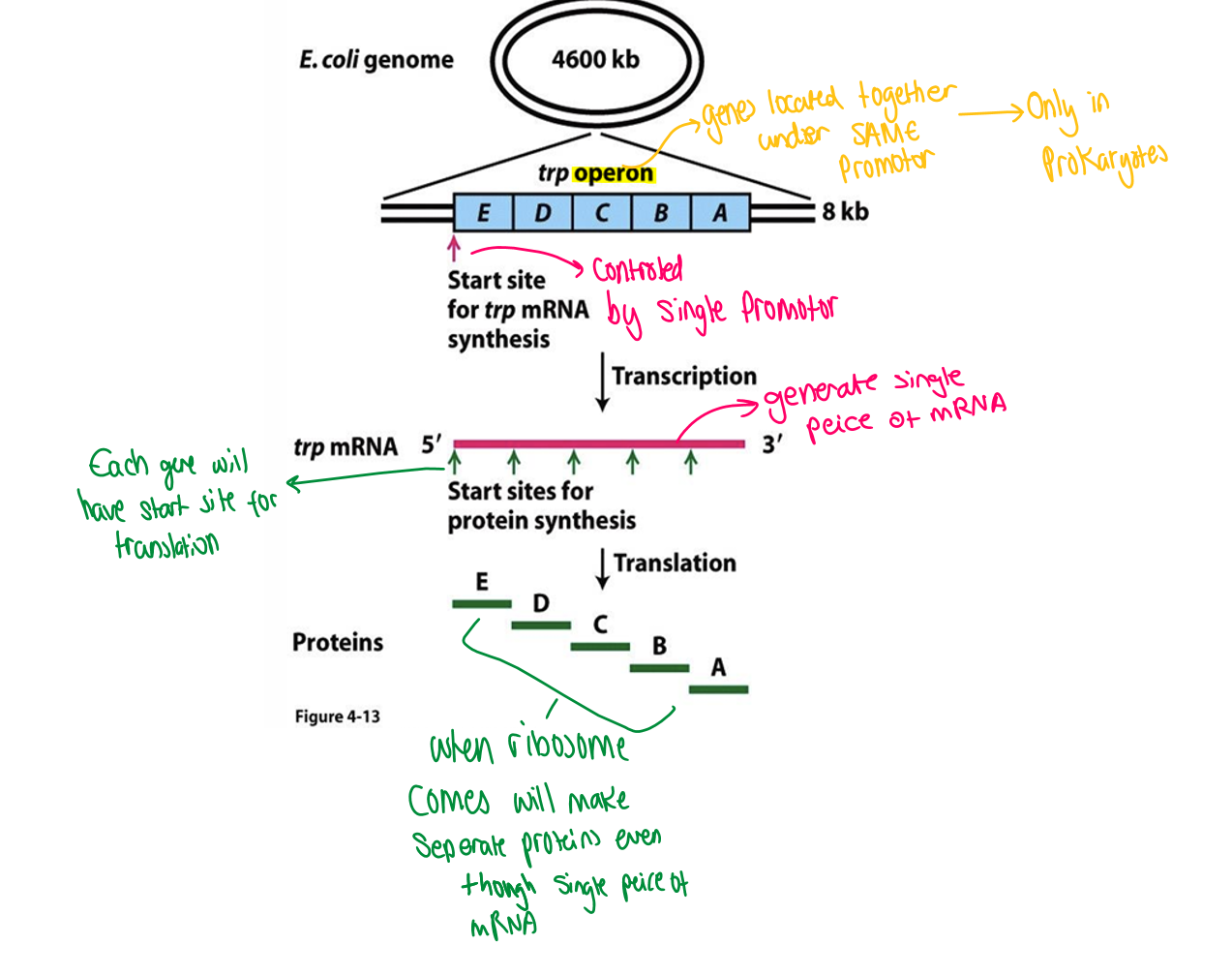
Prok genome gene structure
have Polycistronic gene organisation
gene that are related in function group together ad so share a promotor region
will make a single strand of mRNA but each gene will still have its own promotor
at end of translation will still produce separate proteins even though had a single stand of mRNA
Lac operon in E.coli
in operon have LacZ, lacY and LacA
LacZ —> encodes enzyme beta galactoside which breaks down glucose into lactose and glactose
when not enough glucose breaks down lactose to glucose and galactose to gen gucose for energy
LacY —> encodes lactose eprmase which is imbedded in cel emembrane to allow lactose to move into cell
LacA —> encodes enzyme thioglactoside transacetylase which breask down toxic thiglucatoside that moves into cell with lactose
what is at the opertor region
have LacI in opertor region locate din promotor region
not included in operon
it encodes repressor molecule which regulate transcription of operon
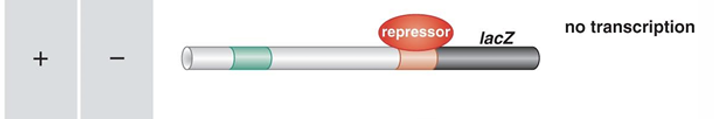
what happens in this situation?
