week 5 - Vertebral column and back
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
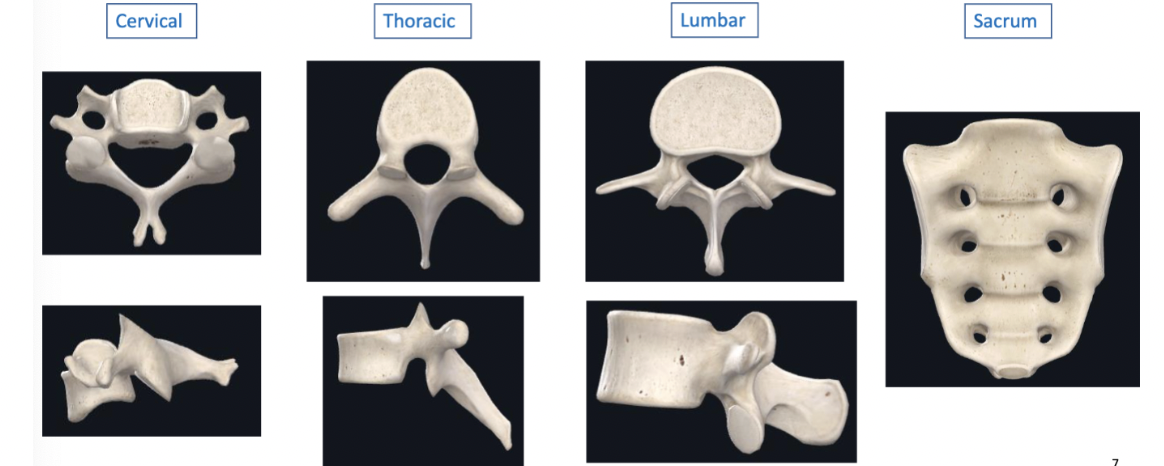
5 divisions of spine
cervical = 7
thoracic = 12
lumbar = 5
sacrum = 5
coccyx = 3-5
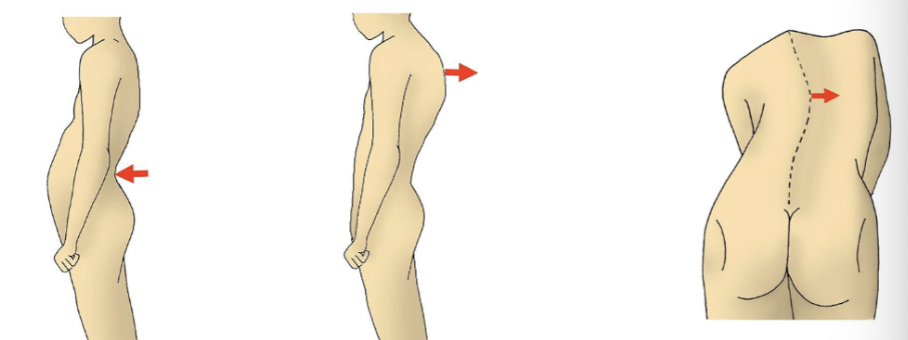
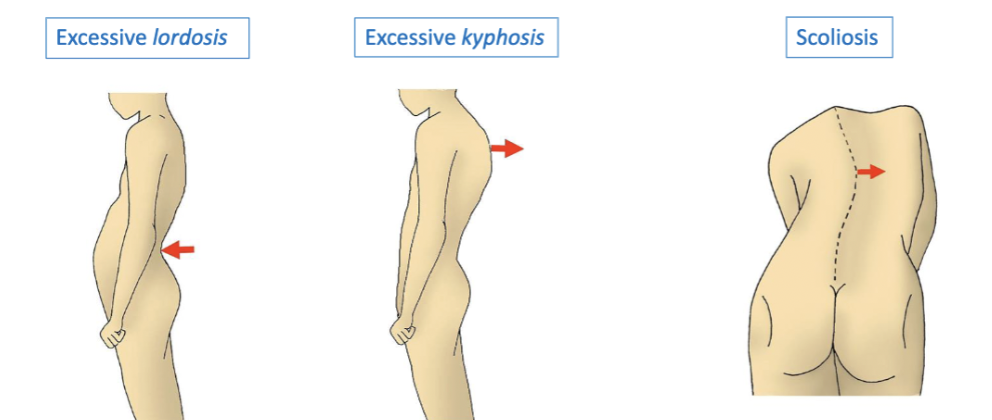
vertebral column curvatures
Primary curvature are 'kyphotic'
Secondary curvatures are 'lordotic'
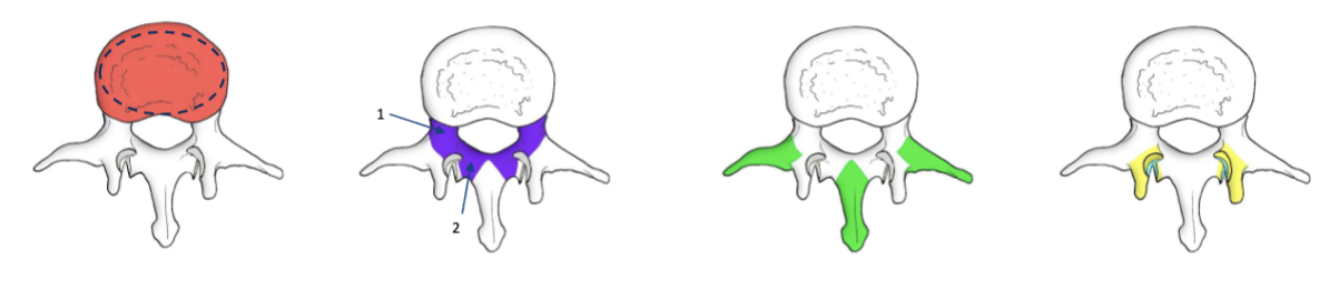
Major anatomical landmarks of typical vertebra
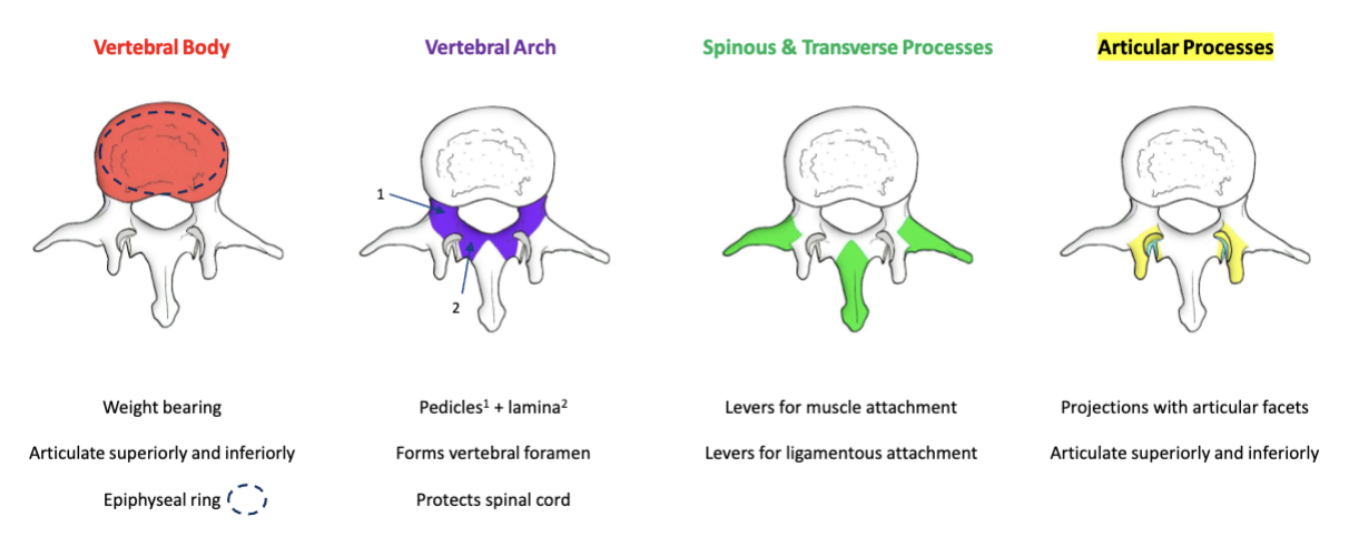
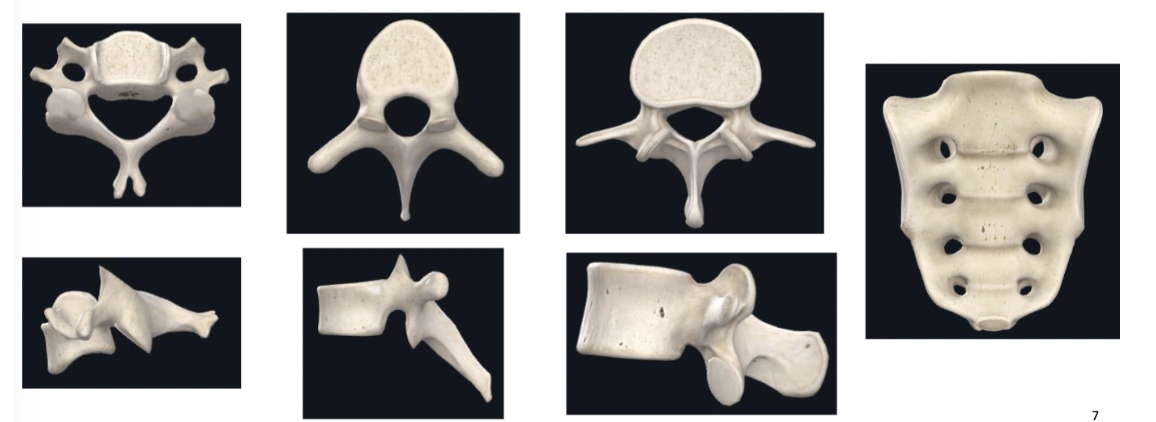
Distinct regional features of vertebrae
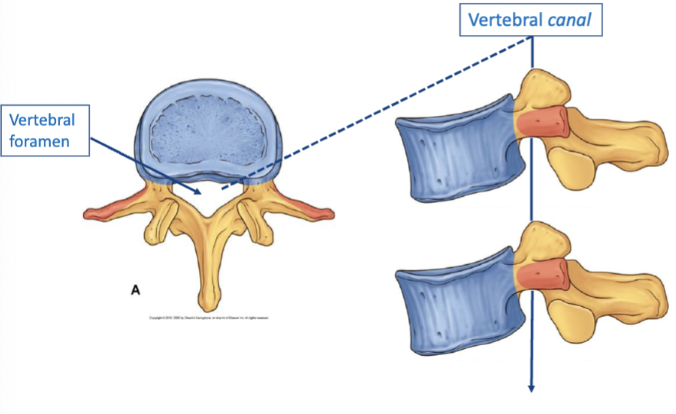
vertebral foramen
The opening in a vertebra that allows the passage of the spinal cord.
hole through which nerves pass
when multiple vertebrae’s are stacked it is called vertebral canal
contents: spinal nerve roots, dorsal root ganglia, vessels
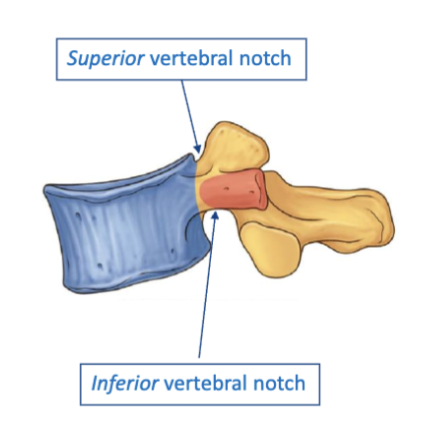
vertebral notches
The indentations located on the superior and inferior borders of the vertebrae that allow for the passage of spinal nerves and vessels.