preferred substrate of glucose is present so do not need lactose
Repressor molecule which is made by LacI (not part of operon) is bound to opperator region
stops RNA polymerise form binding so get no transcription as do not need it
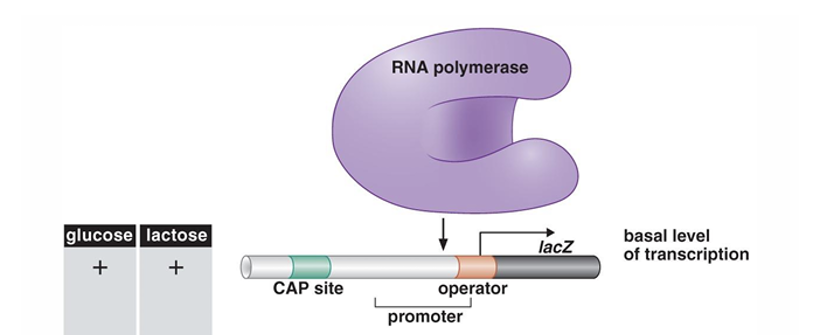
what happens here ?
operator region not boudn to by repressor
so RNA polymerase can bind and transcribe
get low level transcription/basal level as have both glucose and lactose
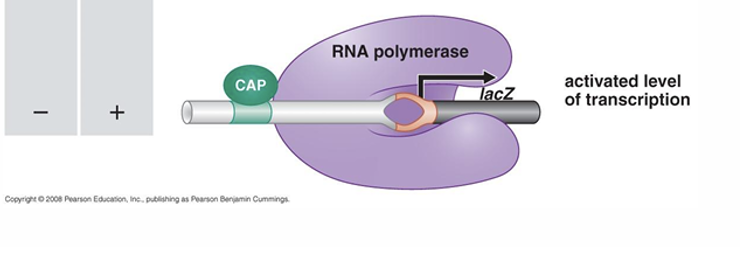
what happens in this situation?
we have no glucose
have CAP binding to cap site which secures RNA polymerase to have elevated level of tarnscription
what happens on a molecular level
when lactose is present have some lactose that change structure to form isomer called allolactose
allolactose binds to repressor changing its shape so no longer able to bind to operator region allowing RNA polymerase to bind and transcribe genes
when have no glucose have high levels of cAMP, cAMP binds to CAP which causes taht to bind to CAP site and so have higher levels of tarsncription as secures RNA polymerase
regulation of transcription in Euk
each gene has its own promotor region
need a set of TF to start
A,B,D,E,F,H are the TF used
D recognises TATA box and bi=rings A + B
the brings RNA polymerase 2 with 2F
THIS THEN BRING E AND H (H is a helicase)
RNA polymerase is then polymerised and actiavted so breaks away from all these TF and transcribes genes
how is transcription upregulated in Euk
area called enhancer region where other DNA binding proteins can bend
when these bind are called enhansersomes which cause DNA to bend backwards on itself for the enhansersomes to interact with RNA polymerase machinary
also have co-activators which also up regulate
what is removed ot make mature mRNA
5’ Cap
Poly(A)
Introns
removing different introns….
results in different proteins being produced
e.g. Calcitonin produced form exons 1,2,3,4 controls Ca levels
but calcitonin gene-related peptide produced form exons 1,2,3,5,6 is an important molecules that causes migraines