notches can form holes only when stacked
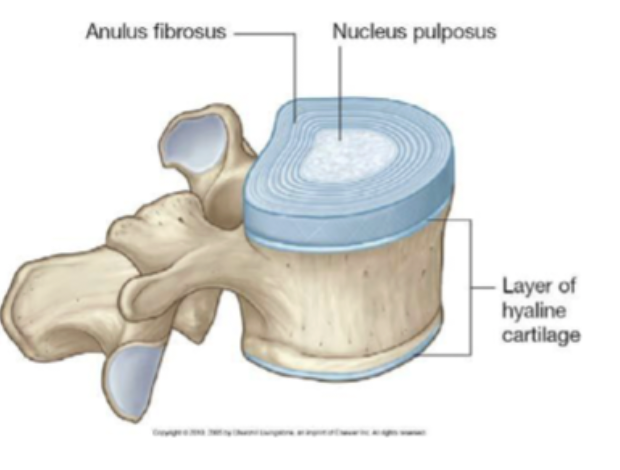
intervertebral joints: vertebral body-disc joints
discs are secondary cartilaginous joints that are in between vertebrae’s
ANNULUS FIBROSUS:
outer layer
attaches to epiphyseal ring
keeps vertebra together
concentric lamellae of collagen
permits movement in all direction
resists excessive rotation
NUCLEUS PULPOSUS:
inner layer
surrounded by annulus fibrosus
keeps vertebra apart
jelly consistency
shock absorber —> disperses compressive forces
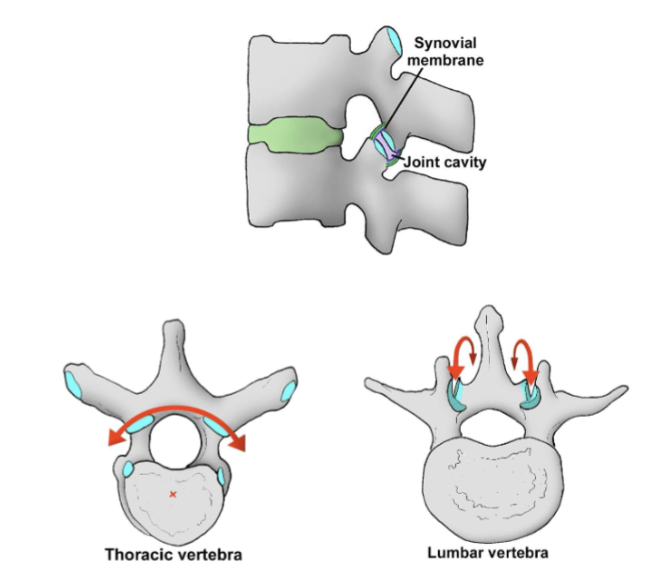
zygapophyseal joints
plane synovial joints
movement dependent on orientation of articular surfaces
superior and inferior articular processes have articular surfaces
thoracic goes across coronal plane and lumbar across sagittal
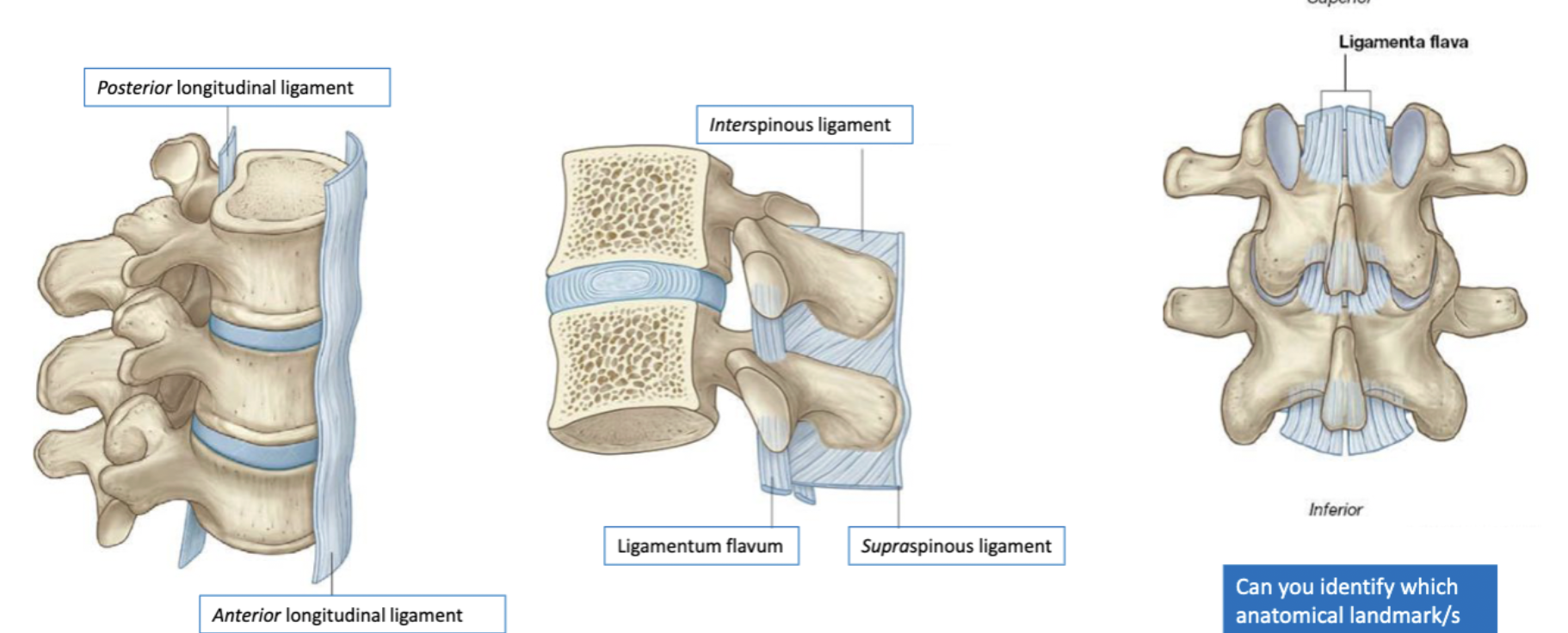
major vertebral column ligaments
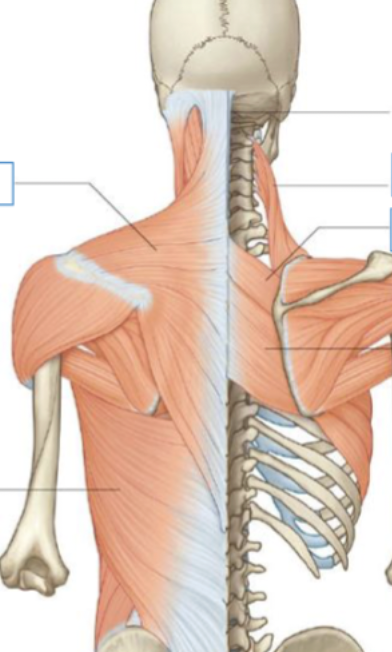
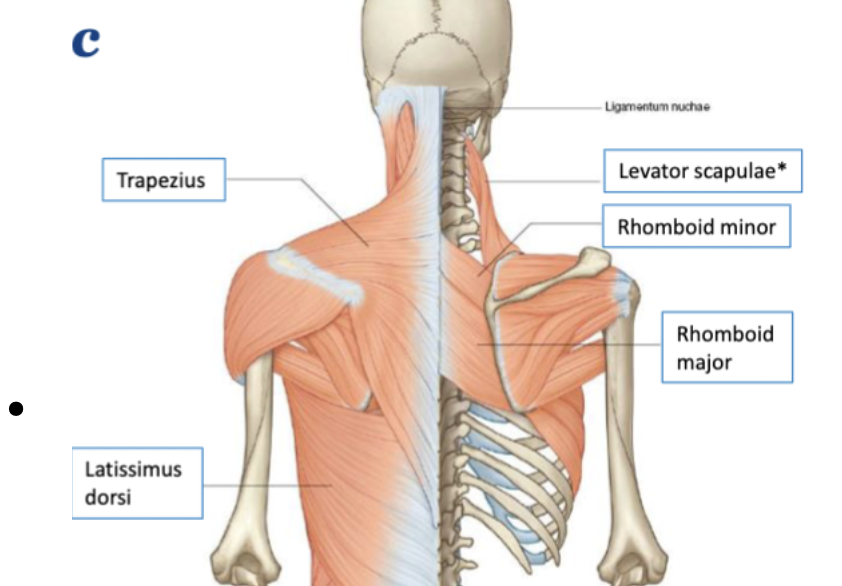
extrinsic muscles of back
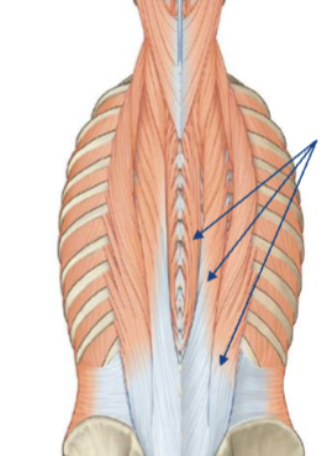
intrinsic muscles on back
erector spinae
concentrically extend the trunk
eccentrically control trunk flexion